Smart Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels: A Tour D’horizon of Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Smart Characteristics of PNIPAM
3. Synthesis of PNIPAM-HYDs
3.1. Free Radical Polymerization
3.2. Controlled Living Radical Polymerization
3.3. Graft Copolymerization
4. Biocompatibility Status of PNIPAM
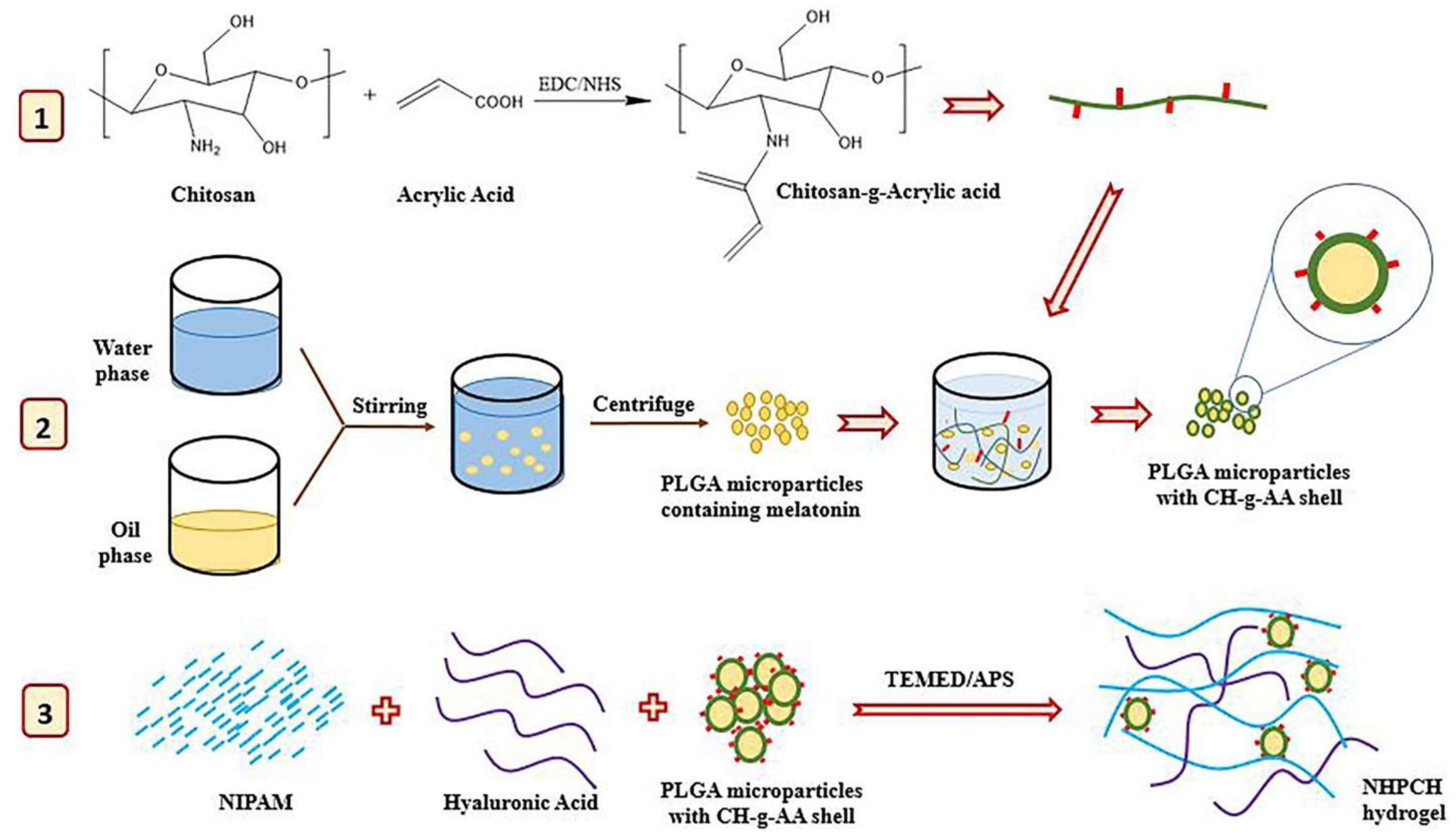
5. Modifications of PNIPAM-HYD
5.1. Physical Crosslinking
5.2. Chemical Crosslinking
5.2.1. PNIPAM Crosslinking Through Elastin-Like Polypeptides
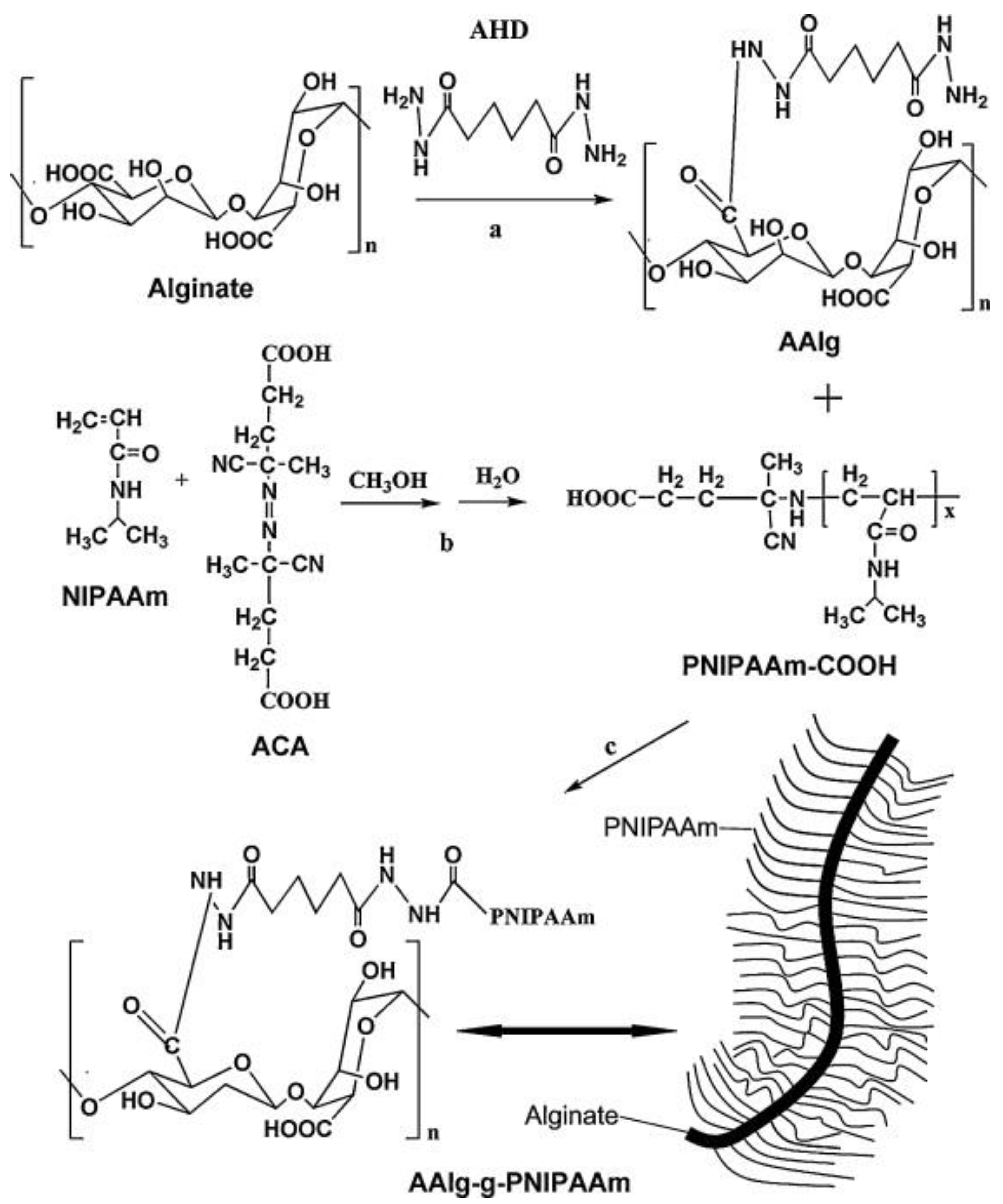
5.2.2. PNIPAM Crosslinking Through Alginate
5.2.3. PNIPAM Crosslinking Through Monoacryloxyethyl Phosphate
6. Routes of Administration
6.1. Parenteral Route
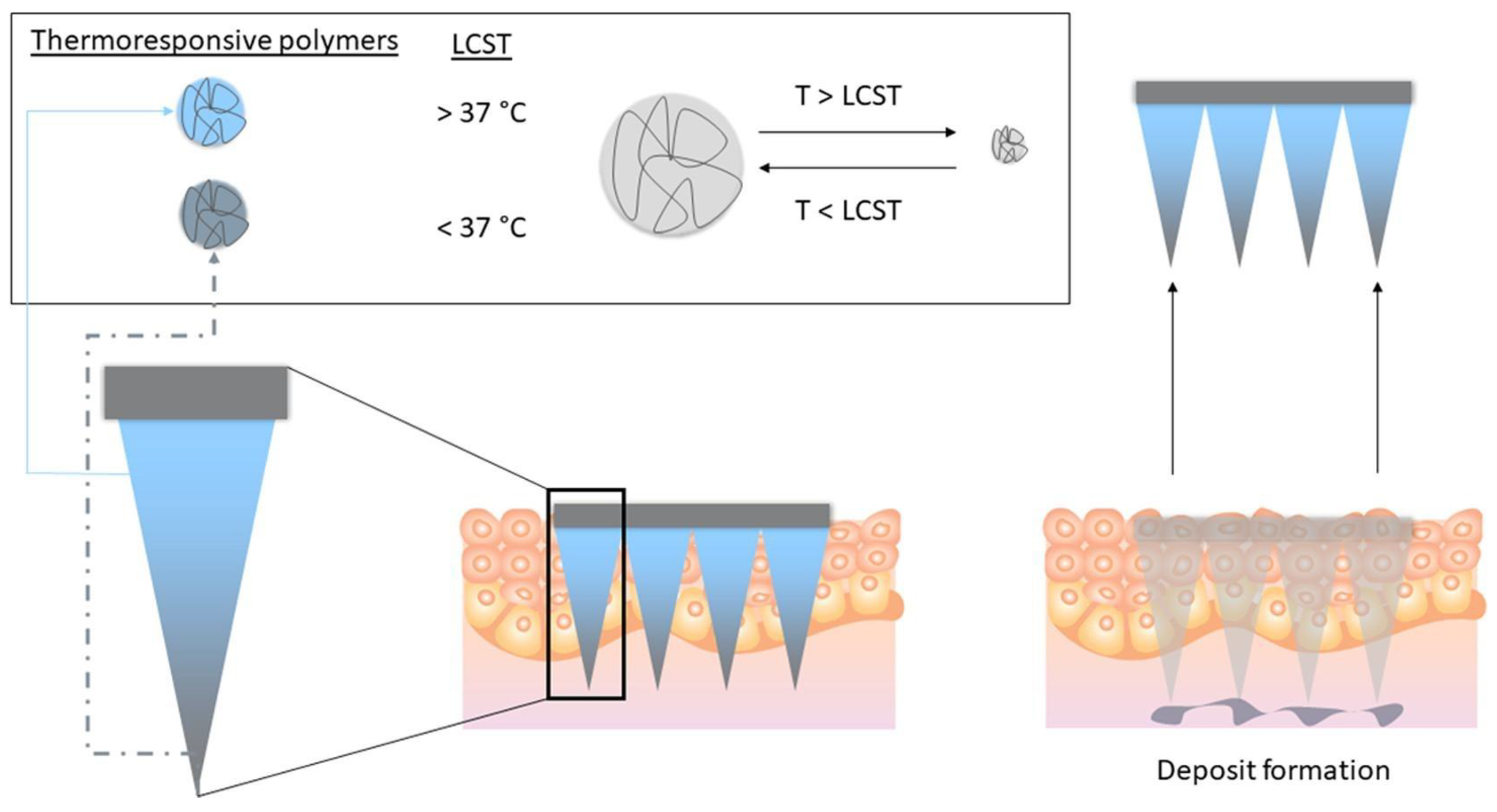
6.2. Transdermal Route
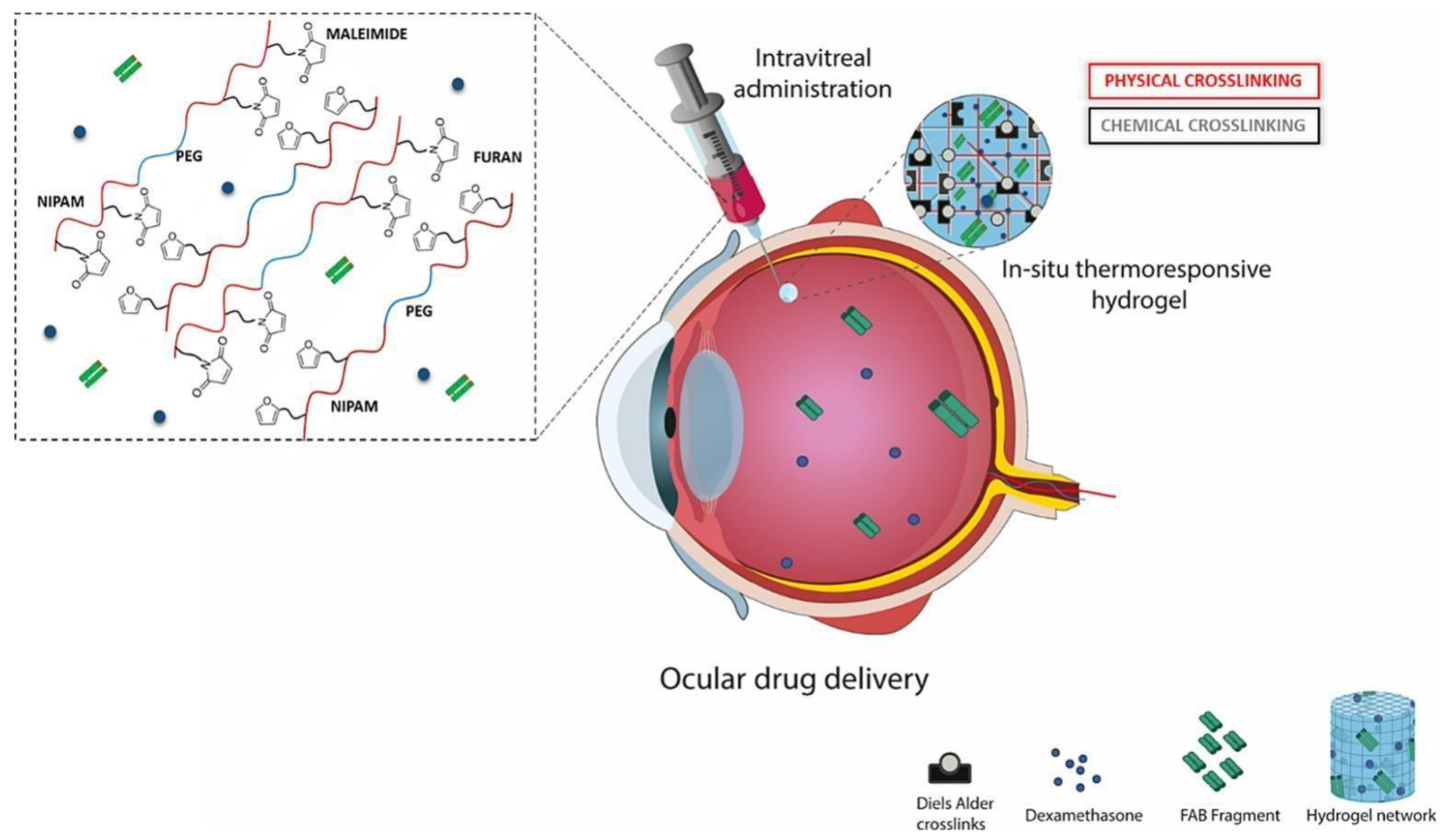
6.3. Ocular Route
7. Biomedical Applications of PNIPAM-HYDs
7.1. Cancer Therapy
7.1.1. Anticancer Agents’ Delivery
7.1.2. Photothermal/Photodynamic Therapy (PTT/PDT)
7.2. Wound Healing
7.3. Tissue Engineering
7.4. Ocular Diseases
7.5. Skin Diseases
7.6. Other Diseases
7.7. Diagnostic Applications
8. Patents
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sastri, T.K.; Gupta, V.N.; Chakraborty, S.; Madhusudhan, S.; Kumar, H.; Chand, P.; Jain, V.; Veeranna, B.; Gowda, D.V. Novel Gels: An Emerging Approach for Delivering of Therapeutic Molecules and Recent Trends. Gels 2022, 8, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Shahrizan, M.S.; Abd Aziz, Z.H.; Katas, H. Fluid Gels: A Systematic Review Towards Their Application in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 67, 102947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cid, P.; Jiménez-Rosado, M.; Romero, A.; Pérez-Puyana, V. Novel Trends in Hydrogel Development for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.; Deng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Janus Gels for Biomedical Applications: Progress and Future Prospective. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2024, 155, 101856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Agrawal, R.; Singh Chauhan, C.; Deshmukh, R. In-Situ Gel: A Smart Carrier for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 652, 123819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caló, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Biomedical Applications of Hydrogels: A Review of Patents and Commercial Products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; Gowda, B.H.J. Preparation and Evaluation of In-Situ Gels Containing Hydrocortisone for the Treatment of Aphthous Ulcer. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2021, 11, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Surya, S. Formulation and Characteristic Evaluation of Tacrolimus Cubosomal Gel for Vitiligo. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2022, 45, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Othman, M.B.H.; Javed, F.; Ahmad, Z.; Akil, H.M. Classification, Processing and Application of Hydrogels: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 57, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, S.; Nasrine, A.; Gulzar Ahmed, M.; Sultana, R.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Surya, S.; Almuqbil, M.; Asdaq, S.M.B.; Alshehri, S.; Arif Hussain, S. Potential Benefits of Using Chitosan and Silk Fibroin Topical Hydrogel for Managing Wound Healing and Coagulation. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanto, S.; Narayana, S.; Merai, K.P.; Kumar, J.A.; Bhunia, A.; Hani, U.; Al Fatease, A.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Nag, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; et al. Advancements in Gelatin-Based Hydrogel Systems for Biomedical Applications: A State-of-the-Art Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, C.; Huang, W.; Lei, Y. Injectable Smart Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels: Pioneering Advancements in Biomedical Applications. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 12, 8–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Husseiny, H.M.; Mady, E.A.; Hamabe, L.; Abugomaa, A.; Shimada, K.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yokoi, A.; Elbadawy, M.; Tanaka, R. Smart/Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels: Cutting-Edge Platforms for Tissue Engineering and Other Biomedical Applications. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 13, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.M. Current Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels as Smart Drug Delivery Carriers. Gels 2023, 9, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, K. Current Hydrogel Advances in Physicochemical and Biological Response-Driven Biomedical Application Diversity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikdar, P.; Uddin, M.M.; Dip, T.M.; Islam, S.; Hoque, M.S.; Dhar, A.K.; Wu, S. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Smart Hydrogels. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4532–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Tian, H. Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels: Fabrication and Biomedical Applications. View 2022, 3, 20200112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xue, W.; Yun, Z.; Liu, Q.; Sun, X. Biomedical Applications of Stimuli-Responsive “Smart” Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 25, 100998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protsak, I.S.; Morozov, Y.M. Fundamentals and Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels and Their Applications: A Review. Gels 2025, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klouda, L. Thermoresponsive Hydrogels in Biomedical Applications: A Seven-Year Update. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 97, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.J.; Tomlins, P.; Sahota, T.S. Thermoresponsive Gels. Gels 2017, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, M.T.; Haddow, P.; Kirton, S.B.; McAuley, W.J. Polymers Exhibiting Lower Critical Solution Temperatures as a Route to Thermoreversible Gelators for Healthcare. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuring, J.; Agarwal, S. Polymers with Upper Critical Solution Temperature in Aqueous Solution: Unexpected Properties from Known Building Blocks. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Hui, P.C.-L.; Kan, C.-W. Thermoresponsive Hydrogels and Their Biomedical Applications: Special Insight into Their Applications in Textile Based Transdermal Therapy. Polymers 2018, 10, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpa, J.S.; Mueller, D.D.; Klotz, I.M. Slow Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange in a Non-α-Helical Polyamide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 6024–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R.H.; Chibante, P. Preparation of Aqueous Latices with N-Isopropylacrylamide. Colloids Surf. 1986, 20, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Throat, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Macromolecular Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) in Cancer Treatment and Beyond. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2024, 2024, 1444990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.W.; Tsai, H.-C.; Wu, T.-Y.; Darge, H.F.; Chen, Y.