Central Nervous System Infections Due to Aspergillus and Other Hyaline Molds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aspergillus Species
2.1. Pathogenesis
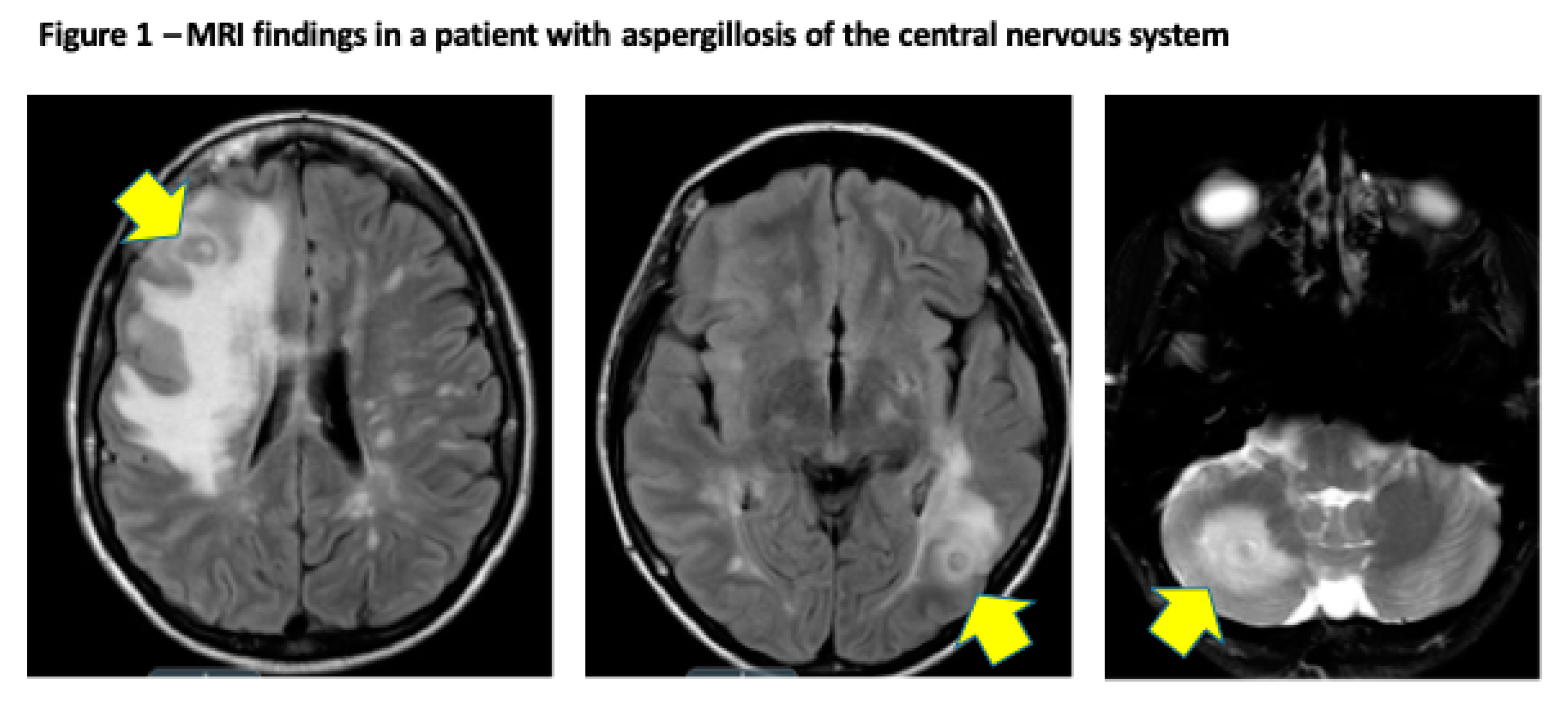
2.2. Clinical Presentation and Outcome
2.3. Diagnosis
2.4. Treatment
3. Other Hyaline Molds
3.1. Fusarium Species
3.2. Scedosporium Species
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patterson, T.F.; Thompson, G.R., 3rd; Denning, D.W.; Fishman, J.A.; Hadley, S.; Herbrecht, R.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Marr, K.A.; Morrison, V.A.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e1–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanganeh, E.; Zarrinfar, H.; Rezaeetalab, F.; Fata, A.; Tohidi, M.; Najafzadeh, M.J.; Alizadeh, M.; Seyedmousavi, S. Predominance of non-fumigatus Aspergillus species among patients suspected to pulmonary aspergillosis in a tropical and subtropical region of the Middle East. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionakis, M.S.; Lewis, R.E.; Torres, H.A.; Albert, N.D.; Raad, I.I.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Increased frequency of non-fumigatus Aspergillus species in amphotericin B or triazole-pre-exposed cancer patients with positive cultures for aspergilli. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2005, 52, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candoni, A.; Klimko, N.; Busca, A.; Di Blasi, R.; Shadrivova, O.; Cesaro, S.; Zannier, M.E.; Verga, L.; Forghieri, F.; Calore, E.; et al. Fungal infections of the central nervous system and paranasal sinuses in onco-haematologic patients. Epidemiological study reporting the diagnostic-therapeutic approach and outcome in 89 cases. Mycoses 2019, 62, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualotto, A.C.; Denning, D.W. Post-operative aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 1060–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.; Guinea, J.; Torres-Narbona, M.; Muñoz, P.; Peláez, T.; Bouza, E. Post-surgical invasive aspergillosis: An uncommon and under-appreciated entity. J. Infect. 2010, 60, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales Zamora, J.A.; Henry, Z.; Gultekin, S.H. Central Nervous System Aspergillosis: An Unexpected Complication following Neurosurgery. Diseases 2018, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.E.; Wiederhold, N.P.; Chi, J.; Han, X.Y.; Komanduri, K.V.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Prince, R.A. Detection of gliotoxin in experimental and human aspergillosis. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.E.; Wiederhold, N.P.; Lionakis, M.S.; Prince, R.A.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Frequency and species distribution of gliotoxin-producing Aspergillus isolates recovered from patients at a tertiary-care cancer center. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 6120–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichner, R.D.; Al Salami, M.; Wood, P.R.; Müllbacher, A. The effect of gliotoxin upon macrophage function. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1986, 8, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, T.; Amitani, R.; Ikegami, Y.; Nawada, R.; Lee, W.J.; Kuze, F. Suppressive effects of Aspergillus fumigatus culture filtrates on human alveolar macrophages and polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Eur. Respir. J. 1996, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.; Hossain, M.A.; German, N.; Al-Ahmad, A.J. Gliotoxin penetrates and impairs the integrity of the human blood-brain barrier in vitro. Mycotoxin Res. 2018, 34, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Economides, M.P.; Ballester, L.Y.; Kumar, V.A.; Jiang, Y.; Tarrand, J.; Prieto, V.; Torres, H.A.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Invasive mold infections of the central nervous system in patients with hematologic cancer or stem cell transplantation (2000–2016): Uncommon, with improved survival but still deadly often. J. Infect. 2017, 75, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadkarni, T.; Goel, A. Aspergilloma of the brain: An overview. J. Postgrad. Med. 2005, 51 (Suppl. 1), S37–S41. [Google Scholar]
