Consensus Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Pneumocystis jirovecii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Investigated Loci and Typing Schemes
2.1. Nuclear rRNA Gene Cluster
2.2. Mitochondrial Genes
2.3. Nuclear Genes
3. Amplification Rate and Variation of Target Loci
4. Case Study: Assessing the Ability to Discriminate between Clinical Isolates
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meenakshi, K.; Gowtham, R.R.; Usha, K. Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia: A Revisit to the Old Malady. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2019, 13, DE01–DE08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.; Lundgren, J.D.; Masur, H.; Walzer, P.D.; Hanson, D.L.; Frederick, T.; Huang, L.; Beard, C.B.; Kaplan, J.E. Current epidemiology of Pneumocystis pneumonia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, L.M.; Chen, S.C.-A.; Kable, K.; Halliday, C.L.; Firacative, C.; Meyer, W.; Wong, G.; Nankivell, B.J. Nosocomial Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: Lessons from a cluster in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation 2011, 92, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokulska, M.; Kicia, M.; Wesołowska, M.; Hendrich, A.B. Pneumocystis jirovecii—From a commensal to pathogen: Clinical and diagnostic review. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 3577–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitte, C.; Leterrier, M.; Le Pape, P.; Miegeville, M.; Morio, F. Multilocus sequence typing of Pneumocystis jirovecii from clinical samples: How many and which loci should be used? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2843–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-J.; Bartlett, M.S.; Shaw, M.M.; Queener, S.F.; Smith, J.W.; Ortiz-Rivera, M.; Leibowitz, M.J.; Lee, C.-H. Typing of Pneumocystis carinii strains that infect humans based on nucleotide sequence variations of internal transcribed spacers of rRNA genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 2904–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolaki, A.G.; Miller, R.F.; Underwood, A.P.; Banerji, S.; Wakefield, A.E. Genetic diversity at the internal transcribed spacer regions of the rRNA operon among isolates of Pneumocystis carinii from AIDS patients with recurrent pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 174, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keely, S.P.; Stringer, J.R. Multi-locus genotype switching in Pneumocystis carinii sp. f. hominis: Evidence for reinfection. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1996, 43, 50S. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, P.M.; Francioli, P.; Bille, J.; Telenti, A.; Blanc, D.S. Typing of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis by single-strand conformation polymorphism of four genomic regions. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 3086–3091. [Google Scholar]
- Keely, S.P.; Stringer, J.R. Sequences of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis strains associated with recurrent pneumonia vary at multiple loci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2745–2747. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, M.; Lidman, C.; Latouche, S.; Björkman, A.; Roux, P.; Linder, E.; Wahlgren, M. Identification of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis gene sequences in filtered air in hospital environments. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsolaki, S.; Ortona, E.; Mazars, E.; Margutti, P.; Tamburrini, E.; Siracusano, A.; Guyot, K.; Nigou, M.; Roux, P. Biodiversity of Pneumocystis carinii hominis: Typing with different DNA regions. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 383–387. [Google Scholar]
- Tsolaki, A.G.; Beckers, P.; Wakefield, A.E. Pre-AIDS era isolates of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis: High genotypic similarity with contemporary isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Helweg-Larsen, J.; Tang, X.; Jin, S.; Li, B.; Bartlett, M.S.; Lu, J.-J.; Lundgren, B.; Lundgren, J.D.; Olsson, M. Update on Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis typing based on nucleotide sequence variations in internal transcribed spacer regions of rRNA genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.D.; Lacube, P.; Latouche, S.; Kac, G.; Mayaud, C.; Marteau, M.; Poirot, J.L.; Maury, E.; Guillot, J.; Roux, P. Contribution of Dihydropteroate synthase gene typing for Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis epidemiology. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 133S. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Borio, L.; Masur, H.; Kovacs, J.A. Pneumocystis carinii dihydropteroate synthase but not dihydrofolate reductase gene mutations correlate with prior trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or dapsone use. