The Destructive Tree Pathogen Phytophthora ramorum Originates from the Laurosilva Forests of East Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
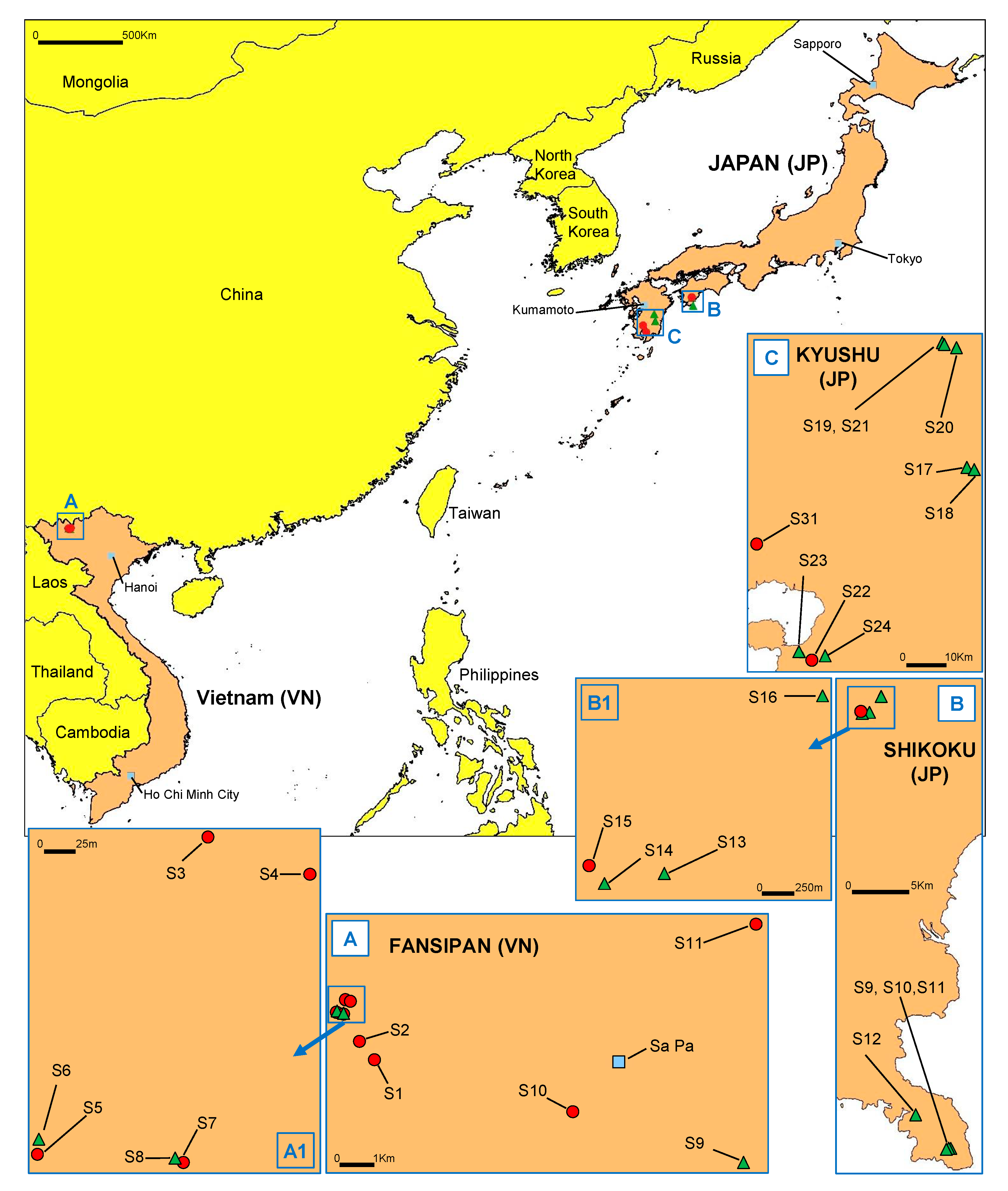
2.1. Sampling Areas, Isolation and Identification of Phytophthora Species
2.2. Growth Media and Culture Maintenance
2.3. Phenotypic Studies
2.3.1. Known Phytophthora ramorum Lineage Isolates
2.3.2. Growth Rates and Colony Characteristics
2.3.3. Gene x Environment Stress Tests
2.3.4. Mating Tests
2.3.5. Statistical Analyses
2.4. DNA Isolation, Amplification and Sequencing
2.5. Phylogenetic and Coalescence Analyses
2.5.1. Maximum-Likelihood, Bayesian Inference and Coalescence Analyses
2.5.2. Phylogenetic Network Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Discovery of P. ramorum in East Asian Ecosystems
3.2. Phenotype Groups Among Vietnamese and Japanese P. ramorum Isolates
3.2.1. Growth Rates and Colony Characteristics
3.2.2. Gene x Environment Stress Tests
3.2.3. Mating Tests
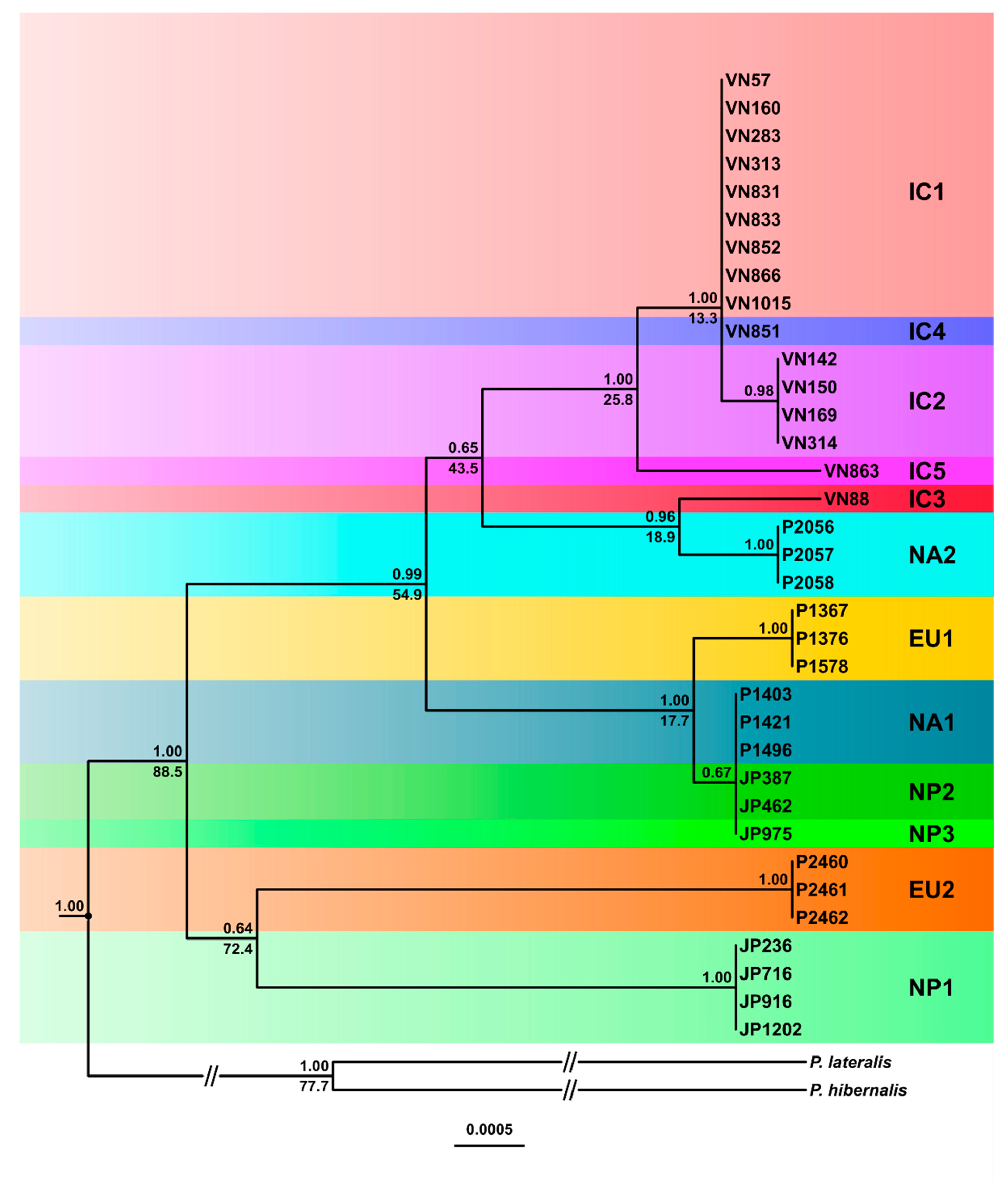
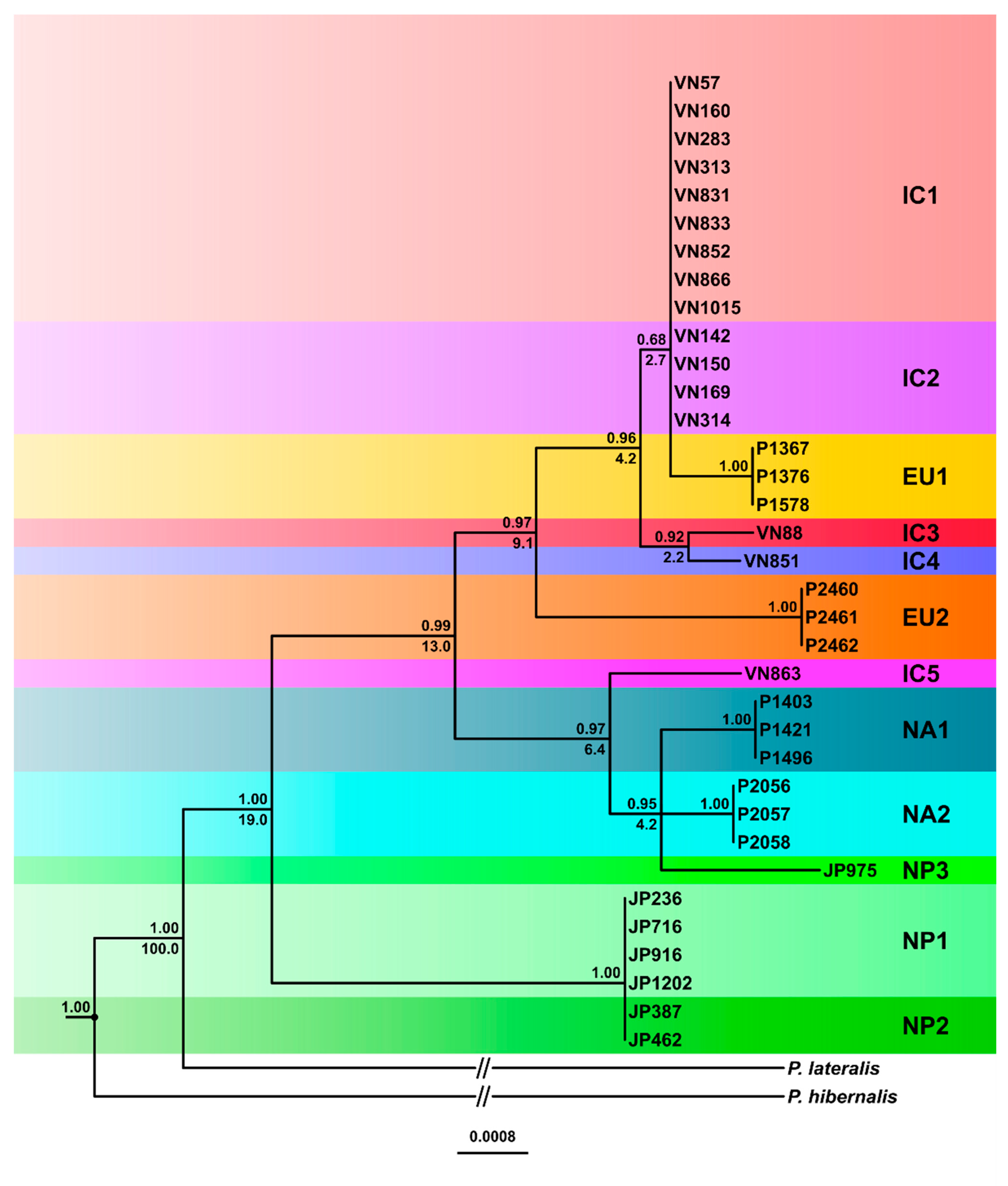
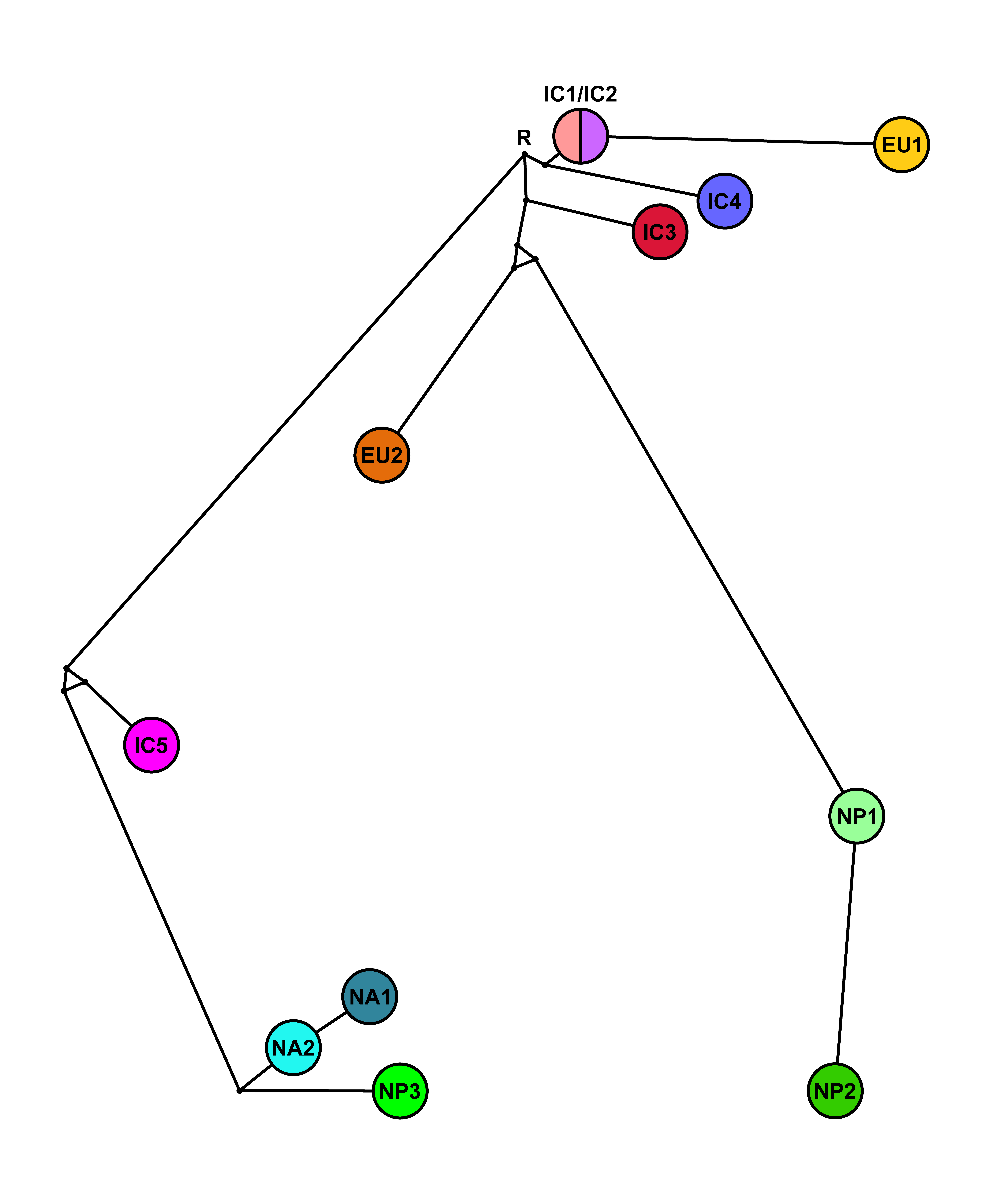
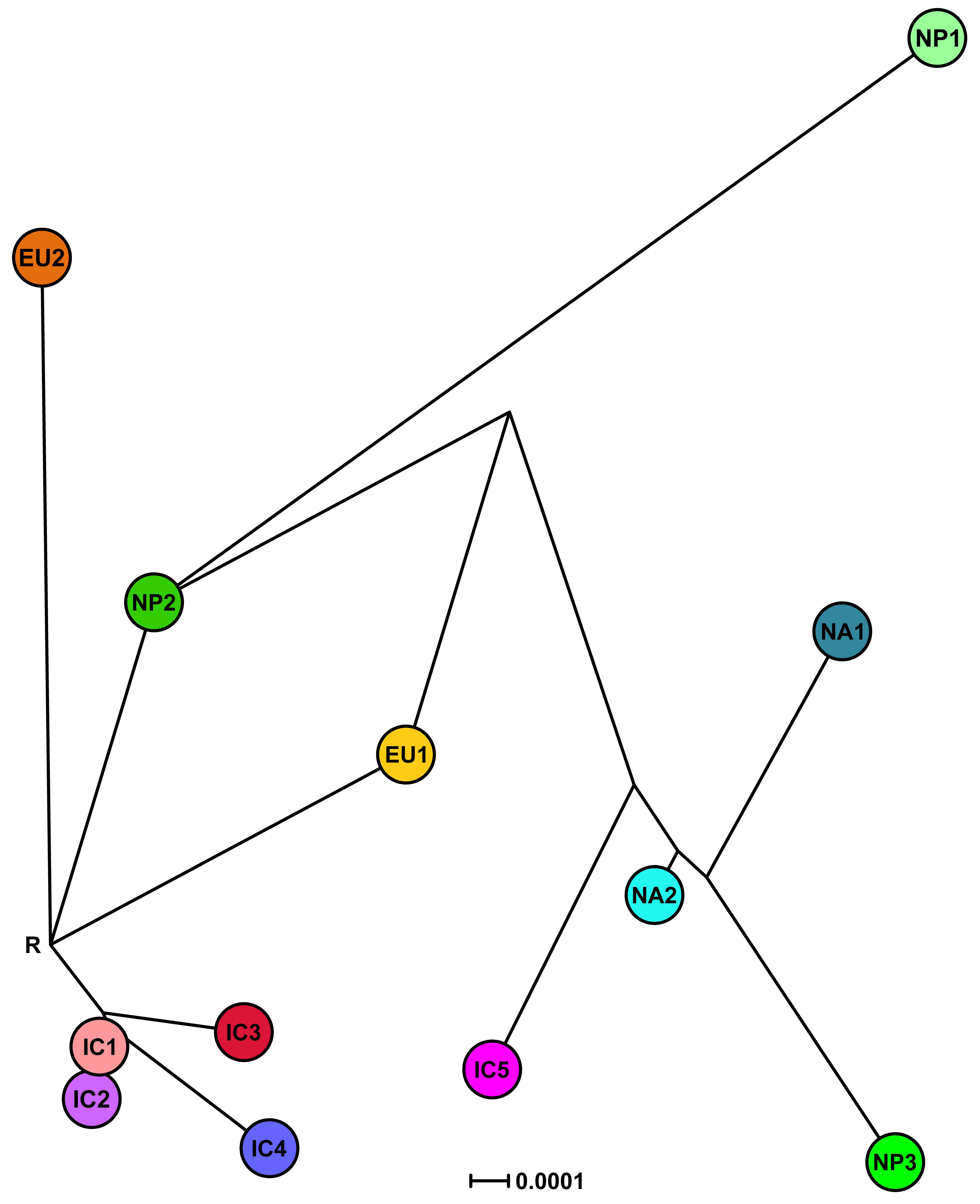
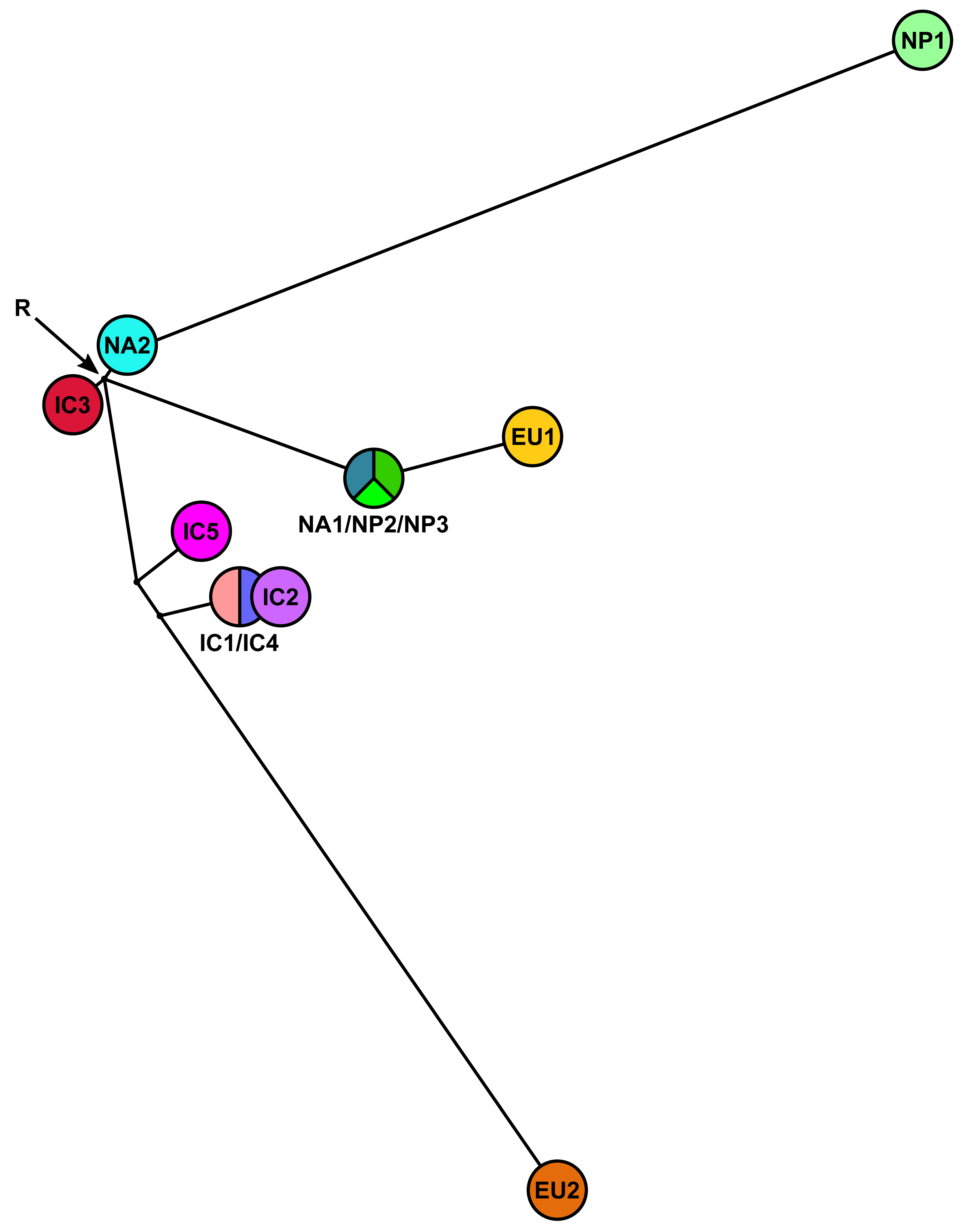
3.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
3.3.1. Phylogenetic Trees
3.3.2. Phylogenetic Networks
3.4. Inferred Evolutionary History of the IC, NP and Introduced Lineages
3.5. Distribution and Sympatry of Evolutionary Lineages and Mating Types Within Vietnam and Japan
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brasier, C.M. The biosecurity threat to the UK and global environment from international trade in plants. Plant Pathol. 2008, 57, 792–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebhold, A.M.; Brockerhoff, E.G.; Garrett, L.J.; Parke, J.L.; Britton, K.O. Live plant imports: The major pathway for forest insect and pathogen invasions of the US. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, A.; Ghelardini, L.; De Pace, C.; Desprez-Loustau, M.L.; Capretti, P.; Chandelier, A.; Cech, T.; Chira, D.; Diamandis, S.; Gaitniekis, T.; et al. Biogeographic patterns and determinants of invasion by alien forest pathogens in Europe. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.; Orlikowski, L.; Henricot, B.; Abad-Campos, P.; Aday, A.G.; Aguin Casal, O.; Bakonyi, J.; Cacciola, S.O.; Cech, T.; Chavarriaga, D.; et al. Widespread Phytophthora infestations in European nurseries put forest, semi-natural and horticultural ecosystems at high risk of Phytophthora diseases. For. Pathol. 2016, 46, 134–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, C.M. Episodic selection as a force in fungal microevolution with special reference to clonal speciation and hybrid introgression. Can. J. Bot. 1995, 73, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, S.B. The population genetics of Phytophthora. Phytopathology 1997, 87, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasier, C.M. Phytophthora biodiversity: How many Phytophthora species are there? Phytophthoras For. Nat. Ecosyst. 2009, 221, 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, T.; Sierra-Perez, A.; Duran, A.; Horta Jung, M.; Balci, Y.; Scanu, B. Canker and decline diseases caused by soil- and airborne Phytophthora species in forests and woodlands. Persoonia 2018, 40, 182–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, D.M.; Garbelotto, M.; Davidson, J.M.; Slaughter, G.W.; Koike, S.T. Phytophthora ramorum as the cause of extensive mortality of Quercus spp. and Lithocarpus densiflorus in California. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, D.M.; Garbelotto, M.; Hansen, E.M. Phytophthora ramorum: Integrative research and management of an emerging pathogen in California and Oregon forests. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 309–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, C.; Webber, J. Sudden larch death. Nature 2010, 466, 824–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grünwald, N.J.; Garbelotto, M.; Goss, E.M.; Heungens, K.; Prospero, S. Emergence of the sudden oak death pathogen Phytophthora ramorum. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.R.; Mullet, M.; Webber, J.F. Changes in the population structure and sporulation behaviour of Phytophthora ramorum associated with the epidemic on Larix (larch) in Britain. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 2313–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivors, K.; Garbelotto, M.; Vries, I.D.E.; Ruyter-Spira, C.; Te Hekkert, B.; Rosenzweig, N.; Bonants, P. Microsatellite analysis identifies three lineages of Phytophthora ramorum in nurseries yet single lineages in US forests and European nursery populations. Mol Ecol. 2006, 15, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss, E.M.; Carbone, I.; Grünwald, N.J. Ancient isolation and independent evolution of the three clonal lineages of the exotic sudden oak death pathogen Phytophthora ramorum. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Poucke, K.; Franceschini, S.; Webber, J.F.; Vercauteren, A.; Turner, J.A.; McCracken, A.R.; Heungens, K.; Braiser, C.M. Discovery of a fourth evolutionary lineage of Phytophthora ramorum: EU2. Fungal Biol. 2012, 116, 1178–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croucher, P.J.; Mascheretti, S.; Garbelotto, M. Combining field epidemiological information and genetic data to comprehensively reconstruct the invasion history and microevolution of the Sudden oak death agent Phytophthora ramorum in California. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 2281–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, A.L.; Feau, N.; Everhart, S.E.; Dhillon, B.; Wong, B.; Sheppard, J.; Bilodeau, G.J.; Brar, A.; Tabima, J.F.; Shen, D.; et al. Mitotic recombination and rapid genome evolution in the invasive forest pathogen Phytophthora ramorum. mBio 2019, 10, e02452-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandelier, A.; Heungens, K.; Werres, S. Change of mating type in an EU1 lineage isolate of Phytophthora ramorum. J. Phytopathol. 2014, 162, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, C.M.; Kirk, S.A.; Rose, J. Differences in the phenotypic stability and adaptive variation between the main European and American lineages of Phytophthora ramorum. In Progress in Research on Phytophthora Disease of Forest Trees; Brasier, C., Jung, T., Oßwald, W., Eds.; Forest Research: Farnham, UK, 2006; pp. 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini, S.; Webber, J.F.; Sancisi-Frey, S.; Brasier, C.M. Gene x environment tests discriminate the new EU2 evolutionary lineage of Phytophthora ramorum and indicate that it is adaptively different. For. Pathol. 2014, 44, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.R.; Brasier, C.M.; Scanu, B.; Webber, J.F. Fitness characteristics of the European lineages of Phytophthora ramorum. Plant Pathol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, C.M.; Denman, S.; Brown, A.; Webber, J.F. Sudden oak death (Phytophthora ramorum) discovered on trees in Europe. Mycol. Res. 2004, 108, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, C.M.; Vettraino, A.M.; Chang, T.T.; Vannini, A. Phytophthora lateralis discovered in an old growth Chamaecyparis forest in Taiwan. Plant Pathol. 2010, 59, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettraino, A.M.; Brasier, C.M.; Brown, A.V.; Vannini, A. Phytophthora himalsilva sp. nov. an unusually phenotypically variable species from a remote forest in Nepal. Fungal Biol. 2011, 115, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huai, W.X.; Tian, G.; Hansen, E.M.; Zhao, W.X.; Goheen, E.M.; Grünwald, N.J.; Cheng, C. Identification of Phytophthora species baited and isolated from forest soil and streams in northwestern Yunnan province, China. For. Pathol. 2013, 43, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.; Chang, T.T.; Bakonyi, J.; Seress, D.; Pérez-Sierra, A.; Yang, X.; Hong, C.; Scanu, B.; Fu, C.H.; Hsueh, K.L.; et al. Diversity of Phytophthora species in natural ecosystems of Taiwan and association with disease symptoms. Plant Pathol. 2017, 66, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.M.; Goheen, D.J.; Jules, E.S.; Ullian, B. Managing Port–Orford–Cedar and the introduced pathogen Phytophthora lateralis. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, C.M.; Franceschini, S.; Vettraino, A.M.; Hansen, E.M.; Green, S.; Robin, C.; Webber, J.F.; Vannini, A. Four phenotypically and phylogenetically distinct lineages in Phytophthora lateralis. Fungal Biol. 2012, 116, 1232–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.; Scanu, B.; Brasier, C.M.; Webber, J.; Milenković, I.; Corcobado, T.; Tomšovský, M.; Pánek, M.; Bakonyi, J.; Maia, C.; et al. A survey in natural forest ecosystems of vietnam reveals high diversity of both new and described phytophthora taxa including P. ramorum. Forests 2020, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.; Blaschke, H.; Neumann, P. Isolation, identification and pathogenicity of Phytophthora species from declining oak stands. Eur. J. For. Path. 1996, 26, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werres, S.; Marwitz, R.; Man In’t veld, W.A.; De Cock, A.W.A.M.; Bonants, P.J.M.; De Weerdt, M.; Themann, K.; Ilieva, E.; Baayen, R.P. Phytophthora ramorum sp. nov., a new pathogen on Rhododendron and Viburnum. Mycol. Res. 2001, 105, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.; Jung, M.H.; Scanu, B.; Seress, D.; Kovács, M.G.; Maia, C.; Pérez-Sierra, A.; Chang, T.-T.; Chandelier, A.; Heungens, K.; et al. Six new Phytophthora species from ITS Clade 7a including two sexually functional heterothallic hybrid species detected in natural ecosystems in Taiwan. Persoonia 2017, 38, 100–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, D.E.L.; Drenth, A.; Duncan, J.M.; Wagels, G.; Brasier, C.M. A molecular phylogeny of Phytophthora and related Oomycetes. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2000, 30, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, C.M.; Beales, P.A.; Kirk, S.A.; Denman, S.; Rose, J. Phytophthora kernoviae sp. nov. an invasive pathogen causing bleeding stem lesions on forest trees and foliar necrosis of ornamentals in Britain. Mycol. Res. 2005, 109, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutet, X.; Vercauteren, A.; Heungens, K.; Laurent, F.; Chandelier, A. Oospore progenies from Phytophthora ramorum. Fungal Biol. 2010, 114, 369–378. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, T.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Hardy, G.E.S.J. New insights into the survival strategy of the invasive soilborne pathogen Phytophthora cinnamomi in different natural ecosystems in Western Australia. For. Pathol. 2013, 43, 266–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, C.M.; Kirk, S.A. Production of gametangia by Phytophthora ramorum in vitro. Mycol. Res. 2004, 108, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Lenth, R. emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means. R package version 1.4.3.01. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Erwin, D.C.; Ribeiro, O.K. Phytophthora Diseases Worldwide; APS Press American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, F.N.; Tooley, P.W. Phylogenetic relationships among Phytophthora species inferred from sequence analysis of mitochondrially encoded cytochrome oxidase I and II genes. Mycologia 2003, 95, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroon, L.P.N.M.; Bakker, F.T.; van den Bosch, G.B.M.; Bonants, P.J.M.; Flier, W.G. Phylogenetic analysis of Phytophthora species based on mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2004, 41, 766–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.E.; Coffey, M.D.; Park, S.-Y.; Greiser, D.M.; Kang, S. A multi-locus phylogeny for Phytophthora utilizing markers derived from complete genome sequences. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2008, 45, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.N. Mitochondrial haplotype determination in the oomycete plant pathogen Phytophthora ramorum. Curr. Genet. 2008, 54, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staden, R.; Beal, K.F.; Bonfield, J.K. The Staden package 1998. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.; Wright, A.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukumaran, J.; Holder, M.T. DendroPy: A Python library for phylogenetic computing. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1569–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A. BEAST 2: A software platform for bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Drummond, A. bModelTest: Bayesian phylogenetic site model averaging and model comparison. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Phillips, M.J.; Rambaut, A. Relaxed phylogenetics and dating with confidence. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. treeio: Base Classes and Functions for Phylogenetic Tree Input and Output. R package version 1.4.1. Available online: https://guangchuangyu.github.io/software/treeio (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T. ggtree: An R package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Lam, T.T.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y. Two methods for mapping and visualizing associated data on phylogeny using ggtree. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 3041–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. Using ggtree to visualize data on tree-like structures. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 69, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkscape’s Contributors (2003–2020). Inkscape. Available online: https://inkscape.org/ (accessed on 2 December 2020).
- Li, W.-H.; Tanimura, M.; Sharp, P.M. An evaluation of the molecular clock hypothesis using mammalian DNA sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1987, 25, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, K.H.; Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.-H. Rates of synonymous substitution in plant nuclear genes. J. Mol. Evol. 1989, 29, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaut, B.S.; Morton, B.R.; McCaig, B.C.; Clegg, M.T. Substitution rate comparisons between grasses and palms: Synonymous rate differences at the nuclear gene Adh parallel rate differences at the plastid gene rbcL. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 10274–10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J.E.; Pennington, R.T.; Pennington, T.D.; Hollingsworth, P.M. Rapid diversification of a species-rich genus of neotropical rain forest trees. Science 2001, 293, 2242–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuga, T.; White, T.J.; Taylor, J.W. Estimation of nucleotide substitution rates in Eurotiomycete fungi. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 2318–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.R. Mutation rates in plastid genomes: They are lower than you might think. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galtier, N.; Nabholz, S.; Glémin, S.; Hurst, G.D.D. Mitochondrial DNA as a marker of molecular diversity: A reappraisal. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 4541–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelt, H.-J.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecies phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Intraspecific gene genealogies: Trees grafting into networks. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassens, I.; Mardulyn, P.; Milinkovitch, M.C. Evaluating intraspecific “network” construction methods using simulated sequence data: Do existing algorithms outperform the Global Maximum Parsimony approach? Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, D.A. Networks in phylogenetic analysis: New tools for population biology. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandelt, H.-J.; Dress, A.W.M. Split decomposition: A new and useful approach to phylogenetic analysis of distance data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1992, 1, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluxus Technology Ltd. (2004–2020). Network 10.1.0.0. Available online: https://www.fluxus-engineering.com (accessed on 2 December 2020).
