Abstract
The genus Hydnellum is an important group of stipitate hydnaceous fungi which can form ectomycorrhiza with many species of woody plants. In recent decades, the frequency and number of basidiocarps observed in China have been declining significantly. So far, however, we know little about the species diversity of Hydnellum in China. In this study, we conducted molecular phylogenetic analyses based on sections of multiple loci, including the large subunit of nuclear ribosomal RNA gene (nLSU), the internal transcribed spacer regions (ITS), the small subunit of nuclear ribosomal RNA gene (SSU) and the second-largest subunit of RNA polymerase II gene (RPB2), as well as morphological studies, of collected samples of Hydnellum from China. We also inferred Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian phylogenies for the order Thelephorales from the dataset of the combined nLSU and ITS. This study has revealed the phylogenetic position of Hydnellum in the order Thelephorales, and phylogenetically confirmed ten major clades in Thelephorales; Twenty-nine taxa are proposed, described or reported, including 10 new subgenera (Hydnellum subgenus Hydnellum, subg. Caesispinosum, subg. Croceum, subg. Inflatum, subg. Rhizomorphum, subg. Scabrosum, subg. Spongiosum, subg. Subindufibulatum, subg. Violaceum and subg. Zonatum), 11 new species (Hydnellum atrorubrum, H. atrospinosum, H. bomiense, H. brunneorubrum, H. fibulatum, H. granulosum, H. inflatum, H. rubidofuscum, H. squamulosum, H. sulcatum and H. yunnanense), 3 newly recorded species (H. caeruleum, H. peckii and H. spongiosipes) and 5 notable specimens (Hydnellum sp 1, H. sp 2, H. sp 3, H. sp 4 and H. sp 5). A classification system based on the morphological characteristics (especially the hyphal structure types) and molecular analyses is proposed to accommodate most species in Hydnellum. The distinguishing characters of the subgenera and the new species with their closely related taxa are discussed. A key to the species of Hydnellum from China is provided.
1. Introduction
The genus Hydnellum, together with Bankera, Phellodon and Sarcodon, are a homogenous group of soil-inhabiting Basidiomycota (with the common characteristic of a hymenophore with a spinulose hymenium) that belongs to the Bankeraceae, Thelephorales [1,2].
All species of Bankeraceae are considered ectomycorrhizal and are associated with woody plants, mainly members of Pinaceae and Fagaceae [3,4,5,6,7], and colonize natural or relatively undisturbed forests [8]. These fungi can absorb organic substances from host plants and also transport nutrients and water from the soil to the plants, which improves the stability of forest ecosystems [9,10]. In addition, some species of Hydnellum have important medicinal functions, including cholesterol-lowering, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, immune enhancement, etc. [11]. For instance, Lee et al. [12] suggested that H. concrescens extracts prevents the expression of NDV-HN glycoprotein on the cell surface by inhibiting the activity of α-glucosidase, thus exhibiting anti-viral function. This can be on par with the health benefit potentials of herbal plant infusions [13].
Due to substantial declines in abundance, they have become the focus of increasing conservation concern [14,15,16]. This is mainly attributed to the effect of habitat loss, aerial pollution, nitrogen deposition and soil acidification [17,18,19,20,21]. Stipitate hydnoid fungi, as symbols for the recent decline of ectomycorrhizal fungi, have been redlisted in, e.g., Norway, Poland, Germany, and the Netherlands [7,14,18,19,22,23,24]. Furthermore, an action plan for 14 rare species of hydnoid fungi has been announced to provide strategic management for their future conservation in the UK [25].
The genus Hydnellum is characterized by single to gregarious or coalescent pileate, stipitate basidiocarps, spinous hymenophore, corky to woody, not duplex to duplex, azonate to zonate context, uninflated to inflated generative hyphae, with or without clamp connections, and brown, irregularly ellipsoid to globose, tuberculate basidiospores. Some species display olivaceous or blue-green colours with KOH [1,2,5,26,27]. However, differentiation between closely related species within Hydnellum becomes significantly difficult on account of their macromorphological polymorphism caused by growing around obstacles or fusing to other adjacent basidiocarps [2,27]. Therefore, molecular sequence data are very important in identifying them. Molecular evidence has confirmed that Hydnellum has a close phylogenetic affiliation with the genus Sarcodon, and both genera aggregated in the same clade, named the “Hydnellum-Sarcodon lineage” [28,29,30]. Furthermore, the phylogenetic analysis of Hydnellum and Sarcodon according to Baird et al. [27] suggested that the generic limits need reassessment. To revise the generic limits and make genera monophyletic, Larsson et al. [31] moved 12 species from Sarcodon to Hydnellum, resulting in the generic circumscription of Hydnellum being amended. Morphologically, basidiospore size appears to separate the genera in most cases.
Most of the described species of Hydnellum are distributed to North America [2,27,32,33,34] and Europe [1,6,35,36], with a few species reported from Singapore, India, Australia, and New Guinea [26]. About 61 species have been described and transferred to the genus according to Index Fungorum (http://www.indexfungorum.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2021)) and MycoBank; however, only three taxa have been previously reported from China, and detailed molecular studies have not been performed [37]. Some specimens of this genus collected from China were identified as H. aurantiacum, H. ferrugineum and H. suaveolens based solely on morphological characteristics. However, molecular methods revealed that these specimens are misidentified, and the specimens need to be re-identified.
Numerous Hydnellum specimens have been collected from field investigations on stipitate hydnoid fungi in China during the past two decades. During the study of these specimens, twenty-nine new taxa have been identified using morphological characters and phylogenetic analyses of nuc rDNA ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 combined with nuc 28S rDNA, nuc 18S rDNA and nuc RPB2 rDNA sequences. In this paper, we present these taxa with illustrated morphological descriptions, phylogeny and comparison with related and/or similar taxa, a key and classification system.
The aims of this study are: (1) To describe the new taxa of Hydnellum from China and confirm or propose infrageneric subdivision (new subgenera, new species and newly recorded species) based on morphological and phylogenetic analyses; (2) To provide a classification system using hyphal structure types, molecularly supported clades and morphological characteristics within Hydnellum and Sarcodon; and (3) To confirm the phylogenetic position of Hydnellum within the Thelephorales.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Morphological Studies
Specimens were deposited at the herbarium of the Institute of Applied Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IFP). Microscopic procedures followed Mu et al. [38]. Structures were examined microscopically from sections mounted in Cotton Blue (CB): 0.1 mg aniline blue dissolved in 60 g pure lactic acid; CB+ = cyanophilous, CB− = acyanophilous. Amyloid and dextrinoid reactions were tested in Melzer’s reagent (IKI): 1.5 g KI (potassium iodide), 0.5 g I (crystalline iodine), 22 g chloral hydrate, 20 mL distilled water; IKI− = neither amyloid nor dextrinoid reaction. Sections were mounted in 5% KOH and studied at magnifications up to 1000× using a Nikon Eclipse E600 microscope (Tokyo, Japan) with phase contrast illumination. Dimensions were measured by the ruler in the eyepiece, with accuracy within 0.1 μm. In presenting basidiospore size ranges, 5% of the measurements at each end of the range are given in parentheses. The following abbreviations are used in the text: Lm = mean spore length, Wm = mean spore width, Q = range of length/width ratios for specimens studied, and n = total number of basidiospores measured from a given number of specimens. The surface morphology for the basidiospores was observed with a Phenom Prox scanning electron microscope (ESEM, Phenom Prox, FEI, The Netherlands) at an accelerating voltage of 20 kV. A thin layer of gold was coated on the samples to avoid charging. Special color terms are from Rayner [39] and Munsell [40].
2.2. Molecular Procedures and Phylogenetic Analyses
Fungal taxa and strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. Phire Plant Direct PCR Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) procedures were used to extract total genomic DNA from the basidiocarps. Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) was performed on a Bio-Rad T100TM Thermal cycler (Bio-RAD Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). Amplification reactions were performed in a 30 μL reaction mixture using the following final concentrations or total amounts: 0.9 μL template DNA, 15 μL of 2× Phire Plant PCR buffer, 1.5 μL of each primer, 0.6 μL Phire HS II DNA Polymerase, and 10.5 μL ddH2O (double distilled water). Primer sequences for the used genes are provided in Table 2. The PCR lthermal cycling program condition was set as follows: initial denaturation at 98 °C for 5 min, followed by 39 cycles at 98 °C for 30 s, × °C (the annealing temperatures for LROR/LR7, ITS1-F/ITS4, NS1/NS4, and bRPB2-6F/bRPB2-7.1R were 47.2 °C, 57.2 °C, 48 °C and 57.2 °C, respectively) for 30 s, 72 °C for 30 s, and a final extension at 72 °C for 1 min. PCR amplification was confirmed on 1% agarose electrophoresis gels stained with ethidium bromide [41]. DNA sequencing was performed at the Beijing Genomics Institute (BGI). All newly generated sequences were submitted to GenBank. Additional LSU rDNA, ITS rDNA, SSU rDNA and RPB2 rDNA sequences in the dataset used to establish phylogenetic relationships were downloaded from GenBank (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/php (accessed on 10 August 2021)) and UNITE (https://unite.ut.ee/index.php (accessed on 10 August 2021)) (Table 1). Nuclear ribosomal RNA genes were used to determine the phylogenetic position of the new species. After PCR amplification, the products were sequenced in both directions and the sequences were assembled using DNAMAN 8.0. DNA sequences were aligned using MAFFT 7.110 [42]. To ensure the repeatability of the results, alignments were not manually adjusted. The best-fit evolutionary models selected by jmodeltest-2.1.10 for genes were GTR+I+G (nLSU), K80+G (ITS1), K80 (5.8S), JC+G (ITS2), TrN+I+G (SSU), K80+G (RPB2) in the first dataset (Hydnellum and Sarcodon dataset) and GTR+I+G (nLSU), K80+G (ITS1), K80+G (5.8S), K80+G (ITS2) in the second dataset (Thelephorales dataset). These models were applied in Bayesian analyses. All gaps were treated as missing data. Maximum Likelihood (ML) analysis was performed in RAxML v8.2.4 with GTR+I+G model [43]. The best tree was obtained by executing 100 rapid bootstrap inferences and thereafter a thorough search for the most likely tree using one distinct model/data partition with joint branch length optimization [44]. Bayesian analyses with MrBayes 3.2.4 [45] implementing the Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) technique and parameters predetermined with MrMODELTEST2.3 [46,47] were performed. Four simultaneous Markov chains were run starting from random trees, keeping one tree every 100th generation until the average standard deviation of split frequencies was below 0.01. The value of burn-in was set to discard 25% of trees when calculating the posterior probabilities. Bayesian posterior probabilities were obtained from the 50% majority rule consensus of the trees kept. Then the FigTree v1.3.1 were used to visualize the resulting trees.

Table 1.
Voucher numbers, geographic origins and GenBank accession numbers for the specimens included; sequences produced in this study are in bold.

Table 2.
The gene fragments, their corresponding primers and primer sequences used in this study.
3. Results
Phylogenetic Analyses
In the first dataset, 272 sequences derived from four gene loci (nLSU, ITS, SSU and RPB2) were used to build phylogenetic trees; 108 of them were newly generated, including 25 of nLSU, 37 sequences of ITS, 25 of SSU and 21 of RPB2. The phylogenetic construction performed with maximum likelihood and Bayesian Inference (BI) analyses for two combined datasets showed similar topology. The combined LSU-ITS-SSU-RPB2 dataset represented 70 taxa and 3629 characters after being trimmed. Polyozellus mariae and P. multiplex were used as the outgroups according to phylogenetic analysis of Thelephorales. Bayesian analysis ran for 8 million generations and resulted in an average standard deviation of split frequencies of 0.005062. The same dataset and alignment were analysed using the ML method. The Maximum Likelihood tree is shown in Figure 1. In the phylogenetic tree, ten clades which correspond to subgenus Hydnellum, subg. Caesispinosum, subg. Croceum, subg. Inflatum, subg. Rhizomorphum, subg. Scabrosum, subg. Spongiosum, subg. Subindufibulatum, subg. Violaceum and subg. Zonatum were revealed. Twenty-eight sampled specimens formed 11 new species (Hydnellum atrorubrum, H. atrospinosum, H. bomiense, H. brunneorubrum, H. fibulatum, H. granulosum, H. inflatum, H. rubidofuscum, H. squamulosum, H. sulcatum and H. yunnanense) and clustered in a clade that comprised most species of Hydnellum. Four sampled specimens (Wei1474a, Yuan13708 and Yuan13720, Yuan14517) that were confirmed as new records from China clustered with Hydnellum caeruleum, H. peckii and H. spongiosipes with strong support. In addition, five notable specimens, Hydnellum sp 1, Hydnellum sp 2, Hydnellum sp 3, Hydnellum sp 4 and Hydnellum sp 5, formed five separate clades, and need further verification. In the second dataset, the combined ITS and nLSU gene also included sequences from 129 specimens representing 58 taxa of Thelephorales, as well as Steccherinum ochraceum and S. murashkinskyi, which were chosen as outgroups according to previous study [31]. The average standard deviation of split frequencies in the Bayesian analyses reached 0.007357 after running for 8 million generations. The calculated values based on the dataset analysed using the ML method. The Maximum Likelihood tree is shown in Figure 2. It revealed that the Hydnellum clade occupies an independent phylogenetic position. The Hydnellum clade is sister to the Sarcodon clade. According to the phylogenetic tree, ten major clades, Amaurodon clade, Boletopsis clade, Hydnellum clade, Lenzitopsis clade, Odontia clade, Phellodon/Bankera clade, Pseudotomentella/Polyozellus clade, Sarcodon clade, Thelephora/Tomentella clade and Tomentellopsis clade, were identified within the Thelephorales (Figure 2). Therefore, in order to use the maximum amount of genetic information when defining new species, we conducted the first dataset. Meanwhile, ITS trees of Hydnellum and Sarcodon were constructed and produced a topology similar to that generated by the first dataset (see Supplementary, Figure S1). The purpose of executing the second dataset was to demonstrate the phylogenetic position of Hydnellum species in the Thelephorales.
