Skin Performance of Innovative NaDES-Based Gels: In Vivo Evaluation of Anti-Irritation Potential and Short-Term Efficacy
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Multifunctionality;
- Improved safety profile compared to synthetic ingredients;
- Compatibility with all skin types;
- Diversity of plant sources;
- Cost-effectiveness (generally less expensive than synthetic ingredients);
- Sustainability, biodegradability, and environmental friendliness [4].
2. Results and Discussion
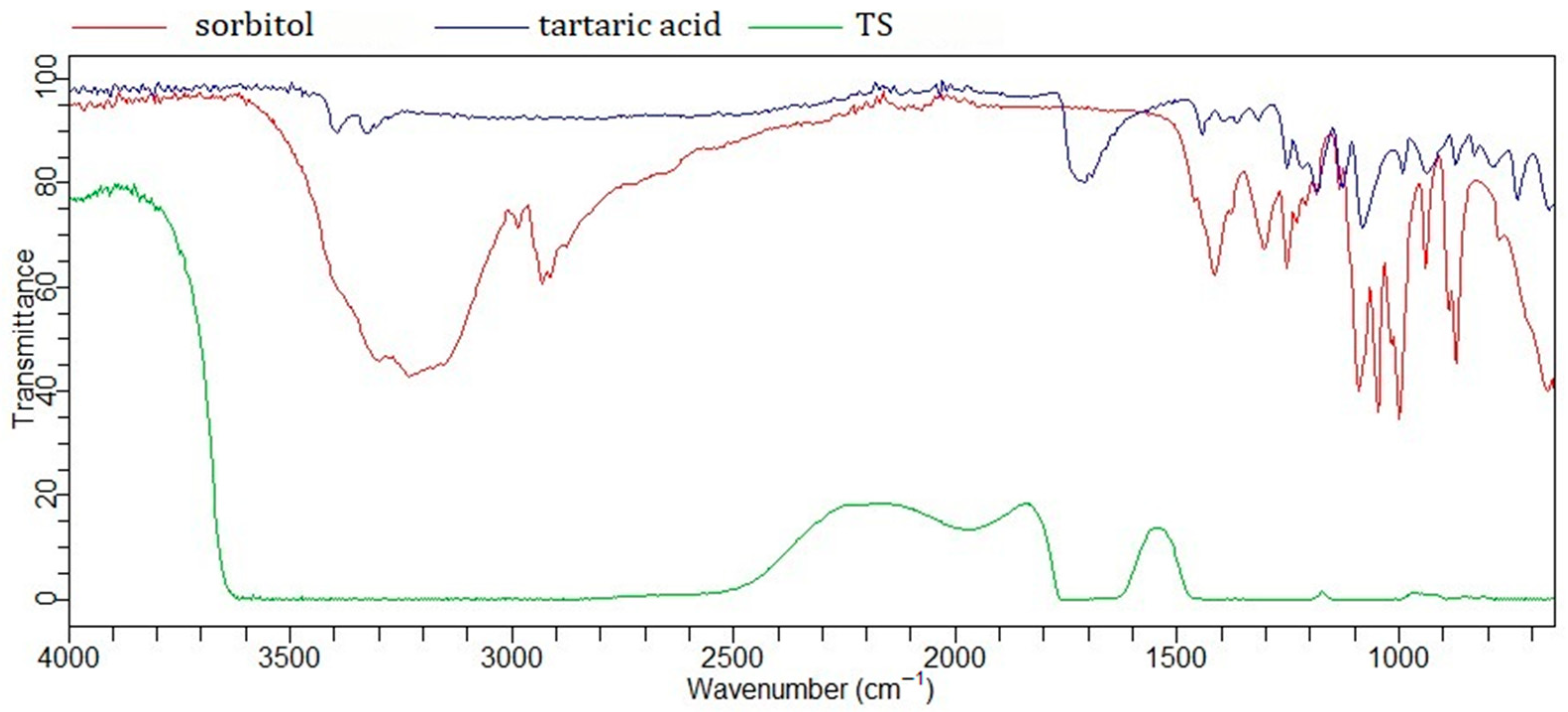
2.1. Characterization and FTIR Analysis of Prepared NaDES
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of Gels
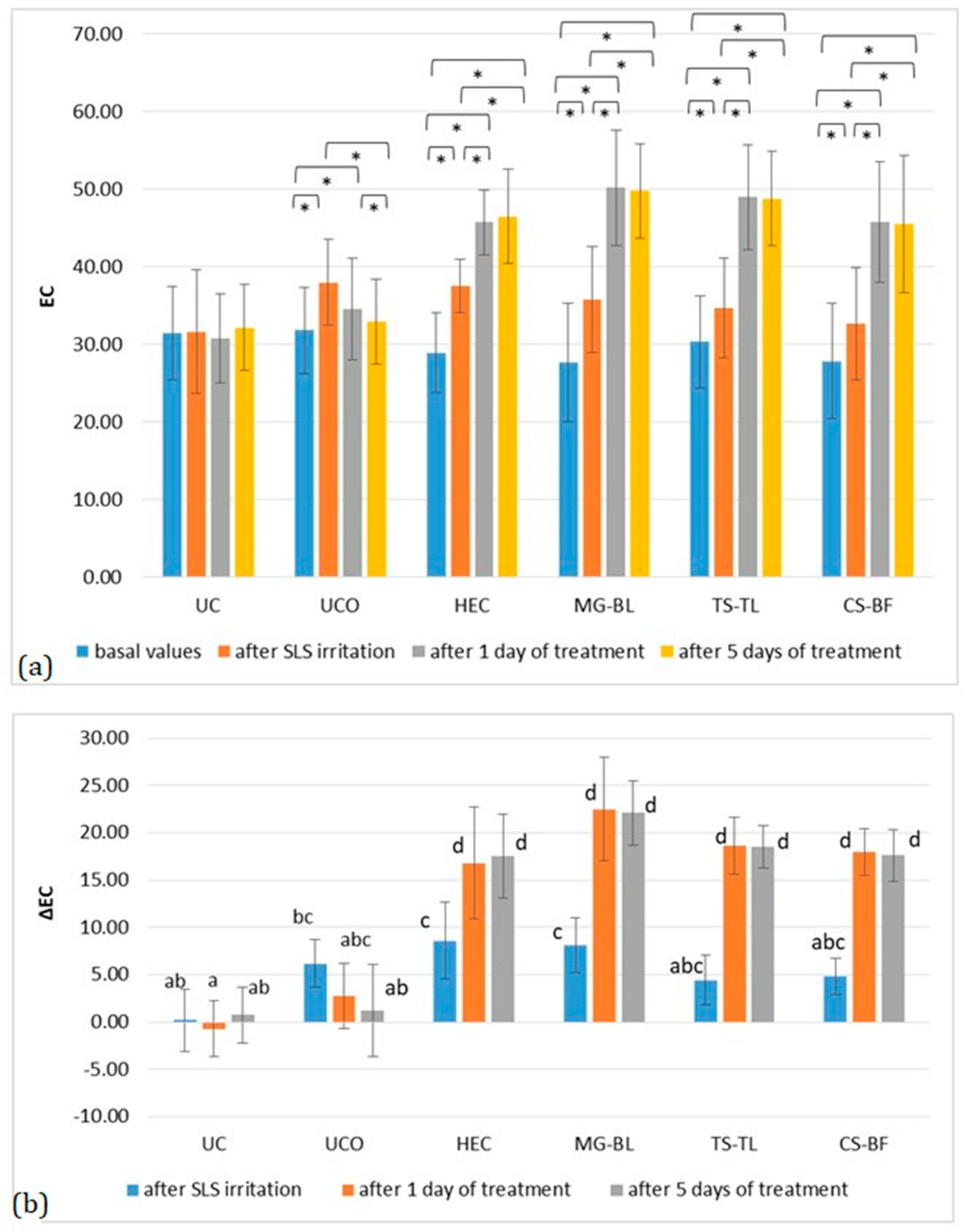
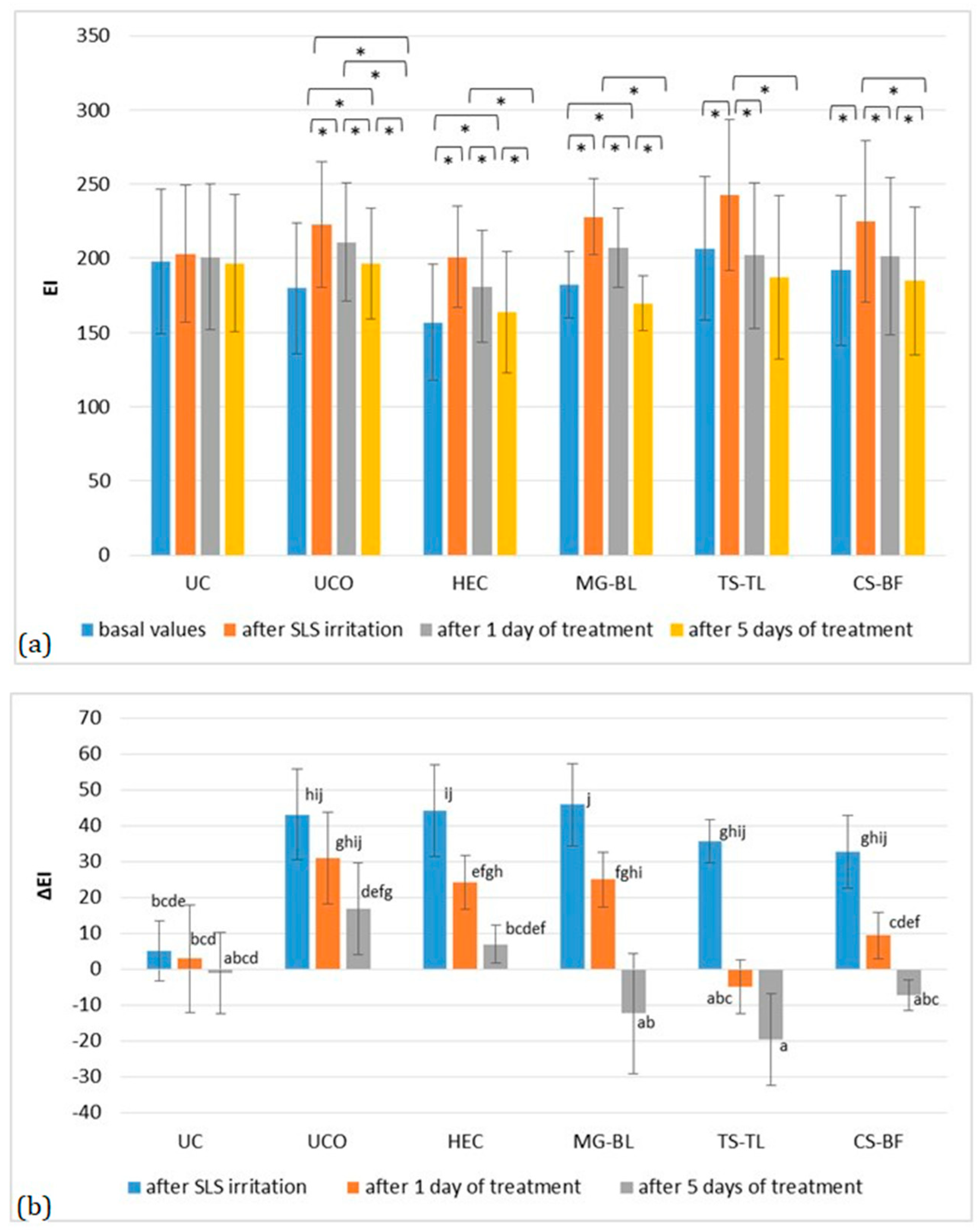
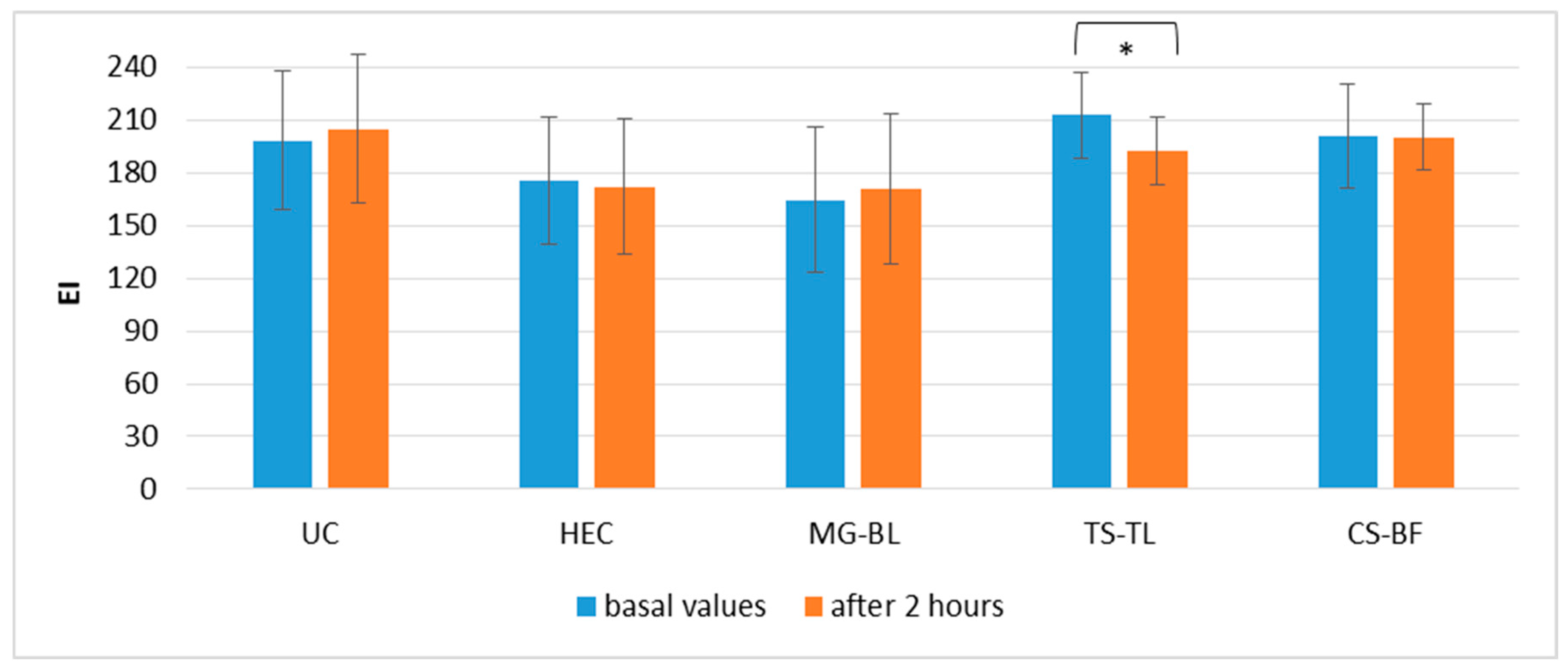
2.3. In Vivo Evaluation of Biophysical Skin Parameters
2.3.1. Anti-Irritant Potential of NaDES-Based Hydrogels
