Morpho-Phylogenetic Evidence Reveals New Species of Fuscosporellaceae and Savoryellaceae from Freshwater Habitats in Guizhou Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Examination of Specimens
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
| Taxon | Source | GenBank Accession Number | References | ||||
| LSU | SSU | ITS | RPB2 | TEF1α | |||
| Ascotaiwania latericolla | ICMP 22739 T | MN699407 | – | MN699390 | MN704312 | – | [16] |
| Ascotaiwania lignicola | NIL 00006 | HQ446365 | HQ446285 | HQ446342 | – | HQ446308 | [12] |
| Bactrodesmiastrum obovatum | FMR 6482 T | FR870266 | – | FR870264 | – | – | [41] |
| Bactrodesmiastrum pyriforme | FMR 10747 T | FR870265 | – | FR870263 | – | – | [41] |
| Bactrodesmiastrum pyriforme | FMR 11931 | HE646637 | – | HE646636 | – | – | [41] |
| Bactrodesmiastrum monilioides | FMR 10756 | KF771879 | – | KF771878 | – | – | [10] |
| Bactrodesmium leptopus | CBS 144542 | MN699423 | MN699374 | MN699388 | MN704297 | MN704321 | [16] |
| Bactrodesmium obovatum | CBS 144407 | MN699426 | MN699377 | MN699397 | MN704299 | MN704324 | [16] |
| Canalisporium elegans | SS 00895 | GQ390271 | GQ390256 | – | HQ446425 | HQ446311 | [12] |
| Canalisporium caribense | SS 03683 | GQ390269 | GQ390254 | – | – | – | [12] |
| Canalisporium grenadoidia | BCC 20507 T | GQ390267 | GQ390252 | GQ390282 | HQ446420 | HQ446309 | [12] |
| Conioscypha hoehnelii | FMR 11592 T | KY853497 | HF937348 | KY853437 | – | – | [14] |
| Conioscypha japonica | CBS 387.84 T | AY484514 | JQ437438 | – | JQ429259 | – | [42,43] |
| Conioscypha lignicola | CBS 335.93 T | AY484513 | JQ437439 | – | JQ429260 | – | [42,43] |
| Conioscypha varia | CBS 113653 | AY484512 | AY484511 | – | JQ429261 | – | [42,43] |
| Dematiosporium aquaticum | MFLU 18-1641 | MK835855 | – | – | MN194029 | MN200286 | [15] |
| Fuscosporella aquatica | MFLUCC 16-0859 | MG388209 | – | MG388212 | – | – | [44] |
| Fuscosporella guizhouensis | CGMCC 3.20884T | OP376725 | OP376721 | OP376715 | OP367755 | OP367761 | This study |
| Fuscosporella guizhouensis | UESTCC 22.0017 | OP376729 | OP376720 | OP376727 | OP367756 | OP367762 | This study |
| Fuscosporella pyriformis | MFLUCC 16-0570 T | KX550896 | KX550900 | MG388217 | KX576872 | – | [7] |
| Mucispora aquatica | CGMCC 3.20882T | OP376717 | OP376726 | OP376713 | OP367752 | OP367757 | This study |
| Mucispora aquatica | UESTCC 22.0018 | OP376716 | OP376718 | OP376712 | – | OP367758 | This study |
| Mucispora infundibulata | MFLUCC 16-0866 T | MH457139 | MH457171 | MH457174 | – | – | [11] |
