Identification of Macadamia integrifolia Leaf Blight Disease Caused by Pestalotiopsis colombiensis in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Isolation
2.2. Morphological Identification
2.3. DNA Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction and Sequencing
2.4. DNA Sequence Analysis
2.5. Pathogenicity Test
3. Results
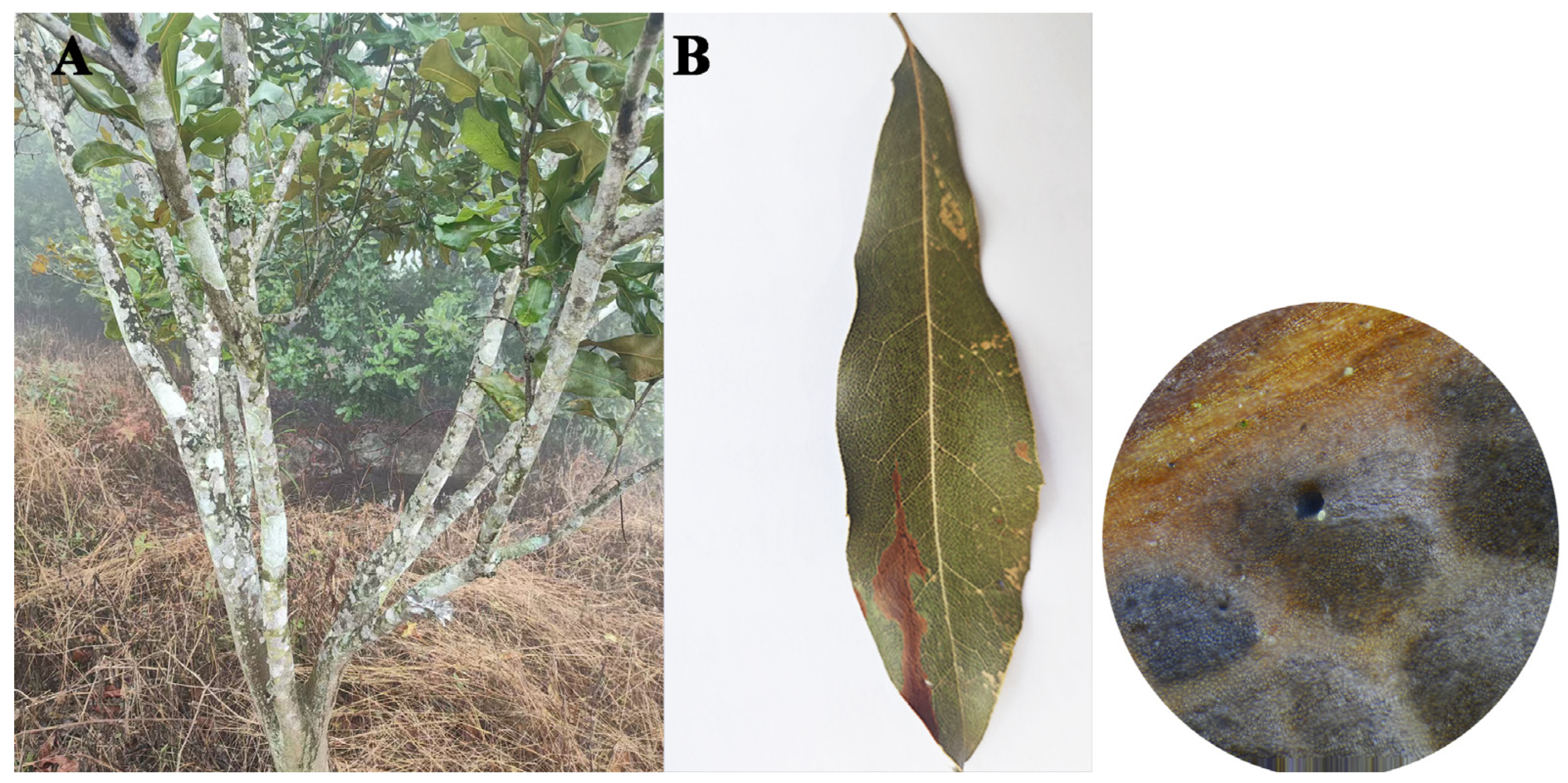
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Morphological Data
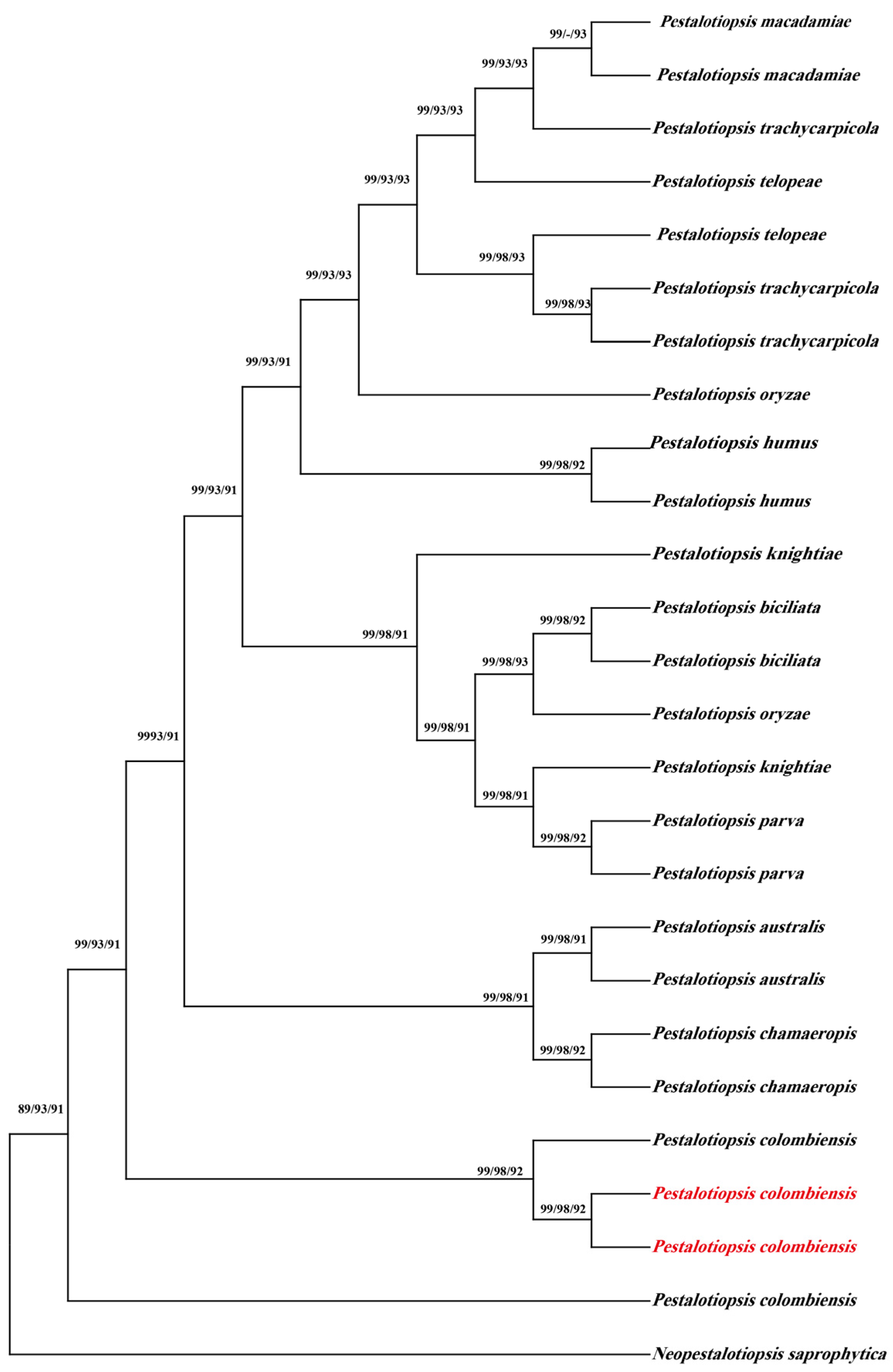
3.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
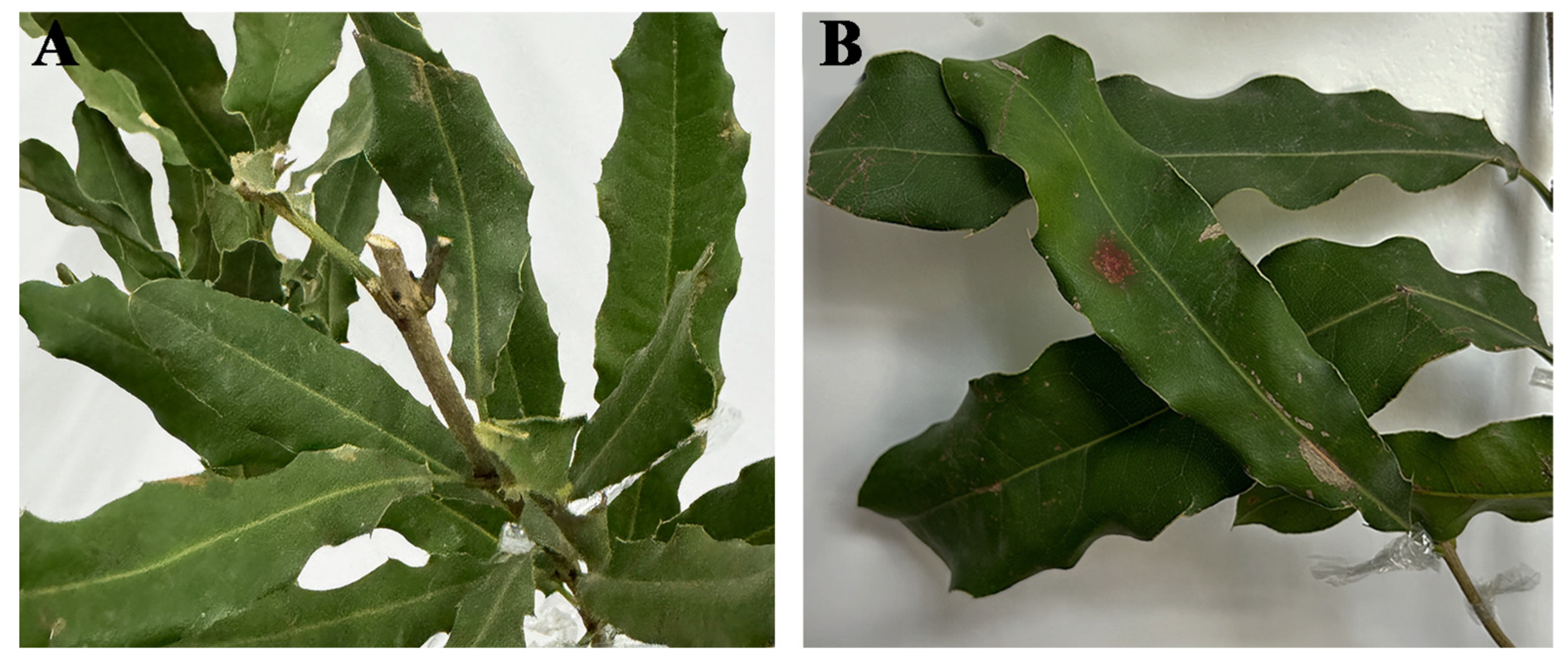
3.4. Pathogenicity Test Using M. Integrifolia Leaves
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aquino-Bolaños, E.N.; Mapel-Velazco, L.; Martín-del-Campo, S.T.; Chávez-Servia, J.L.; Martínez, A.J.; Verdalet-Guzmán, I. Fatty acids profile of oil from nine varieties of Macadamia nut. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeff-Ego, O.S.; Drenth, A.; Topp, B.; Henderson, J.; Akinsanmi, O.A. Prevalence of Phytophthora species in macadamia orchards in Australia and their ability to cause stem canker. Plant Pathol. 2020, 69, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannath, K.; Galea, V.J.; Akinsanmi, O.A. Characterisation of leaf spots caused by Neopestalotiopsis clavispora and Colletotrichum siamense in macadamia in Australia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 156, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeff-Ego, O.S.; Akinsanmi, O.A. Botryosphaeriaceae causing branch dieback and tree death of macadamia in Australia. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2019, 48, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Drenth, A.; Akinsanmi, O.A. Prevalence, identity and seasonal variation of leaf diseases in Australian macadamia nurseries. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2025, 172, 391–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannath, K.; Shivas, R.G.; Galea, V.J.; Akinsanmi, O.A. Neopestalotiopsis Species Associated with Flower Diseases of Macadamia integrifolia in Australia. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyaert, R.L. Contribution à l’étude monographique de Pestalotia de Not. et Monochaetia Sacc. (Truncatella gen. nov. et Pestalotiopsis gen. nov.). Bull. Jard. Bot. État Brux. 1949, 19, 285–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Yang, C.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, F.; Sun, Q.