Sustainable Use of Sewage Sludge as a Casing Material for Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) Cultivation: Experimental and Prediction Modeling Studies for Uptake of Metal Elements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Bioaccumulation Factor and Prediction Modeling of Metal Elements Uptake
2.5. Software and Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of the Mushroom Substrate and Casing Materials
3.2. Effects of Sewage Sludge as Casing Material on Yield and Productivity of A. bisporus
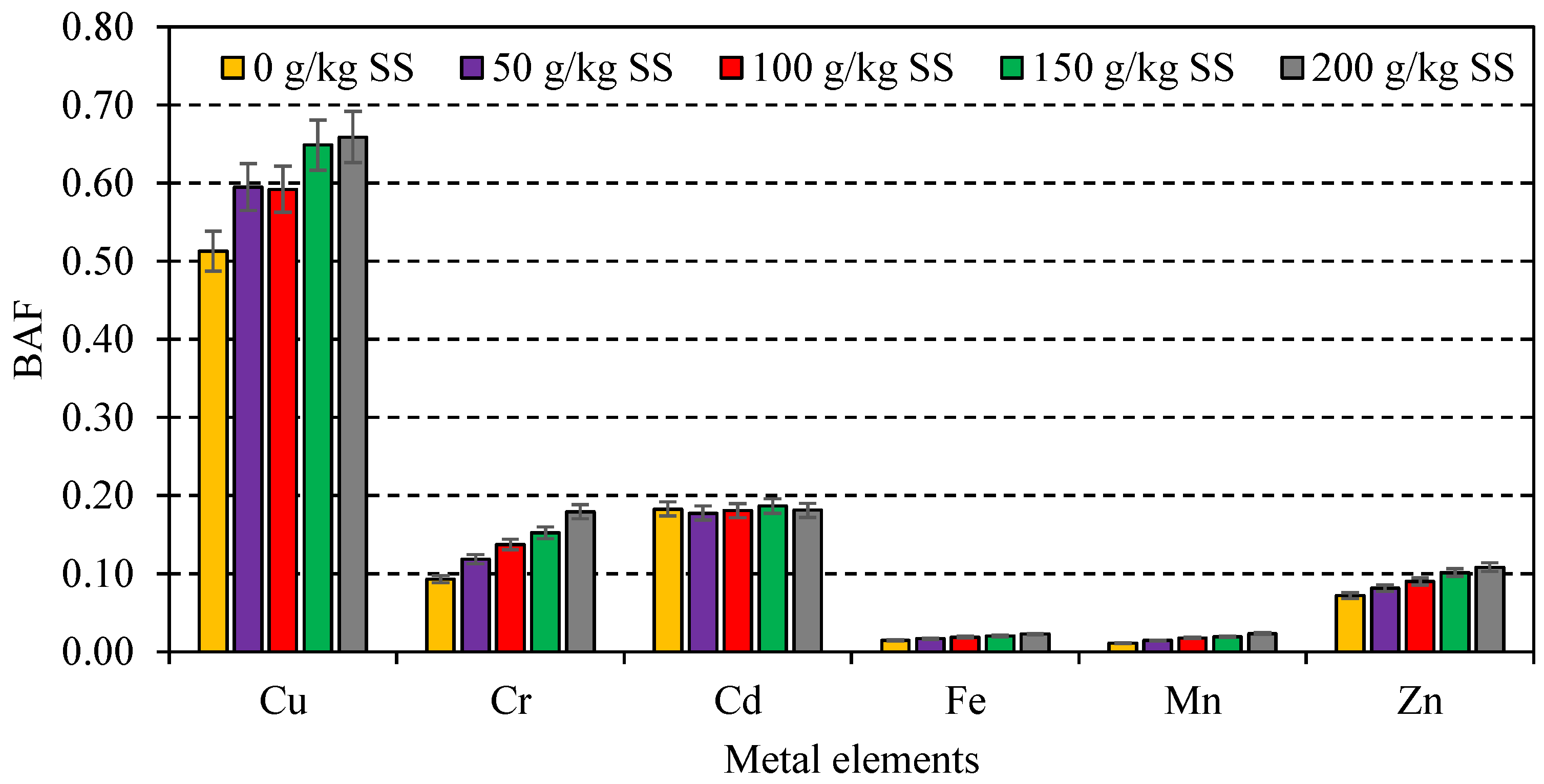
3.3. Effects of Sewage Sludge as Casing Material on Metal Elements Accumulation by A. bisporus
3.4. Prediction Models for Evaluating Metal Elements Accumulation by A. bisporus
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaddel, S.; Bakhtiary-Davijany, H.; Kabbe, C.; Dadgar, F.; Østerhus, S.W. Sustainable sewage sludge management: From current practices to emerging nutrient recovery technologies. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Mao, H.; Li, X. Functional characteristics and influence factors of microbial community in sewage sludge composting with inorganic bulking agent. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ju, R.; Zhou, H.; Chen, H. Migration characteristics of heavy metals during sludge pyrolysis. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinosa, L. Wastewater Sludge: A Global Overview of the Current Status and Future Prospects, 2nd ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2011; Volume 10, ISBN 9781843391425. [Google Scholar]
- Aleisa, E.; Alsulaili, A.; Almuzaini, Y. Recirculating treated sewage sludge for agricultural use: Life cycle assessment for a circular economy. Waste Manag. 2021, 135, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPCB Parivesh Sewage Pollution—News Letter. East Arjun Nagar: Delhi, India. 2005. Available online: https://cpcb.nic.in/openpdffile.php?id=TGF0ZXN0RmlsZS9MYXRlc3RfMTIzX1NVTU1BUllfQk9PS19GUy5wZGY (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Kacprzak, M.; Neczaj, E.; Fijałkowski, K.; Grobelak, A.; Grosser, A.; Worwag, M.; Rorat, A.; Brattebo, H.; Almås, Å.; Singh, B.R. Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, V.; Goala, M.; Singh, J.; Kumar, P. Integrated use of treated dairy wastewater and agro-residue for Agaricus bisporus mushroom cultivation: Experimental and kinetics studies. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 32, 101940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Fayssal, S.; Alsanad, M.A.; El Sebaaly, Z.; Ismail, A.I.H.; Sassine, Y.N. Valorization of Olive Pruning Residues through Bioconversion into Edible Mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus (Jacq. Ex Fr.) P. Kumm. (1871) of Improved Nutritional Value. Scientifica 2020, 2020, 3950357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsanad, M.A.; Sassine, Y.N.; El