-S. Role of Thermal and Reactive Oxygen Species-Responsive Synthetic Hydrogels in Localized Cancer Treatment (Bibliometric Analysis and Review). Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 6118–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, W. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Based Smart Hydrogels: Design, Properties and Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 115, 100702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Babu, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Van Guyse, J.F.R.; Hoogenboom, R.; Maji, S. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) and Its Copolymers: A Review on Recent Advances in the Areas of Sensing and Biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2402432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.A.; Su, Y.; Wang, D. Mechanical Properties of PNIPAM Based Hydrogels: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Du, T.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Guan, M. Silicate-Based Electro-Conductive Inks for Printing Soft Electronics and Tissue Engineering. Gels 2022, 8, 240. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, M.J.; Rajendran, R.R.; Mohanto, S.; Agarwal, U.; Panda, K.; Dhotre, K.; Manne, R.; Deepak, A.; Zafar, A.; Yasir, M.; et al. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: A Review of the State-of-the-Art. Gels 2022, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzalaco, S.; Mingot, J.; Torras, J.; Alemán, C.; Armelin, E. Recent Advances in Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogels and Derivatives as Promising Materials for Biomedical and Engineering Emerging Applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darge, H.F.; Andrgie, A.T.; Tsai, H.C.; Lai, J.Y. Polysaccharide and Polypeptide Based Injectable Thermo-Sensitive Hydrogels for Local Biomedical Applications; Elsevier B.V: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 133, ISBN 8862273037. [Google Scholar]
- Guragain, S.; Bastakoti, B.P.; Malgras, V.; Nakashima, K.; Yamauchi, Y. Multi-Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Materials. Chem. A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 13164–13174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Wang, Z.; Xu, D.; Wang, L.; Xu, T.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Fu, J. Snap-Buckling Motivated Controllable Jumping of Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel Bilayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41724–41731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.N.; Ferreira, L.M.B.; Cardoso, V.M.O.; Boni, F.I.; Souza, A.L.R.; Gremião, M.P.D. Recent Advances in Smart Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: From Self-Assembly to Functional Approaches. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xuan, C.; Qian, X.; Alsaid, Y.; Hua, M.; Jin, L.; He, X. Soft Phototactic Swimmer Based on Self-Sustained Hydrogel Oscillator. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, aax7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yin, J.; Qian, J.; Huang, Y. Nanoclay-Based Self-Supporting Responsive Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Printing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 10461–10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundueanu Gheorghe, M.C.; Sanda, B.; Ascenzi, P. PH/Thermo-Responsive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide-Co-Maleic Acid) Hydrogel with a Sensor and an Actuator for Biomedical Applications. Polymer 2017, 110, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.K.L. Refined Control of Thermoresponsive Swelling/Deswelling and Drug Release Properties of Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogels Using Hydrophilic Polymer Crosslinkers. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2016, 27, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.K.; Martin, J.R.; Dollinger, B.R.; Hattaway, M.E.; Duvall, C.L. Thermogelling, ABC Triblock Copolymer Platform for Resorbable Hydrogels with Tunable, Degradation-Mediated Drug Release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1704107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, D. Origins and Development of Initiation of Free Radical Polymerization Processes. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2010, 2009, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachota, B.; Matějka, L.; Zhigunov, A.; Konefał, R.; Spěváček, J.; Dybal, J.; Puffr, R. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)–Clay Based Hydrogels Controlled by the Initiating Conditions: Evolution of Structure and Gel Formation. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 9291–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quatela, V.C.; Chow, J. Synthetic Facial Implants. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickmann, C.; Meinecke, C.; Korten, T.; Sekulla, H.; Helke, C.; Blaudeck, T.; Reuter, D.; Schulz, S.E. Fabrication of switchable biocompatible, nano-fluidic devices using a thermoresponsive polymer on nano-patterned surfaces. Micro Nano Eng. 2024, 23, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyjaszewski, K. Future Directions for Atom Transfer Radical Polymerizations. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 1775–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyjaszewski, K.; Spanswick, J. Controlled/Living Radical Polymerization. Mater. Today 2005, 8, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Pandey, J.; Raj, V.; Kumar, P. A Review on the Modification of Polysaccharide Through Graft Copolymerization for Various Potential Applications. Open Med. Chem. J. 2017, 11, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, C.; Yang, X.; Shen, B.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Sun, H.; Yu, K.; Yang, B.; et al. PH- and Temperature-Sensitive Hydrogel Nanoparticles with Dual Photoluminescence for Bioprobes. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5856–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassenieux, C.; Tsitsilianis, C. Recent Trends in pH/Thermo-Responsive Self-Assembling Hydrogels: From Polyions to Peptide-Based Polymeric Gelators. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 1344–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedadghavami, A.; Minooei, F.; Mohammadi, M.H.; Khetani, S.; Kolahchi, A.R.; Mashayekhan, S.; Sanati-Nezhad, A. Manufacturing of Hydrogel Biomaterials with Controlled Mechanical Properties for Tissue Engineering Applications. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 42–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.C.; Xu, X.D.; Chen, C.S.; Yun, L.; Song, J.C.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhuo, R.X. In situ formation of thermosensitive PNIPAAm-based hydrogels by Michael-type addition reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biryan, F.; Abubakar, A.M.; Demirelli, K. Product Analysis, Electrical and Dielectric Properties Depending on Thermal Influence of Poly(N-Isopropyl Acrylamide)/Graphite-Filled Composite. Thermochim. Acta 2018, 669, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Lee, B.H.; Pauken, C.; Degradation, B.L.V. Cytotoxicity and Biocompatibility of NIPAAm-Based Thermosensitive, Injectable and Bioresorbable Polymer Hydrogels. Neuron 2009, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Hong, X.; Zhao, M.; Liu, N.