- Huson, D.H.; Bryant, D. Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamming, R.W. Error detecting and error correcting codes. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1950, 29, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dress, A.W.M.; Huson, D.H. Constructing splits graphs. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2004, 1, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassens, I.; Van Waerebeek, K.; Best, P.B.; Crespo, E.A.; Reyes, J.C.; Milinkovitch, M.C. The phylogeography of dusky dolphins (Lagenorhynchus obscurus): A critical examination of network methods and rooting procedures. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 1781–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werres, S.; Kaminski, K. Characterisation of European and North American Phytophthora ramorum isolates due to their morphology and mating behaviour in vitro with heterothallic Phytophthora species. Mycol. Res. 2005, 109, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.; Jung, M.H.; Cacciola, S.O.; Cech, T.; Bakonyi, J.; Seress, D.; Mosca, S.; Schena, L.; Seddaiu, S.; Pane, A.; et al. Multiple new cryptic pathogenic Phytophthora species from Fagaceae forests in Austria, Italy and Portugal. IMA Fungus 2017, 8, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenlid, J.; Oliva, J. Phenotypic interactions between tree hosts and invasive forest pathogens in the light of globalization and climate change. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2016, 371, 20150455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahoo, R.S.; Blomquist, C.L.; Thomas, S.L.; Moulton, J.K.; Cooke, D.E.L.; Lamour, K.H. Phytophthora foliorum sp. nov., a new species causing leaf blight of azalea. Mycol. Res. 2006, 110, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, C.; Piou, D.; Feau, N.; Douzon, G.; Schenck, N.; Hansen, E.M. Root and aerial infections of Chamaecyparis lawsoniana by Phytophthora lateralis: A new threat for European countries. Forest Pathol. 2011, 41, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.; Brasier, C.M.; Schlenzig, A.; McCracken, A.; MacAskill, G.A.; Wilson, M.; Webber, J.F. The destructive invasive pathogen Phytophthora lateralis found on Chamaecyparis lawsoniana across the UK. Forest Pathol. 2013, 43, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, A.R.; Webber, J.F. Insights into the potential host range of Phytophthora foliorum. Forest Pathol. 2019, 49, e12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsov, A.N.; Luong, P. Flora of Fansipan mountain. In Proceedings of the Seminar & Workshop Biodiversity Value of Hoang Lien Mountains & Strategies for Conservation; Sobey, R.T., Ed.; Society for Environmental Exploration: London, UK, 1998; pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki, A. A vegetation - Ecological view of the Japanese archipelago. Bull. Inst. Environ. Sci. Technol. Yokohama Natl. Univ. 1984, 11, 85–101. [Google Scholar]
- Box, E.O.; Fujiwara, K.; Xue-Zhong, Q. Diversity and dissimilarity of three forest types in Xishuangbanna, tropical southern China. Bull. Inst. Environ. Sci. Technol. Yokohama Natl. Univ. 1991, 17, 85–105. [Google Scholar]
- Averyanov, L.V.; Loc, P.K.; Hiep, N.; Harder, D.K. Phytogeographic review of Vietnam and adjacent areas of Eastern Indochina. Komarovia 2003, 3, 1–83. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.Q.; Ohsawa, M. Ecology of subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests of Yunnan, southwestern China as compared to those of southwestern Japan. J. Plant Res. 2009, 122, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; DellaSala, D.A.; Alaback, P. Temperate rainforests of Japan. In Temperate and Boreal Rainforests of the World; DellaSala, D.A., Ed.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- Hukusima, T.; Matsui, T.; Nishio, T.; Pignatti, S.; Yang, L.; Lu, S.-Y.; Kim, M.-H.; Yoshikawa, M.; Honma, H.; Wang, Y. Phytosociology of the Beech (Fagus) Forests in East Asia; Geobotany Studies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Z. The floras of southern and tropical southeastern Yunnan have been shaped by divergent geological histories. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-Fu, H.; Chung-Fu, S.; Kuoh-Cheng, Y. Introduction to the flora of Taiwan, 3: Floristics, phytogeography, and vegetation. Fl. Taiwan 1994, 2, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Laumonier, Y. The vegetation and Physiography of Sumatra; Geobotany 22; Springer Science and Business Media: Dordrecht, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Whitten, T.; Damanik, S.J.; Anwar, J.; Hisyam, N. The Ecology of Sumatra; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lillesø, J.-P.B.; Shrestha, T.B.; Dhakal, L.P.; Nayaju, R.P.; Shrestha, R. The Map of Potential Vegetation of Nepal—A Forestry/Agroecological/Biodiversity Classification System; Development and Environment Series 2; Forest & Landscape: Frederiksberg, Denmark, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.-C.; Ho, H.-H.; Zheng, F.-C. A survey of Phytophthora species on Hainan Island of South China. J. Phytopathol. 2009, 157, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denman, S.; Kirk, S.A.; Brasier, C.; Webber, J.F. In vitro leaf inoculation studies as an indication of tree foliage susceptibility to Phytophthora ramorum in the UK. Plant Pathol. 2005, 54, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, J.F.; Mullett, M.; Brasier, C.M. Dieback and mortality of plantation Japanese larch (Larix kaempferi) associated with infection by Phytophthora ramorum. New Dis. Rep. 2010, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.M.; Patterson, H.A.; Wickland, A.C.; Fichtner, E.J.; Rizzo, D.M. Forest type influences transmission of Phytophthora ramorum in California oak woodlands. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, C.A.; Kozanitas, M.; Garbelotto, M. Population dynamics of aerial and terrestrial populations of Phytophthora ramorum in a California forest under different climatic conditions. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, E.K.; Hansen, E.M.; Kanaskie, A. Temporal epidemiology of sudden oak death in Oregon. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.R.; Webber, J.F. Sporulation potential, symptom expression and detection of Phytophthora ramorum on larch needles and other foliar hosts. Plant Pathol. 2016, 65, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lione, G.; Gonthier, P.; Garbelotto, M. Environmental factors driving the recovery of bay laurels from Phytophthora ramorum infections: An application of numerical ecology to citizen science. Forests 2017, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, C.A.; Garbelotto, M. Detection, diversity, and population dynamics of waterborne Phytophthora ramorum populations. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz Ribeiro, P.; Rapini, A.; Soares e Silva, U.C.; van den Berg, C. Using multiple analytical methods to improve phylogenetic hypotheses in Minaria (Apocynaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 65, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magallon, S. A review of the effect of relaxed clock method, long branches, genes, and calibrations in the estimation of angiosperm age. Bot. Sci. 2014, 92, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, D.B.; Havird, J.C.; Sharbrough, J. The on-again, off-again relationship between mitochondrial genomes and species boundaries. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 2212–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducket, D.J.; Pelletier, T.A.; Carstens, B.C. Identifying model violations under the multispecies coalescent model using P2C2M.SNAPP. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, H.; DeGiorgio, M. Maximum Likelihood estimation of species trees from gene trees in the presence of ancestral population structure. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 3977–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakleh, L.; Ruths, D.; Innan, H. Gene Trees, Species Trees, and Species Networks. In Meta-Analysis and Combining Information in Genetics; Guerra, R., Goldstein, D., Eds.; Chapman & Hall, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 275–293. [Google Scholar]
