Cellulose-Derived Gels for Topical Delivery: HPMC as a Functional Matrix for Porphyrinic Photosensitizers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization of the Gels
2.1.1. FTIR Spectroscopy
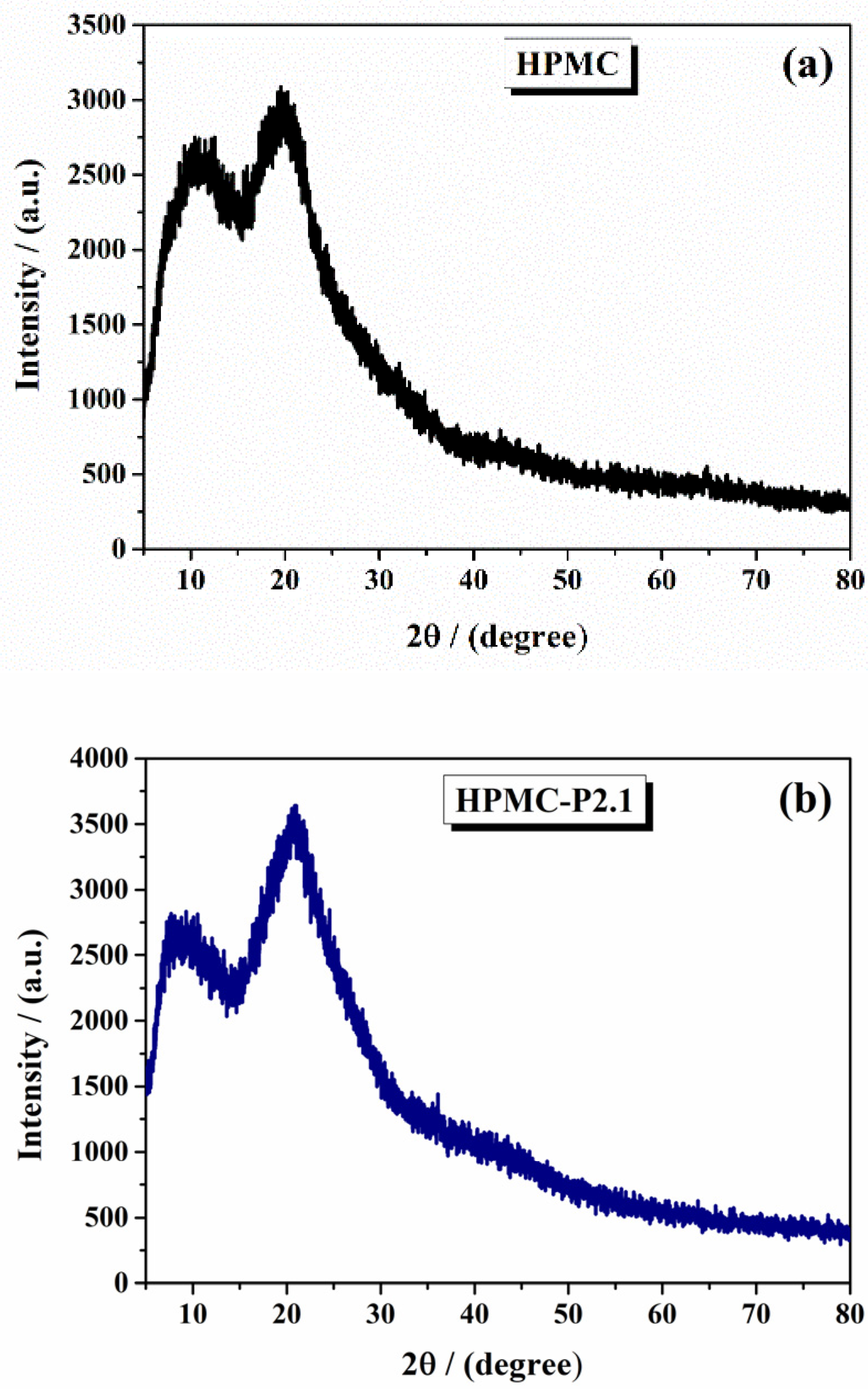
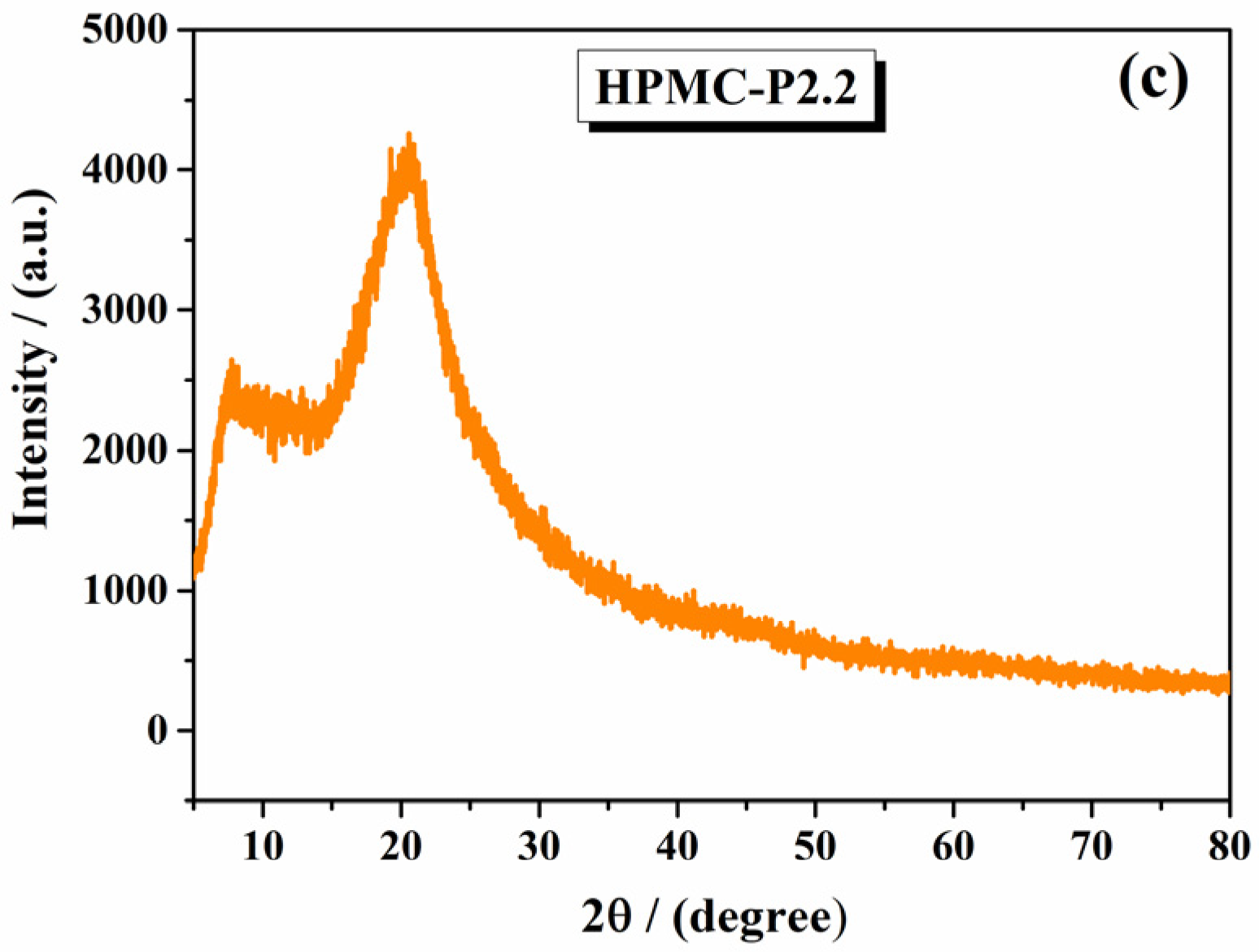
2.1.2. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
2.1.3. Thermal Analysis