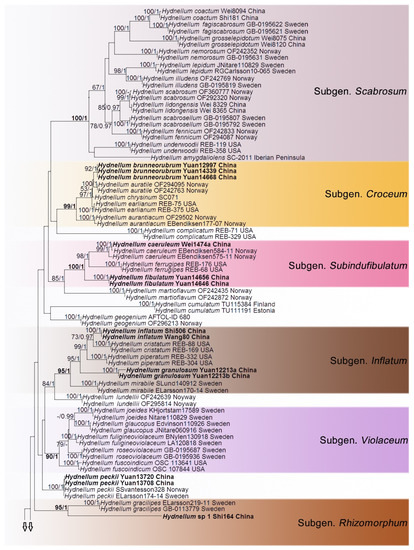
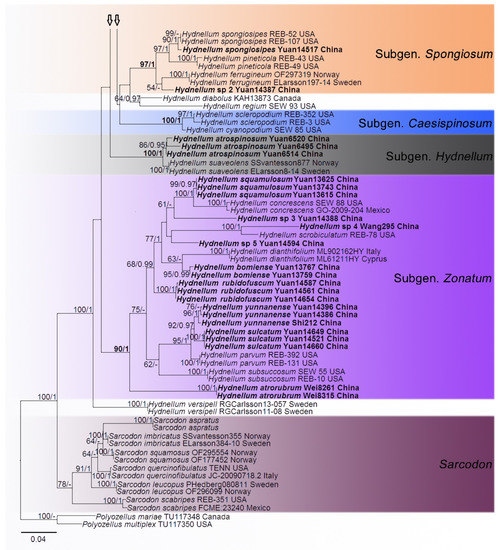
Figure 1.
Maximum likelihood tree illustrating the phylogeny of Hydnellum and Sarcodon based on nLSU, ITS, SSU and RPB2 sequence datasets. Branches are labeled with maximum likelihood bootstrap support greater than 50 % and Bayesian posterior probabilities greater than 0.95. Newly sequenced collections are in bold.
Figure 2.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis based on the nLSU and ITS sequences of Thelephorales. Branches are labeled with maximum likelihood bootstrap support greater than 50 % and Bayesian posterior probabilities greater than 0.95. Newly sequenced collections are in bold.
4. Taxonomy
Hydnellum subg. Hydnellum
MycoBank MB841191
Etymology. Hydnellum (Latin), refers to the subgenus in which the type species of the genus is located.
Included species: Hydnellum atrospinosum, H. suaveolens
Type species: Hydnellum suaveolens (Scop.) P. Karst.
Notes: This subgenus consists of the genus type Hydnellum suaveolens and our new species H. atrospinosum; they share the characteristics of dark blue context, decurrent and dark spines, clamped generative hyphae in the context and the spines trama and irregularly oblong, tuberculate basidiospores of similar size. Furthermore, both species occur in coniferous forests [27,34].
Hydnellum atrospinosum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, sp. nov. (Figure 3)

Figure 3.
Hydnellum atrospinosum. (a): Basidiocarps; (b,c): SEM of basidiospores; (d–f): Microscopic structures (drawn from IFP 018516); (d): Section of hymenophore trama with basidia; (e): Hyphae from pileus context; (f): Basidiospores. —Scale bars: (a) = 1 cm; (b) = 3 μm; (c) = 1 μm; (d,e) = 10 µm; (f) = 5 µm.
MycoBank MB839034
Etymology. Atrospinosum (Latin), refers to the dark violet spines.
Type: CHINA, Qinghai Province, Qilian County, Binggou Forest Park, ground in Picea forest, 8 September 2012, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 6520 (holotype IFP 018516).
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious or concrescent, leathery when fresh, becoming hard and light in weight upon drying; taste mild, odor fragrant when dry. Pileus irregularly ellipsoid to circular, later flabelliform or semicircular and applanate with age, up to 75 mm diam and 6–11 mm thick at center. Pileal surface light orange (5A4) to yellowish brown (5F6), concentrically zonate, scrobiculate when fresh, becoming glabrescent, rugose when dry; margin white (5A1) when fresh, brownish orange (5C6) when dry, even. Spine surface dark violet (15F4) when fresh, violet-gray (15F2) when dry; spines up to 2.5 mm long, base up to 0.4 mm diam, conical, 3–4 per mm, decurrent on stipe, without spines at pileus margin, brittle when dry. Context not duplex, up to 11 mm thick, light yellow (4A4), brownish gray (7F2) to dark violet (16F5) or dark blue (20E6), woody. Stipe lateral, up to 4 cm long and 3 cm diam, sometimes connate, leathery when fresh, woody upon drying, brown (6E6) to violet gray (15F2), glabrous, inside solid, cylindrical to flatted or broadened below with bulbous base when old. Hyphal structure: hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae with clamp-connections, CB+ in slightly thick-walled hyphae, IKI–; tissues olivaceous in KOH. Context: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, moderately branched, clamped, straight, regularly arranged, sometimes flexuous and collapsed, mostly 3–6 μm diam. Spines: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, moderately branched, more or less parallel along spines, clamped, straight, 2–3 μm diam. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, thin-walled, with four sterigmata (2.1–4.2 μm long), clamped at base, 17–45 × 3–6 μm; basidioles similar to basidia. Basidiospores irregular oblong or triangular, brown, thin-walled, tuberculate CB–, IKI–, (4–)4.1–5.1(–5.5) × (3–)3.1–3.9(–4) μm, Lm = 4.6 μm, Wm = 3.2 μm, Q = 1.34–1.44 (n = 60/2); tuberculi isolated, sometimes in groups of two or more, then bi- to trifurcate in shape, up to 1 μm long.
Additional specimens (paratypes) examined: CHINA, Qinghai Province, Qilian County, Binggou Forest Park, ground in Picea forest, 8 September 2012, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 6495 (IFP 018495, paratype); Yuan 6514 (IFP 018510, paratype).
Notes: Hydnellum atrospinosum and H. suaveolens have a close phylogenetic relationship with full support (100% in ML and 1.00 BPP). Morphologically, they both have single to gregarious basidiocarps with glabrous to rugose pileal surface, woody and dark blue context, an eccentric and terete stipe with a bulbous base, conical, decurrent and dark spines, clamped generative hyphae and irregularly oblong, tuberculate basidiospores of similar size. However, H. suaveolens differs from H. atrospinosum by longer spines (up to 6 mm vs. 2.5 mm in H. atrospinosum), context tissues turning light blue to green in KOH and presence of inflated hyphae in the context [27,34]. A special characteristic of H. atrospinosum is that the clamped generative hyphae are present in all parts of the basidiocarp; this trait can also be observed in H. cruentum, H. cyanopodium, H. geogenium and H. scleropodium. H. cruentum differs from H. atrospinosum by plushy to tomentose pileal surface, grayish blue and slightly longer spines (up to 3.5 mm vs. 2.5 mm in H. atrospinosum) and subglobose basidiospores [26,27,51]. H. cyanopodium and H. scleropodium obviously differs in blue spines [27,33,51]. H. geogenium differs in reflexed-multiplex and yellow basidiocarps, pale yellow to brown spines and subglobose basidiospores [1,27,34].
Hydnellum subg. Caesispinosum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, subgen. nov.
MycoBank MB841195
Etymology. Caesispinosum (Latin), refers to the blue spines.
Included species: Hydnellum cyanopodium, H. scleropodium
Type species: Hydnellum cyanopodium K.A. Harrison
Notes: The subgenus is composed of two American species, Hydnellum cyanopodium and H. scleropodium. Blue spines and context and fully clamped hyphae in all parts of basidiocarps are their distinctly common features. In addition, the two species both have rugose and pitted pileal surface and clamped basidia of similar size [33,34,51].
Hydnellum subg. Croceum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, subgen. nov.
MycoBank MB841196
Etymology. Croceum (Latin), refers to the orange basidiocarps.
Included species: Hydnellum aurantiacum, H. auratile, H. brunneorubrum, H. chrysinum, H. earlianum
Type species: Hydnellum aurantiacum (Batsch) P. Karst.
Notes: This subgenus includes five species, Hydnellum aurantiacum, H. auratile, H. brunneorubrum, H. chrysinum and H. earlianum. They often have orange basidiocarps, tomentose to matted pileal surface, yellow to orange spines and context, the monomitic hyphal system with uninflated and unclamped hyphae, clavate basidia with simple-septate at base and irregularly subglobose basidiospores [2,26,27,33,34,51].
Hydnellum brunneorubrum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, sp. nov. (Figure 4)
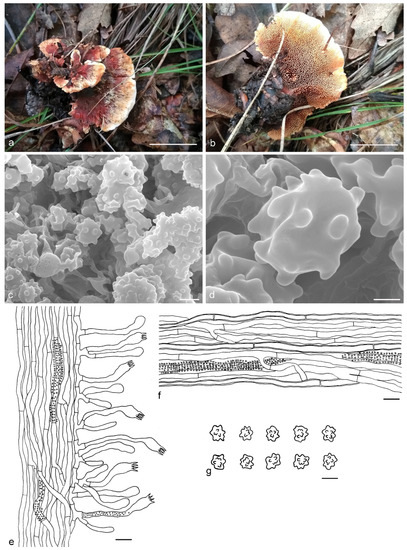
Figure 4.
Hydnellum brunneorubrum. (a,b): Basidiocarps; (c,d): SEM of basidiospores; (e–g): Microscopic structures (drawn from IFP 019384); (e): Section of hymenophore trama with basidia; (f): Hyphae from pileus context; (g): Basidiospores. —Scale bars: (a,b) = 1 cm; (c) = 3 μm; (d) = 1 μm; (e,f) = 10 µm; (g) = 5 µm.
MycoBank MB839036
Type: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Xinbin County, Gangshan Nature Reserve, on the ground in Fagaceous forest, 30 August 2018, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 12997 (holotype IFP 019384).
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious or multiple pilei overlapping and fused to form a compound cluster, soft and leathery when fresh, becoming woody and light in weight upon drying; taste mild, odor none when dry. Pileus applanate and ellipsoid to irregularly circular when young, later depressed or infundibuliform to flabelliform with age, up to 40 mm diam and 5–10 mm thick at center. Pileal surface brownish orange (6C8) to brownish red (10D8), azonate, pubscent to floccose when fresh, becoming matted or fibrillose to glabrous when dry; margin white (6A1) to light orange (6A5) when fresh, light orange (5A4) when dry, involute and wavy, sometimes lobed with age. Spine surface golden yellow (5B6) to light brown (7D8) when fresh, light brown (6D7) to dark brown (7F8) when dry; spines up to 4 mm long, base up to 0.3 mm diam, conical, 3–5 per mm, more or less decurrent on stipe, without spines at pileus margin, brittle when dry. Context not duplex, up to 5 mm thick, grayish orange (5B5), woody. Stipe central to lateral, up to 3 cm long and 1 cm diam, sometimes connate, leathery when fresh, woody upon drying, brownish orange (6C8) to light brown (6D7), tomentose, solid inner, cylindrical to flat or attenuate downwards with bulbous base when old. Hyphal structure: hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae with simple-septa, occasionally encrusted, CB+ in slightly thick-walled hyphae, IKI–; tissues olivaceous in KOH. Context: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, frequently branched, simple-septate, straight, regularly arranged, sometimes flexuous and collapsed, mostly 4–6 μm diam. Spines: generative hyphae hyaline, thin-walled, frequently branched, more or less parallel along spines, frequently simple-septate, straight, 2–5 μm diam. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, thin-walled, with four sterigmata (2.5–5 μm long), simple-septate at base, 12–50 × 3–7 μm; basidioles similar to basidia. Basidiospores irregularly ellipsoid to subglobose, brown, thin-walled, tuberculate, CB–, IKI–, (4–)4.1–5.1(–5.2) × (3.1–)3.2–4.6(–4.8) μm, Lm = 4.9 μm, Wm = 3.9 μm, Q = 1.23–1.26 (n = 60/2); tuberculi usually isolated, sometimes in groups of two or more, then bi- to trifurcate in shape, up to 0.8 μm long.
Additional specimens (paratypes) examined: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Xinbin County, Gangshan Nature Reserve, on the ground in mixed forest, 30 August 2018, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 12999 (IFP 019385, paratype); Yuan 13004 (IFP 019386, paratype); 2 September 2019, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14339 (IFP 019387, paratype); Yuan 14340 (IFP 019388, paratype); Yuan 14341 (IFP 019389, paratype); 12 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14562 (IFP 019390, paratype); 26 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14585 (IFP 019391, paratype); 12 September 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14796 (IFP 019392, paratype); Yuan 14798 (IFP 019393, paratype); Yuan 14799 (IFP 019394, paratype); Benxi County, Guanmenshan National Forest Park, on the ground in mixed forest, 29 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14642 (IFP 019395, paratype); Xinbin County, Qingsongling Forest Park, on the ground in mixed forest, 5 September 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14668 (IFP 019396, paratype); Yuan 14688 (IFP 019397, paratype).