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Shao, L.; Xue, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, P.; et al. Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, e10315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, W.; Yao, M.; Ding, Z.; Xuan, J.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Xia, Y.; Cao, M. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Based Thermoresponsive Composite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, S.; Park, S. Preparation of Uniformly Sized Interpenetrating Polymer Network Polyelectrolyte Hydrogel Droplets from a Solid-State Liquid Crystal Shell. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 99, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegatti, T.; Žnidaršič-Plazl, P. Copolymeric Hydrogel-Based Immobilization of Yeast Cells for Continuous Biotransformation of Fumaric Acid in a Microreactor. Micromachines 2019, 10, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Lee, S.L.; Park, S.N. Properties and In Vitro Drug Release of pH- and Temperature-Sensitive Double Cross-Linked Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels Based on Hyaluronic Acid/Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) for Transdermal Delivery of Luteolin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, M.S.; Vella, J.; Raos, B.J.; Narasimhan, B.N.; Svirskis, D.; Travas-Sejdic, J.; Malmström, J. Conducting Polymer Hydrogels with Electrically-Tuneable Mechanical Properties as Dynamic Cell Culture Substrates. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 134, 112559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Miao, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; Leng, K.; Xie, W.; Yu, Y. Versatile Bilayer Hydrogel for Wound Dressing through PET-RAFT Polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.A.; Georgiou, T.K. Thermoresponsive Polymers for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2011, 3, 1215–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, S.; Ahmed, M.G. Design and Evaluation of Ocular Hydrogel Containing Combination of Ofloxacin and Dexamethasone for the Treatment of Conjunctivitis. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 58, e20180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbitt, M.W.; Anseth, K.S. Hydrogels as Extracellular Matrix Mimics for 3D Cell Culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G. Energy Gels: A Bio-Inspired Material Platform for Advanced Energy Applications. Nano Today 2016, 11, 738–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante-Torres, M.; Romero-Fierro, D.; Arcentales-Vera, B.; Palomino, K.; Magaña, H.; Bucio, E. Hydrogels Classification According to the Physical or Chemical Interactions and as Stimuli-Sensitive Materials. Gels 2021, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Qiu, P.; Wang, Y.; Ren, P.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Gou, D. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels: From Preparation to Applications, a Review. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.M.; Silva, S.M.C.; Antunes, F.E. Adjusting the Low Critical Solution Temperature of Poly(N-Isopropyl Acrylamide) Solutions by Salts, Ionic Surfactants and Solvents: A Rheological study. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 210, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Raheja, K.; Milbrandt, N.B.; Beilharz, S.; Tene, S.; Oshabaheebwa, S.; Gurkan, U.A.; Samia, A.C.S.; Karayilan, M. Thermoresponsive Polymers with LCST Transition: Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Impact on Biomedical Frontiers. RSC Appl. Polym. 2023, 1, 158–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiabani, S.S.; Aghazadeh, M.; Rakhtshah, J.; Davaran, S. A Review of Hydrogel Systems Based on Poly(N-Isopropyl Acrylamide) for Use in the Engineering of Bone Tissues. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 208, 112035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Chan, H.-P.; Chung, T.-W.; Shu, C.-W.; Chuang, K.-P.; Duh, T.-H.; Yang, M.-H.; Tyan, Y.-C. Hydrogels: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despanie, J.; Dhandhukia, J.P.; Hamm-Alvarez, S.F.; MacKay, J.A. Elastin-Like Polypeptides: Therapeutic Applications for an Emerging Class of Nanomedicines. J. Control. Release 2018, 240, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, N.; Girotti, A.; Kose, G.T.; Rodríguez-Cabello, J.C.; Hasirci, V. Dynamic Cell Culturing and Its Application to Micropatterned, Elastin-like Protein-Modified Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Scaffolds. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5417–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and Biomedical Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; She, Z.; Wang, M.; Fang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Q. Thermo-Sensitive Alginate-Based Injectable Hydrogel for Tissue Engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, B.M.; Kasper, F.K.; Engel, P.S.; Mikos, A.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Injectable, Biodegradable, Phosphate-Containing, Chemically Cross-Linkable, Thermoresponsive Macromers for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almawash, S.; Osman, S.K.; Mustafa, G.; El Hamd, M.A. Current and Future Prospective of Injectable Hydrogels—Design Challenges and Limitations. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overstreet, D.J.; Dutta, D.; Stabenfeldt, S.; Vernon, B. Injectable Hydrogels. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2012, 50, 881–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, S.; Liu, M.; Ni, B. Degradable, Injectable Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels with Low Gelation Concentrations for Protein Delivery Application. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atoufi, Z.; Kamrava, S.K.; Davachi, S.M.; Hassanabadi, M.; Garakani, S.S.; Alizadeh, R.; Farhadi, M.; Tavakol, S.; Bagher, Z.; Motlagh, G.H. Injectable PNIPAM/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Containing Multipurpose Modified Particles for Cartilage Tissue Engineering: Synthesis, Characterization, Drug Release and Cell Culture Study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 1168–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-P.; Cheng, T.-H. Preparation and Evaluation of Thermo-Reversible Copolymer Hydrogels Containing Chitosan and Hyaluronic Acid as Injectable Cell Carriers. Polymer 2009, 50, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Song, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, J.-L.; Li, J. Injectable Thermoresponsive Hydrogel Formed by Alginate-g-Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) That Releases Doxorubicin-Encapsulated Micelles as a Smart Drug Delivery System. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35673–35682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.; Arbab, A.; Khan, S.; Fatima, H.; Bibi, I.; Chowdhry, N.P.; Ansari, A.Q.; Ursani, A.A.; Kumar, S.; Hussain, J.; et al. Recent Progress in Thermosensitive Hydrogels and Their Applications in Drug Delivery Area. MedComm-Biomater. Appl. 2023, 2, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Owida, H.; Alnaimat, F. Recent Progress in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels Application for Bone Regeneration. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2023, 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, B.H.J.; Ahmed, M.G.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Donnelly, R.F.; Vora, L.K. Microneedles as an Emerging Platform for Transdermal Delivery of Phytochemicals. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 6007–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, B.H.J.; Ahmed, M.G.; Hani, U.; Kesharwani, P.; Wahab, S.; Paul, K. Microneedles as a Momentous Platform for Psoriasis Therapy and Diagnosis: A State-of-the-Art Review. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 632, 122591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, B.H.J.; Ahmed, M.G.; Sahebkar, A.; Riadi, Y.; Shukla, R.; Kesharwani, P. Stimuli-Responsive Microneedles as a Transdermal Drug Delivery System: A Demand-Supply Strategy. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 1519–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, B.H.J.; Ahmed, M.G.; Sanjana, A. Can Microneedles Replace Hypodermic Needles?: Painless Drug Delivery. Resonance 2022, 27, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Feng, Y.H.; He, Y.T.; Hu, L.F.; Liang, L.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Chen, B.Z.; Guo, X.D.; Guo, X.D. Thermal-Sensitive Hydrogel Microneedle for Controlled Transdermal Drug Delivery. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 153, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, L.K.; Sabri, A.H.; Naser, Y.; Himawan, A.; Hutton, A.R.J.; Anjani, Q.K.; Volpe-Zanutto, F.; Mishra, D.; Li, M.; Rodgers, A.M.; et al. Long-Acting Microneedle Formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 201, 115055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, S.; Udabe, J.; Bin Sabri, A.; Calderón, M.; Donnelly, R. Leveraging Novel Innovative Thermoresponsive Polymers in Microneedles for Targeted Intradermal Deposition. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 652, 123847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liana, D.; Ajiro, H.; Chanthaset, N.; Phanumartwiwath, A. Dual-Responsive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogel Loaded with Poly-l-Lactic Acid Microparticles Encapsulating Boesenbergia Rotunda Extract for Enhanced Topical Delivery. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 9294–9305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, S.; Gulzar Ahmed, M.; Nasrine, A. Effect of Nano-Encapsulation Using Human Serum Albumin on Anti-Angiogenesis Activity of Bevacizumab to Target Corneal Neovascularization: Development, Optimization and In Vitro Assessment. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 68, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, B.H.J.; Vora, L.K.; Gade, S.; Glover, K.; Ahmed, M.G.; Thakur, R.R.S. Therapeutic Applications of Nanobiomaterials for the Management of Ocular Diseases. In Biomaterial-Inspired Nanomedicines for Targeted Therapies; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, S.; Mishra, N.; Mohanto, S.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Kumar, S.; Raikar, A.S.; Masand, P.; Garg, A.; Goswami, P.; Kahwa, I. Overview of Processed Excipients in Ocular Drug Delivery: Opportunities so Far and Bottlenecks. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Nair, A.B.; Shah, J.; Sreeharsha, N.; Gupta, S.; Shinu, P. Emerging Role of Hydrogels in Drug Delivery Systems, Tissue Engineering and Wound Management. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.; Tian, W.-X.; Farooq, M.A.; Khan, D.H. An Overview of Hydrogels and Their Role in Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2021, 70, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilochonwu, B.C.; van der Lugt, S.A.; Annala, A.; Di Marco, G.; Sampon, T.; Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F.; Hennink, W.E.; Vermonden, T. Thermo-Responsive Diels-Alder Stabilized Hydrogels for Ocular Drug Delivery of a Corticosteroid and an Anti-VEGF Fab Fragment. J. Control. Release 2023, 361, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Gong, H.; Li, R.; Cox, H.; Zhang, J.; Waigh, T.A.; Xu, H.; Lu, J.R. Reversible Thermoresponsive Peptide–PNIPAM Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 3601–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbu, R.; Brocchini, S.; Khaw, P.T.; Awwad, S. Antibody Loaded Collapsible Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels for Intraocular Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 124, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Hasan, N.; Gupta, G.; Singh, T.; Shadab, M.; Kesharwani, P. Carbon Nanotube-Mediated Platinum-Based Drug Delivery for the Treatment of Cancer: Advancements and Future Perspectives. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 206, 112800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Y.; Sameeya; Hasan, N.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Gupta, G.; Alsayari, A.; Wahab, S.; Kesharwani, P. Advancements in Dendrimer-Based Drug Delivery for Combinatorial Cancer Therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 97, 105755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, S.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Hani, U.; Shimu, S.S.; Paul, K.; Das, A.; Ashique, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; Tarighat, M.A.; Abdi, G. Inorganic Nanoparticle-Based Treatment Approaches for Colorectal Cancer: Recent Advancements and Challenges. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banazadeh, M.; Behnam, B.; Ganjooei, N.A.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Kesharwani, P.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin-Based Nanomedicines: A Promising Avenue for Brain Neoplasm Therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 89, 105040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Nasir, N.; Wahab, S.; Pichika, M.R.; Sahebkar, A.; Kesharwani, P. Advancements in Dextran-Based Nanocarriers for Treatment and Imaging of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 643, 123276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hani, U.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Siddiqua, A.; Wahab, S.; Begum, M.Y.; Sathishbabu, P.; Usmani, S.; Ahmad, M.P. Herbal Approach for Treatment of Cancer Using curcumin as an anticancer Agent: A Review on Novel Drug Delivery Systems. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 390, 123037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, J.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Almalki, W.H.; Gupta, N.; Sahebkar, A.; Kesharwani, P. Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-Based Approaches for the Treatment of Brain Tumors: Opportunities and Challenges. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 193, 112111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelić, K.; Pavelić, S.K.; Bulog, A.; Agaj, A.; Rojnić, B.; Čolić, M.; Trivanović, D. Nanoparticles in Medicine: Current Status in Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, B.H.J.; Ahmed, M.G.; Almoyad, M.A.A.; Wahab, S.; Almalki, W.H.; Kesharwani, P. Nanosponges as an Emerging Platform for Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2307074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, B.H.J.; Ahmed, M.G.; Alshehri, S.A.; Wahab, S.; Vora, L.K.