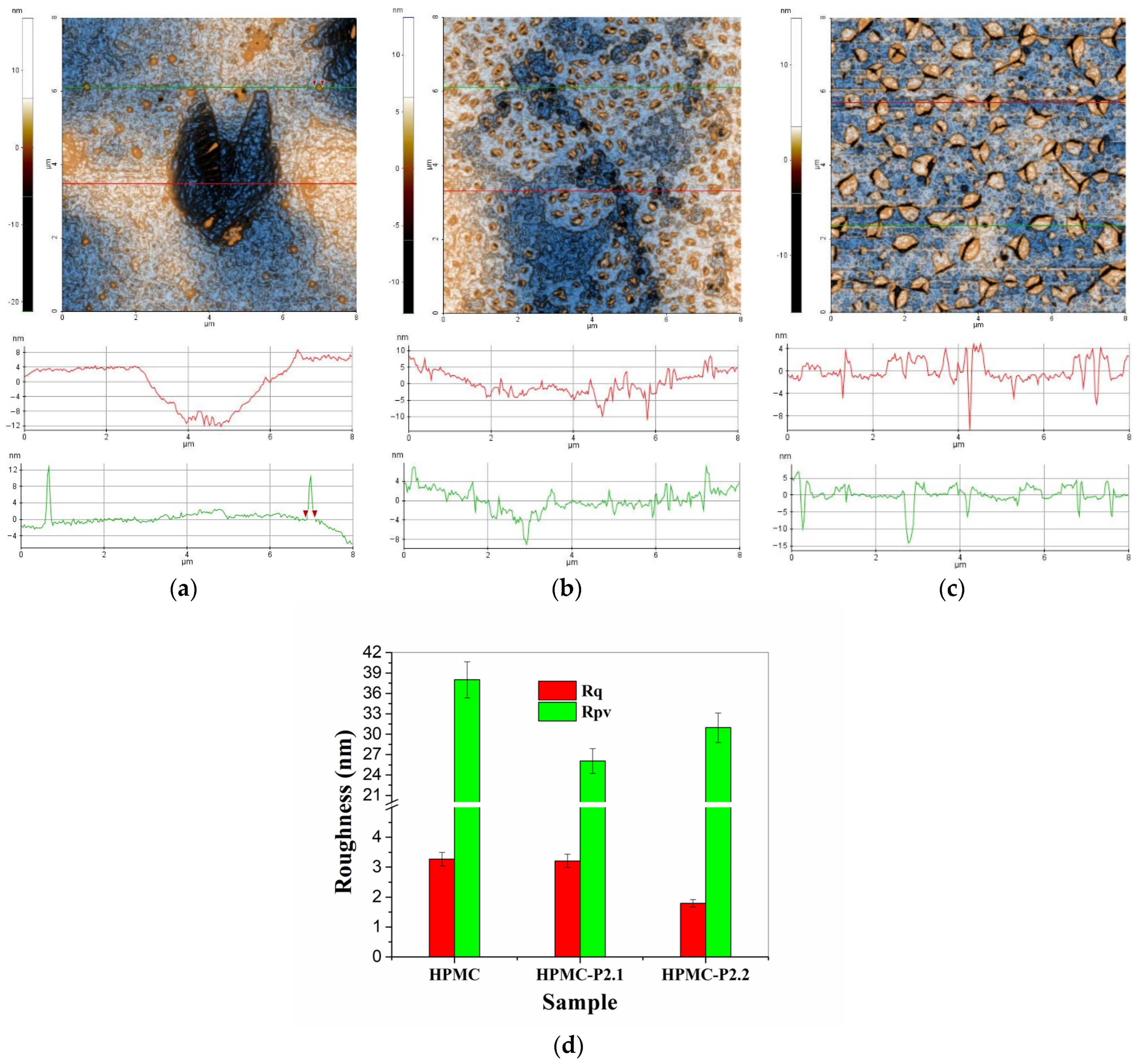
2.1.4. AFM Results
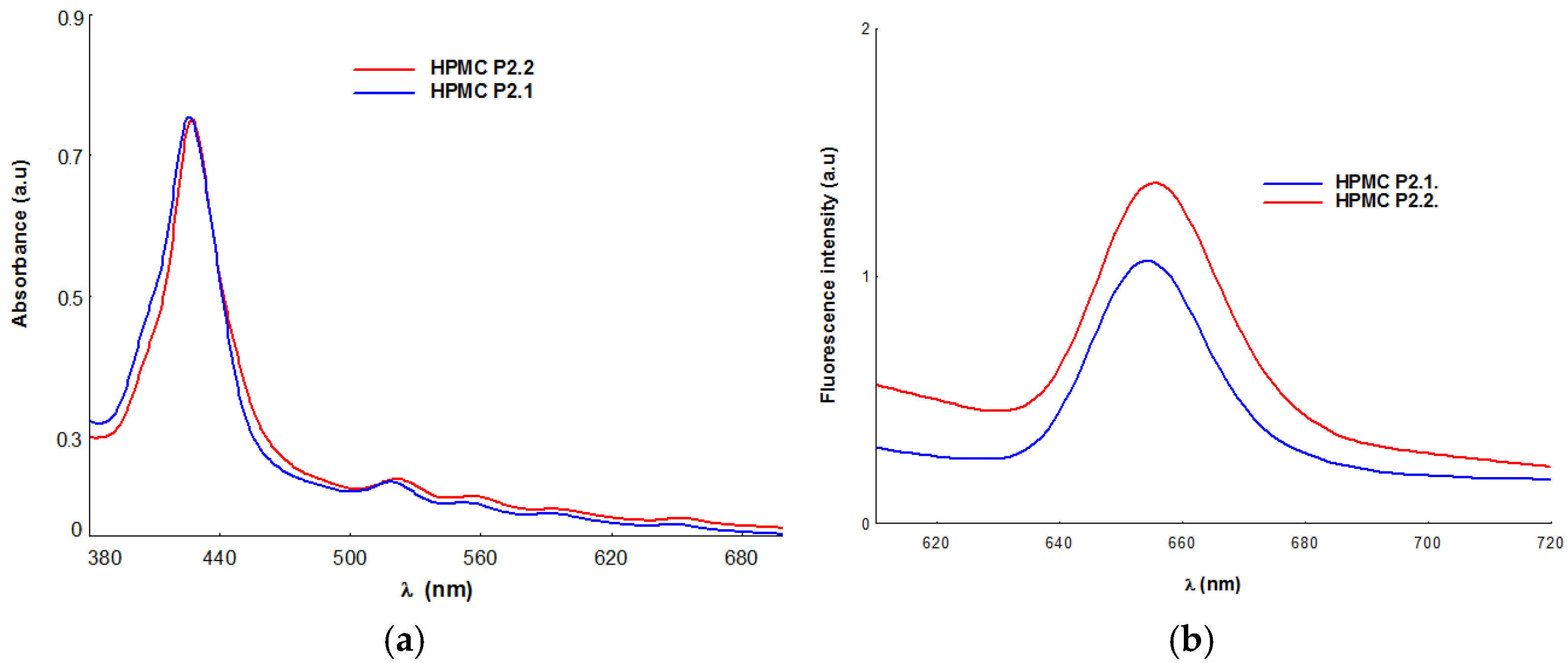
2.1.5. UV-Vis and Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.2. Pharmacotechnical Evaluation of the Porphyrin Gels
2.2.1. Wet Gel Evaluation
pH Determination
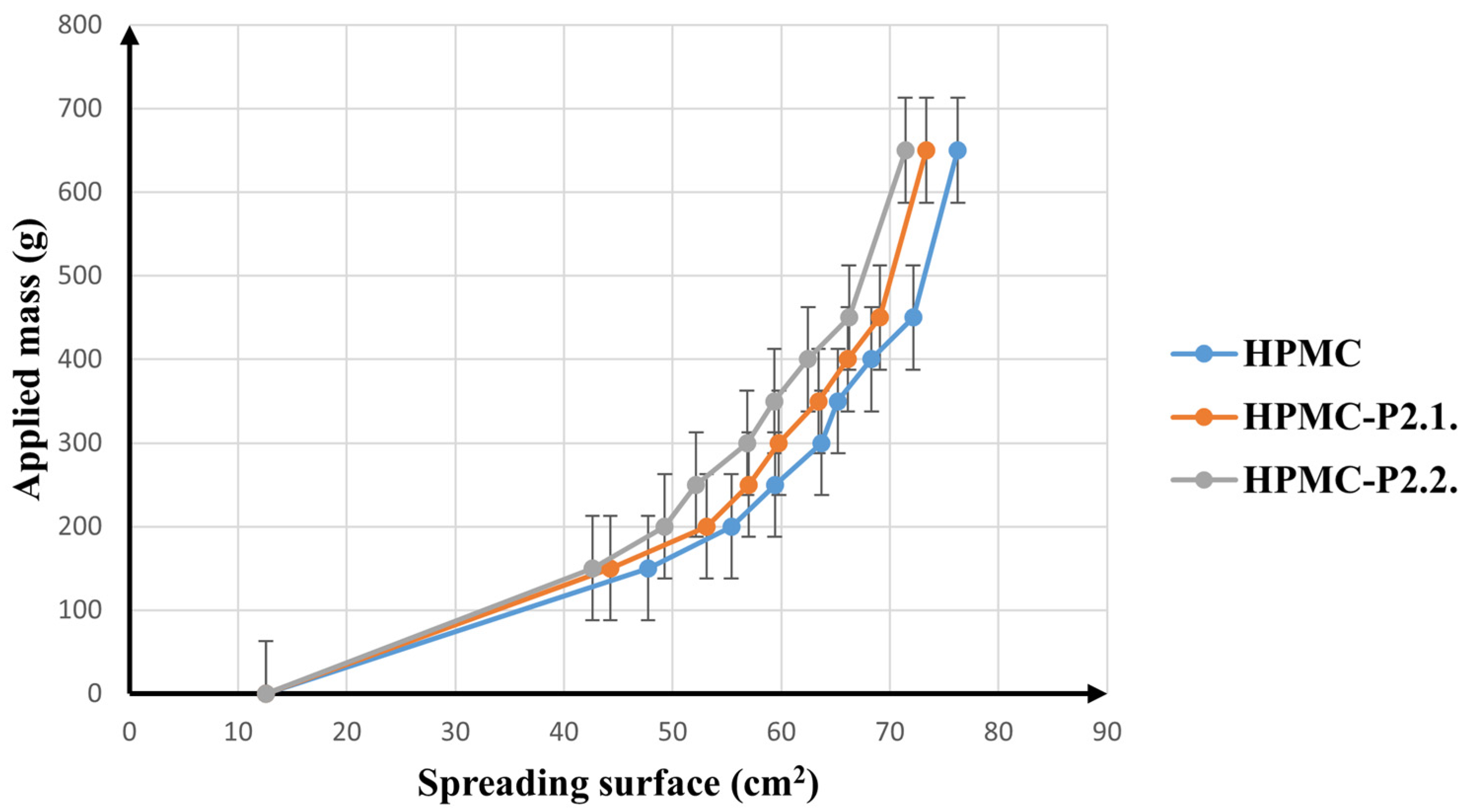
Spreadability
In Vitro Adhesion Ability
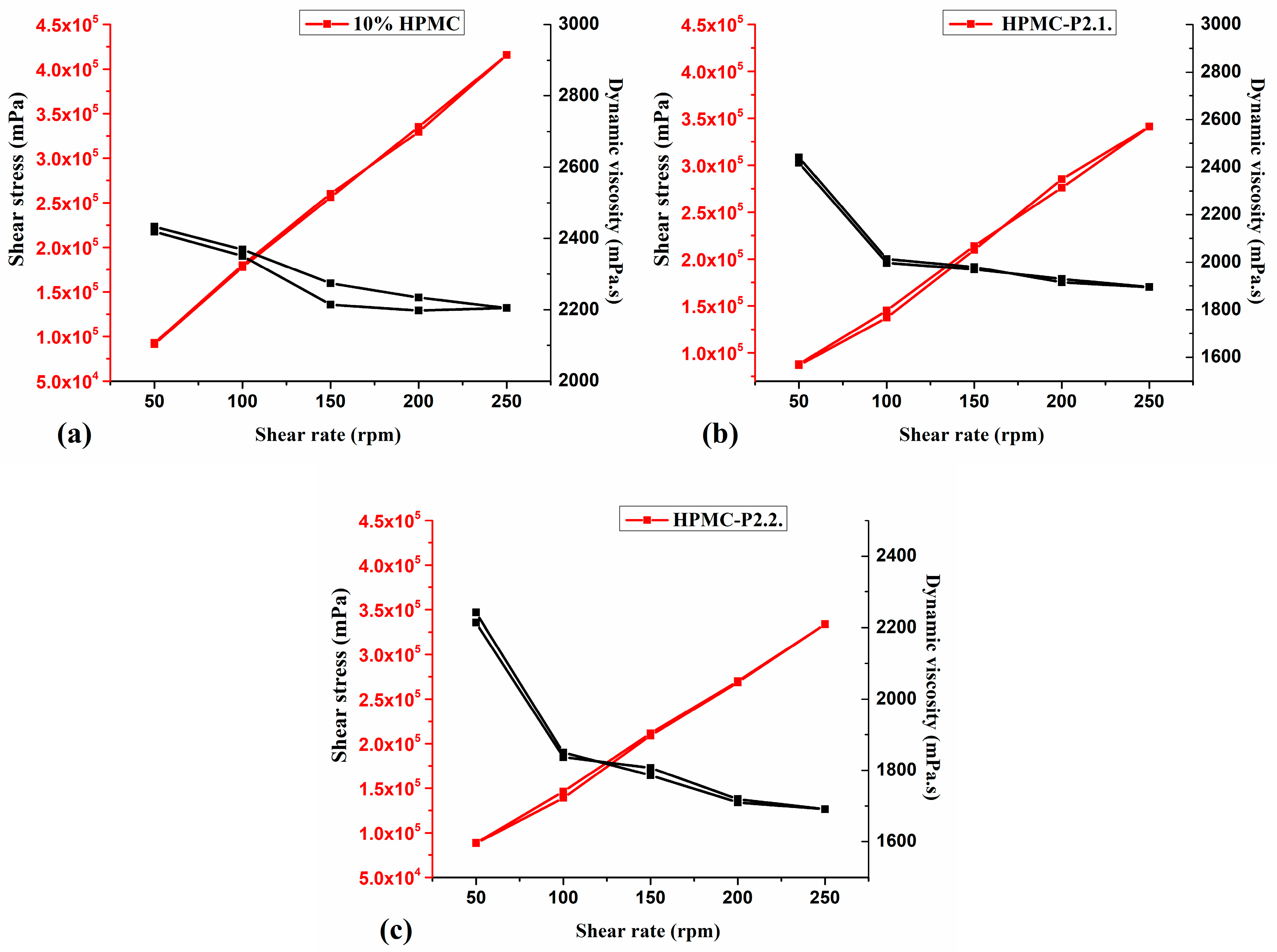