Notes: The orange basidiocarps make Hydnellum brunneorubrum similar to H. aurantiacum, H. auratile, H. chrysinum and H. earlianum. H. aurantiacum differs from H. brunneorubrum in bigger pileus (up to 100 mm vs. 40 mm in H. brunneorubrum) with colliculose and wrinkled pileal surface, longer spines (up to 5 mm vs. up to 4 mm in H. brunneorubrum) and longer basidiospores (6–6.7 μm vs. 4.1–5.1 μm in H. brunneorubrum) [1]. H. auratile differs in squamulose, concentrically zoned and occasionally black stained pileal surface, duplex stipe context with black lines in the centre and longer basidiospores (4.9–5.8 μm vs. 4.1–5.1 μm in H. brunneorubrum); in addition, H. auratile usually grows in coniferous forests [1,26]. H. chrysinum is differentiated by having duplex, slightly zonate context, context tissue turning dark olive or blackish in KOH and slightly longer basidia sterigmata (up to 6 µm vs. up to 5 µm in H. brunneorubrum) [2,33,51]. H. earlianum is differentiated by a larger pileus (up to 90 mm vs. 40 mm in H. brunneorubrum), duplex context, dark brown or black context tissues in KOH and longer basidiospores (5–6 µm vs. 4.1–5.1 μm in H. brunneorubrum) [27,32,34].
Hydnellum subg. Inflatum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, subgen. nov.
MycoBank MB841197
Etymology. Inflatum (Latin), refers to the presence of inflated generative hyphae.
Included species: Hydnellum cristatum, H. granulosum, H. inflatum, H. mirabile, H. piperatum
Type species: Hydnellum mirabile (Fr.) P. Karst.
Notes: There are five species in the subgenus Inflatum, Hydnellum cristatum, H. granulosum, H. inflatum, H. mirabile and H. piperatum. The presence of inflated generative hyphae in the context of the pileus is an important feature they share. As well as, they often have yellow to brown and depressed pileus, cylindrical stipe and unclamped generative hyphae in the context and the spine trama [1,27,34].
Hydnellum granulosum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, sp. nov. (Figure 5)
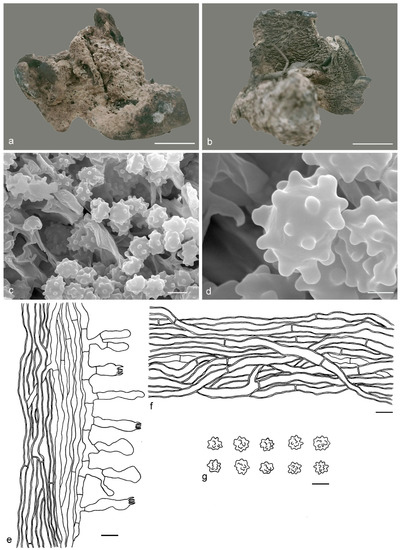
Figure 5.
Hydnellum granulosum. (a,b): Basidiocarps; (c,d): SEM of basidiospores; (e–g): Microscopic structures (drawn from IFP 019400); (e): Section of hymenophore trama with basidia; (f): Hyphae from pileus context; (g): Basidiospores. —Scale bars: (a,b) = 1 cm; (c) = 3 μm; (d) = 1 μm; (e,f) = 10 µm; (g) = 5 µm.
MycoBank MB839038
Etymology. Granulosum (Latin), refers to the granulose pileal surface when dry.
Type: CHINA, Sichuan Province, Guangyuan County, Tianzhaoshan National Forest Park, on the ground in Acer and Cryptomeria mixed forest, 13 August 2017, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 12213b (holotype IFP 019400).
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious or two to three pilei fused to form a complex pileus, soft and leathery when fresh, becoming hard and light in weight upon drying; taste acrid, odor fragrant when dry. Pileus aplanate, irregularly ellipsoid when young, later irregularly flabelliform with age, up to 50 mm diam and 5–10 mm thick at center. Pileal surface light yellow (4A4), light brown to grayish brown (9F3), azonate, granulose when dry; margin yellowish white (4A2), involute and wavy, sometimes lobed. Spine surface grayish orange (5B4) to dark brown (8F7) when dry; spines up to 2 mm long, base up to 0.3 mm diam, conical, 3–6 per mm, more or less decurrent on stipe, without spines at pileus margin, brittle when dry. Context not duplex, up to 9 mm thick, grayish orange (5B4), woody. Stipe central to lateral, up to 4 cm long and 3 cm diam, sometimes connate, hard upon drying, golden brown (5D6) to brown (6E6), rugose, solid inner, terete or attenuate or broadening downwards with bulbous base when old. Hyphal structure: hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae with simple-septa, CB+ in slightly thick-walled hyphae, IKI–; tissues olivaceous in KOH. Context: generative hyphae hyaline, mostly slightly thick-walled, rarely thin-walled, occasionally branched, simple-septate, occasionally inflated, interwoven, mostly 4–7 μm diam. Spines: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, moderately branched, more or less parallel along spines, frequently simple-septate, straight, 3–4 μm diam. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, thin-walled, with four sterigmata (3–5 μm long), simple-septate at base, 15–30 × 5–9 μm; basidioles similar to basidia. Basidiospores irregularly ellipsoid to globose, brown, thin-walled, tuberculate, CB–, IKI–, (4–)4.1–5.1(–5.3) × (3.2–)3.4–4.7(–4.9) μm, Lm = 4.6 μm, Wm = 4.1 μm, Q = 1.12–1.13 (n = 60/2); tuberculi usually isolated, sometimes in groups of two or more, then bi- to trifurcate in shape, up to 1.2 μm long.
Additional specimens (paratypes) examined: CHINA, Sichuan Province, Guangyuan County, Tianzhaoshan National Forest Park, on the ground in Acer and Cryptomeria mixed forest, 12 August 2017, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 12213a (IFP 019401, paratype); 13 August 2017, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 12213c (IFP 019402, paratype).
Notes: Hydnellum granulosum has a close phylogenetic relationship with H. piperatum. In morphology, H. piperatum resembles H. granulosum in having single to gregarious or concrescent basidiocarps, with lobed pileal margin from fused pilei or indeterminate growth, a single to fused, central to eccentric and terete to attenuate downwards stipe, context tissue turning olivaceous in KOH, absence of clamp-connections and the presence of inflated hyphae. However, H. piperatum is distinguishable from H. granulosum by having a comparatively broader pileus (up to 150 mm vs. 50 mm in H. granulosum) with a scaly or squamulose and zonate pileal surface and strongly decurrent and longer spines (up to 5 mm vs. 2 mm in H. granulosum) [27]. The presence of inflated generative hyphae is a shared feature in H. granulosum and H. mirabile. They also have simple or concrescent basidiocarps with light yellow to brown pilei, and hard and cylindrical stipes. However, H. mirabile differs from H. granulosum by the plano-convex to depressed and larger pileus (up to 90 mm vs. 50 mm in H. granulosum), yellowish to purplish brown and longer spines (up to 5 mm vs. 2 mm in H. granulosum), duplex and pallid to pale brownish context and longer basidiospores (5.6–5.8 µm vs. 4.1–5.1 μm in H. granulosum) [1].
Hydnellum inflatum Y.H. Mu, X.H. Wang & H.S. Yuan, sp. nov. (Figure 6)
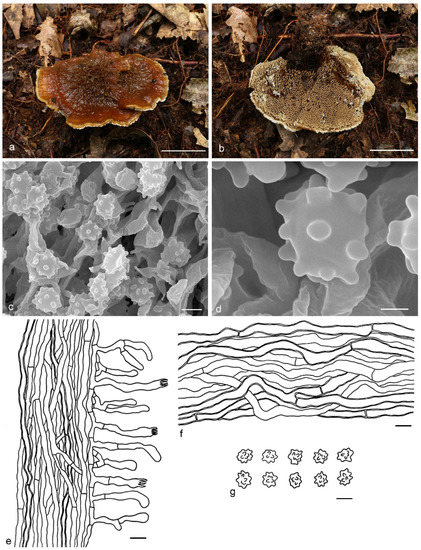
Figure 6.
Hydnellum inflatum. (a,b): Basidiocarps; (c,d): SEM of basidiospores; (e–g): Microscopic structures (drawn from IFP 019403); (e): Section of hymenophore trama with basidia; (f): Hyphae from pileus context; (g): Basidiospores. —Scale bars: (a,b) = 1 cm; (c) = 3 μm; (d) = 1 μm; (e,f) = 10 µm; (g) = 5 µm.
MycoBank MB839040
Etymology. Inflatum (Latin), refers to the mostly inflated generative hyphae in the context of the pileus.
Type: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Maguan County, Dalishu Township, on the ground in Fagaceous forest, 14 October 2017, S. F. Shi, Shi 506 (holotype IFP 019403).
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious, soft and leathery when fresh, becoming corky and light in weight upon drying; taste acrid, odor fragrant when dry. Pileus depressed to aplanate and irregularly circular when young, later flabelliform with age, up to 75 mm diam and 3–8 mm thick at center. Pileal surface grayish orange (5B5) to brown (7E7), azonate, fibrous to colliculose when fresh, becoming scrobiculate when dry; margin light yellow (4A4) when fresh, orange-white (5A2) when dry, involute and wavy, often lobed with age. Spine surface white (5A1) to golden brown (5D7) when fresh, yellowish brown (5D5) to dark brown (7F8) when dry; spines up to 4 mm long, base up to 0.25 mm diam, conical, 4–5 per mm, strongly decurrent on stipe, without spines at pileus margin, brittle when dry. Context duplex, upper layer grayish yellow (4B5), loose and soft, up to 2 mm thick; lower layer pale yellow (4A3), woody, up to 3 mm thick; a dark line present between upper and lower cortical layers. Stipe central to lateral, up to 5 cm long and 2 cm diam, occasionally connate, fleshy when fresh, woody upon drying, light brown (6D7), smooth to rugose, inside solid, context with a dark line present at centre, cylindrical or attenuate downwards with bulbous base when old. Hyphal structure: hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae with simple-septa, CB+ in slightly thick-walled hyphae, IKI–; tissues slightly olivaceous in KOH. Context: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, occasionally branched, simple-septate, mostly inflated, interwoven, mostly 4–8 μm diam. Spines: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, moderately branched, more or less parallel along spines, frequently simple-septate, straight, 2–5 μm diam. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, thin-walled, with four sterigmata (3–5 μm long), simple-septate at base, 19–33 × 4–6 μm; basidioles similar to basidia. Basidiospores irregularly ellipsoid to globose, brown, thin-walled, tuberculate, CB–, IKI–, (4–)4.2–5(–5.1) × (3.2–)3.8–4.3(–5) μm, Lm = 4.8 μm, Wm = 4 μm, Q = 1.18–1.2 (n = 60/2); tuberculi usually isolated, sometimes in groups of two or more, then bi- to trifurcate in shape, up to 1.2 μm long.
Additional specimens (paratypes) examined: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Maguan County, Mabai Town, Caiyuanzi Village, on the ground, 5 August 2017, J. Wang, Wang 80 (IFP 019404, paratype); Wang 82 (IFP 019405, paratype); on the way from Dalishu Township to Damagu Village, on the ground in Fagaceous forest, 6 August 2017, S. F. Shi, Shi 150 (IFP 019406, paratype); Shi 160 (IFP 019407, paratype).
Notes: Hydnellum inflatum is characterized by the presence of inflated generative hyphae, which makes it similar to H. cristatum, H. granulosum, H. mirabile and H. piperatum. This is an important feature that distinguishes from other species. However, H. cristatum can be differentiated from H. inflatum by the larger pileus (up to 100 mm vs. 75 mm in H. inflatum) with tomentose to matted pileal surface, longer spines (up to 5 mm vs. 4 mm in H. inflatum), brown context tissues in KOH, bigger basidia (34–46 × 8–9 μm vs. 19–33 × 4–6 μm in H. inflatum) and basidiospores (5–6 × 4–5 μm vs. 4.2–5 × 3.8–4.3 μm in H. inflatum) [27,34]. H. granulosum differs in granulose pileal surface, not duplex context, mostly slightly thick-walled hyphae in the context and shorter spines (up to 2 mm vs. up to 4 mm in H. inflatum). H. mirabile differs in ochraceous yellow and olive brown pileus, yellowish to purplish brown spines and longer spores (5.6–5.8 μm vs. 4.2–5 μm in H. inflatum) [1]. H. piperatum differs in umbilicate and greatly pileus (up to 100 mm vs. 75 mm in H. inflatum), red haired to sunburn slightly longer spines (up to 5 mm vs. up to 4 mm in H. inflatum) and inflated to cylindrical hyphae in the spines [27].
Hydnellum subg. Rhizomorphum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, subgen. nov.
MycoBank MB841198
Etymology. Rhizomorphum (Latin), refers to the rhizomorphs-like stipe.
Included species: Hydnellum gracilipes, Hydnellum sp 1
Type species: Hydnellum gracilipes (P. Karst.) P. Karst.
Notes: Hydnellum gracilipes and our notable specimen Hydnellum sp 1 comprise the subgenus Rhizomorphum. Rhizomorph-like stipe are their typical common characteristics. Besides, both species have the monomitic hyphal system with simple-septate generative hyphae [35].