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Kesharwani, P. The Cubosome-Based Nanoplatforms in Cancer Therapy: Seeking New Paradigms for Cancer Theranostics. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hani, U.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Haider, N.; Ramesh, K.; Paul, K.; Ashique, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; Narayana, S.; Mohanto, S.; Kesharwani, P. Nanoparticle-Based Approaches for Treatment of Hematological Malignancies: A Comprehensive Review. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Ahmed, M.G.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Chen, Z.-S.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Kesharwani, P. Advancements in Nanoparticle-Based Treatment Approaches for Skin Cancer Therapy. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Almalki, W.H.; Singh, T.; Sahebkar, A.; Kesharwani, P. Unravelling the Potential of Mitochondria-Targeted Liposomes for Enhanced Cancer Treatment. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, M.; Cai, C.; Ye, C.; Guo, T.; Yang, K.; Xiao, H.; Tang, X.; Liu, H. Recent Progress of Hydrogel-Based Local Drug Delivery Systems for Postoperative Radiotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1027254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordbar-Khiabani, A.; Gasik, M. Smart Hydrogels for Advanced Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafael, D.; Melendres, M.M.R.; Andrade, F.; Montero, S.; Martinez-Trucharte, F.; Vilar-Hernandez, M.; Durán-Lara, E.F.; Schwartz, S., Jr.; Abasolo, I. Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels for Cancer Local Therapy: Challenges and State-of-Art. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 606, 120954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasban, S.; Raissi, H. PNIPAM/Hexakis as a Thermosensitive Drug Delivery System for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Santhamoorthy, M.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, S.-C. pNIPAm-Based pH and Thermoresponsive Copolymer Hydrogel for Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Drug Delivery. Gels 2024, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Yang, D.H.; Nah, H.; Min, S.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoo, J.H.; Chun, H.J.; Moon, H.-J.; Hong, Y.K.; et al. Development of a Temperature-Responsive Hydrogel Incorporating PVA into NIPAAm for Controllable Drug Release in Skin Regeneration. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 44076–44085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhamoorthy, M.; Phan, T.T.V.; Ramkumar, V.; Raorane, C.J.; Thirupathi, K.; Kim, S.-C. Thermo-Sensitive Poly (N-Isopropylacrylamide-co-Polyacrylamide) Hydrogel for pH-Responsive Therapeutic Delivery. Polymers 2022, 14, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, P.; Abousalman-Rezvani, Z.; Hajebi, S.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Salami-Kalajahi, M. Controlled Release of Anti-Cancer Drug from the Shell and Hollow Cavities of Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogel Particles Synthesized via Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer Polymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 135, 109877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayar, Z.; Shafieian, M.; Mahmoodi, N.; Sabzevari, O.; Hassannejad, Z. A Rechargeable Drug Delivery System Based on pNIPAM Hydrogel for the Local Release of Curcumin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.S.C.; Denham, A.S.; Bassett, H.H.; Curby, W.T. Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer: A Review. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overchuk, M.; Weersink, R.A.; Wilson, B.C.; Zheng, G. Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapies: Synergy Opportunities for Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 7979–8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Mao, D.; Li, X.; Luo, J.; Gong, C.; Liu, X. Lanthanide-Based Nanoparticles for Cancer Phototherapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 508, 215773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Long, L.; Liao, J.; Chen, W. Recent Advances in Hydrogel-Based Phototherapy for Tumor Treatment. Gels 2023, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, T.S. Improving Cancer Chemotherapy Through Photothermally Triggered Drug Release from Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic Acid)/Prussian Blue Hydrogel. Mater. Des. 2023, 233, 112243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baipaywad, P.; Ryu, N.; Im, S.-S.; Lee, U.; Bin Son, H.; Kim, W.J.; Park, H. Facile Preparation of Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites for Chemo-Photothermal Therapy. Des. Monomers Polym. 2022, 25, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howaili, F.; Özliseli, E.; Küçüktürkmen, B.; Razavi, S.M.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Rosenholm, J.M. Stimuli-Responsive, Plasmonic Nanogel for Dual Delivery of Curcumin and Photothermal Therapy for Cancer Treatment. Front. Chem. 2021, 8, 602941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.H.; Choi, H.W.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Chung, B.G. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Thermo-responsive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Pyrrole Nanocomposites for Chemo-Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algi, M.P.; Sarıgöl, R. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogel Incorporating Squaraine: Synthesis, Drug Delivery and Photodynamic Properties. Mugla J. Sci. Technol. 2024, 10, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, J. Hydrogel Preparation Methods and Biomaterials for Wound Dressing. Life 2021, 11, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Gao, Q.; Ouyang, C.; Zheng, K.; Shan, X. Thermosensitive PNIPAM-Based Hydrogel Crosslinked by Composite Nanoparticles as Rapid Wound-Healing Dressings. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Huang, D. Double-Crosslinked PNIPAM-Based Hydrogel Dressings with Adjustable Adhesion and Contractility. Regen. Biomater. 2023, 10, rbad081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Xue, B.; Cheng, W.; Liu, Y.; Niu, M.; Yang, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, L. Healing Mechanism of Cotton Bandages Loaded with PNIPAM/GO-Ag Hydrogel on Deep Seconddegree Burn Wounds in a Rat Model. Burns 2024, 8, 107235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ge, X.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ou, Z.; Luo, G.; Zhan, R.; Zhang, Y. Construction of Programmed Time-Released Multifunctional Hydrogel with Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Properties for Impaired Wound Healing. J. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, B.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Q.; Cheng, D.-H.; Lu, Y.-H. Wound Microenvironment Self-Adjusting Hydrogels with Thermo-Sensitivity for Promoting Diabetic Wound Healing. Gels 2023, 9, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, T.; Kumar, S.; Chelladurai, S.J.S.; Gnanasekaran, S.; Sivananthan, S.; Geetha, N.K.; Arthanari, R.; Assefa, G.B. Recent Developments in Stimuli Responsive Smart Materials and Applications-An Overview. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 4031059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Candan, Z. Smart Materials-The Next Generation in Science and Engineering. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiabani, S.S.; Zivari-Ghader, T.; Aghazadeh, M.; Keyhanvar, P.; Khiabani, Z.S.; Reyhanifar, F.; Davaran, S. Loading of VEGF and BMP2 to PNIPAAm-Based Hydrogel as a Scaffold for Bone Regeneration. J. Med. Pharm. Chem. Res. 2024, 6, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Guan, X.; Zheng, J.; Guo, H.; Wu, K.; Liang, L.; Lu, M. Biodegradable, Thermoresponsive PNIPAM-Based Hydrogel Scaffolds for the Sustained Release of Levofloxacin. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 32967–32978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.A.; Martins, M.V.S.; Bressiani, A.H.; Bressiani, J.C.; Leyva, M.E.; de Queiroz, A.A.A. Electrochemical Preparation and Characterization of PNIPAM-HAp Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 81, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.; Duan, S.; Yang, X.; Gao, P.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Q. Effective Bone Regeneration Using Thermosensitive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Grafted Gelatin as Injectable Carrier for Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19006–19015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellati, A.; Kiamahalleh, M.V.; Madani, S.H.; Dai, S.; Bi, J.; Jin, B.; Zhang, H. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogel/Chitosan Scaffold Hybrid for Three-Dimensional Stem Cell Culture and Cartilage Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2016, 104, 2764–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.; Chvs, P.; Yamini, M.; Prasad, C. Hydrogels the Three Dimensional Networks: A Review. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2020, 13, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliaraj, G.S.; Shanmugam, D.K.; Dasan, A.; Mosas, K.K.A. Hydrogels—A Promising Materials for 3D Printing Technology. Gels 2023, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thang, N.H.; Chien, T.B.; Cuong, D.X. Polymer-Based Hydrogels Applied in Drug Delivery: An Overview. Gels 2023, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabpour, Z.; Salehi, M.; An, S.; Moghtader, A.; Anwar, K.N.; Baharnoori, S.M.; Shah, R.J.; Abedi, F.; Djalilian, A.R. Exploring Hydrogel Nanoparticle Systems for Enhanced Ocular Drug Delivery. Gels 2024, 10, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annala, A.; Ilochonwu, B.C.; Wilbie, D.; Sadeghi, A.; Hennink, W.E.; Vermonden, T. Self-Healing Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Sustained Release of Dexamethasone for Ocular Therapy. ACS Polym. Au 2023, 3, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.T.; Walsh-Korb, Z.; Barrow, S.J.; Henderson, S.L.; Del Barrio, J.; Scherman, O.A. The Importance of Excess Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) for the Aggregation of Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Coated Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2007, 6, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turturro, S.B.; Guthrie, M.J.; Appel, A.A.; Drapala, P.W.; Brey, E.M.; Pérez-Luna, V.H.; Mieler, W.F.; Kang-Mieler, J.J. The Effects of Cross-Linked Thermo-Responsive PNIPAAm-Based Hydrogel Injection on Retinal Function. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3620–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.H.; Morales, Y.; Cabral, T. Ocular Biocompatibility of Poly-N-Isopropylacrylamide (pNIPAM). J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, N.; Gardoni, G.; Sponchioni, M.; Moscatelli, D. Thermo-Responsive Polymers as Surface Active Compounds-A Review. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 198, 112421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibie, N.A.; Ramli, N.A.; Faizal, N.D.F.M.; Srichana, T.; Amin, M.C.I.M. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Based Polymers: Recent Overview for the Development of Temperature-Responsive Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2023, 224, 2300157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, M.; Pescina, S.; Padula, C.; Santi, P.; Del Favero, E.; Cantù, L.; Nicoli, S. Polymeric Micelles in Drug Delivery: An Insight of the Techniques for Their Characterization and Assessment in Biorelevant Conditions. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 312–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, L.; Boyd, B.J.; Malmsten, M.; Heinz, A. Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems for Inflammatory Skin Conditions. Acta Biomater. 2024, 187, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurdasiper, A.; Şahiner, A.; Gökçe, E.H. Preparation of Thermoresponsive Triclosan Poly (N-Isopropylacrylamide) Nanogels and Evaluation of Antibacterial Efficacy on Cutibacterium Acnes. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartora, V.F.; Passos, J.S.; Osorio, B.; Hung, R.-C.; Nguyen, M.; Wang, A.; Panitch, A. Chitosan Hydrogels with MK2 Inhibitor Peptide-Loaded Nanoparticles to Treat Atopic Dermatitis. J. Control. Release 2023, 362, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, W. Preparation of Soft Hydrogel Nanoparticles with PNIPAm Hair and Characterization of Their Temperature-Induced Aggregation. Langmuir 2010, 26, 2076–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, A.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, H.; Priimagi, A.; Ikkala, O. Fast Switching of Bright Whiteness in Channeled Hydrogel Networks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.S.A.; Fatima, F.; Zhou, D.; Deng, W.; Liu, S. Engineering siRNA Therapeutics: Challenges and Strategies. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mangala, L.S.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Kong, X.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K. RNA Interference-Based Therapy and Its Delivery Systems. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliervoet, L.A.L.; Zhang, H.; van Groesen, E.; Fortuin, K.; Duin, N.J.C.B.; Remaut, K.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Hennink, W.E.; Vermonden, T. Local Release of siRNA Using Polyplex-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogels. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 10347–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, R.; Luo, J.; Hong, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Rational Design of Thermosensitive Hydrogel to Deliver Nanocrystals with Intranasal Administration for Brain Targeting in Parkinson’s Disease. Research 2021, 2021, 9812523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, M.; Valverde, M.G.; Bernal, P.N.; van Trijp, J.P.; Hak, J.; Di Marco, G.; Neumann, M.; Schuurmans, C.C.L.; van Nostrum, C.F.; Masereeuw, R.; et al. Thermal Shrinking of Biopolymeric Hydrogels for High Resolution 3D Printing of Kidney Tubules. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2406098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Fan, S.; Zhu, B.; El-Hout, S.I.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C. Recent Progress on Photothermal Nanomaterials-Design, Mechanism, and Applications. Green Energy Environ. 2024, 1–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X. Photothermal Hydrogel-Integrated Paper-Based Point-of-Care Platform for Visible Distance-Readout of Glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1285, 342035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Ren, H.; Chen, Y.; Yan, S.; Dai, H.; Lv, L. Facile and Portable Multimodal Sensing Platform Driven by Photothermal-Controlled Release System for Biomarker Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 235, 115413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ding, J.; Wu, X.; Zeng, M.; Tian, Y.; Wu, K.; Wei, D.; Sun, J.; Guo, Z.; Fan, H. Flexible and Temperature-Responsive Hydrogel Dressing for Real-Time and Remote Wound Healing Monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 4934–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