| Mucispora obscuriseptata | MFLUCC 15-0618 T | KX550892 | KX550897 | MG388218 | KX576870 | – | [7] |
| Mucispora phangngaensis | MFLUCC 16-0865 | MG388210 | – | MG388213 | – | – | [44] |
| Neoascotaiwania fusiformis | MFLUCC 15-0621 T | KX550893 | – | MG388215 | KX576871 | – | [7] |
| Neoascotaiwania fusiformis | MFLUCC 15-0625 | KX550894 | KX550898 | MG388216 | – | – | [7] |
| Neoascotaiwania guizhouensis | CGMCC 3.20883T | OP376731 | OP376719 | OP376728 | OP367753 | OP367759 | This study |
| Neoascotaiwania guizhouensis | UESTCC 22.0019 | OP718560 | – | OP376730 | OP367754 | OP367760 | This study |
| Neoascotaiwania limnetica | CBS 126576 | KY853513 | KT278689 | KY853452 | MN704308 | MN704331 | [8,14,16] |
| Neoascotaiwania limnetica | CBS 126792 | KY853514 | KT278690 | KY853453 | MN704309 | MN704332 | [8,14,16] |
| Neoascotaiwania terrestris | CBS 144402 | MN699434 | MN699386 | MN699405 | MN704310 | MN704333 | [16] |
| Neoascotaiwania terrestris | CBS 142291 T | KY853515 | KY853547 | KY853454 | – | – | [14,16] |
| Parafuscosporellamoniliformis | MFLUCC 15-0626 T | KX550895 | KX550899 | MG388219 | – | – | [7] |
| Parafuscosporella mucosa | MFLUCC 16-0571 T | MG388211 | – | MG388214 | – | – | [7] |
| Parafuscosporella pyriformis | KUMCC 19-0008 | MN512340 | – | MN513031 | – | – | [45] |
| Parafuscosporella garethii | FF00725.01 T | KX958430 | KX958429 | – | KX958432 | – | [46] |
| Parafuscosporella aquatica | KUMCC 19-0211 T | MN512343 | – | MN513034 | – | – | [45] |
| Phaeoisaria aquatica | MFLUCC 16-1298 T | MF399254 | – | MF399237 | MF401406 | – | [47] |
| Phaeoisaria fasciculata | CBS 127885 T | KT278705 | KT278693 | KT278719 | KT278741 | – | [8] |
| Plagiascoma frondosum | CBS 139031 T | KT278713 | KT278701 | – | KT278749 | – | [8] |
| Pleurotheciella erumpens | CBS 142447 T | MN699435 | MN699387 | MN699406 | MN704311 | MN704334 | [8] |
| Pleurotheciella guttulata | KUMCC 15-0296 T | MF399257 | MF399223 | MF399240 | MF401409 | – | [47] |
| Pleurothecium aquaticum | MFLUCC 17-1331 T | MF399263 | – | MF399245 | – | – | [47] |
| Pleurothecium floriforme | MFLUCC 15-1163 T | KY697277 | KY697279 | KY697281 | – | – | [48] |
| Pseudoascotaiwania persoonii | A57 14C T | AY094190 | – | – | – | – | [49] |
| Savoryella lignicola | NF 00204 | HQ446378 | HQ446300 | HQ446357 | – | HQ446334 | [12] |
| Savoryella nypae | MFLUCC 18-1570 | MK543210 | MK543237 | MK543219 | – | MK542516 | [50] |
| Tolypocladium capitatum | OSC 71233 | AY489721 | AY489689 | – | DQ522421 | AY489615 | [51,52] |
| Tolypocladium japonicum | OSC 110991 | DQ518761 | DQ522547 | – | DQ522428 | DQ522330 | [52] |
