Contribution of Phosphorylation Modification to Stability and Antibacterial Activity of Egg White Protein Nanogels Loaded with Cinnamon Bark Essential Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
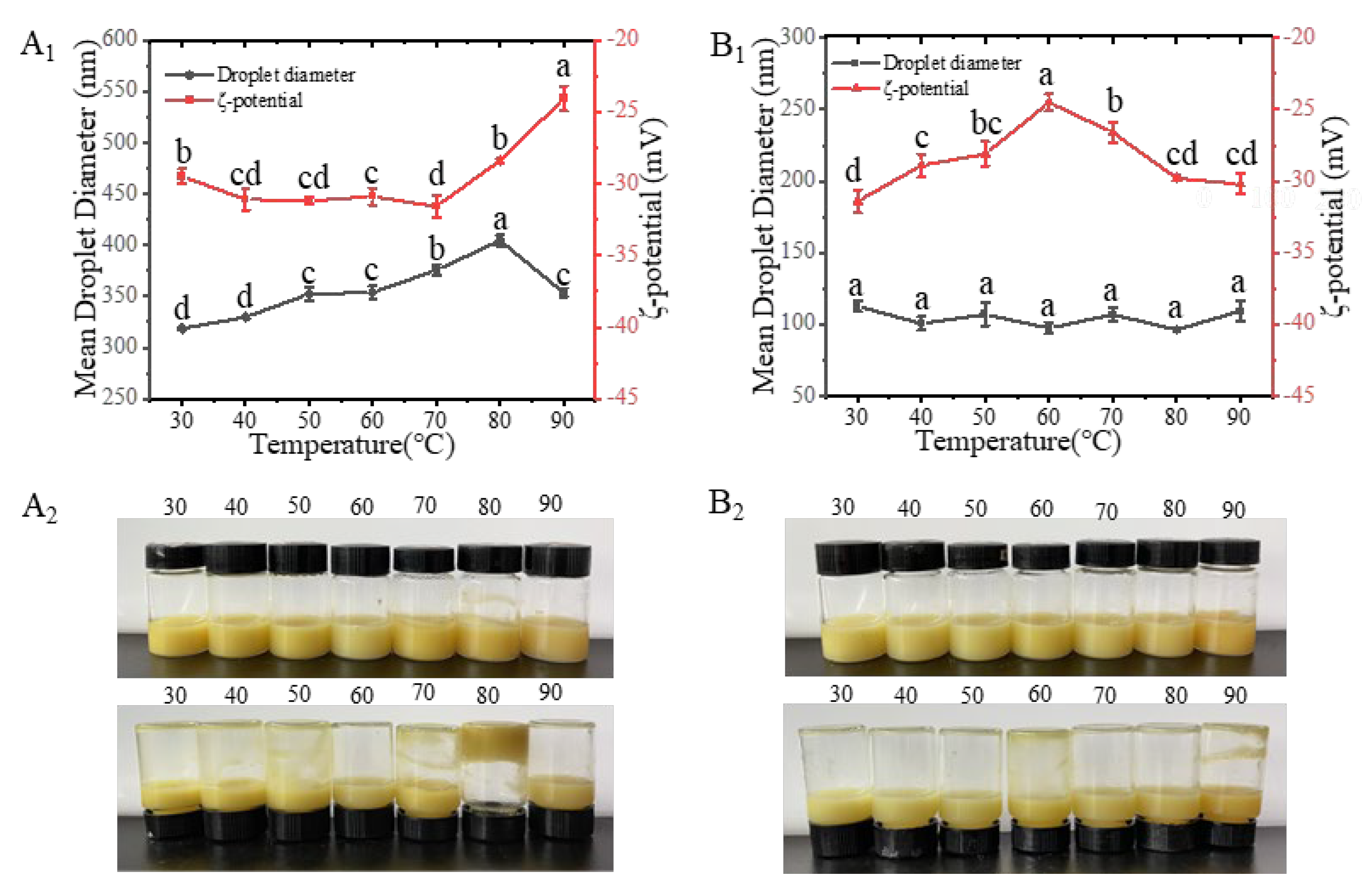
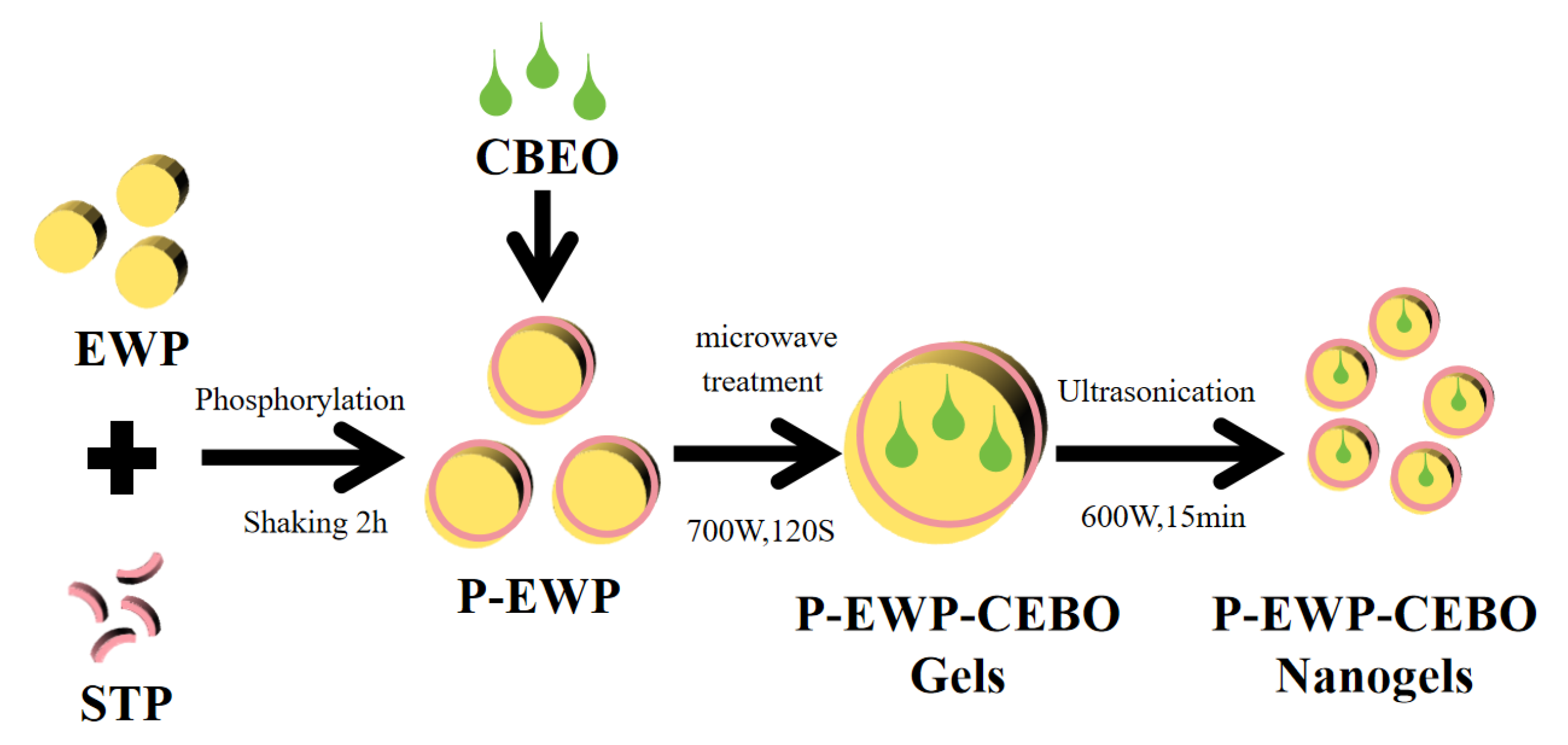
2.1. Preparation of P-EWP-CBEO
2.2. Intermolecular Forces That Maintain Nanoparticle Structure
2.3. Structural Characterization of P-EWP-CBEO
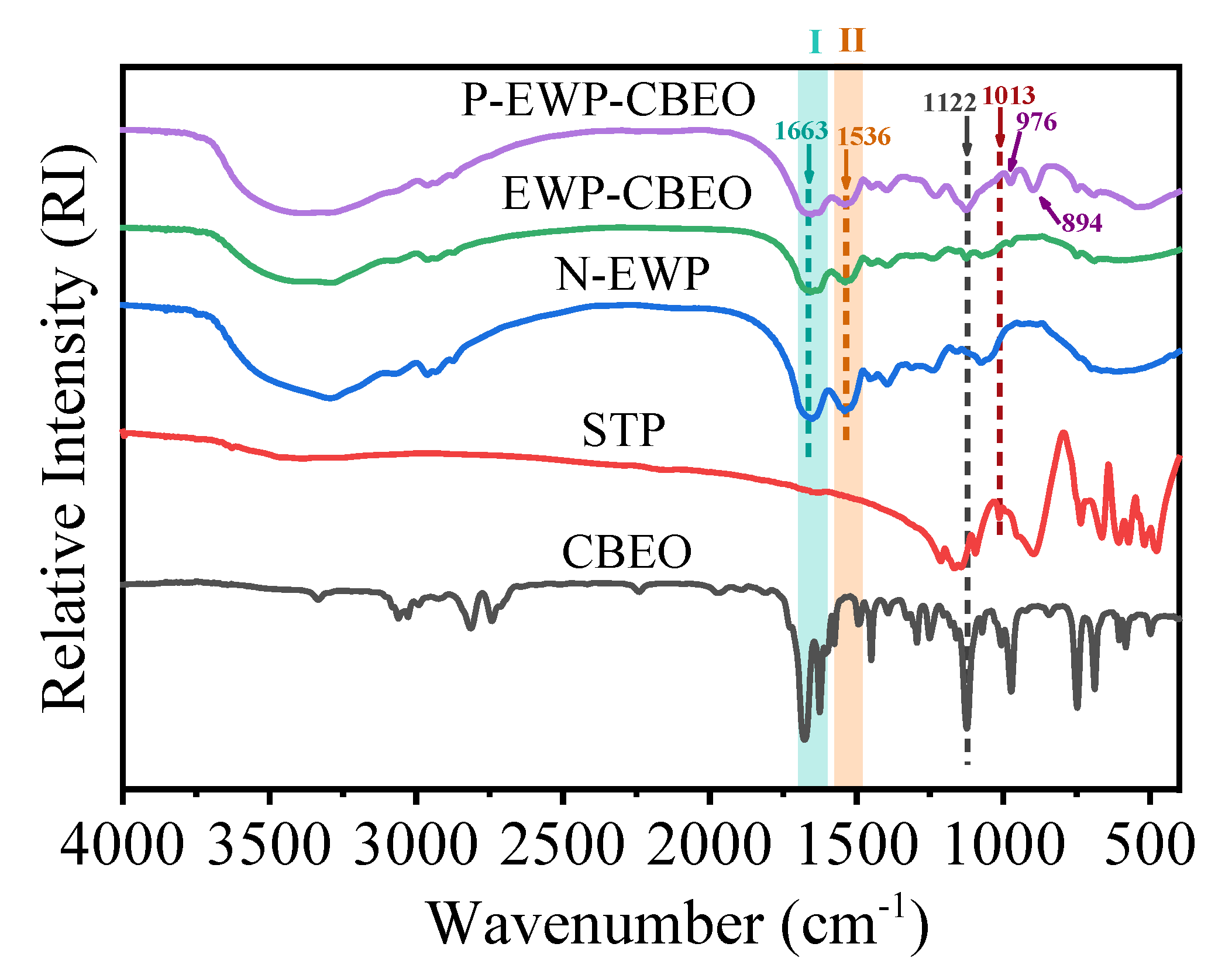
2.3.1. FTIR Analysis
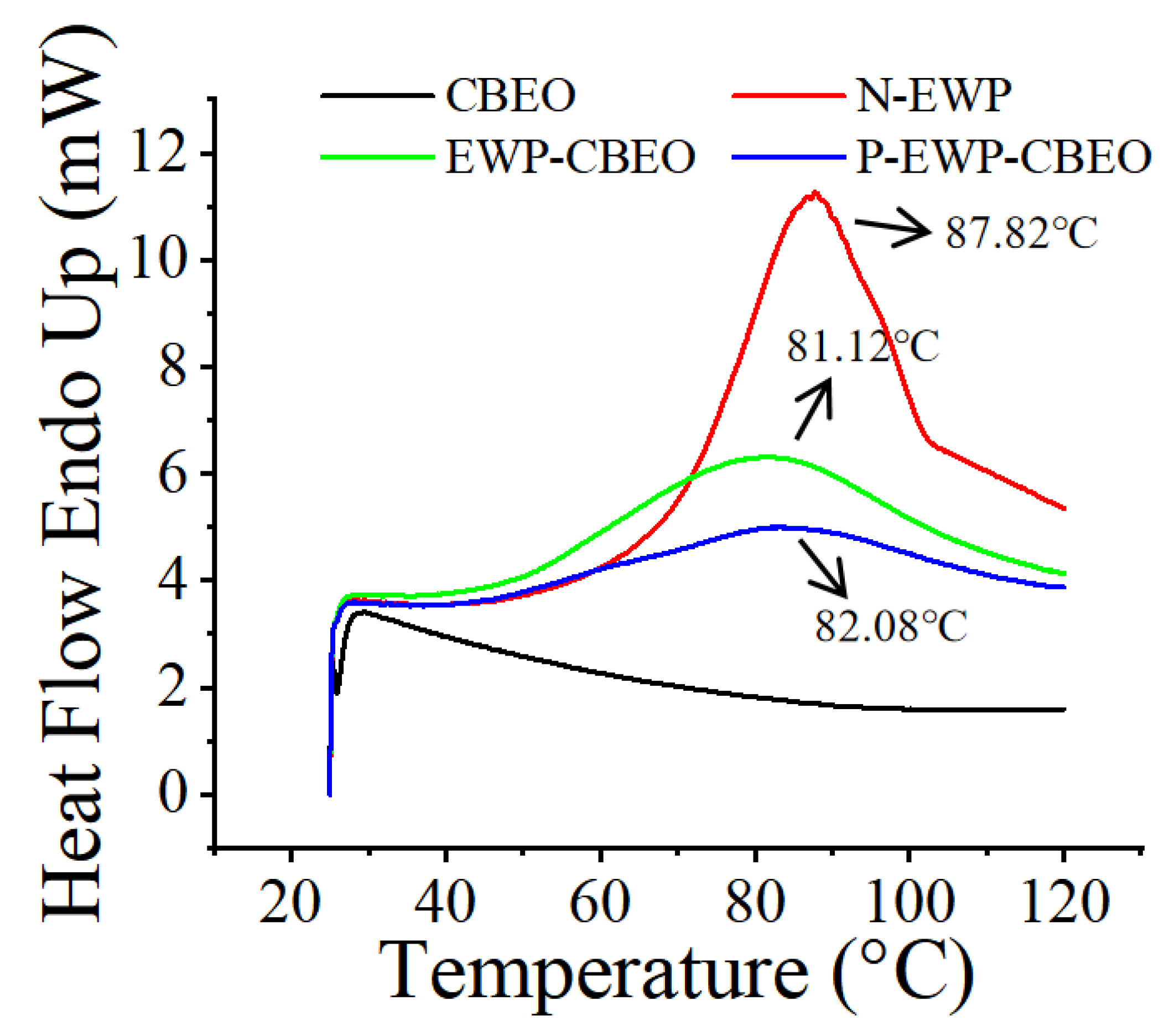
2.3.2. DSC Analysis
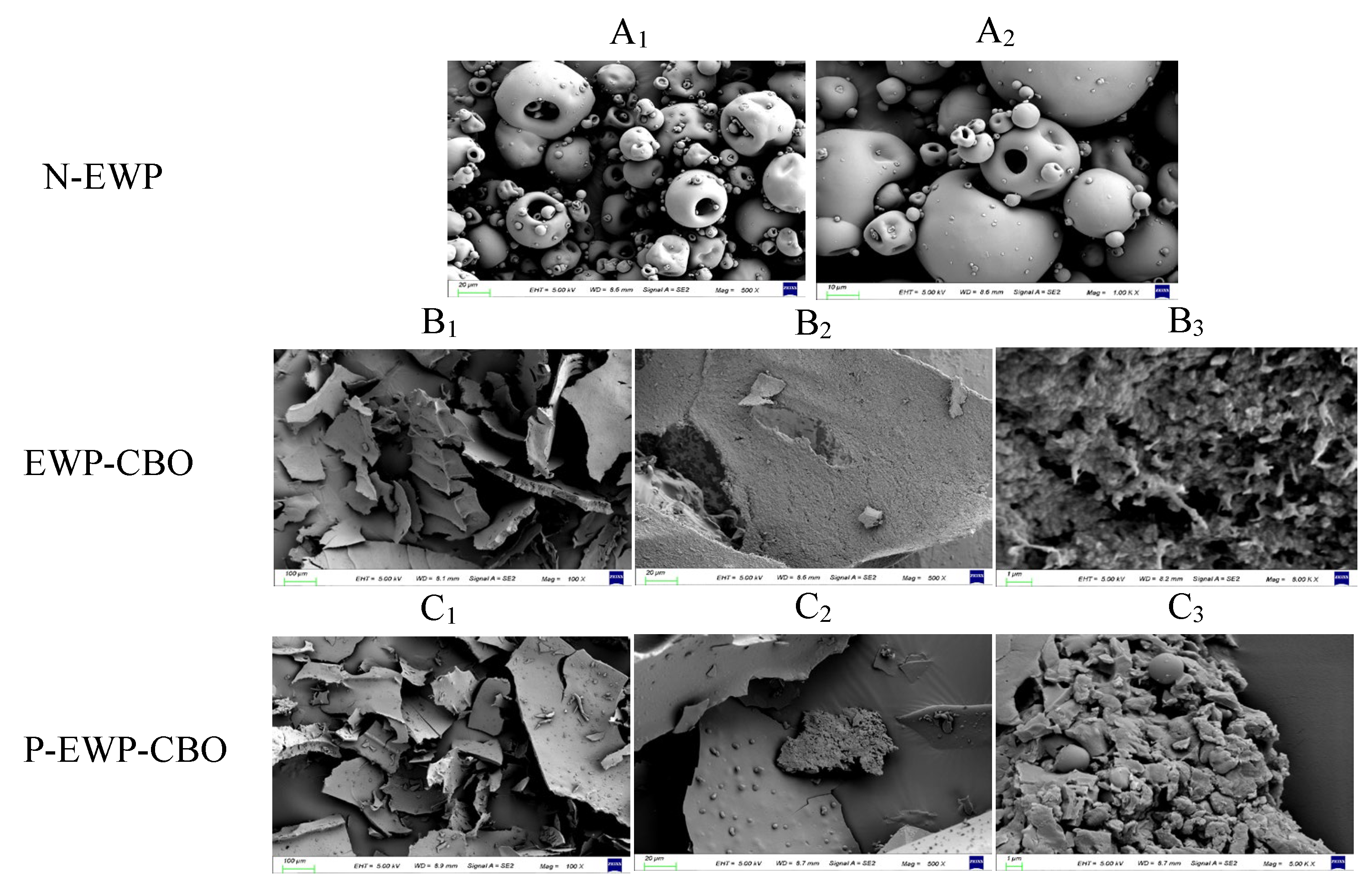
2.3.3. SEM Observation
2.4. Stability Analysis of P-EWP-CBEO
2.4.1. Thermal Stability
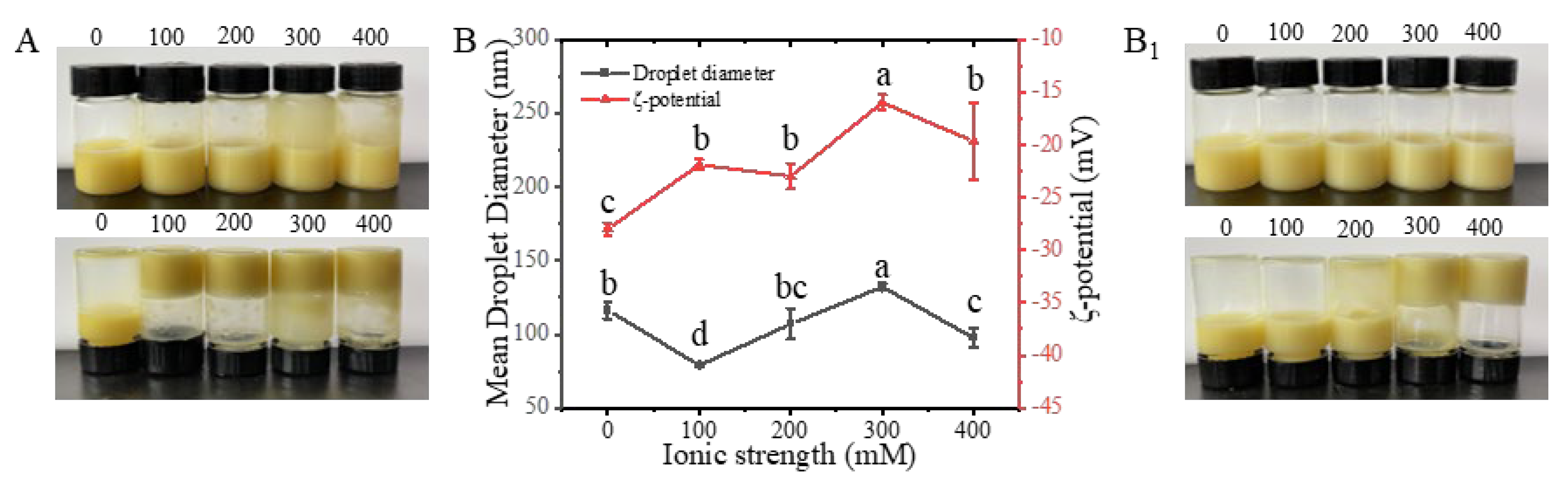
2.4.2. Ionic Strength
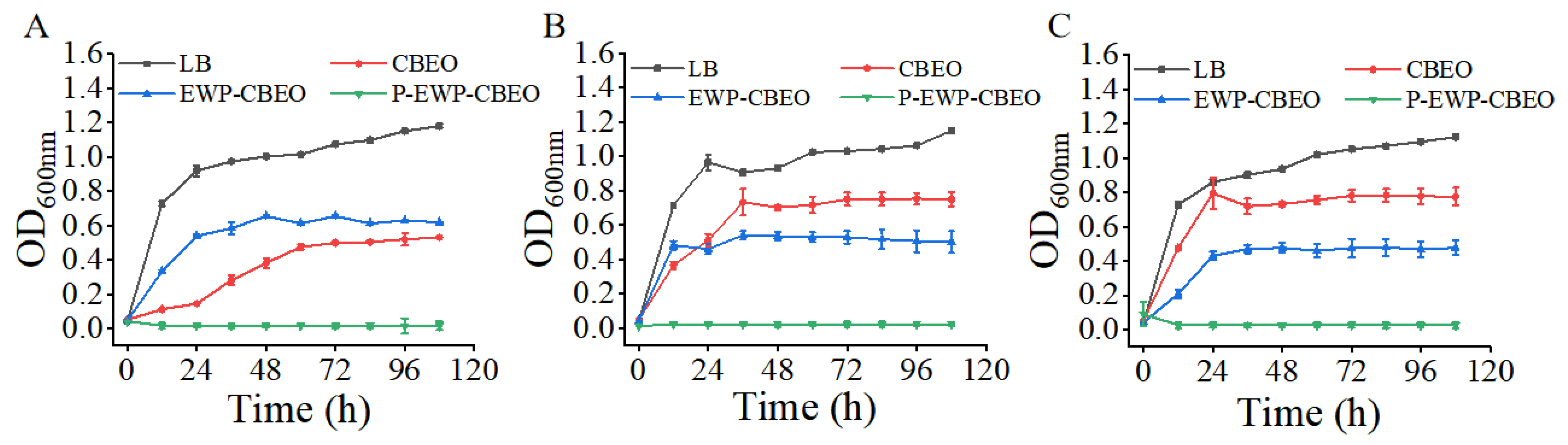
2.5. Antibacterial Activity of P-EWP-CBEO
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Bacterial Strains
4.3. Preparation of P-EWP-CBEO Nanogels
4.4. Particle Size and Zeta Potential of P-EWP-CBEO Nanogels
4.5. Encapsulation Efficiency (EE) of P-EWP-CBEO Nanogels
4.6. Intermolecular Force Assays of P-EWP-CBEO Nanogels
4.7. Structural Characterization of P-EWP-CBEO
4.7.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.7.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.7.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.8. Stability Analysis of P-EWP-CBEO
4.8.1. Thermal Stability
4.8.2. Ionic Strength
4.9. Antibacterial Assays
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yılmaz, S.; Ünal, F.; Yüzbaşıoğlu, D.; Aksoy, H. Clastogenic effects of food additive citric acid in human peripheral lymphocytes. Cytotechnology 2008, 56, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjemaa, M.; Neves, M.A.; Falleh, H.; Isoda, H.; Ksouri, R.; Nakajima, M. Nanoencapsulation of Thymus capitatus essential oil: Formulation process, physical stability characterization and antibacterial efficiency monitoring. Ind. Crop Prod. 2018, 113, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G.; Pavela, R. Beyond mosquitoes-essential oil toxicity and repellency against