Genetic Relationships in the Toxin-Producing Fungal Endophyte, Alternaria oxytropis Using Polyketide Synthase and Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthase Genes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
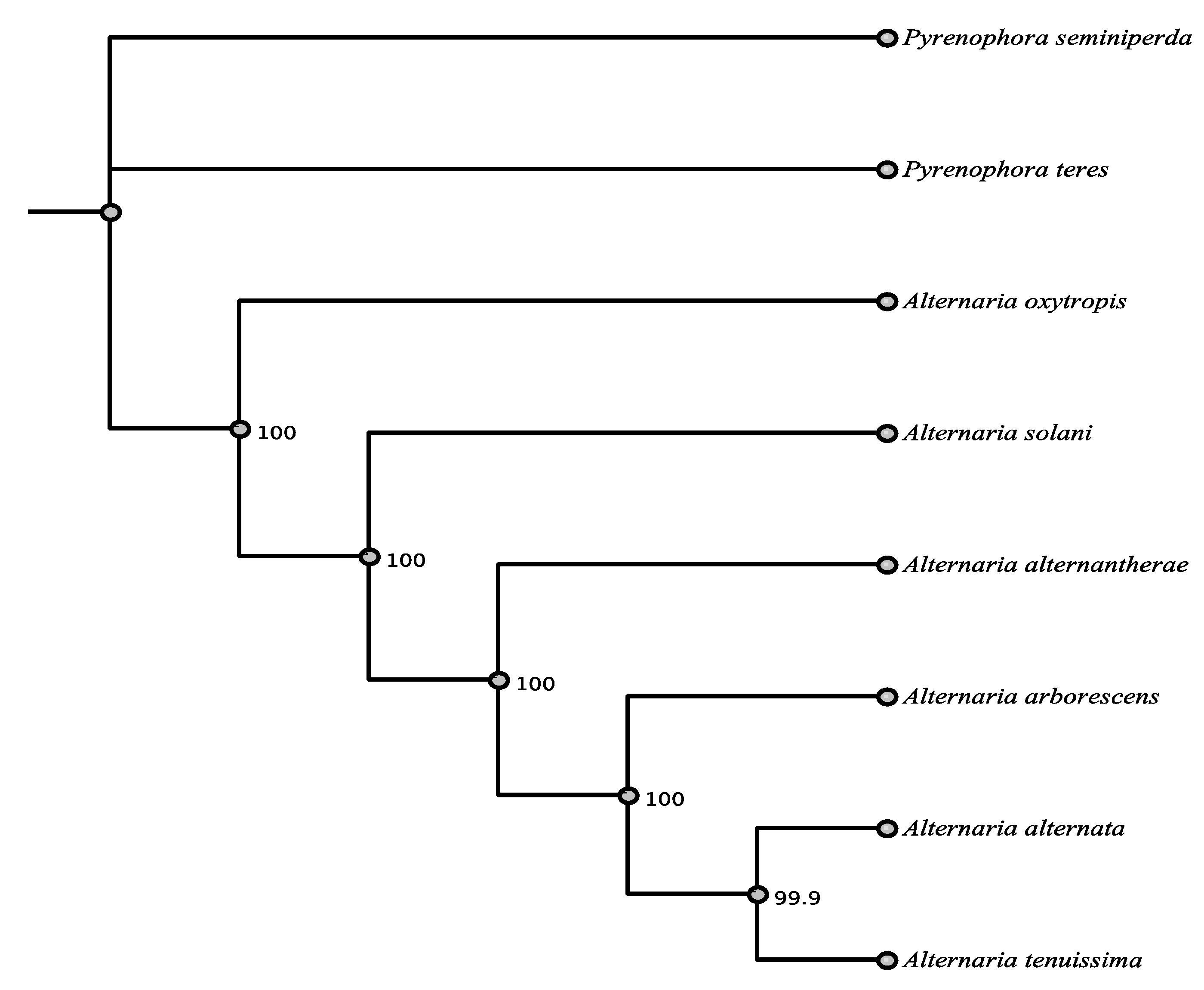
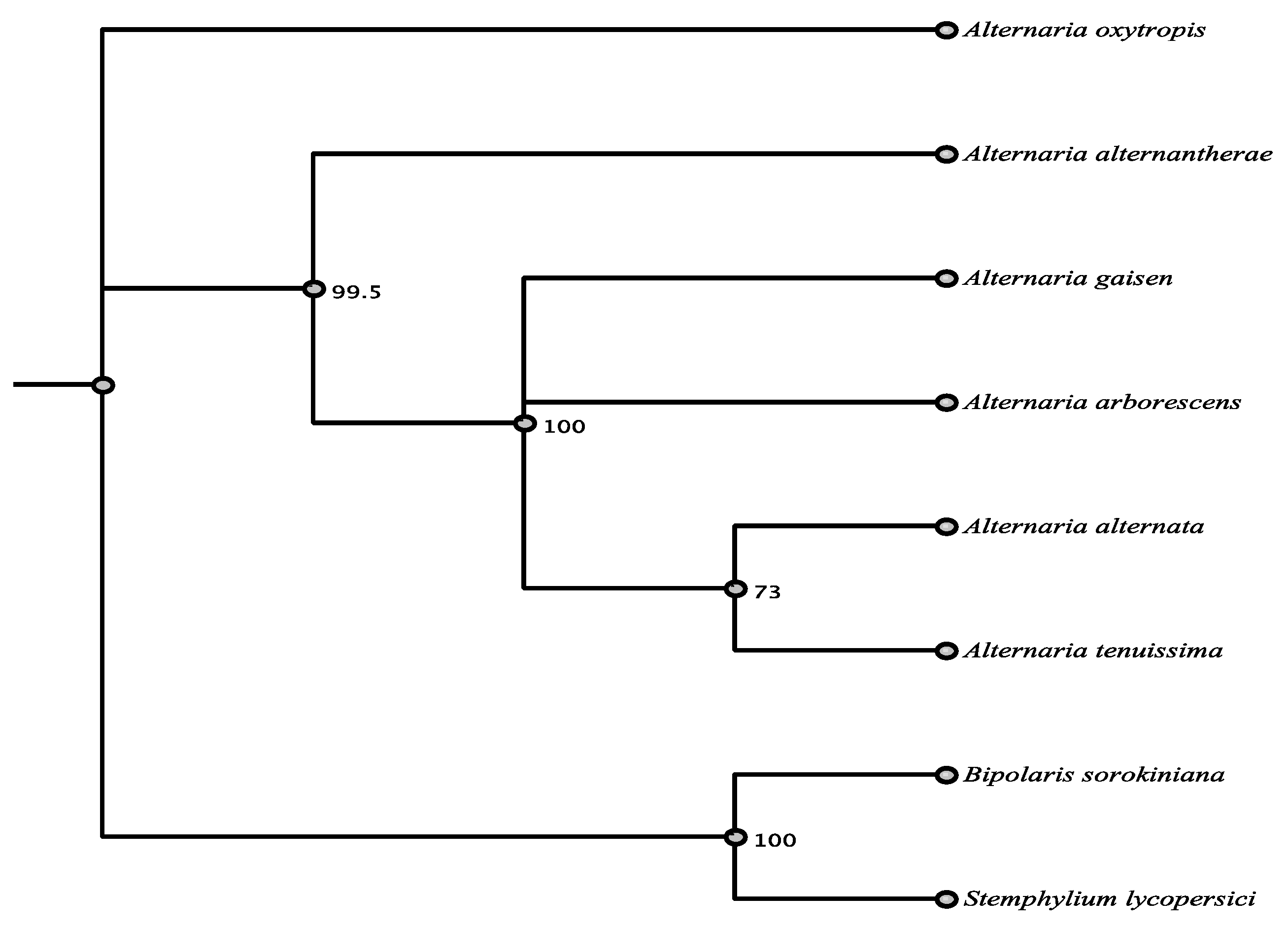
3.1. Phylogenetic Framework
3.2. PKS-NRPS Hybrids
3.3. Type I PKS
3.3.1. Highly Reducing Type I PKSs
3.3.2. Partially Reducing Type I PKS
3.3.3. Non-Reducing Type I PKS
3.4. Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthases
3.5. A Domain Substrates
3.6. Phylogenetic Relationships
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stegelmeier, B.L.; Lee, S.T.; James, L.F.; Gardner, D.R.; Panter, K.E.; Ralphs, M.H.; Pfister, J.A. The Comparative Pathology of Locoweed Poisoning in Livestock, Wildlife and Rodents. In Poisonous Plants: Global Research and Solutions; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2007; pp. 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- James, L.F.; Van Kampen, K.R.; Staker, G.R. Locoweed (Astragalus lentiginosus) poisoning in cattle and horses. J. Am. Veter Med Assoc. 1969, 155, 525–530. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, D.; Grum, D.S.; Gardner, D.R.; Welch, K.D.; Pfister, J.A. Influence of endophyte genotype on swainsonine concentrations in Oxytropis sericea. Toxicon 2013, 61, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, C.M.; Schneider, M.J.; Ungemach, F.S.; Hill, J.E.; Harris, T.M. Biosynthesis of the toxic indolizidine alkaloids slaframine and swainsonine in Rhizoctonia leguminicola: Metabolism of 1-hydroxyindolizidines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, M.; Adlard, M.W.; Keshavarz, T. Production of an indolizidine alkaloid, swainsonine by the filamentous fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae. Biotechnol. Lett. 1993, 15, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.; Donzelli, B.; Creamer, R.; Baucom, D.L.; Gardner, D.R.; Pan, J.; Moore, N.; Krasnoff, S.B.; Jaromczyk, J.W.; Schardl, C.L. Swainsonine Biosynthesis Genes in Diverse Symbiotic and Pathogenic Fungi. Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noor, A.I.; Neyaz, M.; Cook, D.; Creamer, R. Molecular Characterization of a Fungal Ketide Synthase Gene Among Swainsonine-Producing Alternaria Species in the USA. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 2554–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, A.; Wisecaver, J.H.; Lameiras, C.; Wiemann, P.; Palmer, J.; Keller, N.; Rodrigues, F.; Goldman, G.; Rokas, A. Drivers of genetic diversity in secondary metabolic gene clusters within a fungal species. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hertweck, C. The Biosynthetic Logic of Polyketide Diversity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4688–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, M.; Chiang, Y.-M.; Chang, S.-L.; Praseuth, M.B.; Entwistle, R.; Sanchez, J.F.; Lo, H.-C.; Yeh, H.-H.; Oakley, B.R.; Wang, C.C.C. Illuminating the Diversity of Aromatic Polyketide Synthases in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8212–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maiya, S.; Grundmann, A.; Li, X.; Li, S.-M.; Turner, G. Identification of a Hybrid PKS/NRPS Required for Pseurotin a Biosynthesis in the Human PathogenAspergillus fumigatus. ChemBioChem 2007, 8, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddy, C.N. Bioinformatics tools for genome mining of polyketide and non-ribosomal peptides. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chooi, Y.-H.; Tang, Y. Navigating the Fungal Polyketide Chemical Space: From Genes to Molecules. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 9933–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boettger, D.; Hertweck, C. Molecular Diversity Sculpted by Fungal PKS-NRPS Hybrids. ChemBioChem 2012, 14, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, F.T.; Sørensen, J.L.; Giese, H.; Søndergaard, T.; Frandsen, R.J. Quick guide to polyketide synthase and nonribosomal synthetase genes in Fusarium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 155, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, O.D.; Binkley, J.; Skrzypek, M.S.; Arnaud, M.B.; Cerqueira, G.C.; Shah, P.; Wymore, F.; Wortman, J.R.; Sherlock, G. Comprehensive annotation of secondary metabolite biosynthetic genes and gene clusters of Aspergillus nidulans, A. fumigatus, A. niger and A. oryzae. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L. Bioactive metabolites from the plant endophyte Pestalotiopsis fici. Mycology 2011, 2, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Xiang, M.; Wang, W.; Sun, X.; Che, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, G.; Guo, L.