- Kourkoumpetis, T.K.; Desalermos, A.; Muhammed, M.; Mylonakis, E. Central nervous system aspergillosis: A series of 14 cases from a general hospital and review of 123 cases from the literature. Medicine 2012, 91, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finelli, P.F.; Gleeson, E.; Ciesielski, T.; Uphoff, D.F. Diagnostic role of target lesion on diffusion-weighted imaging: A case of cerebral aspergillosis and review of the literature. Neurologist 2010, 16, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boes, B.; Bashir, R.; Boes, C.; Hahn, F.; McConnell, J.R.; McComb, R. Central nervous system aspergillosis. Analysis of 26 patients. J. Neuroimaging 1994, 4, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkey, J.; Moritani, T.; Kirby, P. MRI of CNS fungal infections: Review of aspergillosis to histoplasmosis and everything in between. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2014, 24, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, M.; Metta, H.; Villafañe, M.F.; Yampolsky, C.; Schtirbu, R.; Sevlever, G.; Garrido, D. Stereotactic brain biopsy in the diagnosis of focal brain lesions in AIDS. Medicina (B Aires) 2008, 68, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Miceli, M.H.; Maertens, J. Role of Non-Culture-Based Tests, with an Emphasis on Galactomannan Testing for the Diagnosis of Invasive Aspergillosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 36, 650–661. [Google Scholar]
- Reinwald, M.; Buchheidt, D.; Hummel, M.; Duerken, M.; Bertz, H.; Schwerdtfeger, R.; Reuter, S.; Kiehl, M.G.; Barreto-Miranda, M.; Hofmann, W.K.; et al. Diagnostic performance of an Aspergillus-specific nested PCR assay in cerebrospinal fluid samples of immunocompromised patients for detection of central nervous system aspergillosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbert, S.; Brossas, J.Y.; Palous, M.; Joly, I.; Meyer, I.; Fekkar, A. Performance of Aspergillus PCR in cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnosis of cerebral aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 889.e1–889.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, G.M.; Maertens, J.A.; Lagrou, K.; Driessen, G.J.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Rijnders, B.J. Diagnostic Performance of Galactomannan Antigen Testing in Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, J.L.; Thakur, K.T.; Lee, R.; Watkins, T.; Pardo, C.A.; Carson, K.A.; Markley, B.; Finkelman, M.A.; Marr, K.A.; Roos, K.L.; et al. Utility of measuring (1,3)-β-d-glucan in cerebrospinal fluid for diagnosis of fungal central nervous system infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, C.M.; Chen, T.K.; Toussi, S.S.; DeLaMora, P.; Petraitiene, R.; Finkelman, M.A.; Walsh, T.J. (1→3)-β-d-Glucan in Cerebrospinal Fluid as a Biomarker for Candida and Aspergillus Infections of the Central Nervous System in Pediatric Patients. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2016, 5, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, S.; Ruhnke, M.; Ribaud, P.; Corey, L.; Driscoll, T.; Cornely, O.A.; Schuler, U.; Lutsar, I.; Troke, P.; Thiel, E. Improved outcome in central nervous system aspergillosis, using voriconazole treatment. Blood 2005, 106, 2641–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, S.; Thiel, E. Cerebral aspergillosis: Tissue penetration is the key. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47 (Suppl. 1), S387–S393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, M.H.; Chandrasekar, P. Safety and efficacy of liposomal amphotericin B for the empirical therapy of invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients. Infect. Drug Resist. 