Investigation of Rheological Characteristics of Thermosensitive Nasal In Situ Gels Based on P407 and Their Effect on Spray Pattern
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Rheological Properties of Hydrogels Based on P407
2.2. Rheological Properties of Hydrogels Based on P407 and P188
2.3. Rheological Properties of Hydrogels Based on P407 and P188 with the Addition of Mucoadhesive Polymers
2.4. Results of Viscosity and Density Studies
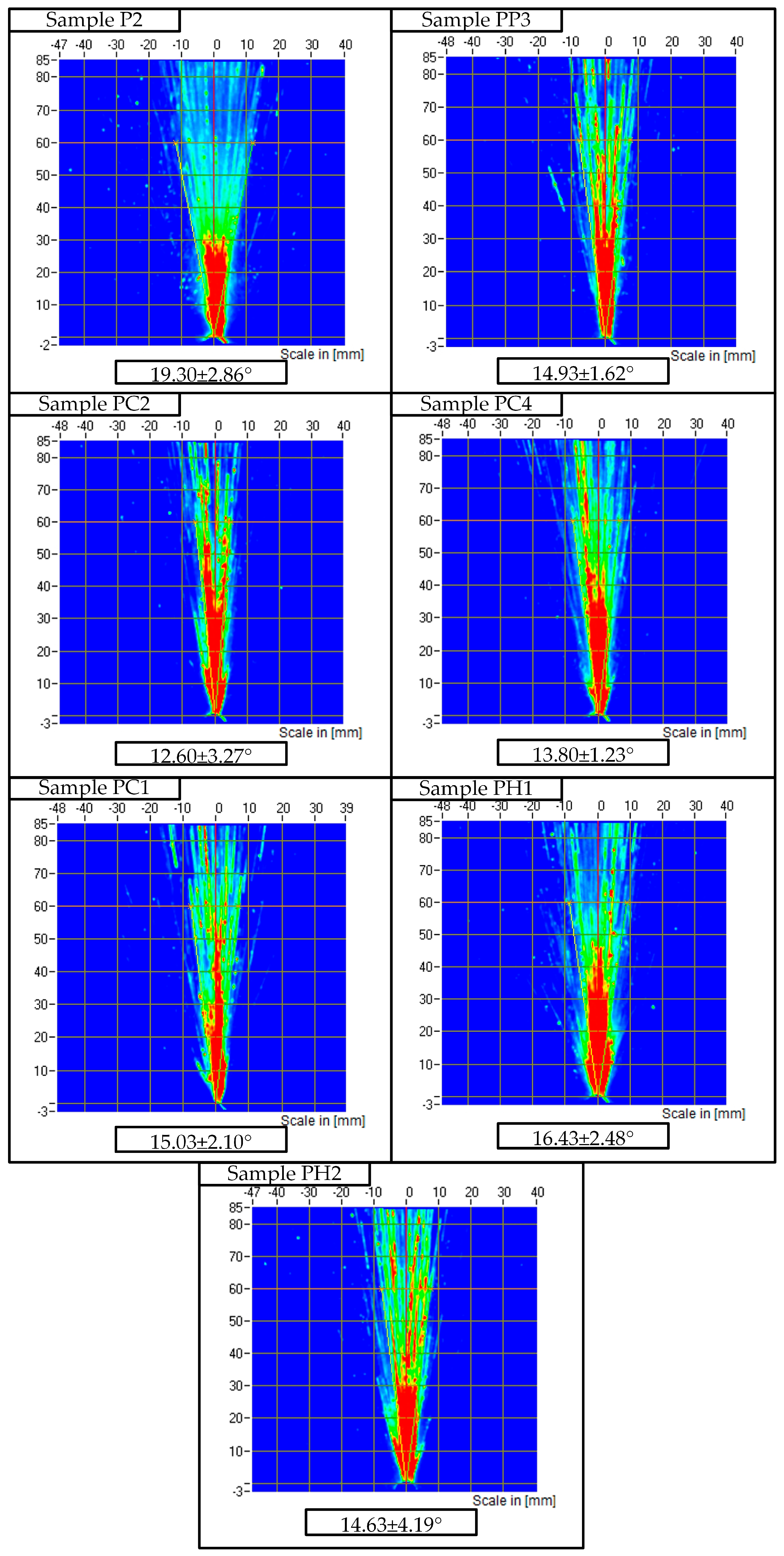
2.5. SprayVIEW Spray Pattern Study Results
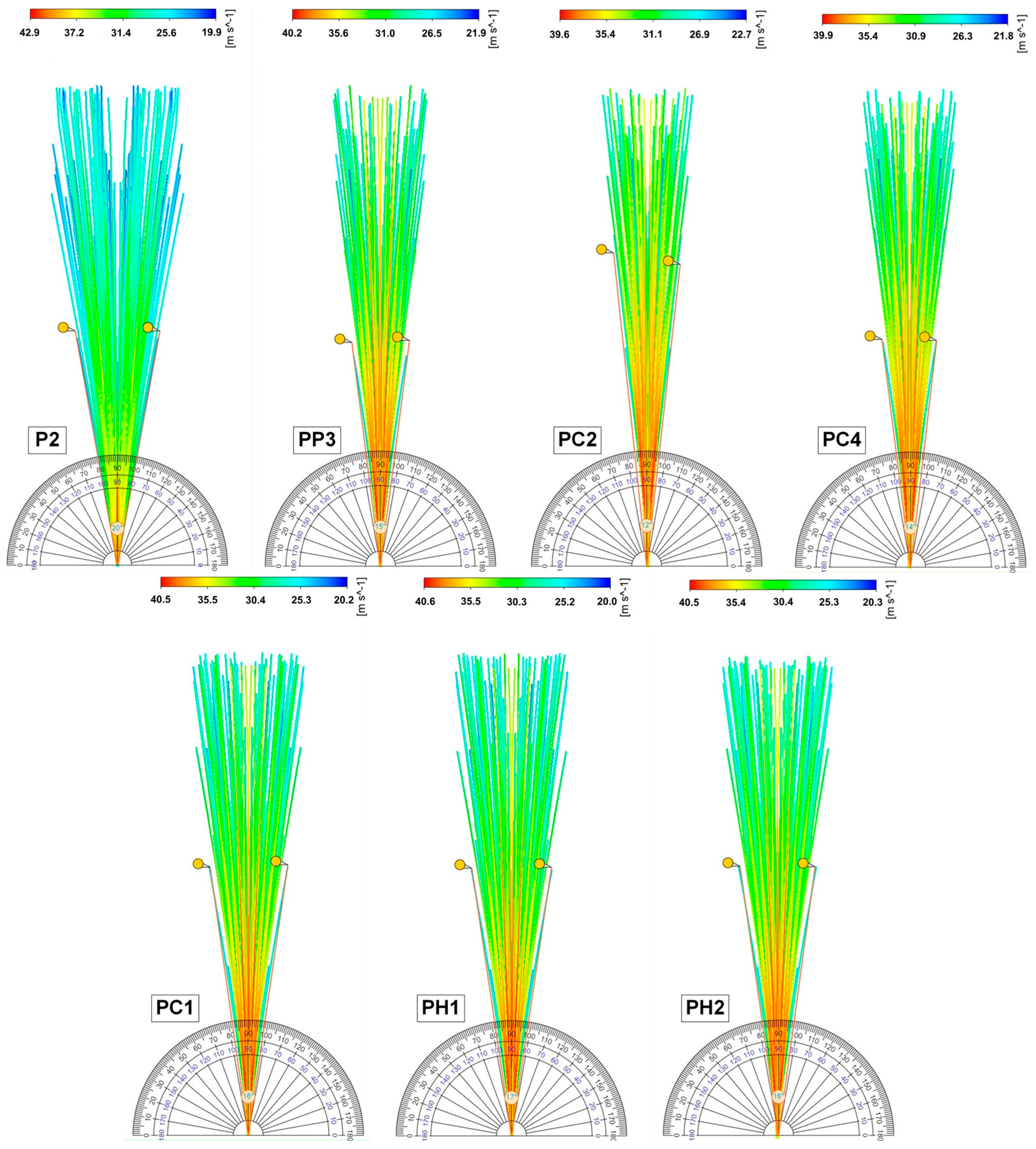
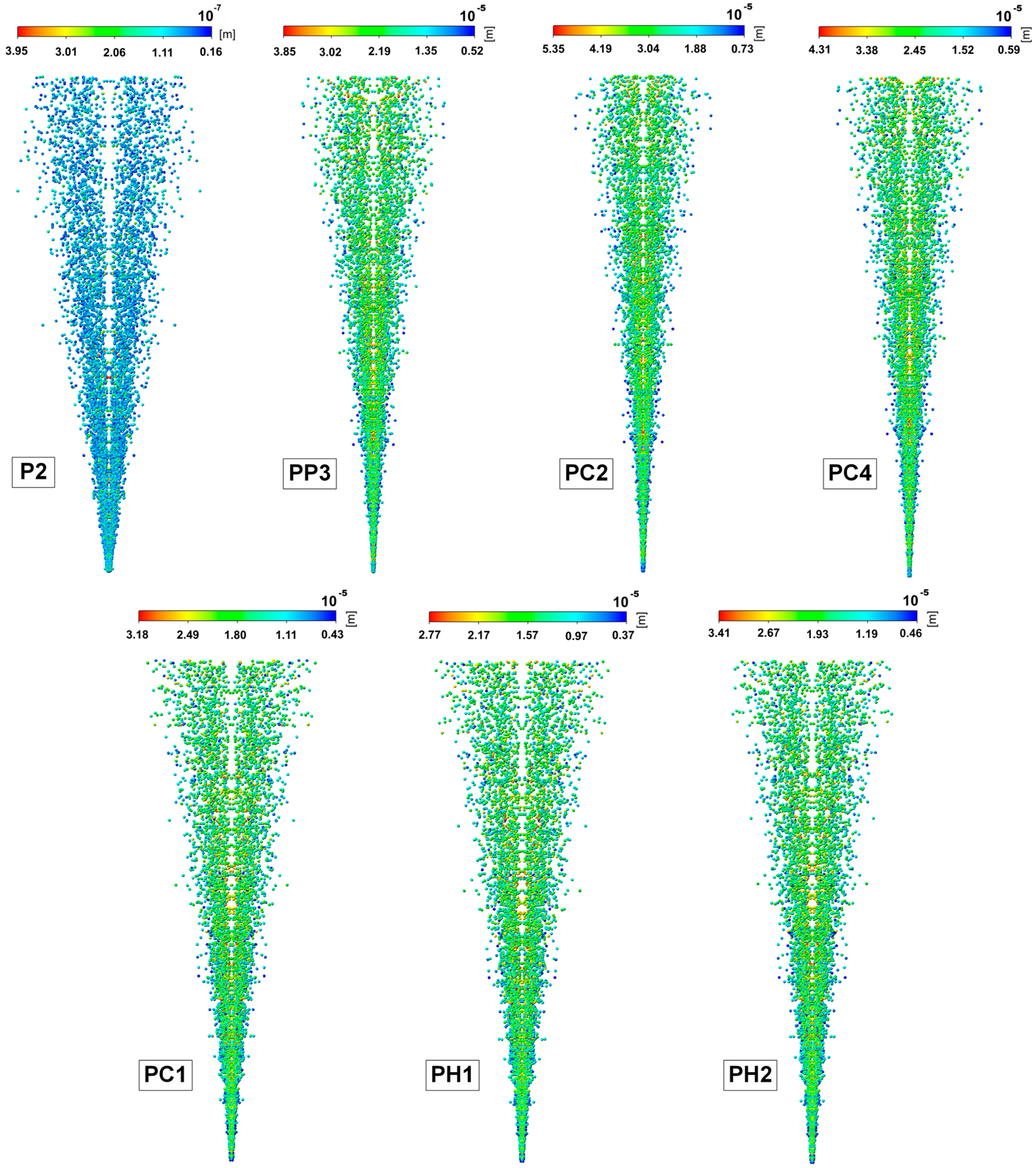
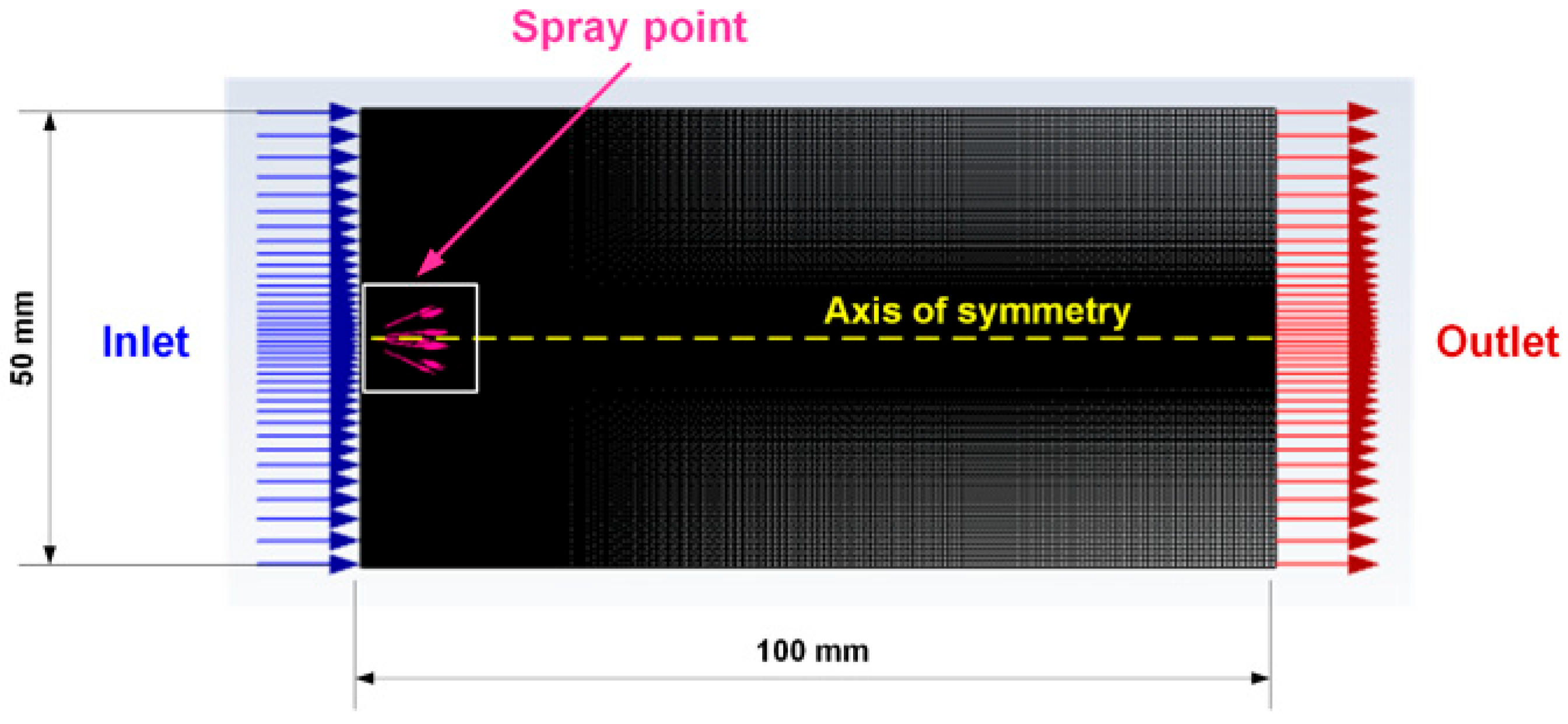
2.6. Results of Mathematical Modeling of the Spray Torch
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Substances Used
4.2. Method for Obtaining Gels
4.3. Method for Measuring the Loss Modulus, Storage Modulus, and Gelation Temperature
4.4. Viscosity Measurement Technique
4.5. Density Measurement Technique
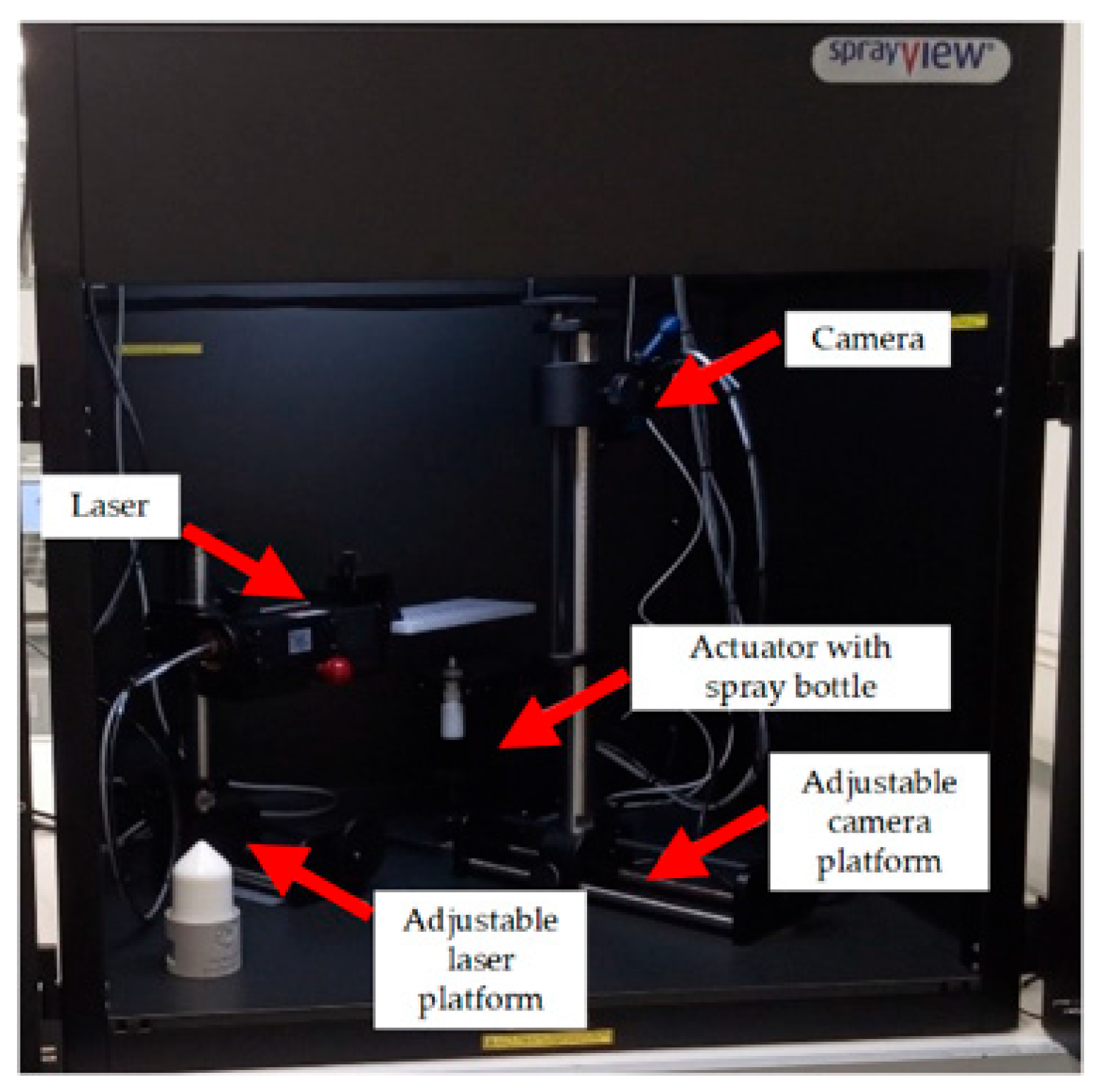
4.6. SprayVIEW Methodology
4.7. Mathematical Modeling of Spray Torch
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| P407 | Poloxamer 407 |
| P188 | Poloxamer 188 |
| HPMC | Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose |
| Tsol–gel | Gelling temperature |
| PPO | Poly(propylene oxide) |
| PEO | Poly(ethylene oxide) |
| G′ | Storage modulus |
| G″ | Loss modulus |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| Alg-Na | Sodium alginate |
| DPM | Discrete particle method |
| P | P407 |
| PP | P407 + P188 |
| PC | P407 + Chitosan |
| PH | P407 + HPMC |
| PA | P407 + Sodium alginate |
References
- Bakhrushina, E.O.; Demina, N.B.; Shumkova, M.M.; Rodyuk, P.S.; Shulikina, D.S.; Krasnyuk, I.I. In situ intranasal delivery systems: Application prospects and main pharmaceutical aspects of development. Drug Dev. Regist. 2021, 10, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Hafeez, A.; Ansari, J.A.; Kaushal, V.P.; Kushwaha, S.P. Intranasal delivery of drug-loaded polymeric nanomicelles for brain targeting: A comprehensive review. J. Nanopart. Res. 2025, 27, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffleur, F.; Bauer, B. Progress in nasal drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 120994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Shastri, D.H.; Shah, J.; Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. Nasal Delivery to the Brain: Harnessing Nanoparticles for Effective Drug Transport. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.N.; Leite, C.M.; Moreno, N.S.; Miranda, R.R.; Pincela Lins, P.M.; Rodero, C.F.; Zucolotto, V. Nose-to-brain delivery of biomimetic nanoparticles for glioblastoma targeted therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 17, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisku, A.; Nishad, A.; Agrawal, S.; Paliwal, R.; Datusalia, A.K.; Gupta, G.; Sulakhiya, K. Recent developments in intranasal drug delivery of nanomedicines for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1463976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassin-Delyle, S.; Buenestado, A.; Naline, E.; Faisy, C.; Blouquit-Laye, S.; Couderc, L.J.; Devillier, P. Intranasal