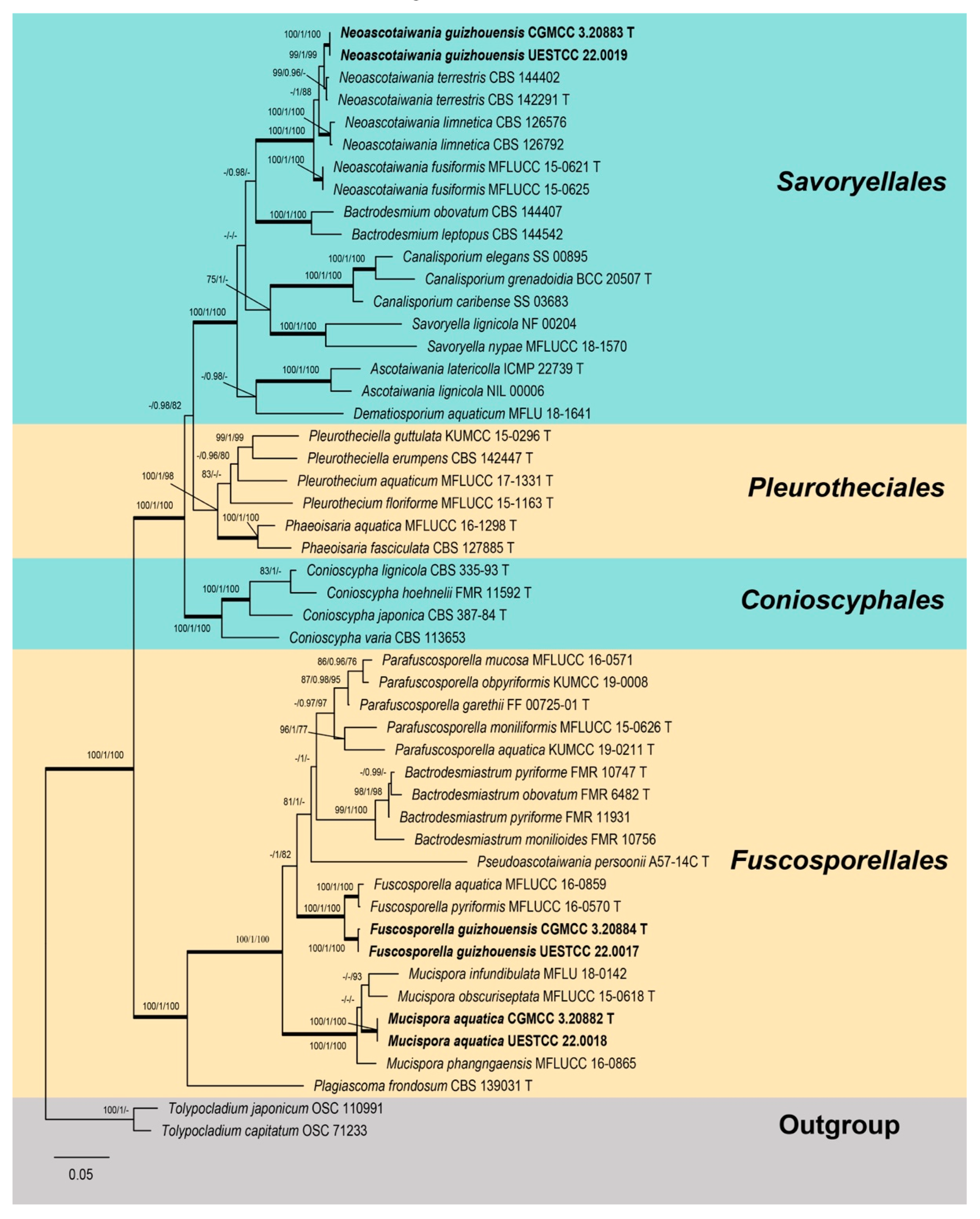
3. Phylogenetic Results
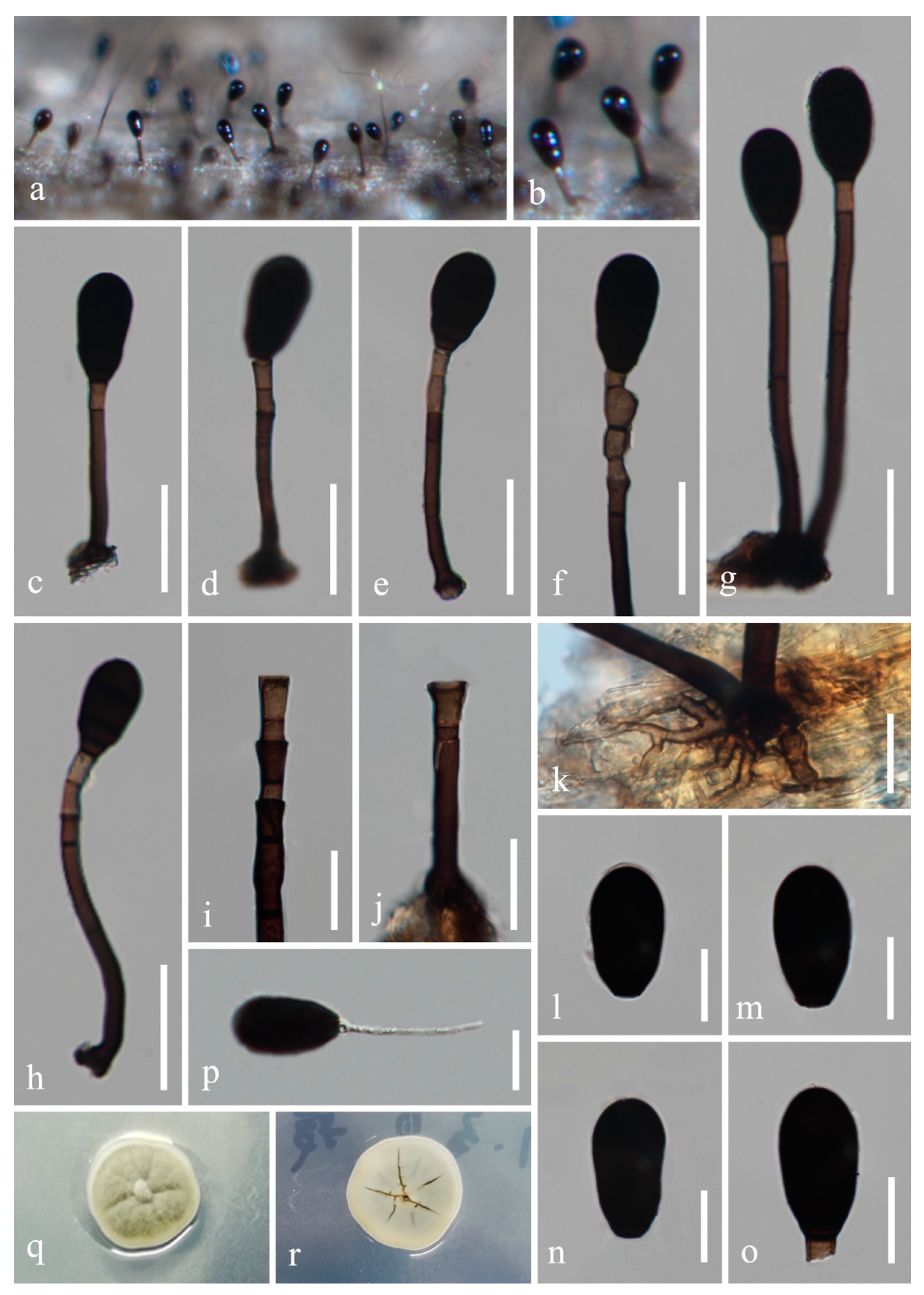
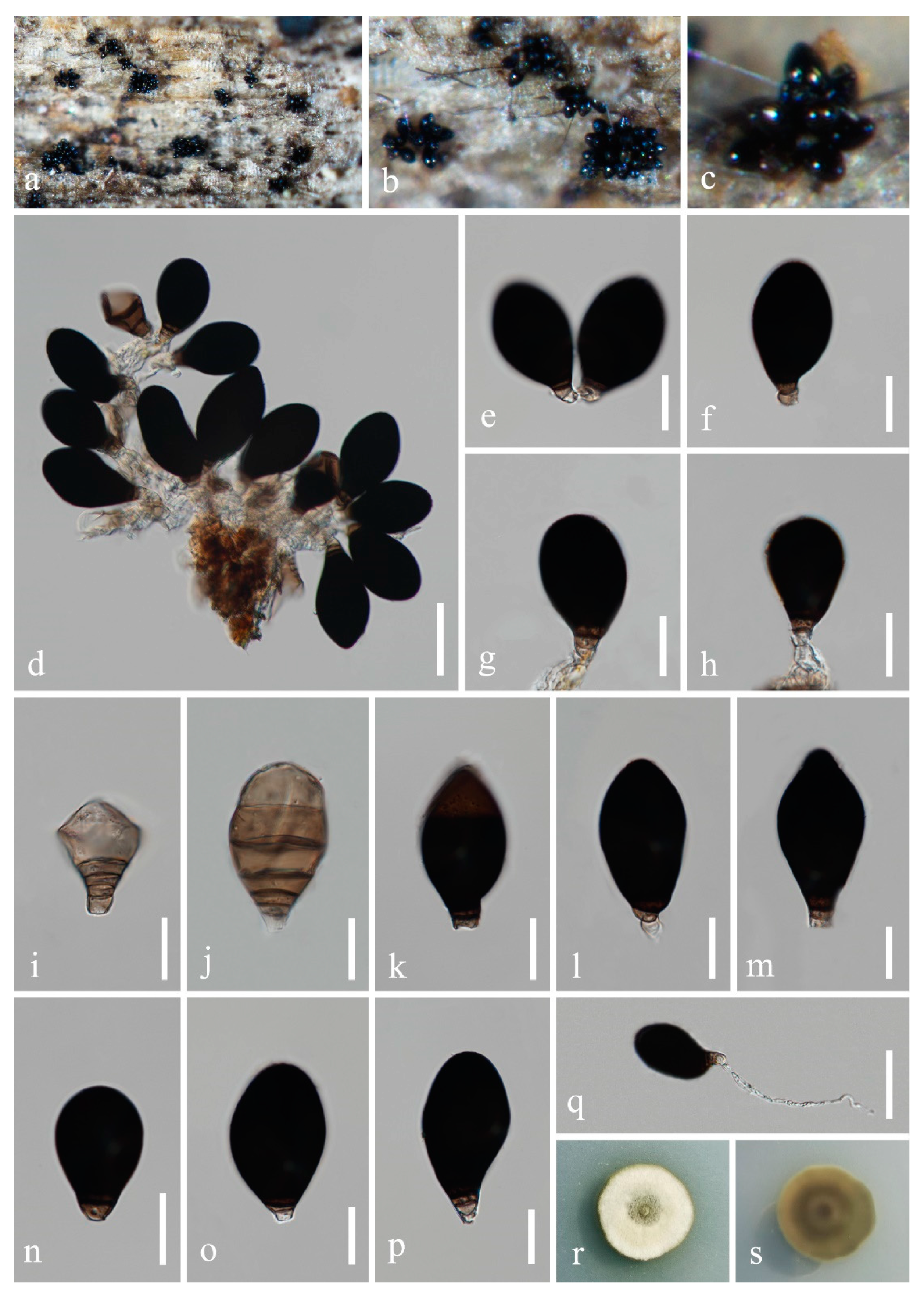
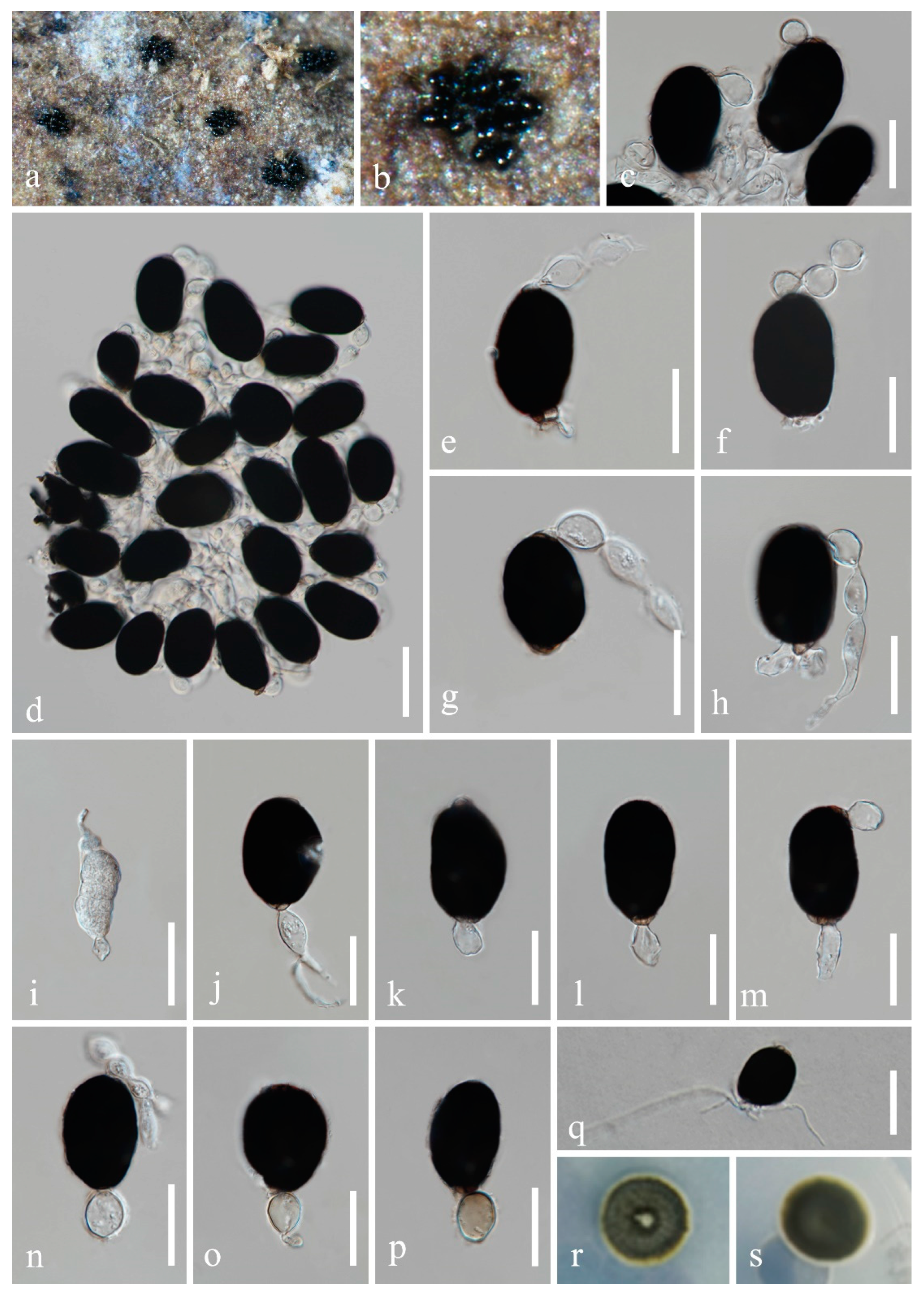
4. Taxonomy
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, K. Australian freshwater fungi. In Fungi of Australia; Introductory Volume to the Fungi (Part 2); Grgurinovic, C.A., Ed.; Australian Biological Resources Study: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 1996; Volume 1B, pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, M.K.M.; Goh, T.-K.; Hodgkiss, I.J.; Hyde, K.D.; Ranghoo, V.M.; Tsui, C.K.M.; Ho, W.-H.; Wong, W.S.W.; Yuen, T.-K. Role of fungi in freshwater ecosystems. Biodivers. Conserv. 1998, 7, 1187–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benstead, J.P.; Rosemond, A.D.; Cross, W.F.; Wallace, J.B.; Eggert, S.L.; Suberkropp, K.; Gulis, V.; Greenwood, J.L.; Tant, C.J. Nutrient enrichment alters storage and fluxes of detritus in a headwater stream ecosystem. Ecology 2009, 90, 2556–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareth Jones, E.B.; Eaton, R.A. Savoryella lignicola gen. et sp.nov. from water-cooling towers. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1969, 52, 161-IN114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udaiyan, K. Some interesting fungi from the industrial water cooling towers of Madras. II. J. Econ. Taxon. Bot. 1991, 15, 649–665. [Google Scholar]
- Calabon, M.S.; Hyde, K.D.; Jones, E.B.G.; Luo, Z.-L.; Dong, W.; Hurdeal, V.G.; Gentekaki, E.; Rossi, W.; Leonardi, M.; Thiyagaraja, V.; et al. Freshwater fungal numbers. Fungal Divers. 2022, 114, 3–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Bhat, D.J.; Hyde, K.D.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Jones, E.B.G.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Lumyong, S. Fuscosporellales, a new order of aquatic and terrestrial hypocreomycetidae (sordariomycetes). Cryptogam. Mycol. 2016, 37, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réblová, M.; Seifert, K.A.; Fournier, J.; Štěpánek, V. Newly recognized lineages of perithecial ascomycetes: The new orders conioscyphales and pleurotheciales. Persoonia 2016, 37, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Věra, H.-J. Bactrodesmiastrum, a new genus of lignicolous hyphomycetes. Folia Geobot. Phytotaxon. 1984, 19, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Restrepo, M.; Castañeda-Ruiz, R.F.; Guarro, J.; Gené, J.; Mena-Portales, J. Emendation of the genus Bactrodesmiastrum (Sordariomycetes) and description of Bactrodesmiastrum monilioides sp novfrom plant debris in Spain. Mycol Prog. 2015, 14, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, K.D.; Norphanphoun, C.