Enhancing Gel-Based Drilling FIuids for Oil Sands Recovery Using Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as AsphaItene Dispersants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization Results
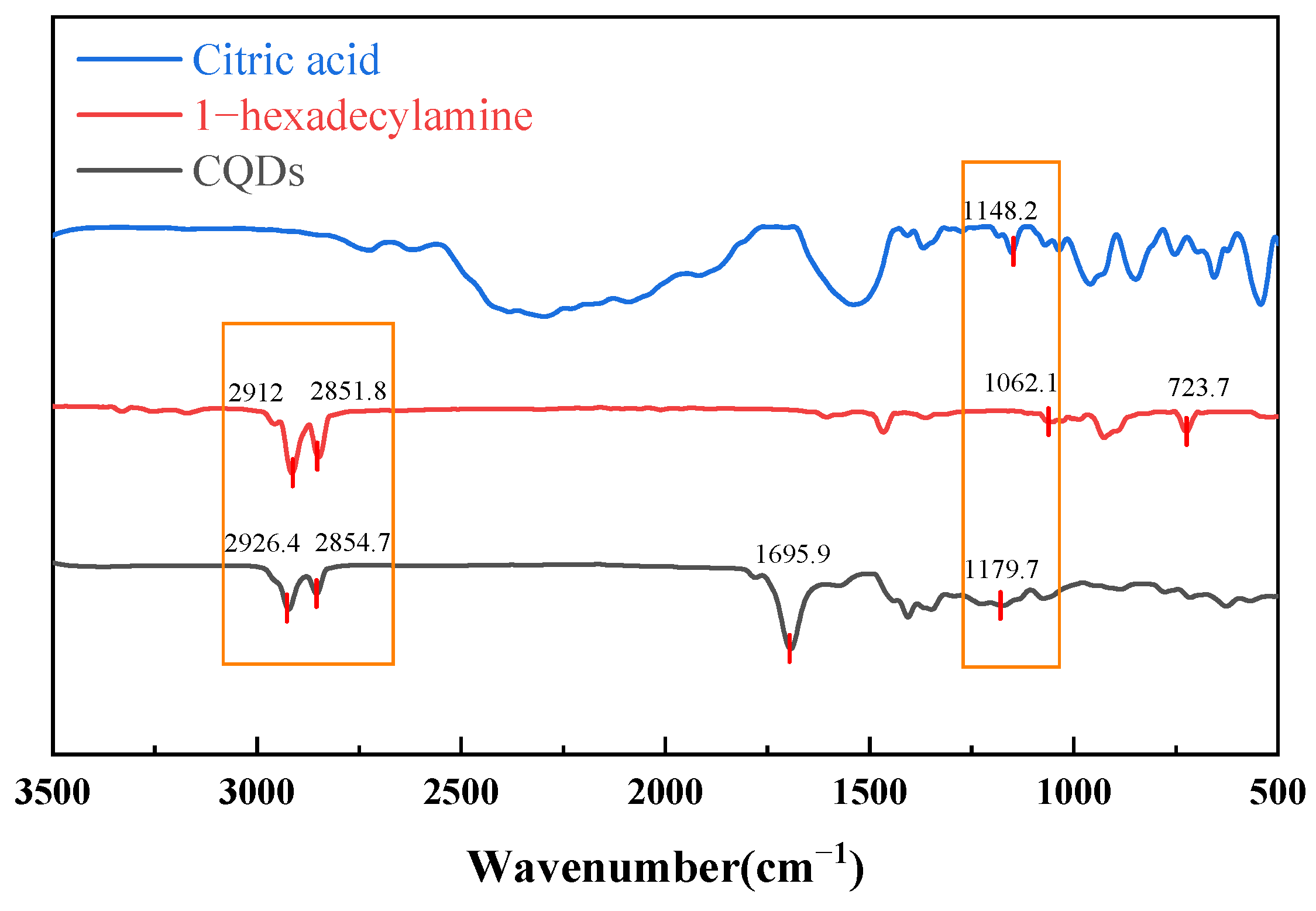
2.1.1. FT-IR Analysis
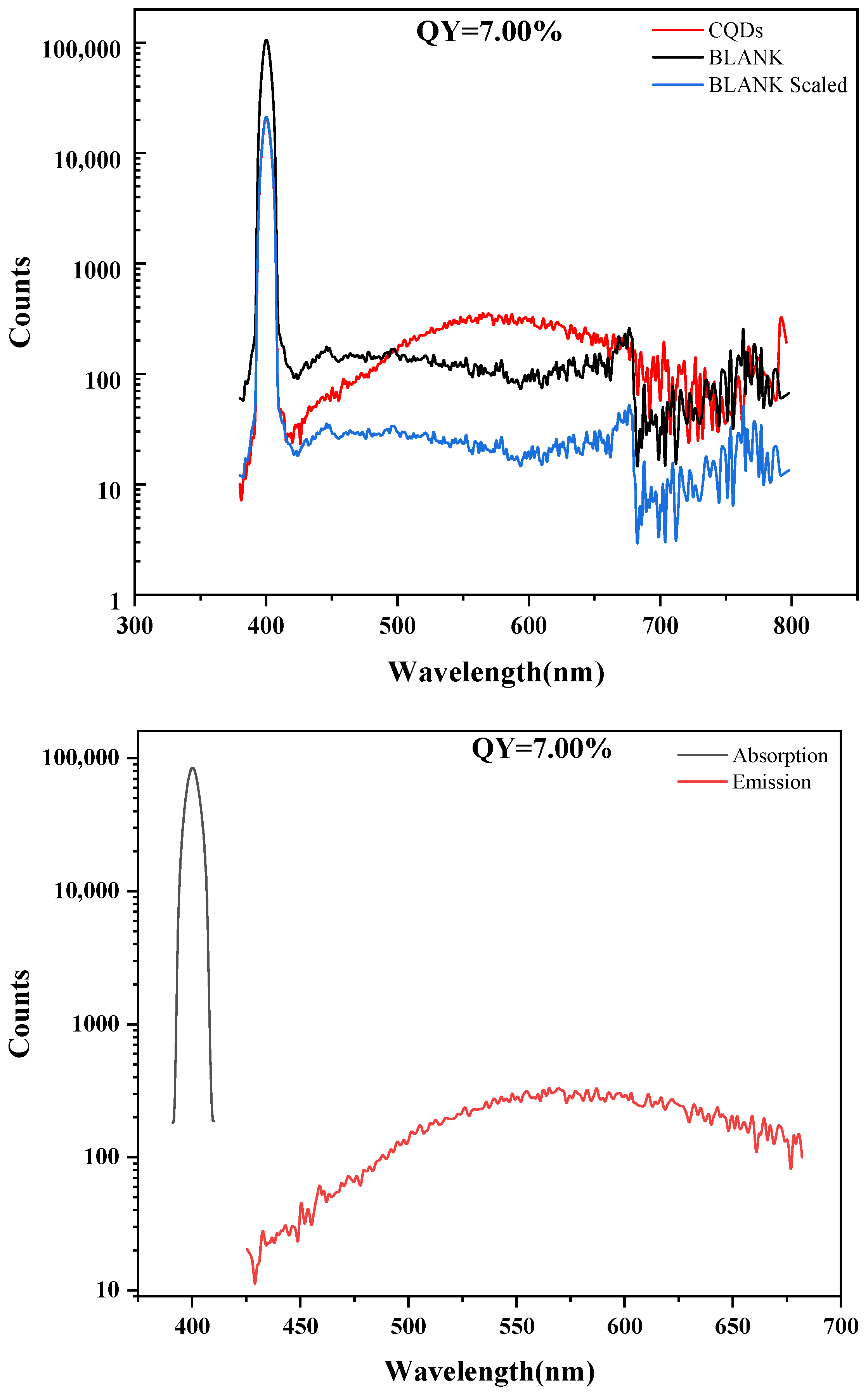
2.1.2. Absolute Fluorescence Quantum Yield
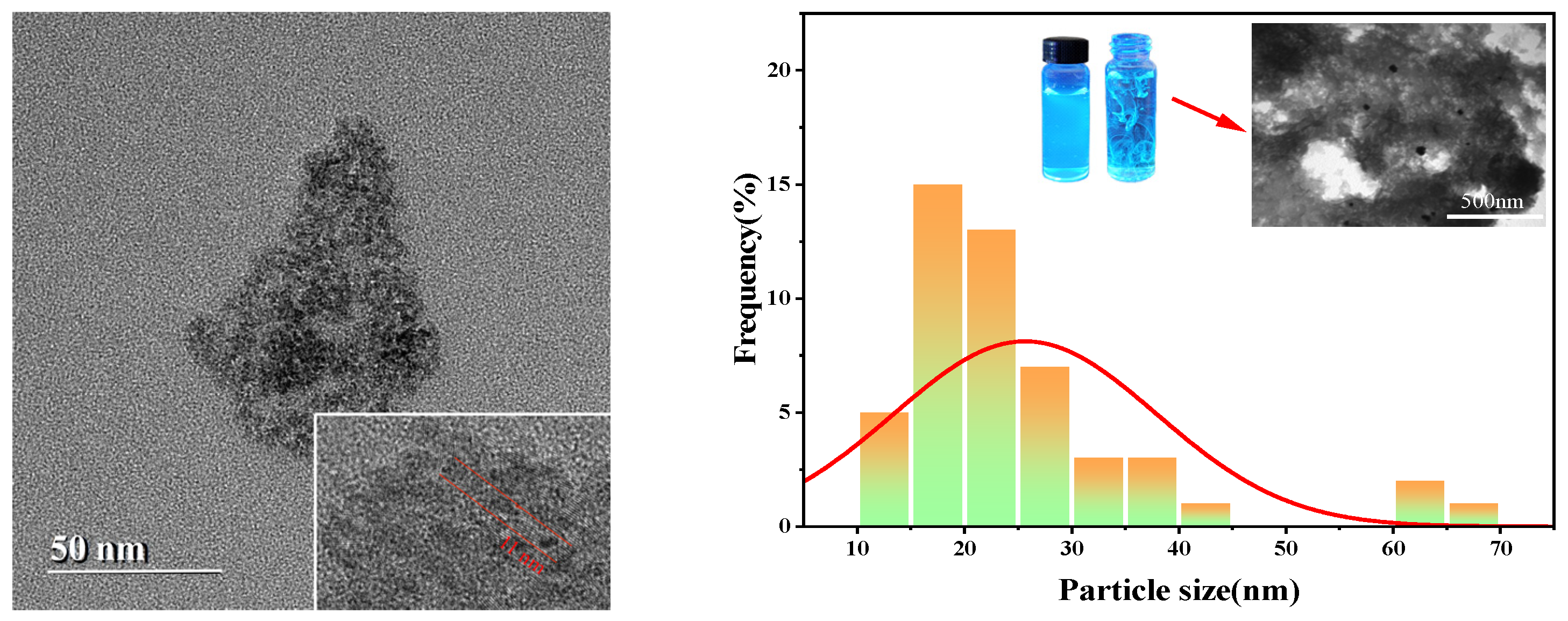
2.1.3. TEM
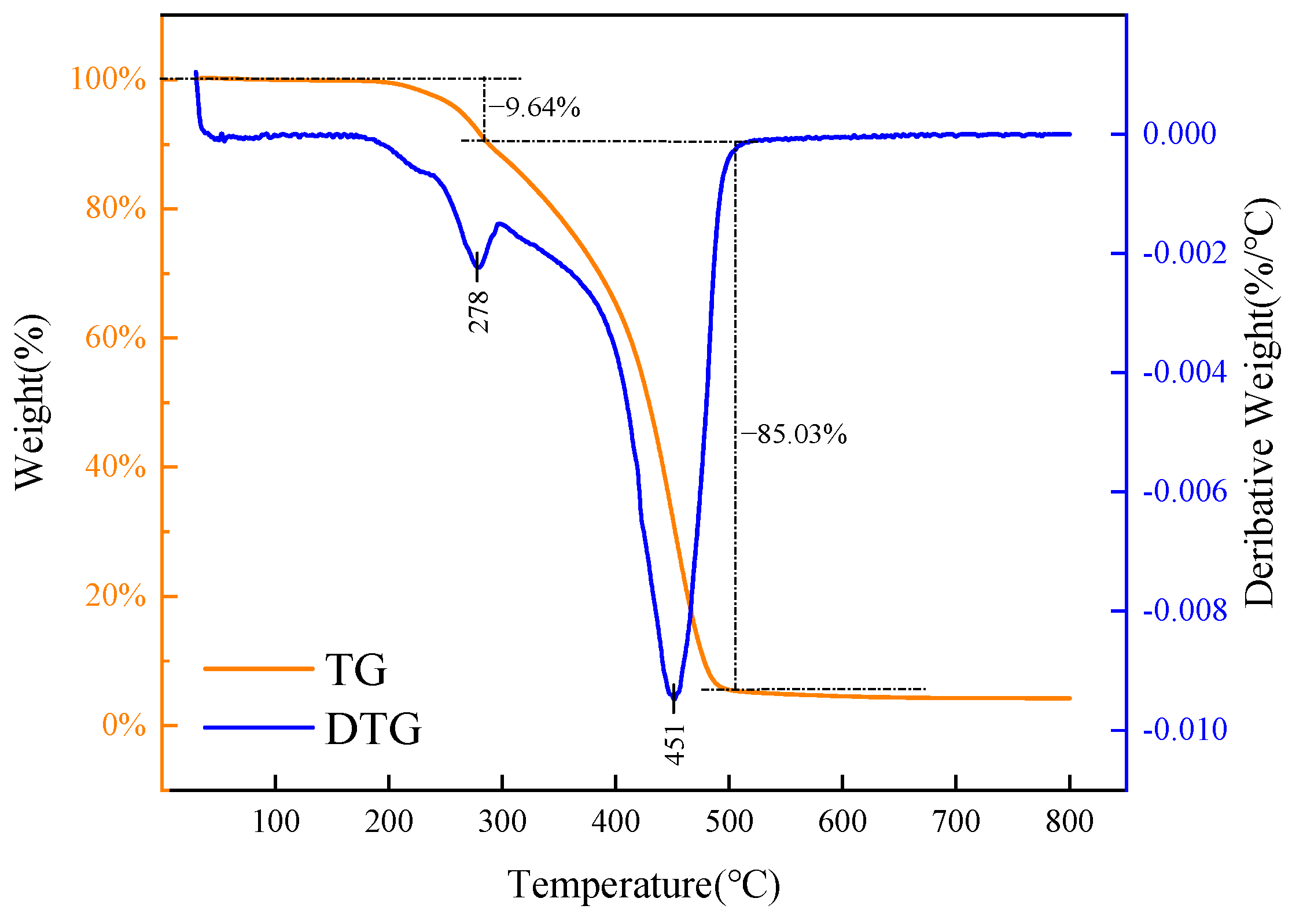
2.1.4. TGA
2.2. Performance Analysis
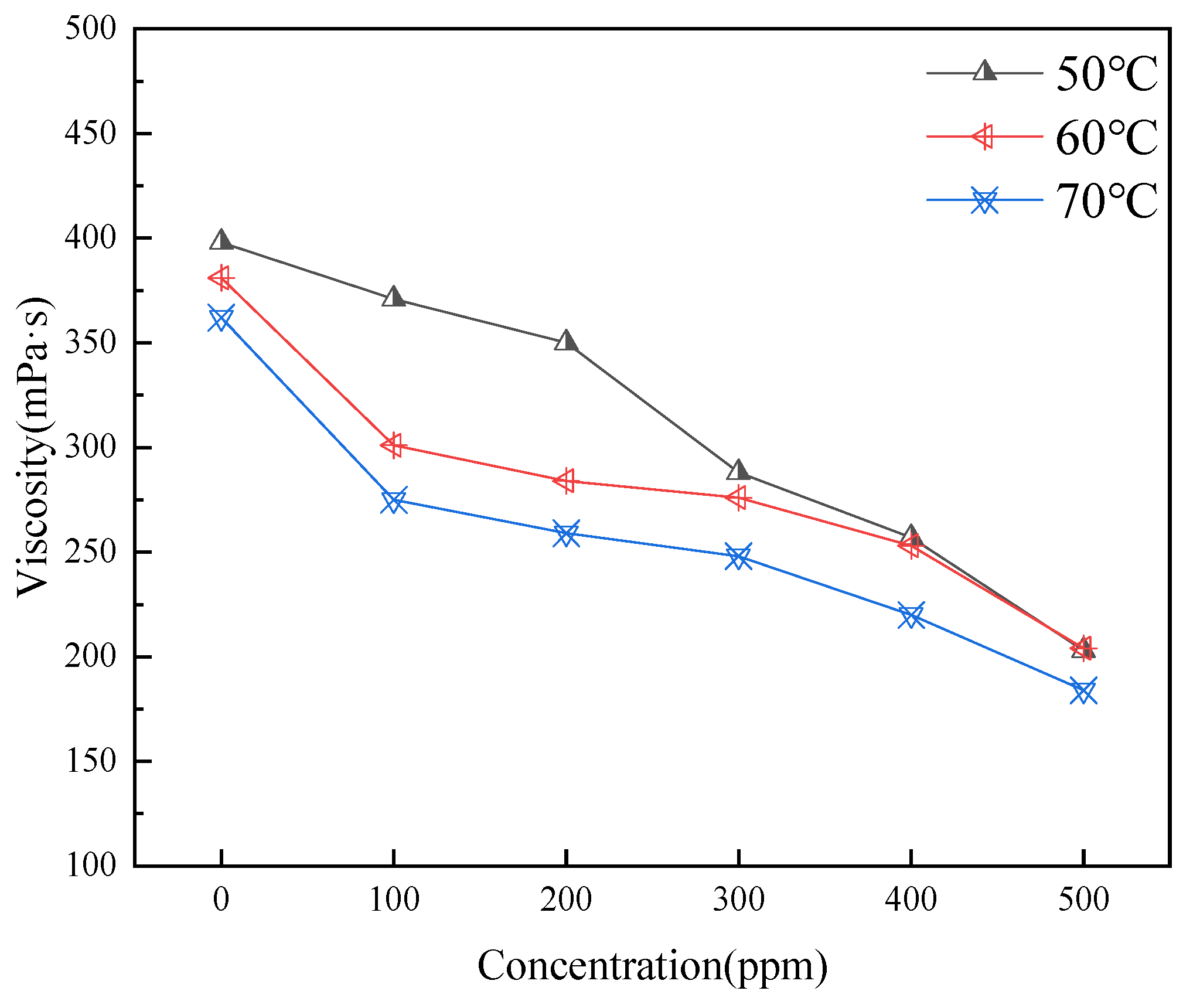
2.2.1. Evaluation of Viscosity Reduction Performance
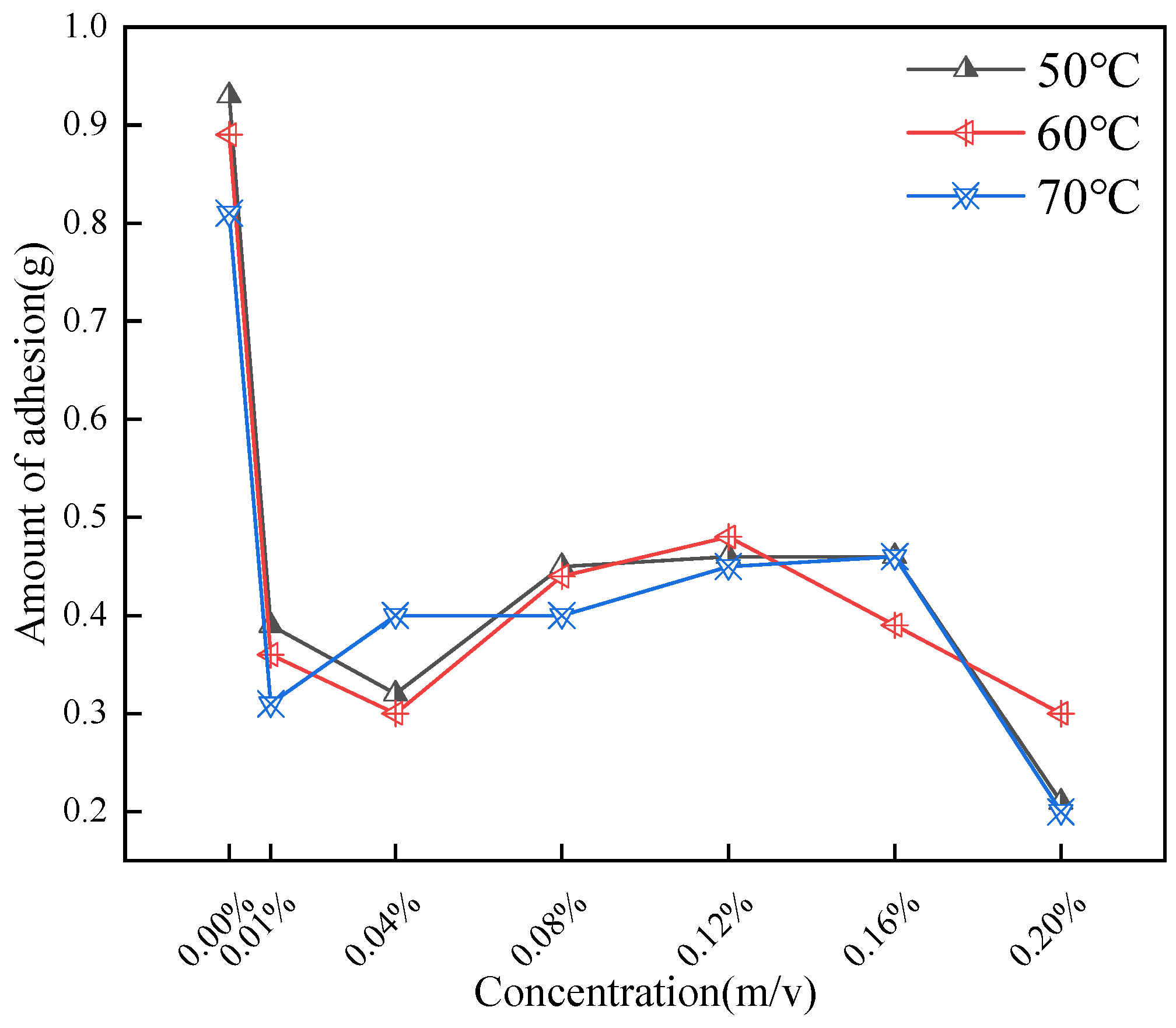
2.2.2. Adhesion Rate Following High-Temperature Aging
2.2.3. Drilling Fluid Rheology
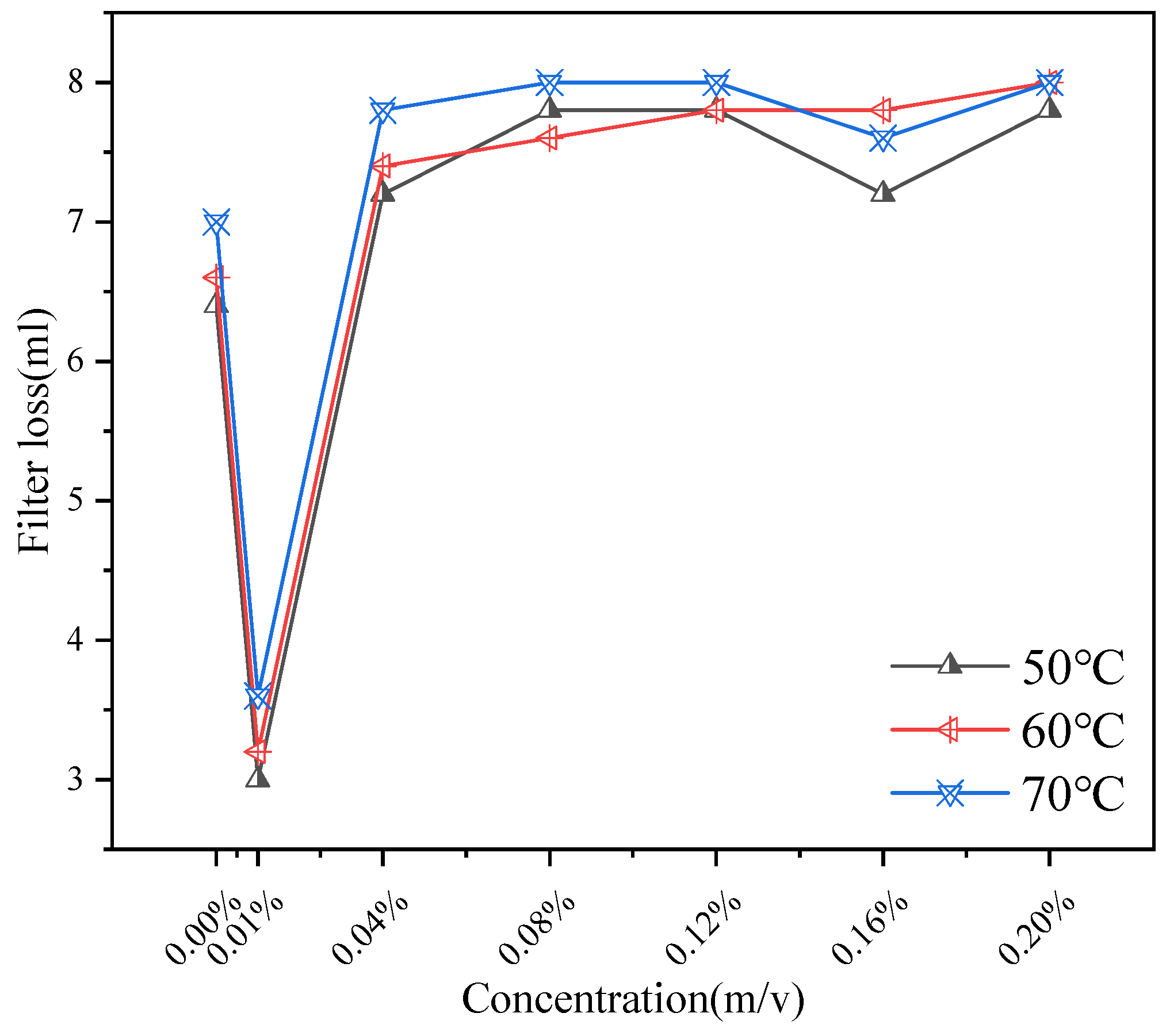
2.2.4. Filtration Loss
2.2.5. Dispersion Properties
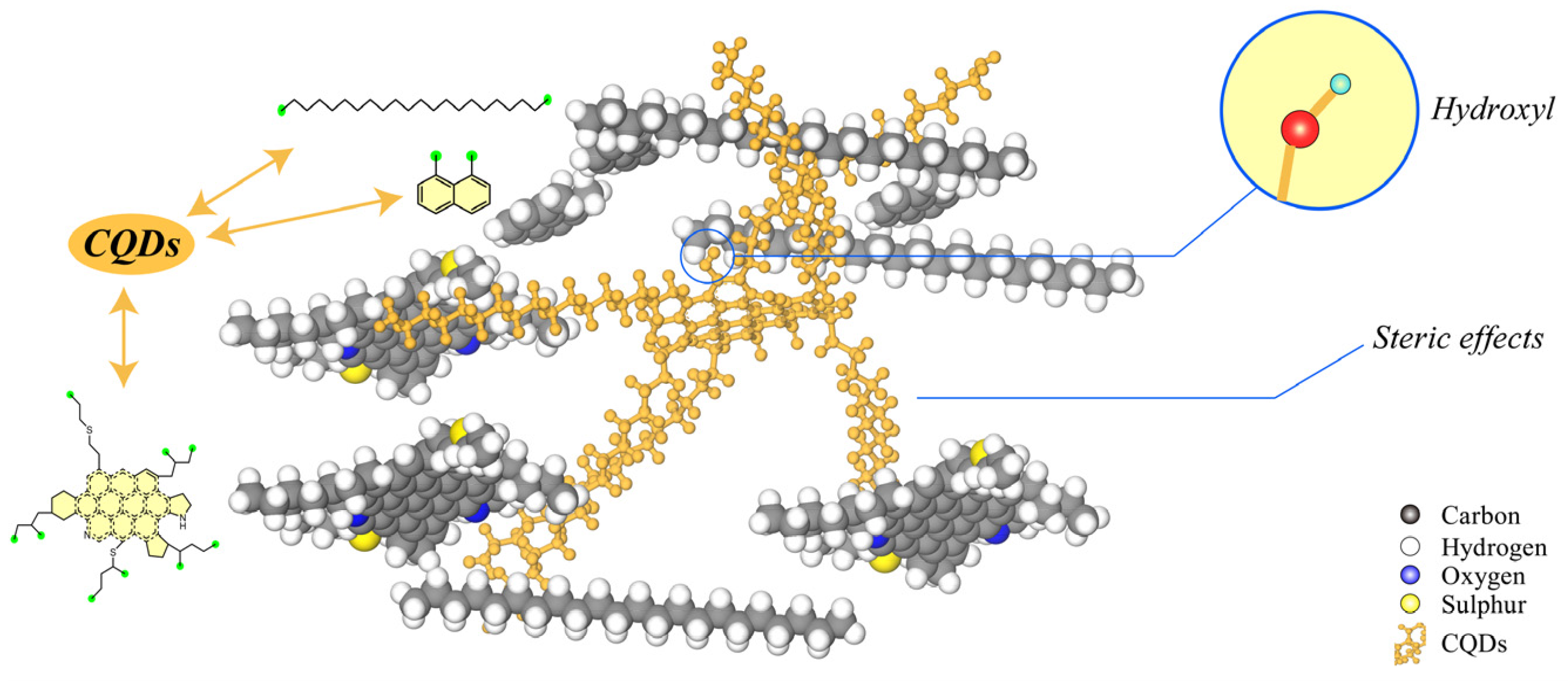
2.3. Mechanism Analysis
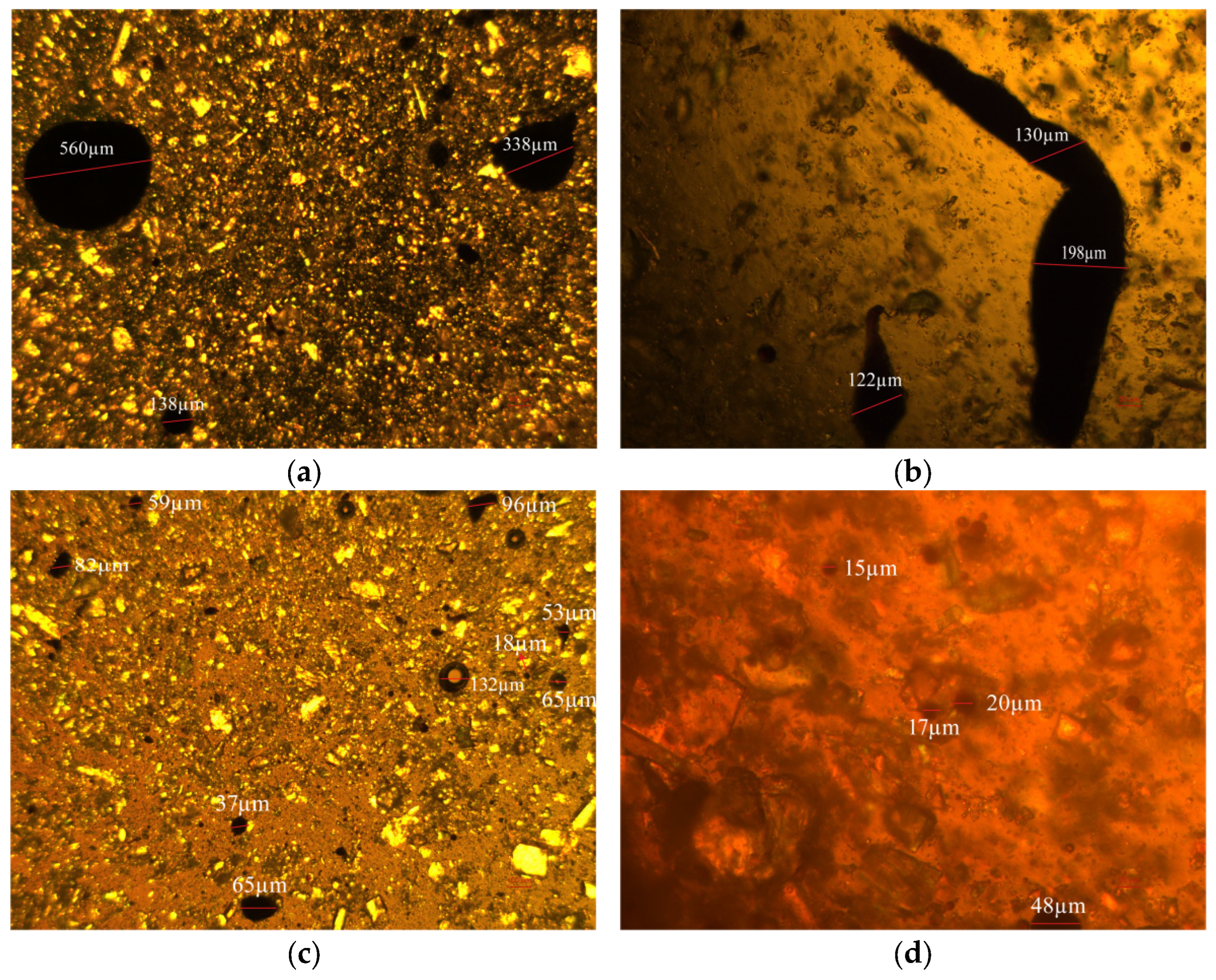
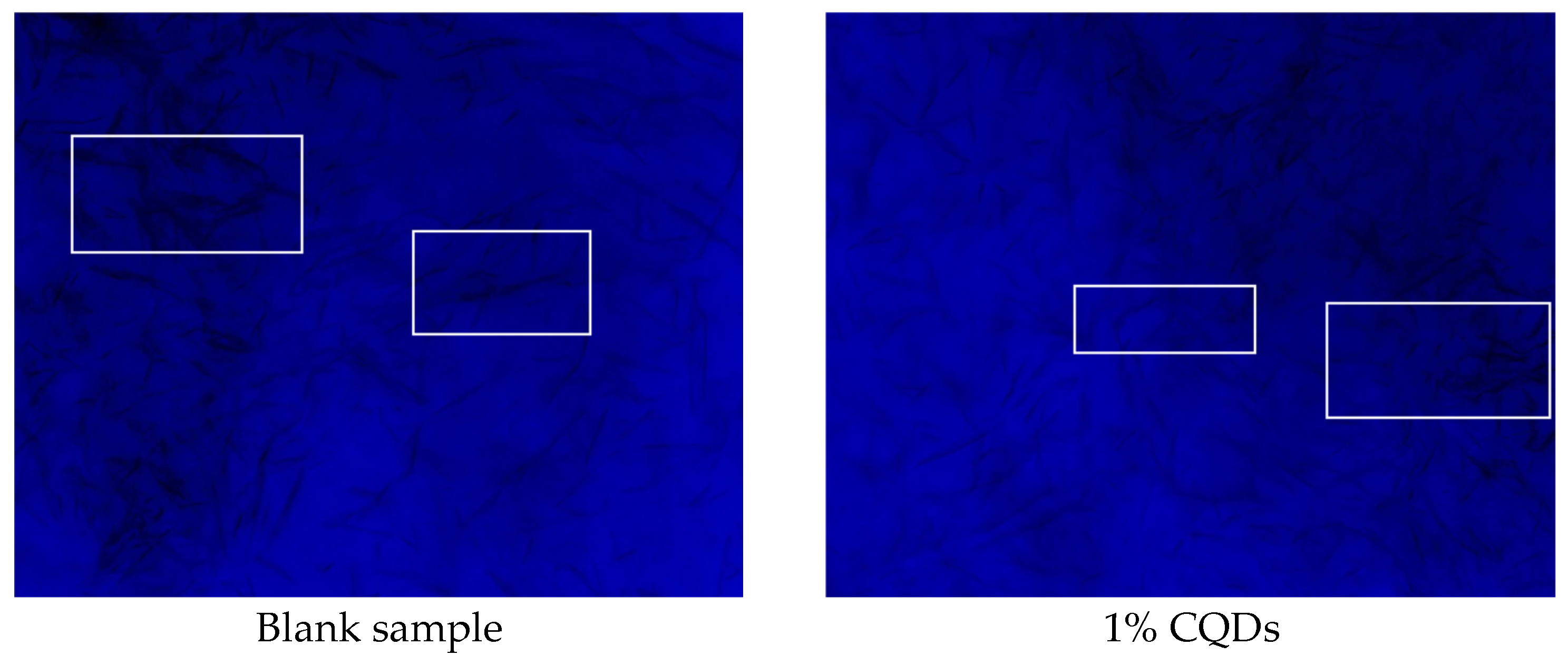
2.3.1. Morphological Characteristics of Wax Crystals
2.3.2. DSC
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Drilling Fluid
