Diversity and Distribution of Non-Reducing Polyketide Synthases (NR-PKSs) in Ascomycota (Fungi)
Abstract
1. Introduction
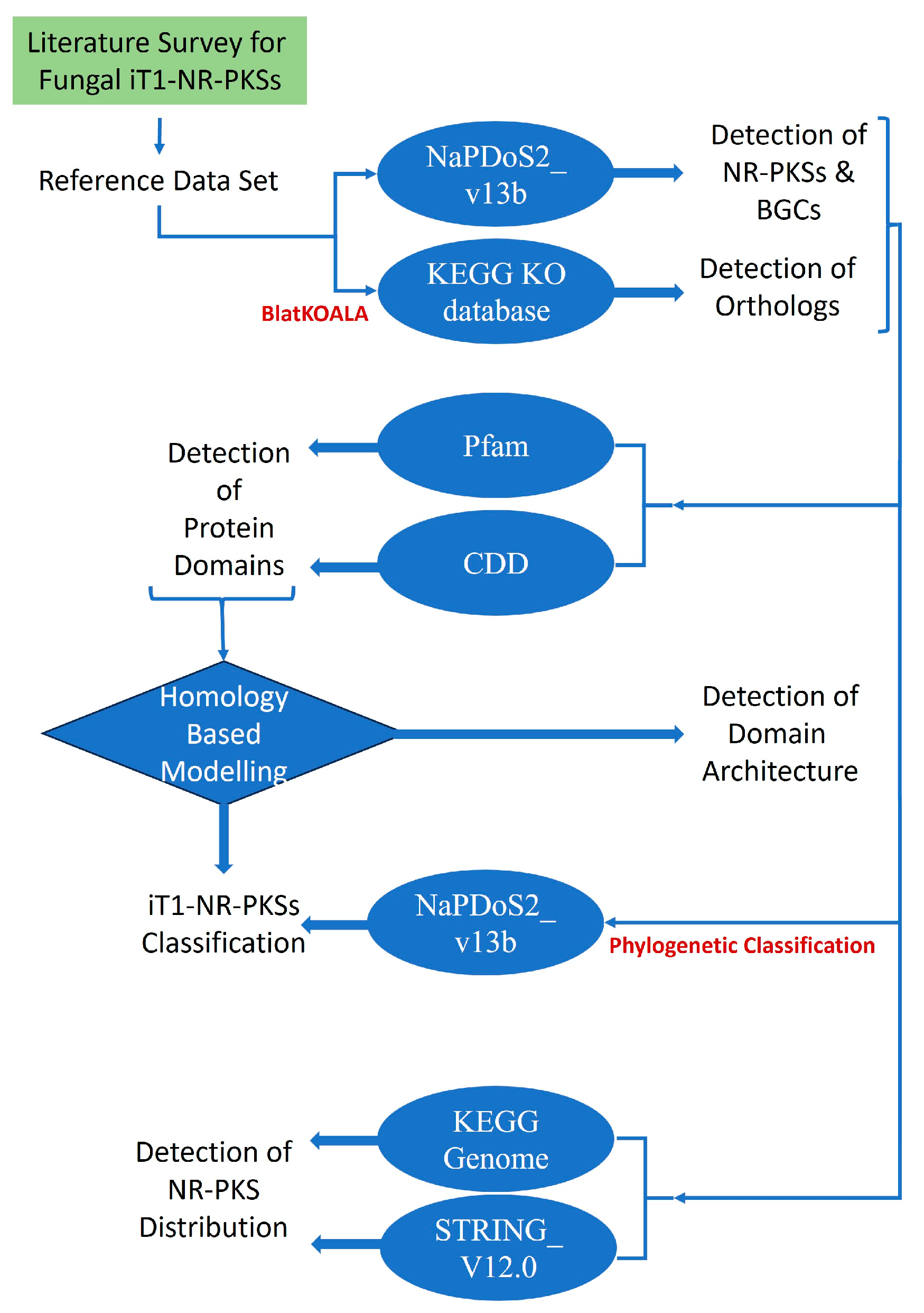
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Retrieval
2.2. Screening for NR-PKSs
2.3. Phylogenetic Classification of NR-PKSs
2.4. Homology Modeling and Evaluation of the Tertiary Structure
2.5. Distribution of NR-PKSs in Ascomycota
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Fungal NR-PKSs
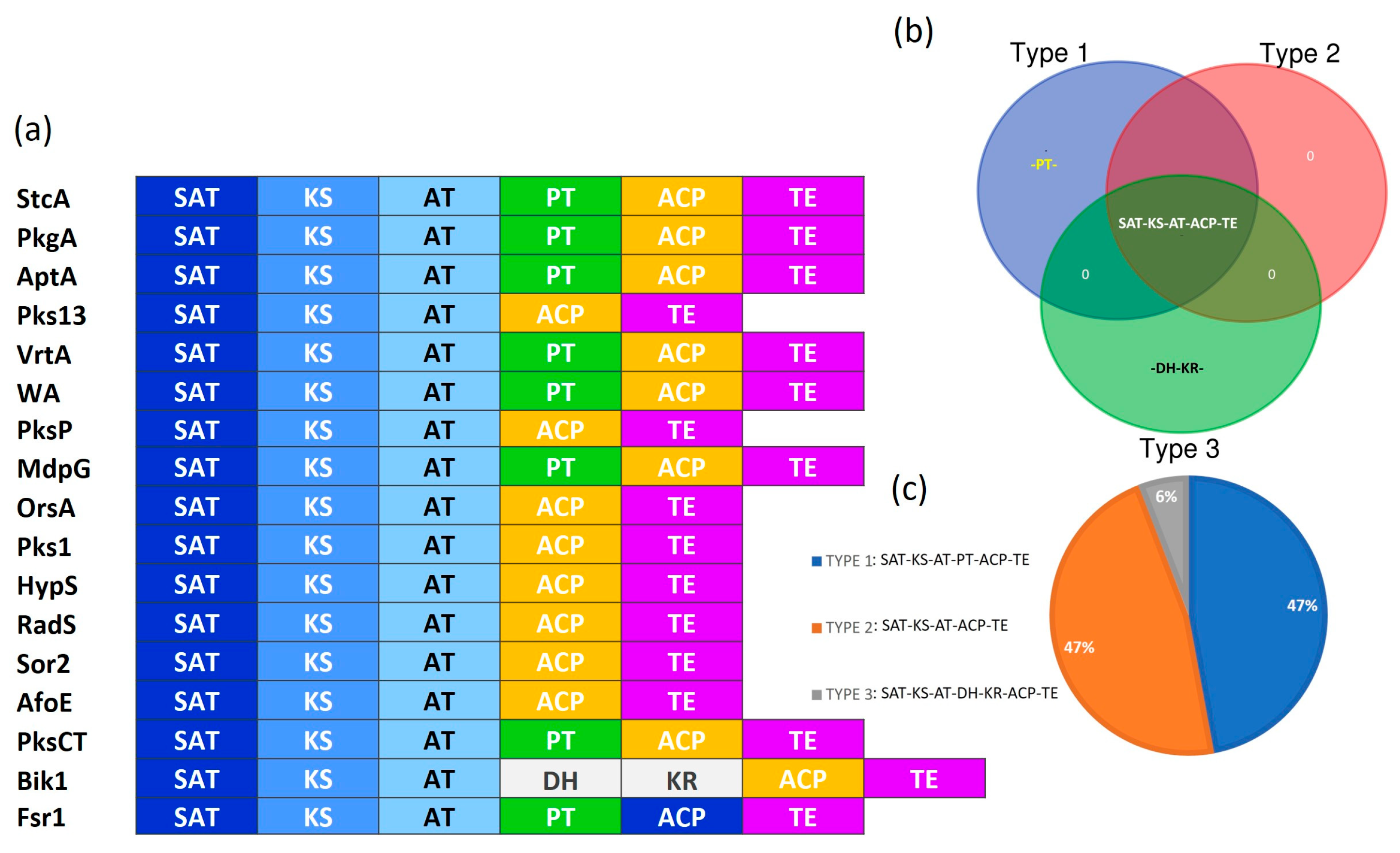
3.2. Identification of the Protein Domains for NR-PKSs
3.3. Classification of Fungal NR-PKSs
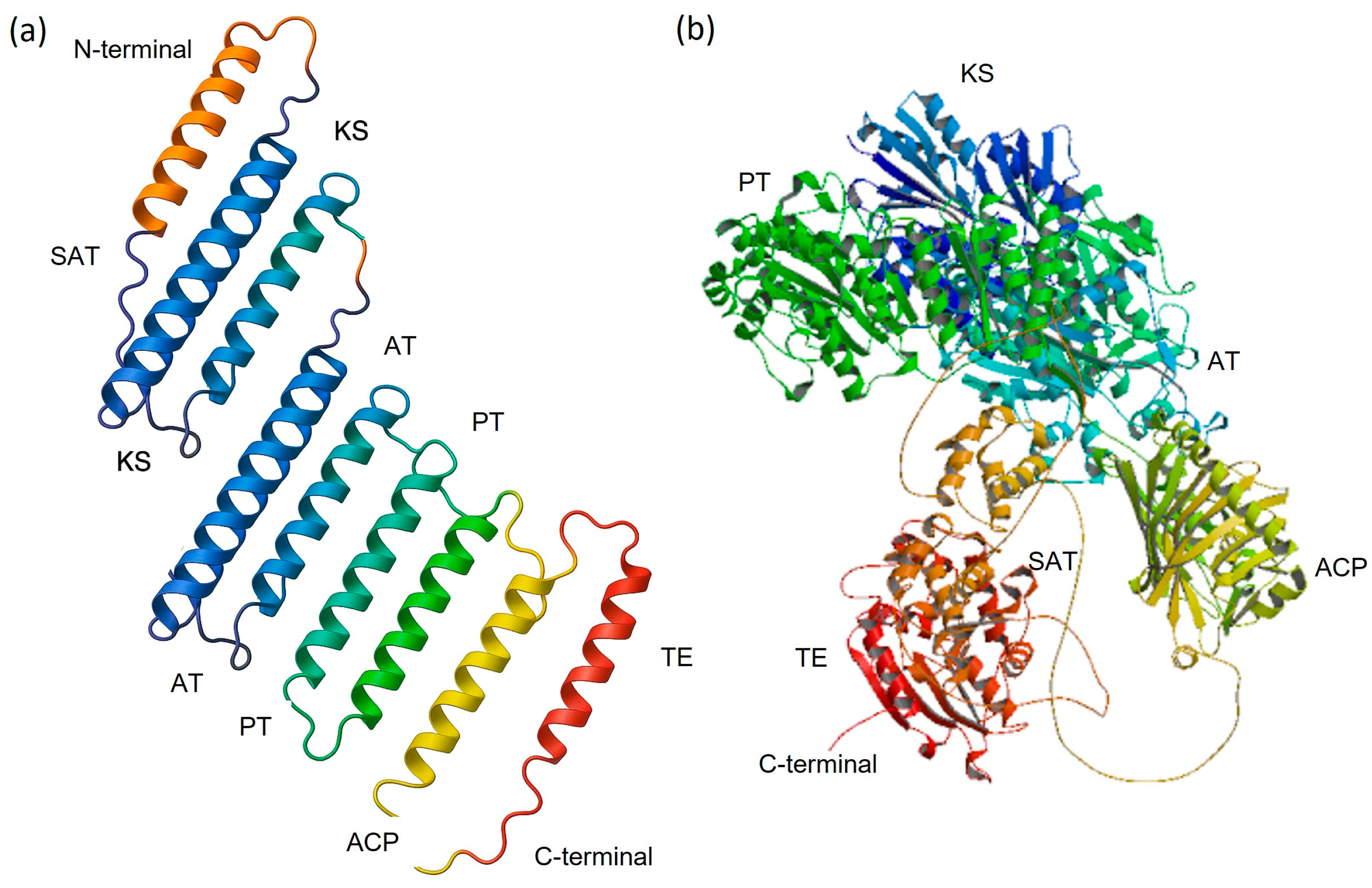
3.4. Tertiary Structures of NR-PKSs and Validation
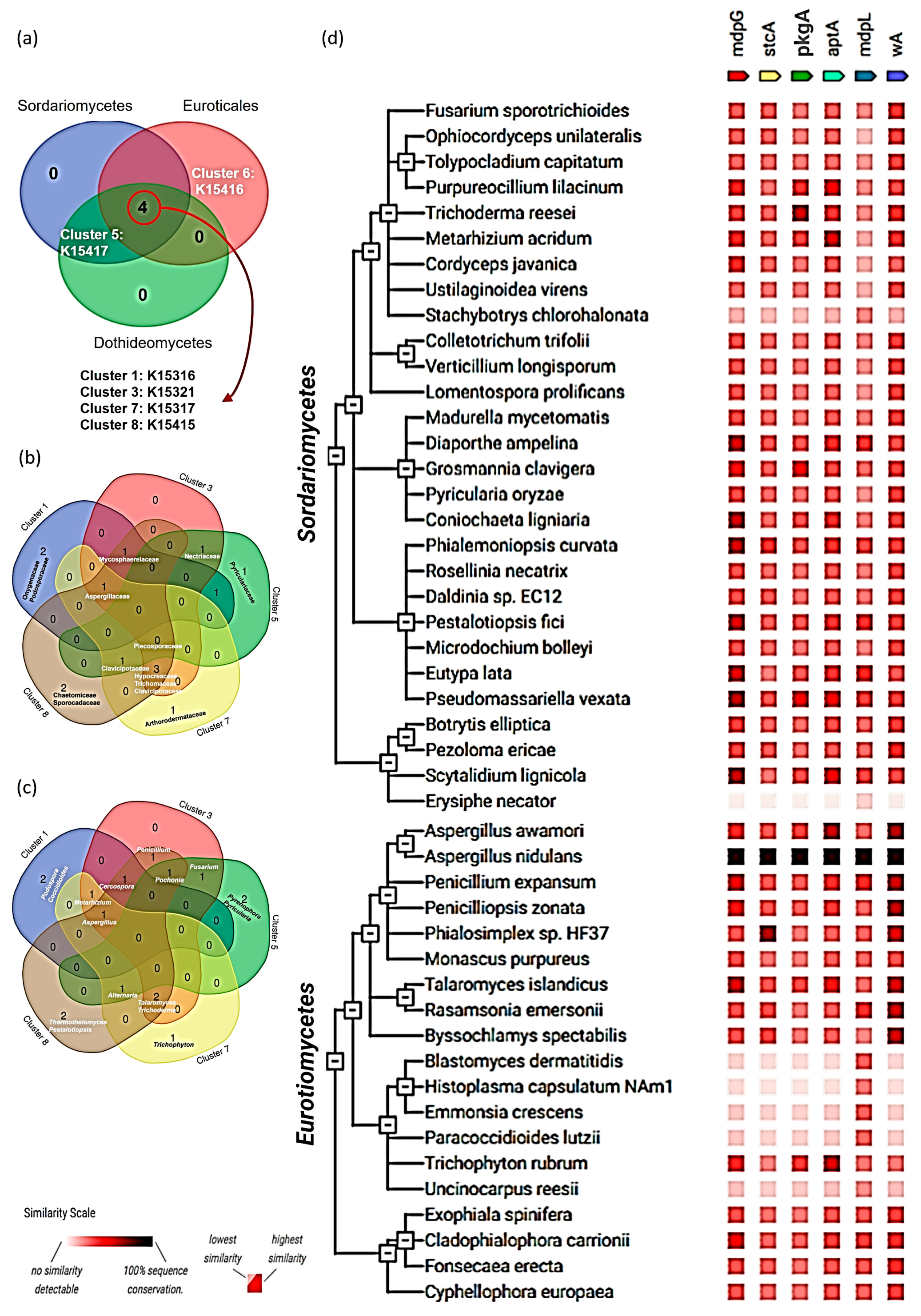
3.5. Distribution of NR-PKSs Among the Members of Ascomycota
4. Discussion
4.1. Domain Architecture of NR-PKSs Among the Members of Ascomycota
4.2. Phylogenetic Classification of NR-PKSs Among the Members of Ascomycota
4.3. Incongruency Between Phylogenetic Classification of Ascomycota and Distribution of NR-PKSs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NR-PKSs | Non-reducing polyketide synthases |
| BGC | Biosynthetic gene cluster |
| KO | KEGG Orthology |
| PKS | Polyketide synthase |
References
- Keller, N.P.; Turner, G.; Bennett, J.W. Fungal secondary metabolism—From biochemistry to genomics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroe, M.C.; Gao, J.; Pitz, M.; Fischer, R. Complexity of fungal polyketide biosynthesis andf unction. Mol. Microbiol. 2024, 121, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, N.A.; Platz, L.; Hoffmeister, D.; Müller, M. From the forest floor to the lab: Insights into the diversity and complexity of mushroom polyketide synthases. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2024, 82, 102510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroken, S.; Glass, N.L.; Taylor, J.W.; Yoder, O.; Turgeon, B.G. Phylogenomic analysis of type I polyketide synthase genes in pathogenic and saprobic ascomycetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15670–15675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-H.; Keller, N. Regulation of secondary metabolism in filamentous fungi. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.F.; Wheeler, M.