Injectable Hydrogels with Tissue-Adaptive Gelation and Mechanical Properties: Enhancing Softness and Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
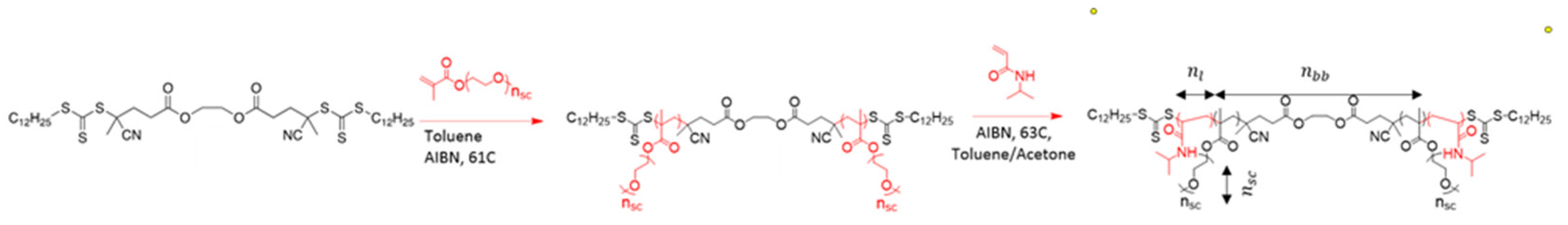
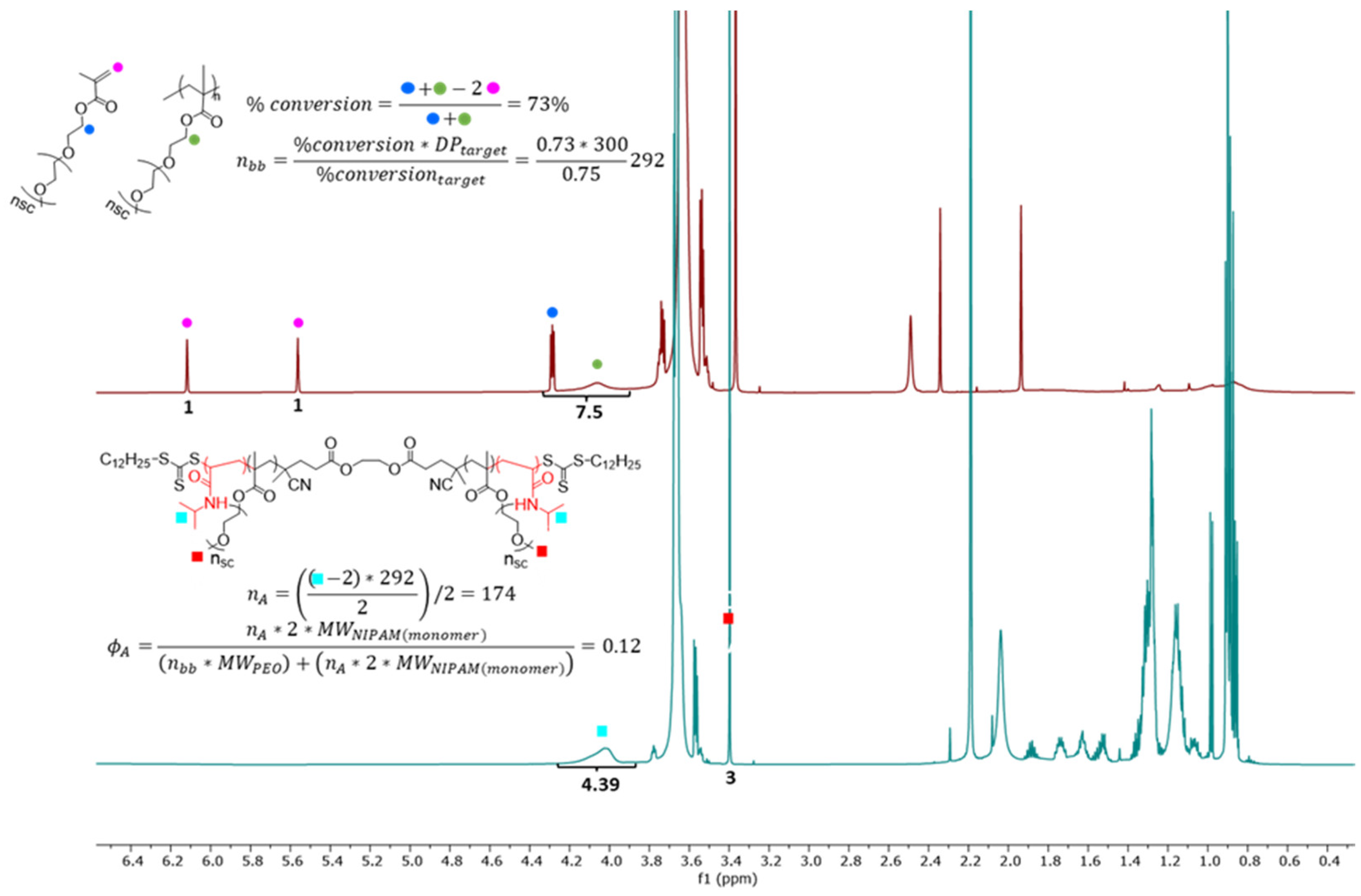
2.1. Structure of Individual Macromolecules and Networks
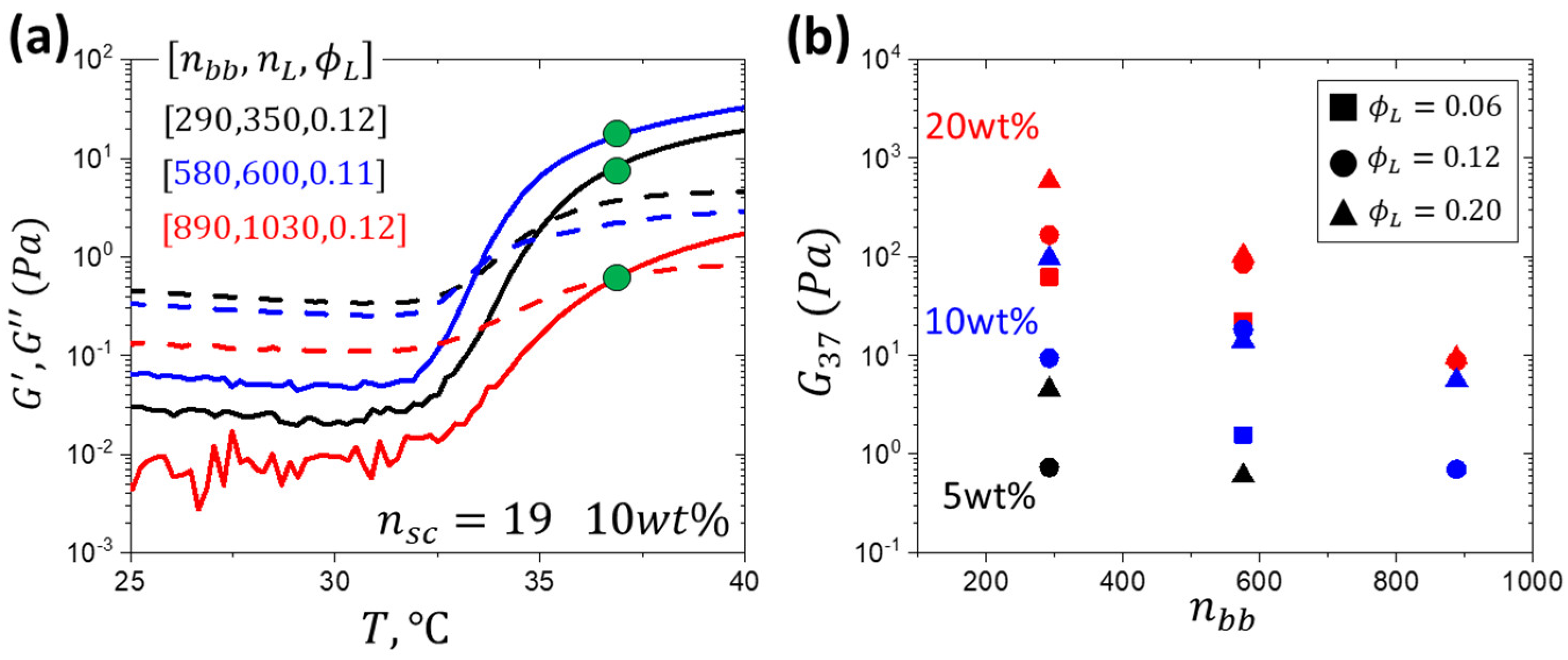
2.2. Monitoring the Gelation Process by Rheology
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LBL | Linear-bottlebrush-linear |
| Bb | Bottlebrush |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| PNIPAM | Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| PEGMA | Poly(ethylene-glycol) methyl ether methacrylate |
| CTA | Chain transfer agent |
| RAFT | Reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer |
| LCST | Lower critical solution temperature |
| USAXS-SAXS | Ultra-small and small-angle X-ray scattering |
| DP | Degree of polymerization |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Synthesis and Molecular Characterization

Appendix A.2. Rheology Data
| (1) | (2) | (3) | wt. % (4) | (5) | (5) | (5) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 290 | 80 | 0.06 | 5 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0.00428 | N/A |
| 10 | 37.9 | 3.08 | 37.0 | 3.10 | 1.96 | 0.9 | |||
| 20 | 33.0 | 15.5 | 31.5 | 14.8 | 62.2 | 1.5 | |||
| 174 | 0.12 | 5 | 36.6 | 0.51 | 35.7 | 0.51 | 0.73 | 0.9 | |
| 10 | 35.1 | 2.13 | 33.3 | 1.9 | 9.43 | 1.8 | |||
| 20 | 32.3 | 11.0 | 30.5 | 10.0 | 77.5 | 1.8 | |||
| 341 | 0.22 | 5 | 34.2 | 0.385 | 32.6 | 0.380 | 4.49 | 1.6 | |
| 10 | 32.5 | 3.90 | 30.9 | 4.75 | 96.1 | 1.6 | |||
| 20 | 26.8 | 44.5 | 21.0 | 46.2 | 580 | 5.8 | |||
| 580 | 188 | 0.07 | 5 | 38.4 | 0.259 | 37.5 | 0.260 | 0.177 | 0.9 |
| 10 | 35.9 | 0.673 | 34.3 | 0.622 | 1.57 | 1.6 | |||
| 20 | 31.8 | 6.58 | 30.1 | 6.64 | 22.4 | 1.7 | |||
| 301 | 0.12 | 5 | 37.4 | 0.335 | 36.3 | 0.320 | 0.278 | 1.1 | |
