Physicochemical and Rheological Properties of Floury Rice Powder with Different Particle Sizes: Effects on Gluten-Free Sponge Cake Qualities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characteristics of Floury Rice Powder (FRP) Fractionated by Particle Size
2.1.1. Chemical Composition
2.1.2. Swelling Power and Solubility
2.1.3. Thermal Property
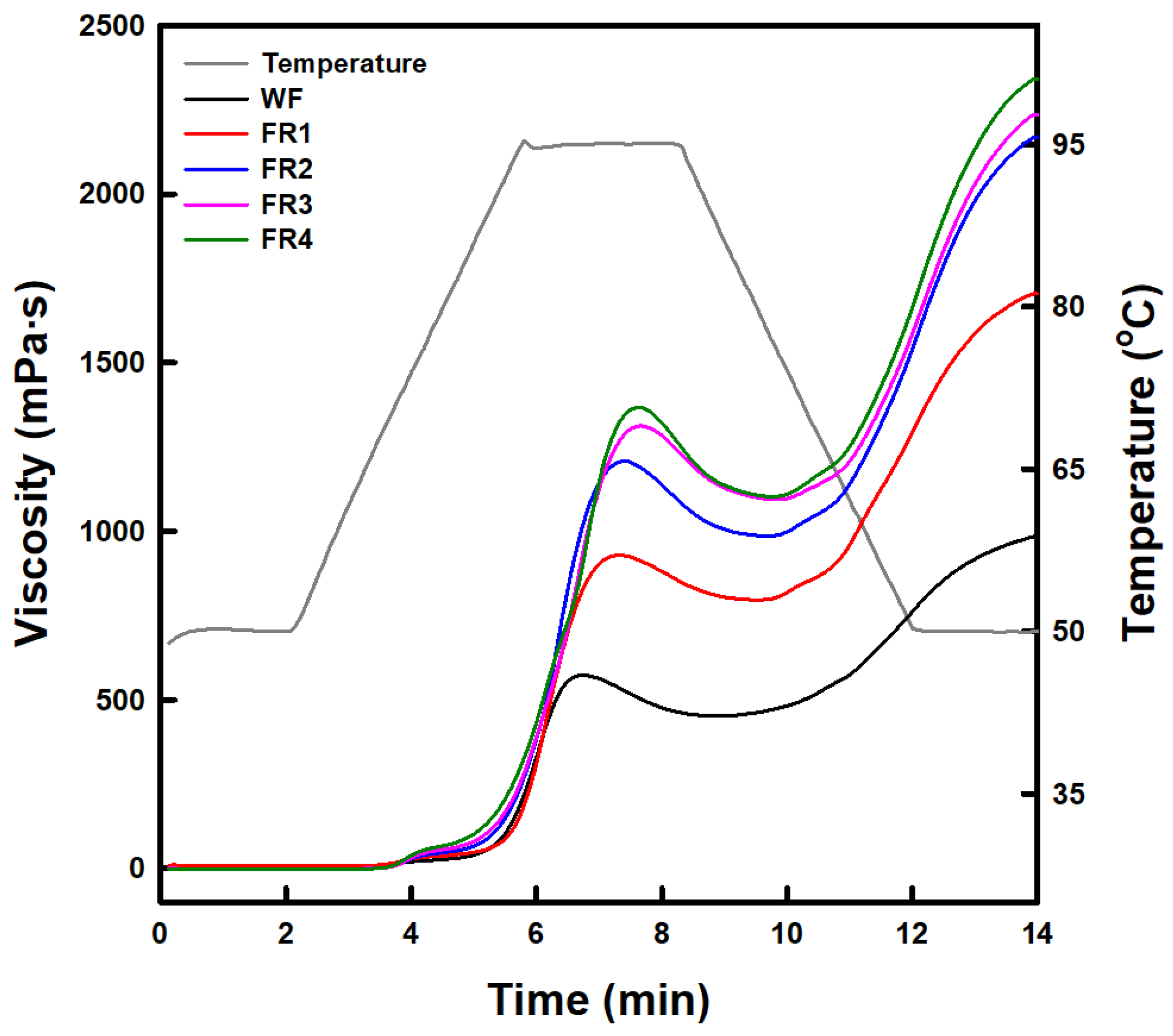
2.1.4. Pasting Property
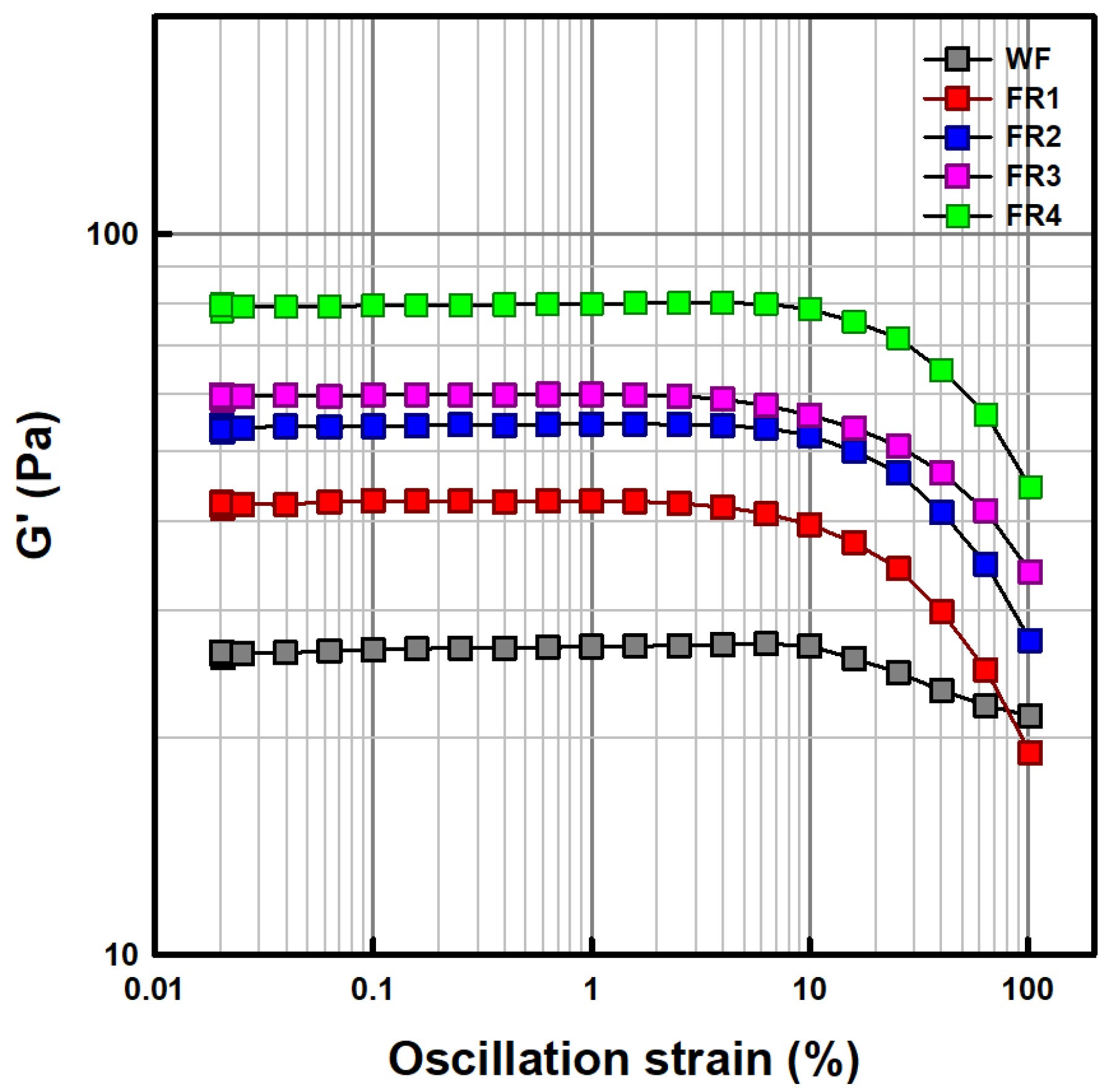
2.1.5. Strain Sweep Characteristic
2.1.6. Frequency Sweep Characteristic
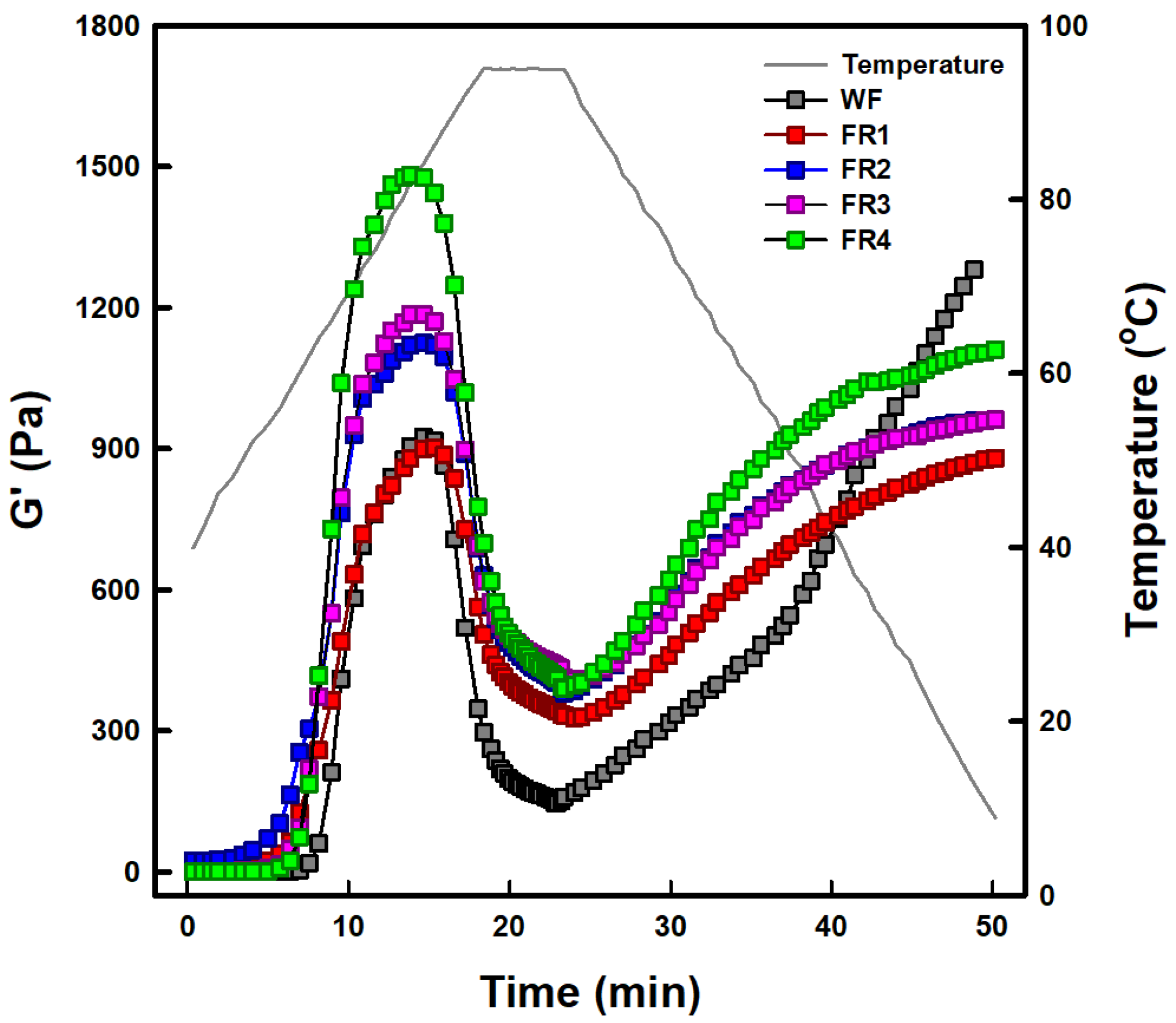
2.1.7. Temperature Sweep Characteristic
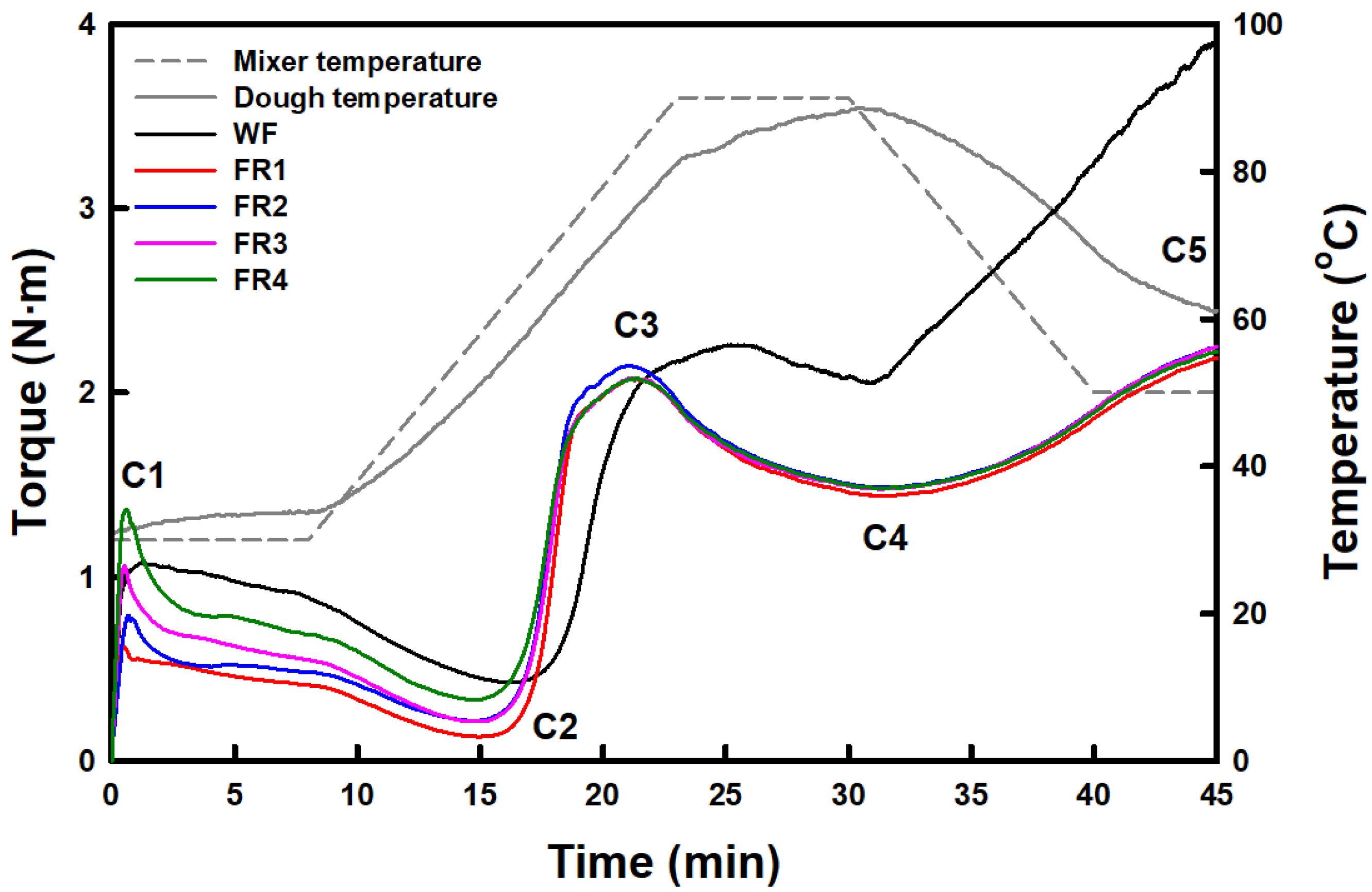
2.1.8. Thermo-Mechanical Properties
2.2. Characteristics of Butter Sponge Cake: Effects of FRP with Different Particle Size
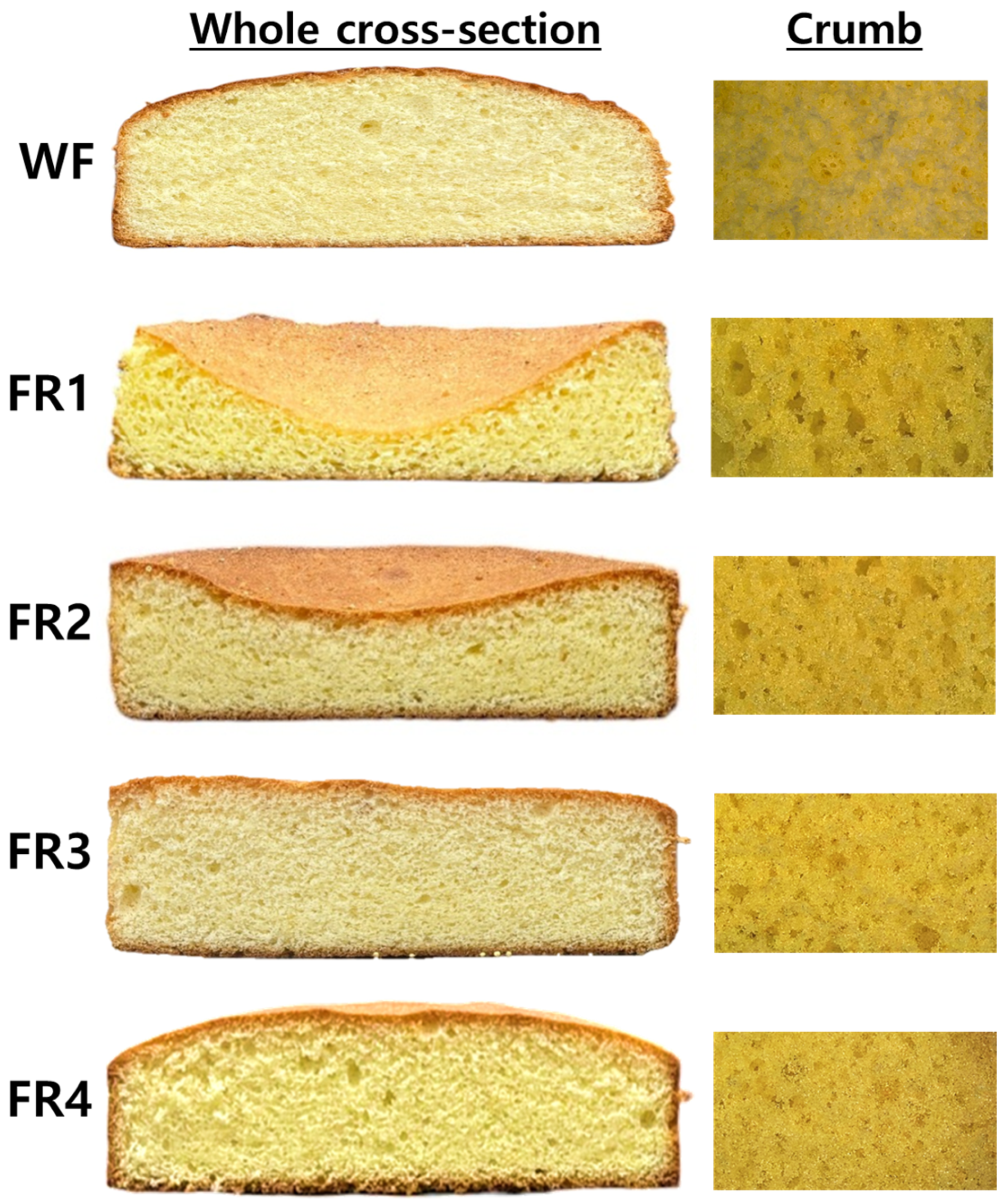
2.2.1. Morphological Characteristics
2.2.2. Quality Characteristics
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation and Fractionation of Floury Rice Powder (FRP)
4.3. Characteristics of FRP Fractions
4.3.1. Chemical Composition
4.3.2. Swelling Power and Solubility
4.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.3.4. Rapid Visco Analyzer (RVA)
4.3.5. Viscoelastic Measurement
4.3.6. Thermo-Mechanical Measurement
4.4. Preparation and Characteristics of Butter Sponge Cakes
4.4.1. Preparation of Butter Sponge Cakes
4.4.2. Appearance Characteristic
4.4.3. Moisture Content, Baking Loss, and Specific Volume
4.4.4. Firmness
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biesiekierski, J.R. What is Gluten? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.-S. Rice-Based Gluten-Free Foods and Technologies: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, F. Improvement of Gluten-Free Bread and Cake Properties Using Natural Hydrocolloids: A Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascuñán, K.A.; Vespa, M.C.; Araya, M. Celiac Disease: Understanding the Gluten-Free Diet. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Qlan, H.; Liu, L.; Tong, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Effect of Milling Methods on the Properties of Rice Flour and Gluten-Free Rice Bread. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 108, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Lin, Z.; Wang, A.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Tong, L.-T. Influence of Particle Size on the Properties of Rice Flour and Quality of Gluten-Free Rice Bread. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Hera, E.; Martinez, M.; Gómez, M. Influence of Flour Particle Size on Quality of Gluten-Free Rice Bread. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 54, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, D.C.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, O.W.; Kim, H.; Lim, S.T.; Lim, S.S. Effects of Rice Flour Size Fractions on Gluten Free Rice Bread. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-Y.; Shin, M. Effects of Soaking and Particle Sizes on the Properties of Rice Flour and Gluten-Free Rice Bread. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2007, 16, 759–764. [Google Scholar]
- de la Hera, E.; Rosell, C.M.; Gomez, M. Effect of Water Content and Flour Particle Size on Gluten-Free Bread Quality and Digestibility. Food Chem. 2014, 151, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Lin, Z.; Wang, A.; Xiao, T.; He, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Tong, L.-T. Influence of Damaged Starch on the Properties of Rice Flour and Quality Attributes of Gluten-Free Rice Bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 101, 103296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Ha, K.-Y.; Shin, M. Properties and Qualities of Rice Flours and Gluten-Free Cupcakes Made with Higher-Yield Rice Varieties in Korea. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 21, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-M.; Shin, M. Effects of Particle Size Distributions of Rice Flour on the Quality of Gluten-Free Rice Cupcakes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahagún, M.; Bravo-Núñez, Á.; Báscones, G.; Gómez, M. Influence of Protein Source on the Characteristics of Gluten-Free Layer Cakes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 94, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsaragkou, K.; Papantoniou, M.; Mandala, I. Rheological, Physical, and Sensory Attributes of Gluten-Free Rice Cakes Containing Resistant Starch. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, E341–E348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Hera, E.; Martinez, M.; Oliete, B.; Gómez, M. Influence of Flour Particle Size on Quality of Gluten-Free Rice Cakes. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, R.S.; Morris, A.; Prinyawiwatku, W.; Moncada, M.; King, J.M. Physicochemical Properties of Frontière Rice Flour and Its Application in A Gluten-Free Cupcake. Cereal Chem. 2022, 99, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.B.; Bhattacharya, S. Characterization of the Batter and Gluten-Free Cake from Extruded Red Rice Flour. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 102, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Kang, W.-S.; Shin, M. Improvement of the Quality of Gluten-Free Rice Pound Cake Using Extruded Rice Flour. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chompoorat, P.; Kantanet, N.; Estrada, Z.J.H.; Rayas-Duarte, P. Physical and Dynamic Oscillatory Shear Properties of Gluten-Free Red Kidney Bean Batter and Cupcakes Affected by Rice Flour Addition. Foods 2020, 9, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Hera, E.; Talegón, M.; Caballero, P.; Gómez, M. Influence of Maize Flour Particle Size on Gluten-Free Breadmaking. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronda, F.; Gómez, H.; Caballero, P.A.; Oliete, B.; Blanco, C.A. Improvement of Quality of Gluten-free Layer Cakes. Food Sci. Tech. Int. 2009, 15, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taromsari, A.; Tarzi, B.G. Optimization of Functional Gluten-Free Cake Formulation Using Rice Flour, Coconut Flour, and Xanthan Gum via D-Optimal Mixture Design. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 10734–10755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turabi, E.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. Quantitative Analysis of Macro and Micro-Structure of Gluten-Free Rice Cakes Containing Different Types of Gums Baked in Different Ovens. Food Hydrocolloid. 2010, 24, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann-Porcel, M.V.; Rinaldoni, A.N.; Campderrós, M.E.; Gómez, M. Evaluation of Gluten-Free Layer Cake Quality Made with Okara Flour. J. Food Mess. Charact. 2020, 14, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhen, N.; Román, L.; Rejeb, I.B.; Martínez, M.M.; Garogouri, M.; Gómez, M. Particle Size Distribution of Soy Flour Affecting the Quality of Enriched Gluten-Free Cakes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadallah, M.G.F. Rheological, Organoleptical and Quality Characteristics of Gluten-Free Rice Cakes Formulated with Sorghum and Germinated Chickpea Flours. Food Nutr. Sci. 2017, 8, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curti, M.I.; Belorio, M.; Palavecino, P.M.; Camiña, J.M.; Ribotta, P.D.; Gómez, M. Effect of Sorghum Flour Properties on Gluten-Free Sponge Cake. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.C.; Chiu, E.T.; Sun, A.; Hsiao, H. Incorporation of Chia Seed Flour into Gluten-Free Rice Layer Cake: Effects on Nutritional Quality and Physicochemical Properties. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Oh, I.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S. Particle Size Effect of Rice Flour in a Rice-Zein Noodle System for Gluten-Free Noodles Slit from Sheeted Dough. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 86, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Lee, S.M.; Shim, J.H.; Yoo, S.