Environmentally Friendly Nanoporous Polymeric Gels for Sustainable Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
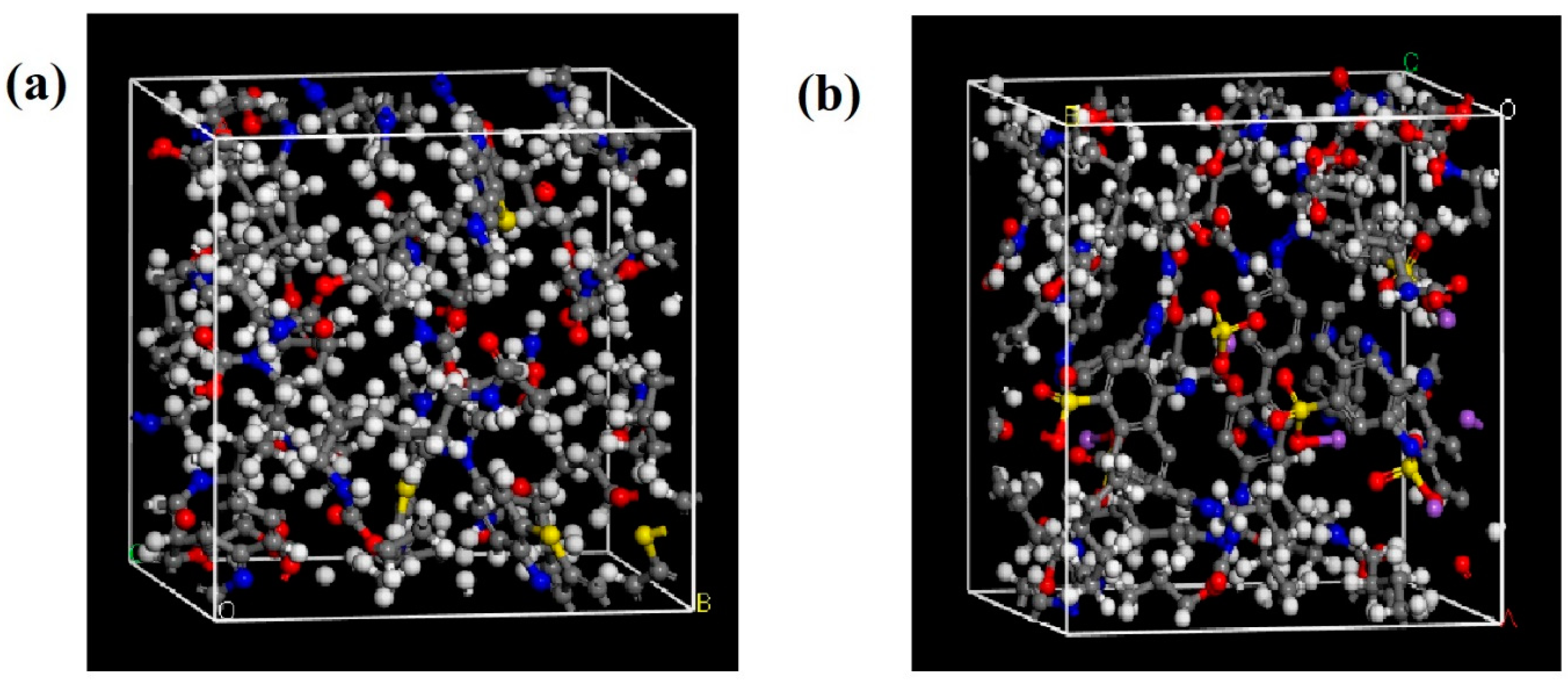
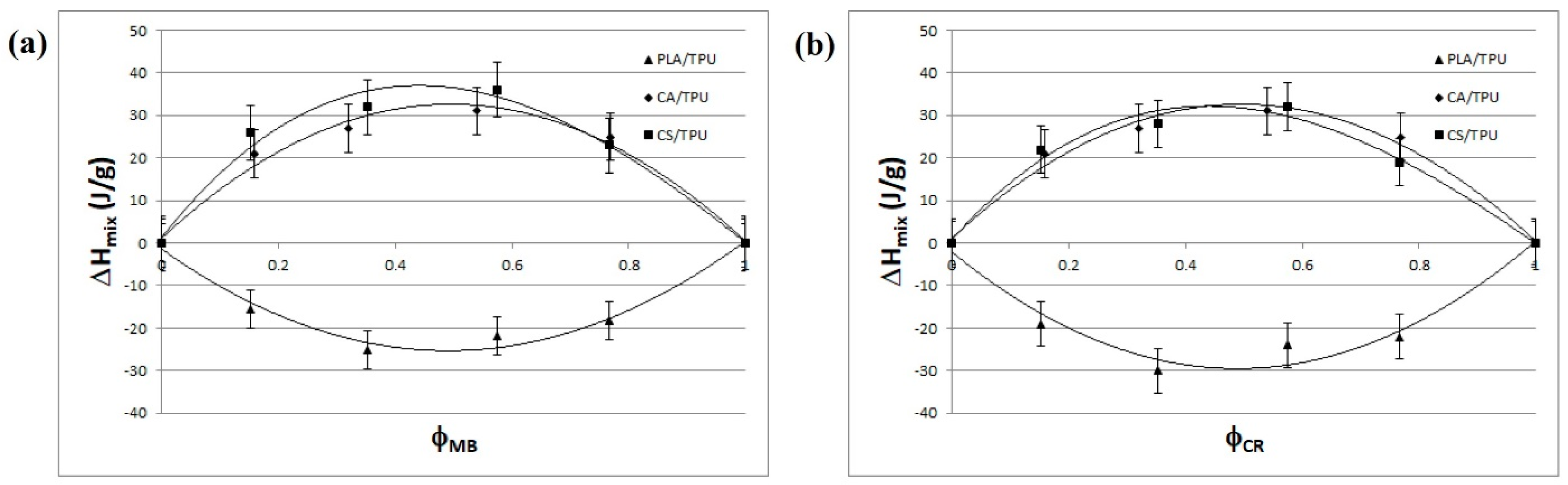