| 10 | 33.5 | 0.812 | 31.9 | 0.677 | 18.34 | 1.6 | |||
| 20 | 27.3 | 29.2 | 25.8 | 0.684 | 84.1 | 1.5 | |||
| 632 | 0.20 | 5 | 35.5 | 0.232 | 33.9 | 0.257 | 0.343 | 1.6 | |
| 10 | 33.4 | 0.912 | 31.6 | 0.823 | 14.0 | 1.8 | |||
| 20 | 28.8 | 12.9 | 25.3 | 14.2 | 102 | 3.5 | |||
| 890 | 237 | 0.06 | 5 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0.0119 | N/A |
| 10 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0.261 | N/A | |||
| 20 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1.95 | N/A | |||
| 512 | 0.12 | 5 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0.0637 | N/A | |
| 10 | 36.9 | 0.621 | 35.7 | 0.632 | 0.650 | 1.2 | |||
| 20 | 33.9 | 5.34 | 32.5 | 5.53 | 8.83 | 1.4 | |||
| 919 | 0.20 | 5 | 36.3 | 0.298 | 34.7 | 0.303 | 0.470 | 1.6 | |
| 10 | 33.2 | 4.12 | 30.7 | 4.20 | 18.1 | 2.5 | |||
| 20 | 31.1 | 7.04 | 29.4 | 7.62 | 24.8 | 1.7 |


References
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gao, J. The Engineering and Application of Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels: A Review. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 3784–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, C.; Liao, L.; Zhang, W. Hydrogels Mimicking the Viscoelasticity of Extracellular Matrix for Regenerative Medicine: Design, Application, and Molecular Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, A.; Gradinaru, L.M.; Gradinaru, V.R.; Bercea, M. Diversity of Bioinspired Hydrogels: From Structure to Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Fraile, H.; Otero, J. Mechanical Properties of the Extracellular Matrix. In Handbook of the Extracellular Matrix: Biologically-Derived Materials; Maia, F.R., Oliveira, J.M., Reis, R.