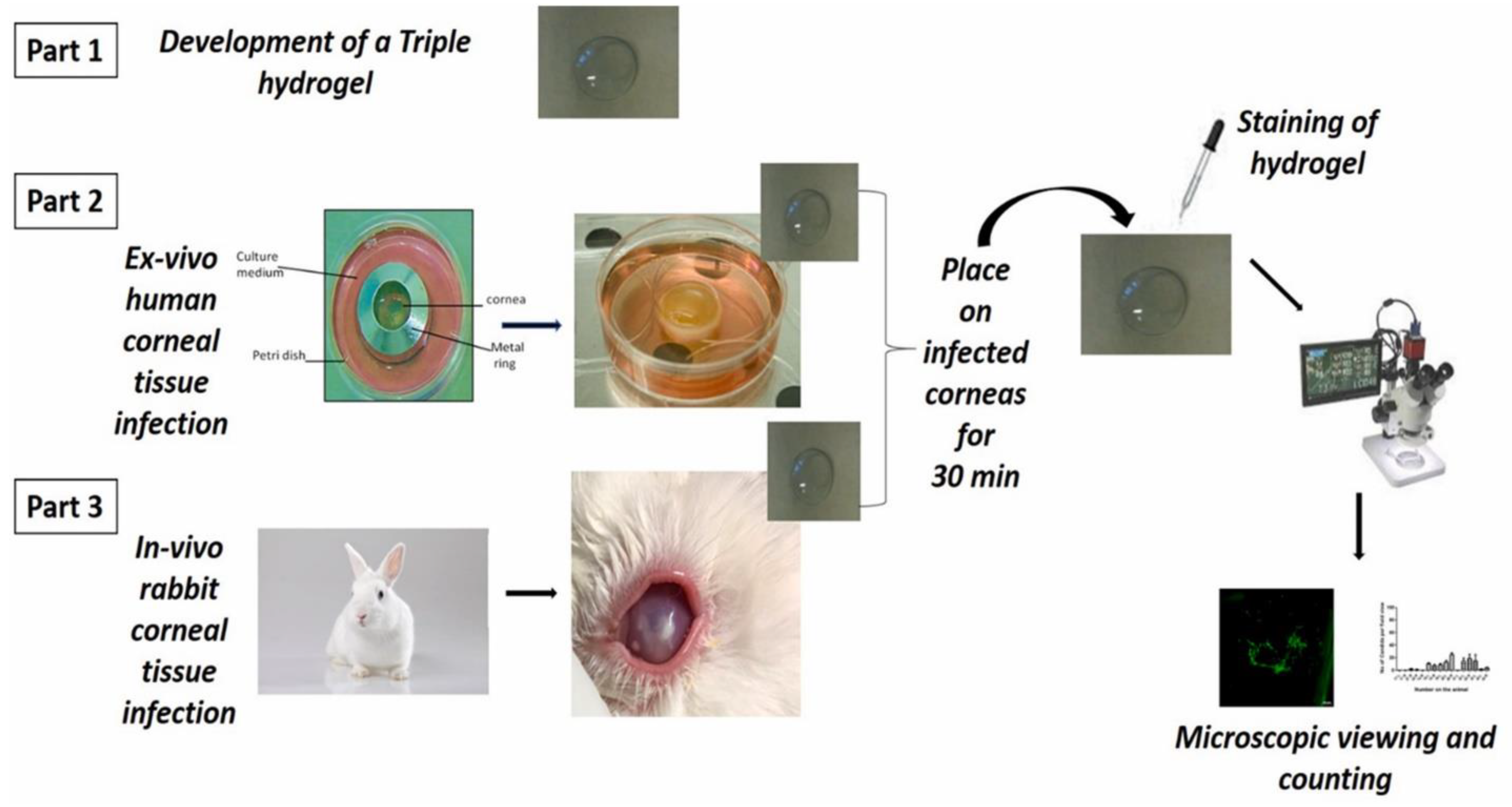
- Shivshetty, N.; Swift, T.; Pinnock, A.; Pownall, D.; Mac Neil, S.; Douglas, I.; Garg, P.; Rimmer, S. Evaluation of Ligand Modified poly (N-Isopropyl Acrylamide) Hydrogel for Etiological Diagnosis of Corneal Infection. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 214, 108881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Ren, H.; Dai, H.; Lv, L.; Lin, Y. Photothermal-Induced Electrochemical Interfacial Region Regulation Enables Signal Amplification for Dual-Mode Detection of Ovarian Cancer Biomarkers. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 6519–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Ji, Q.; Xia, Y. Preparation method of graphene oxide/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) composite hydrogel. CN Patent Application No. CN102580633A, 18 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhenglong, Y.; Xinyan, L. Preparation method of camptothecin controlled release organic/inorganic hybrid material POSS/PNIPAM-b-PDMAEMA. CN Patent Application No. CN104825390A, 12 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jianfeng, Z.; Fang, Y.; Mengting, P.; Zuming, D.; Qi, H. Method for preparing tissue engineering blood vessel based on 3D bioprinting technology. CN Patent Application No. CN104490489A, 08 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Li, Z.; Yun, S.; Di, C.; Changhong, K.; Fulei, Z.; He, Z.; Huafei, L.; Cheng, J. Temperature targeting-based nanogel gene delivery compound, and preparation method and application thereof. CN Patent Application No. CN105561334A, 11 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L.; Yanqiu, M.; Dandan, H.; Weifeng, N.; Lei, M. VEGF antibody-carrying ophthalmic thermosensitive hydrogel implant and preparation method thereof. CN Patent Application No. CN107233570A, 10 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Jingwen, X.; Yanling, L. Temperature and redox-sensitive type drug delivery material connected by diselenide bonds and preparation and application thereof. CN Patent Application No. CN108976356A, 11 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Limin, Z.; Qianqian, Q.; Shiwei, N. Preparation method of breast cancer targeted chitosan grafted polymer medicine-carrying composite material. CN Patent Application No. CN108186607A, 22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shukun, S.; Meijing, L.; Zixuan, S.; Rui, Z.; Yiyun, W.; Lang, B.; Daodao, H.; Jiangang, C. Amino organic silicon liposome/temperature-sensitive hydrogel composite material encapsulating water-soluble medicine. CN Patent Application No. CN109864968A, 11 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaohong, P. and Xiaofeng, M. Thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with copper metal organic skeleton nanoparticles and preparation method of thermosensitive hydrogel. CN Patent Application No. CN109513038A, 26 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaohong, W.; Ping, Z.; Qingguang, L. Synthetic method of antibacterial preparation based on PNIPAM and silver nanometer clusters. CN Patent Application No. CN109528767A, 29 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, X.; Shengxin, H. Intelligent transdermal drug release system for controlling drug dosage of patch based on heart rate variability. CN Patent Application No. CN110064127A, 30 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yun’e, Z.; Jinhai, H.; Mei, Y.; Chenyang, M.; Zhongxing, M.; Luting, P. Reversible thermosensitive sealant for temporarily closing ocular trauma and syringe applied to sealant. CN Patent Application No. CN110152071A, 23 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Baoqiang, L.; Haichang, D.; Yujie, F.; Dechang, J.; Yu, Z. Preparation method of pH and temperature dual-response UV crosslinked chitosan injectable hydrogel. CN Patent Application No. CN111533927A, 14 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liming, Z.; Shuaijun, Z.; Beilei, W.; Qianqian, W.; Qian, H.; Chao, W.; Guoyan, L.; Bo, W.; Fuhai, Z. Preparation method of cyclic gamma-polyglutamic acid modified hydrogel loaded with growth factors. CN Patent Application No. CN111803702A, 23 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiaying, H.; Qian, C.; Zhuang, L. Hydrogel dressing for wound healing and preparation method thereof. CN Patent Application No. CN112999412A, 22 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Geun, C.B.; Hee, S.H.; Woo, C.H.; Jaehyun, L.; Woon, K.J. Temperature-sensitive polymer-based nanocomposite capable of chemo-photothermal treatment by cancer cell targeting and near-infrared ray and method for preparing the same. KR Patent Application No. KR20220043756A, 05 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- John, W.I.; Niki, B.; Yi, Z.; Paulo, F.; Mark, T.; Mark, H. System for sutureless closure of scleral perforations and other ocular tissue discontinuities. US Patent Application No. US11376344B2, 05 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hongbin, L.; Chao, F.; Yingdong, Y. Silver sulfadiazine hydrogel for rapid wound healing as well as preparation method and application of silver sulfadiazine hydrogel. CN Patent Application No. CN115337447A, 15 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chunlei, Z.; Hao, F. Constant-temperature photo-thermal system and application thereof. CN Patent Application No. CN116474159A, 25 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Qihui, Z. Bi-crosslinking hydrogel and application thereof as wound healing dressing. CN Patent Application No. CN116199911A, 02 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shilei, R.; Ruiping, Z.; Rong, D.; Shutong, W.; Lin, C.; Qi, C.; Mingxin, Z. Two-way nano-drug delivery system based on NIR-IIFL guidance and application. CN Patent Application No. CN115970004A, 18 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yingzi, W.; Menglin, W.; Mingrui, J. Emodin nanosuspension temperature-sensitive gel as well as preparation method and application thereof. CN Patent Application No. CN118477038A, 13 August 2024. [Google Scholar]
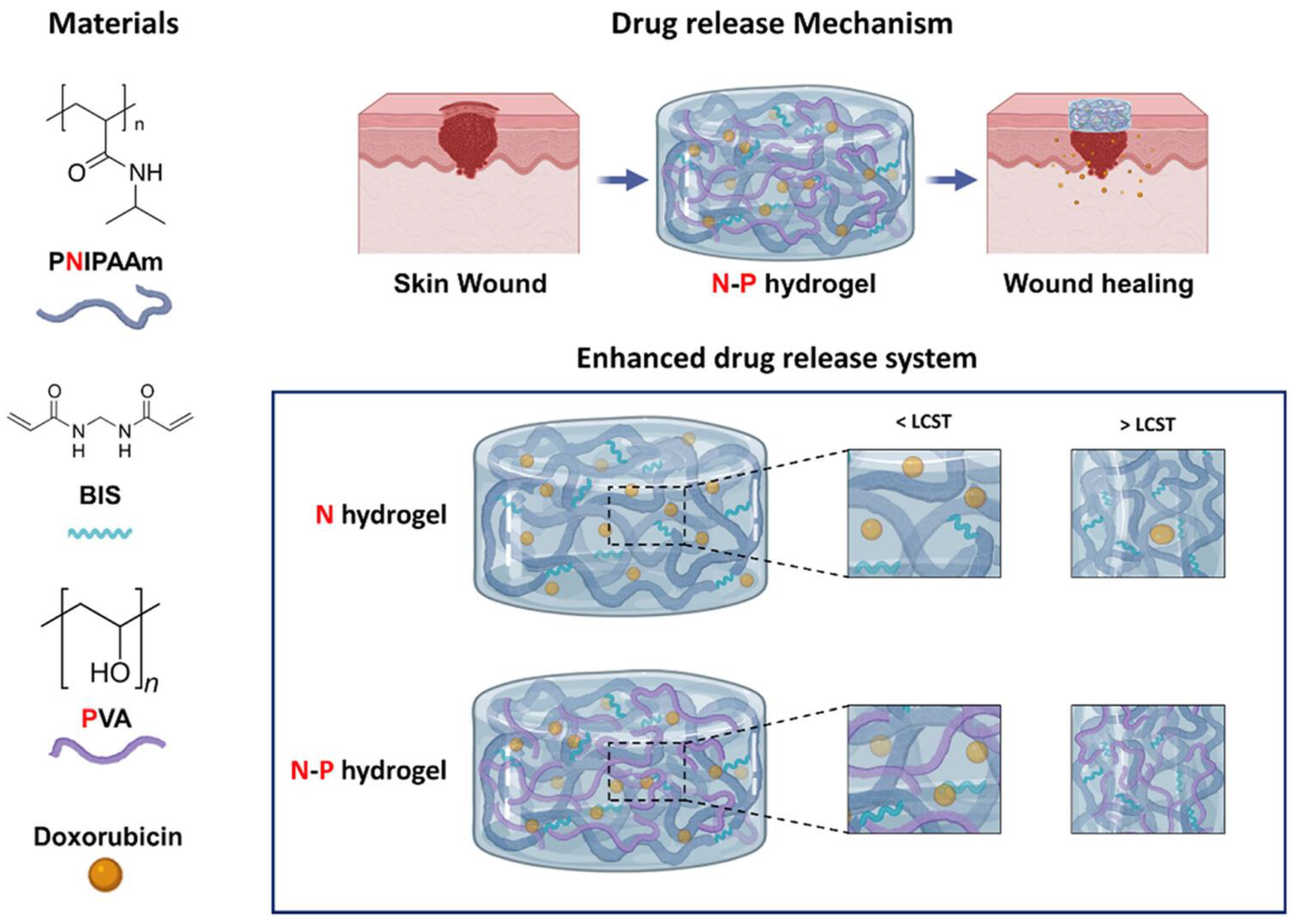
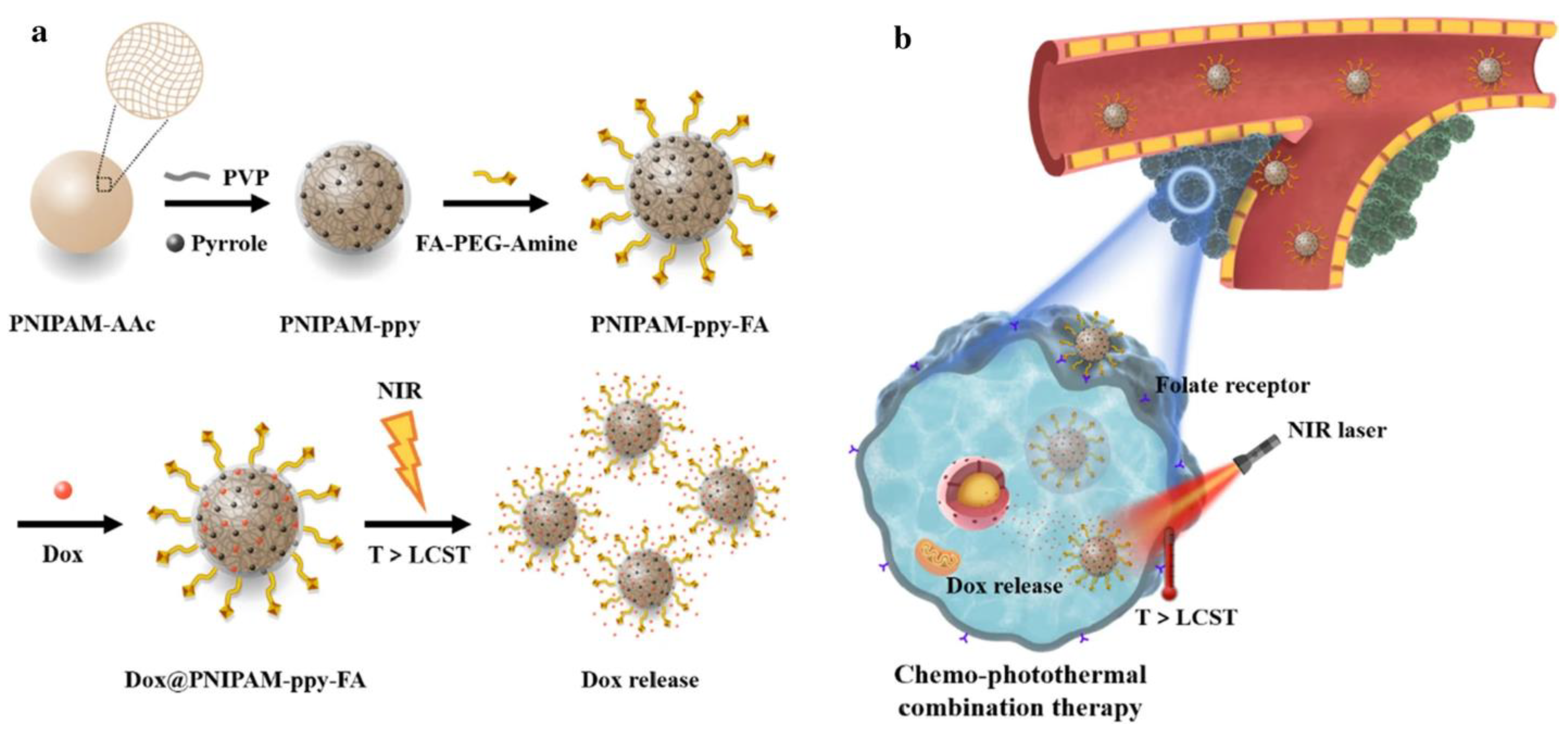
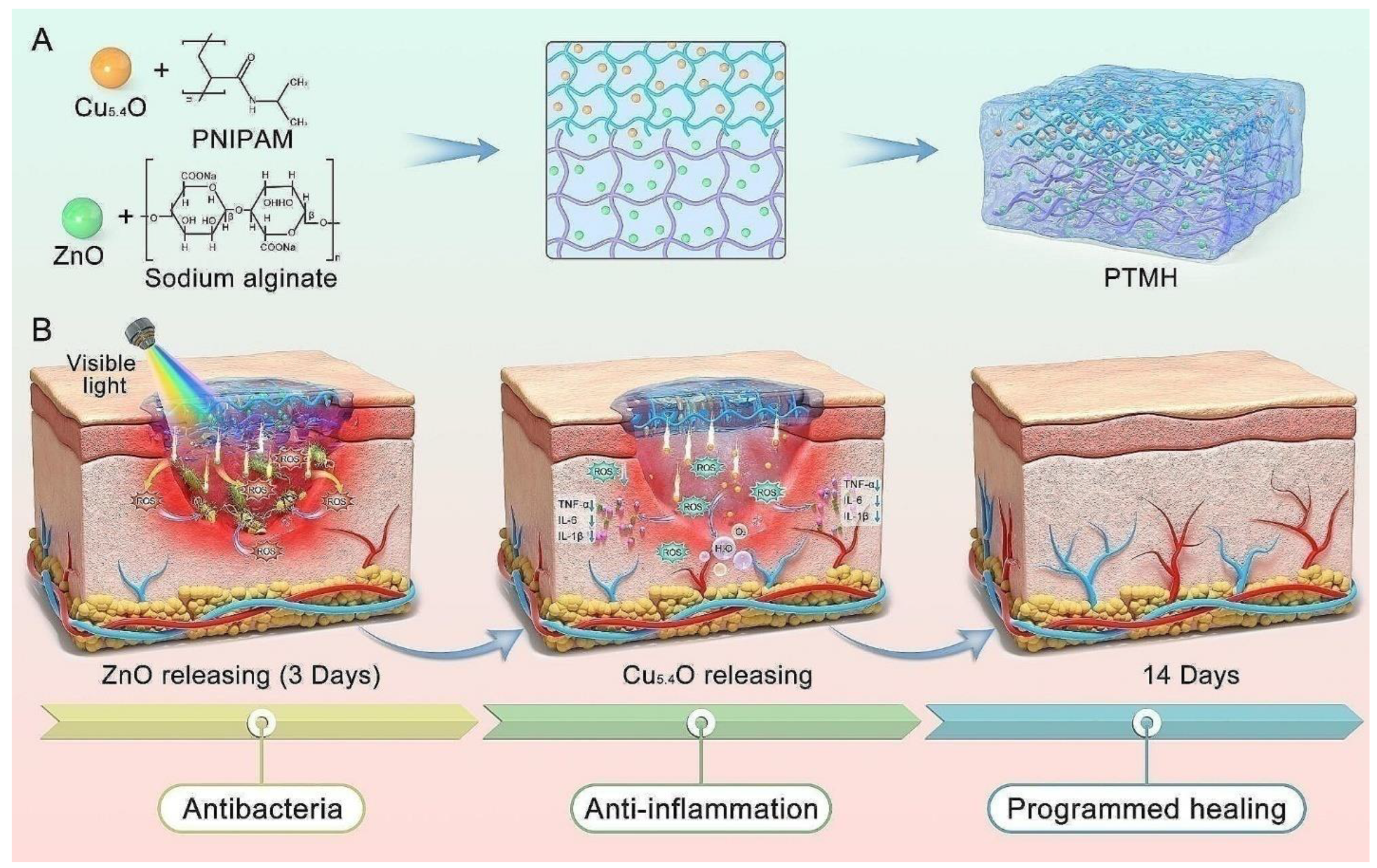
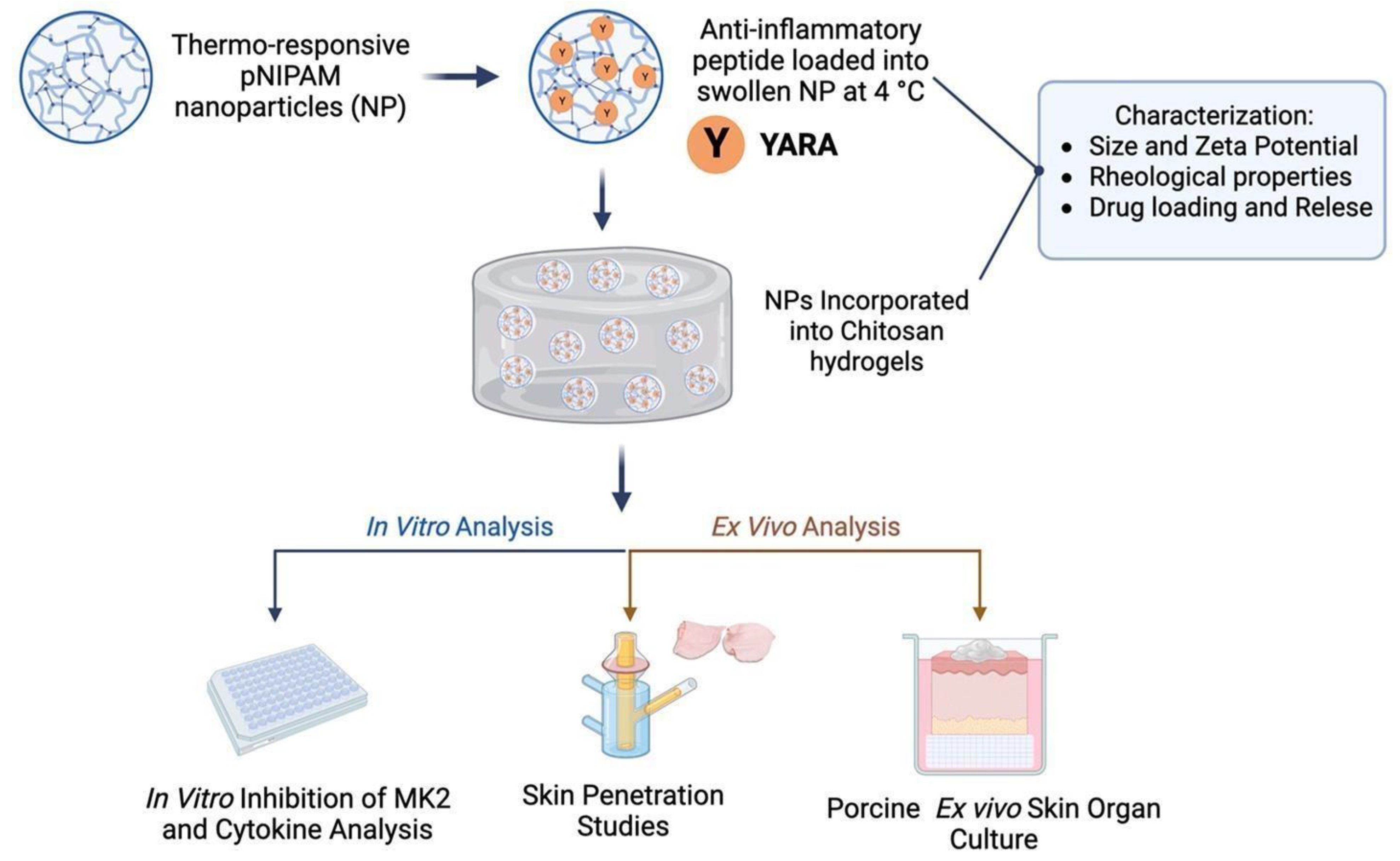
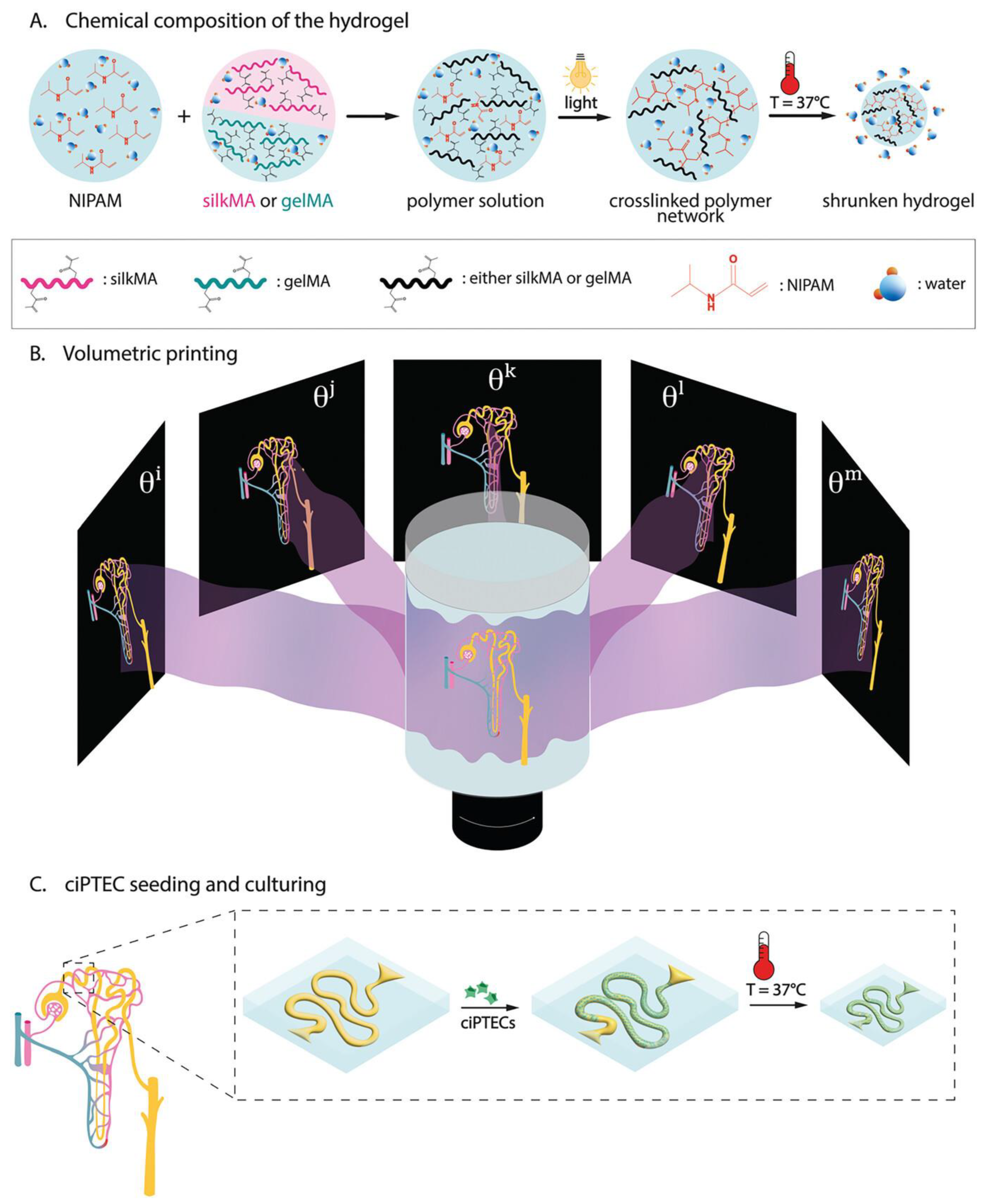
| Composition of Hydrogel | Method of Preparation | Therapeutic Agent/Model Drug | Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIPAM, N,N′-methylene bis acrylamide, Poly-L-lactic acid | UV irradiation | Betamethasone dipropionate, hexane extract derived from Boesenbergia rotunda | Atopic dermatitis | [95] |
| NIPAM, Hyaluronic acid, Tetramethylethylenediamine | Radical polymerization | Luteolin | Transdermal drug delivery | [62] |