bloodsucking insects. Ind. Crop Prod. 2018, 117, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatgheib, N.; Fournel, C.; Calvez, S.; Pouliquen, H.; Moreau, E. In vitro antimicrobial effect of various commercial essential oils and their chemical constituents on Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabraie, M.; Vu, K.D.; Tata, L.; Salmieri, S.; Lacroix, M. Antimicrobial effect of essential oils in combinations against five bacteria and their effect on sensorial quality of ground meat. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, X.G.; Xiao, Z.B.; Bi, W.C. Effect of chitosan nanoparticles loaded with cinnamon essential oil on the quality of chilled pork. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Rojas-Grau, M.A.; Soliva-Fortuny, R.; Martin-Belloso, O. Impact of microfluidization or ultrasound processing on the antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli of lemongrass oil-loaded nanoemulsions. Food Control. 2014, 37, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla-Carvajal, M.X.; Camacho-Diaz, B.H.; Meraz-Torres, L.S.; Chanona-Perez, J.J.; Alamilla-Beltran, L.; Jimenez-Aparicio, A.; Gutierrez-Lopez, G.F. Nanoencapsulation: A new trend in food engineering processing. Food Eng. Rev. 2010, 2, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Liu, A.P.; Hu, A.X.; Li, J.X.; Zen, Z.; Liu, Y.T.; Tang, S.Y.; Li, C. Preparation and characterization of cinnamon essential oil nanocapsules and comparison of volatile components and antibacterial ability of cinnamon essential oil before and after encapsulation. Food Control. 2021, 123, 107783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ni, Z.J.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.G.; Hu, F.; Wei, Z.J. Preparation and characterization of clove essential oil loaded nanoemulsion and pickering emulsion activated pullulan-gelatin based edible film. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.Q.; Xu, G.W.; Zeng, H.W.; Zheng, X.F.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Q.Y.; Yang, Z.Q.; Jiao, X.A. Physicochemical and antibacterial properties of fabricated ovalbumin-carvacrol gel nanoparticles. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5133–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.L.; Xu, K.; Shu, M.; Liu, N.; Li, N.; Chen, X.Y.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O.; Jiang, F.T. Fabrication of iron loaded whey protein isolate/gum arabic nanoparticles and its adsorption activity on oil-water interface. Food Hydrocolloid. 2021, 115, 106610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamtu, I.; Rusu, A.G.; Diaconu, A.; Nita, L.E.; Chiriac, A.P. Basic concepts and recent advances in nanogels as carriers for medical applications. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas, D.M.; Pascual, G.N.; Wagner, J.R.; Palazolo, G.G. Nanoparticles assembled from mixtures of whey protein isolate and soluble soybean polysaccharides. Structure, interfacial behavior and application on emulsions subjected to freeze-thawing. Food Hydrocolloid. 2019, 95, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.L.; Guan, Y.; Wen, H.D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.B.; Zhang, T. Mild heating assisted alkaline ph shifting modify the egg white protein: The mechanism and the enhancement of emulsifying properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.S.; Li, Y.Y.; Ren, Y.X. Research on the phosphorylation of soy protein isolate with sodium tripoly phosphate. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.F.; Dai, L.; Mao, L.K.; Liu, J.F.; Yuan, F.; Li, Z.G.; Gao, Y.X. Effect of sodium tripolyphosphate incorporation on physical, structural, morphological and stability characteristics of zein and gliadin nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, H.; Li, C.P. Improvement of antioxidant activity of egg white protein by phosphorylation and conjugation of epigallocatechin gallate. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Li, X.Y. A unified model for quantification of concentration polarization (cp) of particles during cross-flow membrane filtration. Colloid Surface A 2012, 407, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedzianka, J.; Peksa, A. Effect of ph on phosphorylation of potato protein isolate. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2321–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.M.; Yang, X.Q.; Wu, N.N.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, J.M.; Guo, J.; Yin, S.W. Protein-based pickering emulsion and oil gel prepared by complexes of zein colloidal particles and stearate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2672–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharbi, N.; Labbafi, M. Effect of processing on aggregation mechanism of egg white proteins. Food Chem. 2018, 252, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewmanee, T.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W. Effect of NaCl on thermal aggregation of egg white proteins from duck egg. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.B.; da Costa, A.R.; Garcia-Rojas, E.E. Heteroprotein complex coacervates of ovalbumin and lysozyme: Formation and thermodynamic characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.M.; Bourassa, M.W.; Smith, R.J. FTIR spectroscopic imaging of protein aggregation in living cells. BBA-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.S.; Sun, Z.; Ma, M.H.; Jin, Y.G.; Sheng, L. Effect of microwave-assisted phosphorylation modification on the structural and foaming properties of egg white powder. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 97, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, K.; Markova, N. Value of DSC in characterization and optimization of protein stability. Biol Methods Protoc. 2019, 1964, 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.X.; Chen, T.; Lin, H.H.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.H.; Lyu, F.; Ding, Y.T. Physicochemical properties and microstructure of surimi treated with egg white modified by tea polyphenols. Food Hydrocolloid. 