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Kwon-Chung, K.J. A developmentally regulated gene cluster involved in conidial pigment biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6469–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.-M.; Szewczyk, E.; Davidson, A.D.; Entwistle, R.; Keller, N.P.; Wang, C.C.; Oakley, B.R. Characterization of the Aspergillus nidulans monodictyphenone gene cluster. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2067–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Liu, M.; Yu, M.; Meng, X.; Liang, B.; Sun, C.; Ji, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z. The pks1 gene encodes non-reducing polyketone synthetase involved in anthraquinones biosynthesis in M. purpureus YY-1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 306, 141399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, L.P.; Gomes, D.C.; Cardoso, P.G.; Takahashi, J.A. Recent Findings in Azaphilone Pigments. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Ferrara, M.; Perrone, G. Phylogenetic study of polyketide synthases and nonribosomal peptide synthetases involved in the biosynthesis of mycotoxins. Toxins 2013, 5, 717–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.J. Polyketides, proteins and genes in fungi: Programmed nano-machines begin to reveal their secrets. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 2010–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Throckmorton, K.; Wiemann, P.; Keller, N.P. Evolution of Chemical Diversity in a Group of Non-Reduced Polyketide Gene Clusters: Using Phylogenetics to Inform the Search for Novel Fungal Natural Products. Toxins 2015, 7, 3572–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slot, J.C.; Rokas, A. Horizontal transfer of a large and highly toxic secondary metabolic gene cluster between fungi. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collemare, J.; Lebrun, M.H. Fungal Secondary Metabolites: Ancient Toxins and Novel Effectors in Plant–Microbe Interactions. In Effectors in Plant–Microbe Interactions; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 377–400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Qiao, K.; Gao, Z.; Meehan, M.J.; Li, J.W.-H.; Zhao, X.