Sebaaly, Z.; Fayssal, S.A. Spent coffee grounds influence on Pleurotus ostreatus production, composition, fatty acid profile, and lignocellulose biodegradation capacity. CYTA-J. Food 2021, 19, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, L.; Alsanad, M.A.; El Sebaaly, Z.; Shaban, N.; Fayssal, S.A.; Sassine, Y.N. Variation of Pleurotus ostreatus (Jacq. Ex Fr.) P. Kumm. (1871) performance subjected to differentdoses and timings of nano-urea. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, L.; Alsanad, M.A.; Shaban, N.; El Sebaaly, Z.; Abou Fayssal, S.; Sassine, Y.N. Production and composition of Pleurotus ostreatus cultivated on Lithovit®-Amino25 supplemented spent substrate. AMB Express 2020, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, L.; El Sebaaly, Z.; Abou Fayssal, S.; Alsanad, M.A.; Najjar, R.; Yordanova, M.H.; Sassine, Y.N. The use of nitrogen-rich nano-supplements affects substrate temperature, delays the production cycle, and increases yield of Pleurotus ostreatus. Acta Hortic. 2021, 1327, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Fayssal, S.; El Sebaaly, Z.; Alsanad, M.A.; Najjar, R.; Bohme, M.; Yordanova, M.H.; Sassine, Y.N. Combined effect of olive pruning residues and spent coffee grounds on Pleurotus ostreatus production, composition, and nutritional value. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Fayssal, S.; Alsanad, M.A.; Yordanova, M.H.; El Sebaaly, Z.; Najjar, R.; Sassine, Y.N. Effect of olive pruning residues on substrate temperature and production of oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus). Acta Hortic. 2021, 1327, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaaly, Z.; AlSanad, M.A.; Hayek, P.; Kfoury, L.; Shaban, N.; Sassine, Y.N. Using locally available chicken manure as a substitute to horse manure in compost formulas for growing Agaricus bisporus in Lebanon. Acta Hortic. 2020, 1287, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaaly, Z.; AlSanad, M.A.; Seeman, H.; Rizkallah, J.; Shaban, N.; Sassine, Y.N. Investigating the potential use of composted grape marc in the production of Agaricus bisporus. Acta Hortic. 2020, 1287, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerketta, A.; Shukla, C.S.; Singh, H.K. Evaluation of different casing materials for growth and yield of button Musrhroom (Agaricus bisporus (L.) Sing.). J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 207–209. [Google Scholar]
- Sajyan, T.K.; Abou Fayssal, S.; Bejjani, R.; El Sebaaly, Z.; Sassine, Y.N. Casing and cropping. In Mushrooms Agaricus bisporus; Sassine, Y.N., Ed.; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2021; pp. 240–278. ISBN 9781800620438. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha Zied, D.; Pardo-Gonzalez, J.E.; Almeida Minhoni, M.T.; Arturo Pardo-Gimenez, A. A Reliable Quality Index for Mushroom Cultivation. J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 3, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Giménez, A.; Zied, D.C.; Pardo-González, J.E. The use of peat as casing material in mushroom cultivation. In Peat: Formation, Uses and Biological Effects; Draguhn, C., Ciarimboli, N., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 81–100. ISBN 9781621001621. [Google Scholar]