2019, 90, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Chi, Y.J. Microwave-assisted phosphorylation of soybean protein isolates and their physicochemical properties. Czech J. Food Sci. 2012, 30, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.Y.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Low-field NMR study of heat-induced gelation of pork myofibrillar proteins and its relationship with microstructural characteristics. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.T.; Yu, J.L.; Lu, L.Z.; Fu, X.; Cai, Z.X. Interfacial and enhanced emulsifying behavior of phosphorylated ovalbumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raikos, V. Effect of heat treatment on milk protein functionality at emulsion interfaces. A review. Food Hydrocolloid. 2010, 24, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicorescu, I.; Loisel, C.; Vial, C.; Riaublanc, A.; Djelveh, G.; Cuvelier, G.; Legrand, J. Combined effect of dynamic heat treatment and ionic strength on denaturation and aggregation of whey proteins – Part I. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.J.; Kwon, Y.J. Characterization of β-carotene nanoemulsions prepared by microfluidization technique. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Choi, S.J.; Li, Y.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Protein-stabilized nanoemulsions and emulsions: Comparison of physicochemical stability, lipid oxidation, and lipase digestibility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Qiu, L.; Sun, Y.; Xiong, H.; Ogra, Y. Improvement of the solubility and emulsifying properties of rice bran protein by phosphorylation with sodium trimetaphosphate. Food Hydrocolloid. 2019, 96, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.Y.; Chen, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Lin, X.R.; Li, B. Novel food-grade Pickering emulsions stabilized by tea water-insoluble protein nanoparticles from tea residues. Food Hydrocolloid. 2019, 96, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudzadeh, P.; Aliakbarlu, J.; Moradi, M. Preparation and antibacterial performance of cinnamon essential oil nanoemulsion on milk foodborne pathogens. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2022, 75, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, N.G.; Croda, J.; Simionatto, S. Antibacterial mechanisms of cinnamon and its constituents: A review. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 120, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azeredo, H.M.C. Antimicrobial nanostructures in food packaging. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2013, 30, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Jiang, P.P.; Quek, S. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of cinnamon essential oil against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control. 2016, 59, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penalver, P.; Huerta, B.; Borge, C.; Astorga, R.; Romero, R.; Perea, A. Antimicrobial activity of five essential oils against origin strains of the Enterobacteriaceae family. Apmis 2005, 113, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Jin, P.P.; Gong, H.S.; Sun, Z.L.; Du, L.H.; Wang, D.Y. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of thyme oil against foodborne multiple antibiotics-resistant Enterococcus faecalis. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5127–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.Q.; Xu, G.W.; Lu, X.N.; Zhang, R.Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, Q.Y.; Yang, Z.Q.; Jiao, X.A. Characterization of ovalbumin-carvacrol inclusion complexes as delivery systems with antibacterial application. Food Hydrocolloid. 2020, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.C.; Harris, P.; Kaur, A.; Pastrana, L.; Jauregi, P. Characterisation of β-lactoglobulin nanoparticles and their binding to caffeine. Food Hydrocolloid. 2017, 71, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Batool, Z.; Cai, Z.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Ma, M.H.; Sheng, L.; Jin, Y.G. Production of self-assembling acylated ovalbumin nanogels as stable delivery vehicles for curcumin. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumival, P.; Tadtong, S.; Athikomkulchai, S.; Chittasupho, C. Antifungal activity and the chemical and physical stability of microemulsions containing Citrus hystrix DC leaf oil. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X20957755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, W.L.; Gu, W.; Lu, S.S.; Chen, Z.P.; Cai, B.C.; Yang, X.X. Drug-in-cyclodextrin-inliposomes: A promising delivery system for hydrophobic drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Del. 2014, 11, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H.; Qian, C.; Xu, H.J.; Huang, Y.J. Antibacterial activity of Artemisia asiatica essential oil against some common respiratory infection causing bacterial strains and its mechanism of action in Haemophilus influenzae. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Name | Particle Size/nm | PDI | Zeta/mV | EE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EWP-CBEO | 378.8 ± 28.38 b | 0.418 ± 0.102 b | −24.3 ± 0.416 a | 78.34 ± 2.88% a |
| P-EWP-CBEO | 133.55 ± 0.836 a | 0.265 ± 0.006 a | −35.4 ± 0.057 b | 93.79 ± 1.93% b |
| Samples | TO (°C) | Td (°C) | Tp (°C) | △H (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-EWP-CBEO | 53.65 | 105.68 | 82.08 | 43.876 |
| EWP-CBEO | 52.66 | 106.68 | 81.12 | 84.107 |
| CBEO | 260.77 | 273.43 | 267.02 | 217.123 |
| N-EWP | 70.53 | 104.34 | 87.82 | 201.965 |
| Strain | CBEO (mg/mL) | EWP-CBEO | P-EWP-CBEO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | 0.5 b | 1.0 a | 0.5 b |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 1.0 a | 1.0 a | 0.5 b |
| Listeria monocytogenes | 1.0 a | 1.0 a | 0.5 b |
| Sample | Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm), Disk Diameter 6.0 mm Was Included | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 h | 24 h | 36 h | 48 h | 60 h | 72 h | |
| Escherichia coli | ||||||
| CBEO | 20.38 ± 3.33 a | 20.38 ± 3.47 b | 20.83 ± 2.02 ab | 20.50 ± 2.65 ab | 17.83 ± 0.29 b | 11.83 ± 1.44 c |
| EWP-CBEO | 18.50 ± 2.31 b | 18.50 ± 3.47 b | 18.83 ± 2.02 b | 18.00 ± 2.29 b | 18.67 ± 1.53 b | 15.27 ± 0.25 b |
