Comparative Mitogenome Analysis of Colletotrichum Species Causing Anthracnose of Rubber Trees Unveils Distinct Species Complex-Specific Evolution Trajectories Within the Genus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Single-Spore Isolation, DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.2. Mitogenome Assembly
2.3. mtDNA Copy Number Detection
2.4. Genome Annotation
2.5. Synteny Analysis
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis Based on PCGs
2.7. Composition, Codon Usage and Substitution Rate Analyses
2.8. Program and Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. De Novo Assembly and Structural Annotation
3.2. Comparative Synteny Analysis Revealed Intron-Driven Genome Expansion
3.3. Structural Diversity of Colletotrichum Mitogenomics
3.4. Gene Selective Pressure Analysis
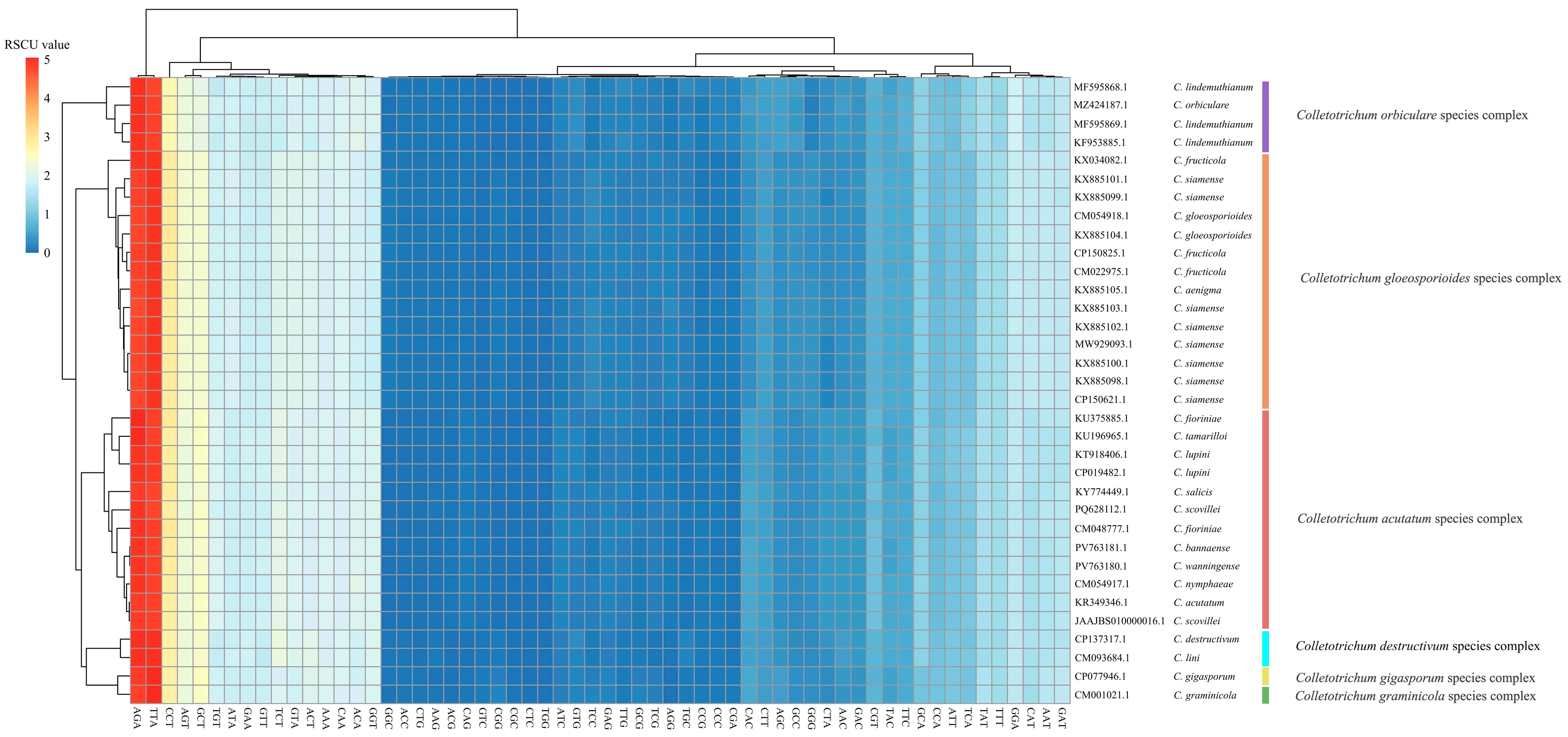
3.5. Codon Usage Patterns Reflect Translational Stability Within Species Complexes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Luo, H.; He, C. Revealing the Dominant Long Noncoding RNAs Responding to the Infection with Colletotrichum Gloeosporioides in Hevea Brasiliensis. Biol. Direct 2019, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhuo, D.; Yang, T.; Dai, L.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Cai, Z. Charactserization of Colletotrichum Causing Anthracnose on Rubber Trees in Yunnan: Two New Records and Two New Species from China. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 3037–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, B.; Cai, J.; Zheng, X.; Feng, Y.; Huang, G. Colletotrichum Species Causing Anthracnose of Rubber Trees in China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, B.; Cai, J.; Shi, T.; Yang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Huang, G. Whole Genome Resequencing Reveal Patterns of Genetic Variation within Colletotrichum acutatum Species Complex from Rubber Trees in China. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2023, 167, 103801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xu, X.; Che, H.; West, J.S.; Luo, D. Three Colletotrichum Species, Including a New Species, Are Associated to Leaf Anthracnose of Rubber Tree in Hainan, China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Cai, J.; Shi, T.; Zheng, X.; Huang, G. Pathogenic Adaptations Revealed by Comparative Genome Analyses of Two Colletotrichum Spp., the Causal Agent of Anthracnose in Rubber Tree. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.L.; Moreno, H.L.A.; Correia, H.L.N.; Santana, M.F.; de Queiroz, M.V. Colletotrichum: Species Complexes, Lifestyle, and Peculiarities of Some Sources of Genetic Variability. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1891–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patkar, R.N.; Ramos-Pamplona, M.; Gupta, A.P.; Fan, Y.; Naqvi, N.I. Mitochondrial Β-Oxidation Regulates Organellar Integrity and Is Necessary for Conidial Germination and Invasive Growth in Magnaporthe Oryzae. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 86, 1345–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, I.; Namiki, F.; Tsuge, T. Plant colonization by the vascular wilt fungus Fusarium oxysporum requires FOW1, a gene encoding a mitochondrial protein. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvelis, V.N.; Hausner, G. Editorial: Mitochondrial Genomes and Mitochondrion Related Gene Insights to Fungal Evolution. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 897981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, R.; Franco, M.E.E.; Bartel, L.C.; Martinez Alcántara, V.; Saparrat, M.C.N.; Balatti, P.A. Fungal Mitogenomes: Relevant Features to Planning Plant Disease Management. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardoya, R. Recent Advances in Understanding Mitochondrial Genome Diversity. F1000Research 2020, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pszczółkowska, A.; Androsiuk, P.; Jastrzębski, J.P.; Paukszto, Ł.; Okorski, A. Rps3 as a Candidate Mitochondrial Gene for the Molecular Identification of Species from the Colletotrichum acutatum Species Complex. Genes 2020, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinget, B.; Bélanger, R.R. Discovery of new group I-D introns leads to creation of subtypes and link to an adaptive response of the mitochondrial genome in fungi. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wai, A.; Hausner, G. The Mitochondrial Genome of Ophiostoma Himal-Ulmi and Comparison with Other Fungi Causing Dutch Elm Disease. Can. J. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xiang, X.; Niu, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; Zheng, A. Comparative Mitogenomic Analysis and the Evolution of Rhizoctonia solani Anastomosis Groups. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 707281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, A.M.; Peluso, P.; Rowell, W.J.; Chang, P.-C.; Hall, R.J.; Concepcion, G.T.; Ebler, J.; Fungtammasan, A.; Kolesnikov, A.; Olson, N.D.; et al. Accurate Circular Consensus Long-Read Sequencing Improves Variant Detection and Assembly of a Human Genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, W.; Lin, C.; He, F.; Yang, J.; Miao, W.; Li, Z. Mitochondrial Characteristics of the Powdery Mildew Genus Erysiphe Revealed an Extraordinary Evolution in Protein-Coding Genes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. New strategies to improve minimap2 alignment accuracy. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 4572–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurk, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Rhie, A.; Vollger, M.R.; Logsdon, G.A.; Grothe, R.; Miga, K.H.; Eichler, E.E.; Phillippy, A.M.; Koren, S. HiCanu: Accurate assembly of segmental duplications, satellites, and allelic variants from high-fidelity long reads. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and Accurate Long-Read Assembly via Adaptive k-Mer Weighting and Repeat Separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuthner, T.C.; Hartman, J.H.; Ryde, I.T.; Meyer, J.N. PCR-Based Determination of Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number in Multiple Species. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2310, 91–111. [Google Scholar]
- Stockinger, H.; Peyret-Guzzon, M.; Koegel, S.; Bouffaud, M.L.; Redecker, D. The largest subunit of RNA polymerase II as a new marker gene to study assemblages of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the field. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valach, M.; Burger, G.; Gray, M.W.; Lang, B.F. Widespread occurrence of organelle genome-encoded 5S rRNAs including permuted molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 13764–13777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Al-Arab, M.; Bernhart, S.H.; Reinhardt, F.; Stadler, P.F.; Middendorf, M.; Bernt, M. Improved annotation of protein-coding genes boundaries in metazoan mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10543–10552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, G.; Yan, Y.; Javadi, P.; Lang, B.F. Group I-Intron Trans-Splicing and mRNA Editing in the Mitochondria of Placozoan Animals. Trends Genet. 2009, 25, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, B.F.; Laforest, M.-J.; Burger, G. Mitochondrial Introns: A Critical View. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; Funk, K.; Kelly, C.; Kim, S.; et al. Database Resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D20–D26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The Conserved Domain Database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Schleiermacher, C. REPuter: Fast Computation of Maximal Repeats in Complete Genomes. Bioinformatics 1999, 15, 426–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem Repeats Finder: A Program to Analyze DNA Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An Information Aesthetic for Comparative Genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Taylor, J..; Lin, V.; Altman, T.; Barbera, P.; Meleshko, D.; Lohr, D.; Novakovsky, G.; Buchfink, B.; Al-Shayeb, B.; et al. Petabase-Scale Sequence Alignment Catalyses Viral Discovery. Nature 2022, 602, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Le, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, F. SeqKit: A Cross-Platform and Ultrafast Toolkit for FASTA/Q File Manipulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.M. BCAWT: Automated Tool for Codon Usage Bias Analysis for Molecular Evolution. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, M.B.; Spellman, P.T.; Brown, P.O.; Botstein, D. Cluster Analysis and Display of Genome-Wide Expression Patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14863–14868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic Analysis by Maximum Likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Li, Z.