Biomedical Trends in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Emphasis on Chitosan-Based Formulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
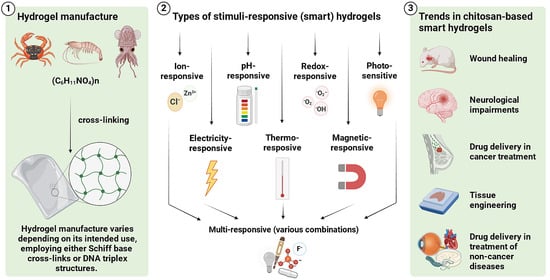
2. Manufacture, Structure, and Administration of Hydrogels
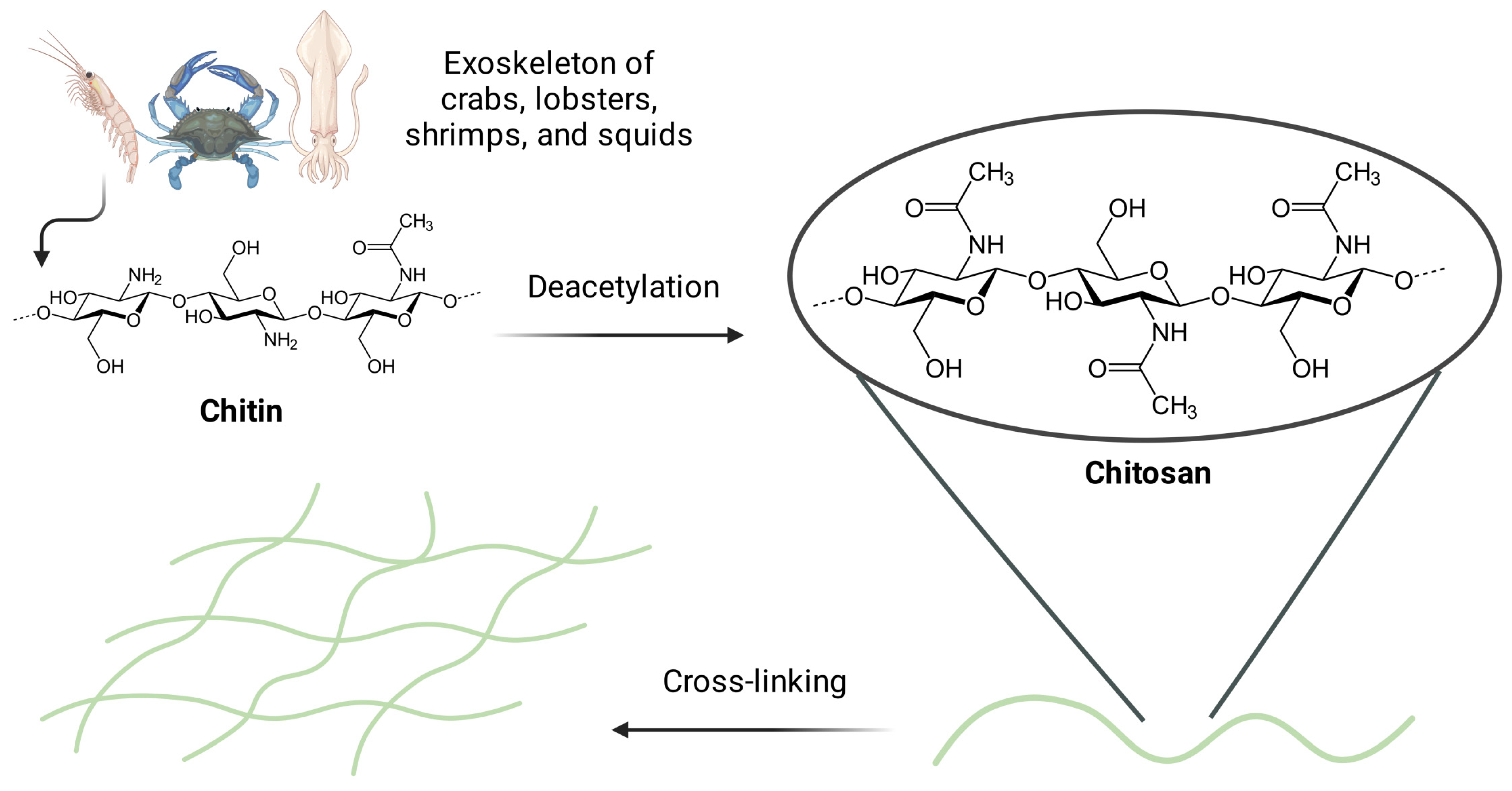
2.1. Manufacturing Hydrogels
2.2. Structure of Chitosan and the Process of Obtaining Hydrogels
2.3. Routes of Administering Hydrogels
2.4. Advantages of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels
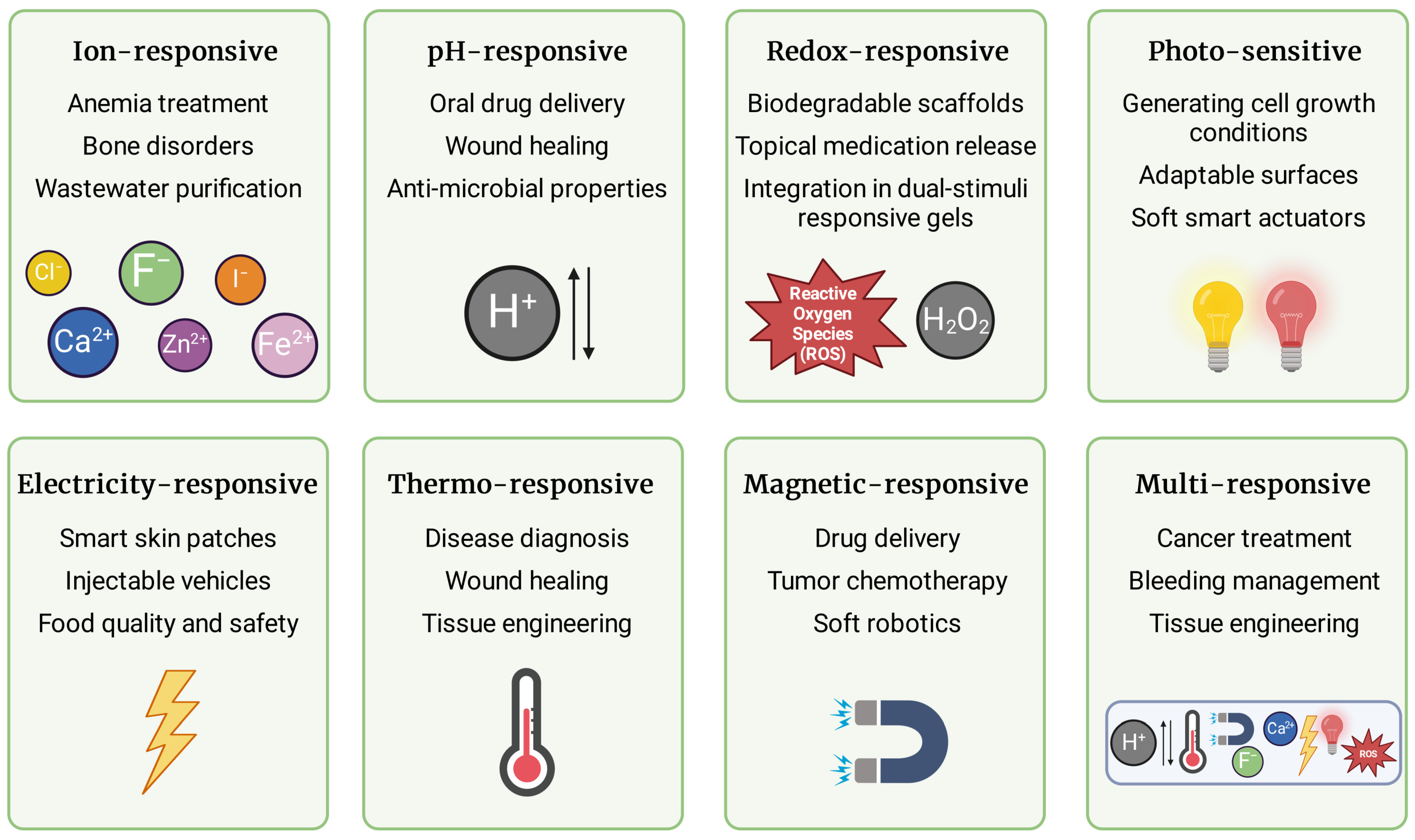
3. Selected Types of Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels
3.1. Ion-Responsive Hydrogels
3.2. pH-Responsive Hydrogels
3.3. Redox-Responsive Hydrogels
3.4. Photo-Sensitive Hydrogels
3.5. Electricity-Responsive Hydrogels
3.6. Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels
3.7. Magnetic-Responsive Hydrogels
3.8. Multi-Responsive Hydrogels
4. Current Trends in the Biomedical Application of Stimuli-Responsive Chitosan-Based Hydrogels
4.1. Wound Healing
4.2. Neurological Impairments
4.3. Tissue Engineering
4.4. Drug Delivery in Cancer Treatment
4.5. Drug Delivery in the Treatment of Non-Cancer Diseases
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vallet-Regí, M. Evolution of Biomaterials. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 864016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshangiti, D.M.; El-Damhougy, T.K.; Zaher, A.; Madani, M.; Mohamady Ghobashy, M. Revolutionizing biomedicine: Advancements, applications, and prospects of nanocomposite macromolecular carbohydrate-based hydrogel biomaterials: A review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 35251–35291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, A.M.; Frazar, E.M.; Klaus, M.V.X.; Paul, P.; Hilt, J.Z. Hydrogels and Hydrogel Nanocomposites: Enhancing Healthcare through Human and Environmental Treatment. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2101820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.L.; Yu, A.C.; Agmon, G.; Appel, E.A. Supramolecular polymeric biomaterials. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 6, 10–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Liu, L.; He, G.; Zhang, T.; Yang, M.; Cai, J.; Fan, L.; Tao, S. Preparation and properties of carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosinski, K.K.; Wach, R.A.; Girek-Bak, M.K.; Rokita, B.; Kolat, D.; Kaluzinska-Kolat, Z.; Klosinska, B.; Duda, L.; Pasieka, Z.W. Biocompatibility and Mechanical Properties of Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogels. Polymers 2022, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, S.H.; Narendrakumar, U.; Manjubala, I. Commercial hydrogels for biomedical applications. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.A.; Rangappa, S.M.; Siengchin, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J. Natural polymers and the hydrogels prepared from them. In Hydrogels Based on Natural Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 17–47. [Google Scholar]
- Contessotto, P.; Orbanic, D.; Da Costa, M.; Jin, C.; Owens, P.; Chantepie, S.; Chinello, C.; Newell, J.; Magni, F.; Papy-Garcia, D.; et al. Elastin-like recombinamers-based hydrogel modulates post-ischemic remodeling in a non-transmural myocardial infarction in sheep. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaaz5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitura, S.; Sionkowska, A.; Jaiswal, A. Biopolymers for hydrogels in cosmetics: Review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2020, 31, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Hoque, M.; Taharat, S.F. Recent advances in extraction of chitin and chitosan. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 39, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherng, J.H.; Lin, C.J.; Liu, C.C.; Yeh, J.Z.; Fan, G.Y.; Tsai, H.D.; Chung, C.F.; Hsu, S.D. Hemostasis and Anti-Inflammatory Abilities of AuNPs-Coated Chitosan Dressing for Burn Wounds. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Cherng, J.H.; Liu, C.C.; Fang, T.J.; Hong, Z.J.; Chang, S.J.; Fan, G.Y.; Hsu, S.D. Procoagulant and Antimicrobial Effects of Chitosan in Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Zeng, Y.; Zaldivar-Silva, D.; Aguero, L.; Wang, S. Chitosan-Based Hemostatic Hydrogels: The Concept, Mechanism, Application, and Prospects. Molecules 2023, 28, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Song, R.; Johnson, M.; A, S.; Shen, P.; Zhang, N.; Lara-Saez, I.; Xu, Q.; Wang, W. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Infected Wound Treatment. Macromol. Biosci. 2023, 23, e2300094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, N.H.N.; Truong, Q.T.; Le, P.K.; Ha, A.C. Recent developments in chitosan hydrogels carrying natural bioactive compounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 294, 119726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Shang, Y.; Nuri Ertas, Y.; Orive, G. Chitosan-functionalized bioplatforms and hydrogels in breast cancer: Immunotherapy, phototherapy and clinical perspectives. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.M. Current Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels as Smart Drug Delivery Carriers. Gels 2023, 9, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoque, J.; Sangaj, N.; Varghese, S. Stimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Hydrogels and Their Applications in Regenerative Medicine. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, e1800259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Han, L. Recent developments in stimuli-responsive hydrogels for biomedical applications. Biosurf. Biotribol. 2022, 8, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, K.; Raorane, C.J.; Ramkumar, V.; Ulagesan, S.; Santhamoorthy, M.; Raj, V.; Krishnakumar, G.S.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, S.C. Update on Chitosan-Based Hydrogels: Preparation, Characterization, and Its Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Applications. Gels 2022, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.C.; Chang, C.C.; Chan, H.P.; Chung, T.W.; Shu, C.W.; Chuang, K.P.; Duh, T.H.; Yang, M.H.; Tyan, Y.C. Hydrogels: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminabhavi, T.M.; Dharupaneedi, S.P. Production of chitosan-based hydrogels for biomedical applications. In Chitosan Based Biomaterials Volume 1; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 295–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, N.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, T. Dynamic Covalent Polymer Networks: A Molecular Platform for Designing Functions beyond Chemical Recycling and Self-Healing. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1716–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, J.; Ponsford, D.; Dreiss, C.A.; Lee, T.C.; Loh, X.J. Supramolecular Hydrogels: Design Strategies and Contemporary Biomedical Applications. Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S.; Ji, S.M.; Park, M.J.; Suneetha, M.; Uthappa, U.T. Pectin Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery Applications: A Mini Review. Gels 2022, 8, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maric, I.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Santiago, G.M.; Pappas, C.G.; Qiu, X.; Dijksman, J.A.; Mikhailov, K.; van Rijn, P.; Otto, S. Tailorable and Biocompatible Supramolecular-Based Hydrogels Featuring two Dynamic Covalent Chemistries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023, 62, e202216475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Yi, S.; Chen, X. Visible-light/temperature dual-responsive hydrogel constructed by alpha-cyclodextrin and an azobenzene linked surfactant. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 6490–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, W.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, H. High-Preservation Single-Cell Operation through a Photo-responsive Hydrogel-Nanopipette System. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 5157–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qin, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Lv, H.; Yang, X. On-demand removable hydrogels based on photolabile cross-linkings as wound dressing materials. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 5669–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabb, C.P.; O’Bryan, C.S.; Deng, C.C.; Angelini, T.E.; Sumerlin, B.S. Photoreversible Covalent Hydrogels for Soft-Matter Additive Manufacturing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16793–16801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; An, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Hu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, F.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Sustained-release of PDGF from PLGA microsphere embedded thermo-sensitive hydrogel promoting wound healing by inhibiting autophagy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S.L.; Huynh, T.H.; Poschko, P.; Fruergaard, A.S.; Jarlstad Olesen, M.T.; Chen, Y.; Birkedal, H.; Subbiahdoss, G.; Reimhult, E.; Thogersen, J.; et al. Remotely Triggered Liquefaction of Hydrogel Materials. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9145–9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, M.; Niu, W.; Winston, D.D.; Cheng, W.; Lei, B. Injectable biodegradation-visual self-healing citrate hydrogel with high tissue penetration for microenvironment-responsive degradation and local tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2020, 261, 120301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.S.; Hu, Y.; Willner, I. Stimuli-Responsive DNA-Based Hydrogels: From Basic Principles to Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Khan, I.; Chen, J.; Akhtar, K.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, S.B. Emerging Fabrication Strategies of Hydrogels and Its Applications. Gels 2022, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jung, Y.; Lee, N.; Lee, I.; Lee, J.H. Nature-Derived Polysaccharide-Based Composite Hydrogels for Promoting Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantha, S.; Pillai, S.; Khayambashi, P.; Upadhyay, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, O.; Pham, H.M.; Tran, S.D. Smart Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Materials 2019, 12, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Meng, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, K. Chitosan Derivatives and Their Application in Biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelu, M.; Musuc, A.M.; Popa, M.; Calderon Moreno, J.M. Chitosan Hydrogels for Water Purification Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarrou, M.; Mitraki, A.; Vamvakaki, M.; Kokotidou, C. Stimuli-Responsive Polysaccharide Hydrogels and Their Composites for Wound Healing Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.C.; Shukla, S.; Skoog, S.A.; Boehm, R.D.; Narayan, R.J. Current Advancements in Transdermal Biosensing and Targeted Drug Delivery. Sensors 2019, 19, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, D.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Zhuang, W.; Yang, X. Intra-articular Injection of Chitosan-Based Supramolecular Hydrogel for Osteoarthritis Treatment. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Zeng, F.; Yu, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Ding, N.; Tian, J.; Li, C. Oral hydrogel nanoemulsion co-delivery system treats inflammatory bowel disease via anti-inflammatory and promoting intestinal mucosa repair. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, J.; Hu, W.; Tian, R.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Optimization and evaluation of a thermoresponsive ophthalmic in situ gel containing curcumin-loaded albumin nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedford, J.G.; Caminschi, I.; Wakim, L.M. Intranasal Delivery of a Chitosan-Hydrogel Vaccine Generates Nasal Tissue Resident Memory CD8(+) T Cells That Are Protective against Influenza Virus Infection. Vaccines 2020, 8, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosecka, M.; Gosecki, M. Antimicrobial Polymer-Based Hydrogels for the Intravaginal Therapies-Engineering Considerations. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, R.; Sanshita; Kumar, A.; Vishvakarma, V.; Huanbutta, K.; Singh, I.; Sangnim, T. Advancements in Rectal Drug Delivery Systems: Clinical Trials, and Patents Perspective. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taokaew, S.; Kaewkong, W.; Kriangkrai, W. Recent Development of Functional Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariatinia, Z.; Jalali, A.M. Chitosan-based hydrogels: Preparation, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 194–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorov, A.R.; Kirichuk, A.A.; Rubanik, V.V.; Rubanik, V.V., Jr.; Tskhovrebov, A.G.; Kritchenkov, A.S. Chitosan and Its Derivatives: Preparation and Antibacterial Properties. Materials 2023, 16, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F.; Oveisi, Z.; Samani, S.M.; Amoozgar, Z. Chitosan based hydrogels: Characteristics and pharmaceutical applications. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zavyalova, O.; Gajewska, S.; Dąbrowska-Wisłocka, D.; Sionkowska, A. Characteristics of physicochemical and rheological properties of chitosan hydrogels based on selected hydroxy acids. Eng. Biomater. 2021, 24, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, B.B.; Saibi, S.; Haroune, L.; Rios, N.S.; Goncalves, L.R.B.; Cabana, H. Genipin and glutaraldehyde based laccase two-layers immobilization with improved properties: New biocatalysts with high potential for enzymatic removal of trace organic contaminants. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2023, 169, 110261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedzierska, M.; Jamrozy, M.; Drabczyk, A.; Kudlacik-Kramarczyk, S.; Bankosz, M.; Gruca, M.; Potemski, P.; Tyliszczak, B. Analysis of the Influence of Both the Average Molecular Weight and the Content of Crosslinking Agent on Physicochemical Properties of PVP-Based Hydrogels Developed as Innovative Dressings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drabczyk, A.; Kudlacik-Kramarczyk, S.; Glab, M.; Kedzierska, M.; Jaromin, A.; Mierzwinski, D.; Tyliszczak, B. Physicochemical Investigations of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels Containing Aloe Vera Designed for Biomedical Use. Materials 2020, 13, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farasati Far, B.; Omrani, M.; Naimi Jamal, M.R.; Javanshir, S. Multi-responsive chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled release of vincristine. Commun. Chem. 2023, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Kim, I.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kim, Y.; Chung, J.J.; Kim, S.W. Comparative Analysis of Antibacterial and Wound Healing Activities of Chitosan and Povidone-Iodine-Based Hydrogels. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2024, 92, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyliszczak, B.; Drabczyk, A.; Kudlacik, S. Comparison of Hydrogels Based on Commercial Chitosan and Beetosan® Containing Nanosilver. Molecules 2016, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, R.; Yousefi, A. Effects of Aloe Vera and Chitosan Nanoparticle Thin-Film Membranes on Wound Healing in Full Thickness Infected Wounds with Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Bull. Emerg. Trauma. 