Physical Properties of Ovalbumin/Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite Gels Induced by Glucono-δ-Lactone and Heat Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Rheological Characteristics of OVA/CMC-Na Composite Gels
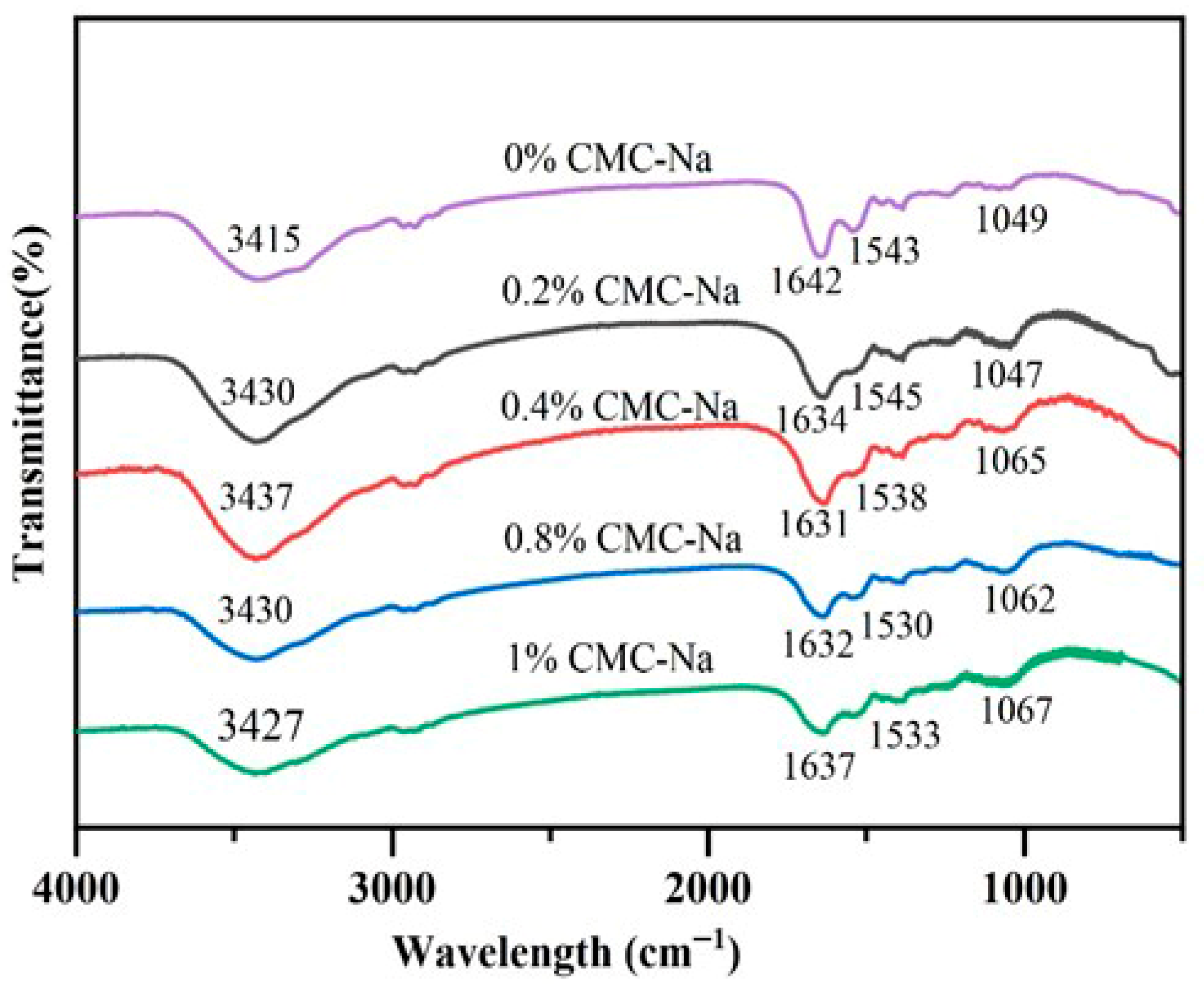
2.2. FTIR of OVA/CMC-Na Composite Gels
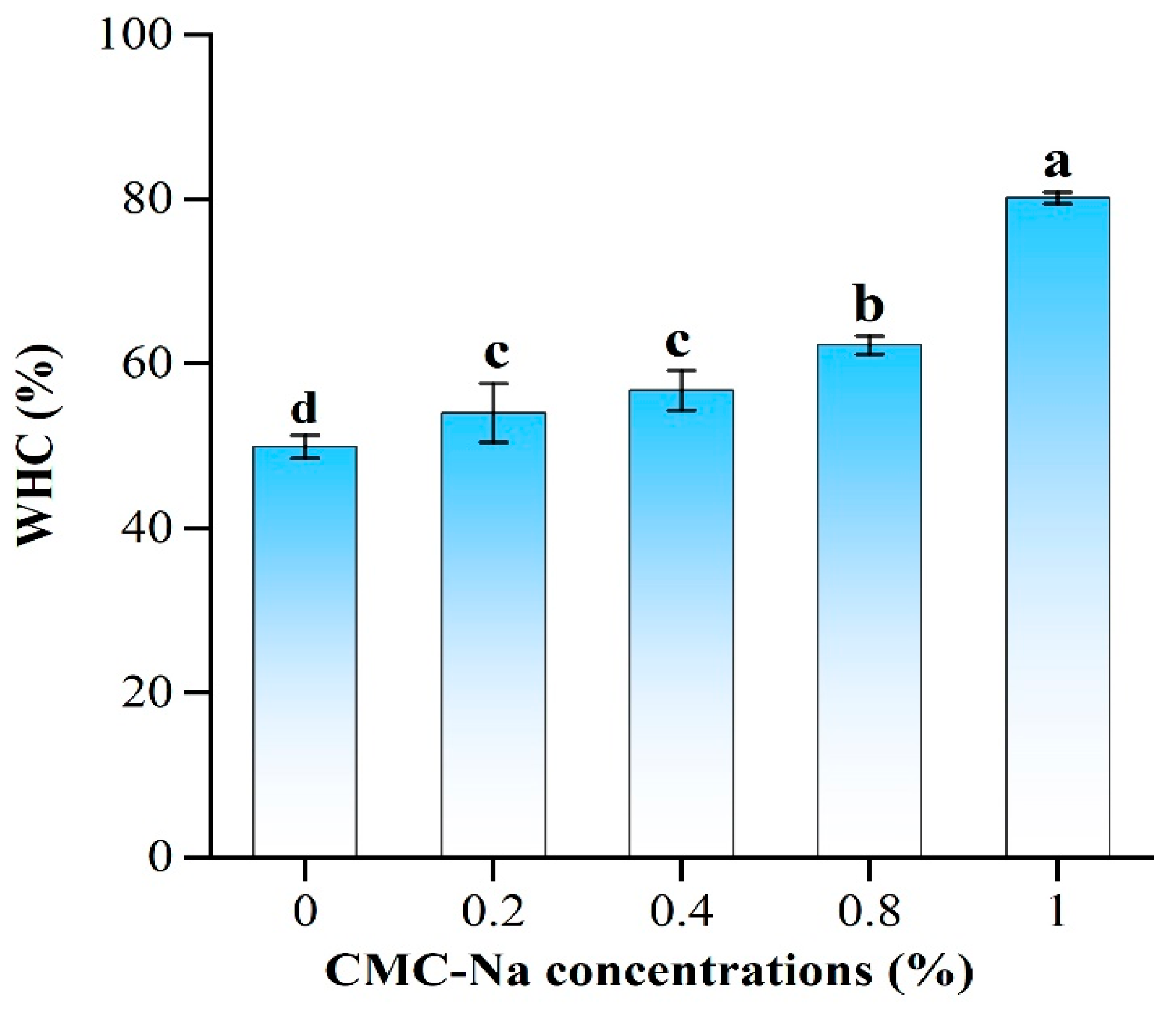
2.3. Water-Holding Capacity of OVA/CMC-Na Composite Gels
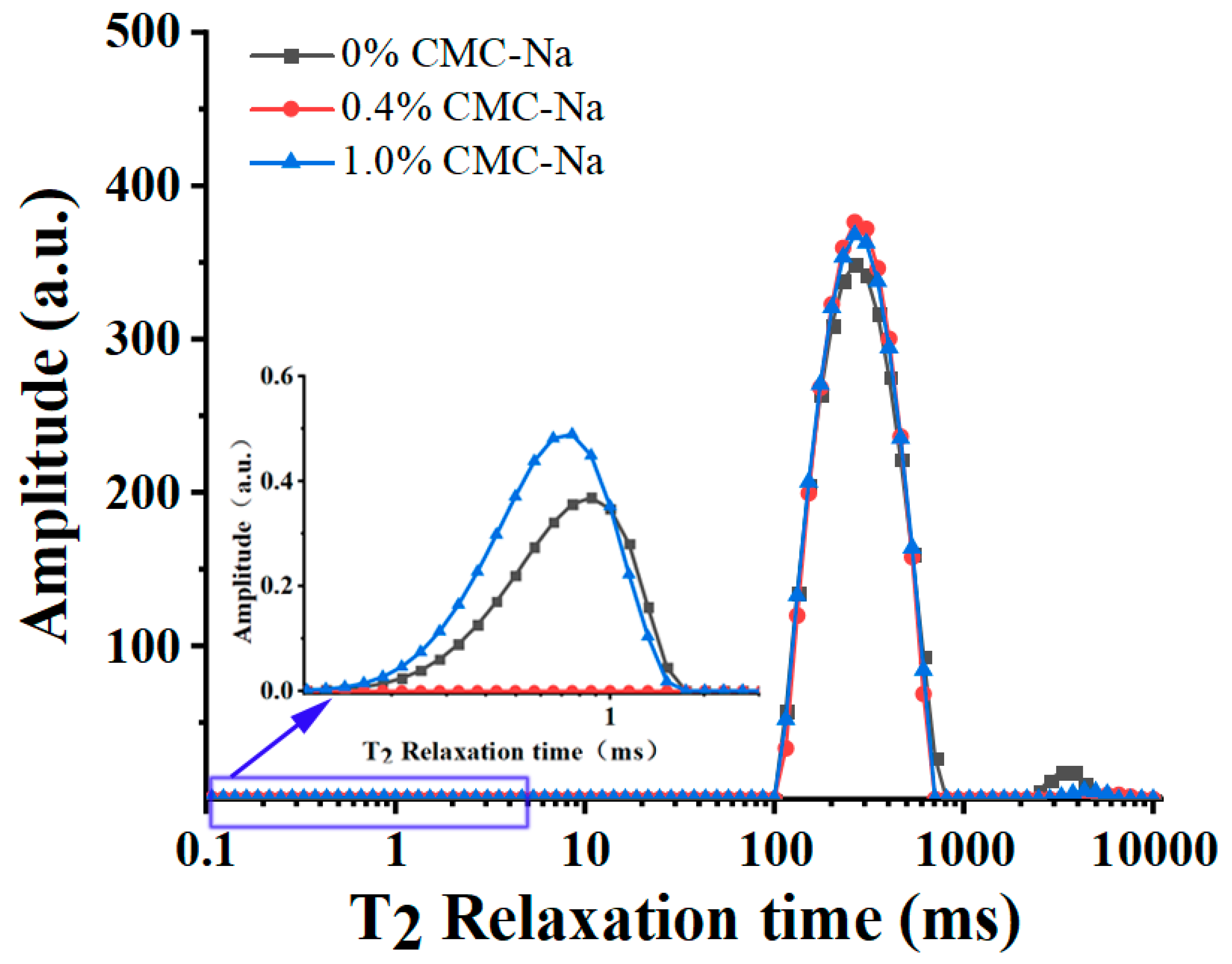
2.4. Water Mobility of OVA/CMC-Na Composite Gels
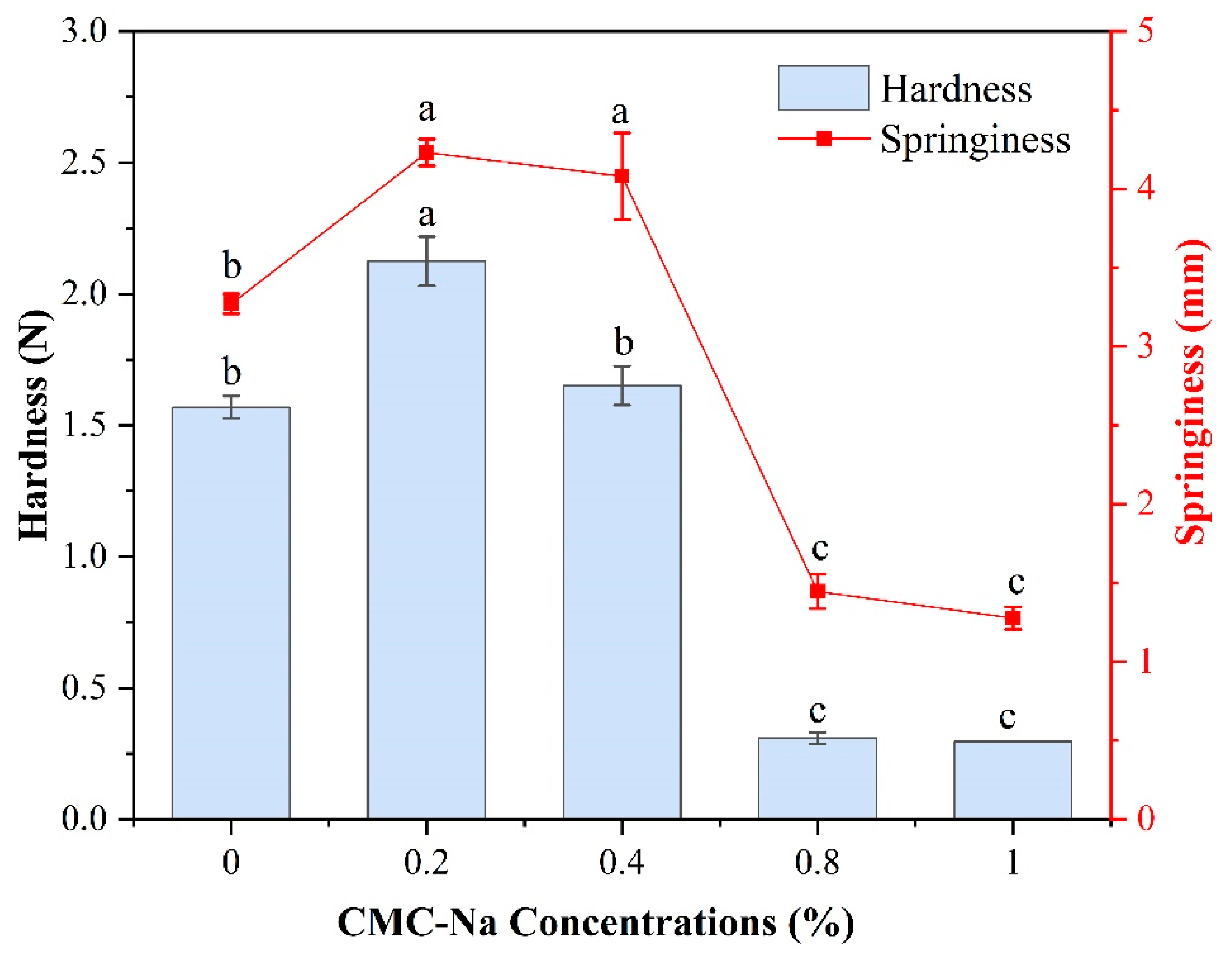
2.5. Texture Properties of OVA/CMC-Na Composite Gels
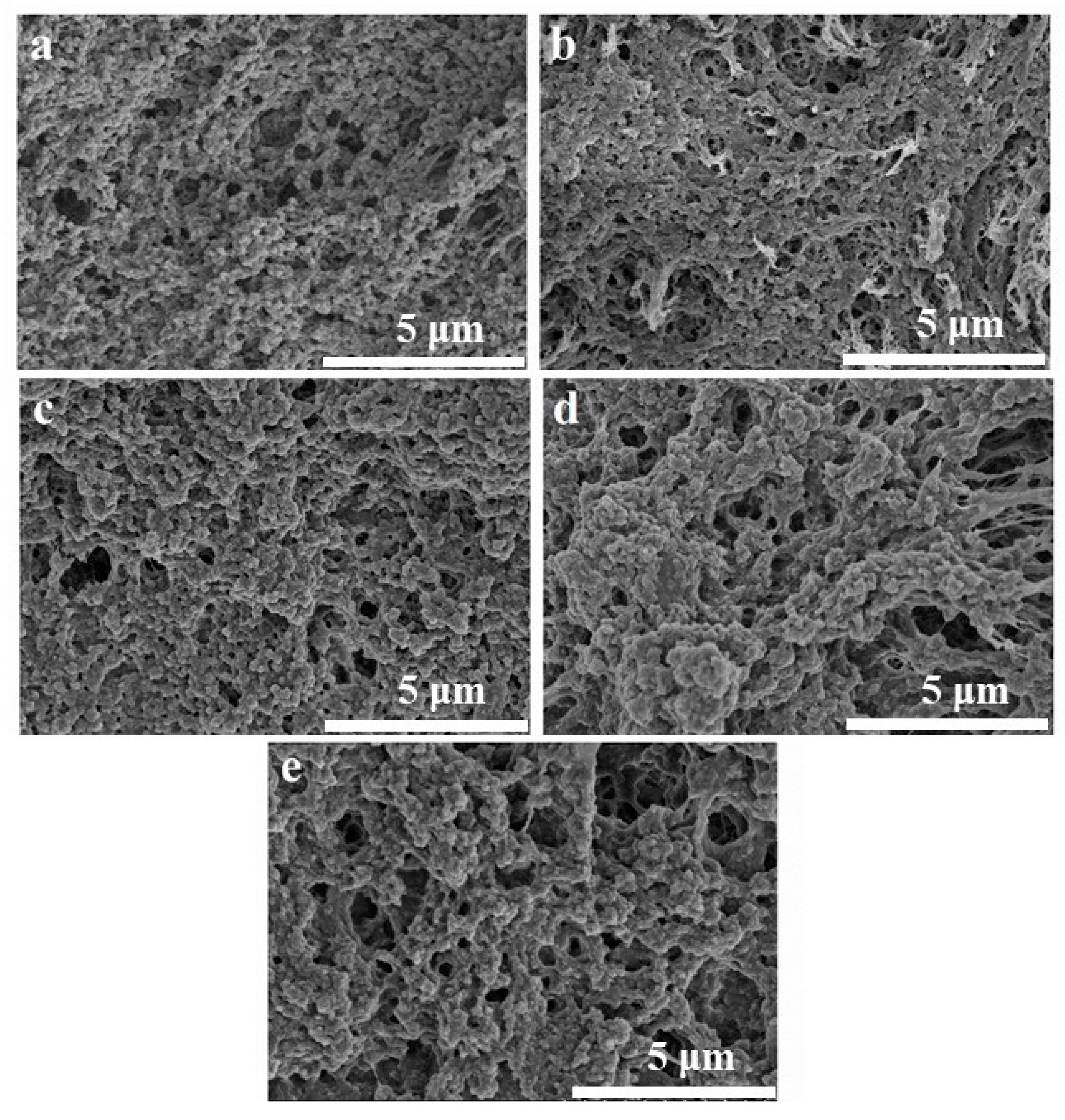
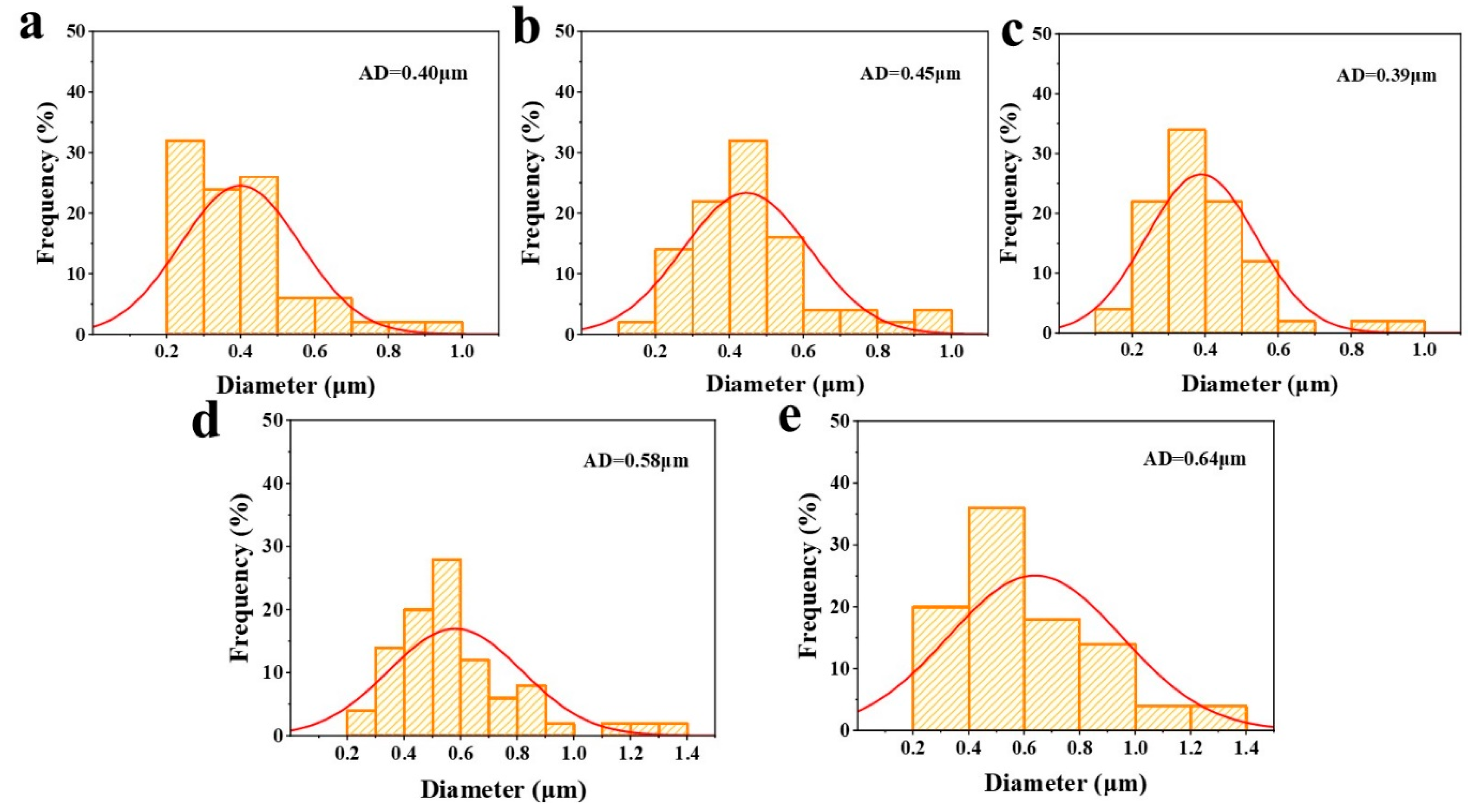
2.6. Microstructure of OVA/CMC-Na Composite Gels
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Composite Gels
4.3. Rheological Characteristics
4.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.5. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC) Measurement
4.6. Low Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR)
4.7. Texture Tests
4.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rostamabadi, H.; Chaudhary, V.; Chhikara, N.; Sharma, N.; Nowacka, M.; Demirkesen, I.; Rathnakumar, K.; Falsafi, S.R. Ovalbumin, An Outstanding Food Hydrocolloid: Applications, Technofunctional Attributes, and Nutritional Facts, A Systematic Review. Food Hydrocolloid. 2023, 139, 108514. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0268005X23000607 (accessed on 25 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Dong, L.Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Xia, Q.; Sang, S.Y.; Wu, Z.F.; Xiao, J.B.; Liu, L.Y.; Liu, L.L. Research Advance of Non-thermal Processing Technologies on Ovalbumin Properties: The Gelation, Foaming, Emulsification, Allergenicity, Immunoregulation and Its Delivery System Application. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 64, 7045–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, G.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Zheng, M. Effect of Transglutaminase in Conjunction with Glucono-δ-lactone Treatment on The Antigenicity and Conformational Structure of β-conglycinin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 2707–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Lee, S.E.; Moon, T.W. Influence of Sodium Chloride and Glucose on Acid-Induced Gelation of Heat-Denatured Ovalbumin. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, C313–C322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, X.; Lan, H.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Pei, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, W.; Chen, W.; et al. Development and Characterization of Novel Ultra-stable High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsions Gel: Interface Structure, Stabilization Mechanism, and Applications. Food Hydrocolloid. 2024, 151, 109817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.N.; Jia, J.; Yan, J.N.; Xu, S.Q.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wu, H.T. Non-covalent Interactions Between Large Yellow Croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) Roe Protein Isolates and Curcumin: Implications for Enhanced Curcumin Delivery. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yang, L.; Dai, T.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Gong, E.S. Flavonoids enhance gel strength of ovalbumin: Properties, structures, and interactions. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Lei, H.; Li, L.Q.; Liu, F.; Li, L.; Yan, J.K. Effects of Direct Addition of Curdlan on The Gelling Characteristics of Thermally Induced Soy Protein Isolate Gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yang, X.; Yin, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Li, L. Gelation