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, C.B.; Carter, J.L.; Keely, S.P.; Huang, L.; Pieniazek, N.J.; Moura, I.N.; Roberts, J.M.; Hightower, A.W.; Bens, M.S.; Freeman, A.R. Genetic variation in Pneumocystis carinii isolates from different geographic regions: Implications for transmission. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, N.; Takahashi, T.; Wada, M.; Endo, T.; Nakamura, T.; Sakashita, H.; Kimura, K.; Ohnishi, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Mizuochi, T. Genotyping of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis isolates in Japan based on nucleotide sequence variations in internal transcribed spacer regions of rRNA genes. Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 44, 591–596. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, P.M.; Blanc, D.S.; Sudre, P.; Manoloff, E.S.; Nahimana, A.; Bille, J.; Weber, R.; Francioli, P. Genetic diversity of Pneumocystis carinii in HIV-positive and-negative patients as revealed by PCR–SSCP typing. Aids 2001, 15, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, P.M.; Sudre, P.; Nahimana, A.; Francioli, P.; Group, S. Prophylaxis failure is associated with a specific Pneumocystis carinii genotype. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1080–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Kovacs, J.A. Genetic analysis of multiple loci suggests that mutations in the Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis dihydropteroate synthase gene arose independently in multiple strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 3213–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, G.; Sbaiz, L.; Avanzini, C.; Caramello, P.; Savoia, D. Genetic diversity of Pneumocystis carinii isolated from human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients in Turin, Italy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2995–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshnick, S.R.; Hossler, P.A.; Enger, K.S.; Kazanjian, P.; Rest, J.S.; Mindell, D.; Li, B.; Lee, C.; Nimri, L.F.; Carter, J.L. Distribution of DHPS mutations among ITS subtypes of P. carinii f. sp. hominis. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Kanda, T.; Iwamoto, A. Genetic diversity of drug targets including Dihydropteroate synthase, Dihydrofolate reductase and Cytochrome b, in Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis isolates in Japan. Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 2002, 112, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.F.; Ambrose, H.E.; Novelli, V.; Wakefield, A.E. Probable mother-to-infant transmission of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1555–1557. [Google Scholar]
- Montes-Cano, M.A.; De la Horra, C.; Martin-Juan, J.; Varela, J.M.; Torronteras, R.; Respaldiza, N.; Medrano, F.J.; Calderón, E.J. Pneumocystis jiroveci genotypes in the Spanish population. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, O.; Lee, C.-H.; Jin, S.; Li, B.; Costa, M.C.; Gonçalves, L.; Antunes, F. Pneumocystis jirovecii in Portuguese immunocompromised patients: Association of specific ITS genotypes with treatment failure, bad clinical outcome and childhood. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2003, 3, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.F.; Lindley, A.R.; Ambrose, H.E.; Malin, A.S.; Wakefield, A.E. Genotypes of Pneumocystis jirovecii isolates obtained in Harare, Zimbabwe, and London, United Kingdom. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3979–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakefield, A.E.; Lindley, A.R.; Ambrose, H.E.; Denis, C.-M.; Miller, R.F. Limited asymptomatic carriage of Pneumocystis jirovecii in human immunodeficiency virus–infected patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.F.; Lindley, A.R.; Ambrose, H.E.; Aliouat-Denis, C.M.; Wakefield, A.E. Multilocus Genotyping of Pneumocystis jirovecii from Adult HIV-Infected Patients with Pneumocystis Pneumonia. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 654–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robberts, F.J.L.; Liebowitz, L.D.; Chalkley, L.J. Genotyping and coalescent phylogenetic analysis of Pneumocystis jirovecii from South Africa. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahimana, A.; Rabodonirina, M.; Helweg-Larsen, J.; Meneau, I.; Francioli, P.; Bille, J.; Hauser, P.M. Sulfa resistance and Dihydropteroate synthase mutants in recurrent Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höcker, B.; Wendt, C.; Nahimana, A.; Tönshoff, B.; Hauser, P.M. Molecular evidence of Pneumocystis transmission in pediatric transplant unit. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medrano, F.J.; Montes-Cano, M.; Conde, M.; De La Horra, C.; Respaldiza, N.; Gasch, A.; Perez-Lozano, M.J.; Varela, J.M.; Calderon, E.J. Pneumocystis jirovecii in general population. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, C.B.; Fox, M.R.; Lawrence, G.G.; Guarner, J.; Hanzlick, R.L.; Huang, L.; del Rio, C.; Rimland, D.; Duchin, J.S.; Colley, D.G. Genetic differences in Pneumocystis isolates recovered from immunocompetent infants and from adults with AIDS: Epidemiological implications. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 1815–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, A.; Tronconi, E.; Mazza, F.; Cargnel, A.; Fantoni, G.; Atzori, C. DHPS -Mutated Isolates of Pneumocystis jirovecii from HIV-Infected Individuals: Analysis of Related ITS Genotypes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2006, 53, S108–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Esteves, F.; Antunes, F.; Matos, O. Multilocus genotyping of Pneumocystis jirovecii in immunocompromised patients: Preliminary results. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2006, 53, S104–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Mirdha, B.R.; Guleria, R.; Mohan, A.; Kabra, S.K.; Kumar, L.; Agarwal, S.K.; Luthra, K. Use of different primer directed sequence amplification by polymerase chain reaction for identification of Pneumocystis jirovecii in clinical samples. Indian J. Chest Dis. Allied Sci. 2008, 50, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Esteves, F.; Montes-Cano, M.A.; De La Horra, C.; Costa, M.C.; Calderón, E.J.; Antunes, F.; Matos, O. Pneumocystis jirovecii multilocus genotyping profiles in patients from Portugal and Spain. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripattanapipong, S.; Leelayoova, S.; Mungthin, M.; Worapong, J.; Tan-Ariya, P. Study of DHPS and DHFR genes of Pneumocystis jirovecii in Thai HIV-infected patients. Med. Mycol. 2008, 46, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, F.; Gaspar, J.; Tavares, A.; Moser, I.; Antunes, F.; Mansinho, K.; Matos, O. Population structure of Pneumocystis jirovecii isolated from immunodeficiency virus-positive patients. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmoldt, S.; Schuhegger, R.; Wendler, T.; Huber, I.; Söllner, H.; Hogardt, M.; Arbogast, H.; Heesemann, J.; Bader, L.; Sing, A. Molecular evidence of nosocomial Pneumocystis jirovecii transmission among 16 patients after kidney transplantation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianella, S.; Haeberli, L.; Joos, B.; Ledergerber, B.; Wuethrich, R.-P.; Weber, R.; Kuster, H.; Hauser, P.-M.; Fehr, T.; Mueller, N.J. Molecular evidence of interhuman transmission in an outbreak of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in renal transplant recipients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2010, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hal, S.J.; Gilgado, F.; Doyle, T.; Barratt, J.; Stark, D.; Meyer, W.; Harkness, J. Clinical significance and phylogenetic relationship of novel Australian Pneumocystis jirovecii genotypes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1818–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes-Cano, M.A.; Chabe, M.; Fontillon-Alberdi, M.; de la Horra, C.; Respaldiza, N.; Medrano, F.J.; Varela, J.M.; Dei-Cas, E.; Calderon, E.J. Vertical transmission of Pneumocystis jirovecii in humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, F.; Tavares, A.; Costa, M.C.; Gaspar, J.; Antunes, F.; Matos, O. Genetic characterization of the UCS and Kex1 loci of Pneumocystis jirovecii. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, F.; Gaspar, J.; Marques, T.; Leite, R.; Antunes, F.; Mansinho, K.; Matos, O. Identification of relevant single-nucleotide polymorphisms in Pneumocystis jirovecii: Relationship with clinical data. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.; Vivancos, R.; Corless, C.; Wood, G.; Beeching, N.J.; Beadsworth, M.B. Increasing frequency of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in renal transplant recipients in the United Kingdom: Clonal variability, clusters, and geographic location. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Beser, J.; Botero-Kleiven, S.; Lebbad, M.; Hagblom, P.; Fernandez, V. A limited number of ITS haplotypes defines the diversity of Pneumocystis jirovecii strains in Sweden. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliquett, R.U.; Asbe-Vollkopf, A.; Hauser, P.M.; Presti, L.L.; Hunfeld, K.P.; Berger, A.; Scheuermann, E.H.; Jung, O.; Geiger, H.; Hauser, I.A. A Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia outbreak in a single kidney-transplant center: Role of cytomegalovirus co-infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 2429–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimonte, S.; Berrilli, F.; D’Orazi, C.; D’Alfonso, R.; Placco, F.; Bordi, E.; Perno, C.F.; Di Cave, D. Molecular analysis based on mtLSU-rRNA and DHPS sequences of Pneumocystis jirovecii from immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients in Italy. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 14, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Armas, Y.; Friaza, V.; Capó, V.; Durand-Joly, I.; Govín, A.; de La Horra, C.; Dei-Cas, E.; Calderón, E.J. Low genetic diversity of Pneumocystis jirovecii among Cuban population based on two-locus mitochondrial typing. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, T.; McCaughey, C.; Coyle, P. V Pneumocystis jirovecii multilocus genotyping profiles in Northern Ireland. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 1170–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debourgogne, A.; Favreau, S.; Ladriere, M.; Bourry, S.; Machouart, M. Characteristics of Pneumocystis pneumonia in Nancy from January 2007 to April 2011 and focus on an outbreak in nephrology. J. Mycol. Med. 2014, 24, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankivell, B.J.; Firacative, C.; Kable, K.; Chen, S.C.-A.; Meyer, W. Molecular epidemiology linking multihospital clusters of opportunistic Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1058–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostved, A.A.; Sassi, M.; Kurtzhals, J.A.L.; Sørensen, S.S.; Rasmussen, A.; Ross, C.; Gogineni, E.; Huber, C.; Kutty, G.; Kovacs, J.A. Outbreak of Pneumocystis Pneumonia in renal and liver transplant patients caused by genotypically distinct strains of Pneumocystis jirovecii. Transplantation 2013, 96, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.Y.L.; Halliday, C.L.; Grote, D.; Meyer, W.; Kesson, A.M.; Chen, S.C.A. Colonisation with Pneumocystis jirovecii in Australian infants. Pathol. RCPA 2015, 47, 489–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanio, A.; Morio, F.; Gits-Muselli, M.; Desnos-Ollivier, M.; Maitte, C.; Bretagne, S. Short tandem repeat genotyping for P. jirovecii is more sensitive to mixed genotype than MLST. J. Mycol. Med. 2015, 25, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depypere, M.; Saegeman, V.; Lagrou, K. Typing of Pneumocystis jirovecii by multilocus sequencing: Evidence of outbreak? Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desoubeaux, G.; Dominique, M.; Morio, F.; Thepault, R.-A.; Franck-Martel, C.; Tellier, A.-C.; Ferrandière, M.; Hennequin, C.; Bernard, L.; Salamé, E. Epidemiological outbreaks of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia are not limited to kidney transplant recipients: Genotyping confirms common source of transmission in a liver transplantation unit. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpentier, E.; Garnaud, C.; Wintenberger, C.; Bailly, S.; Murat, J.-B.; Rendu, J.; Pavese, P.; Drouet, T.; Augier, C.; Malvezzi, P. Added value of next-generation sequencing for multilocus sequence typing analysis of a Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia outbreak. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vindrios, W.; Argy, N.; Le Gal, S.; Lescure, F.-X.; Massias, L.; Le, M.P.; Wolff, M.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Nevez, G.; Houze, S. Outbreak of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection among heart transplant recipients: Molecular investigation and management of an interhuman transmission. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokulska, M.; Kicia, M.; Wesołowska, M.; Piesiak, P.; Kowal, A.; Lobo, M.L.; Kopacz, Ż.; Hendrich, A.B.; Matos, O. Genotyping of Pneumocystis jirovecii in colonized patients with various pulmonary diseases. Med. Mycol. 2018, 56, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, G.; Santos, D.W.; Kovacs, J.A.; Nishikaku, A.S.; de Sandes-Freitas, T.V.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Kutty, G.; Affonso, R.; Silva, H.T.; Medina-Pestana, J.O. Genetic diversity of Pneumocystis jirovecii from a cluster of cases of pneumonia in renal transplant patients: Cross-sectional study. Mycoses 2018, 61, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Mirdha, B.R.; Guleria, R.; Kabra, S.K.; Mohan, A.; Chaudhry, R.; Kumar, L.; Dwivedi, S.N.; Agarwal, S.K. Genetic polymorphisms associated with treatment failure and mortality in pediatric Pneumocystosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevez, G.; Guillaud-Saumur, T.; Cros, P.; Papon, N.; Vallet, S.; Quinio, D.; Minoui-Tran, A.; Pilorgé, L.; de Parscau, L.; Sizun, J. Pneumocystis primary infection in infancy: Additional French data and review of the literature. Med. Mycol. 2020, 58, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sürgeç, E.; Can, H.; Döşkaya, M.; Karakavuk, M.; Atalay Şahar, E.; Değirmenci Döşkaya, A.; Pullukçu, H.; Taşbakan, M.; Sezai Taşbakan, M.; Akyol, D. Genotyping of Pneumocystis jirovecii isolates obtained from clinical samples by multilocus sequencing: A molecular epidemiology study conducted in Turkey. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, S.; Toubas, D.; Totet, A.; Dalle, F.; Abou Bacar, A.; Le Meur, Y.; Nevez, G. Pneumocystis infection outbreaks in organ transplantation units in France: A Nation-wide survey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 2216–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szydłowicz, M.; Jakuszko, K.; Szymczak, A.; Piesiak, P.; Kowal, A.; Kopacz, Ż.; Wesołowska, M.; Lobo, M.L.; Matos, O.; Hendrich, A.B. Prevalence and genotyping of Pneumocystis jirovecii in renal transplant recipients—Preliminary report. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, C.; Zuluaga, A.; Restrepo, A.; Tobón, A.; Cano, L.E.; Gonzalez, A. Molecular diagnosis and detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii DHPS and DHFR genotypes in respiratory specimens from Colombian patients. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 72, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.M.; Meshnick, S.R.; Worodria, W.; Andama, A.; Cattamanchi, A.; Davis, J.L.; Yoo, S.D.; Byanyima, P.; Kaswabuli, S.; Goodman, C.D. Low prevalence of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) but high prevalence of Pneumocystis dihydropteroate synthase (dhps) gene mutations in HIV-infected persons in Uganda. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fahle, G.A.; Kovacs, J.A. Inability to culture Pneumocystis jirovecii. MBio 2018, 9, e00939-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, P.; Lavrard, I.; Poirot, J.L.; Chouaid, C.; Denis, M.; Olivier, J.L.; Nigou, M.; Miltgen, M. Usefulness of PCR for detection of Pneumocystis carinii DNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 2324–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, T.; Ma, Z.; Liu, F.; Du, W.-Q.; He, L.; Ma, L.; An, C.-L. Genotyping of Pneumocystis jirovecii by use of a new simplified nomenclature system based on the internal transcribed spacer regions and 5.8S rRNA gene of the rRNA operon. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, C.; Buitrago, M.J.; Gits-Muselli, M.; Benazra, M.; Sturny-Leclère, A.; Hamane, S.; Guigue, N.; Bretagne, S.; Alanio, A. Copy number variation of mitochondrial DNA genes in Pneumocystis jirovecii according to the fungal load in BAL specimens. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanio, A.; Gits-Muselli, M.; Mercier-Delarue, S.; Dromer, F.; Bretagne, S. Diversity of Pneumocystis jirovecii during infection revealed by ultra-deep pyrosequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Cissé, O.H.; Kovacs, J.A. A molecular window into the biology and epidemiology of Pneumocystis spp. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahimana, A.; Francioli, P.; Blanc, D.S.; Bille, J.; Wakefield, A.E.; Hauser, P.M. Determination of the copy number of the nuclear rDNA and Beta-tubulin genes of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis using PCR multicompetitors. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2000, 47, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancart, F.; Rodriguez-Villalobos, H.; Fonteyne, P.-A.; Peres-Bota, D.; Liesnard, C. Quantitative TaqMan PCR for detection of Pneumocystis jiroveci. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 61, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morilla, R.; González-Magaña, A.; Friaza, V.; de Armas, Y.; Medrano, F.J.; Calderón, E.; de la Horra, C. Genetic polymorphisms of Superoxide Dismutase locus of Pneumocystis jirovecii in Spanish population. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Crothers, K.; Atzori, C.; Benfield, T.; Miller, R.; Rabodonirina, M.; Helweg-Larsen, J. Dihydropteroate synthase gene mutations in Pneumocystis and sulfa resistance. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahimana, A.; Rabodonirina, M.; Bille, J.; Francioli, P.; Hauser, P.M. Mutations of Pneumocystis jirovecii Dihydrofolate reductase associated with failure of prophylaxis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4301–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, O.; Esteves, F. Pneumocystis jirovecii multilocus gene sequencing: Findings and implications. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Esteves, F.; Antunes, F.; Matos, O. Genetic characterization of the Dihydrofolate reductase gene of Pneumocystis jirovecii isolates from Portugal. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 1246–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunkin, S.M.; Stringer, J.R. Translocation of surface antigen genes to a unique telomeric expression site in Pneumocystis carinii. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 19, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procop, G.W.; Haddad, S.; Quinn, J.; Wilson, M.L.; Henshaw, N.G.; Reller, L.B.; Artymyshyn, R.L.; Katanik, M.T.; Weinstein, M.P. Detection of Pneumocystis jiroveci in respiratory specimens by four staining methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3333–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakefield, A.E.; Pixley, F.J.; Banerji, S.; Sinclair, K.; Miller, R.F.; Moxon, E.R.; Hopkin, J.M. Amplification of mitochondrial ribosomal RNA sequences from Pneumocystis carinii DNA of rat and human origin. Mol. Biochem. 1990, 43, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.E.; Scesney, P.E. Visibility of Critical-Exponent Renormalization. Phys. Rev. A 1970, 3, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, D.; Michalak, I. raxmlGUI: A graphical front-end for RAxML. Org. Divers. Evol. 2012, 12, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, M.G.J.; de Fijter, J.W.; Kroon, F.P. Outbreaks and clustering of Pneumocystis pneumonia in kidney transplant recipients: A systematic review. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Han, A.; Lee, H.; Ha, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Han, S.S. Impact of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia on kidney transplant outcome. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanio, A.; Hauser, P.M.; Lagrou, K.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Helweg-Larsen, J.; Matos, O.; Cesaro, S.; Maschmeyer, G.; Einsele, H.; Donnelly, J.P. ECIL guidelines for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with haematological malignancies and stem cell transplant recipients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanio, A.; Desoubeaux, G.; Sarfati, C.; Hamane, S.; Bergeron, A.; Azoulay, E.; Molina, J.M.; Derouin, F.; Menotti, J. Real-time PCR assay-based strategy for differentiation between active Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization in immunocompromised patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ling, G.; Qiang, C.; Ming, Q.; Wu, C.; Wang, K.; Ying, Z. PCR diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia: A bivariate meta-analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 4361–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P.R.; Gaston, M.A. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: An application of Simpson’s index of diversity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 2465–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, S.; Damiani, C.; Rouillé, A.; Grall, A.; Tréguer, L.; Virmaux, M.; Moalic, E.; Quinio, D.; Moal, M.-C.; Berthou, C. A cluster of Pneumocystis infections among renal transplant recipients: Molecular evidence of colonized patients as potential infectious sources of Pneumocystis jirovecii. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, e62–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helweg-Larsen, J.; Benfield, T.L.; Eugen-Olsen, J.; Lundgren, J.D.; Lundgren, B. Effects of mutations in Pneumocystis carinii Dihydropteroate synthase gene on outcome of AIDS-associated P. carinii pneumonia. Lancet 1999, 354, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, I.; Roderus, L.; van Gumpel, E.; Jung, N.; Lehmann, C.; Fätkenheuer, G.; Hartmann, P.; Plum, G.; Rybniker, J. Low prevalence of DHFR and DHPS mutations in Pneumocystis jirovecii strains obtained from a German cohort. Infection 2017, 45, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliades, P.; Meshnick, S.R.; Macreadie, I.G. Mutations in the Pneumocystis jirovecii DHPS gene confer cross-resistance to sulfa drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, C.A.; Chabé, M.; George, C.; Cárdenas, A.; Durán, L.; Guerrero, J.; Bustamante, R.; Matos, O.; Huang, L.; Miller, R.F. High prevalence of Pneumocystis jirovecii Dihydropteroate synthase gene mutations in patients with a first episode of Pneumocystis pneumonia in Santiago, Chile, and clinical response to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01290-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabodonirina, M.; Nahimana, A.; Weber, R.; Francioli, P.; Bille, J.; Hauser, P.M. Geographical variation in the prevalence of Pneumocystis jirovecii Dihydropteroate synthase mutations within Western Europe. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2006, 53, S112–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
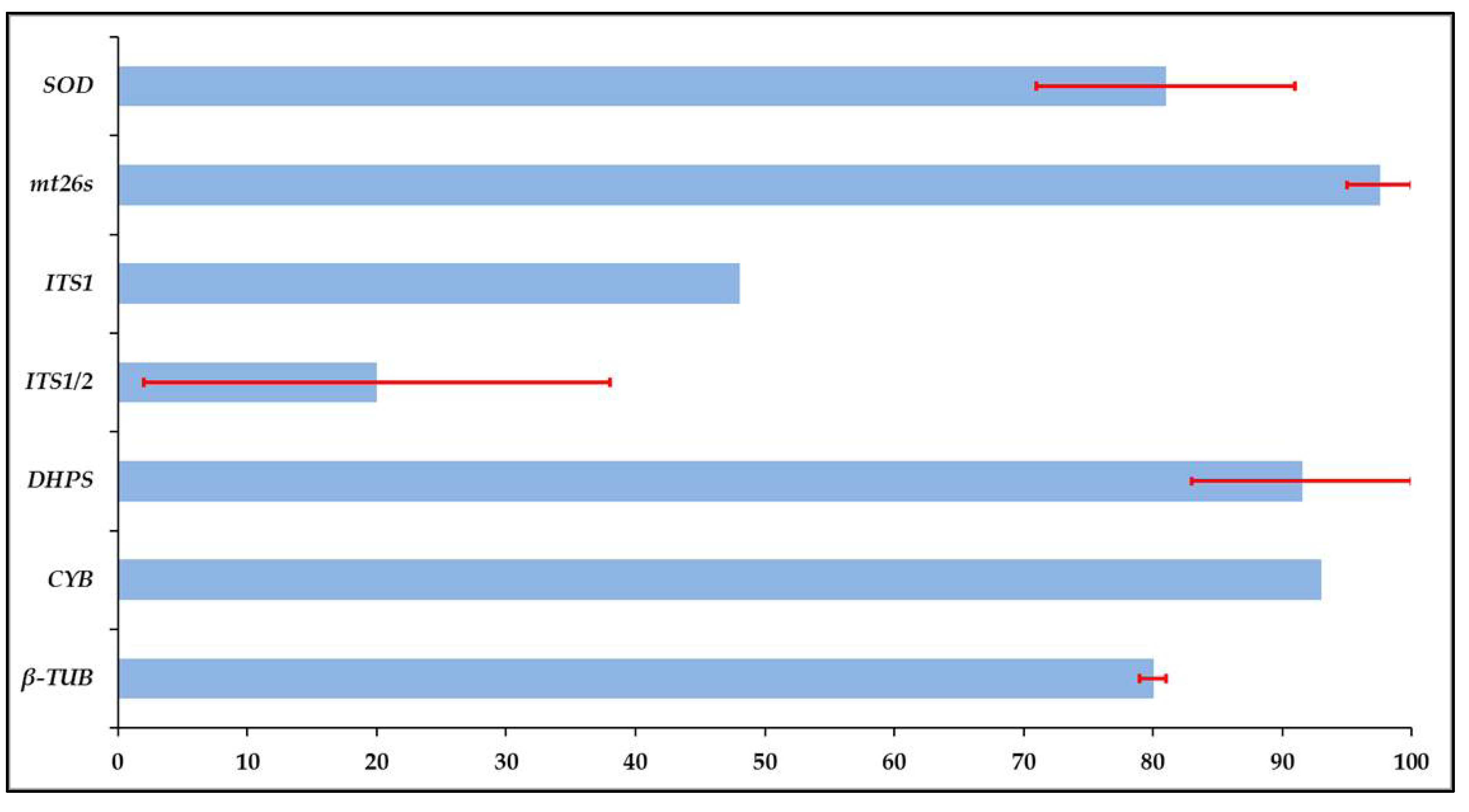
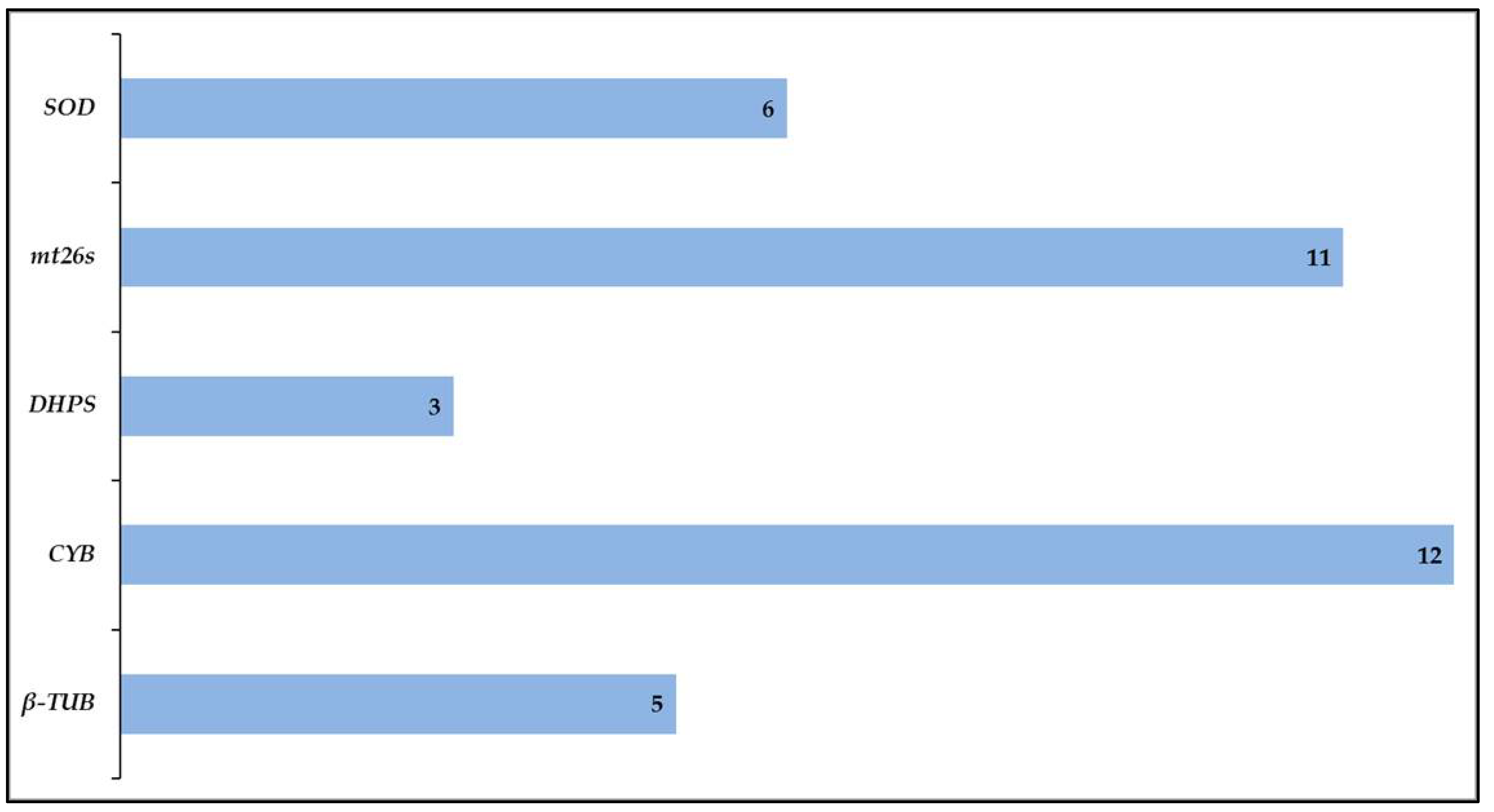

| Schemes (Included Loci) and Reference | Country | Total # of Samples | # of Samples Sequenced | # of Sequence Types | Genetic Locus | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.8S | 18S | 23S | 26S | ITS1 | ITS2 | ITS1/2 | msg | mt26S | β-TUB | TS | arom/EPSP | mtSSU | DHPS | UCS | Kex1 | CYB | SOD | DHRF | TRR1 | |||||
| Scheme 1 (5.8S, 18S, 26S, ITS1, ITS2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [6] | USA | 15 | 15 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | NG | ||||||||||||||
| [7] | GBR | 24 | 24 | NG | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 7 | NG | ||||||||||||||
| Scheme 2 (ITS1, ITS2, msg, mt26S) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [8] | USA | 15 | 15 | NG | NG | NG | NG | NG | ||||||||||||||||
| [38] | IND | 180 | 29 | NG | NG | NG | NG | NG | ||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 3 (26S, β-TUB, ITS1, mt26S) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [9] | CHE | 11 | 11 | NG | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| [20] | EUR | 212 | 212 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| [19] | EUR | 91 | 91 | 28 | NG | NG | NG | NG | ||||||||||||||||
| [33] | DEU | 7 | 7 | 2 | NG | NG | NG | NG | ||||||||||||||||