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis fici reveals its lifestyle and high potential for synthesis of natural products. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, K.R.; Boddy, C.N. ClusterMine360: A database of microbial PKS/NRPS biosynthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D402–D407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geer, L.Y.; Marchler-Bauer, A.; Geer, R.C.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Liu, C.; Shi, W.; Bryant, S.H. The NCBI BioSystems database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 38, D492–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khaldi, N.; Seifuddin, F.T.; Turner, G.; Haft, D.; Nierman, W.C.; Wolfe, K.H.; Fedorova, N.D. SMURF: Genomic mapping of fungal secondary metabolite clusters. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2010, 47, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Steinke, K.; Villebro, R.; Ziemert, N.; Lee, S.Y.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 5.0: Updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W81–W87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medema, M.H.; Blin, K.; Cimermancic, P.; De Jager, V.; Zakrzewski, P.; Fischbach, M.A.; Weber, T.; Takano, E.; Breitling, R. antiSMASH: Rapid identification, annotation and analysis of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters in bacterial and fungal genome sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W339–W346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemert, N.; Podell, S.; Penn, K.; Badger, J.H.; Allen, E.; Jensen, P.R. The Natural Product Domain Seeker NaPDoS: A Phylogeny Based Bioinformatic Tool to Classify Secondary Metabolite Gene Diversity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prieto, C.; Garcia-Estrada, C.; Lorenzana, D.; Martín, J.F. NRPSsp: Non-ribosomal peptide synthase substrate predictor. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 426–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.-Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zierep, P.F.; Padilla, N.; Yonchev, D.G.; Telukunta, K.K.; Klementz, D.; Günther, S. SeMPI: A genome-based secondary metabolite prediction and identification web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W64–W71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baucom, D.L.; Romero, M.; Belfon, R.; Creamer, R. Two