2012, 5, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ng, A.; Gadong, N.; Kelsey, A.; Denning, D.W.; Leggate, J.; Eden, O.B. Successful treatment of aspergillus brain abscess in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2000, 17, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, H.; Adkins, D.; Miller, G.; Goodnough, L.; Brown, R.; DiPersio, J. Resolution of invasive central nervous system aspergillosis in a transplant recipient. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997, 20, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.M.; Hogg, G.G.; Rosenfeld, J.V.; Waters, K.D. Invasive central nervous system aspergillosis: Cure with liposomal amphotericin B, itraconazole, and radical surgery—case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 1995, 36, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbrecht, R.; Denning, D.W.; Patterson, T.F.; Bennett, J.E.; Greene, R.E.; Oestmann, J.W.; Kern, W.V.; Marr, K.A.; Ribaud, P.; Lortholary, O.; et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denning, D.W.; Ribaud, P.; Milpied, N.; Caillot, D.; Herbrecht, R.; Thiel, E.; Haas, A.; Ruhnke, M.; Lode, H. Efficacy and safety of voriconazole in the treatment of acute invasive aspergillosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.; Prideaux, B.; Lee, M.H.; Zimmerman, M.; Dolgov, E.; Perlin, D.S.; Zhao, Y. Tissue Distribution and Penetration of Isavuconazole at the Site of Infection in Experimental Invasive Aspergillosis in Mice with Underlying Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00524-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullmann, A.J.; Aguado, J.M.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Denning, D.W.; Groll, A.H.; Lagrou, K.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Lewis, R.E.; Munoz, P.; Verweij, P.E.; et al. Diagnosis and management of Aspergillus diseases: Executive summary of the 2017 ESCMID-ECMM-ERS guideline. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24 (Suppl. 1), e1–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolton, M.J.; Ray, J.E.; Chen, S.C.; Ng, K.; Pont, L.G.; McLachlan, A.J. Multicenter study of voriconazole pharmacokinetics and therapeutic drug monitoring. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4793–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andes, D.; Pascual, A.; Marchetti, O. Antifungal therapeutic drug monitoring: Established and emerging indications. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, S.; Reisman, A.; Troke, P.F. The efficacy of voriconazole in the treatment of 192 fungal central nervous system infections: A retrospective analysis. Infection 2011, 39, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.J.; Raad, I.; Patterson, T.F.; Chandrasekar, P.; Donowitz, G.R.; Graybill, R.; Greene, R.E.; Hachem, R.; Hadley, S.; Herbrecht, R.; et al. Treatment of invasive aspergillosis with posaconazole in patients who are refractory to or intolerant of conventional therapy: An externally controlled trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitisuttithum, P.; Negroni, R.; Graybill, J.R.; Bustamante, B.; Pappas, P.; Chapman, S.; Hare, R.S.; Hardalo, C.J. Activity of posaconazole in the treatment of central nervous system fungal infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Tanaka, S.; Kashiwagi, M.; Chiba, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Uede, T. Successful treatment of cerebral aspergillosis with a high oral dose of itraconazole after excisional surgery. Intern. Med. 1999, 38, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Maertens, J.; Raad, I.; Petrikkos, G.; Boogaerts, M.; Selleslag, D.; Petersen, F.B.; Sable, C.A.; Kartsonis, N.A.; Ngai, A.; Taylor, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of