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y. Diversity and pathogenicity of pestalotioid fungi infecting Camellia oleifera in China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.S.; Norman, D.; Brennan, M.; Ali, G.S. First Report of Elm Canker Caused by Pestalotiopsis mangiferae in the United States. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, L.M.; Matsumoto, T.K. First Report of Pestalotiopsis Leaf Blotch on Mangosteen in Hawaii. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Huang, B.; Wu, Z.H. First Report of Pestalotiopsis vismiae Causing Trunk Disease of Chinese Hickory (Carya cathayensis) in China. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, A.L.; Torres, R.; Latorre, B.A. First Report of Pestalotiopsis clavispora and Pestalotiopsis spp. Causing Postharvest Stem End Rot of Avocado in Chile. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, P.; Alaniz, S.; Montelongo, M.J.; Rauduviniche, L.; Rebellato, J.; Silvera-Pérez, E.; Mondino, P. First Report of Pestalotiopsis clavispora Causing Dieback on Blueberry in Uruguay. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Xu, J.; Crous, P.W. Pestalotiopsis revisited. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 79, 121–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Xu, G.; Zheng, F.Q.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, L.; Miao, W.G.; Xie, C.P. First Report of Neopestalotiopsis clavispora Causing Leaf Spot on Macadamia (Macadamia integrifolia) in China. Plant Dis. 2019, 104, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.C.; Domingues, J.L.; Santos, R.F.; Spósito, M.B.; Santos, A.; Novaes, Q.S. First Report of Neopestalotiopsis clavispora Causing Leaf Spot on Macadamia in Brazil. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinsanmi, O.A.; Nisa, S.; Jeff-Ego, O.S.; Shivas, R.G.; Drenth, A. Dry Flower Disease of Macadamia in Australia Caused by Neopestalotiopsis macadamiae sp. nov. and Pestalotiopsis macadamiae sp. nov. Plant Dis. 2016, 101, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Yang, G.; Yan, H.; Liu, C.; Ding, Y.; Deng, S.; Niu, Q.; Li, S.; Tao, L. Current Status and Policy Recommendations for the Development of the Macadamia Nut Industry in Yunnan Province. China Agric. Technol. Ext. 2025, 41, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Hao, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Ma, W.; Gao, F. Identification of Caragana arborescens shoot blight disease caused by Phaeobotryon caraganae sp. nov. (Botryosphaeriales) in China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 155, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A Method for Designing Primer Sets for Speciation Studies in Filamentous Ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.; Kistler, H.C.; Cigelnik, E.; Ploetz, R.C. Multiple evolutionary origins of the fungus causing Panama disease of banana: Concordant evidence from nuclear and mitochondrial gene genealogies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2044–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehner, S.A.; Samuels, G.J. Taxonomy and phylogeny of Gliocladium analysed from nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycol. Res. 1994, 98, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J.; Innis, M.; Gelfand, D.; Sninsky, J. Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, D.M.; Bull, J.J. An Empirical Test of Bootstrapping as a Method for Assessing Confidence in Phylogenetic Analysis. Syst. Biol. 1993, 42, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinsanmi, O.A.; Drenth, A. Characterisation of husk rot in macadamia. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2017, 170, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Akinsanmi, O.A.; Drenth, A. Diseases in macadamia nurseries. Aust. Macad. Soc. News Bull. 2022, 50, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Drenth, A.; Akinsanmi, O.A.; Miles, A. Macadamia diseases in Australia. In Proceedings of the 4th International Macadamia Symposium, Skukuza, South Africa, 6–9 September 2009; Volume 17, pp. 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Phanthavong, S.; Daly, A.; Weir, B.; Lee, D.; Park, D.; Balmas, V.; Burgess, L. First report of Calonectria pseudoreteaudii in Lao PDR associated with a leaf spot disease of Macadamia integrifolia. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2023, 52, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Finnegan, P.M.; Liu, M.; Zhao, J.X.; Nie, Y.L.; Tang, L. First report of Neofusicoccum parvum causing leaf spot disease on Macadamia integrifolia in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 107, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Qin, Q.; Wang, H.; Tang, T. First Report of Pestalotiopsis trachicarpicola Causing Leaf Blight on Panax notoginseng in China. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Pestalotiopsis Diversity: Species, Dispositions, Secondary Metabolites, and Bioactivities. Molecules 2022, 27, 8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xue, M.; Shen, Z.; Jia, X.; Hou, X.; Lai, D.; Zhou, L. Phytotoxic Secondary Metabolites from Fungi. Toxins 2021, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, T.; Ando, Y.; Hirota, A. Phytotoxins from Tea Gray Blight Fungi, Pestalotiopsis longiseta and Pestalotiopsis theae. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1992, 56, 810–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evidente, A.; Cimmino, A.; Masi, M. Phytotoxins produced by pathogenic fungi of agrarian plants. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 843–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.J.; Moon, J.H.; Ajuna, H.B.; Choi, S.I.; Maung, C.E.H.; Lee, S.; Ahn, Y.S. Biological Control of Leaf Blight Disease Caused by Pestalotiopsis maculans and Growth Promotion of Quercus acutissima Carruth Container Seedlings Using Bacillus velezensis CE 100. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, J.; Fu, L.; Xu, G.; Lin, X.; Qiao, J.; Xia, Y. Biocontrol of Wheat Crown Rot Using Bacillus halotolerans QTH8. Pathogens 2022, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, R.S.; Souza, A.Q.L.; Barbosa, A.N.; Santiago, S.; Vasconcelos, A.D.S.; Barbosa, R.D.; Alves, T.C.L.; da Cruz, J.C.; da Silva, G.F.; Bentes, J.; et al. Biodiversity and Antifungal Activities of Amazonian Actinomycetes Isolated from Rhizospheres of Inga edulis Plants. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2024, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hu, M.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Lu, G.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J. Five Fungal Pathogens Are Responsible for Bayberry Twig Blight and Fungicides Were Screened for Disease Control. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Yadav, S.; Samota, M.K.; Sharma, H.K.; Roy, S. Trichoderma harzianum TIND02 upregulates the expression of pathogenesis-related genes and enzymes and enhances gray blight resistance in tea. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 205, 106115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, M.Z.; Kong, L.; Jiang, Y.; Asghar, N.; Habib, A.; Lu, C.; Ding, X. Control of Pestalotiopsis Leaf Spot of Palms by Fungicides, Plant Hormones, and Biological Agents. Plant Dis. 2025, 109, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Ma, W.; An, J.; Zhang, B.; Sun, W.; Zhang, G. Nerol as a Novel Antifungal Agent: In Vitro Inhibitory Effects on Fusarium oxysporum, Pestalotiopsis neglecta, and Valsa mali and Its Potential Mechanisms against F. oxysporum. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Zhang, B.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Shi, W.; Yan, S.; Tang, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X. Analysis of fatty acid compositions and concentrations in the kernel of seven main macadamia cultivars in Yunnan. J. Fruit Sci. 2025, 42, 828–839. [Google Scholar]