2.3.2. Short-Term Efficacy of NaDES-Based Hydrogels
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. NaDES Preparation
4.3. FTIR Analysis of Prepared NaDES
4.4. NaDES Extracts Preparation
4.5. Gel Preparation
4.6. Physicochemical Gel Characterization
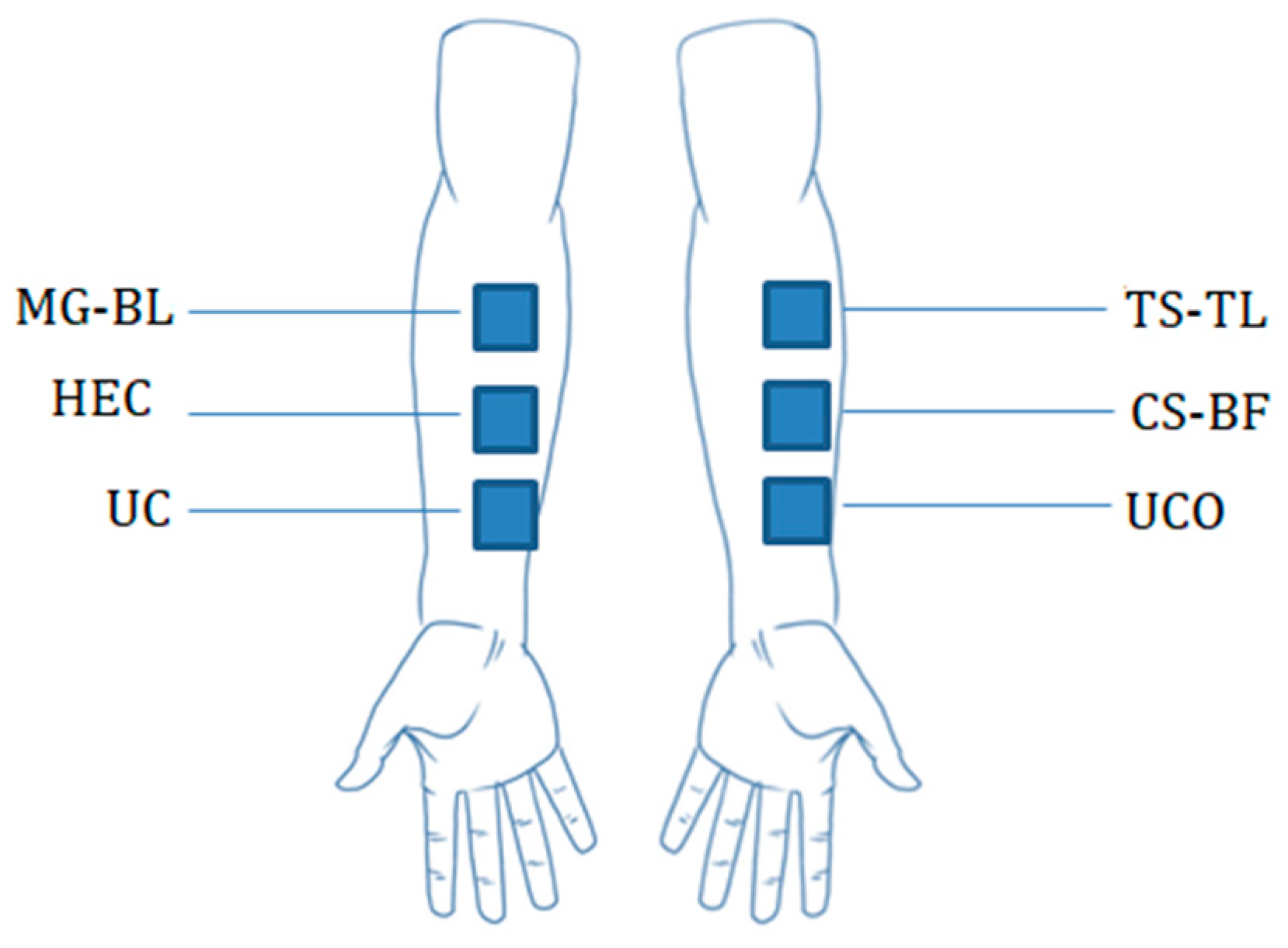
4.7. In Vivo Study
- Corneometer® CM 825—for assessing skin hydration (Stratum Corneum Hydration, SCH) by measuring the electrical capacitance of the skin (EC);
- Tewameter® TM 300—for evaluating transepidermal water loss (TEWL) following a device stabilization period of approximately 40 s; the TEWL value with the lowest standard deviation was recorded;
- Mexameter® MX 18—for determining the melanin index (MI) and erythema index (EI), used to quantify skin pigmentation and redness, respectively;
- Skin-pH-Meter® PH 905—for measuring the skin surface pH.