Rheology Measurements
2.2.2. Dry Gel Evaluation
2.3. In Vitro Studies
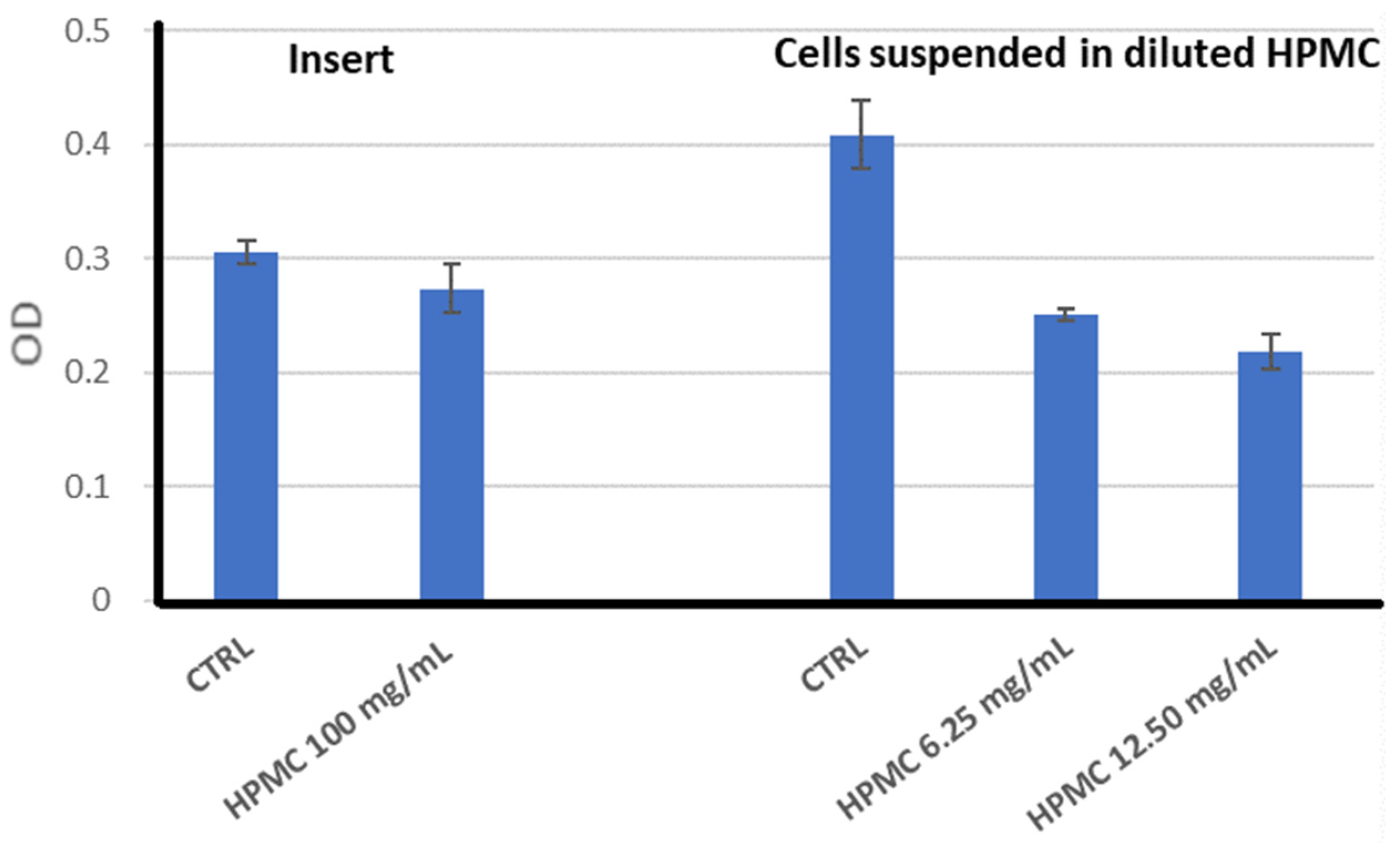
2.3.1. Biocompatibility of the HPMC Gel
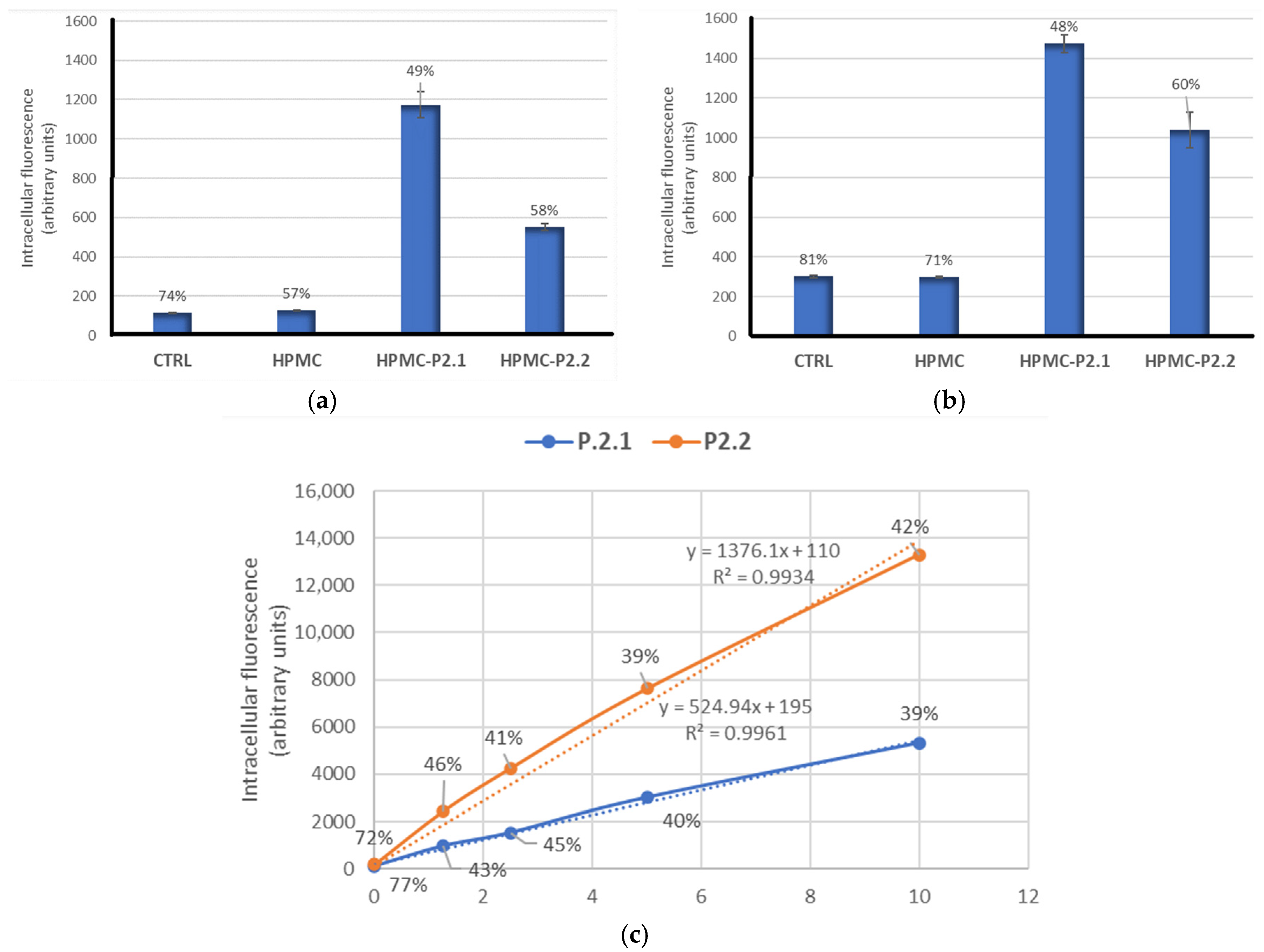
2.3.2. PS Uptake by Cells Formulated in HPMC Gels
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Hydrogel Formulation and Manufacturing
4.2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of the Gels
