Serial Detection of Circulating Mucorales DNA in Invasive Mucormycosis: A Retrospective Multicenter Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and qPCR Assay
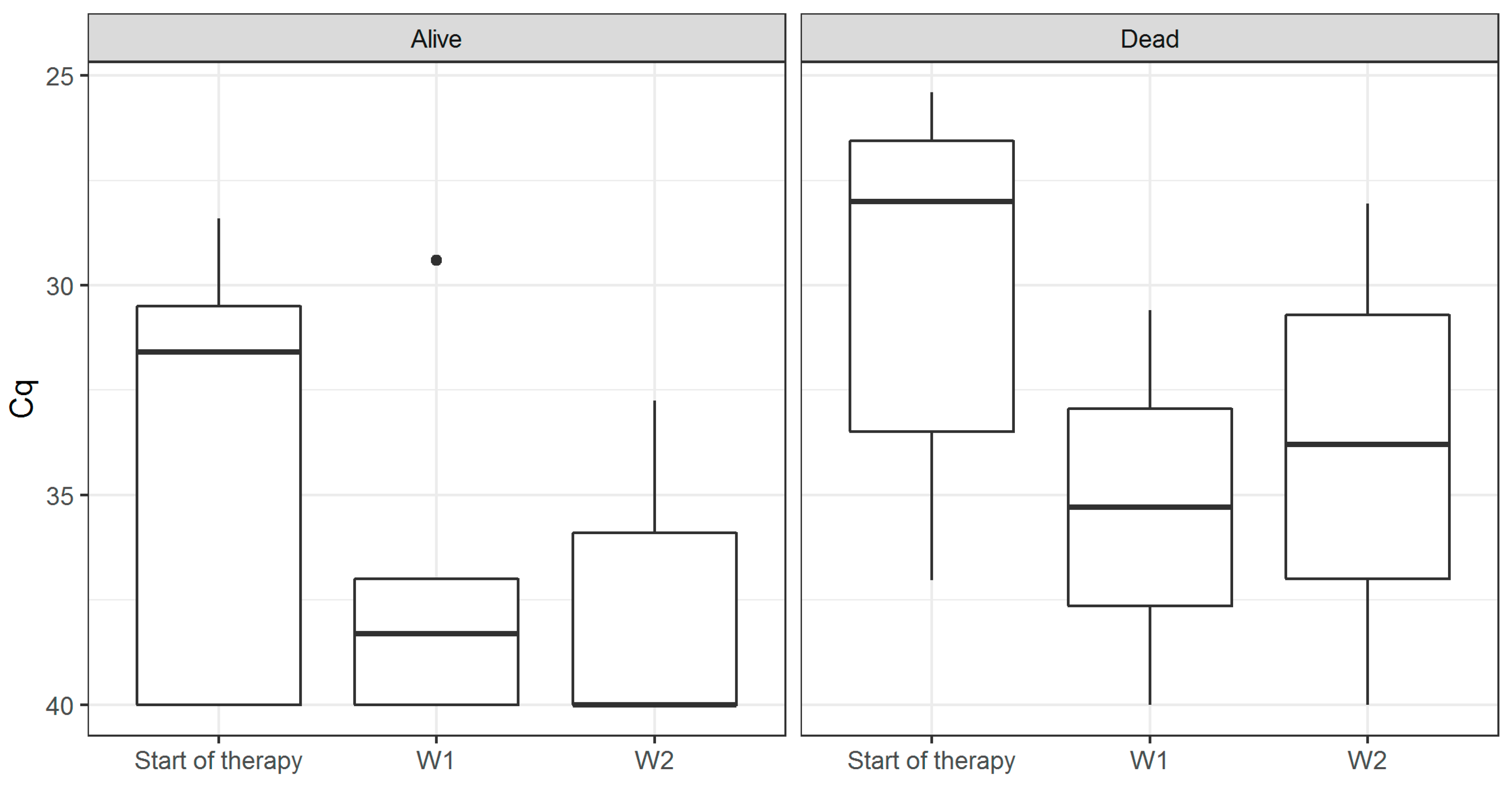
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Yang, H.; Song, J.; Kelkar, S.S.; Yang, X.; Azie, N.; Harrington, R.; Fan, A.; Lee, E.; Spalding, J.R. Prevalence, clinical and economic burden of mucormycosis-related hospitalizations in the United States: A retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saegeman, V.; Maertens, J.; Meersseman, W.; Spriet, I.; Verbeken, E.; Lagrou, K. Increasing Incidence of Mucormycosis in University Hospital, Belgium. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinea, J.; Escribano, P.; Vena, A.; Muñoz, P.; del Carmen Martínez-Jiménez, M.; Padilla, B.; Bouza, E. Increasing incidence of mucormycosis in a large Spanish hospital from 2007 to 2015: Epidemiology and microbiological characterization of the isolates. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tissot, F.; Agrawal, S.; Pagano, L.; Petrikkos, G.; Groll, A.H.; Skiada, A.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Calandra, T.; Viscoli, C.; Herbrecht, R. ECIL-6 guidelines for the treatment of invasive candidiasis, aspergillosis and mucormycosis in leukemia and hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. Haematologica 2017, 102, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornely, O.A.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Dannaoui, E.; Groll, A.H.; Lagrou, K.; Chakrabarti, A.; Lanternier, F.; Pagano, L.; Skiada, A.; Akova, M.; et al. ESCMID and ECMM joint clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and management of mucormycosis 2013. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamilos, G.; Lewis, R.E.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Delaying Amphotericin B–Based Frontline Therapy Significantly Increases Mortality among Patients with Hematologic Malignancy Who Have Zygomycosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélida, H.; Sain, D.; Stajich, J.E.; Bulone, V. Deciphering the uniqueness of Mucoromycotina cell walls by combining biochemical and phylogenomic approaches. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1649–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mery, A.; Sendid, B.; Francois, N.; Cornu, M.; Poissy, J.; Guerardel, Y.; Poulain, D. Application of Mass Spectrometry Technology to Early Diagnosis of Invasive Fungal Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornu, M.; Sendid, B.; Mery, A.; François, N.; Malgorzata, M.; Letscher-Bru, V.; Carolis, E.D.; Damonti, L.; Titecat, M.; Bochud, P.Y.; et al. Evaluation of Mass Spectrometry-Based Detection of Panfungal Serum Disaccharide for Diagnosis of Invasive Fungal Infections: Results from a Collaborative Study Involving Six European Clinical Centers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01867-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Oinuma, K.I.; Niki, M.; Yamagoe, S.; Miyazaki, Y.; Asai, K.; Yamada, K.; Hirata, K.; Kaneko, Y.; Kakeya, H. Identification of a Novel Rhizopus-specific Antigen by Screening with a Signal Sequence Trap and Evaluation as a Possible Diagnostic Marker of Mucormycosis. Med. Mycol. 2017, 55, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoth, F.; Calandra, T. Early diagnosis of invasive mould infections and disease. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, i19–i28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamilos, G.; Luna, M.; Lewis, R.E.; Bodey, G.P.; Chemaly, R.; Tarrand, J.J.; Safdar, A.; Raad, I.I.