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Bhat, D.J.; Jones, E.B.G.; Bundhun, D.; Chen, Y.J.; Bao, D.F.; Boonmee, S.; Calabon, M.S.; et al. Refined families of Sordariomycetes. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 305–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyuen, N.; Chuaseeharonnachai, C.; Suetrong, S.; Sri-Indrasutdhi, V.; Sivichai, S.; Jones, E.B.; Pang, K.L. Savoryellales (Hypocreomycetidae, Sordariomycetes): A novel lineage of aquatic ascomycetes inferred from multiple-gene phylogenies of the genera Ascotaiwania, Ascothailandia, and Savoryella. Mycologia 2011, 103, 1351–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaklitsch, W.M.; Réblová, M. Savoryellaceae Jaklitsch & Réblová. Index Fungorum 2015, 209, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Restrepo, M.; Gené, J.; Castañeda-Ruiz, R.F.; Mena-Portales, J.; Crous, P.W.; Guarro, J. Phylogeny of saprobic microfungi from Southern Europe. Stud. Mycol. 2017, 86, 53–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.-L.; Hyde, K.D.; Liu, J.-K.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Jeewon, R.; Bao, D.-F.; Bhat, D.J.; Lin, C.-G.; Li, W.-L.; Yang, J.; et al. Freshwater sordariomycetes. Fungal Divers. 2019, 99, 451–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réblová, M.; Hernández-Restrepo, M.; Fournier, J.; Nekvindová, J. New insights into the systematics of Bactrodesmium and its allies and introducing new genera, species and morphological patterns in the Pleurotheciales and Savoryellales (Sordariomycetes). Stud. Mycol. 2020, 95, 415–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.B.G.; Hyde, K.D. Taxonomic studies on savoryella jones et eaton (Ascomycotina). Bot. Mar. 1992, 35, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.B.G.; Sakayaroj, J.; Suetrong, S.; Somrithipol, S.; Pang, K.L. Classification of marine ascomycota, anamorphic taxa and basidiomycota. Fungal Divers. 2009, 35, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Sri-indrasutdhi, V.; Boonyuen, N.; Suetrong, S.; Chuaseeharonnachai, C.; Sivichai, S.; Jones, E.B.G. Wood-inhabiting freshwater fungi from Thailand: Ascothailandia grenadoidia gen. et sp. nov., Canalisporium grenadoidia sp. nov. with a key to Canalisporium species (Sordariomycetes, Ascomycota). Mycoscience 2010, 51, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongsanan, S.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Samarakoon, M.C.; Jeewon, R.; Zhao, Q.