2.1. Modeling of the Polymeric Blends
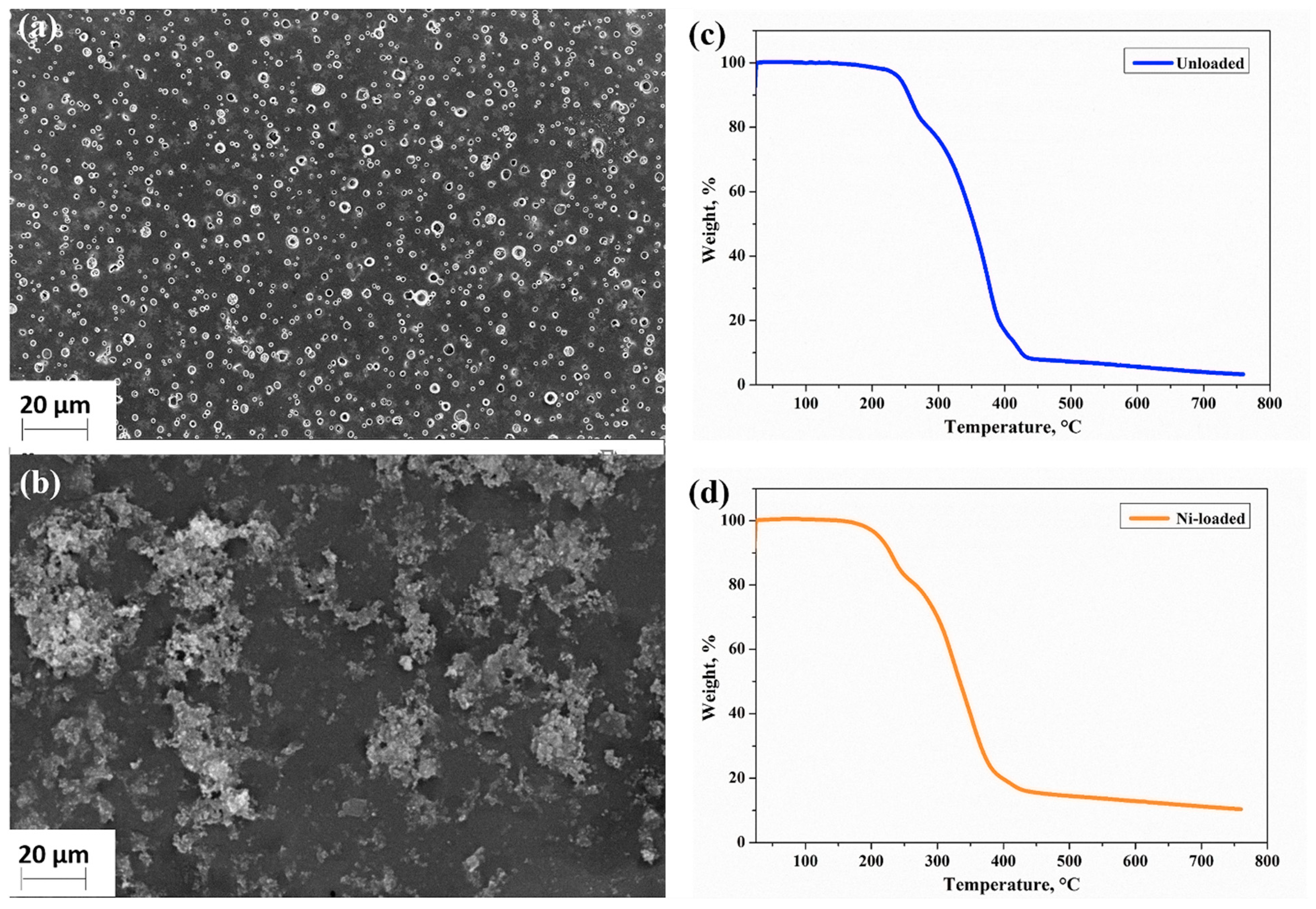
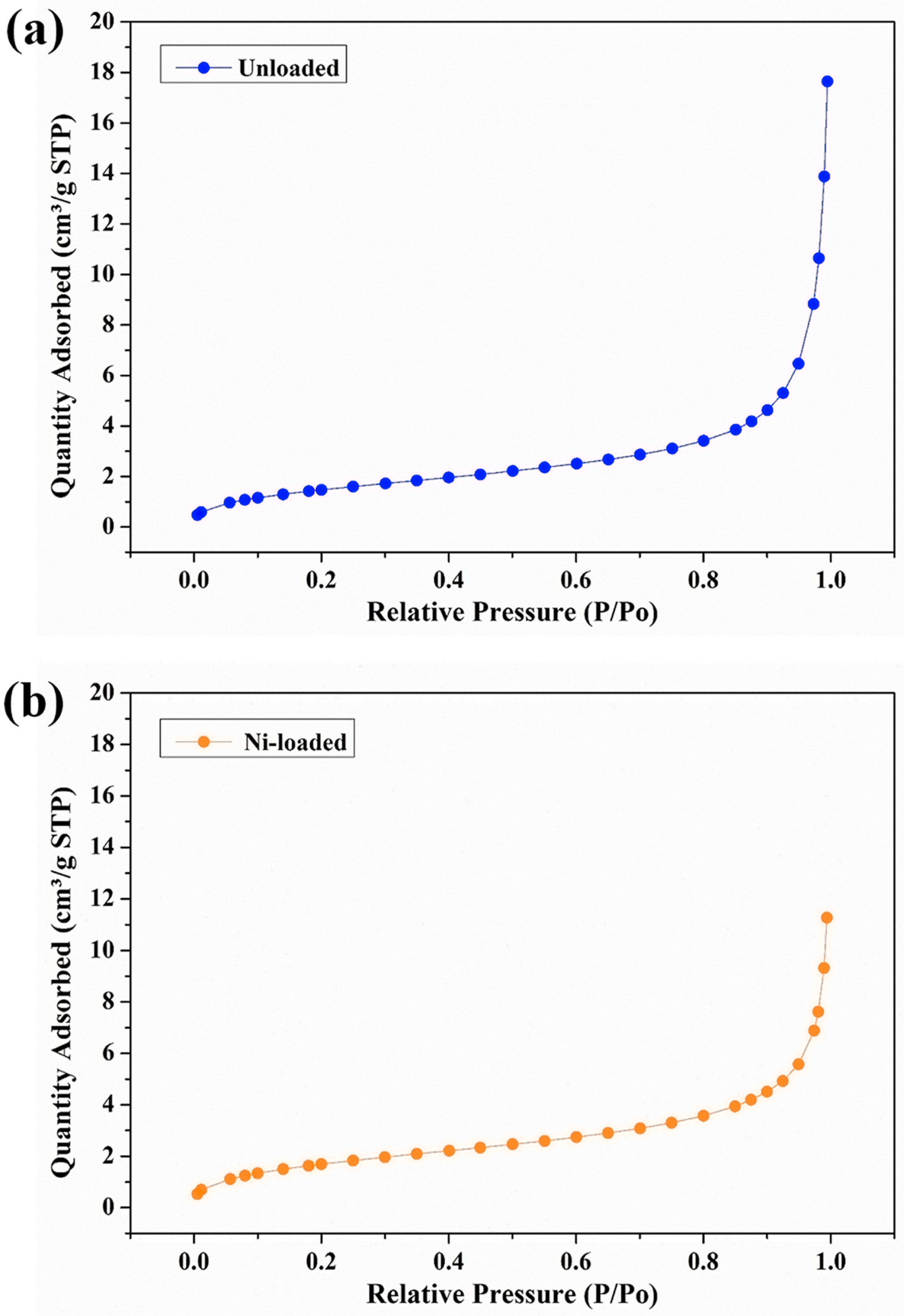
2.2. Characterization of the Physicochemical Characteristics of the Gels
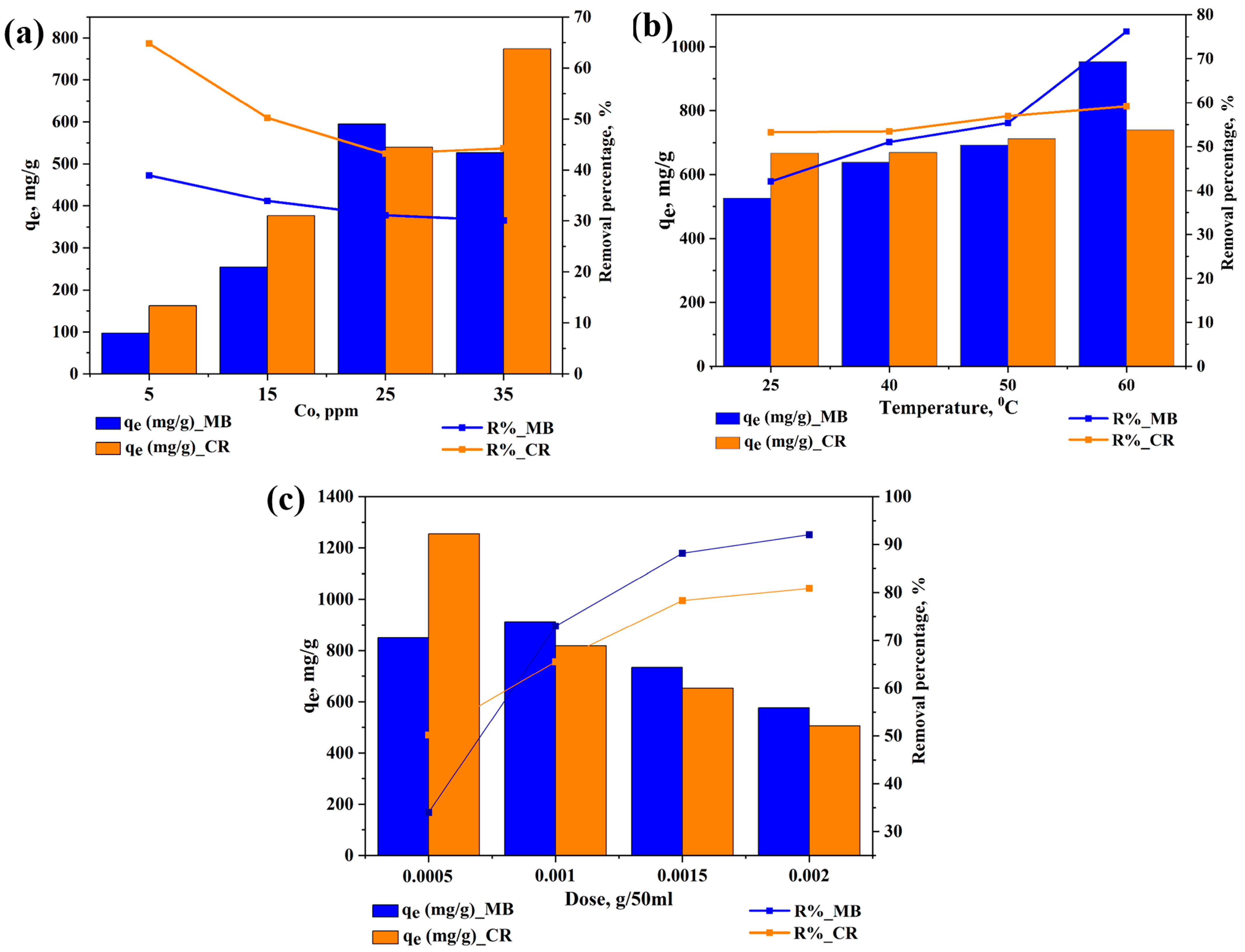