caspofungin for treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients refractory to or intolerant of conventional antifungal therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okugawa, S.; Ota, Y.; Tatsuno, K.; Tsukada, K.; Kishino, S.; Koike, K. A case of invasive central nervous system aspergillosis treated with micafungin with monitoring of micafungin concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 39, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guest, J.M.; Singh, P.K.; Revankar, S.G.; Chandrasekar, P.H.; Kumar, A. Isavuconazole for Treatment of Experimental Fungal Endophthalmitis Caused by Aspergillus fumigatus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01537-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leonardis, F.; Novielli, C.; Giannico, B.; Mariggiò, M.A.; Castagnola, E.; Santoro, N. Isavuconazole Treatment of Cerebral and Pulmonary Aspergillosis in a Pediatric Patient with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Case Report and Review of Literature. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.A.; Shatsky, S.A. Intrathecal amphotericin in the management of coccidioidal meningitis. Semin. Respir. Infect. 2001, 16, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.; Pham, M.H.; Lee, B.; Commins, D.; Cadden, J.; Giannotta, S.L.; Zada, G. Intracranial fusarium fungal abscess in an immunocompetent patient: Case report and review of the literature. J. Neurol. Surg. Rep. 2014, 75, e241–e245. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, R.R.; Min, Z.; Narasimhan, S.; Bhanot, N. Fusarium brain abscess: Case report and literature review. Mycoses 2015, 58, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt-Demasters, B.K. Disseminated Fusarium infection with brain abscesses in a lung transplant recipient. Clin. Neuropathol. 2009, 28, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dignani, M.C.; Anaissie, E. Human fusariosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10 (Suppl. 1), 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsouras, G.W.; Ramos, R.L.; Martinez, L.R. Role of microglia in fungal infections of the central nervous system. Virulence 2017, 8, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nucci, F.; Nouér, S.A.; Capone, D.; Anaissie, E.; Nucci, M. Fusariosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 36, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertero, A.; Spicer, L.J.; Caloni, F. Fusarium mycotoxins and in vitro species-specific approach with porcine intestinal and brain in vitro barriers: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Góralska, K.; Blaszkowska, J.; Dzikowiec, M. Neuroinfections caused by fungi. Infection 2018, 46, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.; Rosengart, A.; Schuetz, A.N.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Walsh, T.J. Mold infections of the central nervous system. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesky, M.A.; McDougal, E.C.; Peacock, J.E., Jr. Pseudallescheria boydii brain abscess successfully treated with voriconazole and surgical drainage: Case report and literature review of central nervous system pseudallescheriasis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signore, S.C.; Dohm, C.P.; Schütze, G.; Bähr, M.; Kermer, P. Scedosporium apiospermum brain abscesses in a patient after near-drowning—A case report with 10-year follow-up and a review of the literature. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2017, 17, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.G.; Choi, J.G.; Son, B.C. Scedosporium apiospermum: An Emerging Fatal Cause of Fungal Abscess and Ventriculitis after Near-drowning. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2018, 13, 792–796. [Google Scholar]