4.2.3. UV-Vis and Fluorescence Studies
4.2.4. Pharmacotechnical Characterization of the Porphyrin Gels
pH Determination
Spreadability
4.2.5. In Vitro Adhesion Ability
4.2.6. Rheology Measurements
4.2.7. Dry Gel Evaluation
4.2.8. Mechanical Properties
Thickness
Tensile Strength and Elongation
Moisture Content
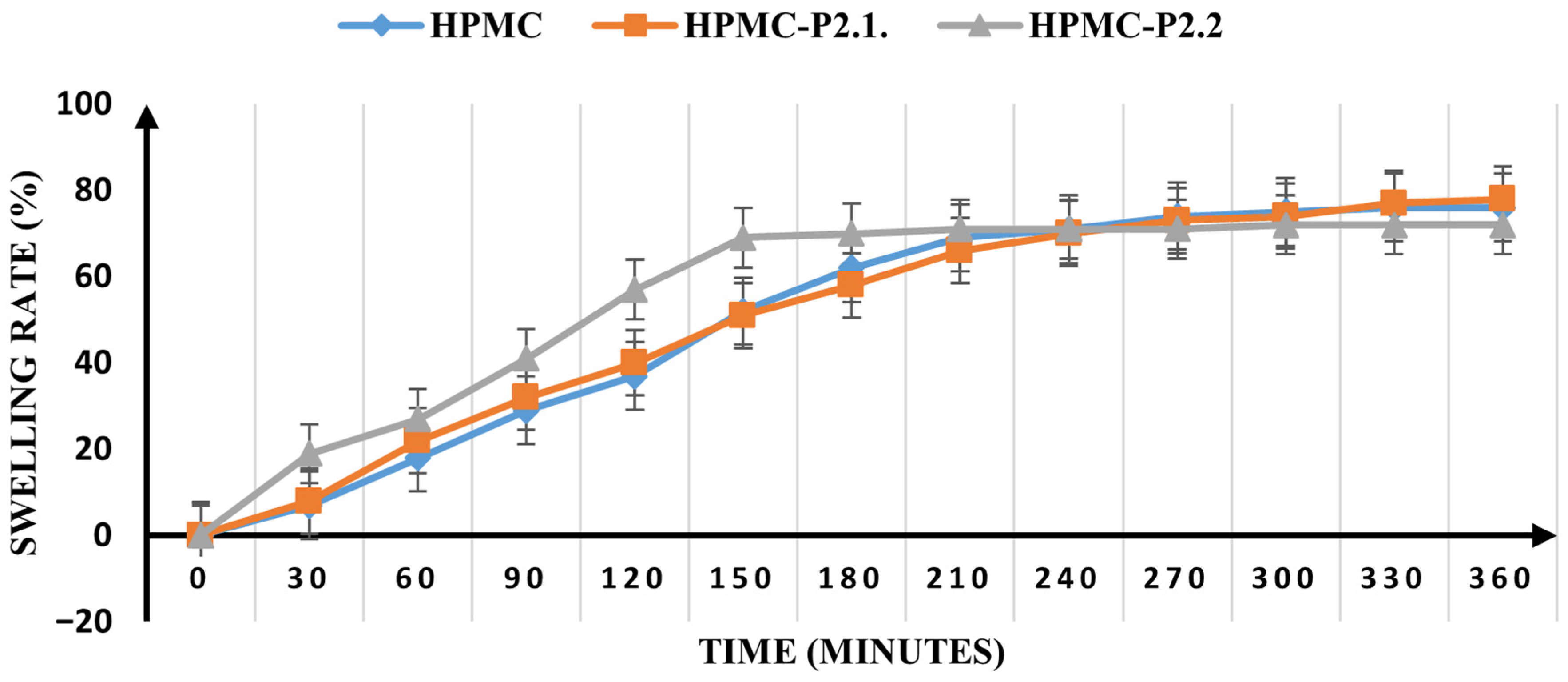
Swelling Ratio
