Airway Mycosis and the Regulation of Type 2 Immunity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Spectrum of Allergic Airway Disease
3. Proteinases and Their Sources
4. Fungal Infections in Allergic Airway Disease
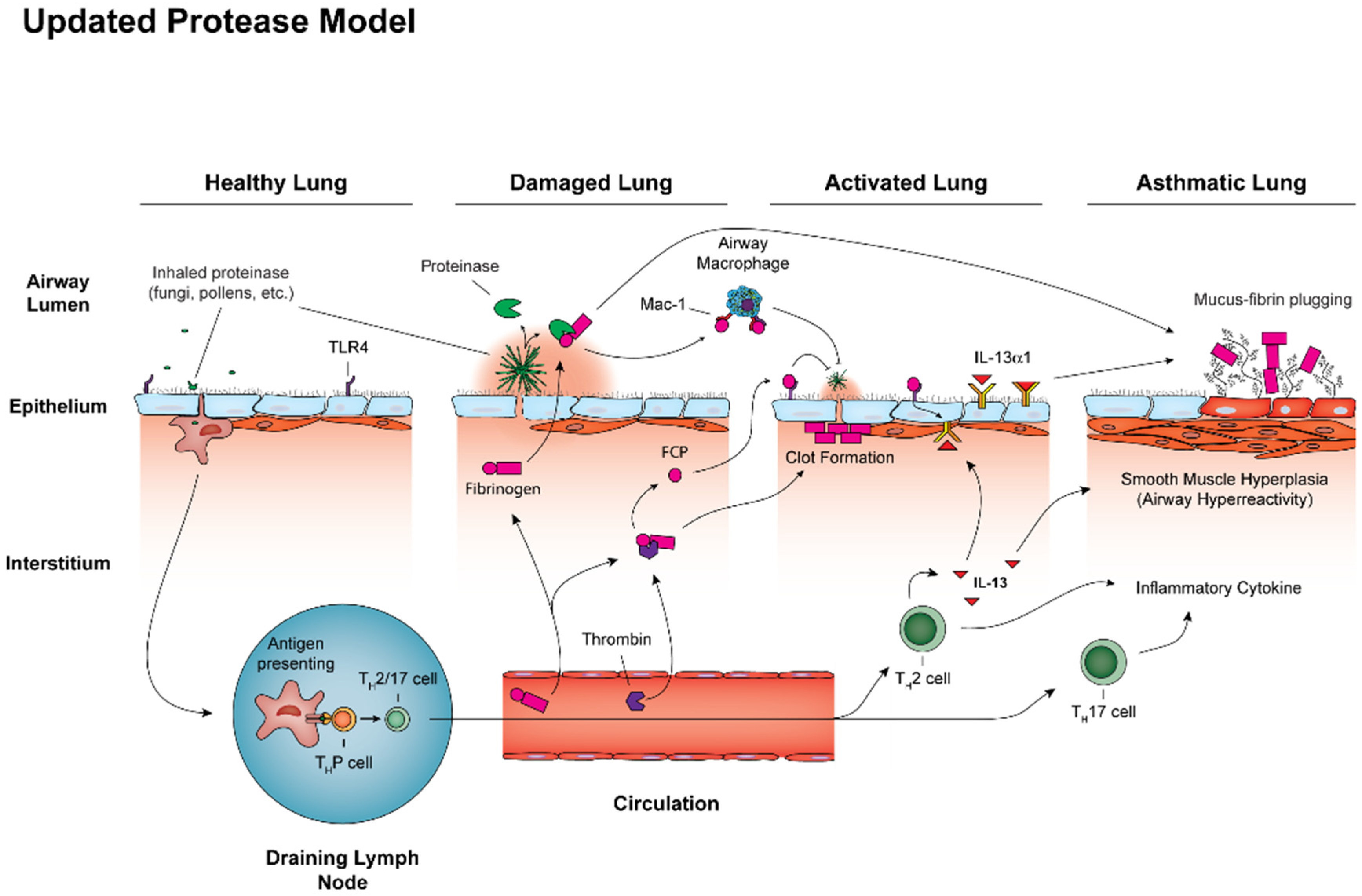
5. Proteolytic Induction of Type 2 Immunity
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, E.; Knight, J.M.; Wu, Y.; Luong, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Kheradmand, F.; Corry, D.B. Airway mycosis in allergic airway disease. Adv. Immunol. 2019, 142, 85–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudarri, D.H. Valuing the Economic Costs of Allergic Rhinitis, Acute Bronchitis, and Asthma from Exposure to Indoor Dampness and Mold in the US. J. Environ. Public Health 2016, 2016, 2386596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, H.Y.; Li, E.; Landers, C.; Nguyen, A.; Kheradmand, F.; Knight, J.M.; Corry, D.B. Advances and Evolving Concepts in Allergic Asthma. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 39, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunig, G.; Warnock, M.; Wakil, A.E.; Venkayya, R.; Brombacher, F.; Rennick, D.M.; Sheppard, D.; Mohrs, M.; Donaldson, D.D.; Locksley, R.M.; et al. Requirement for IL-13 independently of IL-4 in experimental asthma. Science 1998, 282, 2261–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills-Karp, M.; Luyimbazi, J.; Xu, X.; Schofield, B.; Neben, T.Y.; Karp, C.L.; Donaldson, D.D. Interleukin-13: Central mediator of allergic asthma. Science 1998, 282, 2258–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.; Ford, L.; Pearlman, D.; Spector, S.; Sher, L.; Skobieranda, F.; Wang, L.; Kirkesseli, S.; Rocklin, R.; Bock, B.; et al. Dupilumab in persistent asthma with elevated eosinophil levels. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2455–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepys, J. Immunological and clinical findings in workers and consumers exposed to enzymes of Bacillus subtilis. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1973, 66, 930–932. [Google Scholar]
- Pepys, J.; Wells, I.D.; D’Souza, M.F.; Greenberg, M. Clinical and immunological responses to enzymes of Bacillus subtilis in factory workers and consumers. Clin. Allergy 1973, 3, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailhofer, G.; Wilders-Truschnig, M.; Smolle, J.; Ludvan, M. Asthma caused by bromelain: An occupational allergy. Clin. Allergy 1988, 18, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, J.; Brand, S. Occupational asthma after inhalation of dust of the proteolytic enzyme, papain. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1975, 32, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, H.; Takai, T.; Ikeda, S.; Okumura, K.; Ogawa, H. Protease activity of allergenic pollen of cedar, cypress, juniper, birch and ragweed. Allergol. Int. 2008, 57, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vliagoftis, H.; Forsythe, P. Should we target allergen protease activity to decrease the burden of allergic airway inflammation? Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2008, 7, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, S.; Angkasekwinai, P.; Shan, M.; Greenlee, K.J.; Barranco, W.T.; Polikepahad, S.; Seryshev, A.; Song, L.Z.; Redding, D.; Singh, B.; et al. Divergent functions for airway epithelial matrix metalloproteinase 7 and retinoic acid in experimental asthma. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrol, C.; Duval, A.; Schmitt, P.; Roga, S.; Camus, M.; Stella, A.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Gonzalez-de-Peredo, A.; Girard, J.P. Environmental allergens induce allergic inflammation through proteolytic maturation of IL-33. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Winton, H.L.; Soeller, C.; Tovey, E.R.; Gruenert, D.C.; Thompson, P.J.; Stewart, G.A.; Taylor, G.W.; Garrod, D.R.; Cannell, M.B.; et al. Der p 1 facilitates transepithelial allergen delivery by disruption of tight junctions. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, F.; Kiss, A.; Xu, J.; Lee, S.H.; Kolattukudy, P.E.; Corry, D.B. A protease-activated pathway underlying Th cell type 2 activation and allergic lung disease. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 5904–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, A.; Montes, M.; Susarla, S.; Jaensson, E.A.; Drouin, S.M.; Wetsel, R.A.; Yao, Z.; Martin, R.; Hamzeh, N.; Adelagun, R.; et al. A new mechanism regulating the initiation of allergic airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamhamedi-Cherradi, S.-E.; Martin, R.E.; Ito, T.; Kheradmand, F.; Corry, D.B.; Liu, Y.-J.; Moyle, M. Fungal proteases induce Th2 polarization through limited dendritic cell maturation and reduced production of IL-12. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 6000–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, C.L.; Barton, G.M.; Farr, A.G.; Medzhitov, R. A mechanism for the initiation of allergen-induced T helper type 2 responses. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, V.T.; Arora, N.; Singh, B.P. Serine protease activity of Per a 10 augments allergen-induced airway inflammation in a mouse model. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.; Kukreja, N.; Singh, B.P.; Arora, N. Serine protease activity of Cur l 1 from Curvularia lunata augments Th2 response in mice. J. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 29, 292–302. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Lee, S.H.; Porter, P.; Xu, C.; Ohno, A.; Atmar, R.L.; Greenberg, S.B.; Bandi, V.; Gern, J.; Amineva, S.; et al. Human rhinovirus proteinase 2A induces TH1 and TH2 immunity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arizmendi, N.G.; Abel, M.; Mihara, K.; Davidson, C.; Polley, D.; Nadeem, A.; El Mays, T.; Gilmore, B.F.; Walker, B.; Gordon, J.R.; et al. Mucosal allergic sensitization to cockroach allergens is dependent on proteinase activity and proteinase-activated receptor-2 activation. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3164–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boitano, S.; Flynn, A.N.; Sherwood, C.L.; Schulz, S.M.; Hoffman, J.; Gruzinova, I.; Daines, M.O. Alternaria alternata serine proteases induce lung inflammation and airway epithelial cell activation via PAR2. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2011, 300, L605–L614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millien, V.O.; Lu, W.; Shaw, J.; Yuan, X.; Mak, G.; Roberts, L.; Song, L.Z.; Knight, J.M.; Creighton, C.J.; Luong, A.; et al. Cleavage of fibrinogen by proteinases elicits allergic responses through Toll-like receptor 4. Science 2013, 341, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balenga, N.A.; Klichinsky, M.; Xie, Z.; Chan, E.C.; Zhao, M.; Jude, J.; Laviolette, M.; Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Druey, K.M. A fungal protease allergen provokes airway hyper-responsiveness in asthma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, P.; Susarla, S.C.; Polikepahad, S.; Qian, Y.; Hampton, J.; Kiss, A.; Vaidya, S.; Sur, S.; Ongeri, V.; Yang, T.; et al. Link between allergic asthma and airway mucosal infection suggested by proteinase-secreting household fungi. Mucosal Immunol. 2009, 2, 504–517. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, P.; Polikepahad, S.; Qian, Y.; Knight, J.M.; Lu, W.; Tai, W.M.; Roberts, L.; Ongeri, V.; Yang, T.; Seryshev, A.; et al. Respiratory tract allergic disease and atopy: Experimental evidence for a fungal infectious etiology. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49, S158–S163. [Google Scholar]