Hydnellum sp 1
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious or coalescent. Pileus flabelliform to irregularly circular. Pileal surface deep red (10C8) to violet-brown (10F8) and felted. Spines white (10A1) to brownish red (10D7) and more or less decurrent, up to 1.5 mm long. Rhizomorphs stipe-like. Hyphal system monomitic, generative hyphae simple-septa. Basidia clavate, with four sterigmata. Basidiospores irregularly subglobose to globose, tuberculate, (4–)4.1–4.9(–5) × (3.1–)3.2–4(–4.1) μm.
Specimen examined: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Maguan County, on the way from Dalishu Township to Damagu Village, on the ground of angiosperm forest, 6 August 2017, S. F. Shi, Shi 164 (IFP 019436).
Hydnellum subg. Scabrosum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, subgen. nov.
MycoBank MB841199
Etymology. Scabrosum (Latin), refers to the pileal surface with scabrosity.
Included species: Hydnellum amygdaliolens, H. coactum, H. fagiscabrosum, H. fennicum, H. grosselepidotum, H. illudens, H. lepidum, H. lidongensis, H. nemorosum, H. scabrosellum, H. scabrosum, H. underwoodii
Type species: Hydnellum scabrosum (Fr.) E. Larss., K.H. Larss. & Kõljalg
Notes: There are twelve species, namely Hydnellum amygdaliolens, H. coactum, H. fagiscabrosum, H. fennicum, H. grosselepidotum, H. illudens, H. lepidum, H. lidongensis, H. nemorosum, H. scabrosellum, H. scabrosum and H. underwoodii in this subgenus characterised by planar to depressed and brown pileus, azonate pileal surface with scabrosity, variously-brown spines, not duplex and yellow to orange context, inflated and unclamped generative hyphae and irregularly ellipsoid to globose basidiospore [1,2,26,27,32,33,34,38,51,52,53,54].
Hydnellum subg. Spongiosum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, subgen. nov.
MycoBank MB841200
Etymology. Spongiosum (Latin), refers to the spongy pileal surface.
Included species: Hydnellum ferrugineum, H. pineticola, H. spongiosipes, Hydnellum sp 2
Type species: Hydnellum ferrugineum (Fr.) P. Karst.
Notes: This subgenus includes Hydnellum ferrugineum, H. pineticola, H. spongiosipes and Hydnellum sp 2; they all have planoconvex to depressed and brown pileus with spongy pileal surface, purplish brown spines, the monomitic hyphal system with simple-septate generative hyphae and irregularly subglobose basidiospores [1,2,27,34].
Hydnellum spongiosipes (Peck) Pouzar, Česká Mykol. 14(2): 130 (1960)
Hydnum spongiosipes Peck, Ann. Rep. Reg. N.Y. St. Mus. 50: 111 (1898) (1897)
Basidiocarps single to gregarious. Pileus flabelliform, applanate to subdepressed. Pileal surface pale orange (6A3) to dark brown (6F7), velutinous to very spongy, tomentose to fibrillose. Spines pale orange (6A3) to dark brown (6F7), subdecurrent to decurrent, up to 6 mm long. Stipe central to subeccentric, terete, thick and strong. Hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae simple-septate. Basidia clavate, with four sterigmata. Basidiospores irregularly subglobose, tuberculate, (5–)5.1–6.1(–6.2) × (4.3–)4.5–5.3(–5.8) μm.
Specimen examined: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Kuandian County, Baishilazi National Nature Reserve, on the ground of Quercus forest, 8 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14517 (IFP 019435).
Notes: The studied sample clustered with Hydnellum spongiosipes (REB-107 and REB-52) in the multi-gene phylogenetic tree with strong support (90% in ML and 1.00 BPP) (Figure 1). The samples REB-107 and REB-52 both show 0.99 similarity to Yuan 14517 in ITS region. Besides this, morphological analyses also confirmed the new record, which is described in detail by Maas Geesteranus (1975) and Baird (2013). This species was recorded to occur widely in the United States and European countries and usually was found under hardwood tree [1,2,27,34].
Hydnellum sp 2
Basidiocarps annual, coalescent. Pileus compound, multiple pilei fused. Pileal surface violet-brown (10E6) and spongy-tomentose. Spines white (10A1) to violet-brown (10E6) and strongly decurrent, up to 2.5 mm long. Stipe short and connate. Hyphal system monomitic, generative hyphae simple-septa. Basidia clavate, with four sterigmata. Basidiospores irregularly subglobose, tuberculate, (3.1–)4–4.3(–4.5) × (3–)3.1–4(–4.1) μm.
Specimen examined: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Nanjian County, Lingbaoshan National Forest Park, on the ground of angiosperm forest, 19 September 2019, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14387 (IFP 019437).
Hydnellum subg. Subindufibulatum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, subgen. nov.
MycoBank MB841201
Etymology. Subindufibulatum (Latin), refers to the occasionally clamped hyphae in the context of the pileus.
Included species: Hydnellum caeruleum, H. ferrugipes, H. fibulatum
Type species: Hydnellum caeruleum (Hornem.) P. Karst.
Notes: Hydnellum caeruleum, H. ferrugipes and H. fibulatum make up the subgenus Subindufibulatum and occasional presence of clamped hyphae in the context of the pileus is the dominating trait that distinguishes them from other species. Furthermore, they have dark brown and fibrillose to colliculose pileal surface, orange stipe, context tissues turning olivaceous in KOH and the absence of clamp-connections in the spine trama [2,26,27].
Hydnellum caeruleum (Hornem.) P. Karst., [as ‘coeruleum’], Meddn Soc. Fauna Flora Fenn. 5: 41 (1879)
Hydnum caeruleum Hornem., Fl. Danic. 8(23): 7, tab. 1374 (1808)
Basidiocarps single to gregarious or concrescent. Pileus convex to plane. Pileal surface pastel yellow (4A4) to dark blonde (5D4), tomentose and colliculose. Spines decurrent, up to 6 mm long, orange-white (5A2) to dark brown (6F8). Stipe central and terete. Hyphal system monomitic; most of the generative hyphae with simple-septa, rarely with clamps. Basidia clavate, with four sterigmata. Basidiospores irregularly subglobose, tuberculate, (4.9–)5–6(–6.1) × (4–)4.1–4.9(–5) μm.
Specimen examined: CHINA, Xinjiang Autonomous Region, Huocheng County, Guozigou Forest Park, on the ground in Picea forest, 18 August 2004, Y. L. Wei, Wei 1474a (IFP 019432).
Notes: The phylogenetic analyses showed that the studied sample matched with Hydnellum caeruleum (EBendiksen584-11) with full support (100% in ML and 1.00 BPP) (Figure 1). ITS sequence BLAST also revealed it is 100% identical to H. caeruleum. Besides, our collection shares identical characters with H. caeruleum described by Maas Geesteranus [26] in morphology. This is the first report of this species from China.
Hydnellum fibulatum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, sp. nov. (Figure 7)
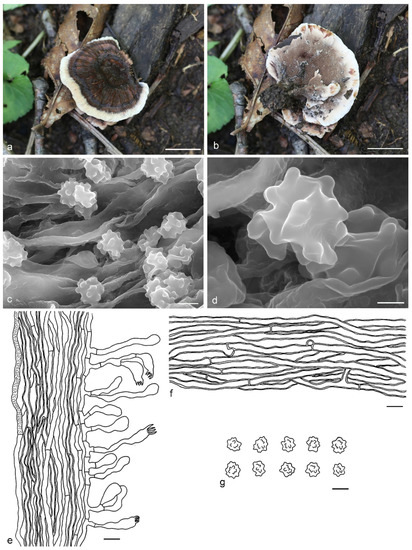
Figure 7.
Hydnellum fibulatum. (a,b): Basidiocarps; (c,d): SEM of basidiospores; (e–g): Microscopic structures (drawn from IFP 019398); (e): Section of hymenophore trama with basidia; (f): Hyphae from pileus context; (g): Basidiospores. —Scale bars: (a,b) = 2 cm; (c) = 3 μm; (d) = 1 μm; (e,f) = 10 µm; (g) = 5 µm.
MycoBank MB839037
Etymology. Fibulatum (Latin), refers to the generative hyphae with occasional clamp-connections.
Type: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Benxi County, Guanmenshan National Forest Park, on the ground in Quercus forest, 29 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14656 (holotype IFP 019398).
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious, soft and leathery when fresh, becoming woody and light in weight upon drying; taste mild, odor none when dry. Pileus applanate, circular when young, later flabelliform with age, up to 45 mm diam and 3–7 mm thick at center. Pileal surface light brown (7D7) to dark brown (8F4), obscurely zonate, pubescent when fresh, becoming fibrillose, rugose when dry; margin white (6A1) when fresh, brown (6E6) when dry, incurved, sometimes lobed. Spine surface pinkish white (7A2) to brown (7E7) when fresh, orange-white (5A2) to brown (6E6) when dry; spines up to 1.5 mm long, base up to 0.2 mm diam, conical, 3–4 per mm, more or less decurrent on stipe, without spines at pileus margin, brittle when dry. Context not duplex, up to 5 mm thick, light brown (6D4) to dark brown (6F4), woody. Stipe central to lateral, up to 3.5 cm long and 1 cm diam, single, leathery when fresh, woody upon drying, light orange (5A5) to brown (6E7), pubescent, solid inner, cylindrical or attenuate downwards with bulbous base when old. Hyphal structure: hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae with mostly simple-septa, occasionally clamped, CB+ in slightly thick-walled hyphae, IKI–; tissues olivaceous in KOH. Context: generative hyphae hyaline, slightly thick-walled, occasionally branched, simple-septate, occasionally clamped, straight, regularly arranged, sometimes flexuous and collapsed, mostly 3–5 μm diam. Spines: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, moderately branched, more or less parallel along spines, frequently simple-septate, straight, 2–4 μm diam. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, thin-walled, with four sterigmata (2–5 μm long), simple-septate at base, 15–47 × 5–9 μm; basidioles similar to basidia. Basidiospores irregularly ellipsoid to globose, brown, thin-walled, tuberculate, CB–, IKI–, (4.2–)4.4–5.8(–6) × (4–)4.1–4.9(–5.1) μm, Lm = 5.2 μm, Wm = 4.3 μm, Q = 1.12–1.21 (n = 60/2); tuberculi usually isolated, sometimes in groups of two or more, then bi- to trifurcate in shape, up to 1 μm long.
Additional specimen (paratype) examined: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Benxi County, Guanmenshan National Forest Park, on the ground in Quercus forest, 29 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14646 (IFP 019399, paratype).
Notes: Hydnellum caeruleum and H. ferrugipes have an adjacent phylogenetic relationship with H. fibulatum according to the phylogenetic tree (Figure 1). H. caeruleum and H. fibulatum have similar morphological characteristics, such as a flat and velutinous pileus when immature, white pileal margin when fresh, central, terete and tomentose stipe, olivaceous context tissue in KOH, presence of occasional clamp-connections in the context and simple-septate hyphae in the spines. However, H. caeruleum can be distinguished by having a larger pileus (up to 80 mm vs. 45 mm in H. fibulatum), rough or colliculose pileal surface when mature, duplex and zonate context [2,26]. H. ferrugipes resembles H. fibulatum in having a white pileal margin when fresh, tomentose and orange to brown stipe, orange-white to brown spines when dry, regularly arranged and occasionally clamped hyphae in the context, unclamped hyphae in the spines and basidia sterigmata with similar size. However, H. ferrugipes differs from H. fibulatum in the infundibuliform pileus with pitted to subnodulose or subcolliculose pileal surface, blue-gray or grayish orange context, considerably longer spines (up to 6 mm vs. 1.5 mm in H. fibulatum) and wider basidiospores (5–6 μm vs. 4.1–4.9 μm in H. fibulatum) [27,34].
Hydnellumsubg.Violaceum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, subgen. nov.
MycoBank MB841202
Etymology. Violaceum (Latin), refers to the violaceous basidiocarps.
Included species: Hydnellum fuligineoviolaceum, H. fuscoindicum, H. glaucopus, H. joeides, H. roseoviolaceum
Type species: Hydnellum fuligineoviolaceum (Kalchbr.) E. Larss., K.H. Larss. & Kõljalg
Notes: Five species, Hydnellum fuligineoviolaceum, H. fuscoindicum, H. glaucopus, H. joeides and H. roseoviolaceum, comprise the subgenus Violaceum. They share the following features: violaceous basidiocarps, pileal surface with appressed scales, purplish context, the presence of inflated generative hyphae and the simple-septate haphae in all tissue [1,26,27,33,53].
Hydnellumsubg.Zonatum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, subgen. nov.
MycoBank MB841203
Etymology. Zonatum (Latin), refers to the concentrically zonate pileal surface.
Included species: Hydnellum atrorubrum, H. bomiense, H. concrescens, H. dianthifolium, H. parvum, H. rubidofuscum, H. scrobiculatum, H. squamulosum, H. subsuccosum, H. sulcatum, H. yunnanense, Hydnellum sp 3, Hydnellum sp 4, Hydnellum sp 5
Type species: Hydnellum scrobiculatum (Fr.) P. Karst.
Notes: The subgenus Zonatum contains fourteen taxa, Hydnellum atrorubrum, H. bomiense, H. concrescens, H. dianthifolium, H. parvum, H. rubidofuscum, H. scrobiculatum, H. squamulosum, H. subsuccosum, H. sulcatum, H. yunnanense, Hydnellum sp 3, Hydnellum sp 4 and Hydnellum sp 5. The concentrically zonate pileal surface is their most prominently mutual peculiarity. Additionally, the absence of clamp-connections in the context of the pileus and the spine trama is another important common feature [1,2,26,27,34,36].