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Bahkali, A.H. An updated phylogeny of Sordariomycetes based on phylogenetic and molecular clock evidence. Fungal Divers. 2017, 84, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.K.; Chomnunti, P.; Cai, L.; Phookamsak, R.; Chukeatirote, R.; Jones, E.B.G.; Moslem, M.; Hyde, K.D. Phylogeny and morphology of Neodeightonia palmicola sp. nov. from palms. Sydowia 2010, 62, 261–276. [Google Scholar]
- Senanayake, I.; Calabon, M.S. Morphological approaches in studying fungi: Collection, examination, isolation, sporulation and preservation. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 2678–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Shinsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Whelen, S.; Hall, B.D. Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetes evidence from an RNA polymerse II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehner, S.A.; Buckley, E. A beauveria phylogeny inferred from nuclear ITS and EF1-a sequences evidence for cryptic diversification and links to Cordyceps teleomorphs. Mycologia 2005, 97, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, A. AliView: A fast and lightweight alignment viewer and editor for large datasets. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3276–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Silla-Martinez, J.M.; Gabaldon, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, G.; Lohman, D.J.; Meier, R. SequenceMatrix concatenation software for the fast assembly of multi gene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics 2011, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, A.J.; Bhunjun, C.S.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Liu, J.K. Applied aspects of methods to infer phylogenetic relationships amongst fungi. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 2652–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A.; Hoover, P.; Rougemont, J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web servers. Syst. Biol. 2008, 57, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES science gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; Volume 14, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hohna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nylander, J. MrModeltest2 v. 2.3 (Program for Selecting DNA Substitution Models Using PAUP*); Evolutionary Biology Centre: Uppsala, Sweden, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rannala, B.; Yang, Z. Probability distribution of molecular evolutionary