- Pepys, J.; Longbottom, J.L.; Hargreave, F.E.; Faux, J. Allergic reactions of the lungs to enzymes of Bacillus subtilis. Lancet 1969, 1, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, X.; Fruhmann, G. Allergic reactions, including asthma, to the pineapple protease bromelain following occupational exposure. Clin. Allergy 1979, 9, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.J.; Mackenzie, J.W.; Uhlman, W.E.; Edelman, N.H. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: Evidence of limited tissue invasion. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1975, 111, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patterson, R.; Rosenberg, M.; Roberts, M. Evidence that Aspergillus fumigatus growing in the airway of man can be a potent stimulus of specific and nonspecific IgE formation. Am. J. Med. 1977, 63, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, G.; Porter, P.C.; Bandi, V.; Kheradmand, F.; Corry, D.B. Tracheobronchial mycosis in a retrospective case-series study of five status asthmaticus patients. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 146, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Porter, P.C.; Lim, D.J.; Maskatia, Z.K.; Mak, G.; Tsai, C.L.; Citardi, M.J.; Fakhri, S.; Shaw, J.L.; Fothergil, A.; Kheradmand, F.; et al. Airway surface mycosis in chronic TH2-associated airway disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.; Tsai, C.-L.; Maskatia, Z.K.; Kakkar, E.; Porter, P.; Rossen, R.D.; Perusich, S.; Knight, J.M.; Kheradmand, F.; Corry, D.B. Benefits of Antifungal Therapy in Asthma Patients with Airway Mycosis: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2018, 6, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, P.; Fields, A.; Qian, Y.; Abramson, S.; Delclos, G.L.; Kheradmand, F.; Corry, D.B. Necessary and sufficient role for T helper cells to prevent fungal dissemination during mucosal airway infection. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 4459–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; O’Driscoll, B.R.; Powell, G.; Chew, F.; Atherton, G.T.; Vyas, A.; Miles, J.; Morris, J.; Niven, R.M. Randomized controlled trial of oral antifungal treatment for severe asthma with fungal sensitization: The Fungal Asthma Sensitization Trial (FAST) study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, G.W., Jr.; Woodfolk, J.A.; Hayden, M.L.; Jackson, S.; Platts-Mills, T.A. Treatment of late-onset asthma with fluconazole. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, H.; Chieppa, M.; Perros, F.; Willart, M.A.; Germain, R.N.; Lambrecht, B.N. House dust mite allergen induces asthma via Toll-like receptor 4 triggering of airway structural cells. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 410–416. [Google Scholar]