| P-EWP-CBEO | 22.75 ± 2.22 a | 21.13 ± 1.60 a | 21.50 ± 2.00 a | 22.50 ± 2.78 a | 21.33 ± 0.58 a | 17.10 ± 1.53 a |
| Staphylococcus aureus | ||||||
| CBEO | 16.88 ± 1.25 b | 16.13 ± 0.63 b | 16.50 ± 0.91 b | 15.50 ± 0.71 b | 13.75 ± 2.06 b | 10.83 ± 1.61 b |
| EWP-CBEO | 17.05 ± 0.42 b | 16.13 ± 0.63 b | 16.25 ± 0.96 b | 14.75 ± 0.50 b | 12.88 ± 1.03 b | 10.38 ± 0.48 b |
| P-EWP-CBEO | 21.20 ± 0.87 a | 21.38 ± 1.37 a | 19.75 ± 2.63 a | 20.00 ± 2.94 a | 16.00 ± 2.31 a | 13.25 ± 1.50 a |
| Listeria monocytogenes | ||||||
| CBEO | 15.75 ± 0.65 b | 15.75 ± 0.65 b | 15.17 ± 1.26 b | 13.33 ± 0.29 c | 11.07 ± 0.29 c | 10.50 ± 1.00 c |
| EWP-CBEO | 14.50 ± 0.77 b | 15.25 ± 0.65 b | 15.00 ± 0.50 b | 14.50 ± 0.20 b | 13.17 ± 0.29 b | 13.67 ± 0.29 b |
| P-EWP-CBEO | 19.63 ± 1.43 a | 18.25 ± 0.65 a | 17.67 ± 0.76 a | 15.83 ± 2.02 a | 15.17 ± 0.29 a | 15.33 ± 0.76 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, S.-Q.; Gao, X.-R.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.-R.; Yang, Z.-Q. Contribution of Phosphorylation Modification to Stability and Antibacterial Activity of Egg White Protein Nanogels Loaded with Cinnamon Bark Essential Oil. Gels 2025, 11, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11010012
Rao S-Q, Gao X-R, Liu H, Wang Z-R, Yang Z-Q. Contribution of Phosphorylation Modification to Stability and Antibacterial Activity of Egg White Protein Nanogels Loaded with Cinnamon Bark Essential Oil. Gels. 2025; 11(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Sheng-Qi, Xin-Ru Gao, Hui Liu, Zhi-Rong Wang, and Zhen-Quan Yang. 2025. "Contribution of Phosphorylation Modification to Stability and Antibacterial Activity of Egg White Protein Nanogels Loaded with Cinnamon Bark Essential Oil" Gels 11, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11010012
APA StyleRao, S.-Q., Gao, X.-R., Liu, H., Wang, Z.-R., & Yang, Z.-Q. (2025). Contribution of Phosphorylation Modification to Stability and Antibacterial Activity of Egg White Protein Nanogels Loaded with Cinnamon Bark Essential Oil. Gels, 11(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11010012