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Vederas, J.C.; Tang, Y. Enzymatic synthesis of resorcylic acid lactones by cooperation of fungal iterative polyketide synthases involved in hypothemycin biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4530–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wen, Z.; Liu, S.-W.; Zhang, L.; Finley, C.; Lee, H.-J.; Fan, H.-J.S. Overview of AlphaFold2 and breakthroughs in overcoming its limitations. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 176, 108620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.P.; Zhu, Z.; You, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, K. InVitro biotransformation (ivBT): Definitions, opportunities, and challenges. Synth. Biol. Eng. 2023, 1, 10013. [Google Scholar]
- Klau, L.J.; Podell, S.; Creamer, K.E.; Demko, A.M.; Singh, H.W.; Allen, E.E.; Moore, B.S.; Ziemert, N.; Letzel, A.C.; Jensen, P.R. The Natural Product Domain Seeker version 2 (NaPDoS2) webtool relates ketosynthase phylogeny to biosynthetic function. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.; Tosatto, S.C.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J. Pfam: The protein families data base in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Lu, S.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; Yamashita, R.A. The conserved domain database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D384–D388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.B.; Henrikson, J.C.; Hoover, A.R.; Lee, A.E.; Cichewicz, R.H. Epigenetic remodeling of the fungal secondary metabolome. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 1895–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, G.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Sasisekharan, V. Stereochemistry of polypeptide chain configurations. J. Mol. Biol 1963, 7, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabala, A.O.; Xu, W.; Chooi, Y.-H.; Tang, Y. Characterization of a silent azaphilone gene cluster from Aspergillus niger ATCC 1015 reveals a hydroxylation-mediated pyran-ring formation. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, I.; Watanabe, A.; Sankawa, U.; Ebizuka, Y. Identification of Claisen cyclase domain in fungal polyketide synthase WA, a naphthopyrone synthase of Aspergillus nidulans. Chem. Biol. 2001, 8, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, J.M.; Thomas, P.M.; Scheerer, J.R.; Vagstad, A.L.; Kelleher, N.L.; Townsend, C.A. Deconstruction of iterative multidomain polyketide synthase function. Science 2008, 320, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.M.; Korman, T.P.; Labonte, J.W.; Vagstad, A.L.; Hill, E.A.; Kamari-Bidkorpeh, O.; Tsai, S.-C.; Townsend, C.A. Structural basis for biosynthetic programming of fungal aromatic polyketide cyclization. Nature 2009, 461, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fujii, I.; Yasuoka, Y.; Tsai, H.-F.; Chang, Y.C.; Kwon-Chung, K.; Ebizuka, Y. Hydrolytic polyketidesh or teningbyayg1p, a novel enzyme involved in fungal melanin biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44613–44620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.F.; Somoza, A.D.; Keller, N.P.; Wang, C.C. Advances in Aspergillus secondary metabolite research in the post-genomic era. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chooi, Y.-H.; Krill, C.; Barrow, R.A.; Chen, S.; Trengove, R.; Oliver, R.P.; Solomon, P.S. Aninplanta-expressed polyketide synthase produces(R)-mellein in the wheat pathogen Parastagonospora nodorum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeckh, V.; Scherlach, K.; Nützmann, H.-W.; Shelest, E.; Schmidt-Heck, W.; Schuemann, J.; Martin, K.; Hertweck, C.; Brakhage, A.A. Intimate bacterial-fungal interaction triggers biosynthesis of archetypal polyketides in Aspergillus nidulans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14558–14563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginolhac, A.; Jarrin, C.; Robe, P.; Perrière, G.; Vogel, T.M.; Simonet, P.; Nalin, R. Type I polyketide synthases may have evolved through horizontal gene transfer. J. Mol. Evol. 2005, 60, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, D.; Jacobsen, J.R.; Luo, G.; Cane, D.E.; Khosla, C. A functional chimeric modular polyketide synthase generated via domain replacement. Chem. Biol. 1996, 3, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.M.; Li, J.W.-H.; Choi, J.W.; Zhou, H.; Lee, K.M.; Moorthie, V.A.; Xie, X.; Kealey, J.T.; DaSilva, N.A.; Vederas, J.C. Complete reconstitution of a highly reducing iterative polyketide synthase. Science 2009, 326, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, J.D. Horizontal genetransfer and the evolution of secondary metabolite gene clustersin fungi: Anhypothesis. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2000, 30, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischbach, M.A.; Walsh, C.T. Assembly-line enzymology for polyketide and nonribosomal Peptide antibiotics: Logic, machinery, and mechanisms. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3468–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, R.H.; McCormick, S.P.; Kim, H.-S.; Cardoza, R.E.; Stanley, A.M.; Lindo, L.; Kelly, A.; Brown, D.W.; Lee, T.; Vaughan, M.M. Evolution of structural diversity of trichothecenes, a family of toxins produced by plant pathogenic and entomopathogenic fungi. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Auclair, K.; Kendrew, S.G.; Park, C.; Vederas, J.C.; Hutchinson, C.R. Modulation of polyketide synthase activity by accessory proteins during lovastatin biosynthesis. Science 1999, 284, 1368–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatafora, J.W.; Aime, M.C.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Martin, F.; Stajich, J.E.; Blackwell, M. The Fungal Tree of Life: From Molecular Systematics to Genome-Scale Phylogenies. In The Fungal Kingdom; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Gaffoor, I.; Trail, F. Characterization of two polyketide synthase genes involved in zearalenone biosynthesis in Gibberella zeae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1793–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærbølling, I.; Vesth, T.C.; Nybo, J.L.; Theobald, S.; Frisvad, J.C.; Kogle, M.E.; Lyhne, E.K.; Kuo, A.; Salamov, A.; Riley, R. Friends and foes-comparative genomics of 23 Aspergillus Flavi species. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Fungal Genetics, Haifa, Israel, 25–28 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nierman, W.C.; Pain, A.; Anderson, M.J.; Wortman, J.R.; Kim, H.S.; Arroyo, J.; Berriman, M.; Abe, K.; Archer, D.B.; Bermejo, C. Genomic sequence of the pathogenic and allergenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature 2005, 438, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galagan, J.E.; Calvo, S.E.; Cuomo, C.; Ma, L.-J.; Wortman, J.R.; Batzoglou, S.; Lee, S.