Hydnellum atrorubrum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, sp. nov. (Figure 8)

Figure 8.
Hydnellum atrorubrum. (a): Basidiocarps; (b,c): SEM of basidiospores; (d–f): Microscopic structures (drawn from IFP 019377); (d): Section of hymenophore trama with basidia; (e): Hyphae from pileus context; (f): Basidiospores. —Scale bars: (a) = 2.5 cm; (b) = 3 μm; (c) = 1 μm; (d,e) = 10 µm; (f) = 5 µm.
MycoBank MB839032
Etymology. Atrorubrum (Latin), refers to the dark ruby red pileal surface.
Type: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Yulong County, on the ground in Fagaceous forest, 23 July 2018, Y. L. Wei, Wei 8261 (holotype IFP 019377).
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious or several pilei fused to form a compound pileus, soft and leathery when fresh, becoming woody and light in weight upon drying; taste slightly bitter, odor slightly fragrant when dry. Pileus applanate and flabelliform to irregularly circular when young, later depressed or subinfundibuliform to rounded with age, up to 48 mm diam and 3–8 mm thick at center. Pileal surface light brown (7D7) to dark ruby (12F8), usually concentrically zoned, flocculose when fresh, becoming fibrillose to glabrescent when dry; margin white (7A1) when fresh, brown (7E5) when dry, even to slightly irregular, occasionally wavy or lobed. Spine surface white (6A1) to dark brown (6F6) when fresh, grayish orange (5B4) to brown (6E8) when dry; spines up to 3.5 mm long, base up to 0.4 mm diam, conical, 3–5 per mm, decurrent to strongly decurrent on stipe, without spines at pileus margin, brittle when dry. Context not duplex, up to 6 mm thick, brown (6E6), corky. Stipe central, up to 3.5 cm long and 1.5 cm diam, sometimes connate, leathery when fresh, corky upon drying, pinkish (8A2) to reddish brown (8E6), velutinous, inside solid, cylindrical or attenuate downwards with bulbous base when old. Hyphal structure: hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae with simple-septa, CB+ in slightly thick-walled hyphae, IKI–; tissues olivaceous in KOH. Context: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, occasionally branched, simple-septate, straight, regularly arranged, sometimes flexuous and collapsed, mostly 4–6 μm diam. Spines: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, moderately branched, more or less parallel along spines, frequently simple-septate, straight, 2–4 μm diam. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, thin-walled, with four sterigmata (4–6 μm long), simple-septate at base, 20–48 × 5–8 μm; basidioles similar to basidia. Basidiospores irregular ellipsoid, brown, thin-walled, tuberculate, CB–, IKI–, (4.1–)4.5–6(–6.1) × (3.2–)3.9–5.1(–6) μm, Lm = 5 μm, Wm = 4.4 μm, Q = 1.14–1.21 (n = 60/2); tuberculi usually isolated, sometimes in groups of two or more, then bi- to trifurcate in shape, up to 1.1 μm long.
Additional specimens (paratypes) examined: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Yulong County, on the ground in Fagaceous forest, Y. L. Wei, 23 July 2018, Wei 8290 (IFP 019378, paratype); Wei 8312 (IFP 019379, paratype); Wei 8315 (IFP 019380, paratype); Wei 8319 (IFP 019381, paratype).
Notes: Phylogenetically, Hydnellum atrorubrum has a close relationship with H. subsuccosum. Morphologically, H. subsuccosum is similar to H. atrorubrum in having gregarious to confluent basidiocarps with zonate pileal surface and lobed pileal margin, brown context, cylindrical or attenuate downwards stipe, decurrent and similar length spines, the monomitic hyphal system with uninflated and simple-septate generative hyphae, basidia of similar shape and width, as well as basidiospores of similar length. However, H. subsuccosum can be differentiated by scabrous to nodulose and orange-white to camel pileal surface, black spines and presence of subglobose basidiospores [27]. H. auratile is comparable to H. atrorubrum in having similar size, depressed to infundibuliform or flabelliform and concentrically zoned pileus with undulate margin, tomentose and reddish-brown stipe, non-duplex context, thin- to slightly thick-walled and unclamped generative hyphae. However, H. auratile differs from H. atrorubrum by orange or orange-brown to dark red-brown pileus with entire or deeply split margin and tawny to purplish brown spines [26].
Hydnellum bomiense Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, sp. nov. (Figure 9)
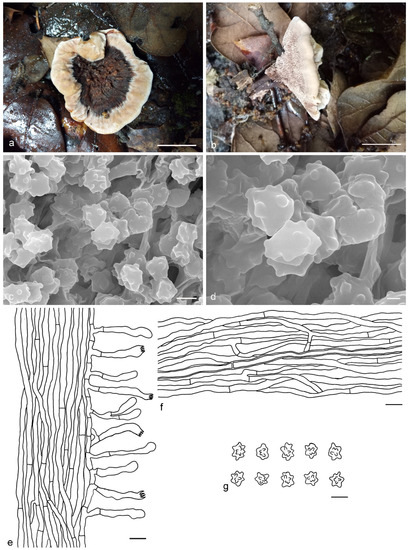
Figure 9.
Hydnellum bomiense. (a,b): Basidiocarps; (c,d): SEM of basidiospores; (e–g): Microscopic structures (drawn from IFP 019382); (e): Section of hymenophore trama with basidia; (f): Hyphae from pileus context; (g): Basidiospores. —Scale bars: (a,b) = 1 cm; (c) = 3 μm; (d) = 1 μm; (e,f) = 10 µm; (g) = 5 µm.
MycoBank MB839035
Etymology. Bomiense, refers to the Bomi County, where the specimens were collected.
Type: CHINA, Xizang Autonomous Region, Bomi County, on the ground in Fagaceous forest, 19 July 2019, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 13767 (holotype IFP 019382).
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious, soft and leathery when fresh, becoming woody and light in weight upon drying; taste acrid, odor slightly fragrant when dry. Pileus infundibuliform when young, later applanate and irregularly circular with age, up to 26 mm diam and 2–4 mm thick at center. Pileal surface grayish yellow (4B4), brown (7E7) to dark brown (7F8), obscurely concentrically zonate, tomentose, scrupose when fresh, becoming fibrillose or glabrous when dry; margin white (5A1) when fresh, grayish orange (5B4) when dry, involute and wavy, sometimes lobed or rimose with age. Spine surface white (6A1) to brown (6E7) when fresh, light brown (6D6) to dark brown (7F8) when dry; spines up to 1.1 mm long, base up to 0.2 mm diam, conical, 4–6 per mm, more or less decurrent on stipe, without spines at pileus margin, brittle when dry. Context not duplex, up to 4 mm thick, brown (6E5), woody. Stipe central to lateral, up to 2 cm long and 0.5 cm diam, woody upon drying, grayish orange (5B5) to dark brown (7F7), rugose, solid inner, terete or attenuate downwards with bulbous base when old. Hyphal structure: hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae with simple-septa, CB+ in slightly thick-walled hyphae, IKI–; tissues olivaceous in KOH. Context: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, frequently branched, simple-septate, straight, regularly arranged, sometimes flexuous and collapsed, mostly 4–6 μm diam. Spines: generative hyphae hyaline, thin-walled, occasionally branched, more or less parallel along spines, frequently simple-septate, straight, 2–4 μm diam. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, thin-walled, with four sterigmata (1.5–3 μm long), simple-septate at base, 15–42 × 4–7 μm; basidioles similar to basidia. Basidiospores irregularly ellipsoid to subglobose, brown, thin-walled, tuberculate, CB–, IKI–, (4–)4.1–5.1(–5.2) × (3–)3.3–4.5(–4.8) μm, Lm = 4.7 μm, Wm = 4 μm, Q = 1.18–1.21 (n = 60/2); tuberculi usually isolated, sometimes in groups of two or more, then bi- to trifurcate in shape, up to 1 μm long.
Additional specimen (paratype) examined: CHINA, Xizang Autonomous Region, Bomi County, on the ground with moss in Fagaceous forest, 19 July 2019, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 13759 (IFP 019383, paratype).
Notes: This species clustered with two samples from Estonia and Costa Rica, and formed an independent clade (Figure S1). Hydnellum bomiense and H. dianthifolium are closely related based on nucleotide sequence analyses and possess common morphological features: separate to coalescing or grouped basidiocarps with decurrent spines, cylindrical stipe, absence of clamp-connections and brown, tuberculate and irregularly ellipsoid to subglobose basidiospores of similar size with isolated to bifurcate tuberculi. However, H. dianthifolium differs from H. bomiense by having slender, turbinate and coralloid basidiocarps that split radially to form erect, coralloid or flower-shaped lobed pilei, not perceptibly zoned context and thick-walled and encrusted context hyphae [36]. Meanwhile, H. concrescens and H. scrobiculatum are also in a big clade with H. bomiense in Figure 1, and concentrically zonate pileal surface is their common characteristic. However, H. concrescens differs by quite larger pileus (up to 120 mm vs. up to 26 mm in H. bomiense), duplex context and longer basidia sterigmata (3–4 µm vs. 1.5–3 µm in H. bomiense) [27,34]. H. scrobiculatum differs in subcolliculose to scrobiculate pileal surface and longer spines (up to 3 mm vs. 1.1 mm in H. bomiense) [27,34].
Hydnellum rubidofuscum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, sp. nov. (Figure 10)

Figure 10.
Hydnellum rubidofuscum. (a): Basidiocarps; (b,c): SEM of basidiospores; (d–f): Microscopic structures (drawn from IFP 019408); (d): Section of hymenophore trama with basidia; (e): Hyphae from pileus context; (f): Basidiospores. —Scale bars: (a) = 1 cm; (b) = 3 μm; (c) = 1 μm; (d,e) = 10 µm; (f) = 5 µm.
MycoBank MB839041
Etymology. Rubidofuscum (Latin), refers to the reddish brown pileal surface.
Type: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Xinbin County, Gangshan Nature Reserve, on the ground in Quercus forest, 12 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14561 (holotype IFP 019408).
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious or multiple pilei overlapping and fused to form a compound cluster, soft and leathery when fresh, becoming woody and light in weight upon drying; taste mild, odor slightly fragrant when dry. Pileus applanate to infundibuliform when young, later depressed to flabelliform or irregularly circular with age, up to 70 mm diam and 4–10 mm thick at center. Pileal surface reddish brown (8E8), obscurely concentrically zonate, glabrous to scrupose when fresh, becoming fibrillose to virgate when dry; margin white (6A1) to orange-white (6A2) when fresh, brownish orange (6C4) when dry, even, sometimes lobed with age. Spine surface grayish brown (8D3) to reddish brown (8E7) when fresh, brown (6E6) to dark brown (6F7) when dry; spines up to 3 mm long, base up to 0.2 mm diam, conical, 4–6 per mm, strongly decurrent on stipe, without spines at pileus margin, brittle when dry. Context not duplex, up to 10 mm thick, brown (6E6), woody. Stipe central to lateral, up to 3.5 cm long and 2 cm diam, sometimes connate, leathery when fresh, woody upon drying, light brown (7D6) to brown (7E6), pubescent, solid inner, cylindrical to flat or attenuate downwards with bulbous base when old. Hyphal structure: hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae with simple-septa, CB+ in slightly thick-walled hyphae, IKI–; tissues olivaceous in KOH. Context: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, occasionally branched, simple-septate, straight, regularly arranged, sometimes flexuous and collapsed, mostly 3–6 μm diam. Spines: generative hyphae hyaline, thin-walled, occasionally branched, more or less parallel along spines, frequently simple-septate, straight, 2–3 μm diam. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, thin-walled, with four sterigmata (1–4 μm long), simple-septate at base, 14–37 × 4–6 μm; basidioles similar to basidia. Basidiospores irregularly ellipsoid to subglobose, brown, thin-walled, tuberculate, CB–, IKI–, (4–)4.1–5(–5.1) × (3.8–)3.9–4.6(–4.8) μm, Lm = 4.6 μm, Wm = 4.1 μm, Q = 1.11–1.12 (n = 60/2); tuberculi usually isolated, sometimes in groups of two or more, then bi- to trifurcate in shape, up to 1 μm long.
Additional specimens (paratypes) examined: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Xinbin County, Gangshan Nature Reserve, on the ground in Quercus forest, 12 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14559 (IFP 019409, paratype); Yuan 14560 (IFP 019410, paratype); Yuan 14563 (IFP 019411, paratype); 26 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14586 (IFP 019412, paratype); Yuan 14587 (IFP 019413, paratype); 12 September 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14792 (IFP 019414, paratype); Yuan 14794 (IFP 019415, paratype); Yuan 14800 (IFP 019416, paratype); Benxi County, Guanmenshan National Forest Park, on the ground in Quercus forest, 29 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14654 (IFP 019417, paratype).
Notes: Phylogenetically, Hydnellum rubidofuscum is closely related to H. bomiense and H. dianthifolium (Figure 1). Morphologically, infundibuliform pileus when young, concentrically zonate pileal surface and irregularly ellipsoid to subglobose basidiospores are their common features. However, H. bomiense can be distinguished by smaller pileus (up to 26 mm vs. up to 70 mm in H. rubidofuscum), yellow to dark brown pileal surface and shorter spines (up to 1.1 mm vs. up to 3 mm in H. rubidofuscum). H. dianthifolium differs by subpubescent pileal surface, reddish-brown to vinaceous-brown context, thick-walled and rarely branched hyphae in the context and context tissue turning blue-green in KOH [36]. The reddish brown pileal surface is very similar to that of H. scrobiculatum. Furthermore, H. scrobiculatum also has a single to gregarious or concrescent basidiocarp with applanate to depressed or infundibuliform pileus, obscurely concentrically zonate pileal surface, simple or connate, central to eccentric and velutinous stipe, reddish brown and decurrent spines and the monomitic hyphal system. However, the major differences are that H. scrobiculatum has a fungoid or no odor, a scrobiculate and rugulose pileal surface, duplex and zonate context and longer basidiospores (5.4–6.4 μm vs. 4.1–5 μm in H. rubidofuscum) [26,27,34].