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J.R.W.; Isomursu, A.; Follain, G.; Härmä, V.; Jou-Ollé, E.; Pasquier, N.; Välimäki, E.P.O.; Rantala, J.K.; Ivaska, J. Defined Extracellular Matrix Compositions Support Stiffness-Insensitive Cell Spreading and Adhesion Signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2304288120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muiznieks, L.D.; Keeley, F.W. Molecular Assembly and Mechanical Properties of the Extracellular Matrix: A Fibrous Protein Perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2013, 1832, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, C.F.; Gasperini, L.; Marques, A.P.; Reis, R.L. The Stiffness of Living Tissues and Its Implications for Tissue Engineering. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, O.; Cooper-White, J.; Janmey, P.A.; Mooney, D.J.; Shenoy, V.B. Effects of Extracellular Matrix Viscoelasticity on Cellular Behaviour. Nature 2020, 584, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyburz, K.A.; Anseth, K.S. Synthetic Mimics of the Extracellular Matrix: How Simple Is Complex Enough? Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, R.; Cavanagh, B.; Cameron, A.R.; Kelly, D.J.; O’Brien, F.J. Material Stiffness Influences the Polarization State, Function and Migration Mode of Macrophages. Acta Biomater. 2019, 89, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lin, M.; Huang, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Bai, G.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F. 3D Spatiotemporal Mechanical Microenvironment: A Hydrogel-Based Platform for Guiding Stem Cell Fate. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, F.; Sommer, F.; Goepferich, A. Rational Design of Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering: Impact of Physical Factors on Cell Behavior. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.R.; Ramli, M.F.H.; Shen, X.; Kannivadi Ramakanth, K.; Chen, D.; Hu, Y.; Vidyasekar, P.; Foo, R.S.; Long, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Hybrid Hydrogel–Extracellular Matrix Scaffolds Identify Biochemical and Mechanical Signatures of Cardiac Ageing. Nat. Mater. 