Relationship Between Aquatic Fungal Diversity in Surface Water and Environmental Factors in Yunnan Dashanbao Black-Necked Crane National Nature Reserve, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Methodology
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing Analysis of Aquatic Fungi
2.3. Determination of Environmental Factors
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Water Samples in Dashanbao Nature Reserve
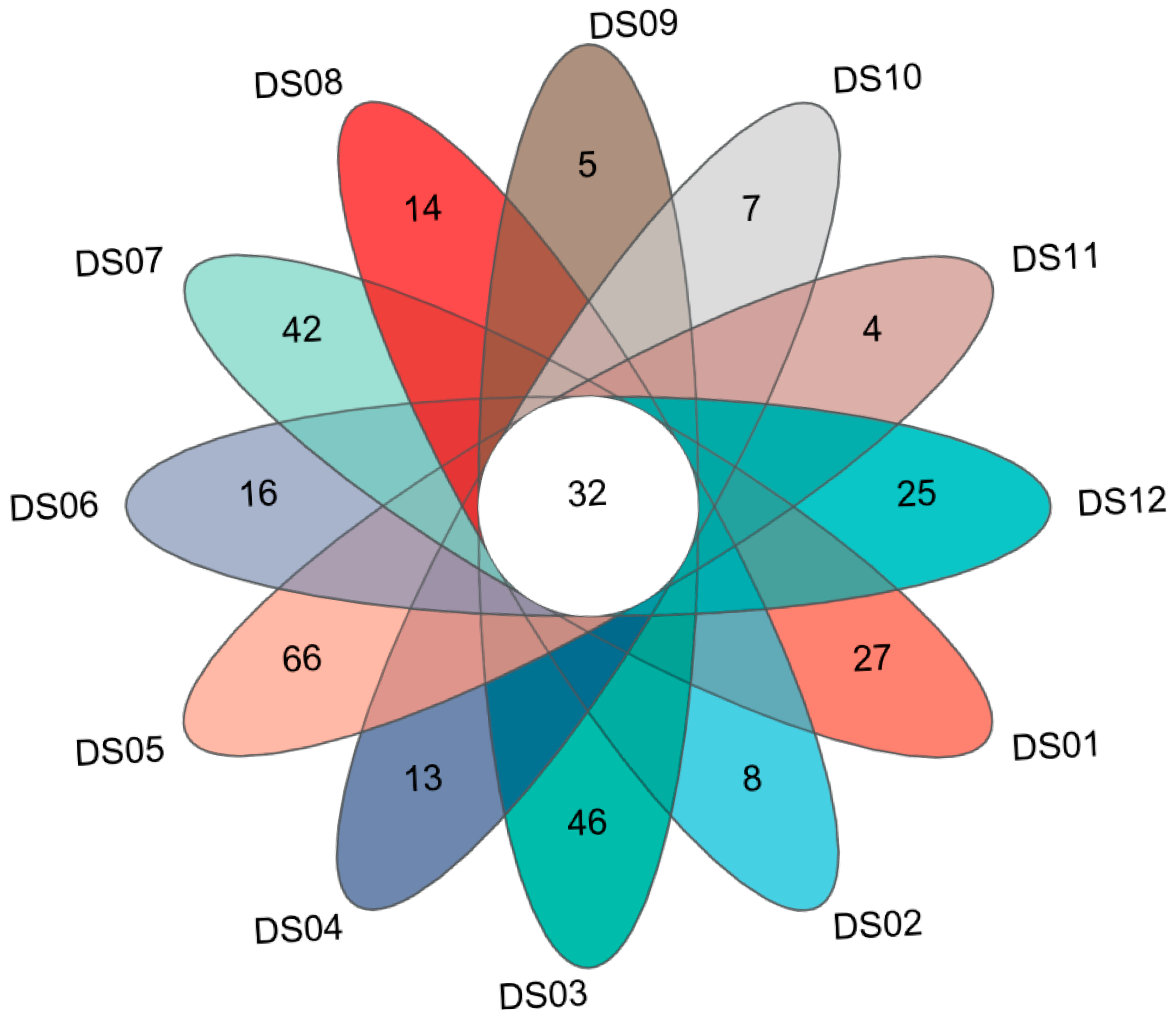
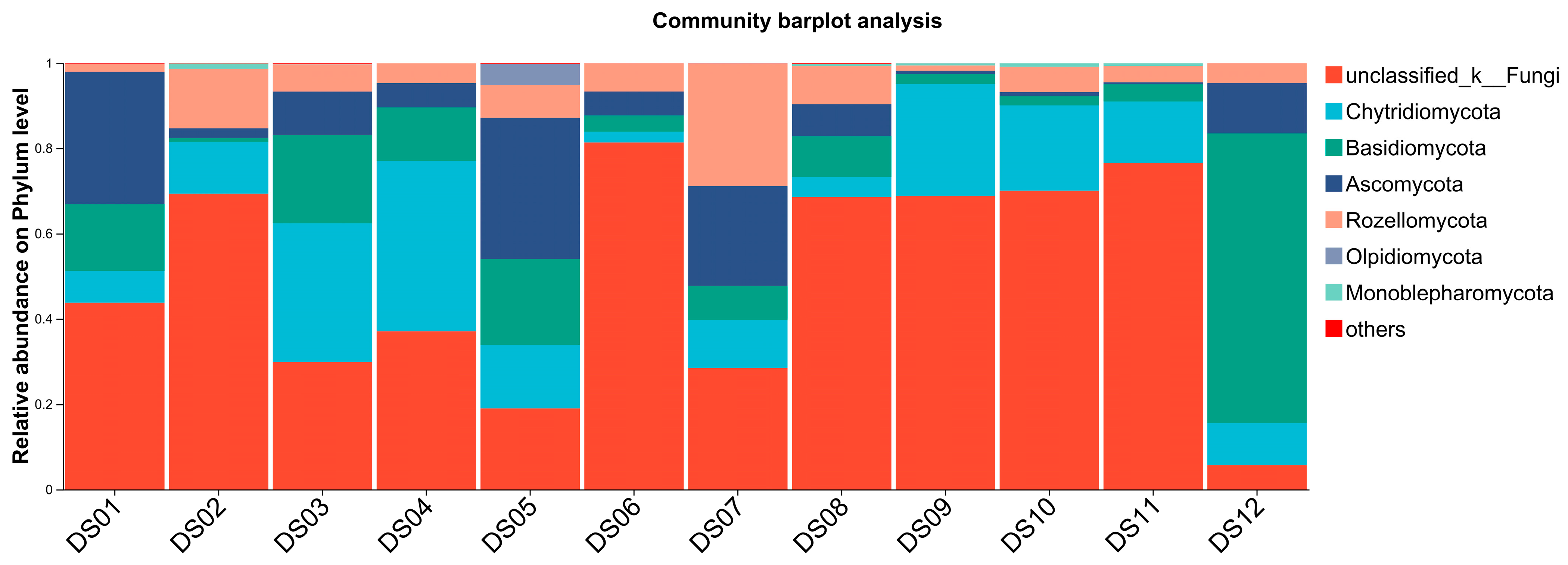
3.2. Composition and Distribution of Aquatic Fungi in Dashanbao Nature Reserve
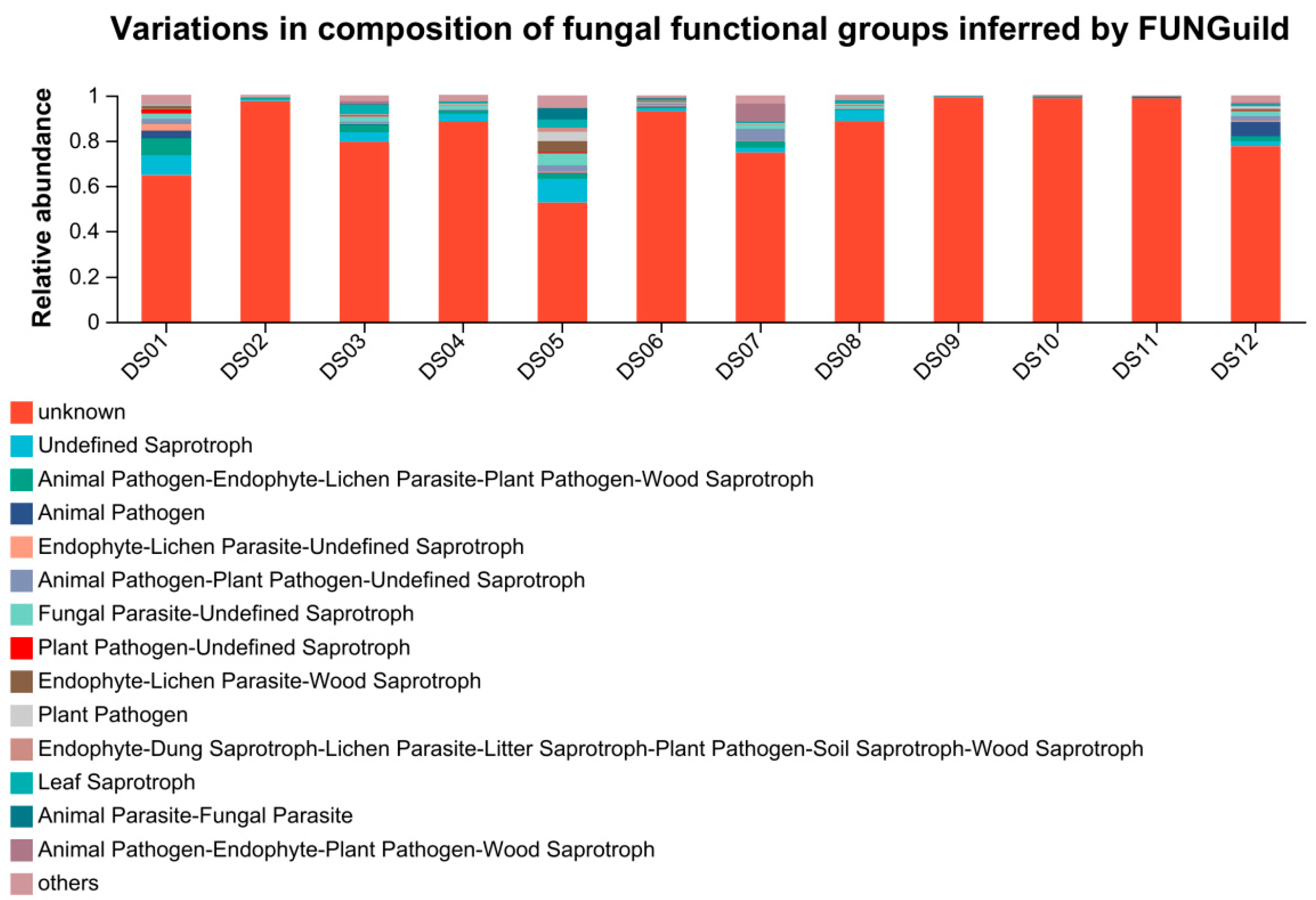
3.3. Function Prediction of Fungi by FUNGuild
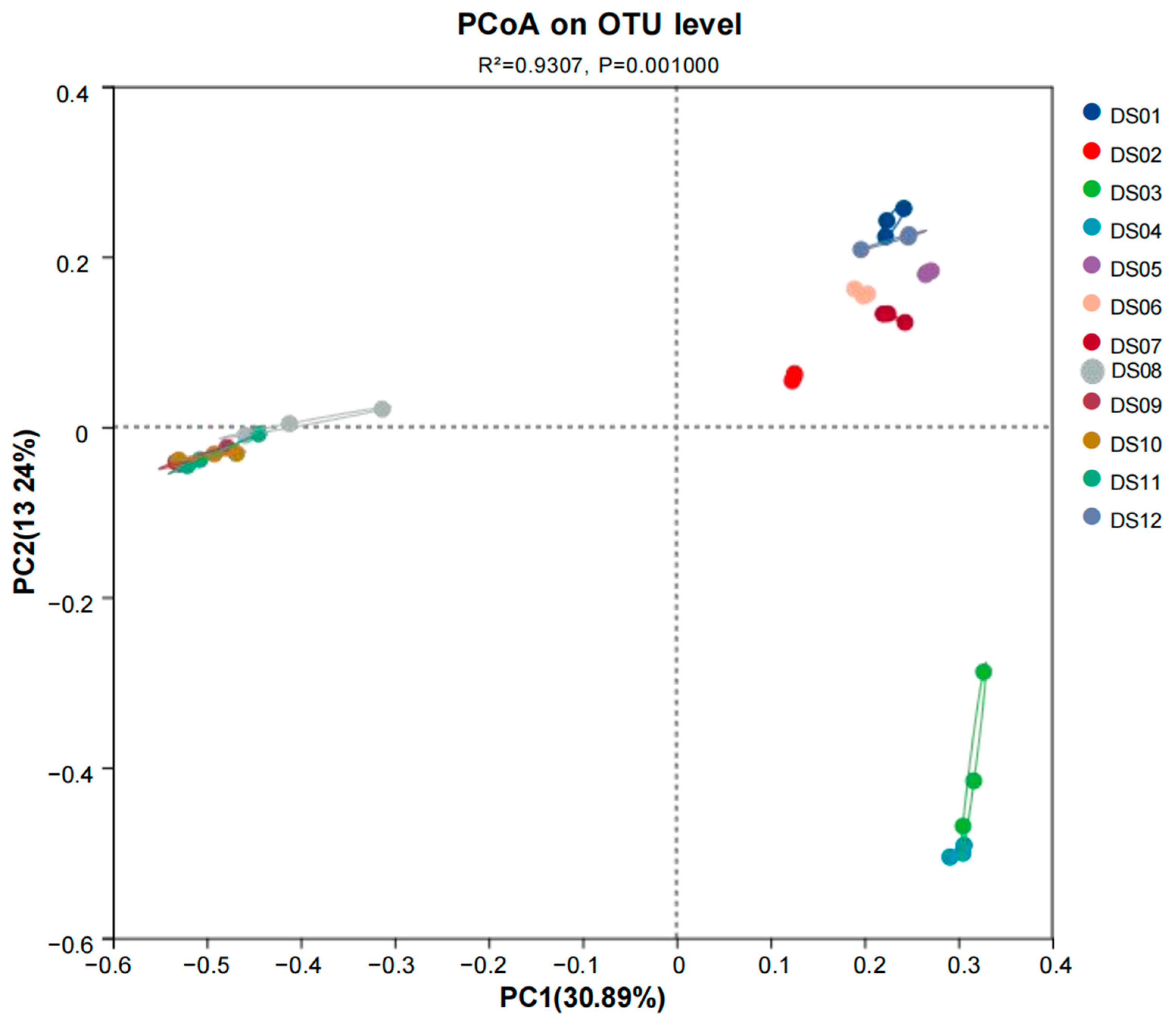
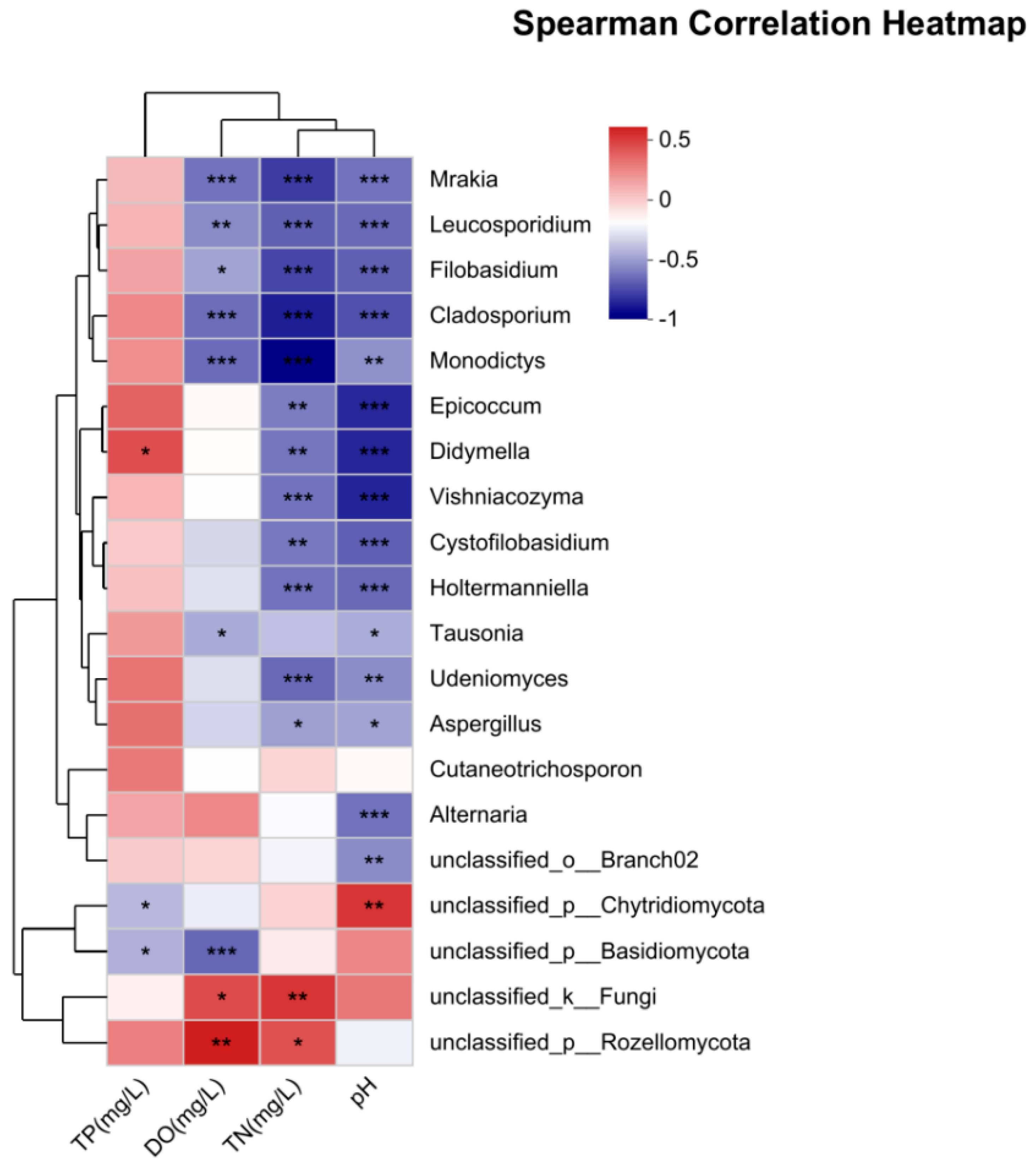
3.4. Correlation Between Fungi and Environmental Factors
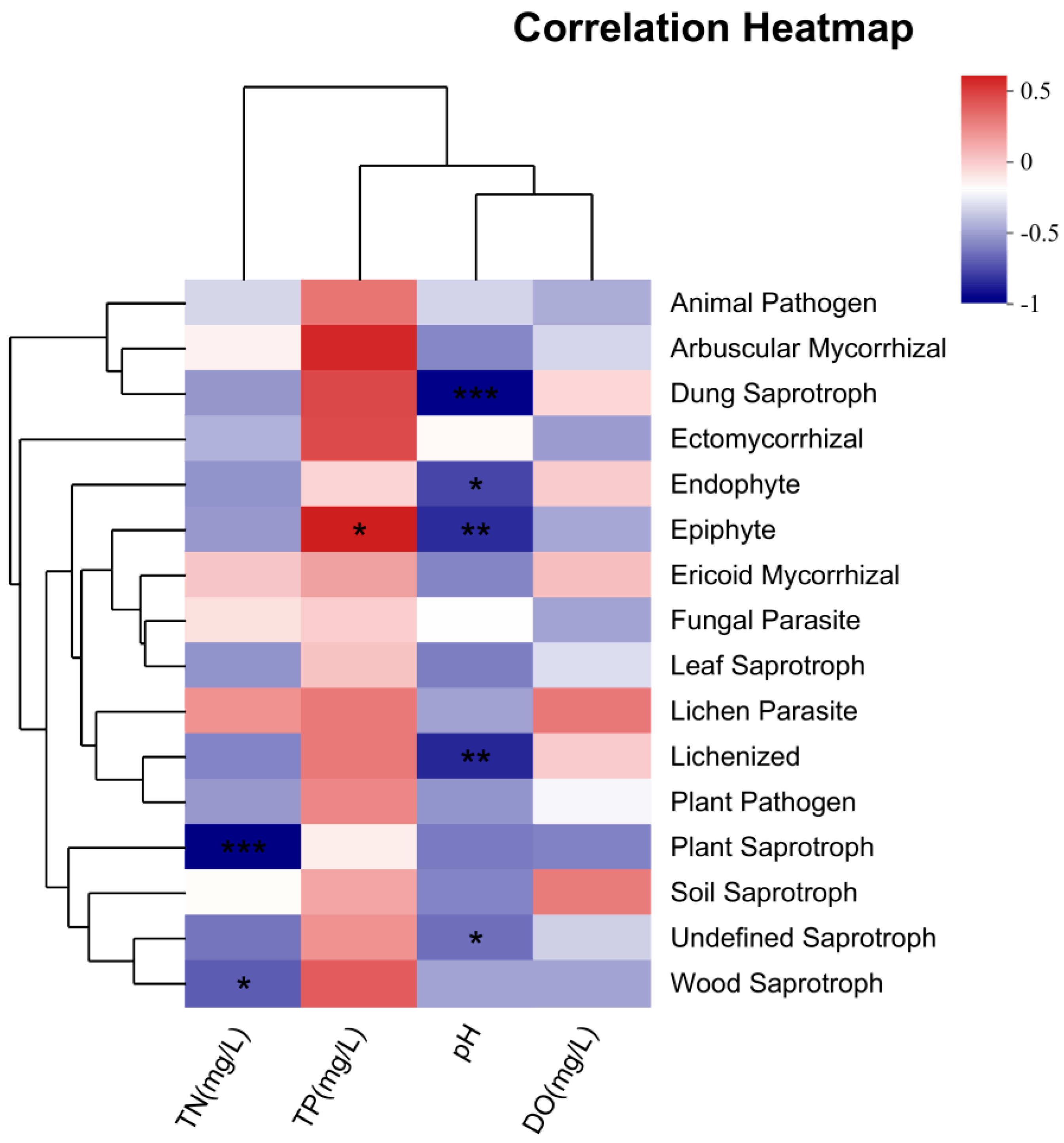
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Trophic Modes and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Environmental Factors in Dashanbao Nature Reserve Water
4.2. Fungal Diversity and Distribution
4.3. Correlation Analysis Between the Fungal Communities and Environmental Factors
4.4. Correlation Between Fungal Function Prediction and Environmental Factors
4.5. Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shearer, C.A.; Descals, E.; Kohlmeyer, B.; Kohlmeyer, J.; Marvanová, L.; Padgett, D.; Porter, D.; Raja, H.A.; Schmit, J.P.; Thorton, H.A.; et al. Fungal biodiversity in aquatic habitats. Biodivers. Conserv. 2006, 16, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Follstad Shah, J.J. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagami, M.; Miki, T.; Takimoto, G. Mycoloop: Chytrids in aquatic food webs. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, A.; West, M.; Berger, L.; Brannelly, L.A. The impacts of water quality on the amphibian chytrid fungal pathogen: A systematic review. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2024, 16, e13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Lin, J.; Yang, D.; Peng, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, C. Fungal pathogen promotes caterpillar feeding and weight gain using a host-like trehalase. Curr. Biol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, C. The freshwater ascomycetes. Nova Hedwig. 1993, 56, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Calabon, M.S.; Hyde, K.D.; Jones, E.G.; Luo, Z.-L.; Dong, W.; Hurdeal, V.G.; Gentekaki, E.; Rossi, W.; Leonardi, M.; Thiyagaraja, V. Freshwater fungal numbers. Fungal Divers. 2022, 114, 3–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossart, H.-P.; Van den Wyngaert, S.; Kagami, M.; Wurzbacher, C.; Cunliffe, M.; Rojas-Jimenez, K. Fungi in aquatic ecosystems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tant, C.J.; Rosemond, A.D.; Mehring, A.S.; Kuehn, K.A.; Davis, J.M. The role of aquatic fungi in transformations of organic matter mediated by nutrients. Freshwat Biol. 2015, 60, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liao, K.; Jian, Z.; Zhao, C.; Qu, J. Fungal community as a bioindicator to reflect anthropogenic activities in a river ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasching, C.; Akotoye, C.; Bižić, M.; Fonvielle, J.; Ionescu, D.; Mathavarajah, S.; Zoccarato, L.; Walsh, D.A.; Grossart, H.P.; Xenopoulos, M.A. Linking stream microbial community functional genes to dissolved organic matter and inorganic nutrients. Limnol Ocean. 2019, 65, S71–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, C.A.; Langsam, D.M.; Longcore, J.E. Fungi in freshwater habitats. In Biodiversity of Fungi: Inventory and Monitoring methods; Elsevier Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 513–531. [Google Scholar]