Hydnellum squamulosum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, sp. nov. (Figure 11)

Figure 11.
Hydnellum squamulosum. (a): Basidiocarps; (b,c): SEM of basidiospores; (d–f): Microscopic structures (drawn from IFP 019418); (d): Section of hymenophore trama with basidia; (e): Hyphae from pileus context; (f): Basidiospores. —Scale bars: (a) = 1 cm; (b) = 3 μm; (c) = 1 μm; (d,e) = 10 µm; (f) = 5 µm.
MycoBank MB839042
Etymology. Squamulosum (Latin) refers to the minutely scaly pileal surface.
Holotype. CHINA, Xizang Autonomous Region, Bomi County, on the ground in Picea mixed forest, 17 July 2019, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 13615 (holotype IFP 019418).
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious or coalescent to form complex pileus, soft and leathery when fresh, becoming corky and light in weight upon drying; taste none, odor none when dry. Pileus circular when young, circular or semicircular with age, applanate, up to 35 mm diam and 4–8 mm thick at center. Pileal surface pastel red (7A4) to dark Magenta (13F7), zonate, floccose to woolly, squamulose when fresh, becoming fibrillose and scrobiculate when dry; margin white (7A1) when fresh, grayish orange (5B3) when dry, involute and wavy, sometimes lobed with age. Spine surface pale red (7A3) to reddish brown (8E8) when fresh, grayish orange (5B4) to dark brown (8F7) when dry; spines up to 2 mm long, base up to 0.2 mm diam, conical, 3–6 per mm, decurrent on stipe, without spines at pileus margin, brittle when dry. Context not duplex, up to 9 mm thick, reddish brown (8E6), soft corky. Stipe central to lateral, up to 4 cm long and 1 cm diam, sometimes connate, leathery or freshy when fresh, soft corky upon drying, pale red (11A3), tomentose, solid inner, context with a dark zone present at centre, terete to flat or attenuate downwards with bulbous base when old. Hyphal structure: hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae with simple-septa, occasionally encrusted, CB+ in slightly thick-walled hyphae, IKI–; tissues olivaceous in KOH. Context: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, moderately branched, simple-septate, straight, regularly arranged, sometimes flexuous and collapsed, mostly 4–5 μm diam. Spines: generative hyphae hyaline, thin-walled, moderately branched, more or less parallel along spines, frequently simple-septate, straight, 2–4 μm diam. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, thin-walled, with four sterigmata (2–3 μm long), simple-septate at base, 8–38 × 4–6 μm; basidioles similar to basidia. Basidiospores irregularly ellipsoid to globose, brown, thin-walled, tuberculate, CB–, IKI–, (4–)4.1–5(–5.1) × (3.2–)3.3–4.1(–4.2) μm, Lm = 4.4 μm, Wm = 3.8 μm, Q = 1.14–1.16 (n = 60/2); tuberculi usually isolated, sometimes in groups of two or more, then bi- to trifurcate in shape, up to 1 μm long.
Additional specimens (paratypes) examined: CHINA, Xizang Autonomous Region, Bomi County, on the ground in Picea mixed forest, 17 July 2019, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 13617 (IFP 019419, paratype); Yuan 13625 (IFP 019420, paratype); Yuan 13626 (IFP 019421, paratype); Yuan 13627 (IFP 019422, paratype); on the ground with moss in Picea mixed forest, 19 July 2019, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 13743 (IFP 019423, paratype).
Notes: Hydnellum squamulosum and H. concrescens are closely related in the phylogenetic tree and share similar morphological and anatomical characteristics: a solitary to gregarious or coalescent basidiocarp with fibrillose, squamulose and zonate pileal surface, irregularly lobed margin, decurrent and reddish-brown spines, not duplex context in the pileus, zonate context in the stipe, context tissue becoming olivaceous in KOH, and tuberculate basidiospores. However, H. concrescens can be differentiated by depressed or infundibuliform basidiocarps, reddish white to dark brown pileal margin, larger pileus (up to 120 mm vs. 35 mm in H. squamulosum), longer basidia sterigmata (up to 5 µm vs. up to 3 µm in H. squamulosum) and larger basidiospores (5–6 × 4–5 µm vs. 4.1–5 × 3.3–4.1 μm in squamulosum) [2,27,34]. H. fraudulentum is similar to H. squamulosum in having a squamulose-fibrillose pileal surface, cylindrical or connate stipe, context tissue olivaceous in KOH, thin- to slightly thick-walled and unclamped hyphae in the context, basidia of similar shape, and brown and tuberculate basidiospores. However, it differs from H. squamulosum in having depressed, azonate and yellow-brown to dark brown pilei, purplish brown and slightly longer spines (up to 2.5 mm vs. 2 mm in H. squamulosum), wider basidia (6–7 µm vs. 4–6 μm in H. squamulosum) with longer sterigmata (3.6–4.5 µm vs. 2–3 μm in H. squamulosum) and bigger basidiospores (6.3–7 × 4.5–4.7 µm vs. 4.1–5 ×3.3–4.1 μm in H. squamulosum) [26].
Hydnellum sulcatum Y.H. Mu & H.S. Yuan, sp. nov. (Figure 12)

Figure 12.
Hydnellum sulcatum. (a): Basidiocarps; (b,c): SEM of basidiospores; (d–f): Microscopic structures (drawn from IFP 019424); (d): Section of hymenophore trama with basidia; (e): Hyphae from pileus context; (f): Basidiospores. —Scale bars: (a) = 2 cm; (b) = 3 μm; (c) = 1 μm; (d,e) = 10 µm; (f) = 5 µm.
MycoBank MB839043;
Etymology. Sulcatum (Latin), refers to the often grooved pileal surface.
Type: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Benxi County, Guanmenshan National Forest Park, on the ground of Quercus forest, 29 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14649 (holotype IFP 019424).
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious or multiple pilei overlapping and fused to form a compound cluster, soft and leathery when fresh, becoming woody and light in weight upon drying; taste mild, odor slightly fragrant when dry. Pileus subinfundibuliform when young, later applanate to flabelliform or circular with age, up to 65 mm diam and 3–6 mm thick at center. Pileal surface dark brown (9F4), obscurely concentrically zonate, often grooved, scabrous to fibrous when fresh, becoming fibrillose, rugose when dry; margin white (6A1) when fresh, light brown (6D5) when dry, even, sometimes lobed. Spine surface brown (7E7) when fresh, brown (6E5) to dark brown (7F5) when dry; spines up to 1.5 mm long, base up to 0.1 mm diam, conical, 5–7 per mm, more or less decurrent on stipe, without spines at pileus margin, brittle when dry. Context not duplex, up to 6 mm thick, brown (7E6), woody. Stipe lateral, up to 2 cm long and 1.5 cm diam, sometimes connate, leathery when fresh, woody upon drying, brown (7E5), pubescent, inside solid, cylindrical to flat or attenuate downwards with bulbous base when old. Hyphal structure: hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae with simple-septa, CB+ in slightly thick-walled hyphae, IKI–; tissues olivaceous in KOH. Context: generative hyphae hyaline, thin-walled, moderately branched, simple-septate, straight, regularly arranged, sometimes flexuous and collapsed, mostly 4–6 μm diam. Spines: generative hyphae hyaline, thin to slightly thick-walled, moderately branched, more or less parallel along spines, often simple-septate, straight, 2–3 μm diam. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, thin-walled, with four sterigmata (2–3 μm long), simple-septate at base, 20–30 × 4–8 μm; basidioles similar to basidia. Basidiospores irregular ellipsoid to subglobose, brown, thin-walled, tuberculate, CB–, IKI–, (4–)4.1–5.8(–5.9) × (3.9–)4–4.6(–4.8) μm, Lm = 4.8 μm, Wm = 4.3 μm, Q = 1.14–1.19 (n = 60/2); tuberculi usually isolated, sometimes in groups of two or more, then bi- to trifurcate in shape, up to 0.9 μm long.
Additional specimens (paratypes) examined: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Kuandian County, Baishilazi National Nature Reserve, on the ground of Quercus forest, 8 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14521 (IFP 019425, paratype); Benxi County, Guanmenshan National Forest Park, on the ground of Quercus forest, 29 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14638 (IFP 019426, paratype); Yuan 14658 (IFP 019427, paratype); Yuan 14660 (IFP 019428, paratype).
Notes: Hydnellum parvum has a close phylogenetic relationship with H. sulcatum. The former species resembles the latter by compound fused pilei and rugulose pileal surface. However, the latter has a thinner stipe (0.7 × 0.2 cm vs. 2 × 1.5 cm in H. sulcatum), slightly longer spines (up to 2 mm vs. 1.5 mm in H. sulcatum) and shorter basidiospores (3–4 μm vs. 4.1–5.8 μm in H. sulcatum) [27]. H. subsuccosum resembles H. sulcatum by concentrically zonate pileus with similar size, context hyphae of similar width, the absence of clamp-connections and brown and subglobose basidiospores. However, H. subsuccosum differs by orange white to camel and nodulose or pitted pileal surface, longer spines (up to 3 mm vs. 1.5 mm in H. sulcatum), blue green to dark brown or black context tissue in KOH and longer basidia sterigmata (3–4 μm vs. 2–3 μm in H. sulcatum) [27]. H. atrorubrum is similar to H. sulcatum in having white to brown and even pileal margin and zonate pileal surface, olivaceous context tissues in KOH and basidiospores of similar shape with isolated or grouped tuberculi. However, H. atrorubrum can be differentiated by a flocculose to fibrillose or glabrescent pileal surface, longer spines (up to 3.5 mm vs. 1.5 mm in H. sulcatum) and basidia sterigmata (4–6 μm vs. 2–3 μm in H. sulcatum) and slightly longer tuberculi (up to 1.1 μm vs. 0.9 μm in H. sulcatum) of basidiospores.
Hydnellum yunnanense Y.H. Mu, X.H. Wang & H.S. Yuan, sp. nov. (Figure 13)
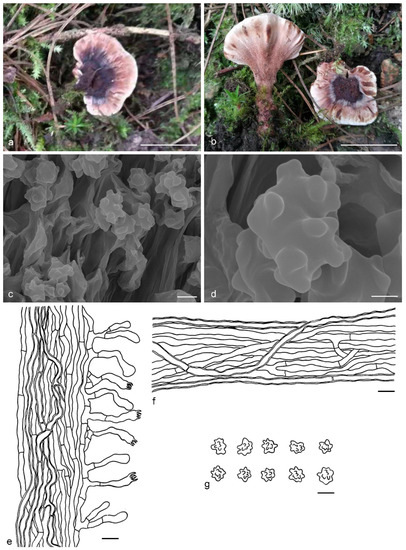
Figure 13.
Hydnellum yunnanense. (a,b): Basidiocarps; (c,d): SEM of basidiospores; (e–g): Microscopic structures (drawn from IFP 019429); (e): Section of hymenophore trama with basidia; (f): Hyphae from pileus context; (g): Basidiospores. —Scale bars: (a,b) = 1 cm; (c) = 3 μm; (d) = 1 μm; (e,f) = 10 µm; g = 5 µm.
MycoBank MB839044
Etymology. Yunnanense, refers to the Yunnan Province, where the specimens were collected.
Type: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Nanjian County, Lingbaoshan National Forest Park, on the ground, 19 September 2019, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14386 (holotype IFP 019429).
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious, soft and leathery when fresh, becoming woody and light in weight upon drying; taste mild, odor slightly fragrant when dry. Pileus subinfundibuliform when young, later flabelliform with age, up to 21 mm diam and 3–5 mm thick at center. Pileal surface grayish red (10D6) to dark brown (9F8), obscurely concentrically zonate, velutinate to tomentose when fresh, becoming rugulose to glabrescent when dry; margin white (6A1) when fresh, light brown (6D4) when dry, even, sometimes eroded with age. Spine surface white (10A1) to grayish red (106) when fresh, pale orange (5A3) to brown (6E7) when dry; spines up to 1.5 mm long, base up to 0.1 mm diam, conical, 5–8 per mm, more or less decurrent on stipe, without spines at pileus margin, brittle when dry. Context not duplex, up to 5 mm thick, reddish brown (8E4), woody. Stipe central to lateral, up to 4 cm long and 0.7 cm diam, sometimes connate, leathery when fresh, woody upon drying, brown (7E6), tomentose, solid inner, context with a dark line present at centre, cylindrical to attenuate downwards or broadening below with bulbous base when old. Hyphal structure: hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae with simple-septa, CB+ in slightly thick-walled hyphae, IKI–; tissues olivaceous in KOH. Context: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, moderately branched, simple-septate, straight, regularly arranged, sometimes flexuous and collapsed, mostly 3–5 μm diam. Spines: generative hyphae hyaline, thin- to slightly thick-walled, frequently branched, more or less parallel along spines, often simple-septate, straight, 2–5 μm diam. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, thin-walled, with four sterigmata (2–4 μm long), simple-septate at base, 13–28 × 4–7 μm; basidioles similar to basidia. Basidiospores irregularly ellipsoid to subglobose, brown, thin-walled, tuberculate, CB–, IKI–, (4.1–)4.2–5.1(–5.3) × (3.4–)3.5–4.5(–5) μm, Lm = 4.7 μm, Wm = 4 μm, Q = 1.17–1.18 (n = 60/2); tuberculi usually isolated, sometimes in groups of two or more, then bi- to trifurcate in shape, up to 1.2 μm long.