new species of Undifilum, fungal endophytes of Astragalus (locoweeds) in the United States. Botany 2012, 90, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujii, I.; Yoshida, N.; Shimomaki, S.; Oikawa, H.; Ebizuka, Y. An Iterative Type I Polyketide Synthase PKSN Catalyzes Synthesis of the Decaketide Alternapyrone with Regio-Specific Octa-Methylation. Chem. Biol. 2005, 12, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fetzner, R.; Seither, K.; Wenderoth, M.; Herr, A.; Fischer, R. Alternaria alternata transcription factor CmrA controls melanization and spore development. Microbiology 2014, 160, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, N.; Tsuge, T. Gene cluster involved in melanin biosynthesis of the filamentous fungus Alternaria alternata. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 4427–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jalal, M.A.F.; Love, S.K.; van der Helm, D. Na-Dimethylcoprogens, Three novel trihydoxamate siderophones from pathogenic fungi. Biol. Met. 1988, 1, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.R.; Gulick, A.W. Structural biology of non-ribosomal peptide synthetases. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1401, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Quan, H.; Ren, Z.; Wang, S.; Xue, R.; Zhao, B. The Genome of Undifilum oxytropis Provides Insights into Swainsonine Biosynthesis and Locoism. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Haynes, S.W.; Ames, B.D.; Wang, P.; Vien, L.P.; Walsh, C.T.; Tang, Y. Cyclization of fungal nonribosomal peptides by a terminal condensation-like domain. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bills, G.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Yue, Q.; Niu, X.-M.; An, Z. New insights into the echinocandins and other fungal non-ribosomal peptides and peptaibiotics. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1348–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloudoff, K.; Schmeing, T.M. Structural and functional aspects of the nonribosomal peptide synthetase condensation domain superfamily: Discovery, dissection and diversity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2017, 1865, 1587–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.-S.; Motoyama, T.; Osada, H. Biosynthesis of the mycotoxin tenuazonic acid by a fungal NRPS–PKS hybrid enzyme. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khayatt, B.I.; Overmars, L.; Siezen, R.J.; Francke, C. Classification of the Adenylation and Acyl-Transferase Activity of NRPS and PKS Systems Using Ensembles of Substrate Specific Hidden Markov Models. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ariyawansa, H.; Kang, J.; Chukeatirote, E.; Hyde, K. Pyrenophora. Mycosphere 2014, 5, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokas, A.; Mead, M.E.; Steenwyk, J.L.; Raja, H.A.; Oberlies, N.H. Biosynthetic gene clusters and the evolution of fungal chemodiversity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slot, J.C.; Rokas, A. Horizontal Transfer of a Large and Highly Toxic Secondary Metabolic Gene Cluster between Fungi. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manning, V.A.; Pandelova, I.; Dhillon, B.; Wilhelm, L.J.; Goodwin, S.; Berlin, A.M.; Figueroa, M.; Freitag, M.; Hane, J.K.; Henrissat, B.; et al. Comparative Genomics of a Plant-Pathogenic Fungus, Pyrenophora tritici-repentis, Reveals Transduplication and the Impact of Repeat Elements on Pathogenicity and Population Divergence. Genes Genomes Genet. 2013, 3, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akagi, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Otani, H.; Kodama, M. Horizontal Chromosome Transfer, a Mechanism for the Evolution and Differentiation of a Plant-Pathogenic Fungus. Eukaryot. Cell 2009, 8, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armitage, A.; Cockerton, H.M.; Sreenivasaprasad, S.; Woodhall, J.; Lane, C.R.; Harrison, R.; Clarkson, J.P. Genomics Evolutionary History and Diagnostics of the Alternaria alternata Species Group Including Apple and Asian Pear Pathotypes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alhawatema, M.S.; Gebril, S.; Cook, D.; Creamer, R. RNAi-mediated down-regulation of a melanin polyketide synthase (pks1) gene in the fungus Slafractonia leguminicola. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-N.; Kroken, S.; Chou, D.Y.T.; Robbertse, B.; Yoder, O.C.; Turgeon, B.G. Functional Analysis of All Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetases in Cochliobolus heterostrophus Reveals a Factor, NPS6, Involved in Virulence and Resistance to Oxidative Stress. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Chung, K.