-H.; Lee, S. Effect of Dry- and Wet-Milled Rice Flours on the Quality Attributes of Gluten-Free Dough and Noodles. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Kim, Y.; Ko, S.; Yoon, M.-R.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, S. Physicochemical Characterization and In-Vitro Digestibility of Extruded Rice Noodles with Different Amylose Contents Based on Rheological Approaches. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 71, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.K.; Kim, B.-K.; Hwang, W.-H.; Mo, Y.-J.; Jeong, J.-M.; Lee, D.-K.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, J.-J.; Jeung, J.-U. Early Maturing Rice Variety “Baromi2” with a Floury Endosperm and Suitable for Dry-Milling of Rice Grain. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 2022, 54, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-M.; Choi, H.-S.; Kwak, J. Physicochemical Properties of Floury-Type Rice upon Soaking and Heating. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2025, 34, 2177–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Oh, W.; Lee, J. Evaluation of Oxidative Stability of Rice Oil from Brown Rice Flour under Thermal Oxidation and Light Irradiation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.W.; Kim, H.-S. Hydroxypropylation and Acetylation of Rice Starch: Effects of Starch Protein Content. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Meng, D.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Xue, L. Modification and Solubility Enhancement of Rice Protein and Its Application in Food Processing: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faurot, A.-L.; Saulnier, L.; Bérot, S.; Popineau, Y.; Petit, M.-D.; Rouau, X.; Thibault, J.-F. Large Scale Isolation of Water-Soluble and Water-Insoluble Pentosans from Wheat Flour. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Huber, K.C. Physicochemical Properties and Amylopectin Fine Structures of A- and B-Type Granules of Waxy and Normal Soft Wheat Starch. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 51, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.-E.; Hong, J.S.; Baik, M.-Y.; Choi, H.-D.; Choi, H.-W.; Kim, H.-S. Impact of Starch Granule-Associated Surface and Channel Proteins on Physicochemical Properties of Corn and Rice Starches. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 250, 116908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.J.; Kim, H.-S. Characterization of Potato Starch-High Amylose Rice Starch Blend as a Substitute of Acetylated Potato Starch in Long-Life Noodle. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 3057–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Rodríguez, M.-C.; Vela, F.; García-González, M.-C.; Muñoz, J. Flaxseed Fiber-Structured Nanoemulgels for Salad Dressing Applications: Processing and Stability. Gels 2025, 11, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiele, M.; Felisberto, M.H.F.; Clerici, M.T.P.S.; Chang, Y.K. MixolabTM for Rheological Evaluation of Wheat Flour Partially Replaced by Soy Protein Hydrolysate and Fructooligosaccharides for Bread Production. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaçar, D.; Sivri Özay, D. Olive Oil Shortenings as an Alternative to Commercial Shortenings in Cake Production: Physical and Sensory Properties. J. Food Mess. Charact. 2019, 13, 2846–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Approved Method of the AACC, 10th ed.; American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Method of Analysis of AOAC Intl., 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, VA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 25, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.J.; Kim, H.-S. Development and Characterization of Potato Amylopectin-Substituted Starch Materials. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FRP Fraction 1 | Crude Protein (%, d.b) | Crude Lipid (%, d.b) | Crude Ash (%, d.b) | Carbohydrate (%, d.b) | Total Starch (%, d.b) | Total Dietary Fiber (%, d.b) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1 | 8.1 ± 0.0 a | 2.2 ± 0.1 a | 0.5 ± 0.0 a | 89.2 ± 0.1 d | 73.4 ± 1.0 b | 1.7 ± 0.3 a |