| Locus | Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | Tm (℃) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEFl-α | EF1-728F | GTACCCGCTGAACTTAAGC | 52 | [20] |
| EF2 | GGA(G/A)GTACAGT(G/C)ATCATGTT | [21] | ||
| LSU | LROR | GTACCCGCTGAACTTAAGC | 47 | [22] |
| LR5 | ATCCTGAGGGAAACTTC | [23] | ||
| ITS | ITS1 | TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG | 50 | [24] |
| ITS4 | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATAT |
| Isolate | Country/Location | Host/Habitat | ITS | LSU | EF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pestalotiopsis telopeae | |||||
| JX16b; CBS 113606; CBS 114161 | China; Thailand | Unknown; Telopea sp. | OR781522 | KM116202 | KM199500 |
| GZ22b; CBS 114137 | China; Thailand | Unknown; Protea sp. | OR781519 | KM116219 | KM199559 |
| P. trachycarpicola | |||||
| ZHKUCC 23-1026; AV-108; GUCC 23-0414 | China; India | Cave subculture; Persea americana; Unknown | PP029403 | PQ299650 | PQ141020 |
| PB2-e; AV-244; OP068 | China; India; Thailand | Panax notoginseng; Persea americana; Trachycarpus fortunei | OR056327 | PQ299673 | JQ845946 |
| YA3; AV-191; OP143 | China; India; Thailand | Unknown; Persea americana; Podocarpus macrophyllus | OR484805 | PQ299666 | KC537816 |
| P. oryzae | |||||
| CBS 171.26 | Thailand | Unknown | KM199304 | MH866374 | KM199494 |
| MWN35; Y2-3; CBS 111522 | Kenya; China; Thailand | Oryza sativa; Unknown; Telopea sp. | OM899910 | PQ432485 | KM199493 |
| P. knightiae | |||||
| KoRLI046217; NSW:7213; CBS 111963 | Korea; Australia; Thailand | Stereocaulon japonicum; Banksia serrata; Knightia sp. | MN341554 | OP082342 | KM199406 |
| CBS 114138 | Thailand | Knightia sp. | KM199310 | KM116227 | KM199408 |
| P. biciliata | |||||
| CBS 236.38 | Netherlands; Thailand | Unknown; Paeonia sp. | MH855953 | KM116214 | KM199506 |
| UMAS P16; CBS 124463 | Malaysia; Thailand | Shorea macrophylla; Platanus x hispanica | KT337374 | KM116224 | KM199505 |
| P. parva | |||||
| D034; CBS 265.37 | Malaysia; Thailand | Cocos nucifera; Delonix regia | OP727543 | KM116226 | KM199508 |
| CBS 278.35 | Thailand | Leucothoe fontanesiana | KM199313 | KM116205 | KM199509 |
| P. humus | |||||