trees a new method of phylogenetic inference. J. Mol. Evol. 1996, 43, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larget, B.; Simon, D.L. Markov chain monte carlo algorithms for the bayesian analysis of phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), 4th ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hillis, D.M.; Bull, J.J. An empirical test of bootstrapping as a method for assessing confidence in phylogenetic analysis. Syst. Biol. 1993, 42, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Restrepo, M.; Mena-Portales, J.; Gené, J.; Cano, J.; Guaarro, J. New bactrodesmiastrum and bactrodesmium from decaying wood in Spain. Mycologia 2013, 105, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Réblová, M.; Seifert, K.A. Conioscyphascus, a new ascomycetous genus for holomorphs with conioscypha anamorphs. Stud. Mycol. 2004, 50, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Réblová, M.; Seifert, K.A.; Fournier, J.; Stepánek, V. Phylogenetic classification of pleurothecium and pleurotheciella gen. nov. and its dactylaria-like anamorph (Sordariomycetes) based on nuclear ribosomal and protein-coding genes. Mycologia 2012, 104, 1299–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, J.K.; Hyde, K.D.; Jones, E.B.G.; Liu, Z.Y. Two new species in Fuscosporellaceae from freshwater habitats in Thailand. Mycosphere 2017, 8, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Dong, W.; Yu, X.D.; Bhat, D.J.; Boonmee, S.; Zhang, H. Four freshwater dematiaceous hyphomycetes in sordariomycetes with two new species of parafuscosporella. Phytotaxa 2020, 441, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyuen, N.; Chuaseeharonnachai, C.; Suetrong, S.; Sujinda, S.; Somrithipol, S. Parafuscosporella garethii sp. nov. (Fuscosporellales) from a rivulet in a community-based northern forest, in Thailand. Mycosphere 2016, 7, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.-L.; Hyde, K.D.; Bhat, D.J.; Jeewon, R.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Bao, D.-F.; Li, W.-L.; Su, X.-J.; Yang, X.-Y.; Su, H.-Y. Morphological and molecular taxonomy of novel species pleurotheciaceae from freshwater habitats in Yunnan, China. Mycol. Prog. 2018, 17, 511–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, K.D.; Norphanphoun, C.; Abreu, V.P.; Bazzicalupo, A.; Thilini Chethana, K.W.; Clericuzio, M.; Dayarathne, M.C.; Dissanayake, A.J.; Ekanayaka, A.H.; He, M.-Q.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 603–708: Taxonomic and phylogenetic notes on genera and species. Fungal Divers. 