Field Evaluation of Promising Indigenous Entomopathogenic Fungal Isolates against Red Palm Weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Entomopathogenic Fungal Source
2.3. Mass Production of Fungal Isolates
2.4. Date Palm Injection Procedures
2.5. Preliminary Study of the Fungal Treatment Effects
2.6. Trunk Injection
2.7. Temperature of Infested Date Palms
2.8. Acoustic Sensor “TreeVibes”
2.9. Acoustic Sensor Placement and Vibrational Signal Collection Procedures
2.10. Signal Processing
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ambient and Inside Temperatures of an Infested Date Palm
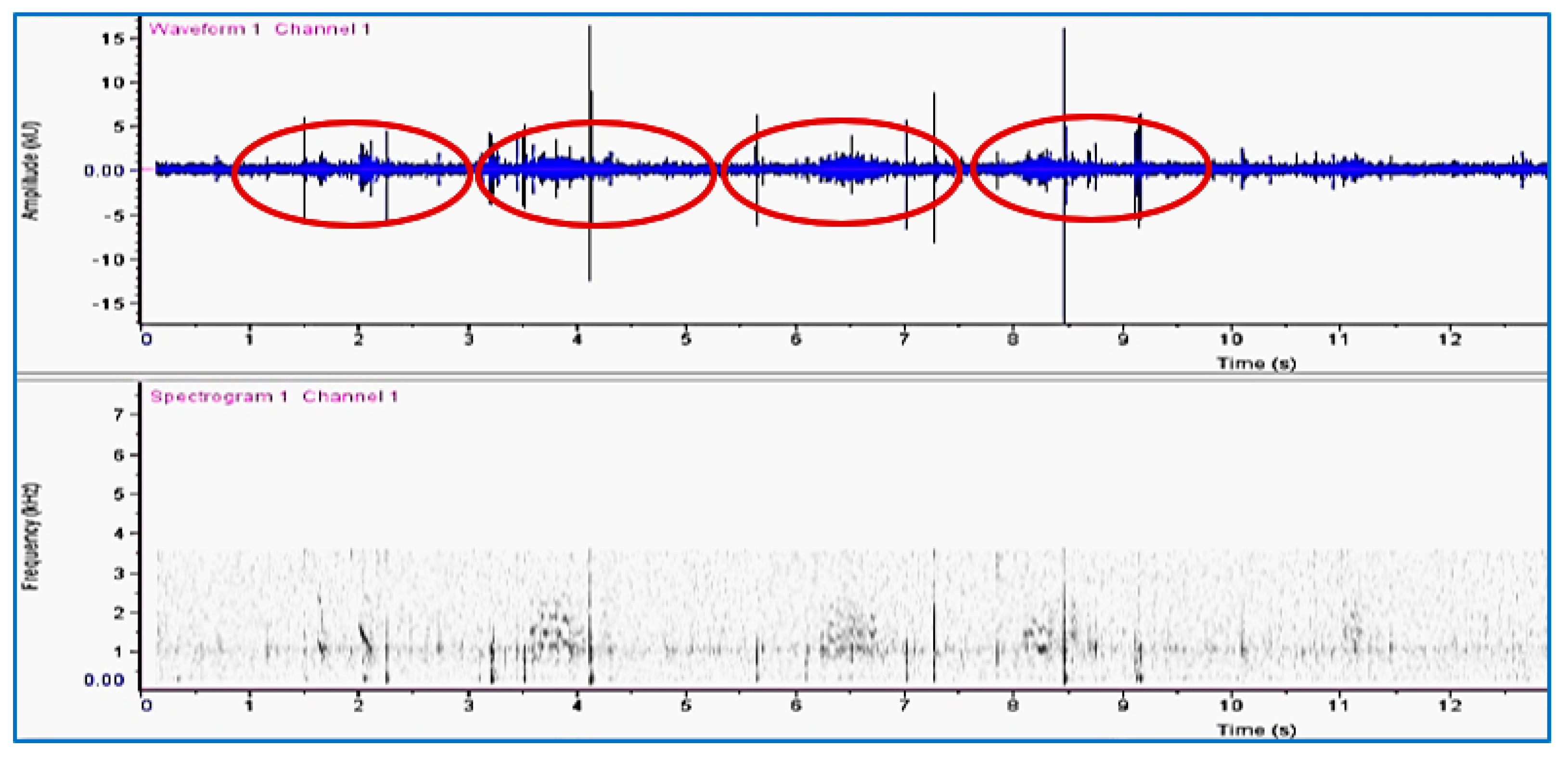
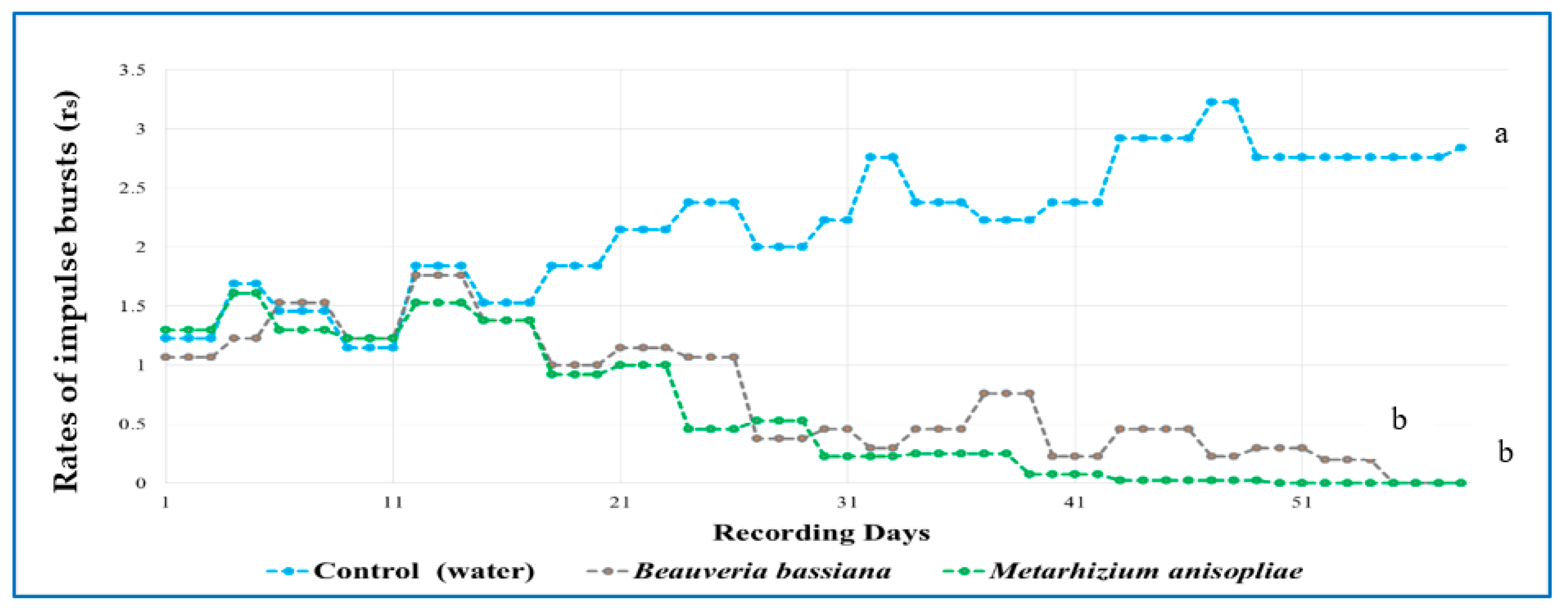
3.2. Sound Recording of RPW Activity in a Date Palm
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abraham, V.A.; Al-Shuaibi, M.; Faleiro, J.R.; Abozuhairah, R.A.; Vidyasagar, P.S. An integrated approach for the management of red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Oliv.—A key pest of date palm in the Middle East. Sultan Qaboos Univ. J. Sci. Res. Agric. Sci. 1998, 3, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sabea, A.M.; Faleiro, J.R.; El-Saad, M.M. The treat of red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus to date plantations of the Gulf Region of the Middle East: An economic perspective. Outlooks Pest Manag. 2009, 20, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, R.H.; Oehlschlager, A.C.; Borden, J.H. Pheromone trapping protocols for the Asian palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Int. J. Pest Manag. 1999, 45, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafie, H.; Faleiro, J.; Al-Abbad, A.; Stoltman, L.; Mafra-Neto, A. Bait-free attract and kill technology (Hook™ RPW) to suppress red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in date palm. Fla. Entomol. 2011, 94, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbass, M.K.; Al-Nasser, A.S. Ecological studies and evaluation of some aggregation pheromone types with measuring the potential of female reproductive system in red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier). Nat. Sci. 2012, 10, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Shar, M.U.; Rustamani, M.A.; Nizamani, S.M.; Buriro, A.S.; Bhutto, L.A.; Lodhi, A.M. Evaluation of different date palm varieties and pheromone traps against red palm weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus) in Sindh. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, F.R.; Cerrella, D.C. Monitoring red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Olivier, with pheromone traps: Five years of experience in Sicily. In Colloque Méditerranéen sur les Ravageurs des Palmiers, Nice, France, 16–18 January 2013; Association Française de Protection des Plantes (AFPP): Alfortville, France, 2013; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Vacas, S.; Primo, J.; Navarro-Llopis, V. Advances in the use of trapping systems for Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): Traps and attractants. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.A.; Abd El-Salam, A.M.E.; El-Kholy, M.Y. Field Evaluation of Red Palm Weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Oliv. (Coleoptera:Curculionidae) Responses to its Fermenting Date Tree Volatiles. Int. J. Chem Tech Res. 2016, 9, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gindin, G.; Levski, S.; Glazer, I.; Soroker, V. Evaluation of the Entomopathogenic Fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana against the Red Palm Weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus. Phytoparasitica 2006, 34, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembilio, Ó.; Llácer, E. Field efficacy of imidacloprid and Steinernema carpocapsae in a chitosan formulation against the red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Phoenix canariensis. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merghem, A. Susceptibility of the Red Palm Weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) to the Green Muscardine Fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae (Metsch.) in the Laboratory and in Palm Trees Orchard. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2011, 21, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Francardi, V.; Benvenuti, C.; Barzanti, G.; Roversi, P.F. Autocontamination trap with entomopathogenic fungi: A possible strategy in the control of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) (Coleoptera Curculionidae). Redia 2013, 96, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Qayyum, M.A.; Saleem, M.A.; Saeed, S.; Wakil, W.; Ishtiaq, M.; Ashraf, W.; Ahmed, N.; Ali, M.; Ikram, R.M.; Yasin, M.; et al. Integration of entomopathogenic fungi and eco-friendly insecticides for management of red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasin, M.; Wakil, W.; Ghazanfar, M.U.; Qayyum, M.A.; Tahir, M.; Beford, G.O. Virulence of entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae against red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier). Entomol. Res. 2019, 49, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, K.D.; Husain, M.; Rasool, K.G.; Al-Qahtani, W.H.; Aldawood, A.S. Pathogenicity of local and exotic entomopathogenic fungi isolates against different life stages of red palm weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Freed, S.; Naeem, A.; Akmal, M. Lethal and trans-generational effects of Metarhizium anisopliae on red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus, using age-stage, two-sex life table. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2022, 25, 101946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakil, W.; Yasin, M.; Shapiro-Ilan, D. Effects of single and combined applications of entomopathogenic fungi and nematodes against Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Baky, N.F.; Hamed, K.E.; Al-Otaibi, N.D.; Aldeghairi, M.A. Bioassay of Some Indigenous Entomopathogens for Controlling Rhynchophorus ferrugineus, Olivier in Saudi Arabia. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. PJBS 2021, 24, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalinas, J.; Erri-Agullo, B.G.; Mankin, R.W.; Follana, R.L.; Lopez-Llorca, L.V. Acoustic Assessment of Beauveria bassiana (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae) Effects on Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae) Larval Activity and Mortality. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankin, R.W. Recent Developments in the use of Acoustic Sensors and Signal Processing Tools to Target Early Infestations of Red Palm Weevil in Agricultural Environments 1. Fla. Entomol. 2011, 94, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, A.; Ruiz, V.; Moltó, E.; Tapia, G.; del Mar Téllez, M. Development of a bioacoustic sensor for the early detection of Red Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Olivier). Crop. Prot. 2010, 29, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, W.B.; Hussein, M.A.; Becker, T. Detection of the red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus using its bioacoustics features. Bioacoustics 2010, 19, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalinas, J.; Güerri-Agulló, B.; Dosunmu, O.G.; Lopez Llorca, L.V.; Mankin, R.W. Acoustic activity cycles of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae) early instars after Beauveria bassiana (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae) treatments. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2017, 110, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudri, N.A.F.R.S.; Mohd Masri, M.M.; Maidin, M.S.T.; Kamarudin, N.; Hussain, M.H.; Abd Ghani, I.; Jalinas, J. Preliminary evaluation of acoustic sensors for early detection of red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus incidence on oil palm and coconut in Malaysia. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 3287–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzroni, A.; Soroker, V.; Cohen, Y. Toward practical acoustic red palm weevil detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 124, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankin, R.; Mizrach, A.; Hetzroni, A.; Levsky, S.; Nakache, Y.; Soroker, V. Temporal and spectral features of sounds of wood-boring beetle larvae: Identifiable patterns of activity enable improved discrimination from background noise. Fla. Entomol. 2008, 91, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosunmu, O.G.; Herrick, N.J.; Haseeb, M.; Hix, R.L.; Mankin, R.W. Acoustic detectability of Rhynchophorus cruentatus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae). Fla. Entomol. 2014, 97, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, N.J.; Mankin, R. Acoustical detection of early instar Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Canary Island date palm, Phoenix canariensis (Arecales: Arecaceae). Fla. Entomol. 2012, 95, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankin, R.; Al-Ayedh, H.; Aldryhim, Y.; Rohde, B. Acoustic detection of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae) and Oryctes elegans (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) in Phoenix dactylifera (Arecales: Arecacae) trees and offshoots in Saudi Arabian orchards. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifian, M.; Bahar, R.; Amani, M.; Rahkhodaei, E. Mass production of EPF Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) by using agricultural products based on liquid- solid diphasic method for date palm pest control. Int. J. Agric. Crop. Sci. 2013, 5, 2338–2341. [Google Scholar]
- Potamitis, I.; Rigakis, I.; Tatlas, N.-A.; Potirakis, S. In-vivo vibroacoustic surveillance of trees in the context of the IoT. Sensors 2019, 19, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charif, R.; Waack, A.; Strickman, L. Raven Pro 1.4 User’s Manual; Idaho National Lab. (INL): Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 2010; p. 25506974.