| FR2 | 7.6 ± 0.6 a | 2.0 ± 0.0 b | 0.5 ± 0.0 a | 89.9 ± 0.1 c | 76.1 ± 2.0 a | 1.8 ± 0.2 a |
| FR3 | 7.6 ± 0.6 a | 1.6 ± 0.1 c | 0.5 ± 0.0 a | 90.3 ± 0.3 c | 77.6 ± 1.2 a | 1.8 ± 0.0 a |
| FR4 | 5.8 ± 0.6 b | 1.6 ± 0.0 c | 0.5 ± 0.0 a | 92.1 ± 0.1 a | 77.6 ± 1.1 a | 1.9 ± 0.1 a |
| WF 2 | 7.3 ± 0.0 a | 0.9 ± 0.1 d | 0.3 ± 0.0 b | 91.5 ± 0.1 b | 71.6 ± 1.4 c | 2.1 ± 0.3 a |
| FRP Fraction 1 | Swelling Power (g/g) | Solubility (%, d.b) |
|---|---|---|
| FR1 | 22.2 ± 0.4 a | 12.3 ± 0.0 d |
| FR2 | 22.2 ± 0.2 a | 13.8 ± 0.7 c |
| FR3 | 22.5 ± 0.0 a | 13.5 ± 0.1 c |
| FR4 | 22.3 ± 0.6 a | 15.1 ± 0.7 b |
| WF 2 | 16.4 ± 0.4 b | 20.0 ± 1.3 a |
| FRP Fraction 1 | Gelatinization Temperature (°C) | Gelatinization Enthalpy (J/g) | Melting Enthalpy (J/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onset | Peak | Completion | |||
| FR1 | 57.7 ± 0.9 a | 68.0 ± 0.3 a | 74.3 ± 0.1 ab | 7.2 ± 1.7 a | 1.4 ± 0.1 a |
| FR2 | 56.5 ± 0.2 ab | 67.8 ± 0.0 ab | 74.7 ± 0.2 a | 9.1 ± 0.2 a | 1.2 ± 0.1 a |
| FR3 | 56.4 ± 0.1 ab | 67.4 ± 0.0 b | 73.8 ± 0.3 ab | 8.8 ± 1.8 a | 1.2 ± 0.0 a |
| FR4 | 55.4 ± 0.1 b | 67.7 ± 0.2 ab | 74.1 ± 0.2 ab | 8.6 ± 1.8 a | 1.4 ± 0.3 a |
| WF 2 | 57.9 ± 0.1 a | 64.6 ± 0.6 c | 70.7 ± 0.2 b | 3.2 ± 0.0 b | 0.5 ± 0.0 b |
| FRP Fraction 1 | Storage Modulus (G′) (Pa) | Loss Modulus (G″) (Pa) | tan δ | Complex Viscosity (η*) (Pa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1 | 47.1 ± 7.1 ab | 9.3 ± 1.7 ab | 0.2 ± 0.0 a | 7.6 ± 1.2 ab |
| FR2 | 53.6 ± 3.0 ab | 10.7 ± 0.5 ab | 0.2 ± 0.0 a | 8.7 ± 0.5 ab |
| FR3 | 62.7 ± 5.2 a | 11.3 ± 0.9 a | 0.2 ± 0.0 a | 10.1 ± 0.8 a |
| FR4 | 63.0 ± 9.1 a | 12.6 ± 2.4 a | 0.2 ± 0.0 a | 10.2 ± 1.5 a |
| WF 2 | 53.0 ± 5.9 ab | 12.4 ± 1.9 a | 0.2 ± 0.1 a | 8.6 ± 2.5 ab |