drug delivery: An efficient and non-invasive route for systemic administration: Focus on opioids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 134, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementino, A.R.; Pellegrini, G.; Banella, S.; Colombo, G.; Cantu, L.; Sonvico, F.; Del Favero, E. Structure and fate of nanoparticles designed for the nasal delivery of poorly soluble drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 3132–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonvico, F.; Colombo, G.; Quarta, E.; Guareschi, F.; Banella, S.; Buttini, F.; Scherlie, R. Nasal delivery as a strategy for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, S.; Shelke, H.; Bonde, S. A comprehensive review on natural polysaccharides based in situ gels for nasal drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 320, 145987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodilo, L.N.; Perkušić, M.; Ugrina, I.; Špoljarić, D.; Brala, C.J.; Klarić, D.A.; Hafner, A. In situ gelling nanosuspension as an advanced platform for fluticasone propionate nasal delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 175, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adwan, S.; Obeidi, T.; Al-Akayleh, F. Chitosan Nanoparticles Embedded in In Situ Gel for Nasal Delivery of Imipramine Hydrochloride: Short-Term Stage Development and Controlled Release Evaluation. Polymers 2024, 16, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhrushina, E.O.; Mikhel, J.B.; Kondratieva, V.M.; Demina, N.B.; Grebennikova, T.V. In situ gels as a modern method of intranasal vaccine delivery. Probl. Virol. 2022, 67, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellotti, D.; D’Accolti, M.; Pula, W.; Huang, N.; Simeliere, F.; Caselli, E.; Esposito, E.; Remelli, M. Calcitermin-Loaded Smart Gels Activity against Candida albicans: A Preliminary In Vitro Study. Gels 2023, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sil, D.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, D.; Saini, V.; Kurmi, B.D.; Pal, R.R.; Srivastava, S. Engineering poloxamer copolymers for in situ gelling systems: Structural, compositional, and functional modifications. Eur. Polym. J. 2025, 239, 114259. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano, E.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Mucosal Applications of Poloxamer 407-Based Hydrogels: An Overview. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shriky, B.; Vigato, A.A.; Sepulveda, A.F.; Machado, I.P.; de Araujo, D.R. Poloxamer-based nanogels as delivery systems: How structural requirements can drive their biological performance? Biophys. Rev. 2023, 15, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, R.; Alexandridis, P.; Lindman, B. Interaction of poloxamer block copolymers with cosolvents and surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 183, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Bahryushina, E.O.; Pomyutkina, M.V.; Popova, A.A.; Khodenok, A.I.; Demina, N.B. Study of poloxamer 188 and polyethylene glycols influence on in situ systems thermoreversible properties. Probl. Biol. Med. Pharm. Chem. 2022, 25, 10–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hirun, N.; Kraisit, P.; Tantishaiyakul, V. Thermosensitive polymer blend composed of poloxamer 407, poloxamer 188 and polycarbophil for the use as mucoadhesive in situ gel. Polymers 2022, 14, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Ren, D.; Zhang, W.; Shu, G.; Fu, H. In-situ gel injection of poloxamer-based metamizole provides long-acting antipyretic effects. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 968–977. [Google Scholar]
- Kojarunchitt, T.; Baldursdottir, S.; Dong, Y.D.; Boyd, B.J.; Rades, T.; Hook, S. Modified thermoresponsive Poloxamer 407 and chitosan sol–gels as potential sustained-release vaccine delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 89, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Hsin, Y.K.; Thangarajoo, T.; Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Meng, L.W.; Gorain, B. Stimuli-responsive in situ spray gel of miconazole nitrate for vaginal candidiasis. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Y.; Wu, C. In situ gelling gelrite/alginate formulations as vehicles for ophthalmic drug delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protopapa, C.; Siamidi, A.; Pavlou, P.; Vlachou, M. Excipients used for modified nasal drug delivery: A mini-review of the recent advances. Materials 2020, 15, 6547. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.N.; Shaikh, M.F.; Bhuvanendran, S.; Date, A.; Ansari, M.T.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Othman, I. Poloxamer 188 (P188), A potential polymeric protective agent for central nervous system disorders: A systematic review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casettari, L.; Illum, L. Chitosan in nasal delivery systems for therapeutic drugs. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, T.A.; Emberlin, J.; Josling, P.; Seifalian, A. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the efficacy and safety of powder hydroxypropylmethylcellulose as nasal mucosal barrier. Med. Devices: Evid. Res. 2020, 13, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, R.M.; Etman, M.A.; Nada, A.H.; Ebian, A.E.A. Sodium alginate-based microspheres of salbutamol sulphate for nasal administration: Formulation and evaluation. Am. J. PharmTech Res. 2012, 2, 289–307. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, R.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Su, J. Mechanical, rheological and release behaviors of a poloxamer 407/poloxamer 188/carbopol 940 thermosensitive composite hydrogel. Molecules 2013, 18, 12415–12425. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, K.A.; Ullah, K.; Shah, A.; Jones, D.S.; Singh, T.R. Poloxamer-based in situ gelling thermoresponsive systems for ocular drug delivery applications. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, G.P.; Rai, V.K.; Pradhan, D.; Halder, J.; Rajwar, T.K.; Mahanty, R.; Rath, G. A doxorubicin loaded chitosan–poloxamer in situ implant for the treatment of breast cancer. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 33952–33967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdeltawab, H.; Svirskis, D.; Sharma, M. Formulation strategies to modulate drug release from poloxamer based in situ gelling systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querobino, S.M.; De Faria, N.C.; Vigato, A.A.; Da Silva, B.G.; Machado, I.P.; Costa, M.S.; Alberto-Silva, C. Sodium alginate in oil-poloxamer organogels for intravaginal drug delivery: Influence on structural parameters, drug release mechanisms, cytotoxicity and in vitro antifungal activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 1350–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathalla, Z.; Mustafa, W.W.; Abdelkader, H.; Moharram, H.; Sabry, A.M.; Alany, R.G. Hybrid thermosensitive-mucoadhesive in situ forming gels for enhanced corneal wound healing effect of L-carnosine. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talasaz, A.H.; Ghahremankhani, A.A.; Moghadam, S.H.; Malekshahi, M.R.; Atyabi, F.; Dinarvand, R. In situ gel forming systems of poloxamer 407 and hydroxypropyl cellulose or hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose mixtures for controlled delivery of vancomycin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 2369–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankova, V.G.; Gribanova, S.V.; Udyanskaya, I.L.; Krasnyuk, I.I.; Lozhkin, Y.A.; Gobyzov, O.A. Investigation of the dynamic characteristics of spray of metered-dose xylometazoline hydrochloride nasal sprayers by a high-speed shadow photography method. Pharmacy 2015, 6, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sundström, E.; Talat, R.; Sedaghat, A.R.; Khosla, S.; Oren, L. Computational modeling of nasal drug delivery using different intranasal corticosteroid sprays for the treatment of eustachian tube dysfunction. J. Eng. Sci. Med. Diagn. Ther. 2022, 5, 031103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleven, M.; Singh, N.P.; Messina, J.C.; Djupesland, P.G.; Inthavong, K. Development of computational fluid dynamics methodology for characterization of exhalation delivery system performance in a nasal airway with Draf-III surgery. J. Aerosol Sci. 2023, 169, 106121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardikasari, S.A.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Orosz, L.; Burián, K.; Csóka, I.; Katona, G. Development of thermoresponsive-gel-matrix-embedded amoxicillin trihydrate-loaded bovine serum albumin nanoparticles for local intranasal therapy. Gels 2022, 8, 750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gratieri, T.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Rocha, E.M.; Sarmento, V.H.; de Freitas, O.; Lopez, R.F.V. A poloxamer/chitosan in situ forming gel with prolonged retention time for ocular delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 75, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, E.; Paolino, D.; Cristiano, M.C.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Rutin-Loaded Poloxamer 407-Based Hydrogels for In Situ Administration: Stability Profiles and Rheological Properties. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, N.; Mignet, N.; Dumortier, G.; Olivier, E.; Seguin, J.; Maury, M.; Boudy, V. Poloxamer bioadhesive hydrogel for buccal drug delivery: Cytotoxicity and trans-epithelial permeability evaluations using TR146 human buccal epithelial cell line. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, M.; Adhikari, A.; Jana, R.; Chattopadhyay, D. Development, evaluation and recent progress of ocular in situ gelling drug delivery vehicle based on poloxamer 407. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 104885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Gull, A.; Aqil, M.; Ansari, M.D.; Sultana, Y. Poloxamer-407 thickened lipid colloidal system of agomelatine for brain targeting: Characterization, brain pharmacokinetic study and behavioral study on Wistar rats. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 181, 426–436. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Meng, M.; Cui, N.; Dai, C.Y.; Jia, Q.; Jiang, H.B. An overview on thermosensitive oral gel based on poloxamer 407. Materials 2021, 14, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojkov, G.; Niyazov, Z.; Picchioni, F.; Bose, R.K. Relationship between structure and rheology of hydrogels for various applications. Gels 2021, 7, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Jin, H.; Cheng, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, Y. The controlled release and anti-inflammatory activity of a tetramethylpyrazine-loaded thermosensitive poloxamer hydrogel. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Dumortier, G.; El Kateb, N.; Sahli, M.; Kedjar, S.; Boulliat, A.; Chaumeil, J.C. Development of a thermogelling ophthalmic formulation of cysteine. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2006, 32, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, S.; Vinayagam, R.; Samivel, R. Thermosensitive Mucoadhesive Intranasal In Situ Gel of Risperidone for Nose-to-Brain Targeting: Physiochemical and Pharmacokinetics Study. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 871. [Google Scholar]
- Vigani, B.; Rossi, S.; Sandri, G.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Caramella, C.M.; Ferrari, F. Recent advances in the development of in situ gelling drug delivery systems for non-parenteral administration routes. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.S.; Ravi, P.R.; Mir, S.I.; Khan, M.S.; Kathuria, H.; Katnapally, P.; Bhatnagar, U. Design, characterization and pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic evaluation of poloxamer and kappa-carrageenan-based dual-responsive in situ gel of nebivolol for treatment of open-angle glaucoma. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.; Hu, J.; Lu, L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, C.; Liu, F.; Wei, Q. Poloxamer 407/188 binary thermosensitive gel as a moxidectin delivery system: In vitro release and in vivo evaluation. Molecules 2022, 27, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshala, R.; Wai, N.Z.; Said, I.D.; Ashraf, K.; Lim, S.M.; Ramasamy, K.; Zeeshan, F. Poloxamer and chitosan-based in situ gels loaded with Orthosiphon stamineus Benth. extracts containing rosmarinic acid for the treatment of ocular infections. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 19, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, H.H.; Pan, X.; Su, W.R.; Liang, D.; Wu, C.B. Doxycycline and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex in poloxamer thermal sensitive hydrogel for ophthalmic delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2011, 1, 254–260. [Google Scholar]