Additional specimens (paratypes) examined: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Nanjian County, Lingbaoshan National Forest Park, on the ground, 19 September 2019, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14396 (IFP 019430, paratype); Maguan County, Dalishu Township, Adushangba Village, on the ground, 7 August 2017, S. F. Shi, Shi 212 (IFP 019431, paratype).
Notes: The phylogenetic analyses support that Hydnellum yunnanense is sister to H. sulcatum (Figure 1). Morphologically, H. sulcatum resembles H. yunnanense in having an annual, solitary to gregarious basidiocarp with subinfundibuliform to flabelliform pileus with equal-length spines, a brown, pubescent, cylindrical stipe, olivaceous context tissue in KOH and basidiospores of similar shape. However, it differs from H. yunnanense in having a broader pileus (up to 65 mm vs. 21 mm in H. yunnanense) with scabrous to squamulose pileal surface and light brown pileal margin and shorter tuberculi (up to 0.9 μm vs. 1.2 μm in H. yunnanense). H. rubidofuscum resembles H. yunnanense by infundibuliform to flabelliform and concentrically zonate pileus, not duplex and woody context, thin- to slightly thick-walled and simple-septate hyphae in the context, basidia of similar width and basidiospores of similar shape and size. However, H. rubidofuscum differs by larger pileus (up to 70 mm vs. up to 21 mm in H. yunnanense) with reddish brown and scrupose, fibrillose to virgate pileal surface, grayish brown to reddish brown and longer spines (up to 3 mm vs. up to 1.5 mm in H. yunnanense) and thin-walled generative hyphae in the spines.
Hydnellumsp 3
Basidiocarps annual, solitary. Pileus applanate, flabelliform. Pileal surface brown (7E7) to dark brown (7F7), concentrically zonate and pubescent. Spines reddish brown (9E6) and more or less decurrent, up to 1 mm long. Stipe lateral, cylindrical and slender. Hyphal system monomitic, generative hyphae simple-septa. Basidia clavate, with four sterigmata. Basidiospores irregularly subglobose, tuberculate, (4.8–)4.9–5.2(–5.3) × (4–)4.1–4.8(–5) μm.
Specimen examined: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Nanjian County, Lingbaoshan National Forest Park, on the ground of angiosperm forest, 19 September 2019, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14388 (IFP 019438).
Hydnellum sp 4
Basidiocarps annual, solitary to gregarious. Pileus irregularly flabelliform. Pileal surface grayish yellow (4B3) to yellowish brown (5E8), obscurely concentrically zonate and glabrescent. Spines yellowish brown (5D5) and more or less decurrent, up to 2 mm long. Stipe lateral and cylindrical. Hyphal system monomitic, generative hyphae simple-septa. Basidia clavate, with four sterigmata. Basidiospores irregularly subglobose, tuberculate, (4.1–)4.2–5.3(–6) × (4–)4.1–4.3(–4.8) μm.
Specimen examined: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Maguan County, Dalishu Township, on the ground in Fagaceous forest, 14 October 2017, J. Wang, Wang 295 (IFP 019439).
Hydnellumsp 5
Basidiocarps annual, solitary. Pileus irregularly circular. Pileal surface zonate, velutinous and strigose with lobed margin. Spines decurrent, up to 1 mm long. Stipe lateral, cylindrical and broadened below with bulbous base when old. Hyphal system monomitic, generative hyphae simple-septa. Basidia clavate, with four sterigmata. Basidiospores irregularly ellipsoid to subglobose, tuberculate, (4–)4.1–5.5(–5.6) × (3–)3.1–4.7(–5.2) μm.
Specimen examined: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Xinbin County, Gangshan Nature Reserve, in the angiosperm forest dominated by Quercus liaotungensis, 26 August 2020, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 14594 (IFP 019440).
OtherHydnellumspecies
Hydnellum complicatum, H. cumulatum, H. diabolus, H. geogenium, H. lundellii, H. martioflavus, H. peckii, H. regium, H. versipelle
Hydnellum peckii Banker, in Peck, Bull. N.Y. St. Mus. 157: 28 (1912) (1911)
Basidiocarps single to concrescent. Pileus turbinate or elliptical, planar to subdepressed. Pileal surface white (6A1) to light orange (6A4), colliculose, rarely scrobiculate and glabrous. Spines brownish orange (7C4), decurrent, up to 3 mm long. Stipe central and terete. Hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae mostly with clamp-connections, minority of simple-septa. Basidia clavate, with simple-septate at base and four sterigmata. Basidiospores irregularly subglobose, tuberculate, (4.1–)4.2–5.1(–5.3) × (3.8–)3.9–4.4(–4.6) μm.
Specimens examined. CHINA, Xizang Autonomous Region, Bomi County, on the ground in Pinus mixed forest, 19 July 2019, H. S. Yuan, Yuan 13708 (IFP 0193433); Yuan 13720 (IFP 019434).
Notes: The studied samples were found in high altitude Pinus mixed forest. These two specimens clustered with two other samples (SSvantesson328 and ELarsson174-14) of Hydnellum peckii from Europe with full support (100% in ML and 1.00 BPP) (Figure 1). The ITS+LSU sequence identity between the specimens from China and Europe was 0.99 in Bioedit pairwise alignment. In morphology, the characters of our specimens overlap with those of H. peckii [1,27]. Therefore, we introduce H. peckii as a new record to China.
| Key to species of Hydnellum from China | |
| 1. Basidiocarps fleshy | 2 |
| 1.→ Basidiocarps woody | 4 |
| 2. Pileal surface not scaled | H. coactum |
| 2.→ Pileal surface scaled | 3 |
| 3. Pileal surface with ascend squama | H. grosselepidotum |
| 3.→ Pileal surface with appressed squama | H. lidongensis |
| 4. Context tissue olivaceous in KOH | 5 |
| 4.→ Context tissue blue-green in KOH | H. peckii |
| 5. Hyphae with clamp-connections in the context | 6 |
| 5.→ Hyphae without clamp-connections in the context and spines | 8 |
| 6. Basidiocarps with dark violet spines underneath pileus | H. atrospinosum |
| 6.→ Basidiocarps with different colored spines underneath pileus | 7 |
| 7. Pileal surface fibrillose, rugose when dry, spines up to 1.5 mm long | H. fibulatum |
| 7.→ Pileal surface pitted, colliculose when dry, spines up to 6 mm long | H. caeruleum |
| 8. Inflated hyphae present from the context | 9 |
| 8.→ Inflated hyphae absent in the context | 10 |
| 9. Generative hyphae mostly inflated in the context, pileal surface scrobiculate when dry | H. inflatum |
| 9.→ Generative hyphae occasionally inflated in the context, pileal surface granulose when dry | H. granulosum |
| 10. Stipe thin, rhizomorphs-like | Hydnellum sp 1 |
| 10.→ Stipe cylindrical to flattened | 11 |
| 11. Pileal surface colored brownish orange to brownish red | H. brunneorubrum |
| 11.→ Pileal surface differently colored | 12 |
| 12. Pileal margin involute and wavy, sometimes lobed or rimose | 13 |
| 12.→ Pileal margin even or effused, sometimes lobed or eroded | 14 |
| 13. Pileal surface glabrescent | Hydnellum sp 4 |
| 13.→ Pileal surface not glabrescent | 15 |
| 14. Pileal surface azonate and spongy | 16 |
| 14.→ Pileal surface obsurely concentrically zonate to zonate and not spongy | 17 |
| 15. Pileal surface floccose to squamulose when fresh, context corky | H. squamulosum |
| 15.→ Pileal surface tomentose and scrupose when fresh, context woody | H. bomiense |
| 16. Basidiocarps single to gregarious and stipe single and long | H. spongiosipes |
| 16.→ Basidiocarps coalescent and stipe connate and short | Hydnellum sp 2 |
| 17. Stipe context with a dark line at centre | 18 |
| 17.→ Stipe context without a dark line at centre | 19 |
| 18. Pileus and spines grayish red | H. yunnanense |
| 18.→ Pileus brown and spines reddish brown | Hydnellum sp 3 |
| 19. Spines up to 3 or 3.5 mm long | 20 |
| 19.→ Spines up to 1 or 1.5 mm long | 21 |
| 20. Pileus light brown to dark ruby | H. atrorubrum |
| 20.→ Pileus reddish brown | H. rubidofuscum |
| 21. Basidiocarps gregarious or multiple pilei overlapping and pileal surface often grooved, scabrous to fibrous | H. sulcatum |
| 21.→ Basidiocarps solitary and pileal surface velutinous and strigose | Hydnellum sp 5 |
5. Discussion
Baird et al. [27] constructed a phylogenetic tree of Bankeraceae using ITS sequences of specimens from the temperate southeastern United States, and suggested that neither Hydnellum nor Sarcodon were monophyletic. In the current study, phylogenetic analyses using four loci (nLSU + ITS + SSU + RPB2) of Hydnellum and Sarcodon were carried out using sequences from Europe, Asia and America. Our results also verify that Sarcodon is paraphyletic; with regard to Hydnellum, some species of Sarcodon nesting among Hydnellum species. Larsson et al. [31] provided phylogenetic analyses on Hydnellum and Sarcodon based on ITS and LSU sequences, confirming that Sarcodon makes Hydnellum paraphyletic and the genus limits were revised, 12 species of Sarcodon moved to Hydnellum. Morphologically, they proposed to use the size of the basidiospores to separate the two genera, delimiting Hydnellum and Sarcodon species with basidiospore lengths in the ranges of 4.45–6.95 µm and 7.4–9 µm, respectively. These results indicate that the traditional classification system based on the consistency of Sarcodon (fleshy) and Hydnellum (woody) did not conform to the monophyletic concept of the two genera.
Based on microscopical hyphal structure species of Hydnellum and Sarcodon can be divided into five groups, as shown in Table 3: (I) Context of the pileus and the spines composed of simple-septate hyphae (includes H. aurantiacum, H. auratile and 49 other taxa); (II) Pileus composed mostly of simple-septate hyphae with occasional clamp-connections and spinal trama composed of simple-septate hyphae (includes H. caeruleum, H. ferrugipes and H. fibulatum); (III) Both pileus and the spines composed of predominantly clamped hyphae with occasional simple-septa (includes H. peckii and H. versipelle); (IV) Pileus composed of only hyphae with clamp-connections and spine with only simple-septate hyphae (includes H. diabolus); (V) Both pileus and the spines composed of clamped hyphae (includes H. atrospinosum, H. cyanopodium, H. geogenium, H. scleropodium, H. suaveolens, S. aspratus, S. imbricatus, S. leucopus, S. quercinofibulatus, S. scabripes and S. squamosus). One species, H. regium, has not been classified into these five groups because the information is not available from the original description [33].

Table 3.
Hyphal-septa type observations in the context of the pileus and the spine trama in the species of Hydnellum and Sarcodon.
In the phylogenetic tree, ten subgenera with moderate to high support in Hydnellum have been distinguished (Figure 1), and each subgenus possesses distinctive morphological characteristics. Group I can be categorized into seven subgenera. The subgenus Croceum has an orange basidiocarps and includes H. aurantiacum, H. auratile, H. brunneorubrum, H. chrysinum and H. earlianum; the subgenus Inflatum has the appearance of inflated hypha in the context of the pileus and includes H. cristatum, H. granulosum, H. inflatum, H. mirabile and H. piperatum; the subgenus Rhizomorphum has rhizomorphs-like stipe and includes H. gracilipes and Hydnellum sp 1; the subgenus Scabrosum has pileal surface with scabrosity and includes H. amygdaliolens, H. coactum, H. fagiscabrosum, H. fennicum, H. grosselepidotum, H. illudens, H. lepidum, H. lidongensis, H. nemorosum, H. scabrosellum, H. scabrosum and H. underwoodii; the subgenus Spongiosum corresponds to a spongy pileal surface and includes H. ferrugineum, H. pineticola, H. spongiosipes and Hydnellum sp 2; the subgenus Violaceum corresponds to the violaceous basidiocarps and includes H. fuligineoviolaceum, H. fuscoindicum, H. glaucopus, H. joeides and H. roseoviolaceum; the subgenus Zonatum has a concentrically zonate pileal surface and includes H. atrorubrum, H. bomiense, H. concrescens, H. dianthifolium, H. parvum, H. rubidofuscum, H. scrobiculatum, H. squamulosum, H. subsuccosum, H. sulcatum, H. yunnanense, Hydnellum sp 3, Hydnellum sp 4 and Hydnellum sp 5. Group II corresponds to the subgenus Subindufibulatum, having occasionally clamped hyphae in the context of the pileus, and includes H. caeruleum, H. ferrugipes and H. fibulatum. Group V corresponds to all hyphae clamped in the pileus and the spines, incorporating two subgenera of Hydnellum and six Sarcodon species; the subgenus Hydnellum has dark spines and includes H. atrospinosum and H. suaveolens; the subgenus Caesispinosum has blue spines and includes H. cyanopodium and H. scleropodium; H. geogenium is morphologically related to other species in Group V, but is distantly related in the phylogenetic tree; Sarcodon clade S. aspratus, S. imbricatus, S. leucopus, S. quercinofibulatus, S. scabripes and S. squamosus have the characteristics of long spores compared with the Hydnellum species. Therefore, the classification system using hyphal structure type and phylogenetic subgenera can fix the positions for most species in Hydnellum and Sarcodon, except for some species in Groups III, IV and those without phylogenetic support.