| CBS 115450 | Thailand | Unknown; Ilex cinerea | KM199319 | KM116208 | KM199487 |
| CBS 336.97 | Thailand | Unknown | KM199317 | KM116230 | KM199484 |
| P. australis | |||||
| CBS 114193; CBS 114474; CBS 111503 | Thailand | Grevillea sp.; Protea susannae | NR145239 | KM116220 | KM199557 |
| CBS 114193 | Thailand | Grevillea sp. | KM199332 | KM116197 | KM199475 |
| P. chamaeropis | |||||
| CBS 186.71 | Thailand; Netherlands | Chamaerops humilis; Unknown | KM199326 | MH871839 | KM199473 |
| CBS 237.38; LC3619 | Australia; Netherlands; China | Prostanthera rotundifolia; Unknown; Camellia sp. | KR259104 | MH867450 | KX895208 |
| P. macadamiae | |||||
| BRIP 63739b; BRIP 70520 | Australia; India | Macadamia sp.; Pongamiea sp. | KX186587 | OP363152 | MZ327136 |
| BRIP 70519 | Australia | Macadamia sp. | MZ303757 | - | MZ327135 |
| P. colombiensis | |||||
| CBS 118553 | Thailand | Eucalyptus grandis | NR147551 | NG069213 | KM199488 |
| 5F; CBS 118553 | Australia; Thailand | Oryza australiensis; Eucalyptus grandis | KU715149 | KM116222 | - |
| SWFUCB2 | China | Macadamia integrifolia | PQ895603 | PQ895623 | PQ997934 |
| SWFUCB1 | China | Macadamia integrifolia | PQ895604 | PQ895622 | PQ997935 |
| Neopestalotiopsis saprophytica | |||||
| CBS 115452 | Thailand | Litsea rotundifolia | KM199345 | KM116251 | KM199538 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Lei, Y.; Ma, L.; He, X.; Dai, W.; Chen, J.; Hao, X. Identification of Macadamia integrifolia Leaf Blight Disease Caused by Pestalotiopsis colombiensis in China. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090613
Yu H, Lei Y, Ma L, He X, Dai W, Chen J, Hao X. Identification of Macadamia integrifolia Leaf Blight Disease Caused by Pestalotiopsis colombiensis in China. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(9):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090613
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Huizhi, Youyan Lei, Ling Ma, Xiahong He, Wenhao Dai, Jie Chen, and Xin Hao. 2025. "Identification of Macadamia integrifolia Leaf Blight Disease Caused by Pestalotiopsis colombiensis in China" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 9: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090613
APA StyleYu, H., Lei, Y., Ma, L., He, X., Dai, W., Chen, J., & Hao, X. (2025). Identification of Macadamia integrifolia Leaf Blight Disease Caused by Pestalotiopsis colombiensis in China. Journal of Fungi, 11(9), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11090613