- Tedersoo, L.; Bahram, M.; Põlme, S.; Kõljalg, U.; Yorou, N.S.; Wijesundera, R.; Ruiz, L.V.; Vasco-Palacios, A.M.; Thu, P.Q.; Suija, A. Global diversity and geography of soil fungi. Science 2014, 346, 1256688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiedje, J.M.; Asuming-Brempong, S.; Nüsslein, K.; Marsh, T.L.; Flynn, S.J. Opening the black box of soil microbial diversity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1999, 13, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, C.R.; Forn, I.; Romac, S.; Logares, R.; de Vargas, C.; Massana, R. Environmental sequencing provides reasonable estimates of the relative abundance of specific picoeukaryotes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4757–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasconi, S.; Niquil, N.; Sime-Ngando, T. Phytoplankton chytridiomycosis: Community structure and infectivity of fungal parasites in aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2151–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraldsson, M.; Gerphagnon, M.; Bazin, P.; Colombet, J.; Tecchio, S.; Sime-Ngando, T.; Niquil, N. Microbial parasites make cyanobacteria blooms less of a trophic dead end than commonly assumed. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1008–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artigas, J.; Romaní, A.; Sabater, S. Effect of nutrients on the sporulation and diversity of aquatic hyphomycetes on submerged substrata in a Mediterranean stream. Aquat. Bot. 2008, 88, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.; Fernandes, I.; Nogueira, M.J.; Cássio, F.; Pascoal, C. Temperature alters interspecific relationships among aquatic fungi. Fungal Ecol. 2013, 6, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.D.; Cunliffe, M. Coastal bacterioplankton community response to diatom-derived polysaccharide microgels. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2017, 9, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monchy, S.; Sanciu, G.; Jobard, M.; Rasconi, S.; Gerphagnon, M.; Chabé, M.; Cian, A.; Meloni, D.; Niquil, N.; Christaki, U. Exploring and quantifying fungal diversity in freshwater lake ecosystems using rDNA cloning/sequencing and SSU tag pyrosequencing. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1433–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, F.; Wu, H.; Gao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Zhong, X.; Yang, X.; Zheng, G. Migration routes and stopover sites of Black-necked Cranes determined by satellite tracking. J. Field Ornithol. 2009, 80, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Li, F.; Gao, L.; Wu, H. First Satellite Tracking of Black necked Cranes in China. Zool. Res. 2005, 26, 657–658. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; López-Carr, D.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Longcore, T. What factors influence the willingness of protected area communities to relocate? China’s ecological relocation policy for Dashanbao Protected Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seena, S.; Baschien, C.; Barros, J.; Sridhar, K.R.; Graça, M.A.; Mykrä, H.; Bundschuh, M. Ecosystem services provided by fungi in freshwaters: A wake-up call. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 2779–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, Y.; Matsuoka, S.; Shimono, Y.; Ushio, M.; Doi, H. Do aquatic fungal environmental DNA assemblages reflect the surrounding terrestrial sporocarp communities? Fungal Ecol. 2024, 67, 101311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yao, Y.; Tian, H.; Sang, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, H. Structural changes in the gut microbiota community of the black-necked crane (Grus nigricollis) in the wintering period. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 6203–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Dossa, G.G.O.; Paudel, E.; Zang, H.; Xu, J.; Harrison, R.D. Changes in Fungal Communities across a Forest Disturbance Gradient. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00080-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nollet, L.M.L. Handbook of Water Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Qiao, M.; Zhong, J.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, P.; Han, L.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Y.; et al. Characterization of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community in selected municipal and industrial sewage treatment plants beside Poyang Lake. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, B.D.; Nilsson, R.H.; Tedersoo, L.; Abarenkov, K.; Carlsen, T.; Kjøller, R.; Kõljalg, U.; Pennanen, T.; Rosendahl, S.; Stenlid, J. Fungal community analysis by high-throughput sequencing of amplified markers–a user’s guide. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Flash, S.S. Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sen, K.; He, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, G. Impact of environmental gradients on the abundance and diversity of planktonic fungi across coastal habitats of contrasting trophic status. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbareche, H.; Veillette, M.; Bilodeau, G.J. In silico study suggesting the bias of primers choice in the molecular identification of fungal aerosols. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorde, S.; Jadhav, M. Assessment of water quality parameters: A review. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2013, 3, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar]
- Dobosy, P.; Almeshal, W.; Illés, Á.; Tserendorj, D.; Sandil, S.; Kovács, Z.; Endrédi, A.; Záray, G. Particle-based nutrients and metal contaminants in the habitat of Unionidae mussels in the Tisza River (Hungary). Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1209118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, A.; Pallasch, M.; Schönfelder, I.; Gelbrecht, J.; Zak, D. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus accumulation in novel ecosystems: Shallow lakes in degraded fen areas. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 66, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Huang, J.; Wei, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J. Spectrophotometric Determination of Total Phosphorus in Fresh Water Using Ammonium Molybdate. Sens. Mater. 2024, 36, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Liu, Y.; Liao, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Mo, L.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, X. Fungal diversity and its relationship with environmental factors in coastal sediments from Guangdong, China. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An Ordination of the Upland Forest Communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhe; Chen, X.; Hou, F.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, Y. Bacterial and Fungal Community Structures in Loess Plateau Grasslands with Different Grazing Intensities. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Duan, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Huang, J.; Fu, J.; Zi, L.; Xu, T. Spatiotemporal variations in water quality parameters and assessment of the current status and challenges of eutrophication in Lake Dian. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 177, 113821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, W.; Felix Dan, S.; Yang, B.; Kang, Z.; Yu, K. Sources and long-term variation characteristics of dissolved nutrients in Maowei Sea, Beibu Gulf, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 615, 128576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, M.; Bergström, A.-K.; Lymer, D.; Vrede, K.; Karlsson, J. Bacterioplankton Growth and Nutrient Use Efficiencies Under Variable Organic Carbon and Inorganic Phosphorus Ratios. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Cerozi, B.; Fitzsimmons, K. The effect of pH on phosphorus availability and speciation in an aquaponics nutrient solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, W.; Boynton, W. Influence of biological and physical processes on dissolved oxygen dynamics in an estuarine system: Implications for measurement of community metabolism. Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci. 1980, 11, 407–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, B.; Pados, T.; Pretterebner, K.; Schiemer, L.; Steckbauer, A.; Haselmair, A.; Zuschin, M.; Stachowitsch, M. Effect of hypoxia and anoxia on invertebrate behaviour: Ecological perspectives from species to community level. Biogeosci. Disc. 2013, 10, 14333–14438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquer-Sunyer, R.; Duarte, C.M. Thresholds of hypoxia for marine biodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15452–15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zou, M.; Jiang, L. Dissolved oxygen control strategies for water treatment: A review. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 1444–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, P.P.; Ferreira, V.; Tonin, A.M.; Medeiros, A.O.; Júnior, J.F.G. Combined effects of dissolved nutrients and oxygen on plant litter decomposition and associated fungal communities. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, S.; Heard, K.M.; Martin, T.G. The relative importance of cattle grazing in subtropical grasslands: Does it reduce or enhance plant biodiversity? J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, L. Effects of planting years of vegetable solar greenhouse on soil microbial flora and enzyme activities. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2013, 24, 2539–2544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Yu, F.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Xia, T.; Kuehl, S.A.; Zong, Y. Anthropogenic impact on the organic carbon sources, transport and distribution in a subtropical semi-enclosed bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 145047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, W.W.; Cartwright, I.; Poh, S.C.; Cook, P. Sources and cycling of nitrogen revealed by stable isotopes in a highly populated large temperate coastal embayment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sha, J.; Wang, Z.