Influence of Polymers Diversity on the Dissolution Kinetics of Encapsulated p-Coumaric Acid in Oral Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Solubility of p-Coumaric Acid
2.2. Capsules and Gels Quality Control
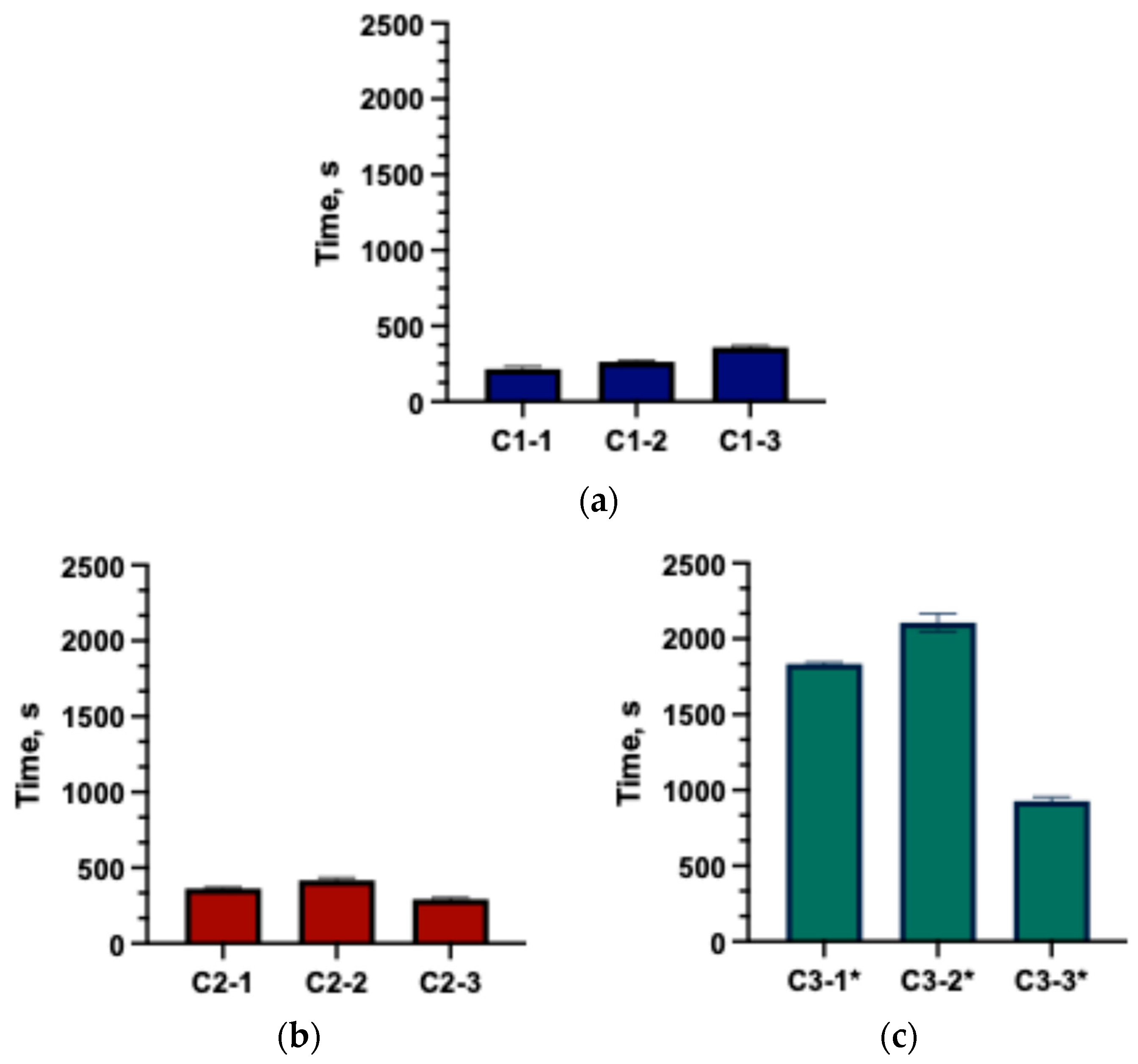
2.2.1. Disintegration Test of Capsules
2.2.2. Physicochemical Properties of Gels
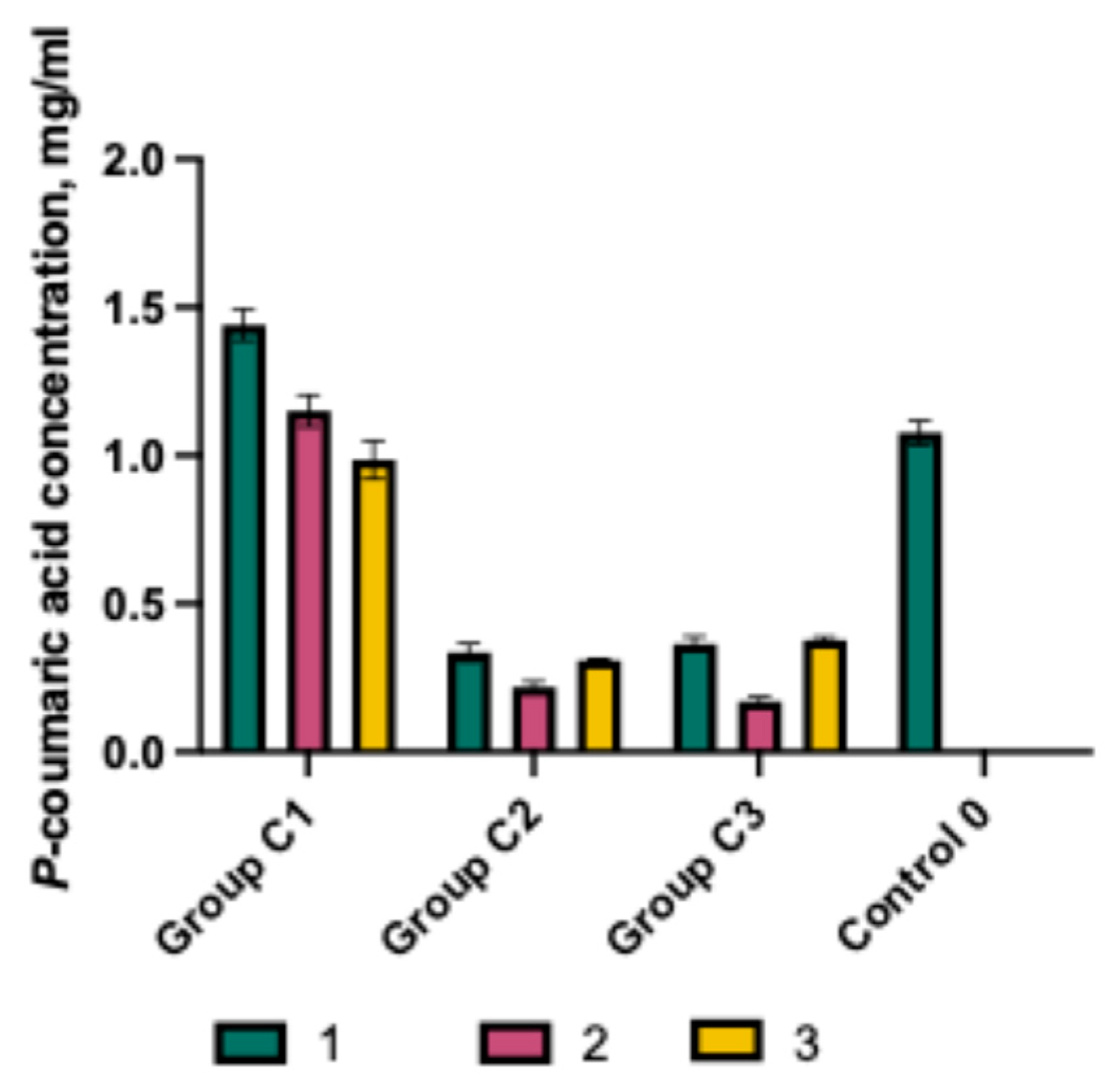
2.3. Dissolution Test of Capsules and Gels Containing p-Coumaric Acid
2.4. Antioxidant Activity
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Formulation and Production of Capsules Hydrogels Containing p-Coumaric Acid
4.3. Quantitative Analysis of p-Coumaric Acid
4.4. p-Coumaric Acid Solubility
4.5. Evaluation of the Physicochemical Properties of Gel Bases
4.6. In Vitro Disintegration Test of Capsules
4.7. In Vitro Dissolution Test of Capsules and Gels
4.8. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pei, K.; Ou, J.; Huang, J.; Ou, S. P-Coumaric Acid and Its Conjugates: Dietary Sources, Pharmacokinetic Properties and Biological Activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2952–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veras, K.S.; Fachel, F.N.S.; de Araújo, B.V.; Teixeira, H.F.; Koester, L.S. Oral Pharmacokinetics of Hydroxycinnamic Acids: An Updated Review. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chang, G.; Dang, Q.; Liu, C.; Song, H.; Chen, A.; Yang, M.; Shi, L.; Zhang, B.; Cha, D. Preparation and Characterization of Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Biocompatible p-Coumaric Acid Modified Quaternized Chitosan Nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Song, X.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Jaiswal, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, W.; Williams, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Protective Effects of P-Coumaric Acid against Oxidant and Hyperlipidemia-an in Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilani-Jaziri, S.; Mokdad-Bzeouich, I.; Krifa, M.; Nasr, N.; Ghedira, K.; Chekir-Ghedira, L. Immunomodulatory and Cellular Anti-Oxidant Activities of Caffeic, Ferulic, and p-Coumaric Phenolic Acids: A Structure–Activity Relationship Study. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 40, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamula, R.; Thong-asa, W. Neuroprotective Effect of P-Coumaric Acid in Mice with Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injuries. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Zeng, M.; Hao, F.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, W.; Zheng, X. P-Coumaric Acid Ameliorates Aβ25–35-Induced Brain Damage in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolites. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Kar, A.; Bannerjee, S.; Jana, S.N.; Haldar, P.K.; Sharma, N. Enhanced Permeability and Photoprotective Potential of Optimized P-Coumaric Acid-Phospholipid Complex Loaded Gel against UVA Mediated Oxidative Stress. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2021, 221, 112246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, P.S.; Victorelli, F.D.; Fonseca-Santos, B.; Chorilli, M. A Review of Analytical Methods for P-Coumaric Acid in Plant-Based Products, Beverages, and Biological Matrices. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 49, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, Y.; An, Y.; Jung, Y.-R.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, Z.; Kim, K. Development of P-Coumaric Acid Analysis in Human Plasma and Its Clinical Application to PK/PD Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, K.; Matsumoto, H. Urinary Excretion Rate and Bioavailability of Chlorogenic Acid, Caffeic Acid, p-Coumaric Acid, and Ferulic Acid in Non-Fasted Rats Maintained under Physiological Conditions. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, L.-Y.; Cosma, G.; Gardner, H.; Shi, X.; Castranova, V.; Vallyathan, V. Effect of Antioxidant Protection by P-Coumaric Acid on Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Oxidation. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2000, 279, C954–C960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilas-Boas, S.M.; Alves, R.S.; Brandão, P.; Campos, L.M.A.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Pinho, S.P.; Ferreira, O. Solid-Liquid Phase Equilibrium of Trans-Cinnamic Acid, p-Coumaric Acid and Ferulic Acid in Water and Organic Solvents: Experimental and Modelling Studies. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2020, 521, 112747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczura, M.; Sip, S.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. The Development of Innovative Dosage Forms of the Fixed-Dose Combination of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayol, L.; Quaglia, F.; Borzacchiello, A.; Ambrosio, L.; Rotonda, M.I.L. A Novel Poloxamers/Hyaluronic Acid in Situ Forming Hydrogel for Drug Delivery: Rheological, Mucoadhesive and in Vitro Release Properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Salas, F.; Marican, A.; Pinochet, S.; Carreño, G.; Valdés, O.; Venegas, B.; Donoso, W.; Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Vijayakumar, S.; Durán-Lara, E.F. Film Dressings Based on Hydrogels: Simultaneous and Sustained-Release of Bioactive Compounds with Wound Healing Properties. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Villa, C. Poloxamer Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, E.; Chikhaoui, E. The Drug Paracetamol and Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Polyvinyl Alcohol Composites, Interactions for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2025, 63, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, I.R.S.; de de Carvalho, A.P.A.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Recent Advances in Biobased and Biodegradable Polymer Nanocomposites, Nanoparticles, and Natural Antioxidants for Antibacterial and Antioxidant Food Packaging Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3673–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugar, R.P.; Gajera, B.Y.; Dave, R.H. Fusion Method for Solubility and Dissolution Rate Enhancement of Ibuprofen Using Block Copolymer Poloxamer 407. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draksiene, G.; Venclovaite, B.; Pudziuvelyte, L.; Ivanauskas, L.; Marksa, M.; Bernatoniene, J. Natural Polymer Chitosan as Super Disintegrant in Fast Orally Disintegrating Meloxicam Tablets: Formulation and Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ur-Rehman, T.; Tavelin, S.; Gröbner, G. Chitosan in Situ Gelation for Improved Drug Loading and Retention in Poloxamer 407 Gels. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 409, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irimia, T.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.-E.; Ghica, M.V.; Lupuleasa, D.; Muntean, D.-L.; Udeanu, D.I.; Popa, L. Chitosan-Based In Situ Gels for Ocular Delivery of Therapeutics: A State-of-the-Art Review. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarji, B.; Abed, S.N.; Bairagi, U.; Deb, P.K.; Al-Attraqchi, O.; Choudhury, A.A.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 18—Four Stages of Pharmaceutical Product Development: Preformulation, Prototype Development and Scale-Up, Biological Aspects, and Commercialization. In Dosage Form Design Considerations; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 637–668. ISBN 978-0-12-814423-7. [Google Scholar]
- Dumortier, G.; Grossiord, J.L.; Agnely, F.; Chaumeil, J.C. A Review of Poloxamer 407 Pharmaceutical and Pharmacological Characteristics. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 2709–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Hasan, S.; Nitai, A.S.; Nam, S.; Karmakar, A.K.; Ahsan, S.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Ahmed, M.B. Recent Developments of Carboxymethyl Cellulose. Polymers 2021, 13, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capanema, N.S.V.; Mansur, A.A.P.; Carvalho, I.C.; Carvalho, S.M.; Mansur, H.S. Bioengineered Water-Responsive Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Hydrogel Hybrids for Wound Dressing and Skin Tissue Engineering Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, P.; Mehra, L.; Mittal, G.; Kumar, A. A Comparative Study on the Efficacy of Chitosan Gel Formulation and Conventional Silver Sulfadiazine Treatment in Healing Burn Wound Injury at Molecular Level. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2022, 56, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ostróżka-Cieślik, A.; Strasser, C.; Dolińska, B. Insulin-Loaded Chitosan–Cellulose-Derivative Hydrogels: In Vitro Permeation of Hormone through Strat-M® Membrane and Rheological and Textural Analysis. Polymers 2024, 16, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalabidis, A.; Sfouni, M.; Bergström, C.; Macheras, P. The Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) and the Biopharmaceutics Drug Disposition Classification System (BDDCS): Beyond guidelines. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigata, M.; Meinert, C.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Bock, N. Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of Current Characterization and Evaluation Techniques. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binti Sarun, N.H.; Nuryanti, A.; Ana, I.D. The Effect of Chitosan Concentration on Disintegration Time of Amoxicillin Tablet. Key Eng. Mater. 