-R. A nonribosomal peptide synthetase mediates siderophore production and virulence in the citrus fungal pathogenAlternaria alternata. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-H.; Yang, S.L.; Chung, K.-R. Resistance to oxidative stress via regulating siderophore-mediated iron acquisition by the citrus fungal pathogen Alternaria alternata. Microbiology 2014, 160, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oide, S.; Moeder, W.; Krasnoff, S.; Gibson, D.; Haas, H.; Yoshioka, K.; Turgeon, B.G. NPS6, Encoding a Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Involved in Siderophore-Mediated Iron Metabolism, Is a Conserved Virulence Determinant of Plant Pathogenic Ascomycetes. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2836–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillemette, T.; Sellam, A.; Simoneau, P. Analysis of a nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene from Alternaria brassicae and flanking genomic sequences. Curr. Genet. 2004, 45, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Type | Contig | Genbank Accession | % Identity | BLASTp Hit | Accession | Protein Match Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKS-NRPS | 58882 | KY365741 | 81 | Slafractonia leguminicola | AQV04236 | M |
| hybrid | 5601 | MK058350 | 69 | Setosphaeria turcica | XP_008025924 | M |
| 21438 | MK058352 | 88 | Pyrenophora teres | XP_003303559 | M | |
| 62407 | MK058351 | 64 | Tolypocladium ophioglossoides | KND87119 | N | |
| Type I, highly | 2122 | MK471354 | 90 | Alternaria solani | Q5KTM9 | A |
| reducing | 1562 | MK495800 | 85 | Bipolaris maydis | AAR90260 | P |
| 59499 | MK492487 | 66 | Aspergillus nomius | KNG90368 | N | |
| 96133 | MK492486 | 88 | Alternaria alternata | AFN68297 | A | |
| 9132 | MK450599 | 73 | Fusraium aywerte | ALQ32761 | N | |
| 39849 | MK492485 | 76 | Pyrenophora tritici-repentis | PZC93669 | M | |
| 12778 | MK471353 | 65 | Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. conglutinans | EXL67078 | N | |
| Type I, partially | 17612 | MK495801 | 63 | Cladosporium cladosporioides | AOAOYOM151 | N |
| reducing | 8407 | MK492484 | 81 | Alternaria solani | Q2ABP6 | A |
| 3398 | MK492483 | 64 | Metarhizium brunneum | KID62944 | N | |
| 42460 | MK507973 | 46 | Colletotrichum fructicola | ELA32259 | N | |
| Type I, | 40283 | MK402071 | 95 | Alternaria alternata | AFN68292 | A |