2.3. Removal Under Different Operating Parameters
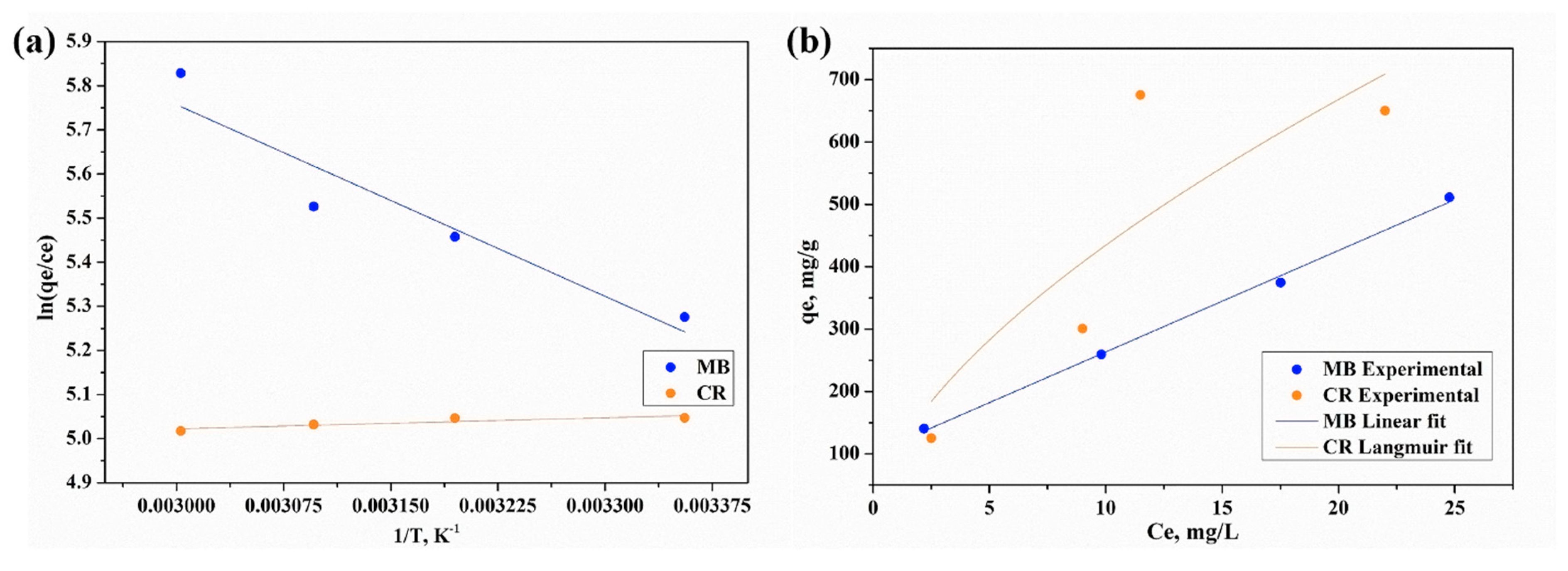
2.4. Characterization of the Adsorption and Degradation Processes
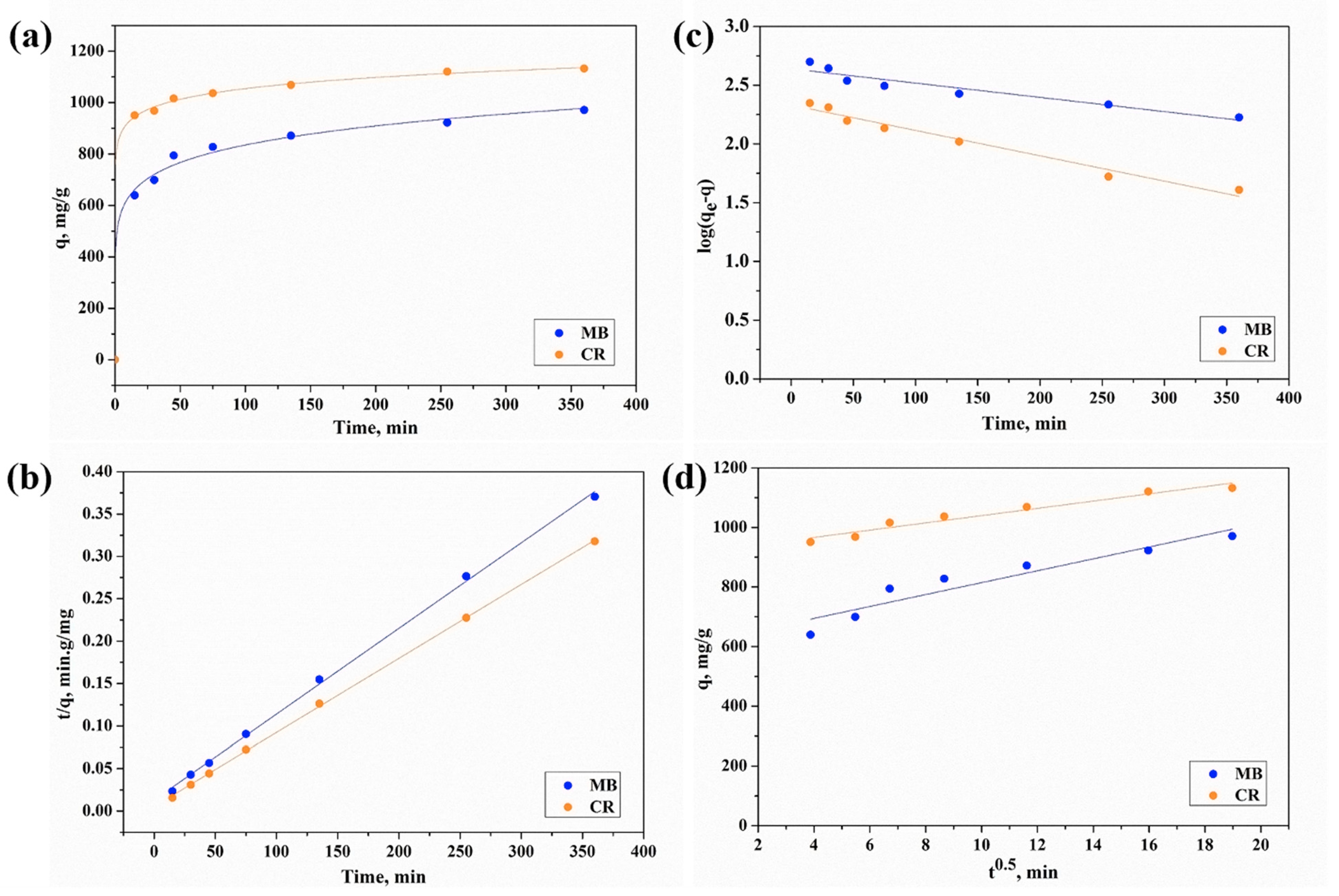