2017, 87, 1–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Shearer, C.A. Annulusmagnus and ascitendus, two new genera in the annulatascaceae. Mycologia 2004, 96, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-N.; Abdel-Wahab, M.A.; Jones, E.B.G.; Hyde, K.D.; Liu, J.-K. Additions to the genus savoryella (savoryellaceae), with the asexual morphs savoryella nypae comb. nov. and S. sarushimana sp. nov. Phytotaxa 2019, 408, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castlebury, L.A.; Rossman, A.Y.; Sung, G.-H.; Hyten, A.S.; Spatafora, J.W. Multigene phylogeny reveals new lineage for Stachybotrys chartarum, the indoor air fungus. Mycol. Res. 2004, 108, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatafora, J.W.; Sung, G.H.; Sung, J.M.; Hywel-Jones, N.L.; White, J.F., Jr. Phylogenetic evidence for an animal pathogen origin of ergot and the grass endophytes. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyuen, N.; Chuaseeharonnachai, C.; Nuankaew, S.; Kwantong, P.; Pornputtapong, N.; Suwannarach, N.; Jones, E.B.G.; Somrithipol, S. Novelties in fuscosporellaceae (fuscosporellales): Two new parafuscosporella from thailand revealed by morphology and phylogenetic analyses. Diversity 2021, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayawardene, N.N.; Dissanayake, L.S.; Dai, D.-Q.; Li, Q.-R.; Xiao, Y.; Wen, T.-C.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Wu, H.-X.; Zhang, H.; Tibpromma, S.; et al. Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau: A mycological hotspot. Phytotaxa 2021, 523, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.S.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Jones, E.B.G.; Read, S.J.; Moss, S.T. New freshwater species of ascotaiwania and savoryella from Taiwan. Mycol. Res. 1998, 102, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-s. Trichocladium anamorph of ascotaiwania hsilio and monodictys-like anamorphic states of ascotaiwania lignicola. Fung. Sci. 2001, 16, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ranghoo, V.M.; Hyde, K.D. Ascomycetes from freshwater habitats: Ascolacicola aquatica gen. et sp. nov. and a new species of ascotaiwania from wood submerged in a reservoir in Hong Kong. Mycologia 1998, 90, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivichai, S.; HyweI-Jones, N.; Jones, E.B.G. Lignicolous freshwater Ascomycota from Thailand: 1. Ascotaiwania sawada and its anamorph state monotosporella. Mycoscience 1998, 39, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayarathne, M.C.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Jones, E.B.G.; Dong, W.; Devadatha, B.; Yang, J.; Ekanayaka, A.H.; De Silva, W.; Sarma, V.V.