4.2.9. In Vitro Study
4.2.10. Gels and Porphyrin Compounds
4.2.11. Cells
4.2.12. Biocompatibility of HPMC Gel
4.2.13. The MTS Reduction Test
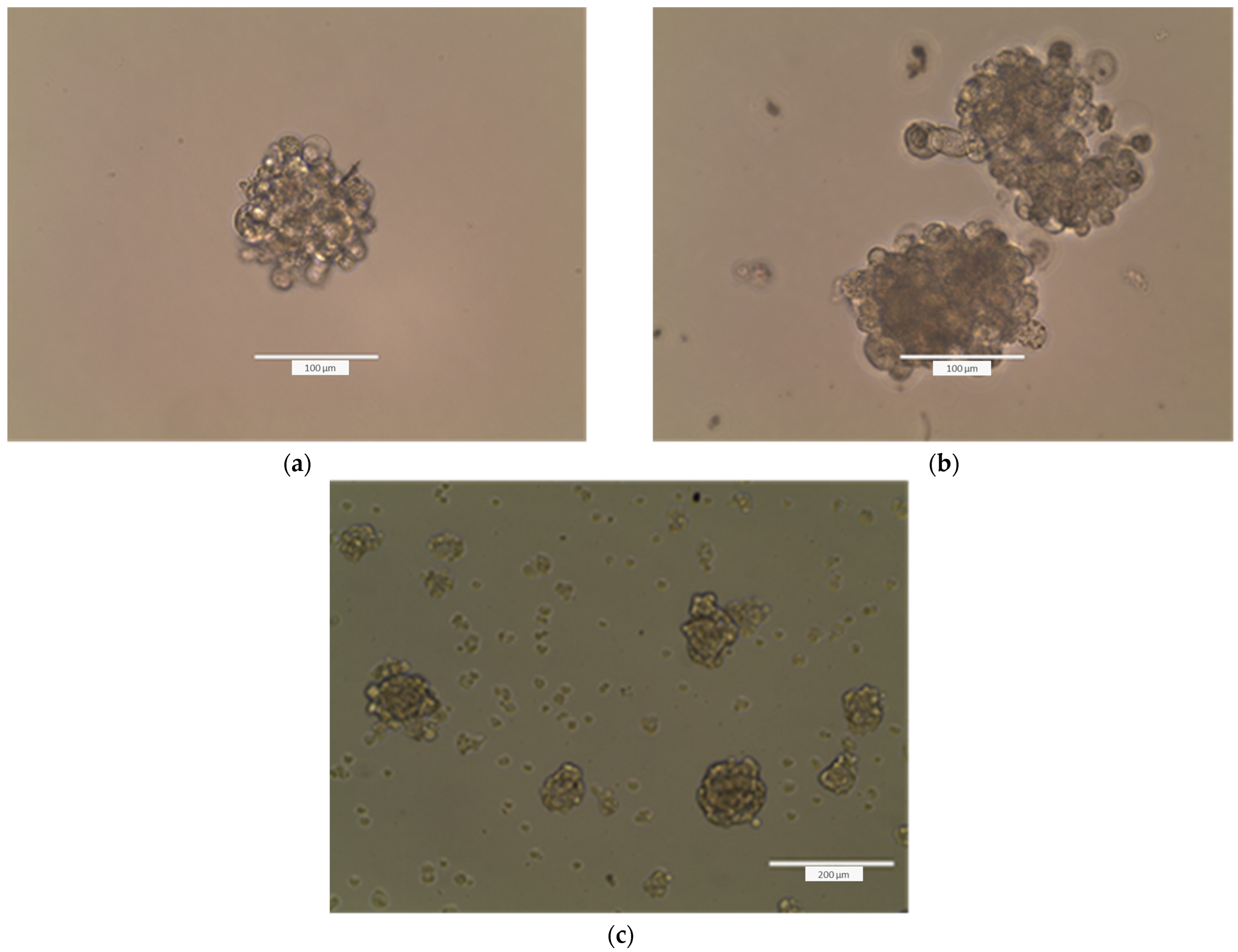
4.2.14. Formation of Tumorspheres
4.2.15. P2.1 and P2.2 Uptakes
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online: https://www.iarc.who.int/cancer-type/skin-cancer/ (accessed on 29 August 2025).