2025, 24, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Pragnere, S.; Kurniawan, N.A. Revisiting the Biophysical Aspects of Extracellular-Matrix-Mimicking Hydrogels: What Cells See vs. What Cells Feel. Biomater. Sci. 2025, 13, 5297–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.G.; Cha, G.D. Extracellular-Matrix-Mimetic Hydrogels by Using Nanomaterials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Sha, D.; Ma, Y.; Kim, B.Y.S.; Jiang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C. Injectable, Viscoelastic Hydrogel Precisely Regulates Developmental Tissue Regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 133860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-A.; Yeom, J.; Hwang, B.W.; Hoffman, A.S.; Hahn, S.K. In Situ-Forming Injectable Hydrogels for Regenerative Medicine. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1973–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ding, J. Injectable Hydrogels as Unique Biomedical Materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, N.; Shin, S.R.; Tamayol, A.; Miscuglio, M.; Bakooshli, M.A.; Assmann, A.; Mostafalu, P.; Sun, J.-Y.; Mithieux, S.; Cheung, L.; et al. Highly Elastic and Conductive Human-Based Protein Hybrid Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, N.; Tamayol, A.; Uquillas, J.A.; Akbari, M.; Bertassoni, L.E.; Cha, C.; Camci-Unal, G.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Peppas, N.A.; Khademhosseini, A. 25th Anniversary Article: Rational Design and Applications of Hydrogels in Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 85–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Vashahi, F.; Moutsios, I.; Umarov, A.Z.; Ageev, G.G.; Wang, Z.; Ivanov, D.A.; Dobrynin, A.V.; Sheiko, S.S. Bottlebrush Hydrogels with Hidden Length: Super-Swelling and Mechanically Robust. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2410905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheiko, S.S.; Vashahi, F.; Morgan, B.J.; Maw, M.; Dashtimoghadam, E.; Fahimipour, F.; Jacobs, M.; Keith, A.N.; Vatankhah-Varnosfaderani, M.; Dobrynin, A.V. Mechanically Diverse Gels with Equal Solvent Content. ACS Cent. Sci. 2022, 8, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.J.; Rajendran, R.R.; Mohanto, S.; Agarwal, U.; Panda, K.; Dhotre, K.; Manne, R.; Deepak, A.; Zafar, A.; Yasir, M.; et al. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: A Review of the State-of-the-Art. Gels 2022, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, W.; Yao, M.; Ding, Z.; Xuan, J.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Xia, Y.; Cao, M. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Based Thermoresponsive Composite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Wang, L.L.; Chung, J.J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Atluri, P.; Burdick, J.A. Methods To Assess Shear-Thinning Hydrogels for Application As Injectable Biomaterials. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 3146–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapkriengkri, I.; Albanese, K.R.; Rhode, A.; Cunniff, A.; Pitenis, A.A.; Chabinyc, M.L.; Bates, C.M. Chemical Botany: Bottlebrush Polymers in Materials Science. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2024, 54, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatankhah-Varnosfaderani, M.; Keith, A.N.; Cong, Y.; Liang, H.; Rosenthal, M.; Sztucki, M.; Clair, C.; Magonov, S.; Ivanov, D.A.; Dobrynin, A.V.; et al. Chameleon-like Elastomers with Molecularly Encoded Strain-Adaptive Stiffening and Coloration. Science 2018, 359, 1509–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtimoghadam, E.; Fahimipour, F.; Keith, A.N.; Vashahi, F.; Popryadukhin, P.; Vatankhah-Varnosfaderani, M.; Sheiko, S.S. Injectable Non-Leaching Tissue-Mimetic Bottlebrush Elastomers as an Advanced Platform for Reconstructive Surgery. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnsorg, M.L.; Mash, K.M.; Khang, A.; Rao, V.V.; Kirkpatrick, B.E.; Bera, K.; Anseth, K.S. Nonlinear Elastic Bottlebrush Polymer Hydrogels Modulate Actomyosin Mediated Protrusion Formation in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2403198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, V.G.; Mukherjee, S.; Xie, R.; Levi, A.E.; Atassi, A.; Uchiyama, T.; Wang, H.; Chabinyc, M.L.; Bates, C.M. Super-Soft Solvent-Free Bottlebrush Elastomers for Touch Sensing. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashahi, F.; Martinez, M.R.; Dashtimoghadam, E.; Fahimipour, F.; Keith, A.N.; Bersenev, E.A.; Ivanov, D.A.; Zhulina, E.B.; Popryadukhin, P.; Matyjaszewski, K.; et al. Injectable Bottlebrush Hydrogels with Tissue-Mimetic Mechanical Properties. Sci. Adv. 2023, 8, eabm2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.C.; Costa, P.C.; Velho, S.; Amaral, M.H. Rheological and Injectability Evaluation of Sterilized Poloxamer-407-Based Hydrogels Containing Docetaxel-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles. Gels 2024, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, M.S.; Ahmad, T.; Yang, M.; Hu, C.; Hahn, L.; Stahlhut, P.; Groll, J.; Luxenhofer, R. Tuning the Thermogelation and Rheology of Poly(2-Oxazoline)/Poly(2-Oxazine)s Based Thermosensitive Hydrogels for 3D Bioprinting. Gels 2021, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkin, A.Y.; Derkach, S.R.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Rheology of Gels and Yielding Liquids. Gels 2023, 9, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

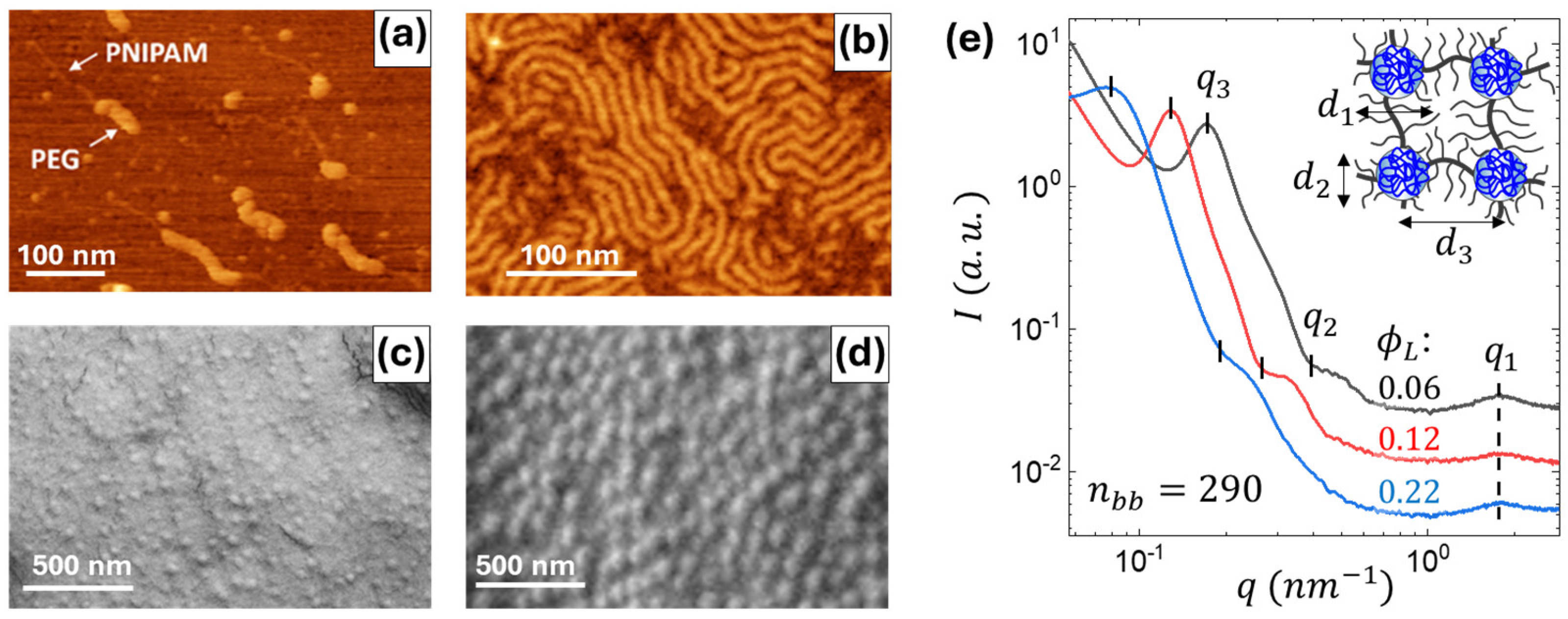
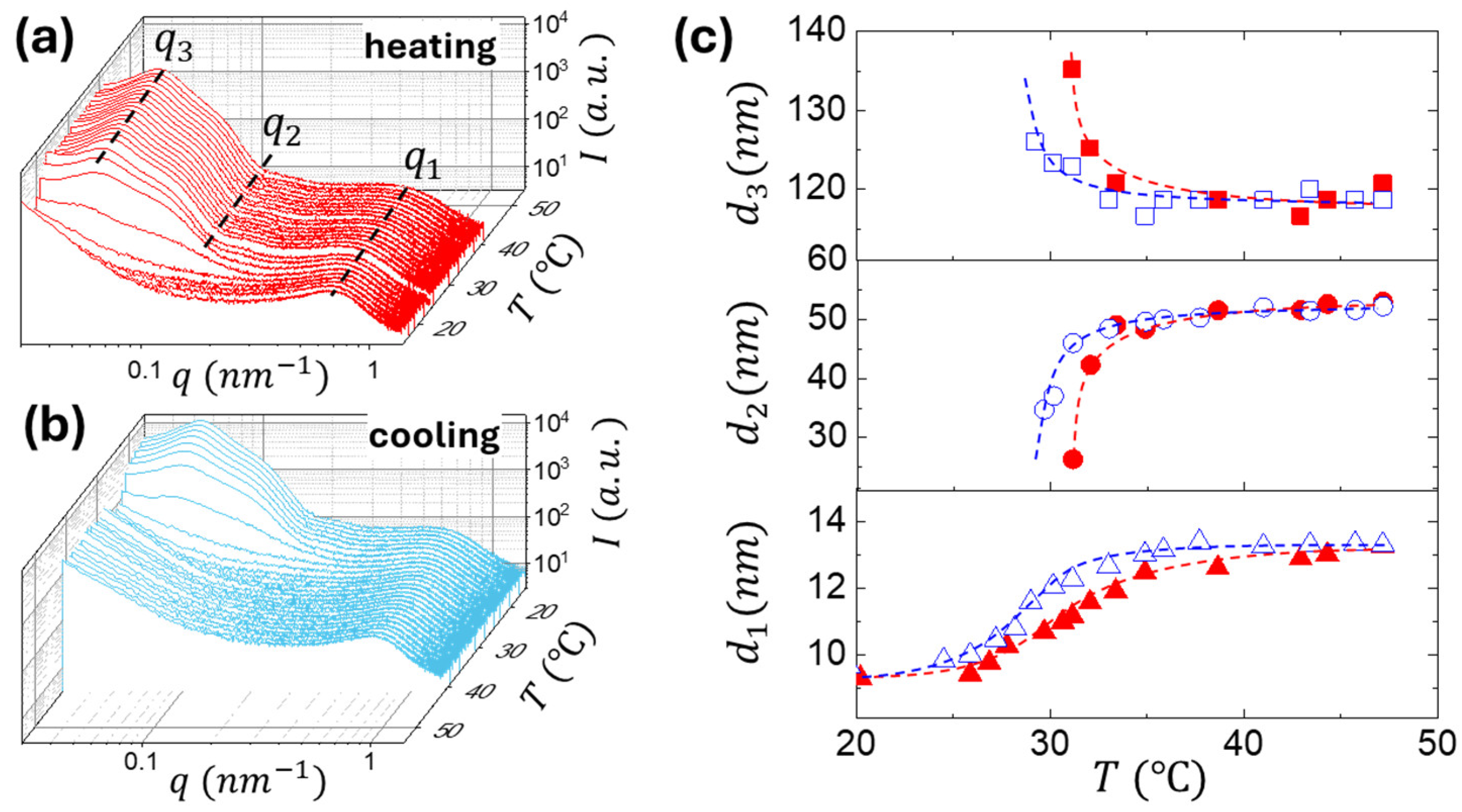