-L. Chlorophyll-a prediction of lakes with different water quality patterns in China based on hybrid neural networks. Water 2017, 9, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Smith, V.H. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in streams. Inland. Waters 2016, 6, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomich, M.; Davey, M.L.; Kauserud, H.; Rasconi, S.; Andersen, T. Fungal communities in Scandinavian lakes along a longitudinal gradient. Fungal Ecol. 2017, 27, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, G.; Bartlam, M.G. Distribution and diversity of fungi in freshwater sediments on a river catchment scale. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Singh, P.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Johnson, Z.I.; Wang, G. Distribution and diversity of planktonic fungi in the West Pacific Warm Pool. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Genetic diversity patterns of microbial communities in a subtropical riverine ecosystem (Jiulong River, southeast China). Hydrobiologia 2011, 678, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiya, N.; Shede, P.; Sharma, A. Diversity and composition of fungal communities across diverse environmental niches in Antarctica. Polar Sci. 2023, 38, 100973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Anees, S.A.; Rehman, A.; Tariq, A.; Liu, Q.; Muhammad, S.; Rabbi, F.; Pan Sa Hatamleh, W.A. Assessing forest cover changes and fragmentation in the Himalayan temperate region: Implications for forest conservation and management. J. For. Res. 2024, 35, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeljak, P.; Baltar, F. Fungal Diversity and Community Composition across Ecosystems. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, M.J.; Albarracín, V.H.; Lara, J.A.; Ferrero, M.A.; Farías, M.E. Culture-dependent and -independent methods reveal dominance of halophilic Euryarchaeota in high-altitude Andean lakes. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 81, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Jimenez, K.; Wurzbacher, C.; Bourne, E.C.; Chiuchiolo, A.; Priscu, J.C.; Grossart, H.-P. Early diverging lineages within Cryptomycota and Chytridiomycota dominate the fungal communities in ice-covered lakes of the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascoal, C.; Marvanová, L.; Cássio, F. Aquatic hyphomycete diversity in streams of Northwest Portugal. Fungal Divers. 2005, 19, 109–128. [Google Scholar]
- Solé, M.; Fetzer, I.; Wennrich, R.; Sridhar, K.; Harms, H.; Krauss, G. Aquatic hyphomycete communities as potential bioindicators for assessing anthropogenic stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 389, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, R.; Rajput, V.; Shah, M.; Yadav, R.; Sarode, P.; Dastager, S.G.; Dharne, M.S.; Khairnar, K. Deciphering taxonomic and functional diversity of fungi as potential bioindicators within confluence stretch of Ganges and Yamuna Rivers, impacted by anthropogenic activities. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, P. On some Advances in the Biological Control of the Fermentation Industries, by the Aid of the Microscope. J. Fed. Inst. Brew. 1895, 1, 547–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdichon, F.; Alper, I.; Bibiloni, R.; Dubois, A.; Laulund, S.; Miks, M.; Morelli, L.; Zuliani, V.; Yao, S. Inventory of microbial food cultures with safety demonstration in fermented food products. Bull. Int. Dairy. Fed. 2018, 495, 5–71. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, T. Nonpoint Source Pollution (NPSP) Induces Structural and Functional Variation in the Fungal Community of Sediments in the Jialing River, China. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 85, 1308–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtarnejad, L.; Arzanlou, M.; Babai-Ahari, A.; Di Mauro, S.; Onofri, A.; Buzzini, P.; Turchetti, B. Characterization of basidiomycetous yeasts in hypersaline soils of the Urmia Lake National Park, Iran. Extremophiles 2016, 20, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavello, I.; Albanesi, A.; Fratebianchi, D.; Garmedia, G.; Vero, S.; Cavalitto, S. Pectinolytic yeasts from cold environments: Novel findings of Guehomyces pullulans, Cystofilobasidium infirmominiatum and Cryptococcus adeliensis producing pectinases. Extremophiles 2017, 21, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.-L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.-F.; Sun, H.-Y.; Song, C.-L.; Chi, Z.-M. Enhanced β-galactosidase production from whey powder by a mutant of the psychrotolerant yeast Guehomyces pullulans 17–1 for hydrolysis of lactose. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyde, K.D.; Fryar, S.; Tian, Q.; Bahkali, A.H.; Xu, J. Lignicolous freshwater fungi along a north–south latitudinal gradient in the Asian/Australian region; can we predict the impact of global warming on biodiversity and function? Fungal Ecol. 2016, 19, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, I.P.; Zak, D.R. Phylogenetic similarity and structure of Agaricomycotina communities across a forested landscape. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 1469–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oide, S.; Moeder, W.; Krasnoff, S.; Gibson, D.; Haas, H.; Yoshioka, K.; Turgeon, B.G. NPS6, encoding a nonribosomal peptide synthetase involved in siderophore-mediated iron metabolism, is a conserved virulence determinant of plant pathogenic ascomycetes. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2836–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, R.; Ye, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C. Monitoring and research of microcystins and environmental factors in a typical artificial freshwater aquaculture pond. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 5921–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, B.; Hussain, M.; Liu, X. Environmental factors driving fungal distribution in freshwater lake sediments across the Headwater Region of the Yellow River, China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Liu, X.; Gong, L.; Liu, R.; Ling, M.; Guo, C.; Meng, H.; Luo, Z.; Du, X.; Guo, Y. Impact of environmental factors on diversity of fungi in sediments from the Shenzhen River Estuary. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianutsevich, E.A.; Danilova, O.A.; Grum-Grzhimaylo, O.A.; Tereshina, V.M. The Role of Osmolytes and Membrane Lipids in the Adaptation of Acidophilic Fungi. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, I.P.; Zak, D.R.; Kellner, H.; Eisenlord, S.D.; Pregitzer, K.S. Simulated atmospheric N deposition alters fungal community composition and suppresses ligninolytic gene expression in a northern hardwood forest. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, K.; Jacoby, G.A. Updated functional classification of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmi, K.; Kuroo, N.; Oide, K.; Zhou, D.; Zimmermann, F. Coherent Beam-Beam Instability in Collisions with a Large Crossing Angle. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 134801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierella Karlusich, J.J.; Pelletier, E.; Lombard, F.; Carsique, M.; Dvorak, E.; Colin, S.; Picheral, M.; Cornejo-Castillo, F.M.; Acinas, S.G.; Pepperkok, R.; et al. Global distribution patterns of marine nitrogen-fixers by imaging and molecular methods. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, A.; Pascoal, C.; Graça, M. Diversity and activity of aquatic fungi under low oxygen conditions. Freshwat Biol. 2009, 54, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, L.; Obst, C.; Edens, B.; Remme, R.P. Progress and challenges in the development of ecosystem accounting as a tool to analyse ecosystem capital. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 14, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Dou, H.; Wei, Q.; Ma, S.; Sun, G.; Wang, L.; Sha, W.; Zhang, H. Environmental factors and stochasticity affect the fungal community structures in the water and sediments of Hulun Lake, China. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z.; Sui, G.; Li, D.; Kan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, W.; Chen, J. The decay of airborne bacteria and fungi in a constant temperature and humidity test chamber. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Gao, L.; Zhang, S. Effects of bird aggregation on the soil properties and microbial community diversity of urban forest fragments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xiang, W.; Wu, H.; Ouyang, S.; Lei, P.; Hu, Y.; Ge, T.; Ye, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Contrasting patterns and drivers of soil fungal communities in subtropical deciduous and evergreen broadleaved forests. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 5421–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Site | GPSN (Latitude) | GPSE (Longitude) | Elevation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DS01 | 27°25′21″ | 103°21′54″ | 2887 |
| DS02 | 27°27′59″ | 103°22′28″ | 2841 |
| DS03 | 27°27′39″ | 103°21′51″ | 2684 |
| DS04 | 27°28′50″ | 103°21′32″ | 2925 |
| DS05 | 27°28′30″ | 103°21′21″ | 2708 |
| DS06 | 27°27′20″ | 103°19′15″ | 2708 |
| DS07 | 27°26′28″ | 103°19′23″ | 3002 |
| DS08 | 27°25′39″ | 103°18′13″ | 3015 |
| DS09 | 27°23′35″ | 103°16′15″ | 3020 |
| DS10 | 27°23′30″ | 103°17′44″ | 3147 |
| DS11 | 27°22′54″ | 103°19′13″ | 3125 |
| DS12 | 27°20′20″ | 103°60′54″ | 2742 |
| Site | Total Nitrogen (mg/L) | Total Phosphorus (mg/L) | pH | Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) | Sampling Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS01 | 0.3982 ± 0.0271 a | 0.0404 ± 0.0018 abc | 7.9 ± 0.3 a | 4.6 ± 0.3 a | 08:00 |
| DS02 | 7.8115 ± 0.3462 g | 0.0427 ± 0.0029 c | 9.2 ± 0.2 c | 12.0 ± 0.3 g | 08:15 |
| DS03 | 1.6577 ± 0.1676 c | 0.0424 ± 0.0062 bc | 8.0 ± 0.3 a | 7.2 ± 0.3 b | 09:30 |
| DS04 | 0.9654 ± 0.2035 b | 0.0388 ± 0.0012 abc | 8.0 ± 0.2 a | 10.0 ± 0.3 e | 10:00 |
| DS05 | 0.3243 ± 0.0222 a | 0.0392 ± 0.0007 abc | 7.9 ± 0.2 a | 9.0 ± 0.3 c | 11:20 |