- Trompette, A.; Divanovic, S.; Visintin, A.; Blanchard, C.; Hegde, R.S.; Madan, R.; Thorne, P.S.; Wills-Karp, M.; Gioannini, T.L.; Weiss, J.P.; et al. Allergenicity resulting from functional mimicry of a Toll-like receptor complex protein. Nature 2009, 457, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gai, Q.; Lin, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Jinxiang, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Liang, D. House dust mite regulate the lung inflammation of asthmatic mice through TLR4 pathway in airway epithelial cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2010, 28, 597–603. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayasekaran, D.; Sambandam, A.P.; Gowrishankar, N.C. Acute plastic bronchitis. Indian Pediatr. 2004, 41, 1257–1259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hodgkinson, C.P.; Patel, K.; Ye, S. Functional Toll-like receptor 4 mutations modulate the response to fibrinogen. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arnot, C.J.; Gay, N.J.; Gangloff, M. Molecular mechanism that induces activation of Spatzle, the ligand for the Drosophila Toll receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 19502–19509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Landers, C.T.; Tung, H.Y.; Knight, J.M.; Madison, M.C.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Porter, P.C.; Rodriguez, A.; Flick, M.J.; Kheradmand, F.; et al. Selective cleavage of fibrinogen by diverse proteinases initiates innate allergic and antifungal immunity through CD11b. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 8834–8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flick, M.J.; Du, X.; Witte, D.P.; Jirouskova, M.; Soloviev, D.A.; Busuttil, S.J.; Plow, E.F.; Degen, J.L. Leukocyte engagement of fibrin(ogen) via the integrin receptor alphaMbeta2/Mac-1 is critical for host inflammatory response in vivo. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1596–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, T.; Garrigo, J.; Danta, I. Preventing bronchoconstriction in exercise-induced asthma with inhaled heparin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ceyhan, B.; Celikel, T. Effect of inhaled heparin on methacholine-induced bronchial hyperreactivity. Chest 1995, 107, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eisenbarth, S.C.; Piggott, D.A.; Huleatt, J.W.; Visintin, I.; Herrick, C.A.; Bottomly, K. Lipopolysaccharide-enhanced, toll-like receptor 4-dependent T helper cell type 2 responses to inhaled antigen. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, A.G.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Q.F.; Zhao, Y.M.; Li, D.D.; Shi, X.Y.; Zhao, J.J. A toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) variant is associated with asthma severity. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 7849–7854. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Xie, X.; Song, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wu, X.; Su, X.; Yang, L.; Li, M. Association of TLR4 (896A/G and 1196C/T) Gene Polymorphisms with Asthma Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 3591–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knight, J.M.; Wu, Y.; Mauk, K.; Weatherhead, J.; Anvari, S.; Kheradmand, F.; Corry, D.B. Airway Mycosis and the Regulation of Type 2 Immunity. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6020074
Knight JM, Wu Y, Mauk K, Weatherhead J, Anvari S, Kheradmand F, Corry DB. Airway Mycosis and the Regulation of Type 2 Immunity. Journal of Fungi. 2020; 6(2):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6020074
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnight, John Morgan, Yifan Wu, Kelsey Mauk, Jill Weatherhead, Sara Anvari, Farrah Kheradmand, and David B. Corry. 2020. "Airway Mycosis and the Regulation of Type 2 Immunity" Journal of Fungi 6, no. 2: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6020074
APA StyleKnight, J. M., Wu, Y., Mauk, K., Weatherhead, J., Anvari, S., Kheradmand, F., & Corry, D. B. (2020). Airway Mycosis and the Regulation of Type 2 Immunity. Journal of Fungi, 6(2), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6020074