| [42] | DEU | 20 | 14 | NG | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| [43] | CHE | 19 | 7 | 1(+) | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| [50] | DE | 18 | 18 | NG | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| [53] | GBR | 670 | 31 | NG | NA | 5 | 4 | NA | ||||||||||||||||
| [54] | FRA | 13 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 4 (ITS1, ITS2, mt26S) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [10] | USA | 15 | 15 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| [11] | SWE, FRA | 7 | 7 | NG | 4 | 4 | NG | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| [48] | GBR | 27 | 27 | NG | NG | NG | 2 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 5 (5.8S, ITS1, ITS2, mt26S, TS) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [12] | FRA, ITA | 20 | 18 | NG | 6 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 4 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Scheme 6 (arom, ITS1, ITS2, mt26S, mtSSU) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [13] | NLD | 6 | 6 | NG | NG | NG | 9 | 3 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||
| Scheme 7 (ITS1, ITS2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [14] | GLO | 207 | 207 | NG | 15 | 14 | NG | |||||||||||||||||
| [18] | JPN | 24 | 24 | NG | 11 | 11 | NG | |||||||||||||||||
| [31] | ZAF | 20 | 20 | NG | 11 | 13 | NG | |||||||||||||||||
| [49] | SWE | 64 | 64 | 12 | 10 | 12 | NG | |||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 8 (DHPS, ITS1, ITS2, mt26S) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [15] | FRA | 14 | 14 | NG | NG | NG | NG | NG | NG | |||||||||||||||
| [39] | PRT, ESP | 108 | ✕ | NG | 12 | 10 | NG | 4 | 4 | |||||||||||||||
| [44] | AUS | 68 | 68 | NG | 8 | 9 | 16 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Scheme 9 (DHFR, DHPS) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [16] | USA | 37 | 37 | NG | 4 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| [32] | FRA | 33 | 33 | NG | 3 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| [40] | THA | 29 | 18 | NG | 3 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| [71] | USA | 13 | 13 | NG | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| [70] | COL | 98 | 45 | NG | 4 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 10 (DHPS, mt26S) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [17] | USA | 324 | 191 | 14 | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| [26] | ESP | 255 | 79 | NG | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| [34] | ESP | 50 | 12 | NG | 4 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| [35] | USA | 442 | ❋ | NG | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| [45] | ESP | 60 | 19 | NG | 3 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| [51] | ITA | 67 | ⚑ | NG | 4 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 11 (26S, β-TUB, DHPS, ITS1, mt26S) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [21] | USA | 22 | 22 | 10 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Scheme 12 (26S, β-TUB, ITS1, ITS2, mt26S) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [22] | ITA | 25 | 18 | 15 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Scheme 13 (DHPS, ITS1, ITS2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [23] | USA | 57 | 37 | NG | 6 | 7 | NG | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| [27] | PRT | 43 | 43 | NG | 15 | 14 | 17 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| [36] | ITA | 261 | 174 | NG | NG | NG | 9 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 14 (CYB, DHFR, DHPS) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [24] | JPN | 34 | 34 | NG | 4 | 2 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 15 (DHPS, ITS1, ITS2, mtSSU) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [25] | GBR | 2 | 2 | NG | NG | NG | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Scheme 16 (DHPS, mt26S, mtSSU) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [28] | GBR, ZWE | 51 | 30 | NG | 3 | 4 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 17 (DHPS, mtSSU, mt26S, SOD) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [29] | GBR | 16 | 16 | NG | NG | NG | NG | NG | ||||||||||||||||
| [30] | NG | 76 | 76 | 15 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 18 (DHFR, DHPS, ITS1, ITS2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [37] | PRT | 68 | 68 | NG | NG | NG | 19 | 4 | 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Scheme 19 (UCS, Kex1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [39] | PRT | 87 | 35 | NG | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 20 (CYB, DHFR, DHPS, mt26S, SOD) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [46] | PRT | 102 | 78 | NG | 9 | 6 | 3 | 6 | 6 | |||||||||||||||
| Scheme 21 (β-TUB, CYB, DHFR, DHPS, mt26S, TRR1, TS, SOD) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [47] | PRT | 70 | ► | 48 | 5 | 3 | ⌘ | 3 | 7 | 4 | 3 | ⌘ | ||||||||||||