- Shin, T.Y.; Lee, M.R.; Kim, J.C.; Nai, Y.S.; Kim, J.S. A new strategy using entomopathogenic fungi for the control of tree borer insects. Entomol. Res. 2022, 52, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewify, G. Egyptian Strain of Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria Bassiana; WO/2007/087813; WIPO Service; World Intellectual Property Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.; Ragheb, D.A.; El-Feshaway, A.A. Pathogenicity Of The Fungus, Beauveria Bassiana To The Red Palm Weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Under Field Conditions. Egypt. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 96, 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Gaviria, J.; Parra, P.P.; Gonzales, A. Selection of strains of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) for endophytic colonization in coconut seedlings. Chil. J. Agric. Anim. Sci. 2020, 36, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jalinas, J.; Güerri-Agulló, B.; Dosunmu, O.G.; Haseeb, M.; Lopez-Llorca, L.V.; Mankin, R.W. Acoustic signal applications in detection and management of Rhynchophorus spp. in fruit-crops and ornamental palms. Fla. Entomol. 2019, 102, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rach, M.M.; Gomis, H.M.; Granado, O.L.; Malumbres, M.P. On the design of a bioacoustic sensor for the early detection of the red palm weevil. Sensors 2013, 13, 1706–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardena, K.; Fernando, L.; Nanayakkara, N.; Perera, K.; Kumara, A.; Nanayakkara, T. Portable acoustic device for detection of coconut palms infested by Rynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Crop. Prot. 2010, 29, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekesi, S. Pathogenicity and antifeedant activity of entomopathogenic hyphomycetes to the cowpea leaf beetle, Ootheca mutabilis Shalberg. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2001, 21, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussenbaum, A.I.; Lecuona, R.E. Selection of Beauveria bassiana sensu lato and Metarhizium anisopliae sensu lato isolates as microbial control agents against the boll weevil (Anthonomus grandis)in Argentina. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankin, R.; Jetter, E.; Rohde, B.; Yasir, M. Performance of a low-cost acoustic insect detector system with Sitophilus oryzae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in stored grain and Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) in flour. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 3004–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Toews, M.D.; Oliveira-Hofman, C.; Behle, R.W.; Simmons, A.M.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I. Environmental tolerance of entomopathogenic fungi: A new strain of Cordyceps javanica isolated from a whitefly epizootic versus commercial fungal strains. Insects 2020, 11, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miętkiewski, R.; Tkaczuk, C.; Żurek, M.; Van Der Geest, L. Temperature requirements of four entomopathogenic fungi. Acta Mycol. 1994, 29, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Amritha De Croos, J.; Bidochka, M.J. Effects of low temperature on growth parameters in the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Can. J. Microbiol. 1999, 45, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Isolate Name | Isolate Code | Insect Species/ Order | Source of Isolation | Origin | Coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metarhizium anisopliae | MaSA–1 | Red palm weevil/Coleoptera | Adult | Riyadh, Saudi Arabia | N: 24.41867°; E: 46.65408° |
| Beauveria bassiana | BbSA–1 | Red palm weevil/Coleoptera | Adult | Al Qatif governorate, Saudi Arabia | N: 26.34437°; E: 43.69217° |
| Treatment * | Ambient Temperature (°C) ** | Temperature inside Date Palm (°C) ** |
|---|---|---|
| Control (water) | 19.93 ± 0a | 27.07 ± 0a |
| B. bassiana (BbSA–1) | 19.70 ± 0.23a | 23.66 ± 0.26b |
| M. anisopliae (MaSA–1) | 19.93 ± 0a | 24.19 ± 0.23b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sutanto, K.D.; Al-Shahwan, I.M.; Husain, M.; Rasool, K.G.; Mankin, R.W.; Aldawood, A.S. Field Evaluation of Promising Indigenous Entomopathogenic Fungal Isolates against Red Palm Weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae). J. Fungi 2023, 9, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9010068
Sutanto KD, Al-Shahwan IM, Husain M, Rasool KG, Mankin RW, Aldawood AS. Field Evaluation of Promising Indigenous Entomopathogenic Fungal Isolates against Red Palm Weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae). Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9010068
Chicago/Turabian StyleSutanto, Koko D., Ibrahim M. Al-Shahwan, Mureed Husain, Khawaja G. Rasool, Richard W. Mankin, and Abdulrahman S. Aldawood. 2023. "Field Evaluation of Promising Indigenous Entomopathogenic Fungal Isolates against Red Palm Weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9010068
APA StyleSutanto, K. D., Al-Shahwan, I. M., Husain, M., Rasool, K. G., Mankin, R. W., & Aldawood, A. S. (2023). Field Evaluation of Promising Indigenous Entomopathogenic Fungal Isolates against Red Palm Weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae). Journal of Fungi, 9(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9010068