- Almutairy, B.K.; Khafagy, E.S.; Abu Lila, A.S. Development of carvedilol nanoformulation-loaded poloxamer-based ın situ gel for the management of glaucoma. Gels 2023, 9, 952. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niyompanich, J.; Chuysinuan, P.; Pavasant, P.; Supaphol, P. Development of thermoresponsive poloxamer in situ gel loaded with gentamicin sulfate for cavity wounds. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Cook, M.T.; Dreiss, C.A. In situ gels for nasal delivery: Formulation, characterization and applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2025, 310, 2400356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeltawab, H.; Svirskis, D.; Hill, A.G.; Sharma, M. Increasing the Hydrophobic Component of Poloxamers and the Inclusion of Salt Extend the Release of Bupivacaine from Injectable In Situ Gels, While Common Polymer Additives Have Little Effect. Gels 2022, 8, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Ramírez, A.; Machado-Cervantes, C.A.; Ortega-Córdova, R.; Fernández-Escamilla, V.V.A.; Rharbi, Y.; Landázuri-Gómez, G.; Macías-Balleza, E.R.; Soltero-Martínez, J.F.A. Effect of PPO/PEO Ratio on the Phase Behavior of Reverse Pluronics. Polymers 2025, 17, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Djabourov, M.; Bourgaux, C.; Bouchemal, K. Nanostructured fluids from pluronic® mixtures. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laquintana, V.; Lopedota, A.A.; Ivone, M.; Denora, N.; Franco, M.; Palazzo, G.; Gentile, L. Celecoxib-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex in a chitosan/PEO-PPO-PEO block copolymer matrix: Structural effect and drug release. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 660, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qutub, M.; Tatode, A.; Premchandani, T.; Taksande, J.; Mane, D.; Umekar, M. Blending induced variations in Poloxamer’s/Pluronic's® gelation: Thermodynamic and rheological perspectives. JCIS Open 2024, 16, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.B.; Cook, M.T.; Bruschi, M.L. Thermoresponsive systems composed of poloxamer 407 and HPMC or NaCMC: Mechanical, rheological and sol-gel transition analysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhrushina, E.O.; Novozhilova, E.V.; Shumkova, M.M.; Pyzhov, V.S.; Nikonenko, M.S.; Bardakov, A.I.; Krasnyuk, I.I. New biopharmaceutical characteristics of in situ systems based on poloxamer 407. Gels 2023, 9, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Feky, Y.A.; Fares, A.R.; Zayed, G.; El-Telbany, R.F.A.; Ahmed, K.A.; El-Telbany, D.F.A. Repurposing of nifedipine loaded in situ ophthalmic gel as a novel approach for glaucoma treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugleva, V.; Michailova, V.; Mihaylova, R.; Momekov, G.; Zaharieva, M.M.; Najdenski, H.; Petrov, P.; Rangelov, S.; Forys, A.; Trzebicka, B.; et al. Formulation and Evaluation of Hybrid Niosomal In Situ Gel for Intravesical Co-Delivery of Curcumin and Gentamicin Sulfate. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hard, S.A.A.A.; Shivakumar, H.N.; Redhwan, M.A.M. Development and optimization of in-situ gel containing chitosan nanoparticles for possible nose-to-brain delivery of vinpocetine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburic, S.; Craig, D.Q. Rheological evaluation of polyacrylic acid hydrogels. Pharm. Pharmacol. Commun. 1995, 1, 107–109. [Google Scholar]
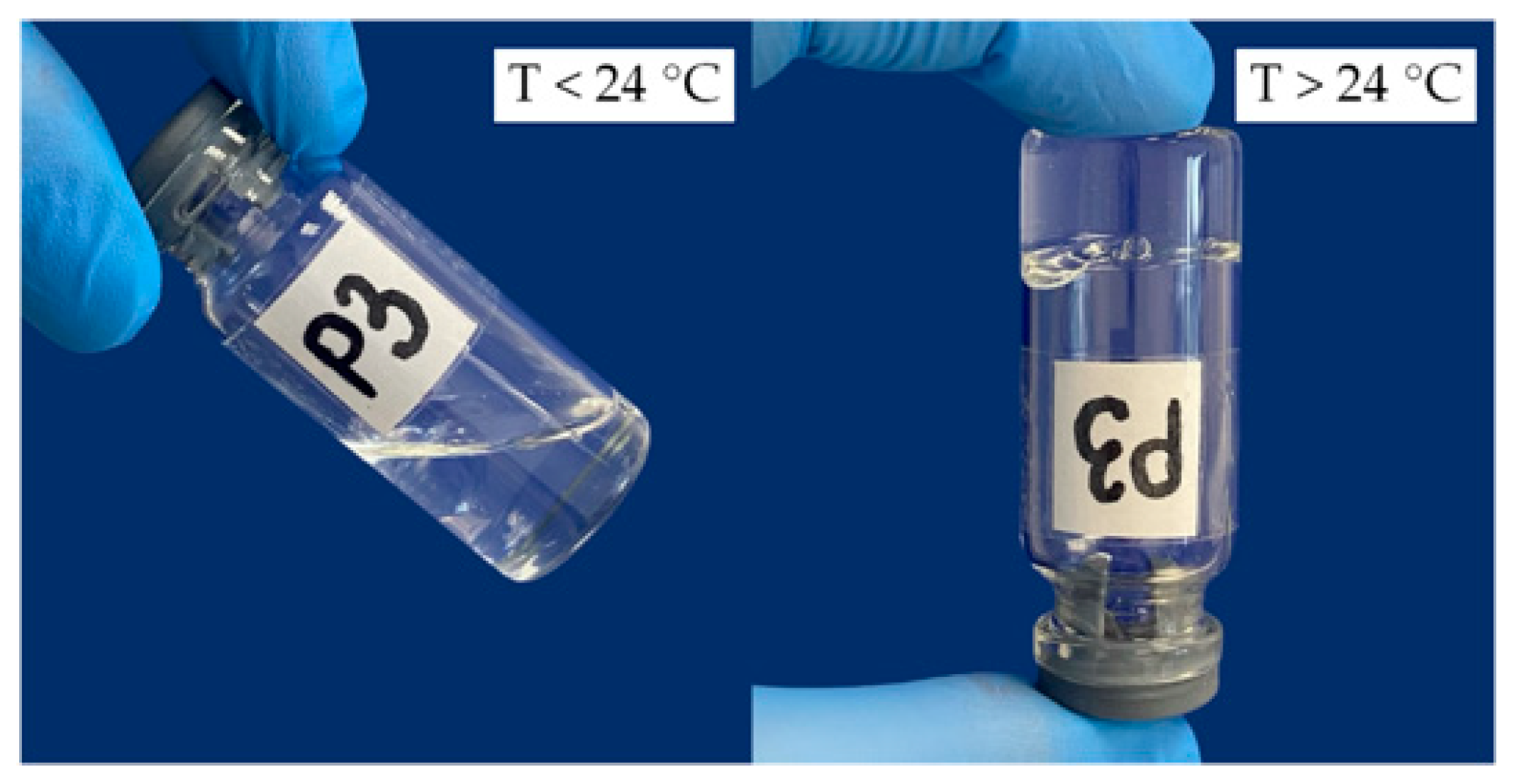
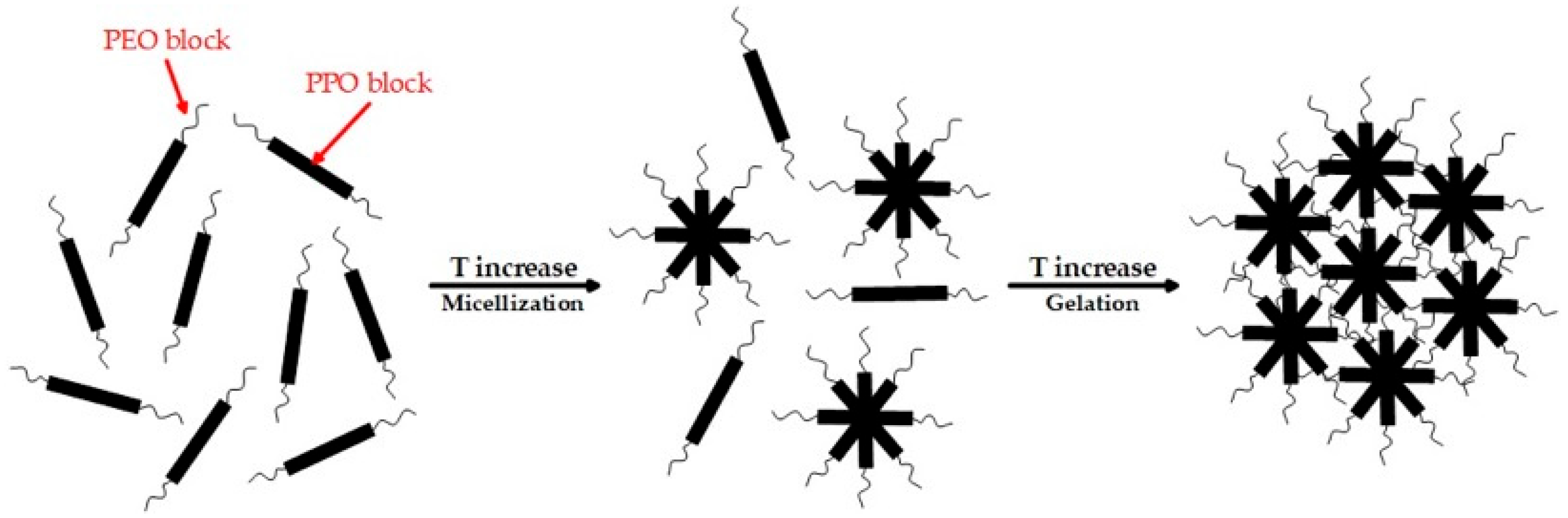
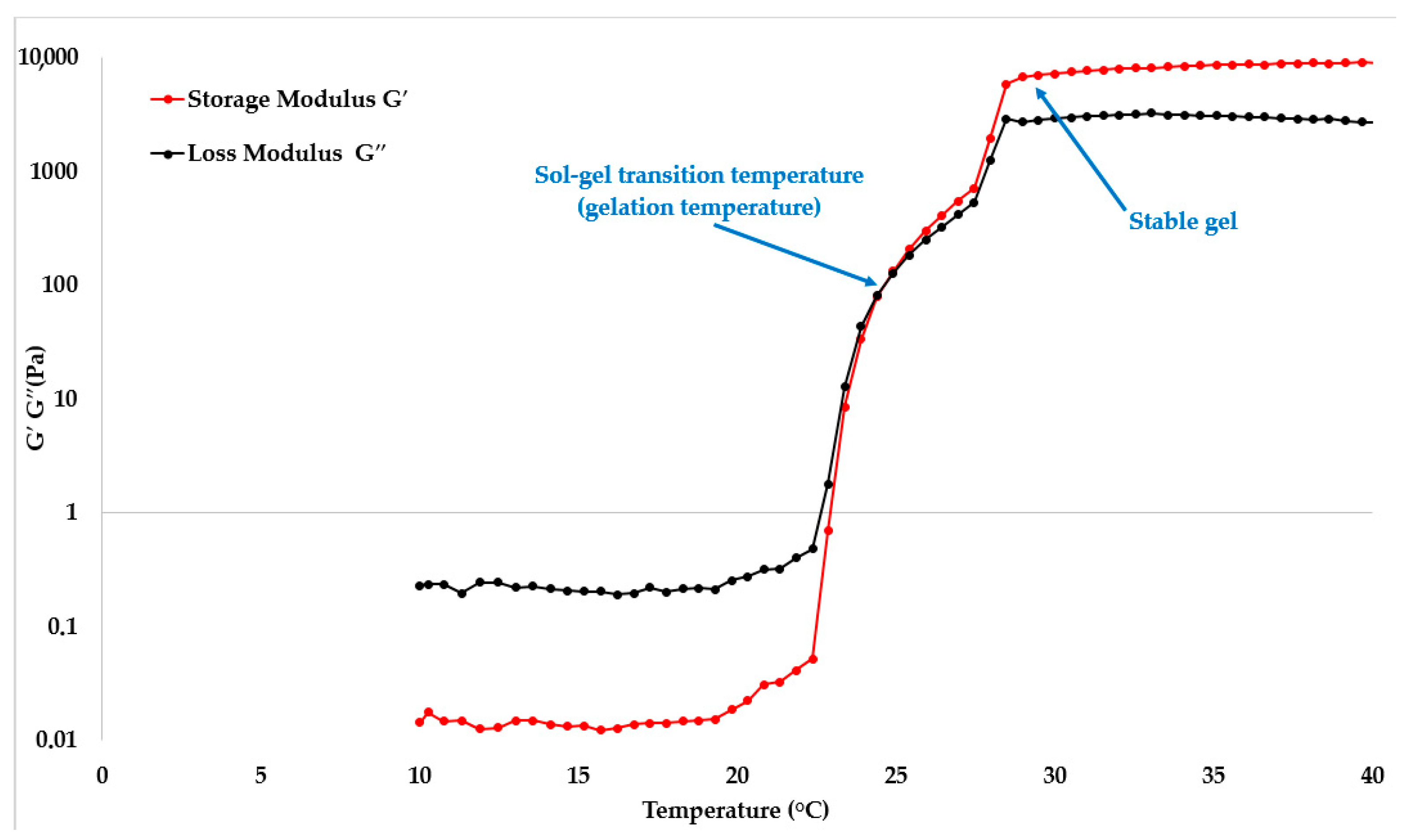

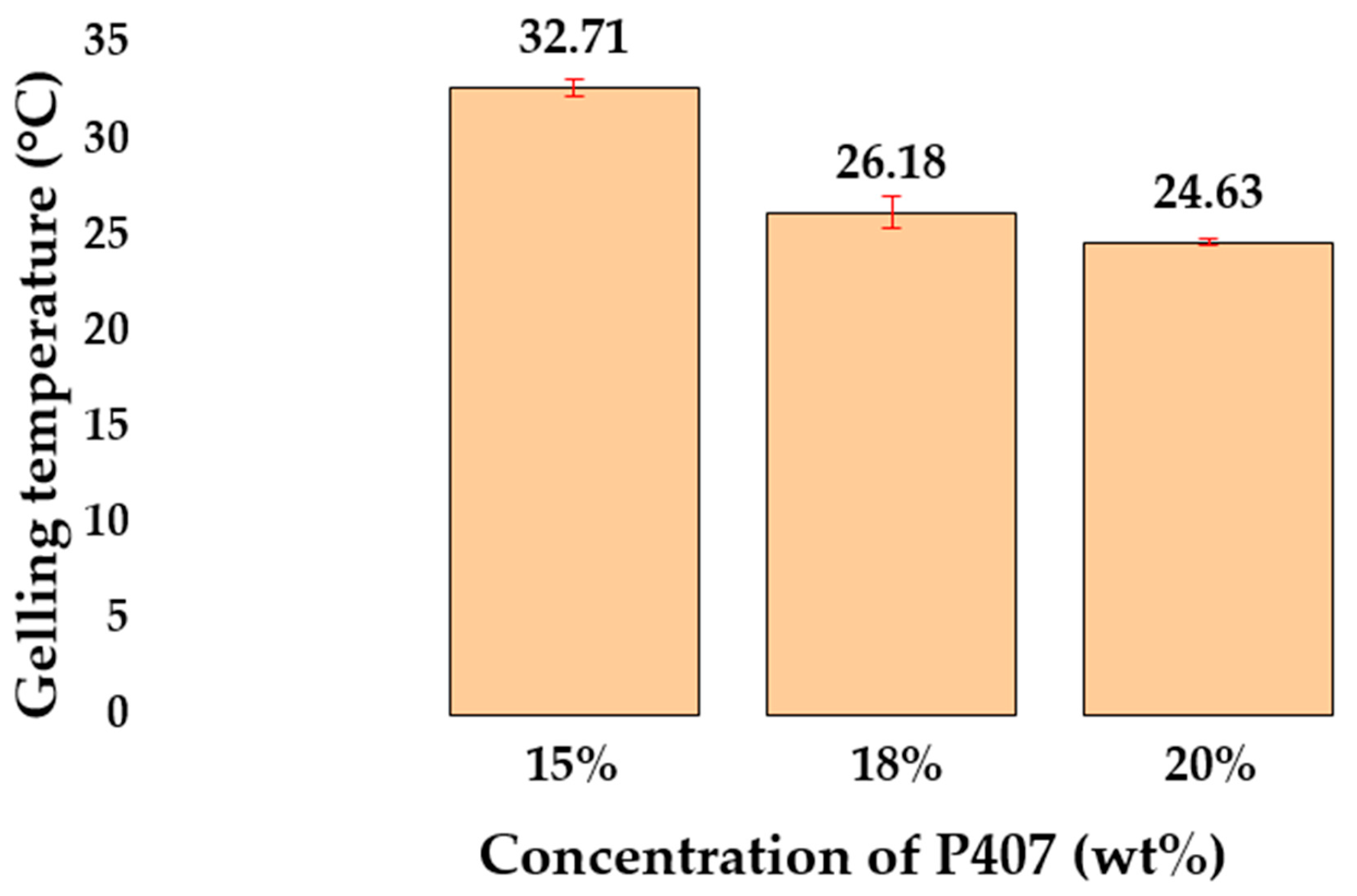
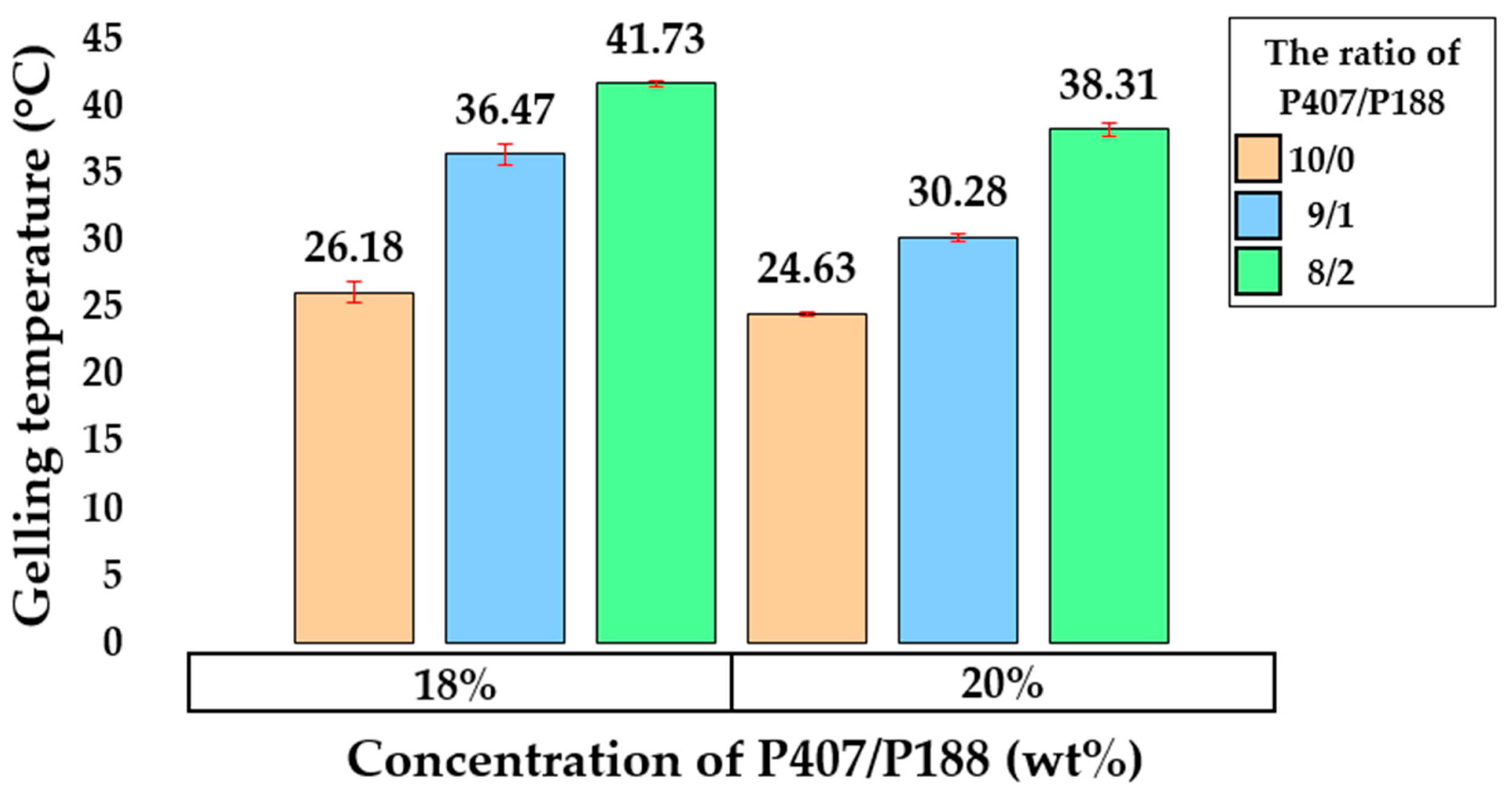
| Sample | P407, wt% | Mean Tsol–Gel Value ± SD (°C, n = 3) | G′ at 35 °C ± SD (Pa, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 15 | 32.71 ± 0.47 | 209.15 ± 23.71 |
| P2 | 18 | 26.18 ± 0.81 | 5501.83 ± 349.47 |
| P3 | 20 | 24.63 ± 0.14 | 8581.36 ± 236.18 |
| Sample | P407 + 188, wt% | P407/P188 Ratio | Mean Tsol–Gel Value ± SD (°C, n = 3) | G′ at 35 °C ± SD (Pa, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP1 | 18 | 9/1 | 36.47 ± 0.73 | 4627.12 ± 203.17 |
| PP2 | 18 | 8/2 | 41.73 ± 0.19 | 3083.94 ± 294.56 |
| PP3 | 20 | 9/1 | 30.28 ± 0.33 | 7294.35 ± 348.81 |
| PP4 | 20 | 8/2 | 38.31 ± 0.48 | 5067.62 ± 294.63 |
| Sample | P407, wt% | Mucoadhesive Polymer, wt% | Mean Tsol–Gel Value ± SD (°C, n = 3) | G′ at 35 °C ± SD (Pa, n = 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | HPMC | Alg-Na | ||||
| PC1 | 18 | 0.2 | - | - | 28.87 ± 0.34 | 407.37 ± 34.81 |
| PC2 | 18 | 0.4 | 27.36 ± 0.48 | 465.22 ± 27.93 | ||
| PC3 | 18 | 0.6 | 25.91 ± 0.69 | 502.51 ± 36.67 | ||
| PC4 | 20 | 0.2 | 26.37 ± 0.43 | 3029.68 ± 321.54 | ||
| PC5 | 20 | 0.4 | 25.85 ± 0.61 | 3187.25 ± 298.37 | ||
| PC6 | 20 | 0.6 | 24.83 ± 0.19 | 3422.92 ± 309.58 | ||
| PH1 | 18 | - | 0.5 | 27.45 ± 0.37 | 5847.13 ± 421.39 | |
| PH2 | 18 | 1 | 26.51 ± 0.53 | 6274.39 ± 481.38 | ||
| PH3 | 18 | 2 | 26.06 ± 0.64 | 6691.57 ± 395.86 | ||
| PH4 | 20 | 0.5 | 25.46 ± 0.38 | 8838.67 ± 513.55 | ||
| PH5 | 20 | 1 | 25.17 ± 0.49 | 8901.29 ± 518.97 | ||
| PH6 | 20 | 2 | 25.39 ± 0.51 | 9084.46 ± 497.83 | ||
| PA1 | 18 | - | 0.2 | 25.43 ± 0.38 | 6326.84 ± 318.57 | |
| PA2 | 18 | 0.4 | 25.45 ± 0.19 | 6681.63 ± 476.24 | ||
| PA3 | 18 | 0.6 | 25.49 ± 0.23 | 7264.91 ± 539.41 | ||
| PA4 | 20 | 0.2 | 24.57 ± 0.18 | 10,125.63 ± 512.85 | ||
| PA5 | 20 | 0.4 | 24.72 ± 0.36 | 10,554.82 ± 618.38 | ||
| PA6 | 20 | 0.6 | 24.40 ± 0.28 | 11,155.37 ± 695.93 | ||
| Sample | Mean Density ± SD (g/cm3, n = 3) | Mean Viscosity at 20 °C ± SD (mPa·s, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1.003 ± 0.004 | 10.44 ± 0.45 |
| P2 | 1.006 ± 0.006 | 18.22 ± 0.46 |
| P3 | 1.007 ± 0.003 | 37.71 ± 1.47 |
| PP1 | 0.994 ± 0.004 | 14.78 ± 0.67 |
| PP2 | 0.997 ± 0.005 | 26.12 ± 0.91 |
| PP3 | 1.000 ± 0.007 | 41.16 ± 1.35 |
| PP4 | 1.003 ± 0.002 | 24.02 ± 0.74 |
| PC1 | 1.001 ± 0.003 | 35.41 ± 2.01 |
| PC2 | 1.000 ± 0.005 | 68.13 ± 6.04 |
| PC3 | 1.006 ± 0.004 | 170.01 ± 10.89 |
| PC4 | 0.999 ± 0.006 | 46.13 ± 3.47 |
| PC5 | 1.000 ± 0.003 | 72.75 ± 6.11 |