-G.; He, F.; Zhang, Z. An Important Role for Purifying Selection in Archaeal Genome Evolution. mSystems 2017, 2, e00112-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Nielsen, R. Estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates under realistic evolutionary models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A Novel Method for Rapid Multiple Sequence Alignment Based on Fast Fourier Transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.P.; Peris, D.; Moriarty, R.V.; Li, X.C.; Fay, J.C.; Hittinger, C.T. Mitochondrial DNAand Temperature Tolerance in Lager Yeasts. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Tian, X.; Liu, W.; Wei, T.; Wang, W.; Dong, Q.; Wang, B.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Gleason, M.L.; et al. Comparative Analysis of the Mitochondrial Genomes of Colletotrichum Gloeosporioides Sensu Lato: Insights into the Evolution of a Fungal Species Complex Interacting with Diverse Plants. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, P.F.; Damm, U.; Johnston, P.R.; Weir, B.S. Colletotrichum: Current Status and Future Directions. Stud. Mycol. 2012, 73, 181–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, F.; Tsui, C.K.M.; Cai, L. Phylogenomics and Adaptive Evolution of the Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Species Complex. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, T.; Van Diepeningen, A.D.; Hausner, G. Editorial: The Significance of Mitogenomics in Mycology. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 628579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyarchuk, B.A.; Derenko, M.V. Evaluating the Role of Selection in the Evolution of Mitochondrial Genomes of Aboriginal Peoples of Siberia. Vavilovskii Zhurnal Genet. Sel. 2023, 27, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, V.P.; Oudemans, P.V.; Rehner, S.A.; Litt, A. Habitat and Host Indicate Lineage Identity in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides s.l. from Wild and Agricultural Landscapes in North America. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelen, V.; De Jonge, R.; Van De Peer, Y.; Javornik, B.; Jakše, J. Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Verticillium-Wilt Causing Plant Pathogen Verticillium nonalfalfae. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethuraman, J.; Majer, A.; Iranpour, M.; Hausner, G. Molecular Evolution of the mtDNA Encoded Rps3 Gene Among Filamentous Ascomycetes Fungi with an Emphasis on the Ophiostomatoid Fungi. J. Mol. Evol. 2009, 69, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwenhuis, M.; Groeneveld, J.; Aanen, D.K. Horizontal Transfer of tRNA Genes to Mitochondrial Plasmids Facilitates Gene Loss from Fungal Mitochondrial DNA. Curr. Genet. 2023, 69, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
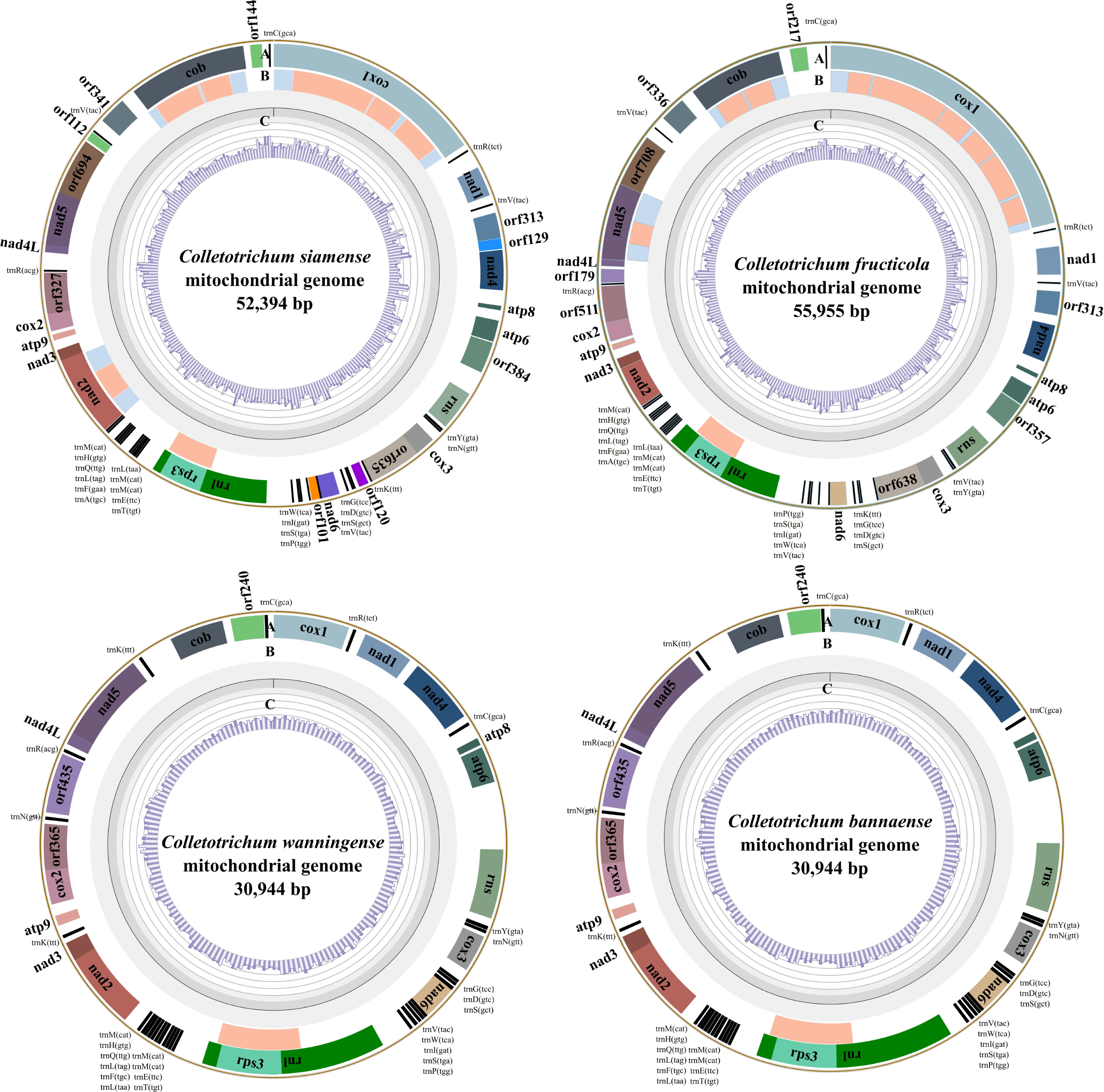
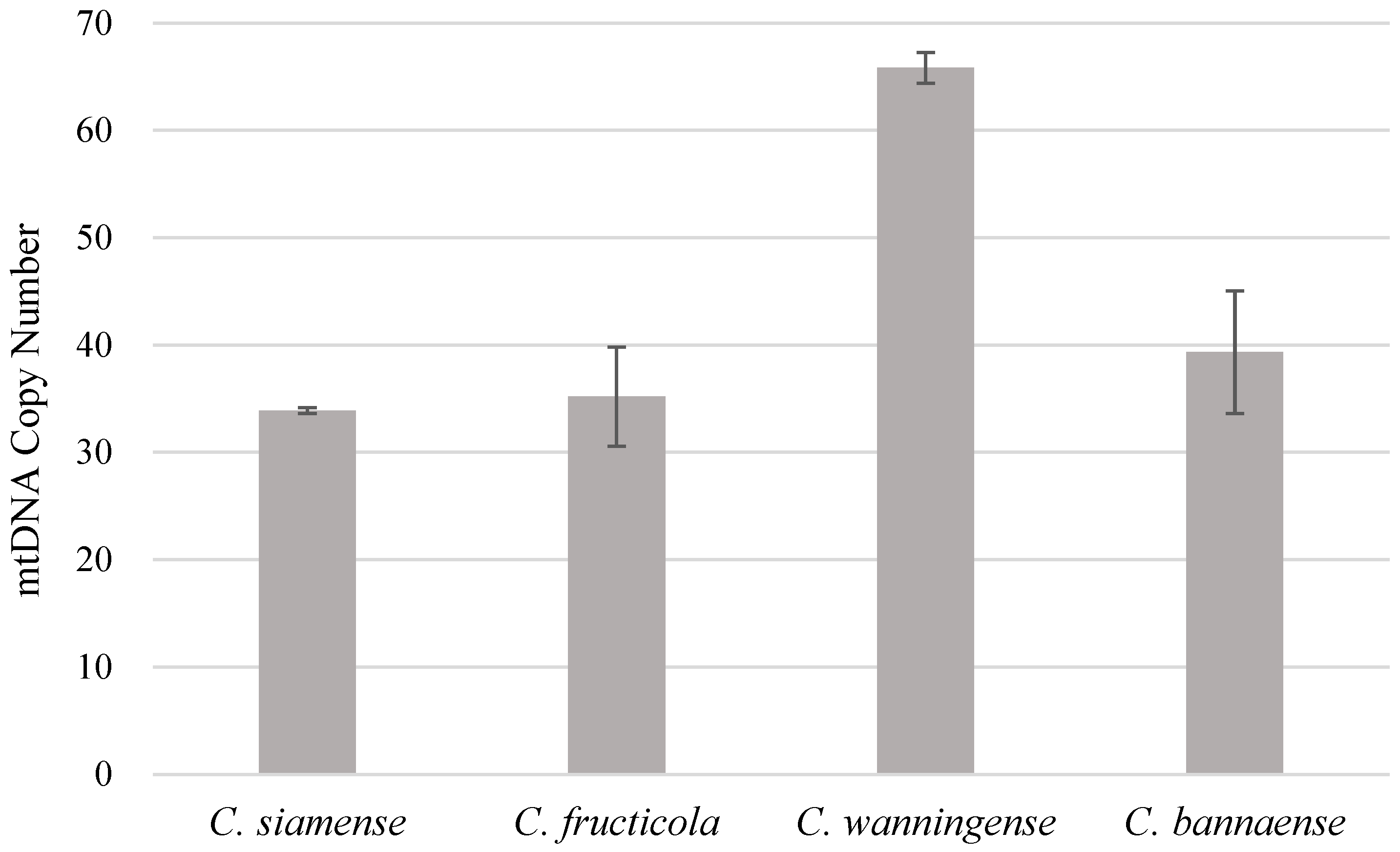
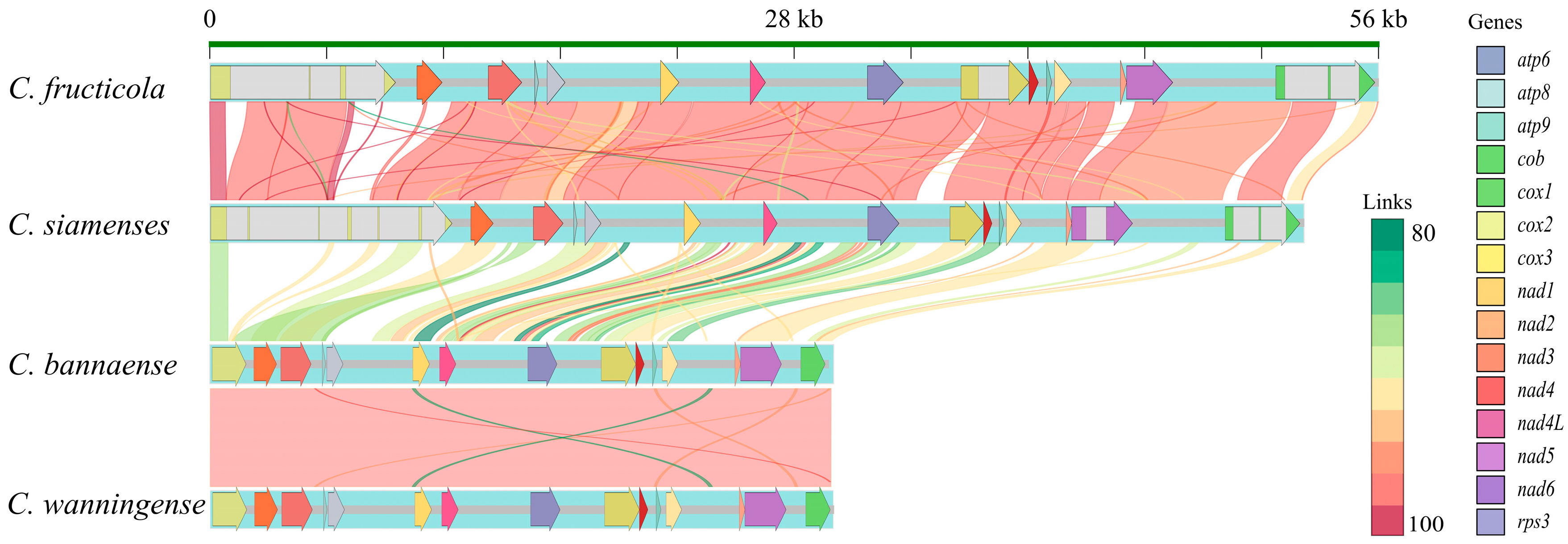

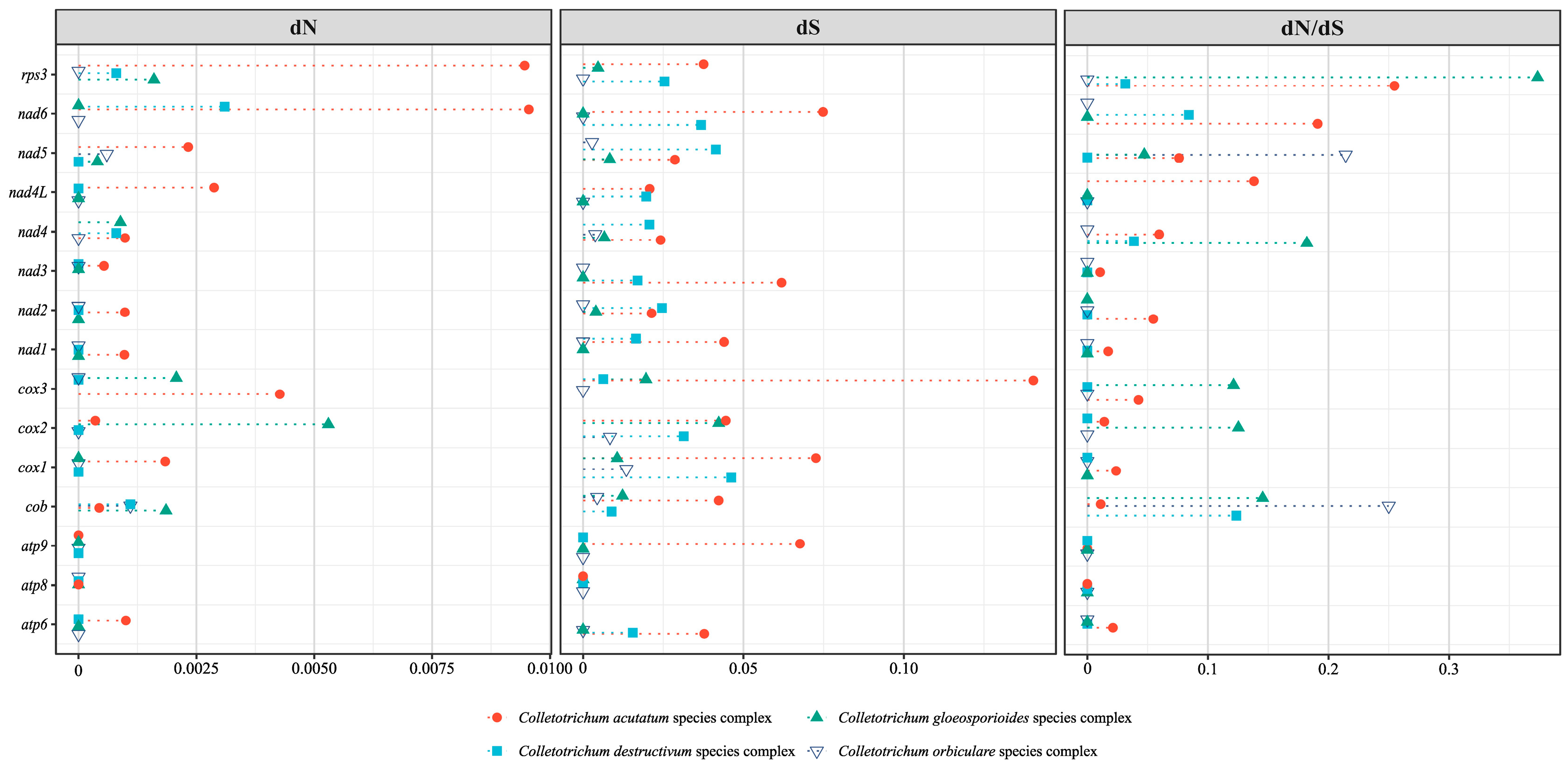
| C. siamense | C. fructicola | C. wanningense | C. bannaense | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GenBank Accession | CP150621.1 | CP150825.1 | PV763180.1 | PV763181.1 |
| Total size (bp) | 52,394 | 55,955 | 30,949 | 30,944 |
| Intergenic regions size (bp) | 12,555 | 13,952 | 9649 | 9644 |
| Intronic regions size (bp) | 5609 | 8383 | 1709 | 1709 |
| Overall GC (%) | 34.52 | 33.98 | 30.59 | 30.59 |
| Core PCGs size (bp) | 27,267 | 30,050 | 16,237 | 16,237 |
| Intergenic regions GC (%) | 41.35 | 41.97 | 30.95 | 30.59 |
| GC-skew(G − C)/(G + C) | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| AT-skew(A − T)/(A + T) | −0.01 | 0 | −0.03 | −0.03 |
| Repetitive DNA regions (bp) | 1579 | 1215 | 208 | 208 |
| Repetitive DNA (%) | 3.01 | 2.17 | 0.67 | 0.67 |
| tRNA | 27 | 27 | 28 | 28 |
| Introns | 7 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| Intronic ORFs | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| GIY-YIG ORFs | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| LAGLIDADG ORFs | 4 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| GenBank Accession | Species | Species Complex | Genome Length (bp) | GC Content (%) | tRNA Count | rRNA Count | Intron Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM093684.1 | C. lini | C. destructivum species complex | 39,089 | 29.62 | 28 | 2 | 3 |
| CP137317.1 | C. destructivum | C. destructivum species complex | 34,391 | 29.72 | 28 | 2 | 2 |
| CM001021.1 | C. graminicola | C. graminicola species complex | 39,649 | 29.89 | 25 | 2 | 2 |
| KY774449.1 | C. salicis | C. acutatum species complex | 33,950 | 30.44 | 28 | 2 | 1 |
| KU375885.1 | C. fioriniae | C. acutatum species complex | 30,020 | 30.04 | 28 | 2 | 1 |
