Physical and Structural Properties of Chitosan–Squid Gelatin Hydrogels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
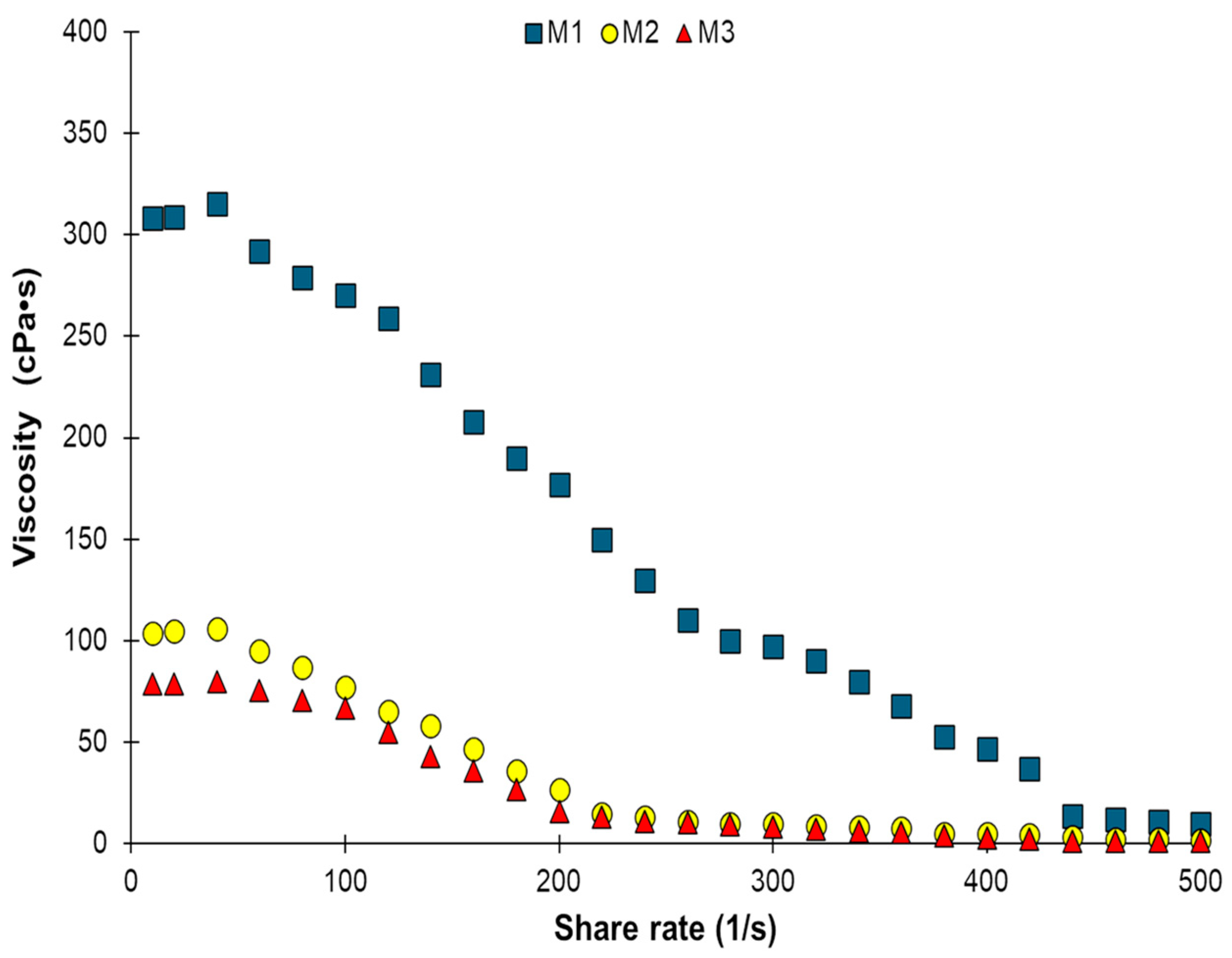
2.1. Steady Shear Measurements
2.2. Stability
2.3. Textural Profile
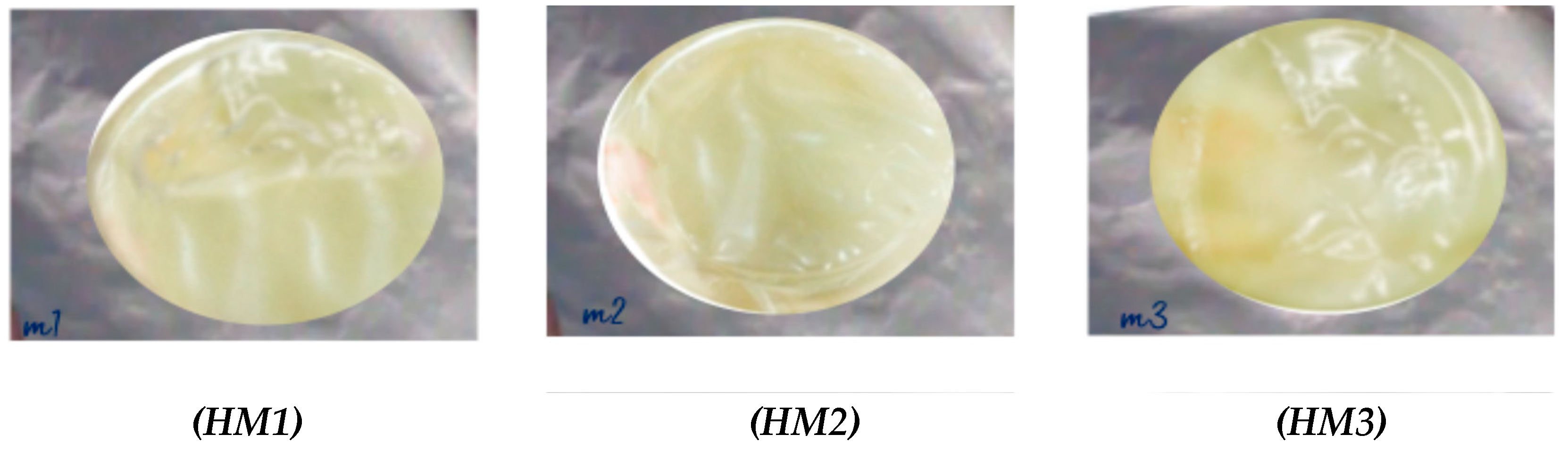
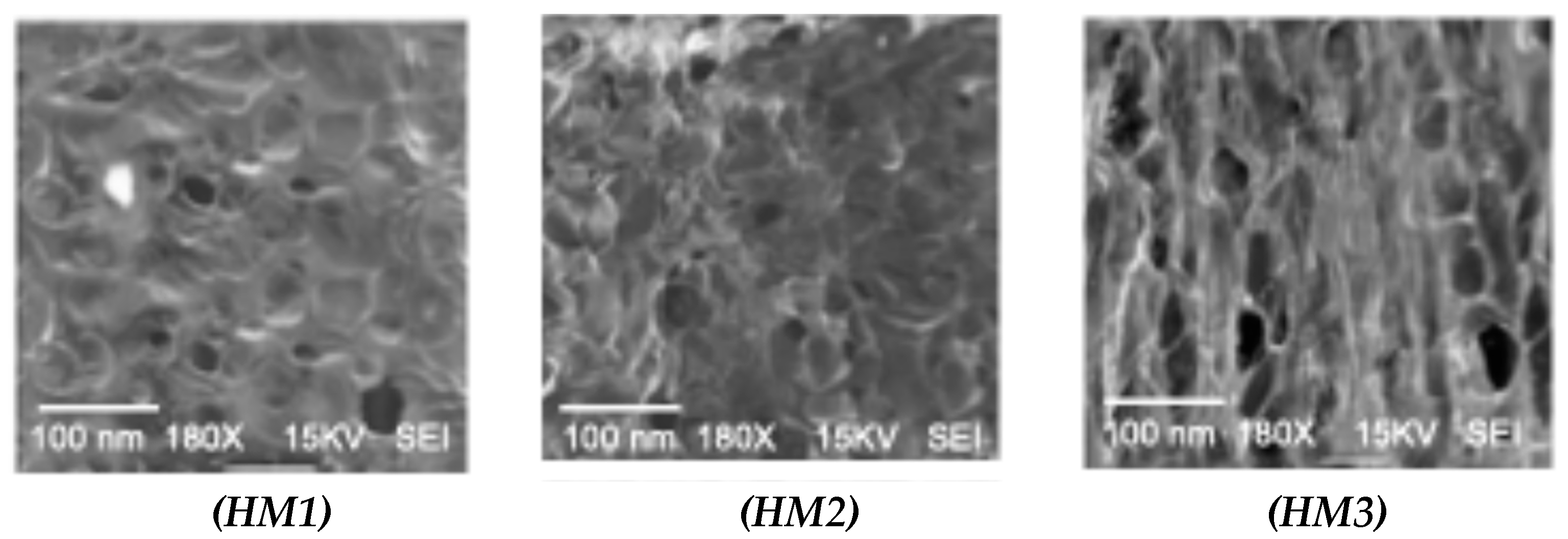
2.4. Appearance and Morphology
2.5. Antioxidant Activity
2.6. Chemical Characterization of Hydrogels
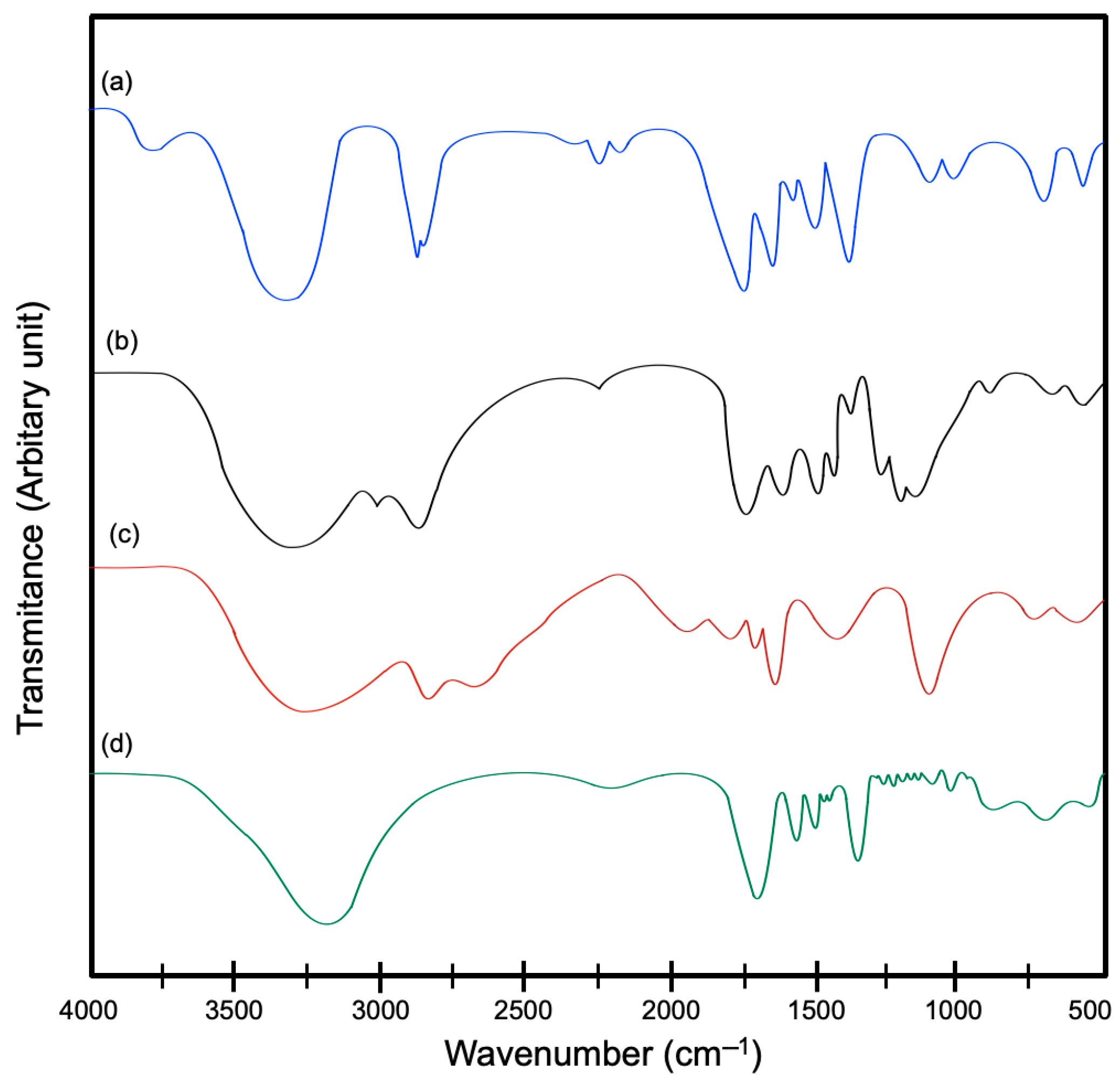
2.6.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR)
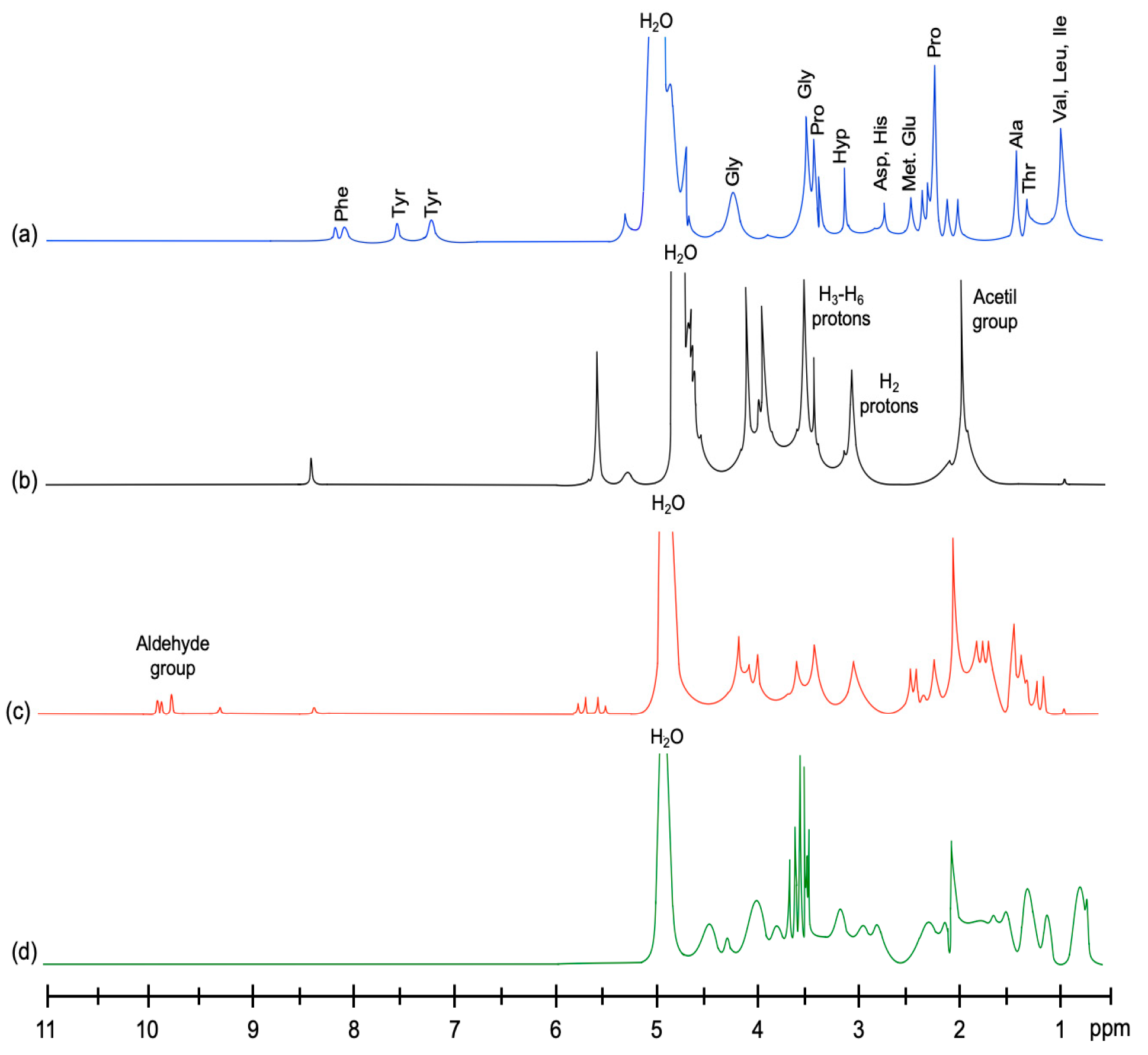
2.6.2. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H-NMR)
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Gelatin Extraction
4.3. Chitosan–Gelatin Hydrogel
4.4. Analysis
4.4.1. Viscosity Determination of Hydrogel-Forming Solutions
4.4.2. Water Content and Hydrogel Stability in Aqueous Solution
4.4.3. Textural Profile
4.4.4. Surface Morphology of Hydrogels
4.4.5. Hydrogel Antioxidant Activity
4.4.6. Chemical Characterization of Hydrogels
- Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR)
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, T.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Chan, H.-P.; Chung, T.-W.; Shu, C.-W.; Chuang, K.-P.; Duh, T.-H.; Yang, M.-H.; Tyan, Y.-C. Hydrogels: Properties and applications in biomedicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagan, D.; Kalim, D.; Deon, B.; Yi-Cheun, Y. Hydrogels: Definition, History, Classifications, Formation, Constitutive Characteristics, and Applications. In Multicomponent Hydrogels: Smart Materials for Biomedical Applications; Jagan, D., Kalim, D., Deon, B., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2023; Biomaterials Science Series; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Peng, Z.; Shen, Y. Fabrication and properties of gelatin/chitosan composite hydrogel. Polim. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2011, 50, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bourakadi, K.; Qaiss, A.; Bouhfid, R. Sustainable hydrogels in food packaging systems. In Sustainable Hydrogels Synthesis, Properties, and Applications, 1st ed.; Sabu, T., Bhasha, S., Purnima, J., Shashank, S., Eds.; Matthew Deans: Oxford, UK, 2023; Volume 1, pp. 355–374. [Google Scholar]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudos, M. Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, P.C.; Tharanathan, R.N. Chitin/chitosan-safe, ecofriendly packaging materials with multiple potential uses. Food Rev. Int. 2007, 23, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.A.; Arumainathan, S. Crosslinked Chitosan−gelatin biocompatible nanocomposite as a neuro drug carrier. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 18732–18744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipal, J.; Mohd Pu’adA, N.A.S.; Lee, T.C.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Sahari, N.; Basri, H.; Idris, M.I.; Abdullah, H.Z. A review of gelatin: Properties, sources, process, applications, and commercialization. Mater. Today 2021, 42, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranga, J.; Etxabide, A.; Cabezudo, S.; de la Caba, K.; Guerrero, P. Valorization of marine-derived biowaste to develop chitin/fish gelatin products as bioactive carriers and moisture scavengers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squid Market Analysis APAC, Europe, North America, South America, Middle East and Africa—China, India, Japan, Spain, Peru—Size and Forecast 2024–2028. Available online: https://www.technavio.com/report/squid-market-industry-analysis (accessed on 29 November 2024).
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/66538eba-9c85-4504-8438-c1cf0a0a3903/content/sofia/2024/capture-fisheries-production.html (accessed on 29 November 2024).
- Squid and Squid By-products. Crops. Available online: https://www.ams.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media/Squid-TR-011216.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2024).