Behaviour of Auricularia Polytricha Polysaccharides-whey Protein Isolate. J. Food Eng. 2024, 377, 112079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yin, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, D.; Kang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Fabrication and characterization of epigallocatechin gallate and β-carotene co-encapsulated Pickering double emulsions stabilized by xanthan gum/lysozyme nanoparticles and konjac glucomannan. Food Res. Int. 2025, 218, 116923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.F.; Zhu, K.X.; Guo, X.N. The Effect of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium on the Proofing Tolerance and Quality of Frozen Dough Steamed Bread. Foods 2024, 13, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, N.; Liu, Z.; Lu, M.; Yang, Y.; Liao, F.; Feng, Y.; Liu, G.; Qiu, S. Preparation and Properties of Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose Soluble Microneedles. Materials 2023, 16, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Song, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. Effect of Metal Cation Crosslinking on The Mechanical Properties and Shrimp Freshness Monitoring Sensitivity of Pectin/carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium/anthocyanin Intelligent Films. Carbohyd. Polym. 2024, 340, 122285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Sun, A.; Cui, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Li, J. The Physicochemical Properties of Cassava Starch/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium Edible Film Incorporated of Bacillus and Its Application in Salmon Fillet Packaging. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Mao, L.; Wang, L. Physicochemical and Foam Properties of Ovalbumin-carboxymethylcellulose Mixtures After Mild Heat Treatment: Comparison of Electrostatic Repulsion and Attraction. Food Hydrocolloid. 