| non-reducing | 29103 | MK471352 | 70 | Epicoccum nigrum | OSS52043 | M |
| NRPS | 33635 | MK409655 | 91 | Alternaria alternata | AFN69082 | A |
| 5682 | MK468800 | 91 | Alternaria alternata | XP_0188382376 | A | |
| 7859 | MK426697 | 76 | Bipolaris maydis | AAX09991 | P | |
| 8194 | MK468799 | 87 | Pyrenophora tritici-repentis | XP_001939433 | P | |
| 40703 | MK471351 | 82 | Alternaria alternata | XP_018389223 | A |
| Contig | Genbank Accession | CD | KSD | Adenylation Domain Substrate | Cyclization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 58882 | KY365741 | − | + | Gly | No |
| 5601 | MK058350 | + | + | Phe | No |
| 21438 | MK058352 | + | + | Phe | No |
| 62407 | MK058351 | + | + | Tyr | No |
| 12778 | MK471353 | + | + | Phe | No |
| 33635 | MK409655 | + | − | Phe | Cyclize |
| 5682 | MK468800 | + | − | Pro, Pro, Phe | Likely |
| 7859 | MK426697 | + | − | Pro, Try, Try | No |
| 8194 | MK468799 | + | − | Try, Pro, Phe | Likely |
| 40703 | MK471351 | + | − | Aminoadipate, Phe, Phe, Val | No |
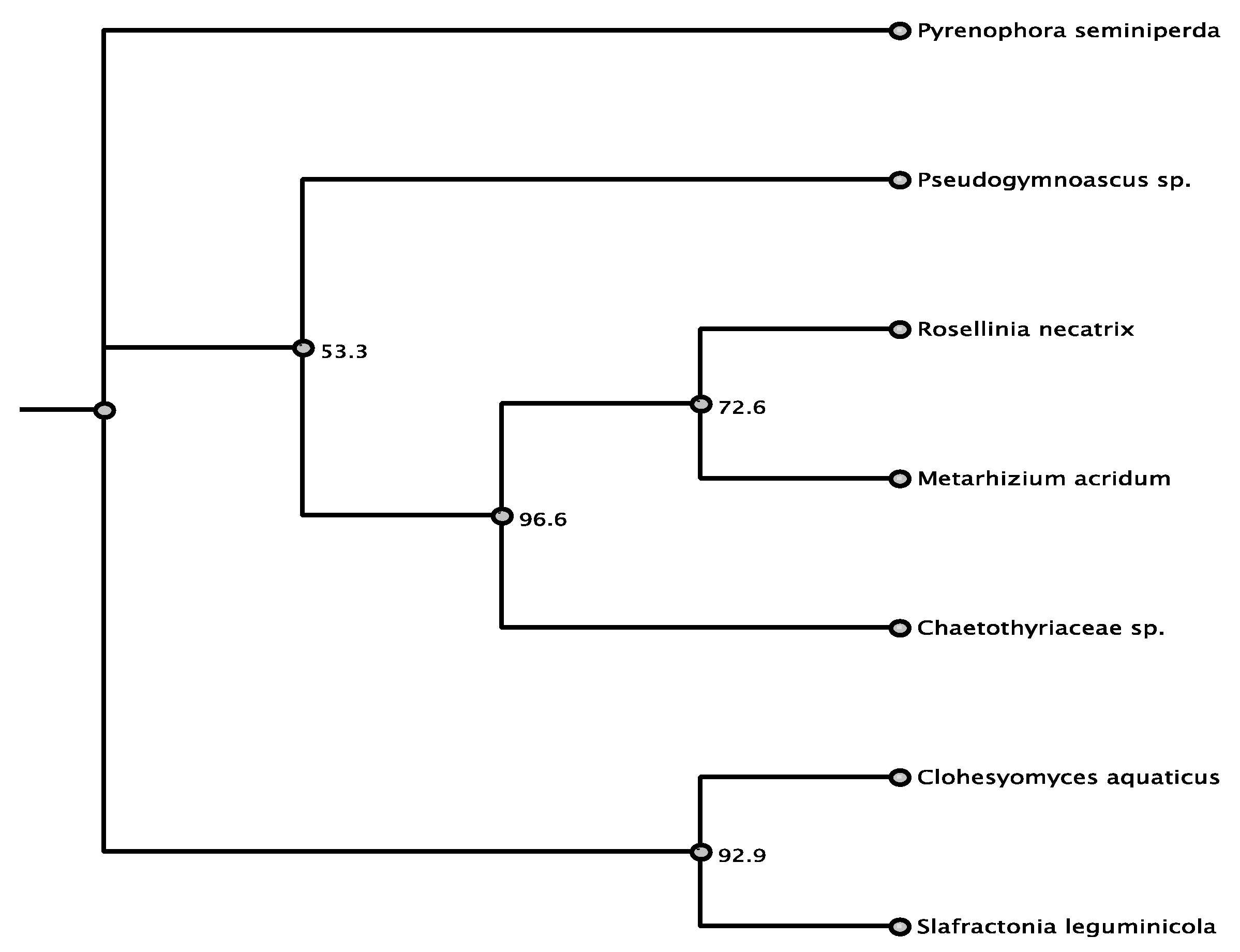
| Organism | Accession | Order/Class | % aa Identity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrenophora seminiperda | RMZ73569.1 | Pleosporales/D | 80.9% |
| Slafractonia leguminicola | AQV04236.1 | Pleosporales/D | 72.7% |
| Clohesyomyces aquaticus | ORY11783.1 | Pleosporales/D | 71.0% |
| Metarhizium acridum | XP_007815889.1 | Sordariomycetes | 69.0% |
| Chaetothyriaceae | AQV04224.1 | Eurotiomycetes | 69.1% |
| Pseudogymnoascus sp. | KFY51099.1 | unknown/D | 67.3% |
| Rosellinia necatrix | GAP93000.1 | Sordariomycetes | 67.0% |
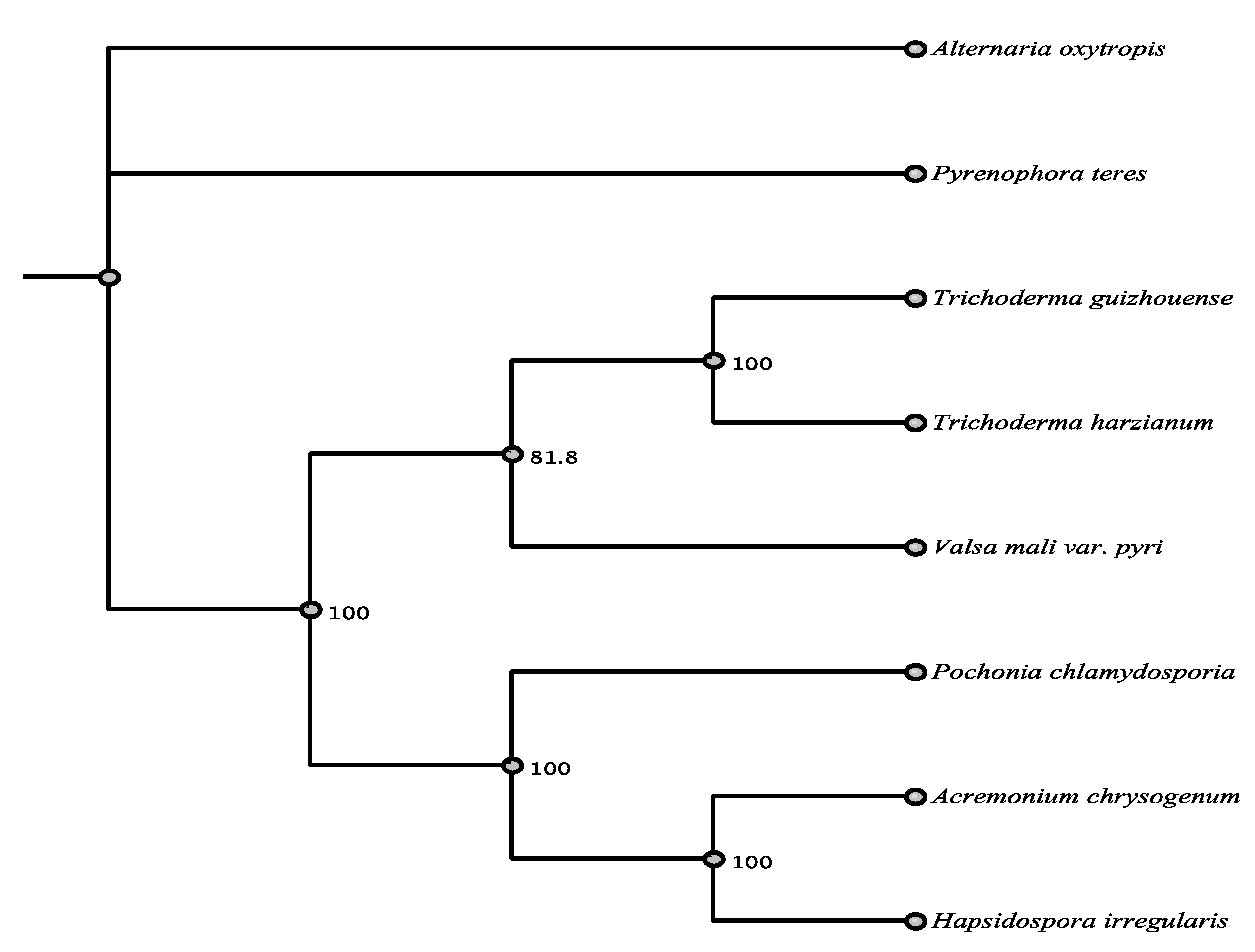
| Organism | Accession | Order/Class | % aa Identity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrenophora teres | EFQ87243.1 | Pleosporales/D | 87.5% |
| Acremonium chrysogenum | KFH40930.1 | Sordariomycetes | 52.7% |
| Hapsidospora irregularis | AKG54858.1 | Sordariomycetes | 52.2% |
| Pochonia chlyamydosporia | XP_018142849.1 | Sordariomycetes | 69.2% |
| Valsa mali var. pyri | KUI56379.1 | Sordariomycetes | 52.0% |
| Trichoderma guizhouense | OPB40675.1 | Sordariomycetes | 48.2% |
| Trichoderma harzianum | PKK52345.1 | Sordariomycetes | 48.0% |
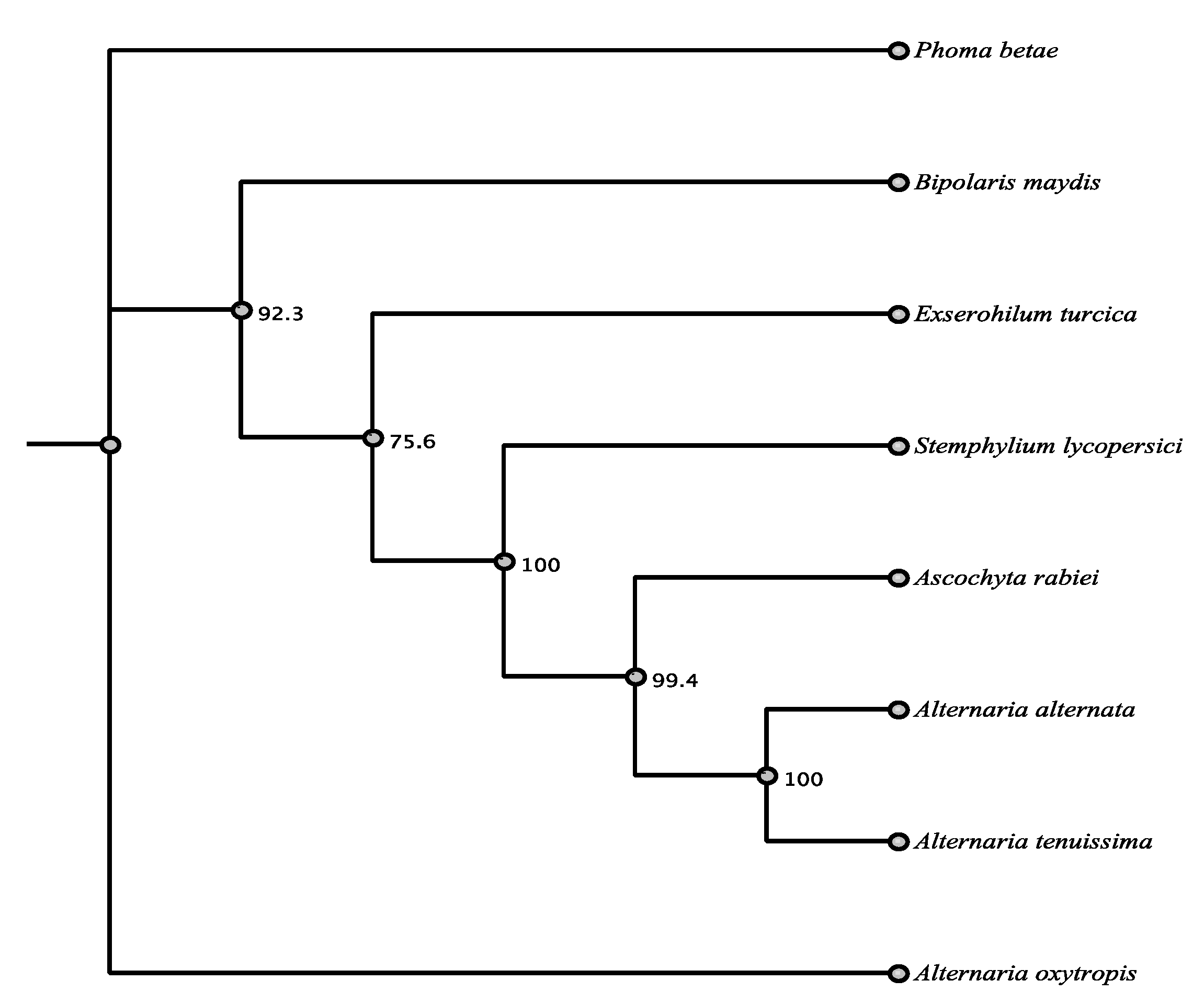
| Organism | Accession | Order | % aa Identity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternaria alternata | AFN68297.1 | Pleosporales | 87.7% |