- Farberg, A.S.; Marson, J.W.; Soleymani, T. Advances in Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment of Actinic Keratosis and Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer: A Narrative Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 689–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manda, G.; Hinescu, M.E.; Neagoe, I.V.; Ferreira, L.F.V.; Boscencu, R.; Vasos, P.; Basaga, S.H.; Cuadrado, A. Emerging Therapeutic Targets in Oncologic Photodynamic Therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 24, 5268–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscencu, R.; Radulea, N.; Manda, G.; Machado, I.F.; Socoteanu, R.P.; Lupuliasa, D.; Burloiu, A.M.; Mihai, D.P.; Ferreira, L.F.V. Porphyrin Macrocycles: General Properties and Theranostic Potential. Molecules 2023, 28, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, M.C.S.; Moura, N.M.M.; Gomes, A.T.P.C.; Joaquinito, A.S.M.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Almeida, A.; Gonçalves, I.; Serra, V.V.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S. The Role of Porphyrinoid Photosensitizers for Skin Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Annunzio, S.R.; Costa, N.C.S.; Mezzina, R.D.; Graminha, M.A.S.; Fontana, C.R. Chlorin, Phthalocyanine, and Porphyrin Types Derivatives in Phototreatment of Cutaneous Manifestations: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Cui, H.; Xia, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhang, W. Illuminating Hope for Tumors: The Progress of Light-Activated Nanomaterials in Skin Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 5081–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, C.; Longo, J.P.F.; Azevedo, R.B.; Zhang, H.; Muehlmann, L.A. An updated overview on the development of new photosensitizers for anticancer photodynamic therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, R.W.; Dolphin, D. Structure and biodistribution relationships of photodynamic sensitizers. Photochem. Photobiol. 1996, 64, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscencu, R.; Manda, G.; Radulea, N.; Socoteanu, R.P.; Ceafalan, L.C.; Neagoe, I.V.; Ferreira Machado, I.; Basaga, S.H.; Vieira Ferreira, L.F. Studies on the synthesis, photophysical and biological evaluation of some unsymmetrical meso-tetrasubstituted phenyl porphyrins. Molecules 2017, 22, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscencu, R.; Oliveira, A.S.; Ferreira, D.P.; Ferreira, L.F.V. Synthesis and spectral evaluation of some unsymmetrical mesoporphyrinic complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8112–8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscencu, R.; Socoteanu, R.; Ilie, M.; Oliveira, A.S.; Constantin, C.; Vieira Ferreira, L.F. Synthesis, spectral and biological evaluation of some mesoporphyrinic complexes of Zn(II). Rev. Chim. 2009, 60, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Boscencu, R.; Socoteanu, R.; Oliveira, A.S.; Vieira Ferreira, L.F.; Nacea, V.; Patrinoiu, G. Synthesis and characterization of some unsymmetrically-substituted mesoporphyrinic mono-hydroxyphenyl complexes of Copper(II). Pol. J. Chem. 2008, 82, 509–522. [Google Scholar]
- Boscencu, R.; Socoteanu, R.; Oliveira, A.S.; Vieira Ferreira, L.F. Studies on Zn(II) monohydroxyphenylmesoporphyrinic complexes. Synthesis and characterization. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2008, 73, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capanema, N.S.V.; Mansur, A.A.P.; Carvalho, S.M.; Carvalho, I.C.; Chagas, P.; de Oliveira, L.C.A.; Mansur, H.S. Bioengineered carboxymethyl cellulose-doxorubicin prodrug hydrogels for topical chemotherapy of melanoma skin cancer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, W.; Cui, M.; Qi, W.; Huang, R.; Su, R. Nanocellulose-based hydrogels for drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 7004–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Pérez, S.; Andrés-Guerrero, V.; López-Cano, J.J.; Molina-Martínez, I.; Herrero-Vanrell, R.; Bravo-Osuna, I. Gelatin Nanoparticles-HPMC Hybrid System for Effective Ocular Topical Administration of Antihypertensive Agents. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Han, D.; Ding, Z.; Zeng, S.; Xiao, X. Construction and evaluation of the hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose-sodium alginate composite hydrogel system for sustained drug release. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Sun, H.; Dai, J.; Hao, J.; Zhou, B. Chitosan-based hydrogels in cancer therapy: Drug and gene delivery, stimuli-responsive carriers, phototherapy and immunotherapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanzholkyzy, A.; Zhumagaliyeva, S.; Sultanova, N.; Abilov, Z.; Ongalbek, D.; Donbayeva, E.; Niyazbekova, A.; Mukazhanova, Z. Hydrogel Delivery Systems for Biological Active Substances: Properties and the Role of HPMC as a Carrier. Molecules 2025, 30, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Gu, H.; Lu, S.; Meng, F.; Ma, Q.; Xing, X.; Pan, S.; Che, Y. Bioinspired multifunctional conductive hydrogel based on hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose for flexible sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 368, 124192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, B.F.O.; Pereira, N.A.M.; Valente, A.J.M.; Pinho e Melo, T.M.V.D.; Pineiro, M. A Review on (Hydro)Porphyrin-Loaded Polymer Micelles: Interesting and Valuable Platforms for Enhanced Cancer Nanotheranostics. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Peng, J.; Liu, R.; Gao, J.; Hua, G.; Fan, X.; Wang, S. Porphyrin-Based Supramolecular Self-Assemblies: Construction, Charge Separation and Transfer, Stability, and Application in Photocatalysis. Molecules 2024, 29, 6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaramani, S.; Shinger, M.I.; Ma, X.; Yao, M.; Zhang, S.; Qin, D.; Lu, X. Porphyrin aggregates decorated MWCNT film for solar light harvesting: Influence of J- and H-aggregation on the charge recombination resistance, photocatalysis, and photoinduced charge transfer kinetics. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 18232–18242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozon, E.A.; Anastasescu, M.; Musuc, A.M.; Burloiu, A.M.; Socoteanu, R.P.; Atkinson, I.; Mitran, R.-A.; Culita, D.C.; Lupuliasa, D.; Mihai, D.P.; et al. Formulation and Characterization of Carbopol-Based Porphyrin Gels for Targeted Dermato-Oncological Therapy: Physicochemical and Pharmacotechnical Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burloiu, A.M.; Ozon, E.A.; Musuc, A.M.; Anastasescu, M.; Socoteanu, R.P.; Atkinson, I.; Culita, D.C.; Anuta, V.; Popescu, I.A.; Lupuliasa, D.; et al. Porphyrin Photosensitizers into Polysaccharide-Based Biopolymer Hydrogels for Topical Photodynamic Therapy: Physicochemical and Pharmacotechnical Assessments. Gels 2024, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burloiu, A.M.; Manda, G.; Lupuliasa, D.; Socoteanu, R.P.; Mihai, D.P.; Neagoe, I.V.; Anghelache, L.-I.; Surcel, M.; Anastasescu, M.; Olariu, L.; et al. Assessment of Some Unsymmetrical Porphyrins as Promising Molecules for Photodynamic Therapy of Cutaneous Disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinosho, H.; Hawkins, S.; Wicker, L. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose substituent analysis and rheological properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupanc, A.; Petkovšek, M.; Zdovc, B.; Žagar, E.; Zupanc, M. Degradation of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) by acoustic and hydrodynamic cavitation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 109, 107020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Mallepogu, P.; Kaur, H.; Singh, R.; Sodhi, I.; Samal, S.K.; Jena, K.C.; Sangamwar, A.T. Explicating the molecular level drug-polymer interactions at the interface of supersaturated solution of the model drug: Albendazole. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 167, 106014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbeiter, D.; Reske, T.; Teske, M.; Bajer, D.; Senz, V.; Schmitz, K.-P.; Grabow, N.; Oschatz, S. Influence of Drug Incorporation on the Physico-Chemical Properties of Poly(l-Lactide) Implant Coating Matrices—A Systematic Study. Polymers 2021, 13, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Ramsey, J.D.; Kabanov, A.V. Polymeric micelles for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs: From nanoformulation to clinical approval. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 156, 80–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkal, M.; Arafat, M.; Yuvaraju, P.; Beiram, R.; AbuRuz, S. Preparation and Characterization of Theophylline Controlled Release Matrix System Incorporating Poloxamer 407, Stearyl Alcohol, and Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose: A Novel Formulation and Development Study. Polymers 2024, 16, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, F.; Sher, M.; Hussain, M.A.; Saadia, M.; Naeem-Ul-Hassan, M.; Rehman, M.F.U.; Haseeb, M.T.; Bukhari, S.N.A.; Abbas, A.; Peng, B.; et al. Pharmaceutical and Pharmacological Evaluation of Amoxicillin after Solubility Enhancement Using the Spray Drying Technique. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 48506–48519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.K.; Zheng, G. Porphyrins as photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy. In The Porphyrin Handbook; Kadish, K.M., Guilard, R., Smith, K.M., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 6, pp. 157–230. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, M.C.; Novikova, I.N. Porphyrins: Electronic structure and ultraviolet/visible absorption spectroscopy. In Fundamentals of Porphyrin Chemistry: A 21st Century Approach; Brothers, P.J., Senge, O.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 505–586. [Google Scholar]
- Gouterman, M. Optical Spectra and Electronic Structure of Porphyrins and Related Rings. In The Porphyrins; Dolphin, D., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; Volume 3, pp. 11–87. [Google Scholar]
- Gouterman, M.; Wagniere, G.H.; Snyder, L.C. Spectra of porphyrins: Part II. Four orbital model. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 1963, 11, 108–127. [Google Scholar]
- Narda, M.; Trullas, C.; Brown, A.; Piquero-Casals, J.; Granger, C.; Fabbrocini, G. Glycolic acid adjusted to pH 4 stimulates collagen production and epidermal renewal without affecting levels of proinflammatory TNF-alpha in human skin explants. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punitha, S.; Uvarani, R.; Panneerselvam, A. Effect of pH in aqueous (Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose) polymer solution. Results Mater. 2020, 7, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, D.; Rakkappan, C. Ultrasonic studies on drug release pattern from different ethylcellulose bases. J. Mol. Liq. 2005, 121, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Meng, L.; Shao, C.; Cui, C.; Yang, J. Physically cross-linked silk hydrogels with high solid content and excellent mechanical properties via a reverse dialysis concentrated procedure. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13324–13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Ren, S.; Li, X.; Guo, J.; Dong, G.; Li, J.; Gao, L. Poly(ethylene glycol)/chitosan/sodium glycerophosphate gel replaced the joint capsule with slow-release lubricant after joint surgery. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 1331–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giang, H.N.; Le, A.T.K.; Huynh, T.N.A.; Phung, T.K.; Sakai, W. Effect of additives on fabrication and properties of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-based hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 2022, 80, 11121–11137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanum, H.; Ullah, K.; Murtaza, G.; Khan, S.A. Fabrication and in vitro characterization of HPMC-g-poly(AMPS) hydrogels loaded with loxoprofen sodium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, F.; Bertoni, M.; Caramella, C.; La Manna, A. Description and validation of an apparatus for gel strength measurements. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 109, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Svirskis, D.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wu, Z. Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Bioadhesive Hydrogels for Topical Application and Sustained Drug Release: The Effect of Polyvinylpyrrolidone on the Physicomechanical Properties of Hydrogel. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.C. Sol-Gel Behavior of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) in Ionic Media Including Drug Release. Materials 2011, 4, 1861–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Song, Y.H.; Song, Y.; Seo, J.H.; Hwang, D.S.; Lee, D.W. Adaptive amphiphilic interaction mechanism of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 565, 150535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanti, G.; Wang, M.; Bergonzi, M.C.; Zhidong, L.; Bilia, A.R. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose hydrogel of berberine chloride-loaded escinosomes: Dermal absorption and biocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc-Musioł, B.; Siemiradzka, W.; Dolińska, B. Formulation and evaluation of hydrogels based on sodium alginate and cellulose derivatives with quercetin for topical application. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, P.; Andrews, G.; Jones, D.; Walker, G. Analysis of in Vitro Drug Dissolution from PCL Melt Extrusion. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 164, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liang, S.; Zhao, P.; Qu, C.; Tan, H.; Du, R.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Correlation of Rheology–orientation–tensile Property in Isotactic Polypropylene/Organoclay Nanocomposites. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 3143–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawi, M. Rheological and Mechanical Investigation into the Effect of Different Molecular Weight Poly(ethylene glycol)s on Polycaprolactone-Ciprofloxacin Filaments. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 5412–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Kumria, R.; Harsha, S.; Attimarad, M.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Alhaider, I.A. In vitro techniques to evaluate buccal films. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, N.; Yang, X.; Fu, Y. Effects of various plasticizers on mechanical and water vapor barrier properties of gelatin films. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.C.; Hao, X.P.; Zhang, C.W.; Zheng, S.Y.; Du, M.; Liang, S.; Wu, Z.L.; Zheng, Q. Engineering Tough Metallosupramolecular Hydrogel Films with Kirigami Structures for Compliant Soft Electronics. Small 2021, 17, 2103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Jiao, D.