| nsc 1 | nbb 2 | nL 3 | ϕL 4 | d1 5 | d2 6 | d3 7 | Q 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | 290 | 80 | 0.06 | 3.6 | 23.2 | 37.9 | 474 |
| 175 | 0.12 | 34.9 | 51.9 | 748 | |||
| 340 | 0.22 | 45.3 | 84.6 | 932 | |||
| 19 | 580 | 190 | 0.07 | 3.6 | 35.8 | 59.6 | 739 |
| 300 | 0.12 | 36.1 | 60.5 | 480 | |||
| 630 | 0.20 | 76.4 | 74.9 | 2166 | |||
| 19 | 890 | 240 | 0.06 | 3.6 | 29.4 | 62.8 | 328 |
| 510 | 0.12 | 37.6 | 67 | 316 | |||
| 920 | 0.20 | 98.0 | 132.6 | 3134 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, J.; Vashahi, F.; Umarov, A.Z.; Dubrovin, E.V.; Konyakhina, A.Y.; Subcheva, E.N.; Ivanov, D.A.; Dobrynin, A.V.; Sheiko, S.S. Injectable Hydrogels with Tissue-Adaptive Gelation and Mechanical Properties: Enhancing Softness and Stability. Gels 2025, 11, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120996
Garcia J, Vashahi F, Umarov AZ, Dubrovin EV, Konyakhina AY, Subcheva EN, Ivanov DA, Dobrynin AV, Sheiko SS. Injectable Hydrogels with Tissue-Adaptive Gelation and Mechanical Properties: Enhancing Softness and Stability. Gels. 2025; 11(12):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120996
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Jessica, Foad Vashahi, Akmal Z. Umarov, Evgeniy V. Dubrovin, Apollinariya Yu. Konyakhina, Elena N. Subcheva, Dimitri A. Ivanov, Andrey V. Dobrynin, and Sergei S. Sheiko. 2025. "Injectable Hydrogels with Tissue-Adaptive Gelation and Mechanical Properties: Enhancing Softness and Stability" Gels 11, no. 12: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120996
APA StyleGarcia, J., Vashahi, F., Umarov, A. Z., Dubrovin, E. V., Konyakhina, A. Y., Subcheva, E. N., Ivanov, D. A., Dobrynin, A. V., & Sheiko, S. S. (2025). Injectable Hydrogels with Tissue-Adaptive Gelation and Mechanical Properties: Enhancing Softness and Stability. Gels, 11(12), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120996