| FRP Fraction 1 | Volume Index (mm) | Symmetry Index (mm) | Uniformity Index (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR1 | 64.7 ± 7.9 e | −8.1 ± 0.8 d | −0.3 ± 0.4 b |
| FR2 | 88.8 ± 2.3 d | −10.0 ± 2.1 d | −0.2 ± 0.3 b |
| FR3 | 126.9 ± 4.9 b | 0.8 ± 0.0 c | 0.0 ± 0.1 b |
| FR4 | 116.7 ± 3.2 c | 6.4 ± 2.7 b | 1.0 ± 0.3 a |
| WF 2 | 185.4 ± 4.8 a | 17.5 ± 7.9 a | 0.4 ± 0.3 ab |
| FRP Fraction 1 | Baking Loss (%) | Moisture Content (%) | Specific Volume (mL/g) | Firmness (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1 | 13.1 ± 0.1 a | 24.8 ± 1.0 b | 2.6 ± 0.0 c | 6.1 ± 0.7 a |
| FR2 | 13.0 ± 0.4 a | 26.7 ± 1.9 ab | 2.4 ± 0.2 c | 4.2 ± 0.5 b |
| FR3 | 11.6 ± 0.8 a | 28.5 ± 0.9 a | 3.3 ± 0.3 b | 3.3 ± 0.4 c |
| FR4 | 13.0 ± 0.8 a | 29.5 ± 0.7 a | 2.9 ± 0.2 b | 2.9 ± 0.3 c |
| WF 2 | 12.8 ± 1.7 a | 29.8 ± 0.7 a | 4.2 ± 0.2 a | 1.5 ± 0.6 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, H.; Lee, J.; Nam, T.G.; Choi, H.; Kim, H.-S. Physicochemical and Rheological Properties of Floury Rice Powder with Different Particle Sizes: Effects on Gluten-Free Sponge Cake Qualities. Gels 2025, 11, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100789
Jeon H, Lee J, Nam TG, Choi H, Kim H-S. Physicochemical and Rheological Properties of Floury Rice Powder with Different Particle Sizes: Effects on Gluten-Free Sponge Cake Qualities. Gels. 2025; 11(10):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100789
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Hyebin, Jungae Lee, Tae Gyu Nam, Hyunwook Choi, and Hyun-Seok Kim. 2025. "Physicochemical and Rheological Properties of Floury Rice Powder with Different Particle Sizes: Effects on Gluten-Free Sponge Cake Qualities" Gels 11, no. 10: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100789
APA StyleJeon, H., Lee, J., Nam, T. G., Choi, H., & Kim, H.-S. (2025). Physicochemical and Rheological Properties of Floury Rice Powder with Different Particle Sizes: Effects on Gluten-Free Sponge Cake Qualities. Gels, 11(10), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100789