- Uriarte-Montoya, M.H.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J.; Rouzaud-Sández, O.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Giant squid skin gelatin: Chemical composition and biophysical characterization. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 3243–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-Higuera, J.E.; Robles-Sánchez, R.M.; Burgos-Hernández, A.; Márquez-Ríos, E.; Velázquez-Contreras, C.A.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Squid by-product gelatines: Effect on oxidative stress biomarkers in healthy rats. Czech J. Food Sci. 2016, 34, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Aubourg, S.P. Bioactive peptides from collagen hydrolysates from squid (Dosidicus gigas) by-products fractionated by ultrafiltration. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomé Machado, A.A.; Martins, V.C.A.; Plepis, A.M.G. Thermal and rheological behavior of collagen. Chitosan Blends. J. Therm. Anal. Cal. 2002, 67, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Amaral Sobral, P.J.; Gebremariam, G.; Drudi, F.; De Aguiar Saldanha Pinheiro, A.C.; Romani, S.; Rocculi, P.; Dalla Rosa, M. Rheological and viscoelastic properties of chitosan solutions prepared with different chitosan or acetic acid concentrations. Foods 2022, 11, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolo, M.R.V.; Martins, V.C.A.; Plepis, A.M.G.; Bogusz, S., Jr. Rheological study of the incorporation of grape seed extract in chitosan and gelatin coatings. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, B.; Alemán, A.; Montero, P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Antioxidant and functional properties of gelatin hydrolysates obtained from skin of sole and squid. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Q.; Xiong, L. Enhanced mechanical properties and gelling ability of gelatin hydrogels reinforced with chitin whiskers. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goder Orbach, D.; Sharabani-Yosef, O.; Hadad, O.; Zilberman, M. Gelatin-based polymers can be processed to highly resilient biocompatible porous hydrogel scaffolds for soft tissue regeneration applications. Gels 2024, 10, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, S.; Khoobbakht, F.; Mirmoghtadaie, L.; Hosseini, S.M. Characterization of gellan gum-chitosan based hydrogel to evaluate as a potential gelatin substitute. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 45, 109038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, M.; Gopal, J.; Chun, S.; Devadoss, A.J.P.; Hasan, N.; Sivanesan, I. Crustacean Waste-Derived Chitosan: Antioxidant Properties and Future Perspective. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, F.; Mahmoodi, M. Controlled release of protein from gelatin/chitosan hydrogel containing platelet-rich fibrin encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles for accelerated wound healing in an animal model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 588–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista-Silva, S.; Bernardes, B.G.; Borges, S.; Rodrigues, I.; Fernandes, R.; Gomes-Guerreiro, S.; Pinto, M.T.; Pintado, M.; Soares, R.; Costa, R.; et al. Exploring silk sericin for diabetic wounds: An in situ- forming hydrogel to protect against oxidative stress and improve tissue healing and regeneration. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinkowska, A.; Wisniewski, M.; Skopinska, J.; Kennedy, C.J.; Wess, T.J. The photochemical stability of collagen–chitosan blends. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2004, 162, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, E.; Rajapakse, N.; Kim, S.K. Antioxidant properties of a radical scavenging peptide purified from enzymatically prepared fish skin gelatin hydrolysates. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.H.; Kim, S.K. Antioxidant effects of chitin, chitosan, and their derivatives. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 73, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staroszczyk, H.; Sztuka, K.; Wolska, J.; Wojtasz-Pająk, A.; Kolodziejska, I. Interaction of fish gelatin and chitosan in uncrosslinked and crosslinked with EDC films: FT-IR study. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, T.; Zeeshan, R.; Zarif, F.; Ilyas, K.; Muhammad, N.; Safi, S.Z.; Rahim, A.; Rizvi, S.A.A.; Rehman, I.U. FTIR analysis of natural and synthetic collagen. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2018, 53, 703–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugnerotto, J.; Lizardi, J.; Goycoolea, F.; Argüelles, W.; Desbrières, J. An infrared investigation in relation with chitin and chitosan characterization. Polymer 2001, 42, 3569–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shan, C.-L.; Zhou, Q.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.-L.; Xu, F.; Han, L.-R.; Ibrahim, M.; Guo, L.-B.; Xie, G.-L.; et al. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity of Cross-Linked Chitosan-Glutaraldehyde. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1534–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, M.R.; Singh, D. Preparation and optimization of chitosan-gelatin films for sustained delivery of lupeol for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Chen, C.; Pettitt, B.M.; Iwahara, J. NMR methods for characterizing the basic side chains of proteins: Electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and conformational dynamics. Methods Enzymol. 2019, 615, 285–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodin, V.V.; Izmailova, V.N. NMR method in the study of the interfacial adsorption layer of gelatin. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspcects 1996, 106, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, G.D.; Nes, E.; Amurao, M.; Rahal, A.; Krasnosselskaia, L.; Cameron, I. An NMR method to characterize multiple water compartments on mammalian collagen. Cell Biol. Int. 2006, 30, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, D.R.; Monnier, V.M. Structure elucidation of a senescence cross-link from human extracellular matrix: Implication of pentoses in the aging process. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 3264, 21597–21602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cervantes, J.; Sánchez-Machado, D.I.; Sánchez-Duarte, R.G.; Correa-Murrieta, M.A. Study of a fixed-bed column in the adsorption of an azo dye from an aqueous medium using a chitosan–glutaraldehyde biosorbent. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, O.A., Jr.; Airoldi, C. Some studies of crosslinking chitosan-glutaraldehyde interaction in a homogeneous system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 26, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.A.; Nguyen, T.H.; Lee, B.Y. Preparation and characterization of electrospun PCL/PLGA membranes and chitosan/gelatin hydrogels for skin bioengineering applications. J. Mat. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhou, D.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Zhou, X.; Gan, T.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Zhou, X. Rational fabrication of anti-freezing, non-drying tough organohydrogels by one-pot solvent displacement. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6568–6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio-Flores, P.B.; García-Amezquita, L.E.; Ramos-Martínez, A.; Tirado Gallegos, J.M.; Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Salgado-Delgado, R. Soluciones formadoras de películas a base de almidón oxidado de avena mezclada con quitosano: Caracterización reológica y propiedades mecánicas de sus películas. Rev. Iberoam. Pol. 2013, 14, 293–304. [Google Scholar]
- Gontard, N.; Guilbert, S.; Cuq, J.L. Edible wheat gluten films influence of the main process variables on film properties using response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. 1992, 57, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.L.; Hoang, H.; Gu, L.; Wu, X.; Bacchiocca, M.; Howard, L.; Hampsch-Woodill, M.; Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Jacob, R. Assays for hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidant capacity (oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORACFL) of plasma and other biological and food samples. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2003, 5, 3273–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Assay | M1 | M2 | M3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| μ (cPa·s) 1 | 308.9 a ± 1.7 | 103.9 b ± 1.4 | 78.6 c ± 1.2 |
| W (%) 2 | 19.9 c ± 1.4 | 26.7 b ± 2.4 | 33.4 a ± 1.9 |
| DPPH (IC50; μg/mL) | 30.7 c | 26.1 b | 22.4 a |
| ORAC (μmol TE/g) 3 | 1.7 c ± 0.3 | 4.2 b ± 0.2 | 5.6 a ± 0.5 |