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Z.L. Recent progress in fabrications and applications of functional hydrogel films. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 61, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balqis, A.I.; Khaizura, M.N.; Russly, A.; Hanani, Z.N. Effects of plasticizers on the physicochemical properties of kappa-carrageenan films extracted from Eucheuma cottonii. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Liang, T.; Tan, W.; Wang, L. Rheological behaviors and physical properties of plasticized hydrogel films developed from κ-carrageenan incorporating hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 85, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; El-Fahmy, S.; Revol-Junelles, A.-M.; Desobry, S. Cellulose derivative based active coatings: Effects of nisin and plasticizer on physico-chemical and antimicrobial properties of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.M.; Laurindo, J.B.; Yamashita, F. Effect of cellulose fibers addition on the mechanical properties and water vapor barrier of starch-based films. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadermazi, R.; Hamdipour, S.; Sadeghi, K.; Ghadermazi, R.; Asl, A.K. Effect of various additives on the properties of the films and coatings derived from hydroxypropyl methylcellulose—A review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3363–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.-F.; Liu, H.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Simon, G.P.; Qian, J. Effect of plasticizers on microstructure, compatibility and mechanical property of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose/hydroxypropyl starch blends. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S.; Kumar, G. Development and evaluation of a buccal bioadhesive system for smoking cessation therapy. Pharmazie 2007, 62, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.M.; Robinson, J.R.; Leung, S.H. Binding of acrylic polymers to mucin/epithelial surfaces: Structure-property relationships. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 1988, 5, 21–67. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, J. The basics and underlying mechanisms of mucoadhesion. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Khar, R.; Ahuja, A.; Kalra, R. Buccoadhesive erodible disk for treatment of oro-dental infections: Design and characterisation. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 238, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, E.-S.; Bahnasawy, A.; Abu Gabal, B.; Abbas, W.; Morsy, O. Effect of adding nano-materials on the properties of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) edible films. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klangmuang, P.; Sothornvit, R. Barrier properties, mechanical properties and antimicrobial activity of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-based nanocomposite films incorporated with Thai essential oils. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriloaia, M.R.; Budura, E.A.; Toma, C.C.; Mitu, M.A.; Karampelas, O.; Arama, C.; Lupuleasa, D. In vitro evaluation of diffusion and rheological profiles for dexamethasone inclusion complexes with beta-cyclodextrin or hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin. Farmacia 2012, 60, 895–904. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Liang, R.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, G. Mechanically strong hydrogels achieved by designing homogeneous network structure. Mater. Des. 2019, 163, 107547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovici, V.; Matei, E.; Cozaru, G.-C.; Bucur, L.; Gîrd, C.E.; Schröder, V.; Ozon, E.A.; Sarbu, I.; Musuc, A.M.; Atkinson, I.; et al. Formulation and Development of Bioadhesive Oral Films Containing Usnea barbata (L.) F.H.Wigg Dry Ethanol Extract (F-UBE-HPC) with Antimicrobial and Anticancer Properties for Potential Use in Oral Cancer Complementary Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, T.-M.; Huang, M.-L.; Chiu, A.-C.; Kuo, K.-H.; Chiu, W.-Y.; Chiu, L.-H. Preparation of thermo-responsive acrylic hydrogels useful for the application in transdermal drug delivery systems. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 107, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derle, D.; Joshi, O.; Pawar, A. Effect of tablet excipients on mucoadhesive properties of polyoxyethylene and carbopol 971 P. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 1, 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Chelu, M.; Popa, M.; Ozon, E.A.; Cusu, J.P.; Anastasescu, M.; Surdu, V.A.; Moreno, J.C.; Musuc, A.M. High-Content Aloe vera Based Hydrogels: Physicochemical and Pharmaceutical Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobre, M.; Boscencu, R.; Neagoe, I.V.; Surcel, M.; Milanesi, E.; Manda, G. Insight into the Web of Stress Responses Triggered at Gene Expression Level by Porphyrin-PDT in HT29 Human Colon Carcinoma Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

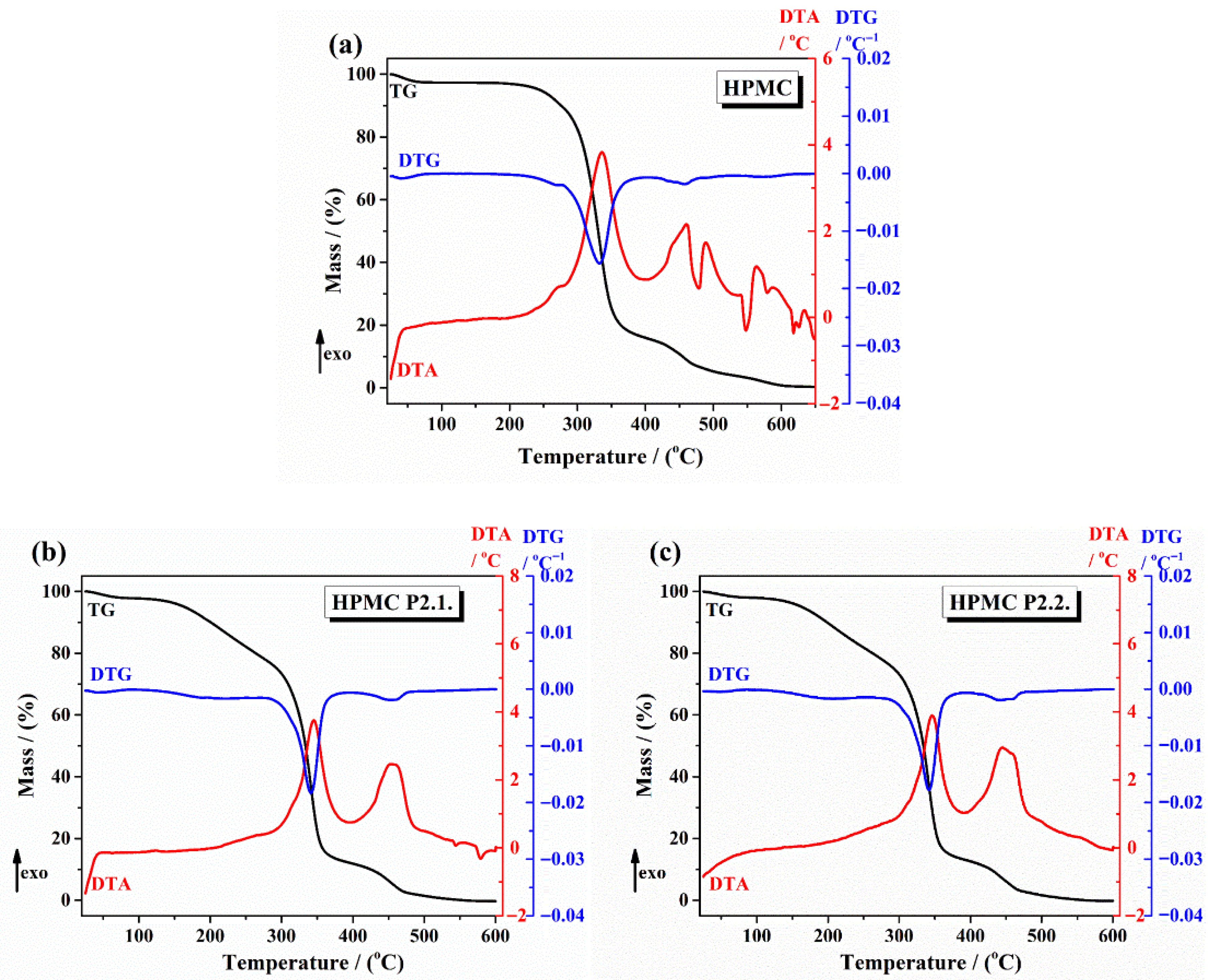

| Gels | 1st Step (Temperature and Mass Loss) | 2nd Step (Maximum Peak Temperatures and Mass Loss) | Remaining Mass at 600 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10% HPMC | Below 100 °C/2.7% | TDTA = 335 °C and TDTG = 330 °C TDTA = 461 °C and TDTG = 458 °C | 0.38% |
| HPMC-P2.1 | Below 100 °C/2.2% | TDTA = 342.16 °C and TDTG = 345 °C TDTA = 453.8 °C and TDTG = 453.5 °C | No residue |
| HPMC-P2.2 | Below 100 °C/2% | TDTA = 342.6 °C and TDTG = 346.5 °C TDTA = 447 °C and TDTG = 443 °C | No residue |
| Absorption λmax (nm) | Emission λmax (nm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soret Band | Qy(1,0) | Qy(0,0) | Qx(1,0) | Qx(0,0) | ||
| HPMC-P2.1 | 426 | 518 | 552 | 591 | 658 | 654 |
| HPMC-P2.2 | 428 | 521 | 556 | 594 | 652 | 656 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ozon, E.A.; Burloiu, A.M.; Musuc, A.M.; Manda, G.; Anuta, V.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.E.; Lupuliasa, D.; Neagoe, I.V.; Anastasescu, M.; Socoteanu, R.P.; et al. Cellulose-Derived Gels for Topical Delivery: HPMC as a Functional Matrix for Porphyrinic Photosensitizers. Gels 2025, 11, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100824
Ozon EA, Burloiu AM, Musuc AM, Manda G, Anuta V, Dinu-Pîrvu CE, Lupuliasa D, Neagoe IV, Anastasescu M, Socoteanu RP, et al. Cellulose-Derived Gels for Topical Delivery: HPMC as a Functional Matrix for Porphyrinic Photosensitizers. Gels. 2025; 11(10):824. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100824
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzon, Emma Adriana, Andreea Mihaela Burloiu, Adina Magdalena Musuc, Gina Manda, Valentina Anuta, Cristina Elena Dinu-Pîrvu, Dumitru Lupuliasa, Ionela Victoria Neagoe, Mihai Anastasescu, Radu Petre Socoteanu, and et al. 2025. "Cellulose-Derived Gels for Topical Delivery: HPMC as a Functional Matrix for Porphyrinic Photosensitizers" Gels 11, no. 10: 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100824
APA StyleOzon, E. A., Burloiu, A. M., Musuc, A. M., Manda, G., Anuta, V., Dinu-Pîrvu, C. E., Lupuliasa, D., Neagoe, I. V., Anastasescu, M., Socoteanu, R. P., Atkinson, I., Mitran, R.-A., Culita, D. C., & Boscencu, R. (2025). Cellulose-Derived Gels for Topical Delivery: HPMC as a Functional Matrix for Porphyrinic Photosensitizers. Gels, 11(10), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100824