- Marco de Lucas, E.; Sádaba, P.; Lastra García-Barón, P.; Ruiz Delgado, M.L.; Cuevas, J.; Salesa, R.; Bermúdez, A.; González Mandly, A.; Gutiérrez, A.; Fernández, F.; et al. Cerebral scedosporiosis: An emerging fungal infection in severe neutropenic patients: CT features and CT pathologic correlation. Eur. Radiol. 2006, 16, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Vicente, A.; Guarro, J.; González, G.M.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Lackner, M.; Capilla, J. Voriconazole MICs are predictive for the outcome of experimental disseminated scedosporiosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.V.; Paterson, D.L.; Rinaldi, M.G.; Veldkamp, P.J. Scedosporium prolificans brain abscess in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease: Successful combination therapy with voriconazole and terbinafine. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 39, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meletiadis, J.; Mouton, J.W.; Meis, J.F.; Verweij, P.E. In vitro drug interaction modeling of combinations of azoles with terbinafine against clinical Scedosporium prolificans isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; McCluskey, P. Scedosporium prolificans sclerokeratitis 10 years after pterygium excision with adjunctive mitomycin C. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2005, 33, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howden, B.P.; Slavin, M.A.; Schwarer, A.P.; Mijch, A.M. Successful control of disseminated Scedosporium prolificans infection with a combination of voriconazole and terbinafine. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 22, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Bernal-Martinez, L.; Gomez-Lopez, A.; Buitrago, M.J.; Mellado, E.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L. In vitro activities of 35 double combinations of antifungal agents against Scedosporium apiospermum and Scedosporium prolificans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1136–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yustes, C.; Guarro, J. In vitro synergistic interaction between amphotericin B and micafungin against Scedosporium spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3498–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antifungal Agent | Molecular Mass | Protein Binding | CSF Concentration * | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voriconazole | 349 Daltons | 58% | ~50% | Small moderately lipophilic molecule |
| Posaconazole | 708 Daltons | >98% | Very low to undetectable | Largest lipophilic compound, limited data |
| Itraconazole | 705 Daltons | 99.8% | <10% | Lipophilic compound |
| Isavuconazole | 437 Daltons | >99% | Low | Water soluble. High concentration in eyes and brain |
| Amphotericin B and lipid formulations | 924 Daltons | 90% | Poor in adults; 40–90% in neonates Limited data with lipid formulations | Large molecule with a hydrophilic polydroxyl chain and a lipophilic polyene hydrocarbon chain, poorly soluble in water |
| Echinocandins | 1140–1292 Daltons | 97–99% | Negligible | Brain tissue concentration may increase with dose escalation and prolonged exposure |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miceli, M.H. Central Nervous System Infections Due to Aspergillus and Other Hyaline Molds. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5030079
Miceli MH. Central Nervous System Infections Due to Aspergillus and Other Hyaline Molds. Journal of Fungi. 2019; 5(3):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5030079
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiceli, Marisa H. 2019. "Central Nervous System Infections Due to Aspergillus and Other Hyaline Molds" Journal of Fungi 5, no. 3: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5030079
APA StyleMiceli, M. H. (2019). Central Nervous System Infections Due to Aspergillus and Other Hyaline Molds. Journal of Fungi, 5(3), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof5030079