- De Juan, J.A.; Pardo, A.; Pardo, J.E. Effect of different casing materials on production and quality of the cultivated mushroom. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2003, 17, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Giménez, A.; Pardo-González, J.E. Evaluation of casing materials made from spent mushroom substrate and coconut fibre pith for use in production of Agaricus bisporus (Lange) Imbach. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2008, 6, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sassine, Y.N.; Ghora, Y.; Kharrat, M.; Bohme, M.; Abdel-Mawgoud, A.M.R. Waste Paper as an Alternative for Casing Soil in Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) Production. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2005, 1, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Sassine, Y.N.; Ghorra, Y.; Bohme, M.; Abdel-Mawgoud, A.M.R.; Kharrat, M. Effect of different mixtures with waste paper on the growth and production of mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2006, 13, 281–293. [Google Scholar]
- Mami, Y.; Peyvast, G.; Ghasemnezhad, M.; Ziaie, F. Supplementation at casing to improve yield and quality of white button mushroom. Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyer, D.M.; Beelman, R.B.; Kremser, J.J.; Rhodes, T.W. Casing additives and their influence on yield and fresh quality of Agaricus bisporus. In Mushroom Biology and Mushroom Products; Sánchez, J.E., Huerta, G., Montiel, E., Eds.; John Willey and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 311–321. [Google Scholar]
- Adibian, M.; Mami, Y. Mushroom supplement added to casing to improve postharvest quality of white button mushroom. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2015, 80, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, S.S. Garbage Composting for Mushroom Production. Appl. Microbiol. 1965, 13, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbrahim, M.; Denaix, L.; Thomas, A.L.; Balet, J.; Carnus, J.M. Metal concentrations in edible mushrooms following municipal sludge application on forest land. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaposts, V.; Karins, Z.; Lazdins, A. Use of sewage sludge in forest cultivation. Balt. For. 2000, 6, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, M.; Chishaki, N.; Yamada, M.; Katahira, T.; Harada, R.; Suemitsu, T.; Yagi, F.; Yamaguchi, T. Mass Production of Mushrooms using Sewage Sludge Compost and Utilization of Waste Beds for Crop Cultivation. J. Jpn. Soc. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 31, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towers, W.; Home, P. Sewage sludge recycling to agricultural land: The environmental scientist’s perspective. J. Comm. Int. Water Environ. J. 1997, 11, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominko, H.; Gorazda, K.; Wzorek, Z. Formulation and evaluation of organo-mineral fertilizers based on sewage sludge optimized for maize and sunflower crops. Waste Manag. 2021, 136, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ding, L.; Lin, R.; Yue, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Fermentative biohydrogen and biomethane co-production from mixture of food waste and sewage sludge: Effects of physiochemical properties and mix ratios on fermentation performance. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Su, H.; Baeyens, J.; Tan, T. Reviewing the anaerobic digestion of food waste for biogas production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malińska, K.; Zabochnicka-Świątek, M. Selection of bulking agents for composting of sewage sludge. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2013, 39, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibulka, J.; Sisak, L.; Pu Lkrab, K.; Miholova, D.; Szakova, J.; Fucikova, A.; Slamova, A.; Stehulova, I.; Arlakova, S. Cadmium, lead, mercury and caesium levels in wild mushrooms and forest berries from different localities of the Czech Republic. Sci. Agric. Bohem. 1996, 27, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sinden, J.W.; Mauser, E. The nature of the composting process and its relation to short composting. Mushroom Sci. 1953, 2, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.P.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, S. Technologies Developed by ICAR-Directorate of Mushroom Research for Commercial Use; ICAR-DMR: Solan, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Abou Fayssal, S.; Hammoud, M.; El Sebaaly, Z.; Sassine, Y.N. Improvement of compost quality. In Mushrooms Agaricus bisporus; Sassine, Y.N., Ed.; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2021; pp. 136–175. ISBN 9781800620438. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC Official Methods of Analysis, 21st ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019.
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, E.M.; Shaltout, K.H.; Alamri, S.A.M.; Alrumman, S.A.; Sewelam, N. Prediction Models Founded on Soil Characteristics for the Estimated Uptake of Nine Metals by Okra Plant, Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench., Cultivated in Agricultural Soils Modified with Varying Sewage Sludge Concentrations. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, K.; Emadi, M.; Bagheri, A.; Mohammadi, M. Casing Material and Thickness Effects on the Yield and Nutrient Concentration of Agaricus bisporus. Sarhad J. Agric. 