4.7.1. Evaluation of the Anti-Irritant Potential of NaDES-Based Gels
4.7.2. Evaluation of the Short-Term Effect of NaDES-Based Gels
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NaDES | Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent |
| TS | Tartaric acid-sorbitol NaDES |
| CS | Citric acid-sorbitol NaDES |
| MG | Malic acid-glycerol NaDES |
| BF | Bilberry fruit |
| BL | Bilberry leaves |
| TL | Green tea leaves |
| SLS | Sodium lauryl sulfate |
| EC | Electrical capacitance |
| TEWL | Transepidermal water loss |
| EI | Erythema index |
| MI | Melanin index |
| FTIR | Fourier-Transform Infrared spectroscopy |
| AHAs | Alpha-hydroxy acids |
References
- Yang, S.; Liu, L.; Han, J.; Tang, Y. Encapsulating Plant Ingredients for Dermocosmetic Application: An Updated Review of Delivery Systems and Characterization Techniques. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2020, 42, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savić, V.L.; Nikolić, V.D.; Arsić, I.A.; Stanojević, L.P.; Najman, S.J.; Stojanović, S.; Mladenović-Ranisavljević, I.I. Comparative Study of the Biological Activity of Allantoin and Aqueous Extract of the Comfrey Root. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsić, I.; Žugić, A.; Tadić, V.; Tasić-Kostov, M.; Mišić, D.; Primorac, M.; Runjaić-Antić, D. Estimation of Dermatological Application of Creams with St. John’s Wort Oil Extracts. Molecules 2012, 17, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Pathan, S.; Sahu, K.; Gupta, B. Herbs as Cosmetics for Natural Care: A Review. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 19, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslov, O.; Kolisnyk, S.; Komisarenko, M.; Golik, M. Study of Total Antioxidant Activity of Green Tea Leaves (Camellia sinensis L.). Herba Pol. 2022, 68, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupam, S.; Ratnali, B.; Malay, D. Green Tea: Current Trends and Prospects in Nutraceutical and Pharmaceutical Aspects. J. Herb. Med. 2023, 41, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, V.M.; Nešić, I.; Martinović, M.; Rój, E.; Brašanac-Vukanović, S.; Maksimović, S.; Žugić, A. Old Plant, New Possibilities: Wild Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L., Ericaceae) in Topical Skin Preparation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukula-Koch, W.; Dycha, N.; Lechwar, P.; Lasota, M.; Okoń, E.; Szczeblewski, P.; Wawruszak, A.; Tarabasz, D.; Hubert, J.; Wilkołek, P.; et al. Vaccinium Species—Unexplored Sources of Active Constituents for Cosmeceuticals. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; van Spronsen, J.; Dai, Y.; Verberne, M.; Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R. Are Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents the Missing Link in Understanding Cellular Metabolism and Physiology? Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenu, M.; Bansal, V.; Rana, S.; Sharma, N.; Kumar, V.; Arora, V.; Garg, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs): Designer Solvents for Green Extraction of Anthocyanin. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 34, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikmawanti, N.P.E.; Ramadon, D.; Jantan, I.; Mun’im, A. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES): Phytochemical Extraction Performance Enhancer for Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Product Development. Plants 2021, 10, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, K.; Yang, Y.; Ding, L.; Li, X. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES) in Drug Delivery Systems: Characteristics, Applications, and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 675, 125509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, C.; Caviglia, D.; Robustelli della Cuna, F.S.; Zuccari, G.; Russo, E. NaDES Application in Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Fields: An Overview. Gels 2024, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siroukane, N.; Kheniche, A.; Souiki, L. Valorization of Date Seed Waste for Sustainable Dermocosmetic Sunscreens: Phytochemical Insights and Formulation Advances. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinović, M.; Krgović, N.; Nešić, I.; Žugić, A.; Tadić, V.M. Conventional vs. Green Extraction Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents—Differences in the Composition of Soluble Unbound Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinović, M.; Nešić, I.; Žugić, A.; Tadić, V.M. Preliminary Analysis of Bilberry NaDES Extracts as Versatile Active Ingredients of Natural Dermocosmetic Products: In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Tyrosinase, Anti-Hyaluronidase, Anti-Collagenase, and UV Protective Properties. Plants 2025, 14, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinović, M.; Nešić, I.; Bojović, D.; Žugić, A.; Blagojević, S.; Blagojević, S.; Tadić, V.M. Plant-Based Sunscreen Emulgel: UV Boosting Effect of Bilberry and Green Tea NaDES Extracts. Gels 2024, 10, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fawal, G.F.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; Hassan, M.A.; Elnouby, M.S. Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Hydrogel for Wound Dressing: Fabrication, Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, F.H.; Hussain, F.S.J.; Rasad, M.S.B.A.; Mohd Yusoff, M. Nanostructured Materials from Hydroxyethyl Cellulose for Skin Tissue Engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risaliti, L.; Yu, X.; Vanti, G.; Bergonzi, M.C.; Wang, M.; Bilia, A.R. Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Hydrogel for Skin Delivery of Khellin Loaded in Ascosomes: Characterization, In Vitro/In Vivo Performance and Acute Toxicity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 179, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-C.; Yang, J.-H. Dual Effects of Alpha-Hydroxy Acids on the Skin. Molecules 2018, 23, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awuchi, C.; Echeta, C. Current Developments in Sugar Alcohols: Chemistry, Nutrition, and Health Concerns of Sorbitol, Xylitol, Glycerol, Arabitol, Inositol, Maltitol, and Lactitol. Int. J. Adv. Acad. Res. 2019, 5, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Koigerova, A.; Gosteva, A.; Samarov, A.; Tsvetov, N. Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Carboxylic Acids and Glycerol or Propylene Glycol as Green Media for Extraction of Bioactive Substances from Chamaenerion angustifolium (L.) Scop. Molecules 2023, 28, 6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Su, J.; Chu, X.; Wang, X. A Green Method of Extracting and Recovering Flavonoids from Acanthopanax senticosus Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2022, 27, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, A.P.R.; Andrade, D.F.; Guimarães, T.G.S.; Amaral, C.D.B.; Oliveira, A.; Gonzalez, M.H. Synthesis of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Using a Mixture Design for Extraction of Animal and Plant Samples Prior to ICP-MS Analysis. Talanta 2020, 216, 120956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, N.; Zhilyakova, E.; Malyutina, A.; Novikov, O.; Pisarev, D.; Abramovich, R.; Potanina, O.; Lazar, S.; Mizina, P.; Sahaidak-Nikitiuk, R. Studying and Modeling of the Extraction Properties of the Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent and Sorbitol-Based Solvents in Regard to Biologically Active Substances from Glycyrrhizae Roots. Molecules 2020, 25, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as New Potential Media for Green Technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Prazitya Shakti, S.O.; Prabowo, W.C.; Hikmawan, B.D.; Arifuddin, M.; Angelina, M.; Prastya, M.E.; Okselni, T.; Alwi, R.S.; Sadikin, R.; et al. Citric Acid-Glycerol-Based NADES for Microwave-Assisted Extraction Enhances the Polyphenols Level of Eleutherine bulbosa Mill. Urb. Bulbs. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 14, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourfarzad, A.; Ahmadian, Z.; Habibi-Najafi, M.B. Interactions between Polyols and Wheat Biopolymers in a Bread Model System Fortified with Inulin: A Fourier Transform Infrared Study. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, I.V.; Sakurai, Y.C.N.; Ferreira, N.R.; Moreira, S.G.C.; da Cruz Rodrigues, A.M.; da Silva, L.H.M. Elaboration and Characterization of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs): Application in the Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Pitaya. Molecules 2022, 27, 8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, H.; Piessens, S.; Bloem, A.; Pronk, H.; Finkel, P. Natural Skin Surface pH Is on Average below 5, Which Is Beneficial for Its Resident Flora. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2006, 28, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remli, S.; Benmounah, A. Rheological Behavior of Hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) Solutions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1045, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurler, J.; Engesland, A.; Poorahmary Kermany, B.; Škalko-Basnet, N. Improved Texture Analysis for Hydrogel Characterization: Gel Cohesiveness, Adhesiveness, and Hardness. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, G.; Gilbert, L.; Grisel, M.; Picard, C. Instrumental and Sensory Methodologies to Characterize the Residual Film of Topical Products Applied to Skin. Skin Res. Technol. 2019, 25, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, C.; Safta, D.A.; Iurian, S.; Petrușcă, D.R.; Moldovan, M.-L. QbD Approach in Cosmetic Cleansers Research: The Development of a Moisturizing Cleansing Foam Focusing on Thickener, Surfactants, and Polyols Content. Gels 2024, 10, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elena, O.B.; Maria, N.A.; Michael, S.Z.; Natalia, B.D.; Alexander, I.B.; Ivan, I.K. Dermatologic Gels Spreadability Measuring Methods Comparative Study. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2022, 14, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törmä, H.; Lindberg, M.; Berne, B. Skin Barrier Disruption by Sodium Lauryl Sulfate-Exposure Alters the Expressions of Involucrin, Transglutaminase 1, Profilaggrin, and Kallikreins during the Repair Phase in Human Skin In Vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stettler, H.; Kurka, P.; Lunau, N.; Manger, C.; Böhling, A.; Bielfeldt, S.; Wilhelm, K.-P.; Dähnhardt-Pfeiffer, S.; Dähnhardt, D.; Brill, F.H.H.; et al. A New Topical Panthenol-Containing Emollient: Results from Two Randomized Controlled Studies Assessing Its Skin Moisturization and Barrier Restoration Potential, and the Effect on Skin Microflora. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2017, 28, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoty-Okombi, S.; Gillaizeau, F.; Leuillet, S.; Douillard, B.; Le Fresne-Languille, S.; Carton, T.; De Martino, A.; Moussou, P.; Bonnaud-Rosaye, C.; André, V. Effect of Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS) Applied as a Patch on Human Skin Physiology and Its Microbiota. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniak, A.B.; du Plessis, J.; John, S.M.; Eloff, F.; Agner, T.; Chou, T.-C.; Nixon, R.; Steiner, M.F.C.; Kudla, I.; Linn Holness, D. International Guidelines for the In Vivo Assessment of Skin Properties in Non-Clinical Settings: Part 1. pH. Skin Res. Technol. 2013, 19, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, M.; Nanu, A. Influence of Cleansing Product Type on Several Skin Parameters after Single Use. Farmacia 2010, 58, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Plessis, J.d.; Stefaniak, A.; Eloff, F.; John, S.; Agner, T.; Chou, T.-C.; Nixon, R.; Steiner, M.; Franken, A.; Kudla, I.; et al. International Guidelines for the In Vivo Assessment of Skin Properties in Non-Clinical Settings: Part 2. Transepidermal Water Loss and Skin Hydration. Skin Res. Technol. 2013, 19, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, N.; Chikaraishi, Y.; Shimazawa, M.; Yokota, S.; Hara, H. Vaccinium myrtillus (Bilberry) Extracts Reduce Angiogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2010, 7, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, B.; Malekzadeh, M.; Goodarzi, M.; Masoudifar, A.; Mirzaei, H. Green Tea and Its Anti-Angiogenesis Effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluhr, J.W.; Darlenski, R.; Surber, C. Glycerol and the Skin: Holistic Approach to Its Origin and Functions. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roure, R.; Lanctin, M.; Nkengne, A.; Nollent, V.; Dayan, L.; Bertin, C. Cosmetic Lifting Effect of a Formula Combining Tetrahydroxypropyl Ethylenediamine, Ononis spinosa and Glycerin as Shown by a New 2-D Imaging Method. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 2013, 3, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeman, A. Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Alpha-Hydroxy Acids in Dermatological Practice: A Comprehensive Clinical and Legal Review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 1661–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milošević, S.; Bebek Markovinović, A.; Teslić, N.; Mišan, A.; Pojić, M.; Brčić Karačonji, I.; Jurica, K.; Lasić, D.; Putnik, P.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; et al. Use of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent (NADES) as a Green Extraction of Antioxidant Polyphenols from Strawberry Tree Fruit (Arbutus unedo L.): An Optimization Study. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wils, L.; Leman-Loubière, C.; Bellin, N.; Clément-Larosière, B.; Pinault, M.; Chevalier, S.; Enguehard-Gueiffier, C.; Bodet, C.; Boudesocque-Delaye, L. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent Formulations for Spirulina: Preparation, Intensification, and Skin Impact. Algal Res. 2021, 56, 102317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.; Rebocho, S.; Craveiro, R.; Paiva, A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Selective Extraction and Stabilization of Bioactive Compounds from Rosemary Leaves Using a Biphasic NADES. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 954835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, P. EEMCO European Group on Efficacy Measurement of Cosmetics and Other Topical Products. Skin Res. Technol. 1995, 1, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardesca, E.; Loden, M.; Serup, J.; Masson, P.; Rodrigues, L.M. The Revised EEMCO Guidance for the in Vivo Measurement of Water in the Skin. Skin Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasić-Kostov, M.; Nešić, I.; Tadic, V.; Pavlovic, D. Correlation between Chemical Composition and Topical Safety and Efficacy of Alchemilla vulgaris L. Extract in Emulsion Vehicle. Riv. Ital. Delle Sostanze Grasse 2024, 101, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
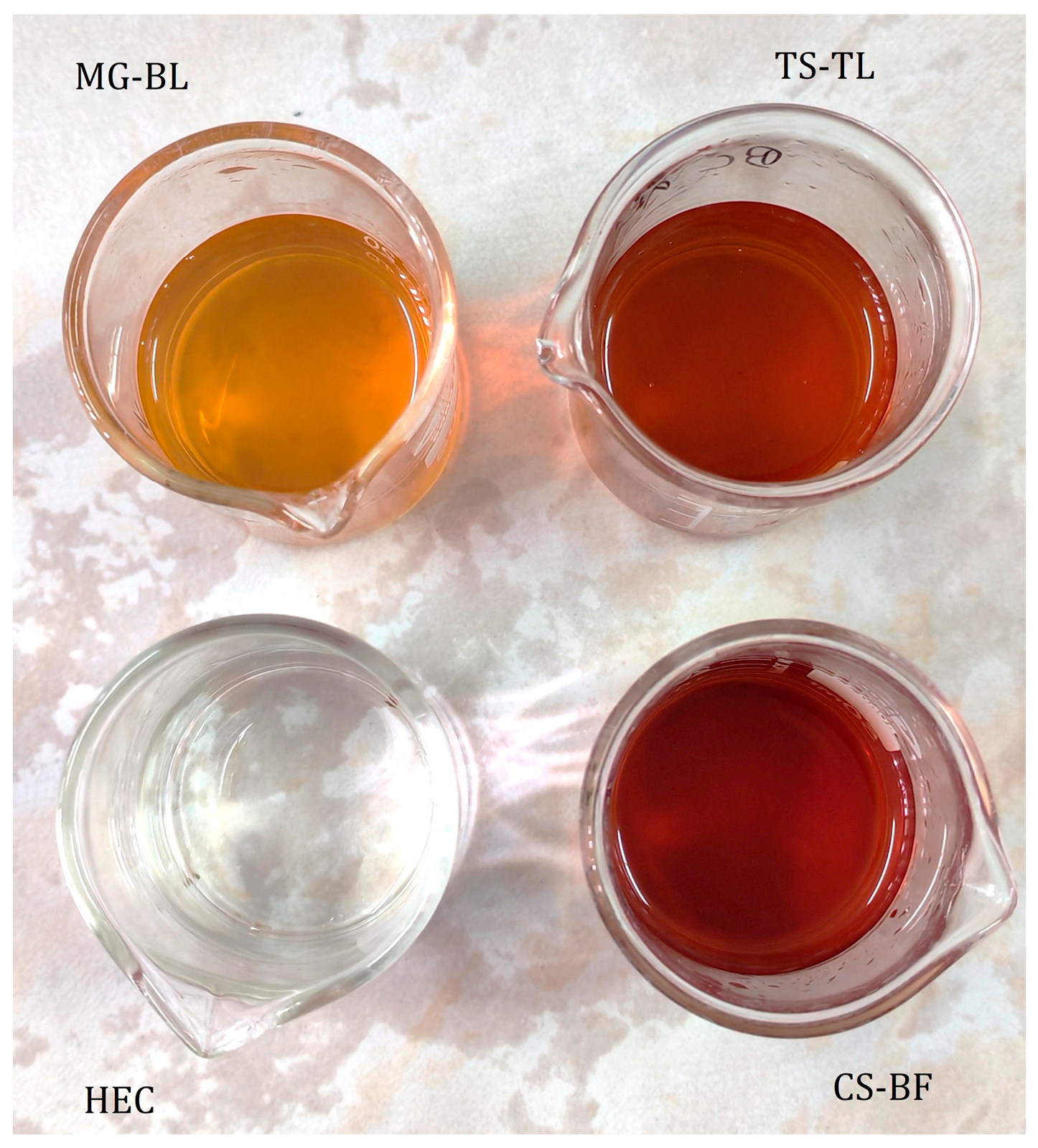






| HEC | MG–BL | CS–BF | TS–TL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (mN) | 930.33 ± 64.08 a | 1791.00 ± 52.09 b | 1670.67 ± 34.95 c | 1699.00 ± 23.26 c |
| Adhesiveness (mJ) | 1.47 ± 0.06 a | 1.90 ± 0.10 b | 1.93 ± 0.06 b | 2.13 ± 0.15 b |
| Cohesiveness | 0.93 ± 0.15 a | 0.80 ± 0.10 a | 0.94 ± 0.17 a | 0.85 ± 0.05 a |
| Spreading area (mm2) | 504.49 ± 45.32 a | 406.11 ± 79.77 a | 680.33 ± 138.46 a | 617.53 ± 87.94 a |
| INCI Name | Composition (%, w/w) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active Gel— Gel with NaDES Extract | Placebo Gel Without Plant Extract (HEC) | ||||
| MG–BL | TS–TL | CS–BF | |||
| Hydroxyethyl cellulose | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Glycerol | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| Sodium benzoate | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| NaDES extracts | MG–BL | 24 | - | - | - |
| TS–TL | - | 24 | - | - | |
| CS–BF | - | - | 24 | - | |
| NaOH, 10% | q.s. ad pH 4.5 | q.s. ad pH 4.5 | q.s. ad pH 4.5 | - | |
| Water | q.s. ad 100 | q.s. ad 100 | q.s. ad 100 | q.s. ad 100 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinović, M.; Nešić, I.; Tadić, V.M.; Žugić, A.; Tasić-Kostov, M.; Blagojević, S.; Tosti, T. Skin Performance of Innovative NaDES-Based Gels: In Vivo Evaluation of Anti-Irritation Potential and Short-Term Efficacy. Gels 2025, 11, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110869
Martinović M, Nešić I, Tadić VM, Žugić A, Tasić-Kostov M, Blagojević S, Tosti T. Skin Performance of Innovative NaDES-Based Gels: In Vivo Evaluation of Anti-Irritation Potential and Short-Term Efficacy. Gels. 2025; 11(11):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110869
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinović, Milica, Ivana Nešić, Vanja M. Tadić, Ana Žugić, Marija Tasić-Kostov, Slavica Blagojević, and Tomislav Tosti. 2025. "Skin Performance of Innovative NaDES-Based Gels: In Vivo Evaluation of Anti-Irritation Potential and Short-Term Efficacy" Gels 11, no. 11: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110869
APA StyleMartinović, M., Nešić, I., Tadić, V. M., Žugić, A., Tasić-Kostov, M., Blagojević, S., & Tosti, T. (2025). Skin Performance of Innovative NaDES-Based Gels: In Vivo Evaluation of Anti-Irritation Potential and Short-Term Efficacy. Gels, 11(11), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110869