| CM048777.1 | C. fioriniae | C. acutatum species complex | 30,009 | 30.10 | 29 | 2 | 1 |
| KU196965.1 | C. tamarilloi | C. acutatum species complex | 30,824 | 30.50 | 28 | 2 | 1 |
| KT918406.1 | C. lupini | C. acutatum species complex | 36,554 | 29.91 | 29 | 2 | 1 |
| CP019482.1 | C. lupini | C. acutatum species complex | 36,554 | 29.91 | 29 | 2 | 1 |
| PV763180 * | C. wanningense | C. acutatum species complex | 30,949 | 30.59 | 28 | 2 | 1 |
| PV763181 * | C. bannaense | C. acutatum species complex | 30,944 | 30.59 | 28 | 2 | 1 |
| CM054917.1 | C. nymphaeae | C. acutatum species complex | 30,928 | 30.54 | 28 | 2 | 1 |
| KR349346.1 | C. acutatum | C. acutatum species complex | 30,892 | 30.51 | 28 | 2 | 1 |
| PQ628112.1 | C. scovillei | C. acutatum species complex | 29,517 | 30.72 | 21 | 2 | 1 |
| JAAJBS010000016.1 | C. scovillei | C. acutatum species complex | 30,952 | 30.51 | 28 | 2 | 1 |
| CP077946.1 | C. gigasporum | C. gigasporum species complex | 58,879 | 31.97 | 29 | 2 | 11 |
| MZ424187.1 | C. orbiculare | C. orbiculare species complex | 36,318 | 31.07 | 28 | 2 | 3 |
| MF595869.1 | C. lindemuthianum | C. orbiculare species complex | 37,446 | 30.86 | 28 | 2 | 4 |
| MF595868.1 | C. lindemuthianum | C. orbiculare species complex | 37,440 | 30.85 | 28 | 2 | 4 |
| KF953885.1 | C. lindemuthianum | C. orbiculare species complex | 36,957 | 30.88 | 28 | 2 | 4 |
| KX885098.1 | C. siamense | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 54,679 | 34.25 | 27 | 2 | 9 |
| KX885099.1 | C. siamense | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 54,658 | 34.10 | 27 | 2 | 9 |
| KX885102.1 | C. siamense | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 54,645 | 34.29 | 27 | 2 | 8 |
| KX885103.1 | C. siamense | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 53,317 | 34.39 | 27 | 2 | 7 |
| MW929093.1 | C. siamense | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 52,710 | 34.45 | 27 | 2 | 7 |
| KX885100.1 | C. siamense | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 52,671 | 34.40 | 27 | 2 | 7 |
| CP150621.1 * | C. siamense | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 52,394 | 34.52 | 27 | 2 | 7 |
| KX885101.1 | C. siamense | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 58,666 | 33.84 | 27 | 2 | 11 |