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; et al. Phylogenetic revision of savoryellaceae and evidence for its ranking as a subclass. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Jeewon, R.; Hyde, K.D.; Yang, E.-F.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.; Wang, G.; Suwannarach, N.; Doilom, M.; Dong, Z. Five novel taxa from freshwater habitats and new taxonomic insights of pleurotheciales and savoryellomycetidae. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Garcia, D.; García, D.; Cano-Lira, J.F.; Gené, J. Two novel genera, neostemphylium and scleromyces (pleosporaceae) from freshwater sediments and their global biogeography. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.M.; Jeewon, R.; Hyde, K.D. Phylogenetic utility of protein (RPB2, beta-tubulin) and ribosomal (LSU, SSU) gene sequences in the systematics of sordariomycetes (Ascomycota, Fungi). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2007, 91, 327–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.-M.; Ju, Y.-M.; Rogers, J.D. Molecular phylogeny of hypoxylon and closely related genera. Mycologia 2005, 97, 844–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, H.-Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, N.-G.; Cheewangkoon, R.; Liu, J.-K. Morpho-Phylogenetic Evidence Reveals New Species of Fuscosporellaceae and Savoryellaceae from Freshwater Habitats in Guizhou Province, China. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8111138
Du H-Z, Yang J, Liu N-G, Cheewangkoon R, Liu J-K. Morpho-Phylogenetic Evidence Reveals New Species of Fuscosporellaceae and Savoryellaceae from Freshwater Habitats in Guizhou Province, China. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(11):1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8111138
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Hong-Zhi, Jing Yang, Ning-Guo Liu, Ratchadawan Cheewangkoon, and Jian-Kui Liu. 2022. "Morpho-Phylogenetic Evidence Reveals New Species of Fuscosporellaceae and Savoryellaceae from Freshwater Habitats in Guizhou Province, China" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 11: 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8111138
APA StyleDu, H.-Z., Yang, J., Liu, N.-G., Cheewangkoon, R., & Liu, J.-K. (2022). Morpho-Phylogenetic Evidence Reveals New Species of Fuscosporellaceae and Savoryellaceae from Freshwater Habitats in Guizhou Province, China. Journal of Fungi, 8(11), 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8111138