2.5. Kinetics of Adsorption
3. Conclusions
4. Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Experimental
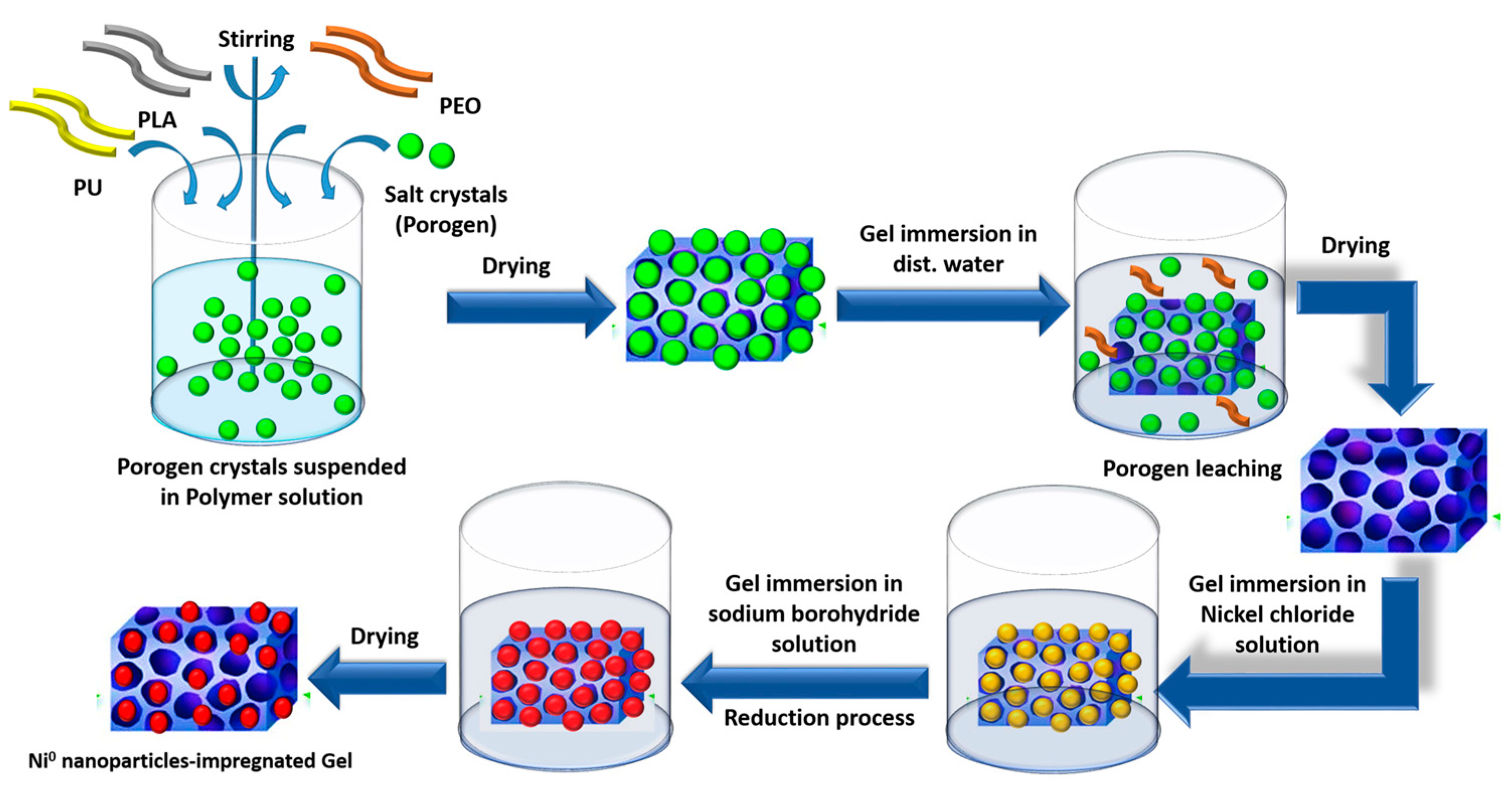
4.2.1. Preparation of the Impregnated Polymeric Gels
4.2.2. Characterization of the Polymeric Gels
4.2.3. Removal of Methylene Blue (MB) and Congo Red (CR) Dyes
- : the equilibrium adsorption capacity given in mg/g,
- C0: the initial dye concentration given in ppm,
- the equilibrium dye concentration given in ppm,
- V: volume of dye solution given in L, and
- m: the mass of nanoparticles loaded onto the porous gel given in g and accounts for 0.2% of the total mass of the gel.