2020, 36, 734–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaphy, S.; Levanon, D.; Tchelet, R.; Henis, Y. Scanning Electron Microscope Studies of Interactions between Agaricus bisporus (Lang) Sing Hyphae and Bacteria in Casing Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 1132–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, E.S.; Zied, D.C.; Pardo-Gimenez, A. Revisiting the casing layer: Casing materials and management in Agaricus mushroom cultivation. Ciênc. Agrotecnol. 2021, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, P.; Singh, J.; Kumar, P. Use of sugar mill wastewater for Agaricus bisporus cultivation: Prediction models for trace metal uptake and health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 26923–26934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goala, M.; Yadav, K.K.; Alam, J.; Adelodun, B.; Choi, K.S.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Hamid, A.A.; Alhoshan, M.; Ali, F.A.A.; Shukla, A.K. Phytoremediation of dairy wastewater using Azolla pinnata: Application of image processing technique for leaflet growth simulation. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Mortimer, P.E.; Hyde, K.D.; Kakumyan, P.; Thongklang, N. Mushroom cultivation for soil amendment and bioremediation. Circ. Agric. Syst. 2021, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Giménez, A.; Pardo González, J.E.; Zied, D.C. Casing Materials and Techniques in Agaricus bisporus Cultivation. In Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; Volume 109, pp. 149–174. ISBN 9781119149415. [Google Scholar]
- Khakimov, A.; Ismailov, A.; Murodullaeva, M. Casing soils selection for cultivation of common mushroom Agaricus bisporus (JE Lange) Imbach, 1946. Bul. Sci. Pract. 2018, 7, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, M.M.; Viana, D.G.; Oliveira, F.C.; Alves, M.C.; Regitano, J.B. Sewage sludge as organic matrix in the manufacture of organomineral fertilizers: Physical forms, environmental risks, and nutrients recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 313, 127774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maknali, F.; Kashi, A.; Salehi Mohammadi, R.; Khalighi, A. Enrichment of casing soil with Fe and soy-flour under Pseudomonas inoculation on yield and quality of button mushroom. Rev. Agric. Neotrop. 2021, 8, e5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhupathi, P.; Subbaiah, K.A.; Balan, V. Influence of Soil Nutrition and Rhizobiome Bacteria on the Growth of Calocybe Indica (P & C). Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 4567–4575. [Google Scholar]