- Matari, N.H.; Blair, J.E. A multilocus timescale for oomycete evolution estimated under three distinct molecular clock models. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M.; Takahata, N. Effective population size, genetic diversity, and coalescence time in subdivided populations. J. Mol. Evol. 1993, 37, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avise, J.C. Phylogeography—The History and Formation of Species; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Henricot, B.; Pèrez-Sierra, A.; Jung, T. Phytophthora pachypleura sp. nov., a new species causing root rot of Aucuba japonica and other ornamentals in the United Kingdom. Plant. Pathol. 2014, 63, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrod, D.I.; Al-Shehbaz, I.; Raven, P.H. History of the modern flora of China. In Floristic Characteristics and Diversity of East Asian Plants; Zhang, A.L., Wu, S.G., Eds.; China Higher Education Press/Springer: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-W.; Ge, S. Phylogeography of the endangered Cathaya argyrophylla (Pinaceae) inferred from sequence variation of mitochondrial and nuclear DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 4109–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; López-Pujol, J.; Wang, H.-W.; Ge, S.; Zhang, Z.-Y. Molecular evidence for glacial expansion and interglacial retreat during Quaternary climatic changes in a montane temperate pine (Pinus kwangtungensis Chun ex Tsiang) in southern China. Plant Syst. Evol. 2010, 284, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Ueno, S.; Kamijo, T.; Setoguchi, H.; Murakami, N.; Kato, M.; Tsumura, Y. Genetic differentiation and genetic diversity of Castanopsis (Fagaceae), the dominant tree species in Japanese broadleaved evergreen forests, revealed by analysis of EST-associated microsatellites. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.M.; Möller, M.; Zhang, X.-M.; Hollingsworth, M.L.; Liu, J.; Mill, R.R.; Gibby, M.; Li, D.-Z. High variation and strong phylogeographic pattern among cpDNA haplotypes in Taxus wallichiana (Taxaceae) in China and North Vietnam. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 4684–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Hongjin, D.; Hua, P. Diversity and distribution of higher plants in Yunnan, China. Biodiv. Sci. 2013, 21, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Hu, N.-Q.; Chen, X.; Li, J.-T.; Jiang, X.-L. Interglacial refugia preserved high genetic diversity of the Chinese mole shrew in the mountains of southwest China. Heredity 2016, 116, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Chen, P.; Bu, W. Terrestrial mountain islands and Pleistocene climate fluctuations as motors for speciation: A case study on the genus Pseudovelia (Hemiptera: Veliidae). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, R.B. Physical geography and geology: Imprints on a landscape, Yunnan, China. Geography 2005, 90, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercauteren, A.; Boutet, X.; D’hondt, L.; Van Bockstaele, E.; Maes, M.; Leus, L.; Chandelier, A.; Heungens, K. Aberrant genome size and instability of Phytophthora ramorum oospore progenies. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasier, C.M. Evolutionary Biology of Phytophthora. I. Genetic system, sexuality and variation. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 1992, 30, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuga, T.; Bui, M.; Bernhardt, E.; Swiecki, T.; Aram, K.; Cano, L.M.; Webber, J.; Brasier, C.; Press, C.; Grünwald, N.J.; et al. Host-induced aneuploidy and phenotypic diversification in the Sudden Oak Death pathogen Phytophthora ramorum. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuzon, J.D.; Travadon, R.; Mathu, M.C.; Tripathy, S.; Rank, N.; Mehl, H.K.; Rizzo, D.M.; Cobb, R.; Small, C.; Tang, T.; et al. Asexual evolution and forest conditions drive genetic parallelism in Phytophthora ramorum. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichtner, E.J.; Lynch, S.C.; Rizzo, D.M. Detection, distribution, survival, and sporulation of Phytophthora ramorum in a California redwood-tanoak forest soil. Phytopathology 2007, 97, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, B.A.; Alexander, H.M.; Davidson, J.; Campbell, F.T.; Burdon, J.J.; Sniezko, R.; Brasier, C. Increasing forest loss worldwide from invasive pests requires new trade regulations. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschen, R.; Britton, K.; Brockerhoff, E.; Burgess, T.; Valley, V.; Epanchin-Niell, R.S.; Gupta, K.; Hardy, G.; Huang, Y.; Kenis, M.; et al. International variation in phytosanitary legislation and regulations governing importation of plants for planting. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 51, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschen, R.; Douma, B.; Grégoire, J.C.; Mayer, F.; Rigaux, L.; Potting, R.P.J. A risk categorisation and analysis of the geographic and temporal dynamics of the European import of plants for planting. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 3243–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, E.M.; Drenth, A.; Kumar, S.; Mack, S.; Mackie, A.E.; McKirdy, S. Pathogens associated with nursery plants imported into Western Australia. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2006, 35, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

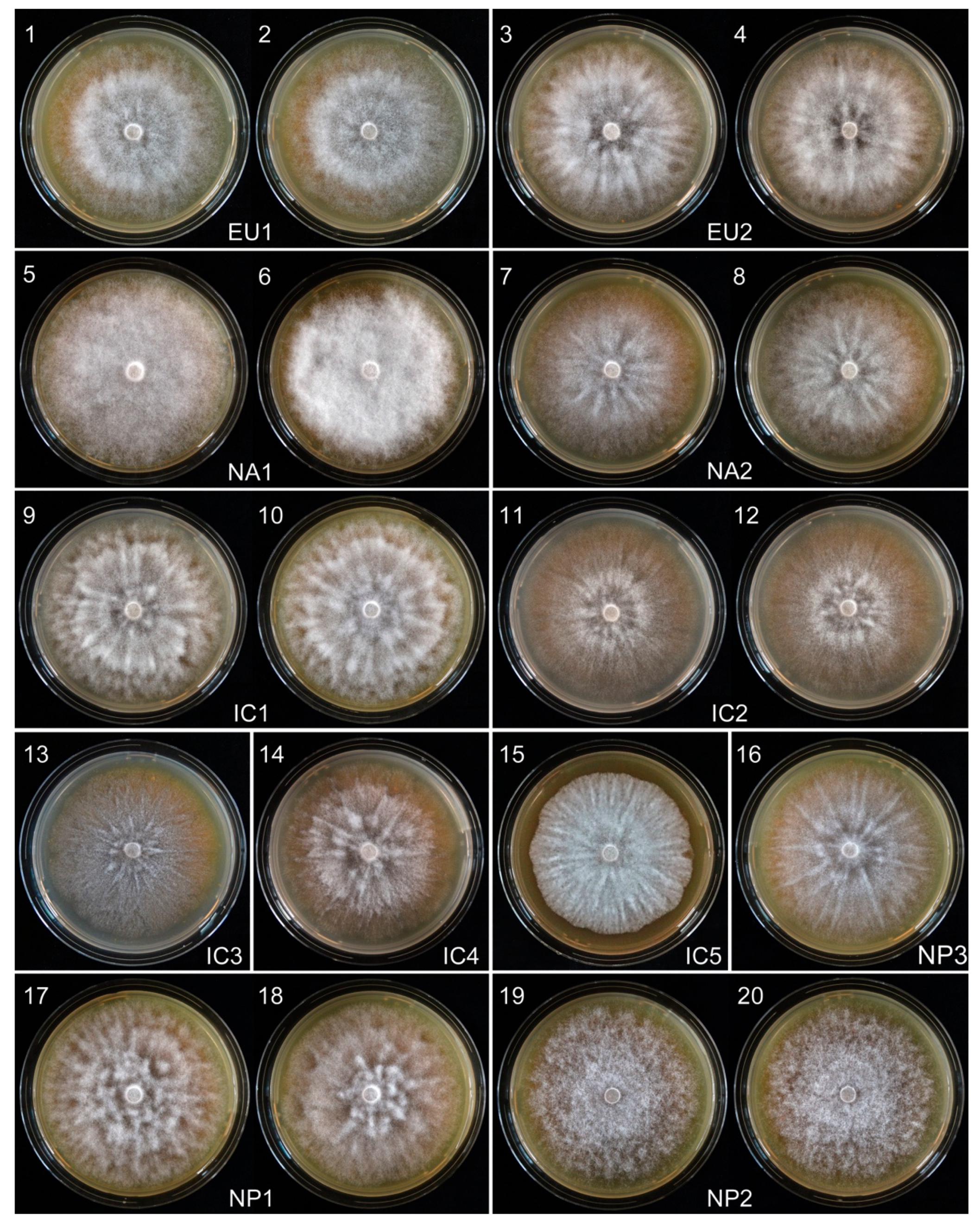
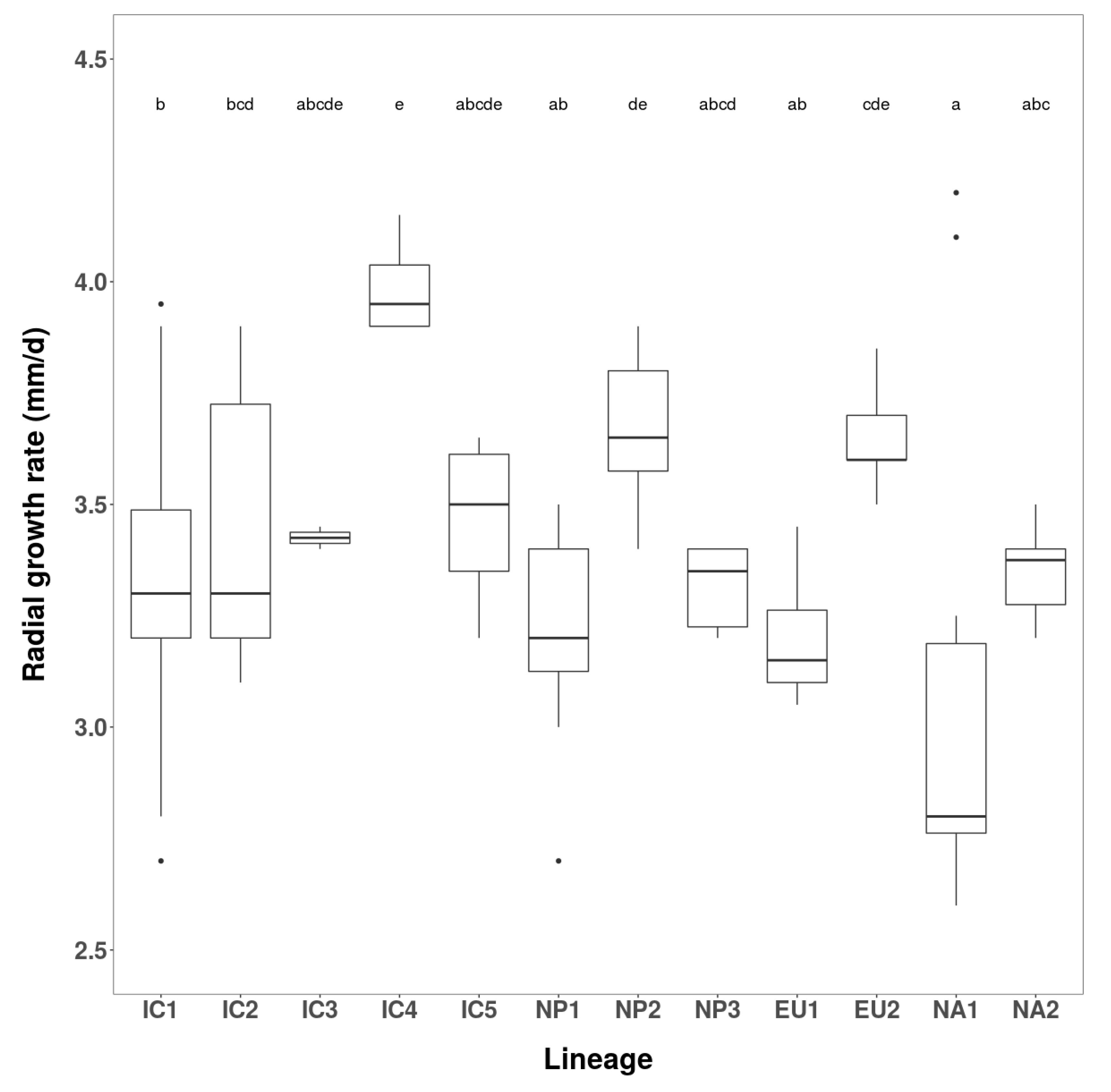
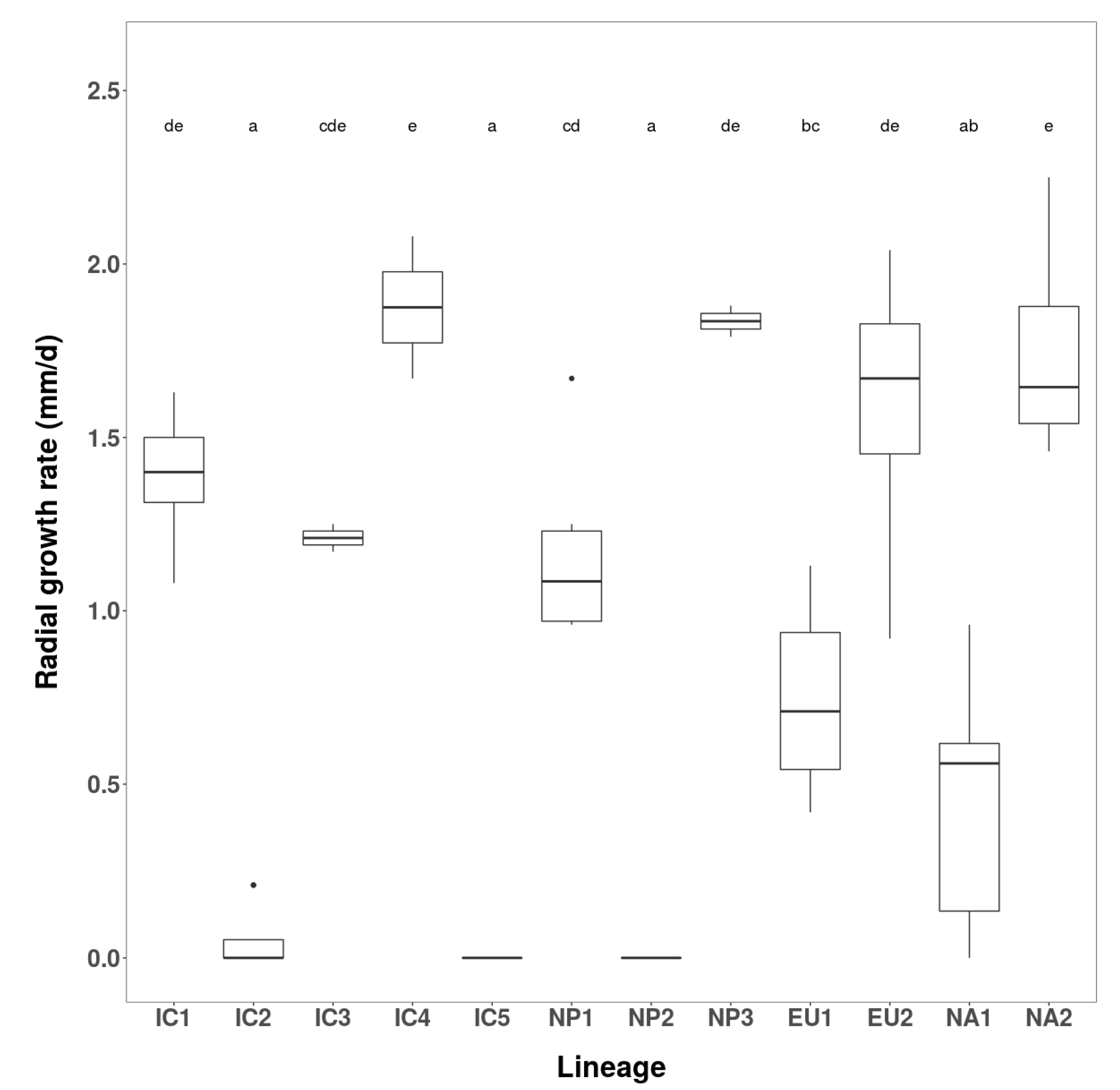


| Phenotype Group | Isolates | Radial Growth (mm/d) over 12 Days | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Codes | Range | Mean | |
| Vietnam | ||||
| IC1 | 2 | VN160, VN856 | 1.5–1.63 | 1.56 |
| IC2 | 2 | VN142, VN150 | 0 | 0.0 |
| IC3 | 1 | VN88 | - | 0.82 |
| IC4 | 1 | VN851 | - | 1.63 |
| IC5 | 1 | VN863 | - | 0.0 |
| Japan | ||||
| NP1 | 3 | JP236, JP718, JP1202 | 0.44–1.25 | 0.76 |
| NP2 | 2 | JP387, JP462 | 0 | 0.0 |
| NP3 | 1 | JP975 | - | 2.15 |
| Known lineages | ||||
| EU1 | 2 | P1367, P1376 | 0–0.42 | 0.21 |
| EU2 | 2 | P2460, P2461 | 2.33–2.46 | 2.39 |
| NA1 | 2 | P1403, P1421 | 0 | 0.0 |
| NA2 | 2 | P2056, P2058 | 2.21–2.46 | 2.33 |
| Region (Altitude (m asl)) | Stream Number 1 | Phenotype Group 2 | No. of Isolates by Mating Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | A2 | A0 3 | |||
| Vietnam (VN) | |||||
| Fansipan (2083) | S1 | IC1 IC5 | 16 | 1 | |
| Fansipan (2007) | S2 | IC1 | 9 | ||
| Fansipan (1913) | S3 | IC2 | 4 | ||
| Fansipan (1904) | S4 | IC1 IC3 | 1 | 1 | |
| Fansipan (1895) | S5 | IC1 | 3 | ||
| Fansipan (1912) | S7 | IC1 | 7 | ||
| Fansipan (1193) | S10 | IC1 | 4 | ||
| Sau-Chua (1308) | S11 | IC4 | 1 | ||
| Japan (JP) | |||||
| Shikoku, Shimanto (523) | S15 | NP1 | 3 | ||
| Kyushu, Tarumizu (546) | S22 | NP2 | 2 | ||
| Kyushu, Kirishima (335) | S31 | NP1 NP3 | 1 | 1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, T.; Horta Jung, M.; Webber, J.F.; Kageyama, K.; Hieno, A.; Masuya, H.; Uematsu, S.; Pérez-Sierra, A.; Harris, A.R.; Forster, J.; et al. The Destructive Tree Pathogen Phytophthora ramorum Originates from the Laurosilva Forests of East Asia. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7030226
Jung T, Horta Jung M, Webber JF, Kageyama K, Hieno A, Masuya H, Uematsu S, Pérez-Sierra A, Harris AR, Forster J, et al. The Destructive Tree Pathogen Phytophthora ramorum Originates from the Laurosilva Forests of East Asia. Journal of Fungi. 2021; 7(3):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7030226
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Thomas, Marília Horta Jung, Joan F. Webber, Koji Kageyama, Ayaka Hieno, Hayato Masuya, Seiji Uematsu, Ana Pérez-Sierra, Anna R. Harris, Jack Forster, and et al. 2021. "The Destructive Tree Pathogen Phytophthora ramorum Originates from the Laurosilva Forests of East Asia" Journal of Fungi 7, no. 3: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7030226
APA StyleJung, T., Horta Jung, M., Webber, J. F., Kageyama, K., Hieno, A., Masuya, H., Uematsu, S., Pérez-Sierra, A., Harris, A. R., Forster, J., Rees, H., Scanu, B., Patra, S., Kudláček, T., Janoušek, J., Corcobado, T., Milenković, I., Nagy, Z., Csorba, I., ... Brasier, C. M. (2021). The Destructive Tree Pathogen Phytophthora ramorum Originates from the Laurosilva Forests of East Asia. Journal of Fungi, 7(3), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7030226