4.2.4. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Evaluation
4.2.5. Kinetics Evaluation
- qt: the uptake capacity at time t,
- k1: pseudo-first-order rate constant, and
- k2: pseudo-second-order rate constant.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, M.R.; Gupta, A. Water Pollution-Sources, Effects and Control; Centre for Biodiversity, Department of Botany, Nagaland University: Nagaland, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brillas, E.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A. Decontamination of Wastewaters Containing Synthetic Organic Dyes by Electrochemical Methods. An Updated Review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 166, 603–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Pollution and Treatment of Dye Waste-Water. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 514, p. 052001. [Google Scholar]
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of Textile Dyes on Health and the Environment and Bioremediation Potential of Living Organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Adhikary, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Roy, D.; Chatterjee, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Banerjee, D.; Ganguly, A.; Nanda, S.; Rajak, P. Contamination of Textile Dyes in Aquatic Environment: Adverse Impacts on Aquatic Ecosystem and Human Health, and Its Management Using Bioremediation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Rafatullah, M.; Salamatinia, B.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Tan, K.B.; Gholami, Z.; Amouzgar, P. Application of Chitosan and Its Derivatives as Adsorbents for Dye Removal from Water and Wastewater: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.X.; Lee, L.; Wang, H.H.; Wang, Z. Removal of an Anionic Dye by Adsorption/Precipitation Processes Using Alkaline White Mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, P.; Basu, S. Removal of Ionic Dyes from Water by Solvent Extraction Using Reverse Micelles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.H. Sonochemical Treatment of Fly Ash for Dye Removal from Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 126, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, N.; Sundaram, M.M. Kinetics and Mechanism of Removal of Methylene Blue by Adsorption on Various Carbons—A Comparative Study. Dye. Pigment. 2001, 51, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Liao, Z.Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhao, C.J.; Lei, Y.X.; Ji, D.B. Electrochemical Degradation of Methylene Blue Using Electrodes of Stainless Steel Net Coated with Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 2757–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Chen, J.T.; Yang, H.C.; Chen, J.H. Decolorization of Dyes Using Ozone in Gas-Induced a Reactor. AIChE J. 2001, 47, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Chen, T.; Xiong, J.; Wang, T.; Lu, G.; Ye, J.; Bi, Y. Visible-Light-Driven Photoelectrochemical and Photocatalytic Performance of Cr-Doped SrTiO3/TiO2 Heterostructured Nanotube Arrays. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuama, A.N.; Alzubaidi, L.H.; Jameel, M.H.; Abass, K.H.; bin Mayzan, M.Z.H.; Salman, Z.N. Impact of electron–hole recombination mechanism on the photocatalytic performance of ZnO in water treatment: A review. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2024, 110, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Zekker, I.; Zhang, B.; Hendi, A.H.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, S.; Zada, N.; Ahmad, H.; Shah, L.A.; et al. Review on Methylene Blue: Its Properties, Uses, Toxicity and Photodegradation. Water 2022, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistan, A.; Mohan, S.; Mahalakshmi, S.; Jayanthi, A.; Ramya, A.J.; Karthik, P.S. Sol-Gel technique, characterization and photocatalytic degradation activity of Manganese doped ZnO nanoparticles. Main Group Chem. 2024, 23, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Falletta, E.; Dash, S.K. Enhanced and rapid photocatalytic degradation of toxic dyes by cobalt oxide and modified cobalt oxide under solar light irradiation. Opt. Mater. 2023, 135, 113368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, W.D.; da Silva Bento, A.M.; de Araújo, J.A.S.; Menezes, J.M.C.; da Costa, J.G.M.; da Cunha, F.A.B.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; de Paula Filho, F.J.; Pereira Teixeira, R.N. Removal of Copper(II) Ions and Lead(II) from Aqueous Solutions Using Seeds of Azadirachta indica A. Juss as Bioadsorbent. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asses, N.; Ayed, L.; Hkiri, N.; Hamdi, M. Congo Red Decolorization and Detoxification by Aspergillus niger: Removal Mechanisms and Dye Degradation Pathway. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3049686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, W.; Li, Y.; He, S.; He, C. Photocatalytic Degradation of Sixteen Organic Dyes by TiO2/WO3-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles under Simulated Visible Light and Solar Light. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammina, S.K.; Mandal, B.K.; Kadiyala, N.K. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Dye by Nonconventional Synthesized SnO2 Nanoparticles. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 10, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, M.I.; Tariq, M.; Hussain, Z.; Khalid, R. Single Step Green Synthesis of Nickel and Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles from Hordeum vulgare for Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Dye. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2020, 50, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, T.M.; Mark, J.E. Simulations on Crystallization in Stereoblock Poly(propylene). Idealized Structures Showing the Effects of Atactic Block Length. Macromol. Theory Simul. 1998, 7, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, T.M.; Mark, J.E. Modeling of the Crystallization of Isotactic Polypropylene Chains. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 1997, 35, 2757–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, A.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Assiri, M.; Du, G.; Ahmad, T.; Ahmad, I.; Pannipara, M. Modified Solvothermal Synthesis of Cobalt Ferrite (CoFe2O4) Magnetic Nanoparticles Photocatalysts for Degradation of Methylene Blue with H2O2/Visible Light. Results Phys. 2018, 8, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, T.M.; Azzam, R.A. Non-Gaussian Behavior of Self-Assembled Thermoplastic Polyurethane Elastomers Synthesized Using Two-Step Polymerization and Investigated Using Constant-Strain Stress Relaxation and Molecular Modeling Techniques. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.G.; Ahmed, S.M.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Removal of Copper (II) Ions by Eco-Friendly Raw Eggshells and Nano-Sized Eggshells: A Comparative Study. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2022, 209, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.M.H.; Elsayed, R.; Attia, A.; Farghal, H.H.; Azzam, R.A.; Madkour, T.M. Novel Nanoporous Gels of Bio-Based Cellulose Acetate, Poly(lactic Acid) and Biodegradable Polyurethane In-Situ Impregnated with Catalytic Cobalt Nanoparticles for the Removal of Methylene Blue and Congo Red Dyes from Wastewater. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100123. [Google Scholar]