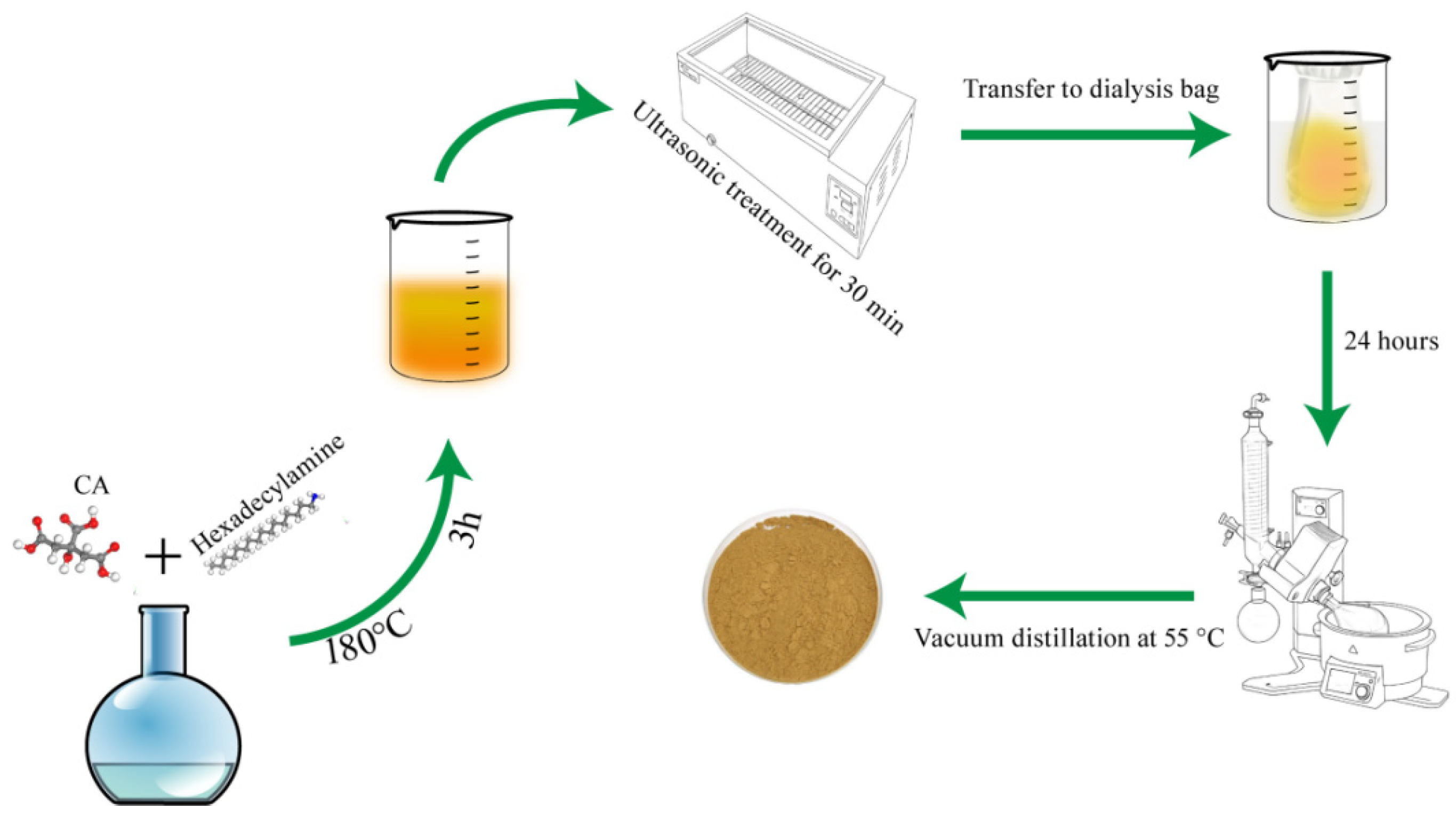
4.3. Preparation of CQDs
4.4. Characterization of CQDs
4.4.1. FT-IR
4.4.2. Absolute Fluorescence Quantum Yield
4.4.3. TEM
4.4.4. TGA
4.5. Performance Evaluation
4.5.1. Evaluation of Viscosity Reduction Performance
4.5.2. Adhesion Rate Following High-Temperature Aging
4.5.3. Drilling Fluid Rheology
4.5.4. Filtration Loss
4.5.5. Dispersion Properties
4.6. Mechanism Analysis
4.6.1. Morphological Characteristics of Wax Crystals
4.6.2. DSC
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hein, F.J. Heavy oil and oil (tar) sands in North America: An overview & summary of contributions. Nat. Resour. Res. 2006, 15, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M. Sustainable In-Situ Heavy Oil and Bitumen Recovery: Techniques, Case Studies, and Environmental Considerations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; ISBN 0323908497. [Google Scholar]