The specimens involved in this study were collected from the northeast, northwest and southwest regions of China, where industrial pollution is relatively low and vegetation is relatively abundant. The forests are primarily dominated by Pinaceae and Fagaceae trees such as Pinus spp., Picea spp., Quercus spp., Lithocarpus spp. and a small portion of other tree families. Thus, we speculated that these species may form an ectomycorrhizal association with Pinaceae and Fagaceae host trees. The species diversity and basidiocarps richness of stipitate hydnoid fungi represented by Hydnellum and Sarcodon species have shown a declining trend across Europe and some regions of North America during the 1970s to 2000s [6,55,56,57]; the phenomenon is most probably caused by forest management, air pollutants, forest soil acidification, nitrogen deposition and forest succession, among other causes [19,58,59,60,61]. Many stipitate hydnoid fungi have been included in national Red Lists in Europe [27,62,63,64]. With the rapid industrialization in China over the past four decades, a significant decline of basidiocarps has also been observed during the course of our field investigation. The identification and description of stipitate hydnoid fungi in this paper will contribute to the understanding of species diversity and provide baseline data for the evaluation and protection of these fungi in China.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jof7100818/s1, Figure S1: Maximum likelihood tree illustrating the phylogeny of Hydnellum and Sarcodon based on ITS sequence dataset.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-H.M. and H.-S.Y.; Methodology, H.-S.Y.; Investigation, Y.-H.M., J.-R.Y., T.C., X.-H.W. and H.-S.Y.; Data Curation, Y.-H.M.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, Y.-H.M.; Writing—Review & Editing, H.-S.Y.; Supervision, H.-S.Y.; Funding Acquisition, H.-S.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 31770028 & 31970017) and the Investigation of Macrofungi of Maguan County issued by Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. All resulting alignments were deposited in TreeBASE (http://www.treebase.org (accessed on 17 August 2021); accession number S28676). All newly generated sequences were deposited in GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/ (accessed on 23 September 2021); Table 1). All new taxa were deposited in Mycobank.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the editor and two anonymous reviewers for comments on an earlier version of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Maas Geesteranus, R.A. Die terrestrischen Stachelpilze Europas. Verh. K. Ned. Akad. van Wet. Afd. Nat. Tweede Reeks 1975, 65, 1–127. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, R.E.; Khan, S.R. The stipitate hydnums (Thelephoraceae) of Florida. Brittonia 1986, 38, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agerer, R. Ectomycorrhizae of Hydnellum peckii on Norway spruce and their chlamydospores. Mycologia 1993, 85, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalpers, J.A. The aphyllophoraceous fungi I. Keys to the species of the Thelephorales. Stud. Mycol. 1993, 35, 1–168. [Google Scholar]
- Pegler, D.N.; Roberts, P.J.; Spooner, B.M. British Chanterelles and Tooth Fungi; Royal Botanic Gardens: Kew, UK, 1997; p. 114. [Google Scholar]
- Arnolds, E. De Stekelzwammen en Pruikzwammen van Nederland en Belgie. Coolia 2003, 46, 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Arnolds, E. The fate of hydnoid fungi in the Netherlands and northwestern Europe. Fungal Ecol. 2010, 3, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnolds, E. E. Former and present distribution of stipitate hydnaceous fungi (Basidiomycetes) in the Netherlands. Nova Hedwig. 1989, 48, 107–142. [Google Scholar]
- Bergelson, J.M.; Crawley, M.J. Mycorrhizal infection and species diversity. Nature 1998, 334, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijden, M.; Klironomos, J.; Ursic, M.; Moutoglis, P.; Streitwolf-Engel, R.; Boller, T.; Wiemken, A.; Sanders, I. Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability and productivity. Nature 1998, 396, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhou, L.W.; Yang, Z.L.; Bau, T.; Li, T.H.; Dai, Y.C. Resource diversity of Chinese macrofungi: Edible, medicinal and poisonous species. Fungal Divers. 2019, 98, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Boo, K.H.; Lee, J.M.; Viet, C.D.; Quyen, N.; Unno, T.; Cho, M.; Riu, K.Z.; Lee, D.S. Anti-viral activity of Hydnellum concrescens, a medicinal mushroom. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 15241–15245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, V.; Carvalho, I.S. A review of the health benefit potentials of herbal plant infusions and their mechanism of actions. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 65, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizon, P. Decline of macrofungi in Europe: An overview. Trans. Mycol. Soc. Repub. China 1993, 8, 21–48. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, A.C.; Holden, E.; Davy, L.M.; Ward, S.D.; Fleming, L.V.; Watling, R. Status and distribution of stipitate hydnoid fungi in Scottish coniferous forests. Biol. Conserv. 2002, 107, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linde, S.; Alexander, I.J.; Anderson, I.C. A PCR-based method for detecting the mycelia of stipitate hydnoid fungi in soil. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 75, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, E.J.; Van Dobben, H.F. Is decline of Cantharellus cibarius in the Netherlands due to air pollution? Ambio 1987, 16, 211–213. [Google Scholar]
- Arnolds, E. A preliminary Red Data List of macrofungi in the Netherlands. Persoonia 1989, 14, 77–125. [Google Scholar]
- Arnolds, E. Decline of ectomycorrhizal fungi in Europe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1991, 35, 209–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termorshuizen, A.J.; Schaffers, A.P. The decline of sporocarps of ectomycorrhizal fungi in stands of Pinus sylvestris L. in The Netherlands: Possible causes. Nova Hedwig. 1991, 53, 267–289. [Google Scholar]
- Wallenda, T.; Kottke, I. Nitrogen deposition and ectomycorrhizas. New Phytol. 1998, 139, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizon, P. Macrofungi reported as extinct or threatened with extinction in European Red Data Lists. Fungi Conserv. Newsl. 1995, 3, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Senn-Irlet, B.; Bieri, G.; Egli, S. Rote Liste Grosspilze. Rote Liste der Gefährdeten Arten der Schweiz; BAFU: Bern, Switzerland, 2007; Volume 18, p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.H.; Suz, L.M.; Ainsworth, A.M.; Smith, J.H.; Suz, L.M.; Ainsworth, A.M. Red List of Fungi for Great Britain: Bankeraceae, Cantharellaceae, Geastraceae, Hericiaceae and Selected Genera of Agaricaceae (Battarrea, Bovista, Lycoperdon & Tulostoma) and Fomitopsidaceae (Piptoporus); Jodrell Laboratory, Royal Botanic Gardens: Kew, UK, 2016; p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- Anon. UK Biodiversity Group. Tranche 2 Actions Plans—Volume III: Plants and Fungi; English Nature: Peterborough, UK, 1999; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Maas Geesteranus, R.A. Hydnaceous fungi of the eastern old world. Vehr. K. Ned. Akad. van Wet. Afd. Nat. 1971, 60, 1–176. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, R.; Wallace, L.E.; Baker, G.; Scruggs, M. Stipitate hydnoid fungi of the temperate southeastern United States. Fungal Divers. 2013, 62, 41–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, M.; Hibbett, D.S.; Larsson, K.H.; Larsson, E.; Langer, E.; Langer, G. The phylogenetic distribution of resupinate forms across the major clades of mushroom-forming fungi (Homobasidiomycetes). Syst. Biodivers. 2005, 3, 113–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheny, P.B.; Curtis, J.M.; Hofstetter, V.; Aime, M.C. Major clades of Agaricales: A multilocus phylogenetic overview. Mycologia 2006, 98, 982–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedersoo, L.; May, T.W.; Smith, M.E. Ectomycorrhizal lifestyle in fungi: Global diversity, distribution, and evolution of phylogenetic lineages. Mycorrhiza 2010, 20, 217–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, K.H.; Svantesson, S.; Miscevic, D.; Kljalg, U.; Larsson, E. Reassessment of the generic limits for Hydnellum and Sarcodon (thelephorales, basidiomycota). MycoKeys 2019, 54, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, H.J. A contribution to a revision of the North American Hydnaceae. Mem. Torrey Bot. Club 1906, 12, 99–194. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, K.A. New or little known North American stipitate hydnums. Can. J. Bot. 1964, 42, 1205–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.E. Study of the stipitate hydnums from the southern Appalachian Mountains—Genera: Bankera, Hydnellum, Phellodon, Sarcodon. Bibl. Mycol. 1986, 104, 1–156. [Google Scholar]
- Koljalg, U.; Renvall, P. Hydnellum gracillipes—A link between stipitate and resupinate Hymenomycetes. Karstenia 2000, 40, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Loizides, M.; Alvarado, P.; Assyov, B.; Arnolds, E.; Moreau, P.A. Hydnellum dianthifolium sp nov. (Basidiomycota, Thelephorales), a new tooth-fungus from southern Europe with notes on H. concrescens and H. scrobiculatum. Phytotaxa 2016, 280, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.C. A revised checklist of corticioid and hydnoid fungi in China for 2010. Mycoscience 2011, 52, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.H.; Hu, Y.P.; Wei, Y.L.; Yuan, H.S. Hydnaceous fungi of China 8. morphological and molecular identification of three new species of Sarcodon and a new record from southwest China. MycoKeys 2020, 66, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, R.W. A Mycological Colour Chart; Commonweath Mycological Institute and British Mycological Society: Kew, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Munsell, A.H. Munsell Soil-Color Charts with Genuine Munsell Color Chips; Munsell Color: Grand Rapids, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stöger, A.; Schaffer, J.; Ruppitsch, W. A rapid and sensitive method for direct detection of Erwinia amylovora in symptomatic and asymptomatic plant tissues by polymerase chain reaction. J. Phytopathol. 2006, 154, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A.; Hoover, P.; Rougemont, J. A rapid bootstrap alogarithm for the RAxML webservers. Syst. Biol. 2008, 75, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannatella, D. Xenopus in space and time: Fossils, node calibrations, tip-dating, and paleobiogeography. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2015, 145, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. MODELTEST: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nylander, J. MrModeltest v2. Program Distributed by the Author; Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, F.; White, T.; Lee, S.H.; Taylor, L.; Shawetaylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR Protoc. Guide Methods Appl. 1990, 18, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Whelen, S.; Hall, B.D. Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetes: Evidence from an RNA polymerse II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.E. Type studies of North American and other related taxa of stipitate hydnums: Genera Bankera, Hydnellum, Phellodon, Sarcodon. Bibl. Mycol. 1986, 103, 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio Casas, L.; Rubio Roldán, L.; Català, S. Sarcodon amygdaliolens, a new species of Sarcodon Quél. ex P. Karst. found in the Iberian Peninsula. Boletín Soc. Micológica Madr. 2011, 35, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Nitare, J.; Ainsworth, A.M.; Larsson, E.; Parfitt, D.; Suz, L.M.; Svantesson, S.; Larsson, K.H. Four new species of Hydnellum (Thelephorales, Basidiomycota) with a note on Sarcodon illudens. Fungal Syst. Evol. 2021, 7, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, C.; Friebes, G.; Krisai-Greilhuber, I. Sarcodon fennicus, a boreo-montane stipitate hydnoid fungus with a remarkable smell. Austrian Mycol. Soc. 2018, 27, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, P. Die Terrestrischen Stachelpilze der DDR—Taxonomie, Ökologie, Verbreitung und Rückgang. Doctoral Dissertation, Martin-Luther-Universität, Halle-Wittenberg, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hrouda, P. Hydnaceous fungi of the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Czech Mycol. 1999, 51, 99–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linde, S.; Alexander, I.J.; Anderson, I.C. Spatial distribution of sporocarps of stipitate hydnoid fungi and their belowground mycelium. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thompson, G.W.; Medwe, R.J. Effects of aluminimum and manganese on the growth of ectomycorrhizal fungi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 48, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, H. Der “Satanspilzhang” bei Glesse (Ottenstein), Siid-Niedersachsen. Westffilische Pilzbr. 1986, 10–11, 289–351. [Google Scholar]
- Termorshuizen, A.J.; Schaffers, A.P. Occurrence of carpophores of mycorrhizal fungi in selected stands of Pinus sylvestris in the Netherlands in relation to stand vitality and air pollution. Plant Soil 1987, 104, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnolds, E. The changing macromycete flora in the Netherlands. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1988, 90, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrouda, P. Bankeraceae in central Europe. 1. Czech Mycol. 2005, 57, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrouda, P. Bankeraceae in central Europe. 2. Czech Mycol. 2005, 57, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnolds, E.; Veerkamp, M. Basisrapport Rode Lijst Paddenstoelen; Ministry of Agriculture, Nature and Food Safety: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Maas Geesteranus, R.A. Notes on Hydnums–VII. Persoonia 1967, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mleczko, P.; Zubek, S.; Kozak, M. Description of ectomycorrhiza and a new Central European locality of the rare hydnoid species Sarcodon leucopus (Pers.) Maas Geest. et Nannf. (Thelephorales, Basidiomycota). Nova Hedwig. 2011, 92, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-De-Gregorio, M.A.; Macau, N.; Carbó, J. Sarcodon quercinofibulatum, una nueva especie del género con hifas fibulíferas. Rev. Catalana Micol. 2011, 33, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).