| Stemphylium lycopersici | RAR01042.1 | Pleosporales | 85.4% |
| Alternaria tenuissima | RYN28010.1 | Pleosporales | 86.9% |
| Ascochyta rabiei | KZM21157.1 | Pleosporales | 86.6% |
| Phoma betae | BAQ25466.1 | Pleosporales | 86.1% |
| Bipolaris maydis | AAR90270.1 | Pleosporales | 85.9% |
| Exserohilum turcica | XP_008031663.1 | Pleosporales | 87.1% |
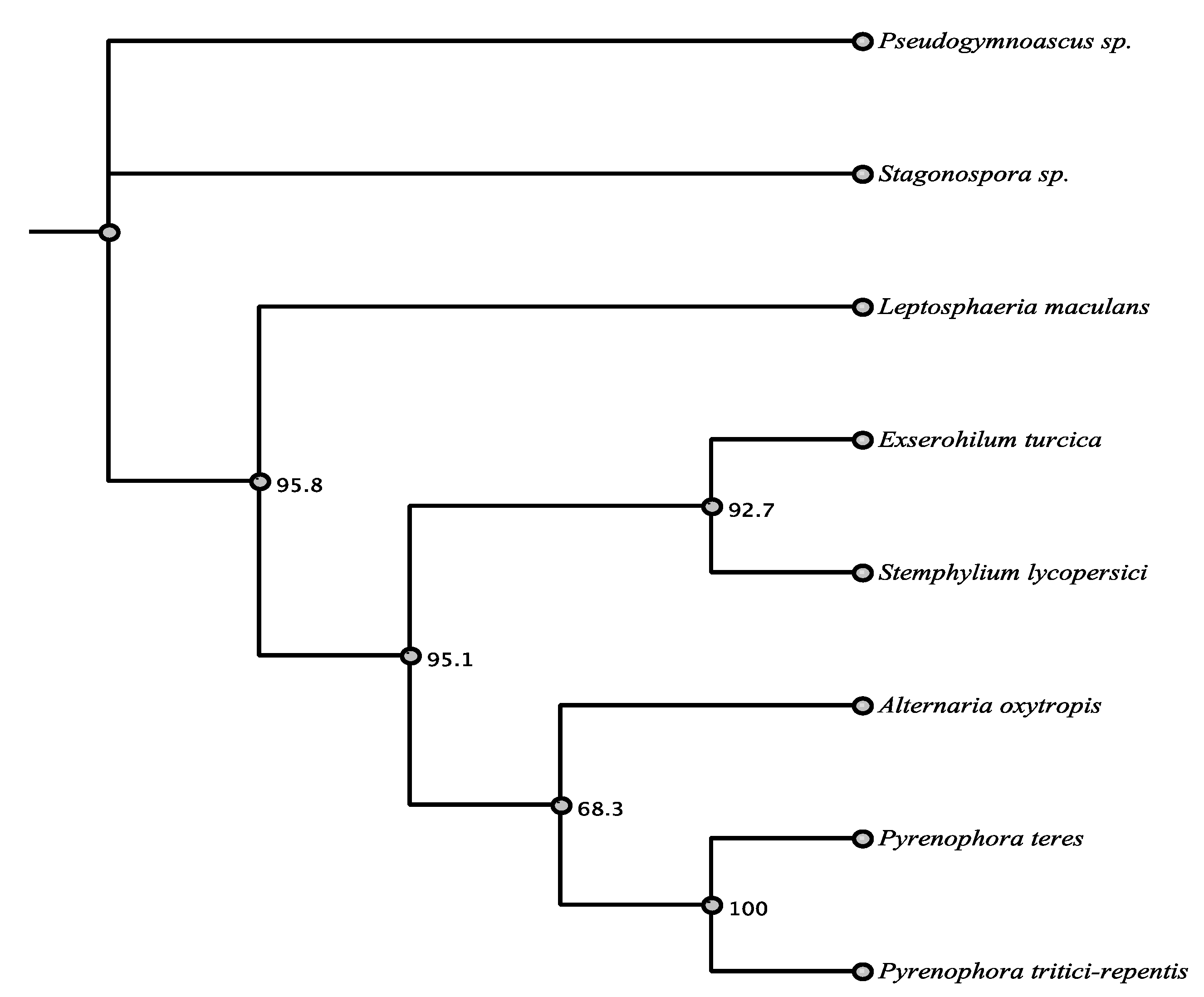
| Organism | Accession | Order | % aa Identity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrenophora teres | EFQ87243.1 | Pleosporales | 74.5% |
| Stemphylium lycopersici | KNG47890.1 | Pleosporales | 73.9% |
| Pyrenophora tritici-repentis | XP_001937136.1 | Pleosporales | 72.9% |
| Exserohilum turcica | XP_008026829.1 | Pleosporales | 69.2% |
| Leptosphaeria maculans | XP_003842471.1 | Pleosporales | 66.8% |
| Stagonospora sp. | OAK96687.1 | Pleosporales | 60.4% |
| Pseudogymnoascus sp. | KFY81215.1 | Unknown | 50.3% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Creamer, R.; Hille, D.B.; Neyaz, M.; Nusayr, T.; Schardl, C.L.; Cook, D. Genetic Relationships in the Toxin-Producing Fungal Endophyte, Alternaria oxytropis Using Polyketide Synthase and Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthase Genes. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070538
Creamer R, Hille DB, Neyaz M, Nusayr T, Schardl CL, Cook D. Genetic Relationships in the Toxin-Producing Fungal Endophyte, Alternaria oxytropis Using Polyketide Synthase and Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthase Genes. Journal of Fungi. 2021; 7(7):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070538
Chicago/Turabian StyleCreamer, Rebecca, Deana Baucom Hille, Marwa Neyaz, Tesneem Nusayr, Christopher L. Schardl, and Daniel Cook. 2021. "Genetic Relationships in the Toxin-Producing Fungal Endophyte, Alternaria oxytropis Using Polyketide Synthase and Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthase Genes" Journal of Fungi 7, no. 7: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070538
APA StyleCreamer, R., Hille, D. B., Neyaz, M., Nusayr, T., Schardl, C. L., & Cook, D. (2021). Genetic Relationships in the Toxin-Producing Fungal Endophyte, Alternaria oxytropis Using Polyketide Synthase and Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthase Genes. Journal of Fungi, 7(7), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070538