-I.; Baştürkmen, M.; Spevak, C.C.; Clutterbuck, J. Sequencing of Aspergillus nidulans and comparative analysis with A. fumigatus and A. oryzae. Nature 2005, 438, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga, M.E.; Timberlake, W.E. The developmentally regulated Aspergillus nidulans wA gene encodes a polypeptide homologous to polyketide and fatty acid synthases. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1992, 235, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortman, J.R.; Gilsenan, J.M.; Joardar, V.; Deegan, J.; Clutterbuck, J.; Andersen, M.R.; Archer, D.; Bencina, M.; Braus, G.; Coutinho, P. The 2008 update of the Aspergillus nidulans genome annotation: A community effort. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2009, 46, S2–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chooi, Y.-H.; Sheng, Y.; Valentine, J.S.; Tang, Y. Comparative characterization of fungal anthracenone and naphthacenedione biosynthetic pathways reveals an α-hydroxylation-dependent Claisen-like cyclization catalyzed by a dimanganese thioesterase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15773–15785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Espinosa-Artiles, P.; Schubert, V.; Xu, Y.-m.; Zhang, W.; Lin, M.; Gunatilaka, A.L.; Sïssmuth, R.; Molnïr, I. Characterization of the biosynthetic genes for 10, 11-dehydrocurvularin, a heat shock response-modulating anticancer fungal polyketide from Aspergillus terreus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, L.; Davis, C.R.; Roach, C.; Nguyen, D.K.; Aldrich, T.; McAda, P.C.; Reeves, C.D. Lovastatin biosynthesis in Aspergillus terreus: Characterization of blocked mutants, enzyme activities and a multifunctional polyketide synthase gene. Chem. Biol. 1999, 6, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Hao, X.; Lou, J.; Zhang, P.; Pan, J.; Zhu, X. A PKS gene, pks-1, is involved in chaetoglobosin biosynthesis, pigmentation and sporulation in Chaetomium globosum. Sci. China Life Sci. 2012, 55, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Linnemannstöns, P.; Schulte, J.; del Mar Prado, M.; Proctor, R.H.; Avalos, J.; Tudzynski, B. The polyketide synthase gene pks4 from Gibberella fujikuroi encodes a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of the red pigment bikaverin. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2002, 37, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, T.E.; Harris, L.J.; Nguyen, H.D.; Hermans, A.; Johnston, A.; Sproule, A.; Dettman, J.R.; Boddy, C.N.; Overy, D.P. Apicidin biosynthesis is linked to accessory chromosomes in Fusarium poae isolates. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, Z.; Kortsinoglou, A.M.; Kouvelis, V.N.; Butt, T.M. Telomere length de novo assembly of all 7 chromosomes and mitogenome sequencing of the model entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium brunneum, by means of a novel assembly pipeline. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Kinoshita, H.; Ishihara, S.; Sakai, K.; Nagai, S.; Nihira, T. Polyketide synthase gene responsible for citrinin biosynthesis in Monascus purpureus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3453–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Luciano, L.B.; Tsai, I.J.; Chuma, I.; Tosa, Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Li, J.-Y.; Li, M.-Y.; Lu, M.-Y.J.; Nakayashiki, H.; Li, W.-H. Blast fungal genomes show frequent chromosomal changes, gene gains and losses, and effector gene turnover. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, D.; Berka, R.M.; Henrissat, B.; Saloheimo, M.; Arvas, M.; Baker, S.E.; Chapman, J.; Chertkov, O.; Coutinho, P.M.; Cullen, D. Genome sequencing and analysis of the biomass-degrading fungus Trichoderma reesei (syn. Hypocrea jecorina). Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sl. No. | Cand_Id | Domain Class | Domain Subclass | KO No. | Definition | BGC Product Match |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | StcA (XP_050468055.1) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | K15316 | PKSA; noranthrone synthase [EC:2.3.1.221] | Sterigmatocystin |
| 2. | PkgA (Q5AXA9) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | K15317 | APTA; asperthecin synthase | Alternariol |
| 3. | AptA (Q5B0D0) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | Asperthecin | ||
| 4. | Pks13 (G3KLH6.1) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | TAN-1612 | ||
| 5. | VrtA (XP_014544259.1) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | Viridicatumtoxin | ||