2024, 153, 110042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, T.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z. Effect of Glycosylation on Soy Protein Isolate–sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose Conjugates Heat-Induced Gels and Their Applications as Carriers of Riboflavin. Food Hydrocolloid. 2024, 153, 110072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Shen, R.; Zhang, L.; He, L.; Qu, Y.; Ma, X.; Ma, G.; Guo, Z.; Chen, C.; et al. Effect of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Physicochemical Properties of Bovine Plasma Protein-Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite Gel. Foods 2024, 13, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, M.; Perez-Puyana, V.; Romero, A.; Guerrero, A. Development of Thermally Processed Bioactive Pea Protein Gels: Evaluation of Mechanical and Antioxidant Properties. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 101, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Huang, M.; Bi, J.; Sun, D.; Li, H.; Yang, H. Effects of Kappa-carrageenan on Egg White Ovalbumin for Enhancing the Gelation and Rheological Properties via Electrostatic Interactions. Food Hydrocolloid. 2023, 134, 108031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Yang, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; Zhu, X.; Tong, L. Preparation of Bovine Serum Albumin-arabinoxylan Cold-set Gels by Glucono-δ-lactone and Salt Ions Double Induction. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 133596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Tang, R.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Zou, L.; Shi, Q. Influence of Dextrans on The Textural, Rheological, and Microstructural Properties of Acid-Induced Faba Bean Protein Gels. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Chen, W.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Gliadin/Soybean Polysaccharide Composite Colloidal Nanoparticle: Physicochemical Properties and Its Application on Washing of Fresh-cut Cabbage. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ye, J.; Ahmad, H.N.; Zhu, J. Salt Reduction in Myofibrillar Protein Gel via Inhomogeneous Distribution of Sodium-Containing Encapsulated Fish Oil Coacervate: Mucopenetration Ability of Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268, 131998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Han, K.; Wang, S.; Muhindo, E.M.; Wei, W.; Li, J.; Wu, T.; Fersht, V.; Zhang, M. Design and Structural Characterization of Edible Double Network Gels Based on Wheat Bran Arabinoxylan and Pea Protein Isolate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalesi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, C.; Lu, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kadkhodaee, R.; Fang, Y. Influence of Amyloid Fibril Length and Ionic Strength on WPI-Based Fiber-Hydrogel Composites: Microstructural, Rheological and Water Holding Properties. Food Hydrocolloid. 2024, 148, 109499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, H.; Lou, H.; Acharya, D.R.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Q. Synthesis and Characterization of Neurospora Intermedia-Based Composite Mycoprotein Gel Meat: Insight into the Effect of pH and Soluble Starch on Water-Holding Capacity and Texture Properties. Food Hydrocolloid. 2024, 155, 110190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, R.; Sasaki, K.; Kuwano, T.; Eguchi, S.; Nakatani, M.; Yuasa, M.; Yoshimura, M. Physical Properties, Palatability, and Mastication of Breads with Different Compositions of Soy Protein Isolate and Soybean Soluble Polysaccharide. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2024, 37, 100961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Ge, Y.; Wang, B.; Tang, J.; Qin, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q. Characterization of the Effects of Insoluble Soybean Polysaccharides on the Formation and Physicochemical Properties of Soybean Isolate Protein Gel. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Xu, T.; Su, R.; Dai, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W.; Yang, B.; Tong, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Composite Gel Based on K-Carrageenan-Soybean Isolate Protein/Soy Protein Fibrils: Focus on Structural Differences and Gel Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 307, 142274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Guo, C.; Lin, L.; Si, Y.; Gao, X.; Xu, D.; Jia, R.; Yang, W. Combined Use of Rheology, LF-NMR, and MRI for Characterizing the Gel Properties of Hairtail Surimi with Potato Starch. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Tan, L.; Sun, H.; Chong, C.; Li, L.; Sun, B.; Yao, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, L. Manipulating Gelatinization, Retrogradation, and Hydrogel Properties of Potato Starch Through Calcium Chloride-Controlled Crosslinking and Crystallization Behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 357, 123371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, P.; Jiang, S.; Bourouis, I.; Pang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, P. Effect of Flaxseed Gum on the Textural, Rheological, and Tribological Properties of Acid-Induced Soy Protein Isolate Gels. Polymers 2023, 15, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, N.; Wu, L.; Nirasawa, S.; Jia, X.; Cao, W. Rheological, Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Heat-Induced Egg