| DS06 | 1.0679 ± 0.0588 b | 0.0400 ± 0.0012 abc | 7.8 ± 0.3 a | 10.0 ± 0.3 e | 12:30 |
| DS07 | 2.8115 ± 0.1387 d | 0.0408 ± 0.0034 abc | 7.8 ± 0.1 a | 10.8 ± 0.3 f | 13:15 |
| DS08 | 5.8500 ± 0.0666 f | 0.0385 ± 0.0024 abc | 8.0 ± 0.2 a | 11.1 ± 0.3 f | 13:45 |
| DS09 | 2.6192 ± 0.0385 d | 0.0373 ± 0.0007 ab | 9.1 ± 0.2 c | 9.5 ± 0.2 d | 14:00 |
| DS10 | 2.7987 ± 0.0222 d | 0.0369 ± 0.0007 a | 8.5 ± 0.1 b | 9.4 ± 0.1 cd | 14:30 |
| DS11 | 4.1321 ± 0.0444 e | 0.0392 ± 0.0018 abc | 8.7 ± 0.2 b | 9.4 ± 0.2 cd | 15:15 |
| DS12 | 1.4782 ± 0.0222 c | 0.0402 ± 0.0032 abc | 8.4 ± 0.1 b | 9.4 ± 0.2 cd | 15:45 |
| Site | Sequence Number | OTUs | Chao1 | ACE | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS01 | 61412 ± 3575 a | 741 ± 108 b | 849 ± 132 b | 842 ± 141 b | 4.53 ± 0.25 ab | 0.0333 ± 0.0116 ab |
| DS02 | 78279 ± 4075 cde | 371 ± 42 a | 421 ± 45 a | 421 ± 60 a | 2.87 ± 0.21 bcde | 0.1400 ± 0.0265 bc |
| DS03 | 76049 ± 1396 cd | 766 ± 40 b | 879 ± 47 b | 871 ± 53 b | 4.20 ± 0.26 ab | 0.0633 ± 0.0252 ab |
| DS04 | 61069 ± 11892 a | 377 ± 22 a | 407 ± 39 a | 402 ± 37 a | 3.37 ± 0.25 abcd | 0.1133 ± 0.0208 abc |
| DS05 | 62240 ± 7667 a | 1455 ± 108 c | 1710 ± 163 d | 1699 ± 184 e | 5.50 ± 0.00 a | 0.0100 ± 0.0000 a |
| DS06 | 69028 ± 5308 abc | 727 ± 64 b | 1065 ± 52 c | 1060 ± 64 c | 2.77 ± 0.29 def | 0.2300 ± 0.0346 cd |
| DS07 | 75022 ± 8635 bcd | 706 ± 71 b | 833 ± 84 b | 828 ± 68 b | 3.77 ± 0.21 abc | 0.0800 ± 0.0173 ab |
| DS08 | 76078 ± 1947 cd | 700 ± 61 b | 862 ± 59 b | 863 ± 47 b | 3.27 ± 0.59 def | 0.2200 ± 0.1015 cd |
| DS09 | 81796 ± 1229 de | 278 ± 40 a | 375 ± 33 a | 366 ± 8 a | 2.10 ± 0.35 f | 0.2933 ± 0.0723 d |
| DS10 | 81475 ± 1563 de | 310 ± 36 a | 373 ± 29 a | 373 ± 13 a | 2.53 ± 0.38 def | 0.2267 ± 0.0808 cd |
| DS11 | 89872 ± 5679 e | 307 ± 12 a | 378 ± 13 a | 375 ± 17 a | 2.47 ± 0.50 ef | 0.2633 ± 0.1102 d |
| DS12 | 63928 ± 5490 ab | 786 ± 193 b | 1125 ± 147 c | 1321 ± 38 d | 3.10 ± 0.72 cdef | 0.2067 ± 0.1026 cd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, K.; Tang, Y.; Shi, J.; Hu, Z.; He, M.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Shao, M.; Liu, H. Relationship Between Aquatic Fungal Diversity in Surface Water and Environmental Factors in Yunnan Dashanbao Black-Necked Crane National Nature Reserve, China. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070526
Shen K, Tang Y, Shi J, Hu Z, He M, Li J, Wang Y, Shao M, Liu H. Relationship Between Aquatic Fungal Diversity in Surface Water and Environmental Factors in Yunnan Dashanbao Black-Necked Crane National Nature Reserve, China. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(7):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070526
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Kaize, Yufeng Tang, Jiaoxu Shi, Zhongxiang Hu, Meng He, Jinzhen Li, Yuanjian Wang, Mingcui Shao, and Honggao Liu. 2025. "Relationship Between Aquatic Fungal Diversity in Surface Water and Environmental Factors in Yunnan Dashanbao Black-Necked Crane National Nature Reserve, China" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 7: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070526
APA StyleShen, K., Tang, Y., Shi, J., Hu, Z., He, M., Li, J., Wang, Y., Shao, M., & Liu, H. (2025). Relationship Between Aquatic Fungal Diversity in Surface Water and Environmental Factors in Yunnan Dashanbao Black-Necked Crane National Nature Reserve, China. Journal of Fungi, 11(7), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070526