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Invasive fungal infections in patients with hematologic malignancies in a tertiary care cancer center: An autopsy study over a 15-year period (1989–2003). Haematologica 2006, 91, 986–989. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Millon, L.; Scherer, E.; Rocchi, S.; Bellanger, A.P. Molecular Strategies to Diagnose Mucormycosis. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, J.; Goldenberger, D.; Schmidt, F.; Weisser, M.; Wehrle-Wieland, E.; Einsele, H.; Frei, R.; Löffler, J. Development and application of two independent real-time PCR assays to detect clinically relevant Mucorales species. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millon, L.; Larosa, F.; Lepiller, Q.; Legrand, F.; Rocchi, S.; Daguindau, E.; Scherer, E.; Bellanger, A.P.; Leroy, J.; Grenouillet, F. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Detection of Circulating DNA in Serum for Early Diagnosis of Mucormycosis in Immunocompromised Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, e95–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, J.; Lackner, M.; Ensinger, C.; Risslegger, B.; Morton, C.O.; Nachbaur, D.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Einsele, H.; Heinz, W.J.; Loeffler, J. Clinical evaluation of a Mucorales-specific real-time PCR assay in tissue and serum samples. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, M.; Gits-Muselli, M.; Boutin, L.; Garcia-Hermoso, D.; Maurel, V.; Soussi, S.; Benyamina, M.; Ferry, A.; Chaussard, M.; Hamane, S.; et al. Detection of Circulating Mucorales DNA in Critically Ill Burn Patients: Preliminary Report of a Screening Strategy for Early Diagnosis and Treatment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1312–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millon, L.; Herbrecht, R.; Grenouillet, F.; Morio, F.; Alanio, A.; Letscher-Bru, V.; Cassaing, S.; Chouaki, T.; Kauffmann-Lacroix, C.; Poirier, P.; et al. Early diagnosis and monitoring of mucormycosis by detection of circulating DNA in serum: Retrospective analysis of 44 cases collected through the French Surveillance Network of Invasive Fungal Infections (RESSIF). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, S.; Mengoli, C.; White, P.; Barnes, R.; Donnelly, P.; Loeffler, J.; Millon, L. An Inter-Laboratory Multi-Centre Evaluation of the Performance of Mucorales PCR Assays When Testing Serum Specimens: A study by the Fungal PCR Initiative and the ModiMucor study group. In Proceedings of the 9th Trends in Medical Mycology, Nice, France, 11–14 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- De Pauw, B.; Walsh, T.J.; Donnelly, J.P.; Stevens, D.A.; Edwards, J.E.; Calandra, T.; Pappas, P.G.; Maertens, J.; Lortholary, O.; Kauffman, C.A.; et al. Revised Definitions of Invasive Fungal Disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann, A.J.; Aguado, J.M.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Denning, D.W.; Groll, A.H.; Lagrou, K.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Lewis, R.E.; Munoz, P.; Verweij, P.E.; et al. Diagnosis and management of Aspergillus diseases: Executive summary of the 2017 ESCMID-ECMM-ERS guideline. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, e1–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.L.; Barnes, R.A.; Springer, J.; Klingspor, L.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Morton, C.O.; Lagrou, K.; Bretagne, S.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Mengoli, C.; et al. Clinical Performance of Aspergillus PCR for Testing Serum and Plasma: A Study by the European Aspergillus PCR Initiative. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2832–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patient | Sex, Age (Years) | Underlying Disease | Localization | Classification | Identification in Culture | Aspergillus Co-Infection | Survival at Week 6 | Survival at Week 12 | Start of Appropriate Therapy, Antifungal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M, 57 | ALL | Disseminated (cutaneous, lung) | Proven | Rhizopus microsporus | Yes (Culture A. fumigatus/A. terreus. BDG > 500 pg/mL. Serum GM 6.0) | Dead | Dead | D+6, L-AmB 10 mg/kg |