2018, 6, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudko, M.; Urbaniak, T.; Musial, W. Recent Developments in Ion-Sensitive Systems for Pharmaceutical Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, I.R.; Gamble, G.D.; Bolland, M.J. Circulating calcium concentrations, vascular disease and mortality: A systematic review. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 279, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portbury, S.D.; Adlard, P.A. Zinc Signal in Brain Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacon, A.; Albota, F.; Mocanu, A.; Brincoveanu, O.; Podaru, A.I.; Rotariu, T.; Ahmad, A.A.; Rusen, E.; Toader, G. Dual-Responsive Hydrogels for Mercury Ion Detection and Removal from Wastewater. Gels 2024, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cui, W.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y. Supramolecular self-assembly of two-component systems comprising aromatic amides/Schiff base and tartaric acid. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, R.; Zheng, R.; Huang, Y. Anions-responsive supramolecular gels: A review. Mater. Des. 2021, 205, 109759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.S.; Ahmad, M.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Mahmood, A.; Barkat, K.; Khan, M.T.; Tulain, U.R.; Rashid, A. beta-cyclodextrin chitosan-based hydrogels with tunable pH-responsive properties for controlled release of acyclovir: Design, characterization, safety, and pharmacokinetic evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Liu, S.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, and Biomedical Application of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Polymers 2023, 15, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, C.; Jian, Y.; Deng, H.; Du, Y.; Shi, X. Ion-responsive chitosan hydrogel actuator inspired by carrotwood seed pod. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 276, 118759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegad, U.; Patel, M.; Khunt, D.; Zupancic, O.; Chauhan, S.; Paudel, A. pH stimuli-responsive hydrogels from non-cellulosic biopolymers for drug delivery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1270364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Ullah, H.; Vu, Q.L.; Khan, A.; Tsai, M.J.; Wu, P.C. Preparation of pH-Responsive Hydrogels Based on Chondroitin Sulfate/Alginate for Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Paschew, G.; Klatt, S.; Lienig, J.; Arndt, K.F.; Adler, H.P. Review on Hydrogel-based pH Sensors and Microsensors. Sensors 2008, 8, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Yahya, R.; Hassan, A.; Yar, M.; Azzahari, A.D.; Selvanathan, V.; Sonsudin, F.; Abouloula, C.N. pH Sensitive Hydrogels in Drug Delivery: Brief History, Properties, Swelling, and Release Mechanism, Material Selection and Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofridam, F.; Tarhini, M.; Lebaz, N.; Gagnière, É.; Mangin, D.; Elaissari, A. pH-sensitive polymers: Classification and some fine potential applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1455–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woraphatphadung, T.; Sajomsang, W.; Rojanarata, T.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Tonglairoum, P.; Opanasopit, P. Development of Chitosan-Based pH-Sensitive Polymeric Micelles Containing Curcumin for Colon-Targeted Drug Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, S.; Rasool, A.; Islam, A.; Bibi, I.; Rizwan, M.; Azeem, M.K.; Qureshi, A.U.R.; Iqbal, M. Loading of Cefixime to pH sensitive chitosan based hydrogel and investigation of controlled release kinetics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mahrouk, G.M.; Aboul-Einien, M.H.; Makhlouf, A.I. Design, Optimization, and Evaluation of a Novel Metronidazole-Loaded Gastro-Retentive pH-Sensitive Hydrogel. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezati, P.; Rhim, J.-W. pH-responsive chitosan-based film incorporated with alizarin for intelligent packaging applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauler Riera, P.; Volterrani, M.; Iellamo, F.; Fallo, F.; Ermolao, A.; Kraemer, W.J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Faigenbaum, A.; Philp, A.; Baar, K. Redox Status. In Encyclopedia of Exercise Medicine in Health and Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 751–753. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Liu, Y. Redox-responsive hydrogels. In Biopolymer-Based Composites; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Abed, H.F.; Abuwatfa, W.H.; Husseini, G.A. Redox-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems: A Chemical Perspective. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhang, S.; Wei, C.; Xu, Y.; Lu, W. ROS-responsive selenium-containing polyphosphoester nanogels for activated anticancer drug release. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 9, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Peng, F.; Cai, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, P. Redox dual-stimuli responsive drug delivery systems for improving tumor-targeting ability and reducing adverse side effects. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, K. Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.T.; Yadav, S.; Reddy, O.S.; Jo, S.H.; Joo, S.B.; Kim, B.K.; Park, E.J.; Park, S.H.; Lim, K.T. Reduction-Responsive Chitosan-Based Injectable Hydrogels for Enhanced Anticancer Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.; Dai, C.; Cao, P.; Sun, D.; Ouyang, R.; Miao, Y. The role of reactive oxygen species in tumor treatment. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 7740–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, M.; Yuan, J.; Tao, L.; Wei, Y. Redox-responsive polymers for drug delivery: From molecular design to applications. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, T.; Wu, L. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Bioelectronic Sensing: Recent Advances and Applications in Biomedicine and Food Safety. Biosensors 2023, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, F.; Roca-Melendres, M.M.; Duran-Lara, E.F.; Rafael, D.; Schwartz, S., Jr. Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels for Cancer Treatment: The Role of pH, Light, Ionic Strength and Magnetic Field. Cancers 2021, 13, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Zeng, B.; Yang, W. Light responsive hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1075670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomatsu, I.; Peng, K.; Kros, A. Photoresponsive hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Liu, H.; Tang, D.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, F. Bioactuators based on stimulus-responsive hydrogels and their emerging biomedical applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2019, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Duan, L.; Kong, M.; Wen, X.; Guan, F.; Ma, S. Applications and Mechanisms of Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels in Traumatic Brain Injury. Gels 2022, 8, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Svirskis, D.; Rees, S.W.P.; Barker, D.