| Textural Properties 1 | HM1 | HM2 | HM3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (g force) | 1339.6 a ± 29.7 | 1170.3 b ± 20.1 | 1041.9 c ± 18.8 |
| Springiness (%) | 0.92 c ± 0.04 | 0.95 b ± 0.06 | 0.97 a ± 0.01 |
| Chewiness (g force) | 1026.2 a ± 3.2 | 1007.4 b ± 6.1 | 917.2 c ± 8.6 |
| Resilience (%) | 18.9 b ± 1.8 | 34.2 a ± 3.1 | 35.6 a ± 2.1 |
| Assignments | Squid Gelatin | Chitosan | Chitosan Hydrogel | Chitosan–Squid Gelatin Hydrogel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-H stretching, Amide A | 3431 | 3260 | 3250 | 3175 |
| CH2 and NH3+asymmetric stretch, Amide B | 2830 | 2835 | 2750 | – |
| C=O stretching, Amide I | 1635 | 1645 | 1635 | 1630 |
| N–H and C–N torsional vibration, Amide II | 1585 | 1581 | 1581 | 1545 |
| CH residual groups, Amide III | 1283 | – | – | 1285 |
| Primary alcohol OH group | 1480 | 1480 | 1406 | 1480 |
| -CH2 torsion and C-N tension vibration | – | 1406–1249 | – | – |
| Pyranosic and C-O-C groups | – | 1080 | 1050 | – |
| N-H and C-OH out-of-plane bending | 672–562 | 675–564 | 670–549 | 665–550 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Campas, U.; Aubourg, S.P.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Physical and Structural Properties of Chitosan–Squid Gelatin Hydrogels. Gels 2025, 11, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11020109
Ramírez-Campas U, Aubourg SP, Torres-Arreola W, Plascencia-Jatomea M, Ezquerra-Brauer JM. Physical and Structural Properties of Chitosan–Squid Gelatin Hydrogels. Gels. 2025; 11(2):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11020109
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Campas, Uriel, Santiago P. Aubourg, Wilfrido Torres-Arreola, Maribel Plascencia-Jatomea, and Josafat Marina Ezquerra-Brauer. 2025. "Physical and Structural Properties of Chitosan–Squid Gelatin Hydrogels" Gels 11, no. 2: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11020109
APA StyleRamírez-Campas, U., Aubourg, S. P., Torres-Arreola, W., Plascencia-Jatomea, M., & Ezquerra-Brauer, J. M. (2025). Physical and Structural Properties of Chitosan–Squid Gelatin Hydrogels. Gels, 11(2), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11020109