| 2 | M, 8 | AML | Disseminated (cerebral, lung) | Probable | Rhizomucor pusillus | No | Alive | Alive | D-2, L-AmB 5 mg/kg |
| 3 | F, 34 | Lung transplant | Lung | Probable | Mucor species | No | Alive | Alive | D+13, L-AmB 5 mg/kg |
| 4 | M, 29 | Lung transplant | Lung | Probable | Rhizopus species | Yes (Culture A. fumigatus) | Alive | Alive | D+32, posaconazole |
| 5 | F, 54 | Crohn’s disease | Sinus | Probable | Lichtheimia species | No | Alive | Alive | D+0, L-AmB 5 mg/kg |
| 6 | F, 50 | COPD | Lung | Proven | Rhizopus rhizopodiformis | Yes (Culture Aspergillus spp., BAL GM 0.5) | Alive | Alive | D+84, isavuconazole |
| 7 | M, 54 | Diabetic ketoacidosis | Lung | Putative | Rhizopus microsporus | Yes (Culture A. fumigatus, BAL GM 5.0) | Alive | Alive | D+8, L-AmB 5 mg/kg |
| 8 | M, 61 | ALL | Disseminated (pleura, pericardium, lungs, myocardium, spleen) | Proven | Rhizomucor pusillus | Yes (Culture A. fumigatus, BAL GM 2.2) | Dead | Dead | D-3, L-AmB 5 mg/kg |
| 9 | M, 58 | AML | Disseminated (lung, liver) | Proven | Lichtheimia species | Yes (Culture and PCR A. fumigatus, BAL GM 5.1, Serum GM 3.9) | Dead | Dead | D-12, L-AmB 5 mg/kg |
| 10 | M, 54 | Lung transplant | Lung | Probable | Rhizopus species | No | Alive | Alive | D-1, posaconazole |
| 11 | M, 78 | MDS | Lung | Putative | Rhizopus species | Yes (Culture A. fumigatus, BAL GM 5.6) | Alive | Alive | D+12, L-AmB 10 mg/kg |
| 12 | M, 66 | Allogeneic SCT | Lung | Probable | Rhizomucor pusillus | No | Alive | Alive | D-1, L-AmB 5 mg/kg |
| 13 | F, 63 | Solid tumor | Lung | Probable | Lichtheimia species | Yes (Culture A. fumigatus, BAL GM 5.1, Serum GM 0.7) | Dead | Dead | None |
| 14 | F, 63 | Aplastic anemia | Disseminated (lung, spleen) | Proven | Rhizopus species | No | Dead | Dead | D+2, ABLC 10 mg/kg |
| 15 | F, 63 | AML | Lung | Proven | Rhizopus species | No | Dead | Dead | D-12, posaconazole |
| 16 | F, 64 | AML | Disseminated (lung, liver, diaphragm) | Proven | Rhizopus microsporus | No | Alive | Alive | D-87, L-AmB 5 mg/kg |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mercier, T.; Reynders, M.; Beuselinck, K.; Guldentops, E.; Maertens, J.; Lagrou, K. Serial Detection of Circulating Mucorales DNA in Invasive Mucormycosis: A Retrospective Multicenter Evaluation. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5040113
Mercier T, Reynders M, Beuselinck K, Guldentops E, Maertens J, Lagrou K. Serial Detection of Circulating Mucorales DNA in Invasive Mucormycosis: A Retrospective Multicenter Evaluation. Journal of Fungi. 2019; 5(4):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5040113
Chicago/Turabian StyleMercier, Toine, Marijke Reynders, Kurt Beuselinck, Ellen Guldentops, Johan Maertens, and Katrien Lagrou. 2019. "Serial Detection of Circulating Mucorales DNA in Invasive Mucormycosis: A Retrospective Multicenter Evaluation" Journal of Fungi 5, no. 4: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5040113
APA StyleMercier, T., Reynders, M., Beuselinck, K., Guldentops, E., Maertens, J., & Lagrou, K. (2019). Serial Detection of Circulating Mucorales DNA in Invasive Mucormycosis: A Retrospective Multicenter Evaluation. Journal of Fungi, 5(4), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5040113