2021, 884, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soraya, M.; Laksono, H.; Putri, R.P.G.; Royanti, I.; Perwatasari, D.D.; Dewi, R.A.P.; Purwoto, H. Exploring Disintegration and Swelling Dynamics in Kappa-Carrageenan-Based Seaweed Capsule Shells. South Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2025, 53, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, S.; Pervaiz, F.; Ijaz, M.; Shoukat, H. Synthesis and Characterization of pH-Sensitive Chemically Crosslinked Block Copolymer [Hyaluronic Acid/Poloxamer 407-Co-Poly (Methacrylic Acid)] Hydrogels for Colon Targeting. Polym. Technol. Mater. 2022, 61, 1071–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šedbarė, R.; Janulis, V.; Ramanauskiene, K. Formulation and Biopharmaceutical Evaluation of Capsules Containing Freeze-Dried Cranberry Fruit Powder. Plants 2023, 12, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, M.S.; Nawaz, A.; Asmari, M.; Uddin, J.; Ullah, H.; Ahmad, S. Formulation Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoemulsion Gel Formulations for Enhanced Topical Delivery. Gels 2023, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinea, M.; Ellis, A.; Golding, M.; Loveday, S.M. Delivering Phenolic Acids in Soy Protein Gels: Noncovalent Interactions Control Gastrointestinal Bioaccessibility. Food Biophys. 2023, 18, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, S.J.; Santos, M.A.; Neto, J.E.; Silva, H.N.; Barbosa, M.C.S.; Fook, M.V.; Navarro, R.F.; Silva, S.M. Combined Effect of pH and Neutralizing Solution Molarity on the Rheological Properties of Chitosan Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, G.P.; Rai, V.K.; Pradhan, D.; Halder, J.; Rajwar, T.K.; Mahanty, R.; Saha, I.; Mishra, A.; Dash, P.; Dash, C.; et al. A Doxorubicin Loaded Chitosan–Poloxamer in Situ Implant for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 33952–33967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedel, H.D.; Brown, C.K.; Barker, A.R.; Buhse, L.F.; Keitel, S.; Kraemer, J.; Morris, J.M.; Reppas, C.; Sperry, D.C.; Sakai-Kato, K.; et al. FIP Guidelines for Dissolution Testing of Solid Oral Products. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 2995–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbakhsh, M.; Jabraili, M.; Akbari, M.; Jaymand, M.; Jahanban Esfahlan, R. Poloxamer-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Frontiers for Treatment of Solid Tumors. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 32, 101727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarak, I.; Varela, C.L.; Tavares da Silva, E.; Roleira, F.F.M.; Veiga, F.; Figueiras, A. Pluronic-Based Nanovehicles: Recent Advances in Anticancer Therapeutic Applications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 206, 112526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.; Furubayashi, T.; Yamasaki, H.; Takano, K.; Kawakami, M.; Kimura, S.; Inoue, D.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. The Enhancement of Nasal Drug Absorption From Powder Formulations by the Addition of Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 2016, 15, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.; Furubayashi, T.; Matsushita, A.; Inoue, D.; Kimura, S.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Nasal Absorption of Macromolecules from Powder Formulations and Effects of Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose on Their Absorption. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, D.; Levina, M.; Nokhodchi, A.; Douroumis, D.; Farrell, T.; Rajabi-Siahboomi, A. The Influence of Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose on Drug Release from Polyethylene Oxide Extended Release Matrices. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirsa, S.; Hafezi, K. Hydrocolloids: Structure, Preparation Method, and Application in Food Industry. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-B.; Xing, L.-Y.; Liu, T.-F.; Li, M.; Geng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Wang, R.-C.; Sarsenbekuly, B.; Kang, W.-L.; et al. Swelling Kinetics of Polymer Microspheres Used for Conformance Control and Their Matching Mechanisms with Oil Reservoir Fractures. Pet. Sci. 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Kiliç, I.; Yeşiloğlu, Y. Spectroscopic Studies on the Antioxidant Activity of P-Coumaric Acid. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 115, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, M.C.; Orellana Palacios, J.C.; Hesami, G.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Domínguez, R.; Moreno, A.; Hadidi, M. Spectrophotometric Methods for Measurement of Antioxidant Activity in Food and Pharmaceuticals. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbettaieb, N.; Nyagaya, J.; Seuvre, A.-M.; Debeaufort, F. Antioxidant Activity and Release Kinetics of Caffeic and p-Coumaric Acids from Hydrocolloid-Based Active Films for Healthy Packaged Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6906–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Du, H.; Li, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, Z. A Transparent P-Coumaric Acid-Grafted-Chitosan Coating with Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Antifogging Properties for Fruit Packaging Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 339, 122238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.M.; Pereira, C.F.; Ribeiro, A.A.; Casanova, F.; Freixo, R.; Pintado, M.; Ramos, O.L. Characterization and Evaluation of Commercial Carboxymethyl Cellulose Potential as an Active Ingredient for Cosmetics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y.; Sohail Khan, M.; Bansal, M.; Kumar Singh, M.; Pragatheesh, K.; Thakur, A. A Review of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite-Based Hydrogels in Drug Delivery Applications. Results Chem. 2024, 10, 101695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, T.; Arora, S.; Pahwa, R. Cellulose and Its Derivatives: Structure, Modification, and Application in Controlled Drug Delivery. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K.; Yang, J.-M.; Chang, Y.-H.; Su, W.-W. Modification of Different Molecular Weights of Chitosan by P-Coumaric Acid: Preparation, Characterization and Effect of Molecular Weight on Its Water Solubility and Antioxidant Property. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Smith, G.; Khan, K.A.; Bukhari, N.I.; Pedge, N.I.; Ermolina, I. Solubility and Dissolution Rate Enhancement of Ibuprofen by Co-Milling with Polymeric Excipients. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 123, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare (EDQM). European Pharmacopoeia; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2022; Volume 11.2.