| 6. | WA (Q03149) PksP (Q4WZA8) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | K15321 | WA; naphtho-gamma-pyrone polyketide synthase | Naphthopyrone |
| 7. | MdpG (XP_657754.1) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | K15415 | MDPG; monodictyphenone synthase | Endocrocin |
| 8. | OrsA (Q5AUX1) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | K15416 | ORSA; orsellinic acid synthase | Elsinochrome |
| 9. | Pks1 (L7XAV2.1) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | K15417 | ZEA1; zearalenone synthase | Dehydrocurvularin |
| 10. | HypS (XP_030988075.1) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | Hypothemycin | ||
| 11. | RadS (XP_029743834.1) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | Radicicol | ||
| 12. | Sor2 (G0R6S9.1) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | NA | Citrinin synthase | Stipitatic acid |
| 13. | AfoE (A0A5N6H990) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | Chaetoviridin | ||
| 14. | PksCT (Q65Z23) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | Citrinin | ||
| 15. | Bik1 (Q9P855) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | NA | Bikaverin synthase | Bikaverin |
| 16. | Fsr1 (XP_044704191.1) | Type I iterative cis-AT | non-reducing | NA | Fusarubin synthase | Fusarubin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chattopadhyay, P.; Banerjee, G. Diversity and Distribution of Non-Reducing Polyketide Synthases (NR-PKSs) in Ascomycota (Fungi). J. Fungi 2025, 11, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090641
Chattopadhyay P, Banerjee G. Diversity and Distribution of Non-Reducing Polyketide Synthases (NR-PKSs) in Ascomycota (Fungi). Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(9):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090641
Chicago/Turabian StyleChattopadhyay, Pritam, and Goutam Banerjee. 2025. "Diversity and Distribution of Non-Reducing Polyketide Synthases (NR-PKSs) in Ascomycota (Fungi)" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 9: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090641
APA StyleChattopadhyay, P., & Banerjee, G. (2025). Diversity and Distribution of Non-Reducing Polyketide Synthases (NR-PKSs) in Ascomycota (Fungi). Journal of Fungi, 11(9), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090641