- Morcos, G.S.; Ibrahim, A.A.; El-Sayed, M.M.H.; El-Shall, M.S. High Performance Functionalized UiO Metal Organic Frameworks for the Efficient and Selective Adsorption of Pb(II) Ions in Concentrated Multi-Ion Systems. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.G.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Removal of Imidacloprid Pesticide Using Nanoporous Activated Carbons Produced via Pyrolysis of Peach Stone Agricultural Wastes. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2021, 208, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, T.; Mark, J.E. Elastomeric Properties of Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Networks Having Bimodal and Trimodal Distributions of Network Chain Lengths. Macromol. Rep. 1994, 31, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Bayomie, O.S.; Kandeel, H.; Shoeib, T.; Yang, H.; Youssef, N.; El-Sayed, M.M. Novel Approach for Effective Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Water Using Fava Bean Peel Waste. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, A.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M.; Noreen, S. Basic Dye Adsorption onto Clay/MnFe2O4 Composite: A Mechanistic Study. Water Environ. Res. 2017, 89, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.A.; de Sousa Ribeiro, L.A.; Thim, G.P.; Ferreira, R.R.; Alvarez-Mendez, M.O.; Coutinho, A.D.R. Activated Carbon Derived from Macadamia Nut Shells: An Effective Adsorbent for Phenol Removal. J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Yu, W.; Qin, Z.; Nie, X.; Yang, S.; Wan, Q. Adsorption Characteristics of Copper Ion on Nanoporous Silica. Acta Geochim. 2019, 38, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Prasad, B.; Mishra, I.M.; Chand, S. Decolorization and COD Reduction of Dyeing Wastewater from a Cotton Textile Mill Using Thermolysis and Coagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Hu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q.; He, C. Rapid Degradation of Congo Red by Molecularly Imprinted Polypyrrole-Coated Magnetic TiO2 Nanoparticles in Dark at Ambient Conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 294, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.H.; Fu, C.C.; Juang, R.S. Degradation of Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange by Palladium-Doped TiO2 Photocatalysis for Water Reuse: Efficiency and Degradation Pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, M.A.; Meetani, M.A.; Khaleel, A.; Ahmed, A. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Using a Mixed Catalyst and Product Analysis by LC/MS. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, M.; McCrindle, R.I.; Maity, A. Enhanced Adsorptive Degradation of Congo Red in Aqueous Solutions Using Polyaniline/Fe0 Composite Nanofibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaa, M.W.; Madkour, T.M.; Yassin, A.A. Polymerization Products of p-Benzoquinone as Bound Antioxidants for SBR. Part II—The Antioxidizing Efficiency. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1988, 22, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Cascio, F.; Kayed, R. Azure C Targets and Modulates Toxic Tau Oligomers. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemoğlu, S.; Aksu, S.K.; Sayılkan, F.; Izgi, B.; Asiltürk, M.; Sayılkan, H.; Frimmel, F.; Güçer, Ş. Photocatalytic Degradation of Congo Red by Hydrothermally Synthesized Nanocrystalline TiO2 and Identification of Degradation Products by LC–MS. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chepape, K.F.; Mofokeng, T.P.; Nyamukamba, P.; Mubiayi, K.P.; Moloto, M.J. Enhancing Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Blue Using PVP-Capped and Uncapped CdSe Nanoparticles. J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 2017, 5340784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ΔH (J/mol) | ΔS (J/mol.K) | ΔG * (J/mol) | Keq * | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MB | 1237.87 | 43.92 | −13387.1 | 125.88 | 0.9149 |
| CR | 580.56 | 40.04 | −12751.72 | 100.07 | 0.9544 |
| Kinetic Model | Kinetic Parameters | Dye | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | k1 (min−1) | MB | CR |
| 0.0027 | 0.0050 | ||
| qe (calc) (mg/g) | 436.01 | 214.09 | |
| R2 | 0.9056 | 0.9714 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | k2 (g/mg·min−1) | 0.0001 | 0.0002 |
| qe (calc) (mg/g) | 1000 | 1111.11 | |
| R2 | 0.9988 | 0.9997 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion | Kid (mg/(g·min0.5) | 20.003 | 12.216 |
| C (mg/g) | 614.27 | 917.63 | |
| R2 | 0.9012 | 0.9544 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madkour, T.M.; Elsayed, R.E.; Azzam, R.A. Environmentally Friendly Nanoporous Polymeric Gels for Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Gels 2024, 10, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120756
Madkour TM, Elsayed RE, Azzam RA. Environmentally Friendly Nanoporous Polymeric Gels for Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Gels. 2024; 10(12):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120756
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadkour, Tarek M., Rasha E. Elsayed, and Rasha A. Azzam. 2024. "Environmentally Friendly Nanoporous Polymeric Gels for Sustainable Wastewater Treatment" Gels 10, no. 12: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120756
APA StyleMadkour, T. M., Elsayed, R. E., & Azzam, R. A. (2024). Environmentally Friendly Nanoporous Polymeric Gels for Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Gels, 10(12), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10120756