| NIPAM, N,N′ Methylenebis(acrylamide), Polyvinyl alcohol | Precipitation polymerization | PNIPAM | Microneedle-based drug delivery | [94] |
| NIPAm, glycidyl methacrylate, tetrahydrofuran, 2,2-azobisisobutyronitrile, | Free radical polymerization | Ibuprofen and 5-fluorouracil | Hydrophilic and hydrophobic drug delivery | [121] |
| NIPAM, N,N′-Methylenebis(acrylamide), Ammonium peroxdisulfate, N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylethylenediamine, Polyvinyl alcohol | Free radical polymerization | Doxorubicin | Cancer | [122] |
| NIPAM, N,N′-methylenebis (acrylamide), Acetic acid, Hydrofluoric acid, Sodium ethyl xanthate, Span 80, Tween 20, Azobisisobutyronitrile | Reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization | Doxorubicin | Cancer | [124] |
| NIPAM, Tetramethylethylenediamine, Ammonium peroxdisulfate, N,N′-methylene Bis (acrylamide), Graphene oxide, Chitosan, Sodium alginate | Free radical polymerization | Graphene oxide | Wound healing | [138] |
| NIPAM, Graphite oxide–nano silver, Ammonium persulfate, Tetramethylethylenediamine | Free radical polymerization | Graphite oxide, nano silver | Wound healing | [139] |
| NIPAM, N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylethylenediamine, N,N-Methylenebisacrylamide, Bis-acrylamide, Ammonium persulfate | Free radical polymerization | Metformin hydrochloride | Diabetic wound healing | [141] |
| NIPAM, HEMA, Poly(ε-caprolactone) | Polymerization | Recombinant human BMP-2 and VEGF | Bone regeneration | [144] |
| NIPAM, 2-methylene-bis-acrylamide, Hydroxyapatite | Electrochemical polymerization method | Oxacillin | Tissue engineering | [146] |
| NIPAM, Gelatin, N,N,N′,N′,N″-pentamethyl diethylenetriamine, N-hydroxysuccinimide | Atom transfer radical polymerization | Gelatin | Bone regeneration | [147] |
| NIPAM, N-acryloxysuccinimide, Poly(ethylene glycol) | Reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization | Dexamethasone | Ocular drug delivery | [153] |
| NIPAM, Polyethylene glycol, N,N,N0,N0-tetramethylethylenediamine | Free radical polymerization | - | Ocular drug delivery | [155] |
| NIPAM, 2, 2-azobisisobutyronitrile | Bulk polymerization | - | Ocular bioadhesive | [156] |
| NIPAM, 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate, | Atom transfer radical polymerization | siRNA | Sustained drug delivery | [167] |
| NIPAM, Adenosine triphosphate | Free radical polymerization | Magnolol (MAG) nanocrystals | Parkinson’s disease | [168] |
| NIPAM, Gelatin, Silk fibroin | Light-induced radical polymerization | - | 3D printing of kidney tubules | [169] |
| Patent No. | Title of Invention | Application | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102580633A | Preparation method of graphene oxide/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) composite hydrogel | Drug delivery and tissue engineering | 2012 | [176] |
| CN104825390A | Preparation method of camptothecin controlled release organic/inorganic hybrid material POSS/PNIPAM-b-PDMAEMA | Cancer | 2015 | [177] |
| CN104490489A | Method for preparing tissue engineering blood vessel based on 3D bioprinting technology | Tissue engineering | 2015 | [178] |
| CN105561334A | Temperature targeting-based nanogel gene delivery compound, and preparation method and application thereof | Cancer | 2016 | [179] |
| CN107233570A | VEGF antibody-carrying ophthalmic thermosensitive hydrogel implant and preparation method thereof | Ocular drug delivery | 2017 | [180] |
| CN108976356A | Temperature and redox-sensitive type drug delivery material connected by diselenide bonds and preparation and application thereof | Cancer | 2018 | [181] |
| CN108186607A | Preparation method of breast cancer targeted chitosan grafted polymer medicine-carrying composite material | Breast cancer | 2018 | [182] |
| CN109864968A | Amino organic silicon liposome/temperature-sensitive hydrogel composite material encapsulating water-soluble medicine | Transdermal drug delivery | 2019 | [183] |
| CN109513038A | Thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with copper metal organic skeleton nanoparticles and preparation method of thermosensitive hydrogel | Wound healing | 2019 | [184] |
| CN109528767A | Synthetic method of antibacterial preparation based on PNIPAM and silver nanometer clusters | Wound healing | 2019 | [185] |
| CN110064127A | Intelligent transdermal drug release system for controlling drug dosage of patch based on heart rate variability | Transdermal drug delivery | 2019 | [186] |
| CN110152071A | Reversible thermosensitive sealant for temporarily closing ocular trauma and syringe applied to sealant | Ocular sealant | 2019 | [187] |
| CN111533927A | Preparation method of pH and temperature dual-response UV crosslinked chitosan injectable hydrogel | Tissue engineering | 2020 | [188] |
| CN111803702A | Preparation method of cyclic gamma-polyglutamic acid modified hydrogel loaded with growth factors | Wound healing | 2020 | [189] |
| CN112999412A | Hydrogel dressing for wound healing and preparation method thereof | Wound healing | 2021 | [190] |
| KR20220043756A | Temperature-sensitive polymer-based nanocomposite capable of chemo-photothermal treatment by cancer cell targeting and near-infrared ray and method for preparing the same | Cancer | 2022 | [191] |
| US11376344B2 | System for sutureless closure of scleral perforations and other ocular tissue discontinuities | Ocular sealant | 2022 | [192] |
| CN115337447A | Silver sulfadiazine hydrogel for rapid wound healing as well as preparation method and application of silver sulfadiazine hydrogel | Wound healing | 2022 | [193] |
| CN116474159A | Constant-temperature photo-thermal system and application thereof | Wound healing | 2023 | [194] |
| CN116199911A | Bi-crosslinking hydrogel and application thereof as wound healing dressing | Wound healing | 2023 | [195] |
| CN115970004A | Two-way nano-drug delivery system based on NIR-IIFL guidance and application | Cancer theranostics | 2023 | [196] |
| CN118477038A | Emodin nanosuspension temperature-sensitive gel as well as preparation method and application thereof | Wound healing | 2024 | [197] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Narayana, S.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Hani, U.; Ahmed, M.G.; Asiri, Z.A.; Paul, K. Smart Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels: A Tour D’horizon of Biomedical Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030207
Narayana S, Gowda BHJ, Hani U, Ahmed MG, Asiri ZA, Paul K. Smart Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels: A Tour D’horizon of Biomedical Applications. Gels. 2025; 11(3):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030207
Chicago/Turabian StyleNarayana, Soumya, B. H. Jaswanth Gowda, Umme Hani, Mohammed Gulzar Ahmed, Zahrah Ali Asiri, and Karthika Paul. 2025. "Smart Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels: A Tour D’horizon of Biomedical Applications" Gels 11, no. 3: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030207
APA StyleNarayana, S., Gowda, B. H. J., Hani, U., Ahmed, M. G., Asiri, Z. A., & Paul, K. (2025). Smart Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels: A Tour D’horizon of Biomedical Applications. Gels, 11(3), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030207