| PC6 | 1.004 ± 0.003 | 201.72 ± 18.29 |
| PH1 | 1.006 ± 0.007 | 32.31 ± 2.99 |
| PH2 | 1.009 ± 0.005 | 38.90 ± 2.28 |
| PH3 | 1.011 ± 0.002 | 48.16 ± 3.76 |
| PH4 | 1.010 ± 0.006 | 51.84 ± 5.29 |
| PH5 | 1.011 ± 0.003 | 60.83 ± 5.93 |
| PH6 | 1.014 ± 0.005 | 71.34 ± 6.19 |
| PA1 | 1.003 ± 0.004 | 99.45 ± 7.57 |
| PA2 | 1.004 ± 0.005 | 206.03 ± 20.52 |
| PA3 | 1.007 ± 0.007 | 457.14 ± 51.19 |
| PA4 | 1.010 ± 0.002 | 167.61 ± 18.05 |
| PA5 | 1.013 ± 0.006 | 310.40 ± 48.47 |
| PA6 | 1.017 ± 0.003 | 573.45 ± 60.12 |
| Sample | Mean Viscosity at 20 °C ± SD (mPa·s, n = 3) | Mean Spray Angle ± SD (°, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|
| P2 | 18.22 ± 0.46 | 19.30 ± 2.86 |
| PP3 | 41.16 ± 1.35 | 14.93 ± 1.62 |
| PC1 | 35.41 ± 2.01 | 15.03 ± 2.10 |
| PC2 | 68.13 ± 6.04 | 12.6 ± 3.27 |
| PC4 | 46.13 ± 3.47 | 13.80 ± 1.23 |
| PH1 | 32.31 ± 2.99 | 16.43 ± 2.48 |
| PH2 | 38.90 ± 2.28 | 14.63 ± 4.19 |
| Sample | Spray Angle, ° | δ, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment | Model | ||
| P2 | 19.30 | 20 | 3.63 |
| PP3 | 14.93 | 15 | 0.47 |
| PC1 | 15.03 | 16 | 6.45 |
| PC2 | 12.6 | 12 | 4.76 |
| PC4 | 13.80 | 14 | 1.45 |
| PH1 | 16.43 | 17 | 3.47 |
| PH2 | 14.63 | 16 | 9.36 |
| Sample | P407, wt% | P188, wt% | Chitosan, wt% | HPMC, wt% | Alg-Na, wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 15 | - | - | - | - |
| P2 | 18 | ||||
| P3 | 20 | ||||
| PP1 | 18 (9/1) | - | - | - | |
| PP2 | 18 (8/2) | ||||
| PP3 | 20 (9/1) | ||||
| PP4 | 20 (8/2) | ||||
| PC1 | 18 | - | 0.2 | – | – |
| PC2 | 18 | 0.4 | |||
| PC3 | 18 | 0.6 | |||
| PC4 | 20 | - | 0.2 | - | - |
| PC5 | 20 | 0.4 | |||
| PC6 | 20 | 0.6 | |||
| PH1 | 18 | - | - | 0.5 | - |
| PH2 | 18 | 1 | |||
| PH3 | 18 | 2 | |||
| PH4 | 20 | - | - | 0.5 | - |
| PH5 | 20 | 1 | |||
| PH6 | 20 | 2 | |||
| PA1 | 18 | - | - | - | 0.2 |
| PA2 | 18 | 0.4 | |||
| PA3 | 18 | 0.6 | |||
| PA4 | 20 | - | - | - | 0.2 |
| PA5 | 20 | 0.4 | |||
| PA6 | 20 | 0.6 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menshutina, N.; Derkach, V.; Mokhova, E.; Gordienko, M. Investigation of Rheological Characteristics of Thermosensitive Nasal In Situ Gels Based on P407 and Their Effect on Spray Pattern. Gels 2025, 11, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100841
Menshutina N, Derkach V, Mokhova E, Gordienko M. Investigation of Rheological Characteristics of Thermosensitive Nasal In Situ Gels Based on P407 and Their Effect on Spray Pattern. Gels. 2025; 11(10):841. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100841
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenshutina, Natalia, Vladislav Derkach, Elizaveta Mokhova, and Mariia Gordienko. 2025. "Investigation of Rheological Characteristics of Thermosensitive Nasal In Situ Gels Based on P407 and Their Effect on Spray Pattern" Gels 11, no. 10: 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100841
APA StyleMenshutina, N., Derkach, V., Mokhova, E., & Gordienko, M. (2025). Investigation of Rheological Characteristics of Thermosensitive Nasal In Situ Gels Based on P407 and Their Effect on Spray Pattern. Gels, 11(10), 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100841