| Scheme 22 (β-TUB, DHPS, ITS1/2, mt26S) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [3] | AUS | 11 | 11 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| [55] | AUS | 48 | 48 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| [57] | AUS | 7 | 7 | NG | NG | NG | NG | NG | ||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 23 (mt26S, mtSSU) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [52] | FRA, CUB, ESP | 75 | 75 | NG | 5 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 24 (26S, β-TUB, CYB, DHFR, DHPS, ITS1, mt26S, SOD) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [5] | FRA | 23 | 23 | NG | 7 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 3 | ||||||||||||
| Scheme 25 (26S, ITS1, ITS2, mt26S) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [56] | DNK | 22 | 18 | 3 | NG | NG | NG | NG | NG | |||||||||||||||
| Scheme 26 (CYB, ITS1, mt26S, SOD) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [58] | FRA | 37 | 32 | NG | NG | NG | NG | NG | ||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 27 (β-TUB, CYB, DHFR, mt26S, SOD) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [59] | BEL | 20 | 20 ^ | NG | NA | 4 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||
| Scheme 28 (CYB, mt26S, SOD) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [60] | FRA | 24 | ◎ | 14 | 6 | 5 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| [61] | FRA | 32 | 32 | 18 | 22 | 14 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
| [62] | FRA | 7 | 7 | NG | 4 | 3 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| [63] | POL | 17 | ◉ | 8 | 13 | 6 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| [66] | FRA | 192 | 35 | 17 | 11 | 5 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| [67] | TUR | 31 | 26 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| [68] | REU, GUF, FRA | 47 | 47 | 23 | 5 | 9 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 29 (23S, 26S, DHPS) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [64] | BRA | 30 | 30 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Scheme 30 (DHFR, DHPS, mt26S) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [65] | IND | 37 | 37 | 13 | 3 | 3 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Scheme31 (CYB, DHPS, mt26S, SOD) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [69] | POL | 72 | N/A | N/A | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| Locus | Primer Name | Ref. | Nucleotide Sequence | Product Size (Base Pairs) | PCR Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-TUB | PneumoβTub_F | - | 5′-TCATTAGGTGGTGGAACGGG-3′ | 303 | 95 °C 3 min; 45 cycles: 94 °C 30 s, 60 °C 45 s, 72 °C 45 s; 72 °C 7 min |
| PneumoβTub_R | 5′-ATCACCATATCCTGGATCCG-3′ | ||||
| SOD | MnSODFw | 5 | 5′-GGGTTTAATTAGTCTTTTTAGGCAC-3′ | 602 | |
| MnSODRw | 5′-CATGTTCCCACGCATCCTAT-3′ | ||||
| CYB | CytbFw | 5 | 5′-CCCAGAATTCTCGTTTGGTCTATT-3′ | 579 | 95 °C 3 min; 45 cycles: 94 °C 30 s, 55 °C 45 s, 72 °C 45 s; 72 °C 7 min |
| CytbRw | 5′-AAGAGGTCTAAAAGCAGAACCTCAA-3′ | ||||
| mt26S | PneumoLSU_F | - | 5′-TCAGGTCGAACTGGTGTACG-3′ | 297 | |
| PneumoLSU_R | 5′-TGTTCCAAGCCCACTTCTT-3′ |
| Strain Number | Country of Origin | Date of Sample | β-TUB | CYB | mt26S | SOD | Sequence Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HVH21 | Spain | Jan 2015 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | ST21 |
| HVH22 | Spain | Jan 2015 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | ST21 |
| Case 63 | Australia | Dec 2016 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4 | ST42 |
| Case 71 | New Zealand | May 2017 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 | ST44 |
| 1794 | Chile | Feb 2011 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 1 | ST7 |
| 2165 | Chile | Oct 2014 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | ST2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pasic, L.; Goterris, L.; Guerrero-Murillo, M.; Irinyi, L.; Kan, A.; Ponce, C.A.; Vargas, S.L.; Martin-Gomez, M.T.; Meyer, W. Consensus Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Pneumocystis jirovecii. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040259
Pasic L, Goterris L, Guerrero-Murillo M, Irinyi L, Kan A, Ponce CA, Vargas SL, Martin-Gomez MT, Meyer W. Consensus Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Pneumocystis jirovecii. Journal of Fungi. 2020; 6(4):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040259
Chicago/Turabian StylePasic, Lana, Lidia Goterris, Mercedes Guerrero-Murillo, Laszlo Irinyi, Alex Kan, Carolina A. Ponce, Sergio L. Vargas, M. Teresa Martin-Gomez, and Wieland Meyer. 2020. "Consensus Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Pneumocystis jirovecii" Journal of Fungi 6, no. 4: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040259
APA StylePasic, L., Goterris, L., Guerrero-Murillo, M., Irinyi, L., Kan, A., Ponce, C. A., Vargas, S. L., Martin-Gomez, M. T., & Meyer, W. (2020). Consensus Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Pneumocystis jirovecii. Journal of Fungi, 6(4), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040259