| CM054918.1 | C. gloeosporioides | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 59,695 | 34.13 | 27 | 2 | 11 |
| KX885105.1 | C. aenigma | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 57,252 | 34.28 | 27 | 2 | 10 |
| KX034082.1 | C. fructicola | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 56,051 | 34.04 | 27 | 2 | 10 |
| CP150825.1 * | C. fructicola | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 55,955 | 33.98 | 27 | 2 | 10 |
| CM022975.1 | C. fructicola | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 55,177 | 34.00 | 27 | 2 | 10 |
| KX885104.1 | C. gloeosporioides | C. gloeosporioides species complex | 55,169 | 34.55 | 27 | 2 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Chen, Q.; He, L.; Zang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, C.; Miao, W.; Li, Z. Comparative Mitogenome Analysis of Colletotrichum Species Causing Anthracnose of Rubber Trees Unveils Distinct Species Complex-Specific Evolution Trajectories Within the Genus. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090679
Wu Y, Zhou F, Chen Q, He L, Zang Y, Wang Z, Lin C, Miao W, Li Z. Comparative Mitogenome Analysis of Colletotrichum Species Causing Anthracnose of Rubber Trees Unveils Distinct Species Complex-Specific Evolution Trajectories Within the Genus. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(9):679. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090679
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yehao, Fan Zhou, Qingqin Chen, Lijuan He, Yining Zang, Zirui Wang, Chunhua Lin, Weiguo Miao, and Zhigang Li. 2025. "Comparative Mitogenome Analysis of Colletotrichum Species Causing Anthracnose of Rubber Trees Unveils Distinct Species Complex-Specific Evolution Trajectories Within the Genus" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 9: 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090679
APA StyleWu, Y., Zhou, F., Chen, Q., He, L., Zang, Y., Wang, Z., Lin, C., Miao, W., & Li, Z. (2025). Comparative Mitogenome Analysis of Colletotrichum Species Causing Anthracnose of Rubber Trees Unveils Distinct Species Complex-Specific Evolution Trajectories Within the Genus. Journal of Fungi, 11(9), 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090679