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare (EDQM). 2.9.1. Disintegration of Tablets and Capsules. In European Pharmacopoeia; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2020; pp. 321–323. [Google Scholar]
- Rezzoug, M.; Bakchiche, B.; Gherib, A.; Roberta, A.; FlaminiGuido; Kilinçarslan, Ö.; Mammadov, R.; Bardaweel, S.K. Chemical Composition and Bioactivity of Essential Oils and Ethanolic Extracts of Ocimum Basilicum L. and Thymus Algeriensis Boiss. & Reut. from the Algerian Saharan Atlas. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, G.K.; Makola, R.T. In-Vitro Analysis of Free Radical Scavenging Activities and Suppression of LPS-Induced ROS Production in Macrophage Cells by Solanum Sisymbriifolium Extracts. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No | pH (Mean ± SD) | pH (Mean ± SD) After 30 Days | Viscosity 22 °C (mPa·s) | Viscosity 22 °C (mPa·s) After 30 Days | Viscosity 37 °C (mPa·s) | Viscosity 37 °C (mPa·s) After 30 Days | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1C | 5.05 ± 0.25 | 5.19 ± 0.14 | 43.1 ± 2.2 | 37.9 ± 2.0 | 320 ± 16 | 299.7 ± 9.0 |  |
| G2C | 5.50 ± 0.28 | 5.55 ± 0.16 | 5500 ± 275 | 5470.3 ± 45.1 | 4770 ± 239 | 4698.0 ± 190 |  |
| G3C | 3.71 ± 0.19 | 3.51 ± 0.17 | 8029 ± 401 | 80,213 ± 293 | 7487 ± 374 | 7604 ± 236 |  |
| G4C | 5.57 ± 0.28 | 5.64 ± 0.12 | 26,271 ± 1314 | 26,459.3 ± 525 | 58,255 ± 2913 | 57,971 ± 952 |  |
| G5C | 5.81 ± 0.29 | 5.83 ± 0.13 | 48,773 ± 2439 | 49,141 ± 907 | 32,465 ± 1623 | 32,238 ± 564 |  |
| (a) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | p-Coumaric Acid Content, mg | PROSOLV SMCCTM 50 mg | P407, mg | NaCMC, mg | Chitosan, mg | Polymer Concentration in Capsule | Mean Mass of Capsule, mg (mean ± SD) |
| C0 | 100 | - | - | - | - | 99.7 ± 2.3 | |
| C1-1 | 50 | 25 | - | - | 14.3% | 174.0 ± 2.0 | |
| C1-2 | 50 | 50 | - | - | 25% | 198.7 ± 2.1 | |
| C1-3 | 50 | 100 | - | - | 40% | 252.7 ± 5.9 | |
| C2-1 | 50 | - | 25 | - | 14.3% | 175.7 ± 2.3 | |
| C2-2 | 50 | - | 50 | - | 25% | 199.0 ± 3.6 | |
| C2-3 | 50 | - | 10 | - | 6.67% | 153.3 ± 1.5 | |
| C3-1 | 50 | - | - | 25 | 14.3% | 175.3 ± 2.3 | |
| C3-2 | 50 | - | - | 50 | 25% | 201.0 ± 2.6 | |
| C3-3 | 50 | - | - | 10 | 6.67% | 159.7 ± 2.3 | |
| (b) | |||||||
| Group | p-Coumaric Acid Content, g | P407, g | NaCMC, g | Chitosan, g | Water | ||
| G1C | 1 | 14 | Add 100 | ||||
| G2C | 7 | ||||||
| G3C | 5 | ||||||
| G4C | 25 | ||||||
| G5C | 14 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jokubaite, M.; Jokubaityte-Tunkeviciene, V.; Ramanauskiene, K. Influence of Polymers Diversity on the Dissolution Kinetics of Encapsulated p-Coumaric Acid in Oral Systems. Gels 2025, 11, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120983
Jokubaite M, Jokubaityte-Tunkeviciene V, Ramanauskiene K. Influence of Polymers Diversity on the Dissolution Kinetics of Encapsulated p-Coumaric Acid in Oral Systems. Gels. 2025; 11(12):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120983
Chicago/Turabian StyleJokubaite, Monika, Vakare Jokubaityte-Tunkeviciene, and Kristina Ramanauskiene. 2025. "Influence of Polymers Diversity on the Dissolution Kinetics of Encapsulated p-Coumaric Acid in Oral Systems" Gels 11, no. 12: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120983
APA StyleJokubaite, M., Jokubaityte-Tunkeviciene, V., & Ramanauskiene, K. (2025). Influence of Polymers Diversity on the Dissolution Kinetics of Encapsulated p-Coumaric Acid in Oral Systems. Gels, 11(12), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120983