- Eid, E.M.; Kumar, P.; Adelodun, B.; Choi, K.S.; Singh, J.; Kumari, S.; Kumar, V. Modeling of mineral elements uptake and localization in cabbage inflorescence (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) grown on sugar mill pressmud-amended soils. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indolean, C.; Măicăneanu, A.; Cristea, V.M. Prediction of Cu(II) biosorption performances on wild mushrooms Lactarius piperatus using Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) model. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 95, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
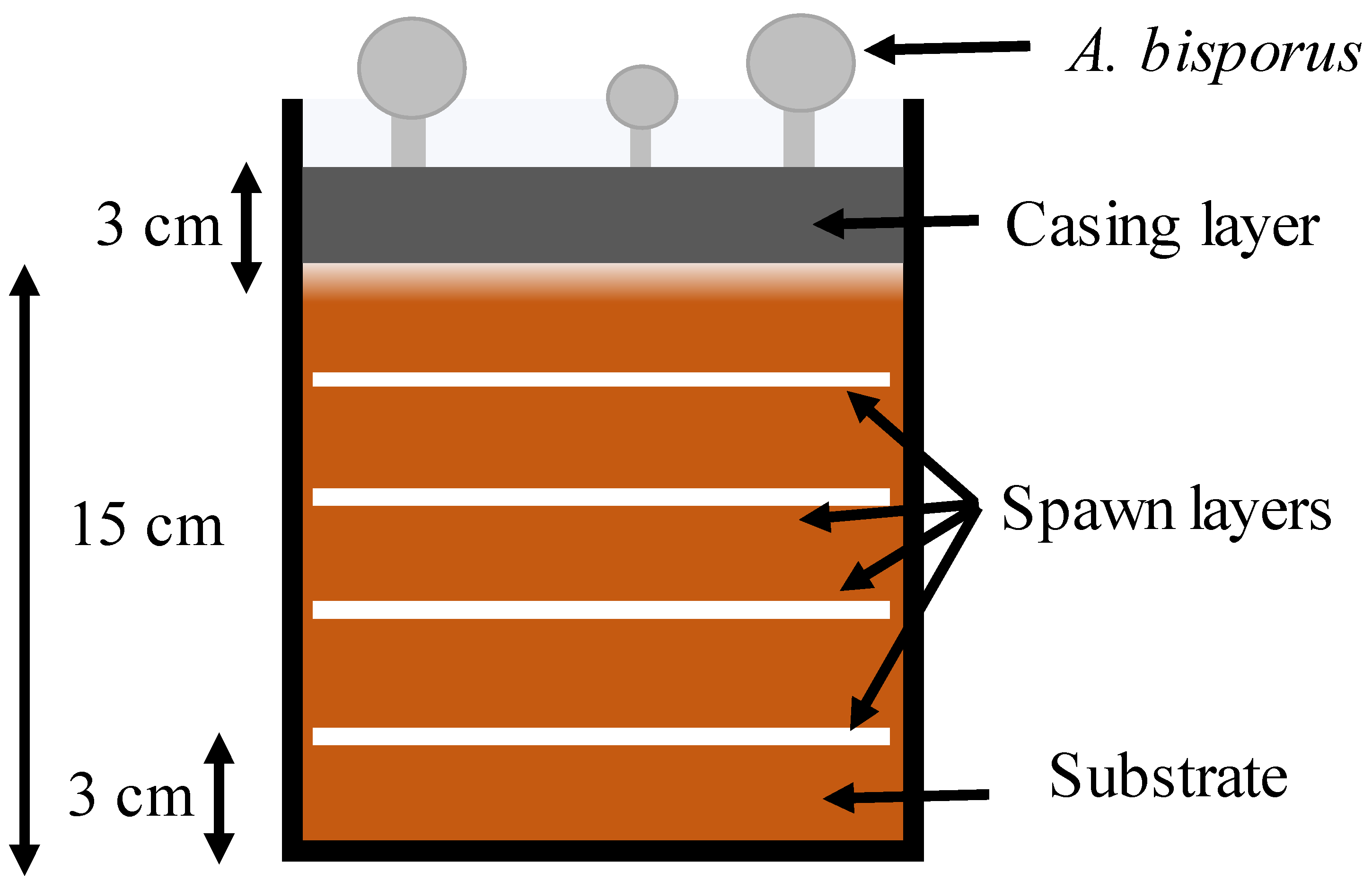

| Parameter | WS-Substrate | Loam Soil (LS) | Sewage Sludge (SS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | CV (%) | Value | CV (%) | Value | CV (%) | |
| pH | 7.06 ± 0.03 | 0.37 | 7.31 ± 0.01 | 0.16 | 6.10 ± 0.01 | 0.16 |
| Electrical conductivity (dS/m) | 6.13 ± 0.04 | 0.60 | 5.31 ± 0.04 | 0.75 | 6.92 ± 0.02 | 0.30 |
| Organic carbon (g/kg) | 494.86 ± 2.86 | 0.57 | 10.10 ± 0.61 | 0.53 | 122.62 ± 0.42 | 1.00 |
| TKN (g/kg) | 17.26 ± 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.56 ± 0.04 | 7.14 | 6.44 ± 0.10 | 1.55 |
| C/N ratio | 28.67 | - | 18.03 | - | 18.63 | - |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 34.43 ± 0.57 | 1.67 | 5.07 ± 0.03 | 0.68 | 56.03 ± 0.07 | 0.12 |
| Cr (mg/kg) | 8.20 ± 0.12 | 1.54 | 2.75 ± 0.01 | 0.15 | 10.51 ± 0.03 | 0.26 |
| Cd (mg/kg) | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 0.56 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 1.31 | 2.49 ± 0.01 | 0.24 |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 3091.92 ± 0.38 | 0.01 | 16.68 ± 0.09 | 0.52 | 51.87 ± 0.17 | 0.32 |
| Mn (mg/kg) | 310.73 ± 0.89 | 0.28 | 5.80 ± 0.01 | 0.14 | 12.06 ± 0.05 | 0.44 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 385.89 ± 0.80 | 0.20 | 3.05 ± 0.01 | 0.34 | 117.98 ± 0.45 | 0.38 |
| Characteristics | Sewage Sludge Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (0 g/kg) | 50 g/kg | 100 g/kg | 150 g/kg | 200 g/kg | |
| pH | 7.31 ± 0.01 | 7.19 ± 0.01 a | 7.05 ± 0.03 a | 6.77 ± 0.02 a | 6.50 ± 0.02 a |
| Electrical conductivity (dS/m) | 5.31 ± 0.04 | 5.61 ± 0.01 a | 6.03 ± 0.03 a | 6.29 ± 0.03 a | 6.51 ± 0.03 a |
| Organic carbon (g/kg) | 10.10 ± 0.61 | 12.41 ± 0.73 a | 14.76 ± 0.58 a | 20.15 ± 1.03 a | 23.44 ± 0.82 a |
| TKN (g/kg) | 0.56 ± 0.04 | 0.70 ± 0.05 a | 0.84 ± 0.09 a | 0.94 ± 0.06 a | 1.12 ± 0.10 a |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 5.07 ± 0.03 | 6.53 ± 1.16 b | 10.53 ± 0.16 a | 13.40 ± 0.15 a | 16.24 ± 0.08 a |
| Cr (mg/kg) | 2.75 ± 0.01 | 3.24 ± 0.03 a | 3.75 ± 0.05 a | 4.31 ± 0.06 a | 4.80 ± 0.04 a |
| Cd (mg/kg) | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.01 a | 0.40 ± 0.01 a | 0.52 ± 0.01 a | 0.64 ± 0.01 a |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 16.68 ± 0.09 | 19.25 ± 0.06 a | 21.61 ± 0.26 a | 24.32 ± 0.18 a | 27.16 ± 0.14 a |
| Mn (mg/kg) | 5.80 ± 0.01 | 6.40 ± 0.01 a | 7.05 ± 0.04 a | 7.60 ± 0.02 a | 8.21 ± 0.01 a |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 3.05 ± 0.01 | 8.98 ± 0.03 a | 14.79 ± 0.14 a | 20.88 ± 0.17 a | 26.61 ± 0.12 a |