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wu, Z. Photosensitive drug delivery systems for cancer therapy: Mechanisms and applications. J. Control Release 2021, 338, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasinski, A.; Zielinska-Pisklak, M.; Oledzka, E.; Sobczak, M. Smart Hydrogels-Synthetic Stimuli-Responsive Antitumor Drug Release Systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4541–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Scheiger, J.M.; Levkin, P.A. Design and Applications of Photoresponsive Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1807333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azagarsamy, M.A.; McKinnon, D.D.; Alge, D.L.; Anseth, K.S. Coumarin-Based Photodegradable Hydrogel: Design, Synthesis, Gelation, and Degradation Kinetics. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.R.; Yong, K.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Cowie, A.C. Recent advances in photo-crosslinkable hydrogels for biomedical applications. Biotechniques 2019, 66, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Wu, Q.; Han, X.; Zhang, W.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Huang, W. Photosensitive hydrogels: From structure, mechanisms, design to bioapplications. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 1813–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, F.; Qiu, P.; Wang, Y.; Ren, P.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Gou, D. Chitosan-based hydrogels: From preparation to applications, a review. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Chitosan-based electroactive hydrogel. Polymer 2008, 49, 5520–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, B.; Zarrintaj, P.; Surwase, S.S.; Baheiraei, N.; Saeb, M.R.; Mozafari, M.; Kim, Y.C.; Park, O.O. Self-gelling electroactive hydrogels based on chitosan-aniline oligomers/agarose for neural tissue engineering with on-demand drug release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 184, 110549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.H.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Chung, B.G. Electro-Responsive Conductive Blended Hydrogel Patch. Polymers 2023, 15, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Gu, X.; Ding, J.; Lv, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Xu, W. Advances in preparation, design strategy and application of electroactive hydrogels. J. Power Sources 2023, 581, 233485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peers, S.; Montembault, A.; Ladaviere, C. Chitosan hydrogels for sustained drug delivery. J. Control Release 2020, 326, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Valle, L.J.; Diaz, A.; Puiggali, J. Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: Cellulose, Chitosan, and Protein/Peptide Derivatives. Gels 2017, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiz-Fernandez, S.; Perez-Alvarez, L.; Silvan, U.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. pH-Induced 3D Printable Chitosan Hydrogels for Soft Actuation. Polymers 2022, 14, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Xue, K.; Loh, X.J. Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels: From Recent Progress to Biomedical Applications. Gels 2021, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Song, S.; Zheng, A. Thermosensitive Hydrogels and Advances in Their Application in Disease Therapy. Polymers 2022, 14, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazar, E.M.; Shah, R.A.; Dziubla, T.D.; Hilt, J.Z. Multifunctional temperature-responsive polymers as advanced biomaterials and beyond. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z. Thermo-sensitive hydrogels for delivering biotherapeutic molecules: A review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Chen, X.; Tan, H. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels: From Polymer to Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.J.; Tomlins, P.; Sahota, T.S. Thermoresponsive Gels. Gels 2017, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, E.; Schilling, A.L.; Little, S.R.; Decuzzi, P. Injectable thermoresponsive hydrogels as drug delivery system for the treatment of central nervous system disorders: A review. J. Control Release 2021, 329, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhu, C.; Li, B.; Wang, T.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, D.; Shen, Y. Improving the Anti-Ovarian Cancer Activity of Docetaxel by Self-Assemble Micelles and Thermosensitive Hydrogel Drug Delivery System. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2020, 16, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.; Farooq, M.A.; Parveen, A. Thermosensitive Chitosan-Based Injectable Hydrogel as an Efficient Anticancer Drug Carrier. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20450–20460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Husseiny, H.M.; Mady, E.A.; El-Dakroury, W.A.; Doghish, A.S.; Tanaka, R. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels: Smart state of-the-art platforms for cardiac tissue engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1174075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Han, W.J.; Jang, H.S.; Choi, H.J. Highly Tough, Biocompatible, and Magneto-Responsive Fe3O4/Laponite/PDMAAm Nanocomposite Hydrogels. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Cheng, Y. Magnetic-responsive hydrogels: From strategic design to biomedical applications. J. Control Release 2021, 335, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yin, H.; Chu, J.; Eglin, D.; Serra, T.; Docheva, D. An anisotropic nanocomposite hydrogel guides aligned orientation and enhances tenogenesis of human tendon stem/progenitor cells. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, P.; Liang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Duan, L.; Liu, W.; Zhu, F.; Bian, L.; et al. Magnetic Enhancement of Chondrogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 2200–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antman-Passig, M.; Shefi, O. Remote Magnetic Orientation of 3D Collagen Hydrogels for Directed Neuronal Regeneration. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2567–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, K.; Niu, Z.; Zou, S.; Zhang, D.; Qian, Z.; Liao, J.; Xie, J. Hydrogel platform with tunable stiffness based on magnetic nanoparticles cross-linked GelMA for cartilage regeneration and its intrinsic biomechanism. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 25, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Iwanaga, A.; Shirosaki, Y.; Kawashita, M. In situ synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in chitosan hydrogels as a reaction field: Effect of cross-linking density. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 179, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadban, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Ping, Y.; Ramos, R.; Arfin, N.; Cantaert, B.; Ramanujan, R.V.; Miserez, A. Bioinspired pH and magnetic responsive catechol-functionalized chitosan hydrogels with tunable elastic properties. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Hosta-Rigau, L.; Chandrawati, R.; Cui, J. Multi-Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Particles, Films, and Hydrogels for Drug Delivery. Chem 2018, 4, 2084–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Q.; Wang, G.J. Multi-Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Materials: Particles, Films, and Bulk Gels. Chem. Rec. 2016, 16, 1398–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yuan, P.; Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C. Advances in the Research and Application of Smart-Responsive Hydrogels in Disease Treatment. Gels 2023, 9, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Heydarpour, R.; Tehrani, Z.M. Multi-stimuli-responsive hydrogels and their medical applications. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 15705–15717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, W.; Liu, H. Fabrication of chitosan functionalized dual stimuli-responsive injectable nanogel to control delivery of doxorubicin. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2023, 301, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Husseiny, H.M.; Mady, E.A.; Doghish, A.S.; Zewail, M.B.; Abdelfatah, A.M.; Noshy, M.; Mohammed, O.A.; El-Dakroury, W.A. Smart/stimuli-responsive chitosan/gelatin and other polymeric macromolecules natural hydrogels vs. synthetic hydrogels systems for brain tissue engineering: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari Maroufi, L.; Ghorbani, M. Injectable chitosan-quince seed gum hydrogels encapsulated with curcumin loaded-halloysite nanotubes designed for tissue engineering application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, P.C.; Zhang, Y.; Abebe, F. Recent Applications of Dual-Stimuli Responsive Chitosan Hydrogel Nanocomposites as Drug Delivery Tools. Molecules 2021, 26, 4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garshasbi, H.; Salehi, S.; Naghib, S.M.; Ghorbanzadeh, S.; Zhang, W. Stimuli-responsive injectable chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled drug delivery systems. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1126774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madivoli, E.S.; Schwarte, J.V.; Kareru, P.G.; Gachanja, A.N.; Fromm, K.M. Stimuli-Responsive and Antibacterial Cellulose-Chitosan Hydrogels Containing Polydiacetylene Nanosheets. Polymers 2023, 15, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Hua, D.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Bio-based stimuli-responsive materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 458–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Sharma, A.; Puri, V.; Aggarwal, G.; Maman, P.; Huanbutta, K.; Nagpal, M.; Sangnim, T. Chitosan-Based Polymer Blends for Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubbs, H.; Manna, B. Wound Physiology; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Pazyar, N.; Houshmand, G.; Yaghoobi, R.; Hemmati, A.A.; Zeineli, Z.; Ghorbanzadeh, B. Wound healing effects of topical Vitamin K: A randomized controlled trial. Indian. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 51, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarbrink, K.; Ni, G.; Sonnergren, H.; Schmidtchen, A.; Pang, C.; Bajpai, R.; Car, J. Prevalence and incidence of chronic wounds and related complications: A protocol for a systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, X.; Zhao, T.; Hu, J.; Yang, K.; Ma, N.; Li, A.; Sun, Q.; Ding, C.; Ding, Q. Application of Chitosan-Based Hydrogel in Promoting Wound Healing: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Luo, Y.; Ke, C.; Qiu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, R.; Xu, L.; Wu, S. Chitosan-Based Functional Materials for Skin Wound Repair: Mechanisms and Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 650598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbar Ahovan, Z.; Esmaeili, Z.; Eftekhari, B.S.; Khosravimelal, S.; Alehosseini, M.; Orive, G.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Pal Singh Chauhan, N.; Janmey, P.A.; Hashemi, A.; et al. Antibacterial smart hydrogels: New hope for infectious wound management. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 17, 100499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosinski, K.K.; Wach, R.A.; Kruczkowska, W.; Duda, L.; Kolat, D.; Kaluzinska-Kolat, Z.; Arkuszewski, P.T.; Pasieka, Z.W. Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogels for Effective Wound Healing-An Animal Study. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. A functional chitosan-based hydrogel as a wound dressing and drug delivery system in the treatment of wound healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7533–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yan, Y.; Huang, J.; Liang, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Ma, B.; Bianco, A.; Ge, S.; Shao, J. A multifunctional chitosan-based hydrogel with self-healing, antibacterial, and immunomodulatory effects as wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 231, 123149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hao, Y.; Francesco, S.; Mao, X.; Huang, W.C. A chitosan-based antibacterial hydrogel with injectable and self-healing capabilities. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2024, 6, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Chen, C.; Yang, K.; Wang, H.; Xia, H.; Zhao, Y.; Teng, Y.; Feng, G.; Chen, Y.M. Hyaluronic acid and chitosan-based injectable and self-healing hydrogel with inherent antibacterial and antioxidant bioactivities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatarusanu, S.M.; Sava, A.; Profire, B.S.; Pinteala, T.; Jitareanu, A.; Iacob, A.T.; Lupascu, F.; Simionescu, N.; Rosca, I.; Profire, L. New Smart Bioactive and Biomimetic Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Wounds Care Management. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Bratlie, K.M. pH sensitive methacrylated chitosan hydrogels with tunable physical and chemical properties. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 132, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, E.; Machado, S.; Soares, G. Smart Hydrogel for the pH-Selective Drug Delivery of Antimicrobial Compounds. Macromol. Symp. 2019, 385, 1800182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mu, L.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Bacterial Growth-Induced Tobramycin Smart Release Self-Healing Hydrogel for Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Infected Burn Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 13022–13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Iqbal, I.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Razak, S.I.A.; Raza, M.A.; Sajjad, A.; Jabeen, F.; Riduan Mohamad, M.; Jusoh, N. Development of Antibacterial, Degradable and pH-Responsive Chitosan/Guar Gum/Polyvinyl Alcohol Blended Hydrogels for Wound Dressing. Molecules 2021, 26, 5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Cheng, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, K.; Ning, X. A photoactive self-healing carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogel for accelerated infected wound healing through simultaneously modulating multiple critical tissue repair factors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, B.; Jia, M.; Liu, S.; Sheng, Z.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P. Smart Hydrogel-Based DVDMS/bFGF Nanohybrids for Antibacterial Phototherapy with Multiple Damaging Sites and Accelerated Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 10156–10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.M.; Abueva, C.; Ho, H.V.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, B.T. In vitro and in vivo acute response towards injectable thermosensitive chitosan/TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofiber hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Zhong, Y.; Jiang, X. An injectable photothermally active antibacterial composite hydroxypropyl chitin hydrogel for promoting the wound healing process through photobiomodulation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 4567–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, M.A.; Khatoon, F. In Vitro Study of Temperature and pH-Responsive Gentamycin Sulphate-Loaded Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Films for Wound Dressing Applications. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2014, 54, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSabato, D.J.; Quan, N.; Godbout, J.P. Neuroinflammation: The devil is in the details. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139 (Suppl. S2), 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danon, J.J.; Reekie, T.A.; Kassiou, M. Challenges and Opportunities in Central Nervous System Drug Discovery. Trends Chem. 2019, 1, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achar, A.; Myers, R.; Ghosh, C. Drug Delivery Challenges in Brain Disorders across the Blood-Brain Barrier: Novel Methods and Future Considerations for Improved Therapy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, H.; Cheng, S.; Pozzoli, M.; Messerotti, E.; Traini, D.; Young, P.; Kourmatzis, A.; Ong, H.X. Smart thermosensitive chitosan hydrogel for nasal delivery of ibuprofen to treat neurological disorders. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzitaki, A.T.; Jesus, S.; Karavasili, C.; Andreadis, D.; Fatouros, D.G.; Borges, O. Chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles for the nasal delivery of ropinirole hydrochloride: In vitro and ex vivo evaluation of efficacy and safety. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Patil, K.; Bobade, N.; Yeole, P.; Gaikwad, R. Formulation of intranasal mucoadhesive temperature-mediated in situ gel containing ropinirole and evaluation of brain targeting efficiency in rats. J. Drug Target. 2010, 18, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hsu, Y.H.; Huang, A.P.; Hsu, S.H. Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network of Hyaluronan and Chitosan Self-Healing Hydrogels for Central Nervous System Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 40108–40120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almuhayawi, M.S.; Ramadan, W.S.; Harakeh, S.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Bharali, D.J.; Mousa, S.A.; Almuhayawi, S.M. The potential role of pomegranate and its nano-formulations on cerebral neurons in aluminum chloride induced Alzheimer rat model. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1710–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Li, Z.; Mei, J. Resveratrol-loaded selenium/chitosan nano-flowers alleviate glucolipid metabolism disorder-associated cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Samanta, M.K.; Santhi, K.; Kumar, K.P.; Ramasamy, M.; Suresh, B. Chitosan nanoparticles as a new delivery system for the anti-Alzheimer drug tacrine. Nanomedicine 2010, 6, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, A.; Yoyen-Ermis, D.; Caban-Toktas, S.; Horzum, U.; Aktas, Y.; Couvreur, P.; Esendagli, G.; Capan, Y. Evaluation of brain-targeted chitosan nanoparticles through blood-brain barrier cerebral microvessel endothelial cells. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 34, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamanickam, G.; Manju, S.L. Formulation and characterization of chitosan nanoparticles loaded with neuroprotective flavonoid from Phyllanthus niruri Linn. Macromol. Res. 2023, 31, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, M.; Elangovan, A.; Sennimalai, R.; Babu, H.W.S.; Thiruvenkataswamy, S.; Krishnan, J.; Yadav, M.K.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V.; Narayanasamy, A.; Vellingiri, B. Chitosan—An alternative drug delivery approach for neurodegenerative diseases. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2024, 7, 100460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Dawson, C.; Lamb, M.; Mueller, E.; Stefanek, E.; Akbari, M.; Hoare, T. Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering: Addressing Key Design Needs Toward Clinical Translation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 849831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahranavard, M.; Zamanian, A.; Ghorbani, F.; Shahrezaee, M.H. A critical review on three dimensional-printed chitosan hydrogels for development of tissue engineering. Bioprinting 2020, 17, e00063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Chakraborty, E. Hydrogel based tissue engineering and its future applications in personalized disease modeling and regenerative therapy. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.P.; Leong, K.W. Scaffolding in tissue engineering: General approaches and tissue-specific considerations. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 17 (Suppl. S4), 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaharwar, A.K.; Singh, I.; Khademhosseini, A. Engineered biomaterials for in situ tissue regeneration. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 686–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburaci, S.; Tihminlioglu, F. Development of Si doped nano hydroxyapatite reinforced bilayer chitosan nanocomposite barrier membranes for guided bone regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 128, 112298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani Nazhvani, F.; Mohammadi Amirabad, L.; Azari, A.; Namazi, H.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Samanipour, R.; Khojasteh, A.; Golchin, A.; Hashemi, S. Effects of in vitro low oxygen tension preconditioning of buccal fat pad stem cells on in Vivo articular cartilage tissue repair. Life Sci. 2021, 280, 119728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Nada, A.A.; Valmikinathan, C.M.; Lee, P.; Liang, D.; Yu, X.; Kumbar, S.G. In situ gelling polysaccharide-based hydrogel for cell and drug delivery in tissue engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 131, 39934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.Z.; Wang, H.F.; Guan, J.; Fu, J.N.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Chen, Y.R.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.K. Fabrication of Injectable Chitosan-Chondroitin Sulfate Hydrogel Embedding Kartogenin-Loaded Microspheres as an Ultrasound-Triggered Drug Delivery System for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Yang, J.; Xu, J. Structural and biological investigation of chitosan/hyaluronic acid with silanized-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as an injectable reinforced interpenetrating network hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Z.; Ji, Y.R.; Kang, Z.W.; Li, F.; Ge, S.F.; Yang, D.P.; Ruan, J.; Fan, X.Q. Integrating eggshell-derived CaCO3/MgO nanocomposites and chitosan into a biomimetic scaffold for bone regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, K.; Chandran, S.V.; Balagangadharan, K.; Selvamurugan, N. Temperature- and pH-responsive chitosan-based injectable hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 111, 110862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Qazvini, N.T.; Sadati, M.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, S.; De La Lastra, A.L.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, B.; et al. A pH-Triggered, Self-Assembled, and Bioprintable Hybrid Hydrogel Scaffold for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Based Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 8749–8762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, R.; Koushik, C.; Saravanan, S.; Moorthi, A.; Vairamani, M.; Selvamurugan, N. A novel injectable temperature-sensitive zinc doped chitosan/beta-glycerophosphate hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 54, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi-Aghdam, F.; Jahed, V.; Dehghan-Niri, M.; Ganji, F.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E. Injectable chitosan hydrogel embedding modified halloysite nanotubes for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, E.; Seifalian, A.; Mellati, A.; Saremi, J.; Asadpour, S.; Enderami, S.E.; Nekounam, H.; Mahmoodi, N. Injectable hydrogels in central nervous system: Unique and novel platforms for promoting extracellular matrix remodeling and tissue engineering. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 20, 100614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, N.; Bhardwaj, A.; Mehta, S.; Mehta, A. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 758–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Fan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xie, X.; Guan, J. Regulating myogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells using thermosensitive hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2015, 26, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zeng, X.; Ma, C.; Yi, H.; Ali, Z.; Mou, X.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; He, N. Injectable hydrogels for cartilage and bone tissue engineering. Bone Res. 2017, 5, 17014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Tang, P. Recent Advances on Magnetic Sensitive Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaudo, M.A.; Krishnakumar, G.S.; Giusto, E.; Furlani, F.; Bassi, G.; Rossi, A.; Molinari, F.; Lista, F.; Montesi, M.; Panseri, S. Bioactive injectable hydrogels for on demand molecule/cell delivery and for tissue regeneration in the central nervous system. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Kaufman, L.J. Flow and magnetic field induced collagen alignment. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.P.; Moses, J.C.; Bhardwaj, N.; Mandal, B.B. Injectable hydrogels: A new paradigm for osteochondral tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 5499–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaing, Z.Z.; Ehsanipour, A.; Hofstetter, C.P.; Seidlits, S.K. Injectable Hydrogels for Spinal Cord Repair: A Focus on Swelling and Intraspinal Pressure. Cells Tissues Organs 2016, 202, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.D.; Duan, H.M.; Hao, F.; Zhao, W.; Gao, Y.D.; Hao, P.; Yang, Z.Y.; Li, X.G. Biomimetic chitosan scaffolds with long-term controlled release of nerve growth factor repairs 20-mm-long sciatic nerve defects in rats. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Li, X.; Tong, A.; Guo, G. Multi-functional chitosan-based smart hydrogels mediated biomedical application. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeya, H.; Itai, S.; Kimura, H.; Kurashina, Y.; Amemiya, T.; Nagoshi, N.; Iwamoto, T.; Sato, K.; Shibata, S.; Matsumoto, M.; et al. Schwann cell-encapsulated chitosan-collagen hydrogel nerve conduit promotes peripheral nerve regeneration in rodent sciatic nerve defect models. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Liu, C.; Hai, B.; Ma, T.; Zhang, W.; Tan, J.; Fu, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Song, C. Chitosan conduits filled with simvastatin/Pluronic F-127 hydrogel promote peripheral nerve regeneration in rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Soury, M.; Garcia-Garcia, O.D.; Tarulli, I.; Chato-Astrain, J.; Perroteau, I.; Geuna, S.; Raimondo, S.; Gambarotta, G.; Carriel, V. Chitosan conduits enriched with fibrin-collagen hydrogel with or without adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the repair of 15-mm-long sciatic nerve defect. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boido, M.; Ghibaudi, M.; Gentile, P.; Favaro, E.; Fusaro, R.; Tonda-Turo, C. Chitosan-based hydrogel to support the paracrine activity of mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injury treatment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzione, A.; Polini, A.; La Pesa, V.; Quattrini, A.; Romano, A.; Gigli, G.; Moroni, L.; Gervaso, F. Thermosensitive chitosan-based hydrogels supporting motor neuron-like NSC-34 cell differentiation. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 7492–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Sriwastawa, B.; Bhati, L.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Bannerjee, S.K. Drug delivery systems: An updated review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Karp, J.M.; Langer, R.; Joshi, N. The Future of Drug Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehelgerdi, M.; Chehelgerdi, M.; Allela, O.Q.B.; Pecho, R.D.C.; Jayasankar, N.; Rao, D.P.; Thamaraikani, T.; Vasanthan, M.; Viktor, P.; Lakshmaiya, N.; et al. Progressing nanotechnology to improve targeted cancer treatment: Overcoming hurdles in its clinical implementation. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Akhtar, N.; Minhas, M.U.; Badshah, S.F. pH/Thermo-Dual Responsive Tunable In Situ Cross-Linkable Depot Injectable Hydrogels Based on Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)/Carboxymethyl Chitosan with Potential of Controlled Localized and Systemic Drug Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalabi-Dchar, M.; Fenouil, T.; Machon, C.; Vincent, A.; Catez, F.; Marcel, V.; Mertani, H.C.; Saurin, J.C.; Bouvet, P.; Guitton, J.; et al. A novel view on an old drug, 5-fluorouracil: An unexpected RNA modifier with intriguing impact on cancer cell fate. NAR Cancer 2021, 3, zcab032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritharan, S.; Sivalingam, N. A comprehensive review on time-tested anticancer drug doxorubicin. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Zhao, N.; Wang, C.; Yuan, W. Injectable self-healing polysaccharide hydrogel loading CuS and pH-responsive DOX@ZIF-8 nanoparticles for synergistic photothermal-photodynamic-chemo therapy of cancer. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 127, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; LoGiudice, K.; Mays, G.; Schorr, A.; Rowey, R.; Yang, H.; Trivedi, S.; Srivastava, V. Increasing Chemotherapeutic Efficacy Using pH-Modulating and Doxorubicin-Releasing Injectable Chitosan-Poly(ethylene glycol) Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 45626–45639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. pH-responsive self-healing injectable hydrogel based on N-carboxyethyl chitosan for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Acta Biomater. 2017, 58, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. Injectable redox and light responsive MnO2 hybrid hydrogel for simultaneous melanoma therapy and multidrug-resistant bacteria-infected wound healing. Biomaterials 2020, 260, 120314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Guo, L.; Shi, D.; Sun, X.; Shang, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, J. Charge-conversion and ultrasound-responsive O-carboxymethyl chitosan nanodroplets for controlled drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 2549–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, E.; Rohondia, S.; Khan, R.; Dou, Q.P. Repurposing Disulfiram as An Anti-Cancer Agent: Updated Review on Literature and Patents. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzazzadeh, A.; Dizaji, B.F.; Kianinejad, N.; Nouri, A.; Irani, M. Fabrication of poly(acrylic acid) grafted-chitosan/polyurethane/magnetic MIL-53 metal organic framework composite core-shell nanofibers for co-delivery of temozolomide and paclitaxel against glioblastoma cancer cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heragh, B.K.; Taherinezhad, H.; Mahdavinia, G.R.; Javanshir, S.; Labib, P.; Ghasemsolb, S. pH-responsive co-delivery of doxorubicin and saffron via cross-linked chitosan/laponite RD nanoparticles for enhanced-chemotherapy. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourian, P.; Ji, J.; Lotocki, V.; Moquin, A.; Hanna, R.; Frounchi, M.; Maysinger, D.; Kakkar, A. Facile design of autogenous stimuli-responsive chitosan/hyaluronic acid nanoparticles for efficient small molecules to protein delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 7275–7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lin, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, C.; Zhao, C.; Lu, L.; Zhou, C.; Tian, J.; et al. Temperature- and pH-responsive injectable chitosan hydrogels loaded with doxorubicin and curcumin as long-lasting release platforms for the treatment of solid tumors. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1043939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghbani, F.; Chegeni, M.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Hadian-Ghazvini, S.; Raz, M. Novel ultrasound-responsive chitosan/perfluorohexane nanodroplets for image-guided smart delivery of an anticancer agent: Curcumin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 74, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aycan, D.; Alemdar, N. Development of pH-responsive chitosan-based hydrogel modified with bone ash for controlled release of amoxicillin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chang, C.H.; Wu, Y.S.; Hsu, Y.M.; Chiou, S.F.; Chen, Y.J. Development of pH-responsive chitosan/heparin nanoparticles for stomach-specific anti-Helicobacter pylori therapy. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3332–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutzkus, J.C.; Shahrokhi, M.; Varacallo, M. Naproxen; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K.; Zhou, X.; He, T. The synthesis of bacterial cellulose-chitosan zwitterionic hydrogels with pH responsiveness for drug release mechanism of the naproxen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Bao, Y. Nanodelivery of natural isothiocyanates as a cancer therapeutic. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 167, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Q.; Meng, Z.; Wu, X.; Xu, K. Inhibition of autophagy potentiates the anti-metastasis effect of phenethyl isothiocyanate through JAK2/STAT3 pathway in lung cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 522–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haloi, P.; Chawla, S.; Konkimalla, V.B. Thermosensitive smart hydrogel of PEITC ameliorates the therapeutic efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 181, 106367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fea, A.M.; Novarese, C.; Caselgrandi, P.; Boscia, G. Glaucoma Treatment and Hydrogel: Current Insights and State of the Art. Gels 2022, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storgaard, L.; Tran, T.L.; Freiberg, J.C.; Hauser, A.S.; Kolko, M. Glaucoma Clinical Research: Trends in Treatment Strategies and Drug Development. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 733080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prum, B.E., Jr.; Rosenberg, L.F.; Gedde, S.J.; Mansberger, S.L.; Stein, J.D.; Moroi, S.E.; Herndon, L.W., Jr.; Lim, M.C.; Williams, R.D. Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Preferred Practice Pattern® Guidelines. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, P41–P111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhassen, M.; Laforest, L.; Licaj, I.; Van Ganse, E. Early adherence to anti-glaucoma therapy: An observational study. Therapie 2016, 71, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Saha, D.; Majumdar, S.; Giri, L. Imaging Methods for the Assessment of a Complex Hydrogel as an Ocular Drug Delivery System for Glaucoma Treatment: Opportunities and Challenges in Preclinical Evaluation. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, K.S.; Rajpurohit, R.; Sharma, S. Glaucoma: Current treatment and impact of advanced drug delivery systems. Life Sci. 2019, 221, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Tsai, T.H.; Jhan, Y.Y.; Chiu, A.W.; Tsai, K.L.; Chien, C.S.; Chiou, S.H.; Liu, C.J. Thermosensitive chitosan-based hydrogel as a topical ocular drug delivery system of latanoprost for glaucoma treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakzad, Y.; Fathi, M.; Omidi, Y.; Mozafari, M.; Zamanian, A. Synthesis and characterization of timolol maleate-loaded quaternized chitosan-based thermosensitive hydrogel: A transparent topical ocular delivery system for the treatment of glaucoma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeerapan, I.; Imani, S.; Cho, T.N.; Bandodkar, A.; Cinti, S.; Mercier, P.P.; Wang, J. Noninvasive Alcohol Monitoring Using a Wearable Tattoo-Based Iontophoretic-Biosensing System. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Song, S.; Jia, F.; Gao, G. A flexible, adhesive and self-healable hydrogel-based wearable strain sensor for human motion and physiological signal monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4638–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ding, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Gui, X.; Li, C.; Hu, N.; Tao, K.; Wu, J. Engineering Smart Composite Hydrogels for Wearable Disease Monitoring. Nanomicro Lett. 2023, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpa, R.; Remizovschi, A.; Culda, C.A.; Butiuc-Keul, A.L. Inherent and Composite Hydrogels as Promising Materials to Limit Antimicrobial Resistance. Gels 2022, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancı Bozoğlan, B.; Duman, O.; Tunç, S. Smart antifungal thermosensitive chitosan/carboxymethylcellulose/scleroglucan/montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogels for onychomycosis treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 610, 125600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmingsen, L.M.; Julin, K.; Ahsan, L.; Basnet, P.; Johannessen, M.; Skalko-Basnet, N. Chitosomes-In-Chitosan Hydrogel for Acute Skin Injuries: Prevention and Infection Control. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frade, M.L.; de Annunzio, S.R.; Calixto, G.M.F.; Victorelli, F.D.; Chorilli, M.; Fontana, C.R. Assessment of Chitosan-Based Hydrogel and Photodynamic Inactivation against Propionibacterium acnes. Molecules 2018, 23, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, G.S. Biochemical Markers of Myocardial Damage. EJIFCC 2016, 27, 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Tohidi, H.; Maleki-Jirsaraei, N.; Simchi, A.; Mohandes, F.; Emami, Z.; Fassina, L.; Naro, F.; Conti, B.; Barbagallo, F. An Electroconductive, Thermosensitive, and Injectable Chitosan/Pluronic/Gold-Decorated Cellulose Nanofiber Hydrogel as an Efficient Carrier for Regeneration of Cardiac Tissue. Materials 2022, 15, 5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kruczkowska, W.; Gałęziewska, J.; Grabowska, K.; Liese, G.; Buczek, P.; Kłosiński, K.K.; Kciuk, M.; Pasieka, Z.; Kałuzińska-Kołat, Ż.; Kołat, D. Biomedical Trends in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Emphasis on Chitosan-Based Formulations. Gels 2024, 10, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050295
Kruczkowska W, Gałęziewska J, Grabowska K, Liese G, Buczek P, Kłosiński KK, Kciuk M, Pasieka Z, Kałuzińska-Kołat Ż, Kołat D. Biomedical Trends in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Emphasis on Chitosan-Based Formulations. Gels. 2024; 10(5):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050295
Chicago/Turabian StyleKruczkowska, Weronika, Julia Gałęziewska, Katarzyna Grabowska, Gabriela Liese, Paulina Buczek, Karol Kamil Kłosiński, Mateusz Kciuk, Zbigniew Pasieka, Żaneta Kałuzińska-Kołat, and Damian Kołat. 2024. "Biomedical Trends in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Emphasis on Chitosan-Based Formulations" Gels 10, no. 5: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050295
APA StyleKruczkowska, W., Gałęziewska, J., Grabowska, K., Liese, G., Buczek, P., Kłosiński, K. K., Kciuk, M., Pasieka, Z., Kałuzińska-Kołat, Ż., & Kołat, D. (2024). Biomedical Trends in Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Emphasis on Chitosan-Based Formulations. Gels, 10(5), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10050295