Albumin/Sesbania Gum Mixed Gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Qu, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L. Effect and Mechanism of Acid-Induced Soy Protein Isolate Gels as Influenced by Cellulose Nanocrystals and Microcrystalline Cellulose. Foods 2022, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Guo, C.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y. Gelation Mechanism and Physical Properties of Glucono-δ-Lactone Induced Alginate Sodium/Casein Composite Gels. Food Hydrocolloid. 2021, 118, 106775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Huang, D.; Zhu, S. Influence Mechanism of Components and Characteristics on Structural and Oxidative Stability of Emulsion Gel. Food Hydrocolloid. 2024, 151, 109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrana, E.F.; D’Oria, G.; Mota-Santiago, P.; Czaja, T.P.; Lillevang, S.; Andersen, U.; Ahrné, L. Emulsification of Milk Fat and Skimmed Milk Curds—Effect of Temperature on Rheological Properties and Structure of Emulsion Gels at Different Length Scales. Int. Dairy J. 2025, 162, 106153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zang, J.; Du, S.; Zhang, C.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. Sodium Caseinate Stabilized Camellia Oil Emulsion with Konjac Glucomannan as Fat Replacer in Low-Alcohol Ice Cream. LWT 2025, 225, 117943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbari, Z.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Askari, G.; Pero, M. Rheological and textural characterization of lentil protein isolate-κ-carrageenan emulsion gels: Insights into coagulant-driven protein gelation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chu, Z.; Mao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fei, P.