| Parameter | Flush | Sewage Sludge Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (0 g/kg) | 50 g/kg | 100 g/kg | 150 g/kg | 200 g/kg | ||
| Mushroom yield (g/kg fresh substrate) | 1st | 64.32 ± 0.26 | 72.55 ± 0.28 a | 75.75 ± 0.55 a | 80.79 ± 0.40 a | 76.74 ± 2.24 a |
| 2nd | 57.77 ± 0.35 | 60.95 ± 0.49 a | 65.70 ± 0.22 a | 64.83 ± 0.65 a | 65.95 ± 1.69 a | |
| 3rd | 43.45 ± 0.33 | 45.99 ± 0.39 a | 48.24 ± 0.47 a | 46.81 ± 1.47 a | 52.39 ± 0.70 a | |
| Average | 55.18 ± 10.67 | 59.83 ± 13.32 b | 63.23 ± 13.92 b | 64.14 ± 17.00 b | 65.02 ± 12.20 b | |
| Total | 165.53 | 179.49 | 189.69 | 192.43 | 195.07 | |
| Biological efficiency (%) | - | 55.18 | 59.83 | 63.23 | 64.14 | 65.02 |
| Metal Element (mg/kg dwt.) | Flush | Sewage Sludge Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (0 g/kg) | 50 g/kg | 100 g/kg | 150 g/kg | 200 g/kg | ||
| Cu | 1st | 21.52 ± 0.02 | 24.97 ± 0.01 | 27.06 ± 0.01 | 31.12 ± 0.01 | 33.46 ± 0.01 |
| 2nd | 20.28 ± 0.01 | 24.28 ± 0.06 | 26.58 ± 0.01 | 31.01 ± 0.01 | 33.40 ± 0.01 | |
| 3rd | 18.97 ± 0.01 | 23.86 ± 0.01 | 26.23 ± 0.01 | 30.94 ± 0.01 | 33.31 ± 0.01 | |
| Average | 20.25 ± 1.27 | 24.37 ± 0.55 a | 26.62 ± 0.41 a | 31.02 ± 0.09 a | 33.39 ± 0.07 a | |
| Cr | 1st | 1.07 ± 0.05 | 1.41 ± 0.01 | 1.69 ± 0.01 | 1.93 ± 0.01 | 2.28 ± 0.01 |
| 2nd | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 1.38 ± 0.01 | 1.63 ± 0.01 | 1.91 ± 0.01 | 2.25 ± 0.01 | |
| 3rd | 0.98 ± 0.01 | 1.27 ± 0.01 | 1.59 ± 0.01 | 1.87 ± 0.01 | 2.45 ± 0.01 | |
| Average | 1.02 ± 0.01 | 1.35 ± 0.07 a | 1.64 ± 0.05 a | 1.90 ± 0.03 a | 2.33 ± 0.11 a | |
| Cd | 1st | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| 2nd | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | |
| 3rd | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | |
| Average | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 0.17 ± 0.01 a | 0.19 ± 0.01 a | 0.21 ± 0.01 a | |
| Fe | 1st | 48.77 ± 0.01 | 52.42 ± 0.33 | 58.13 ± 0.01 | 63.71 ± 0.01 | 70.45 ± 0.04 |
| 2nd | 44.28 ± 0.01 | 51.57 ± 0.22 | 57.57 ± 0.09 | 62.50 ± 0.01 | 69.70 ± 0.02 | |
| 3rd | 43.06 ± 0.01 | 50.17 ± 0.06 | 57.23 ± 0.06 | 62.13 ± 0.01 | 68.37 ± 0.01 | |
| Average | 45.37 ± 3.01 | 51.39 ± 1.13 a | 57.64 ± 0.45 a | 62.78 ± 0.82 a | 69.51 ± 1.05 a | |
| Mn | 1st | 3.53 ± 0.01 | 4.76 ± 0.04 | 5.58 ± 0.01 | 6.14 ± 0.01 | 7.53 ± 0.25 |
| 2nd | 3.40 ± 0.01 | 4.64 ± 0.01 | 5.59 ± 0.05 | 6.13 ± 0.01 | 7.34 ± 0.01 | |
| 3rd | 3.28 ± 0.01 | 4.41 ± 0.17 | 5.46 ± 0.11 | 6.12 ± 0.01 | 7.30 ± 0.01 | |
| Average | 3.40 ± 0.12 | 4.60 ± 0.20 a | 5.54 ± 0.07 a | 6.13 ± 0.01 a | 7.39 ± 0.12 a | |
| Zn | 1st | 30.28 ± 0.08 | 32.52 ± 0.03 | 36.39 ± 0.01 | 41.81 ± 0.01 | 45.15 ± 0.01 |
| 2nd | 27.29 ± 0.05 | 32.21 ± 0.01 | 36.11 ± 0.01 | 41.00 ± 0.01 | 44.68 ± 0.01 | |