- Abdrabou, M.K.; Han, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, Y. Recent developments in the utilization of unconventional resources: A focus on partial upgrading techniques and sustainability of Canadian Oil sand bitumen. Resour. Chem. Mater. 2025, 4, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Jia, C.; Bai, J. Thermal evolution of chemical structure and mechanism of oil sands bitumen. Energy 2022, 244, 123190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hoff, I.; Chen, H. Characterization of various bitumen exposed to environmental chemicals. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, F.J. Geology of bitumen and heavy oil: An overview. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 154, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Guo, J.; Kiyingi, W.; Hu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Wang, L.; Tan, B. Numerical model of asphaltene deposition in vertical wellbores: Considerations of particle shape and drag force. Powder Technol. 2024, 448, 120284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhosani, A.; Daraboina, N. Modeling of asphaltene deposition during oil/gas flow in wellbore. Fuel 2020, 280, 118617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocabas, I.; Islam, M.R.; Modarress, H. A wellbore model for field-scale modeling of asphaltene plugging. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2000, 26, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, K.; Benyounes, K.; Khodja, M. Removal and prevention of asphaltene deposition during oil production: A literature review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 158, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori Mosleh, F.; Mortazavi, Y.; Hosseinpour, N.; Khodadadi, A.A. Asphaltene adsorption onto carbonaceous nanostructures. Energy Fuels 2019, 34, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, M.; Ahmadi, Y. A comparative review on the application of green and efficient nanoparticles in EOR with the focus on asphaltene deposition. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 413, 125860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarbeigi, E.; Sahraei, E.; Maroufi, K. A novel functionalized nanoparticle for inhibiting asphaltene precipitation and deposition. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 017164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic Analysis and Purification of Fluorescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, K.; Horikoshi, S.; Serpone, N. Photoluminescent carbon quantum dots: Synthetic approaches and photophysical properties. Chem. A Eur. J. 2021, 27, 9466–9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, H.; Liao, H.; Dai, Q.; Tiong, M.; Xian, C.; Luo, D. Mitigating Asphaltene Deposition in CO2 Flooding with Carbon Quantum Dots. Energies 2024, 17, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyandeh, M.; Mousavi Khadem, S.S.; Habibzadeh, S.; Esmaeili, A.; Abida, O.; Vatanpour, V.; Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Iravani, S.; Saeb, M.R.; et al. Quantum dots for photocatalysis: Synthesis and environmental applications. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 4931–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García de Arquer, F.P.; Talapin, D.V.; Klimov, V.I.; Arakawa, Y.; Bayer, M.; Sargent, E.H. Semiconductor quantum dots: Technological progress and future challenges. Science 2021, 373, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Min, Z.; Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Shi, Z. Influence of curing agent ratio, asphalt content and crosslinking degree on the compatibility and component distribution of epoxy asphalt in compound curing agent system. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2136375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Gu, L.; Chen, Y.; Shi, S. Study on Plugging Microfracture by Using High-Temperature Emulsified Bitumen. Coatings 2024, 14, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Kong, L.; Peng, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Feng, B.; Jian, O.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z. Long-chain alkyl emulsifiers induced asphalt particle dispersion: Lipophilicity-enhancement effect. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Zhang, C.; Xiu, J.; Xu, S.; Lu, L. Molecular dynamic simulation on the mechanism of viscosity reduction to asphaltene and resin in heavy oil. J. Shandong Univ. 2017, 47, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, W.I.; Kyei, S.K.; Ajienka, J.; Akaranta, O. Effect of bio-based flow improver on the microscopic and low-temperature flow properties of waxy crude oil. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. 2021, 11, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
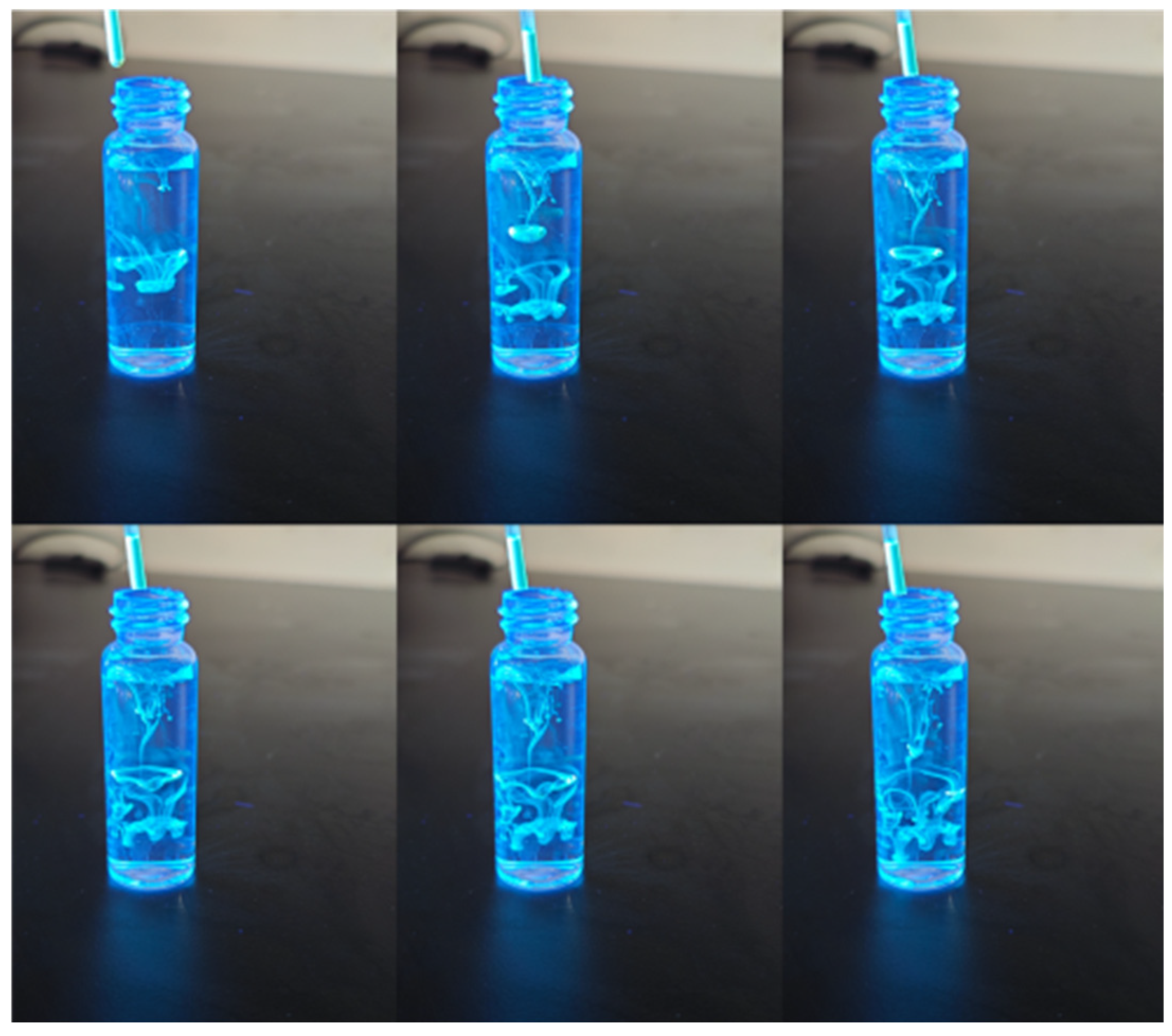
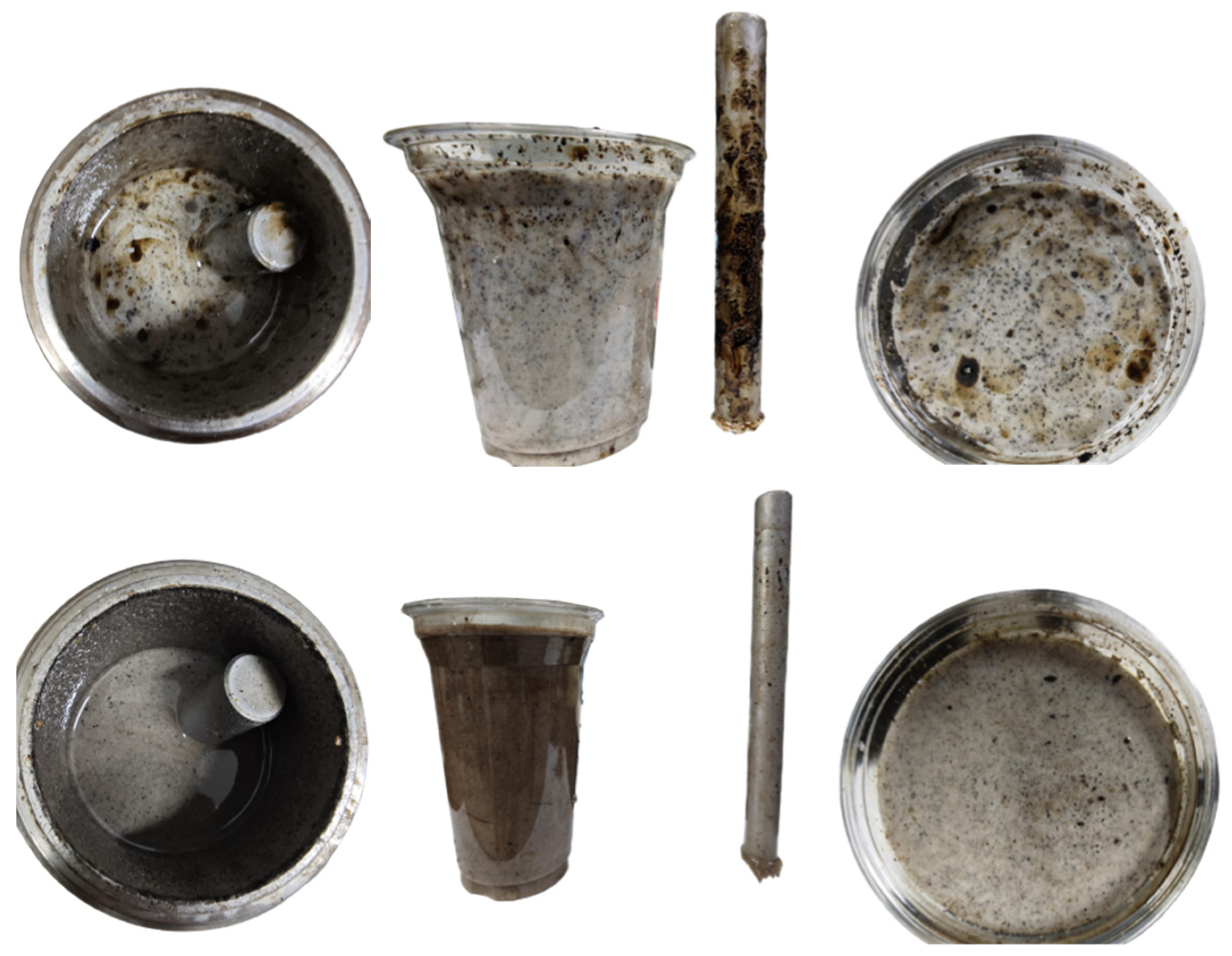





| Concentration (%) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 53.5 |
| 0.1 | 54.7 |
| 0.4 | 53.5 |
| 0.8 | 53.5 |
| 1 | 54.7 |
| 1.2 | 54.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, W.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Shan, W.; Xue, L.; Chen, G. Enhancing Gel-Based Drilling FIuids for Oil Sands Recovery Using Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as AsphaItene Dispersants. Gels 2025, 11, 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120942
Du W, Feng X, Zhang Y, Wang W, Shan W, Xue L, Chen G. Enhancing Gel-Based Drilling FIuids for Oil Sands Recovery Using Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as AsphaItene Dispersants. Gels. 2025; 11(12):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120942
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Weichao, Xueqi Feng, Yi Zhang, Wei Wang, Wenjun Shan, Le Xue, and Gang Chen. 2025. "Enhancing Gel-Based Drilling FIuids for Oil Sands Recovery Using Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as AsphaItene Dispersants" Gels 11, no. 12: 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120942
APA StyleDu, W., Feng, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, W., Shan, W., Xue, L., & Chen, G. (2025). Enhancing Gel-Based Drilling FIuids for Oil Sands Recovery Using Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as AsphaItene Dispersants. Gels, 11(12), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120942