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Liu, J. Structural characteristics and acid-induced emulsion gel properties of heated soy protein isolate–soy oligosaccharide glycation conjugates. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CMC-Na Addition (%) | Final G′ (Pa) | Final G″ (Pa) | Final Tanδ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 609.34 | 126.07 | 0.21 |
| 0.2 | 1840.52 | 260.52 | 0.14 |
| 0.4 | 904.01 | 143.67 | 0.16 |
| 0.8 | 366.22 | 67.17 | 0.18 |
| 1.0 | 180.00 | 39.41 | 0.22 |
| CMC-Na (%) | PT21 (%) | PT22 (%) | PT23 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.05 ± 0.05 a | 98.12 ± 0.66 b | 1.85 ± 0.65 b |
| 0.4 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 99.52 ± 0.47 a | 0.81 ± 0.37 ab |
| 1.0 | 0.14 ± 0.02 a | 99.67 ± 0.29 a | 0.35 ± 0.26 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, W. Physical Properties of Ovalbumin/Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite Gels Induced by Glucono-δ-Lactone and Heat Treatment. Gels 2025, 11, 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100779
Zhang X, Li L, Wang L, Xu W. Physical Properties of Ovalbumin/Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite Gels Induced by Glucono-δ-Lactone and Heat Treatment. Gels. 2025; 11(10):779. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100779
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaofan, Lala Li, Liye Wang, and Wei Xu. 2025. "Physical Properties of Ovalbumin/Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite Gels Induced by Glucono-δ-Lactone and Heat Treatment" Gels 11, no. 10: 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100779
APA StyleZhang, X., Li, L., Wang, L., & Xu, W. (2025). Physical Properties of Ovalbumin/Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite Gels Induced by Glucono-δ-Lactone and Heat Treatment. Gels, 11(10), 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100779