| 3rd | 26.13 ± 0.01 | 31.47 ± 0.02 | 35.86 ± 0.01 | 40.82 ± 0.01 | 44.11 ± 0.01 | |
| Average | 27.90 ± 2.14 | 32.07 ± 0.54 a | 36.12 ± 0.26 a | 41.21 ± 0.52 a | 44.65 ± 0.52 a | |
| Metal Element | Model Equation | R2 | ME | RMSE | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | y = 20.217 + (0.067 × pHC) + (1.276 × OCC) − (0.360 × MES+C) | 0.9918 | 0.98 | 0.375 | 588.47 | <0.001 |
| Cr | y = −2.814 − (0.335 × pHC) − (0.017 × OCC) + (0.593 × MES+C) | 0.9900 | 0.99 | 0.044 | 375.89 | <0.001 |
| Cd | y = 0.079 − (0.003 × pHC) + (0.006 × OCC) + (0.004 × MES+C) | 0.9956 | 0.99 | 0.004 | 833.15 | <0.001 |
| Fe | y = −6963.721 + (4.645 × pHC) + (0.313 × OCC) + (2.242 × MES+C) | 0.9976 | 0.98 | 0.410 | 1542.49 | <0.001 |
| Mn | y = −906.571 − (0.096 × pHC) − (0.237 × OCC) + (2.885 × MES+C) | 0.9924 | 0.98 | 0.003 | 479.34 | <0.001 |
| Zn | y = −63.503 + (0.058 × pHC) + (0.891 × OCC) + (0.208 × MES+C) | 0.9988 | 0.99 | 0.002 | 323.58 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, P.; Kumar, V.; Adelodun, B.; Bedeković, D.; Kos, I.; Širić, I.; Alamri, S.A.M.; Alrumman, S.A.; Eid, E.M.; Abou Fayssal, S.; et al. Sustainable Use of Sewage Sludge as a Casing Material for Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) Cultivation: Experimental and Prediction Modeling Studies for Uptake of Metal Elements. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8020112
Kumar P, Kumar V, Adelodun B, Bedeković D, Kos I, Širić I, Alamri SAM, Alrumman SA, Eid EM, Abou Fayssal S, et al. Sustainable Use of Sewage Sludge as a Casing Material for Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) Cultivation: Experimental and Prediction Modeling Studies for Uptake of Metal Elements. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(2):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8020112
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Pankaj, Vinod Kumar, Bashir Adelodun, Dalibor Bedeković, Ivica Kos, Ivan Širić, Saad A. M. Alamri, Sulaiman A. Alrumman, Ebrahem M. Eid, Sami Abou Fayssal, and et al. 2022. "Sustainable Use of Sewage Sludge as a Casing Material for Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) Cultivation: Experimental and Prediction Modeling Studies for Uptake of Metal Elements" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 2: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8020112
APA StyleKumar, P., Kumar, V., Adelodun, B., Bedeković, D., Kos, I., Širić, I., Alamri, S. A. M., Alrumman, S. A., Eid, E. M., Abou Fayssal, S., Goala, M., Arya, A. K., Bachheti, A., Choi, K. S., Ajibade, F. O., & Silva, L. F. O. (2022). Sustainable Use of Sewage Sludge as a Casing Material for Button Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) Cultivation: Experimental and Prediction Modeling Studies for Uptake of Metal Elements. Journal of Fungi, 8(2), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8020112















