Enhancing Monacolin K and GABA Biosynthesis in Monascus pilosus via GAD Overexpression: Multi-Omics Elucidation of Regulatory Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Media
2.2. Construction of GAD Eukaryotic Expression Vector
2.3. Transformation of M. pilosus via Agrobacterium-Mediated Method
2.4. PCR Verification of M. pilosus Transformants
2.5. Solid-State Fermentation of Transformant Strains
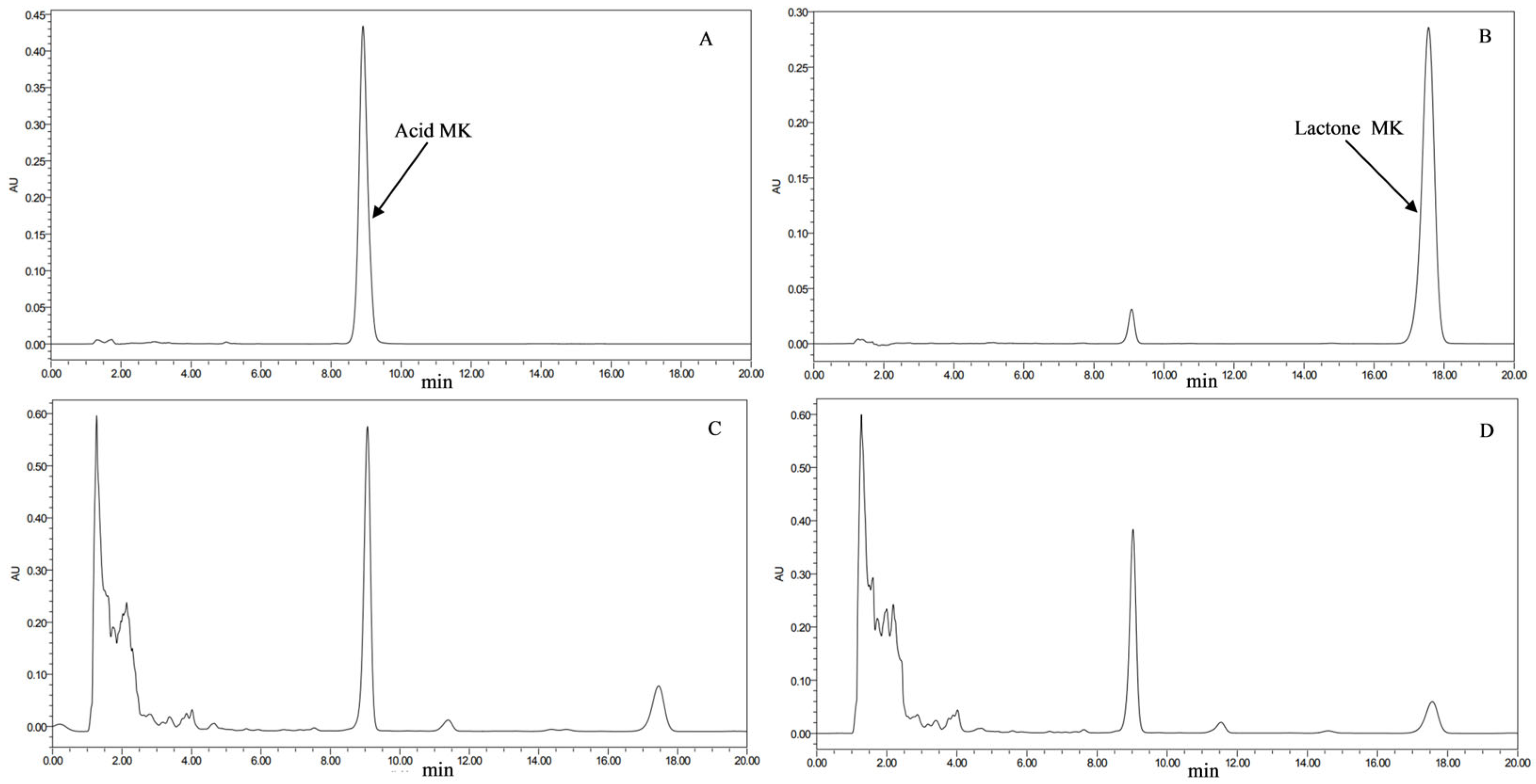
2.6. HPLC Detection of MK Content in Transformant Strains
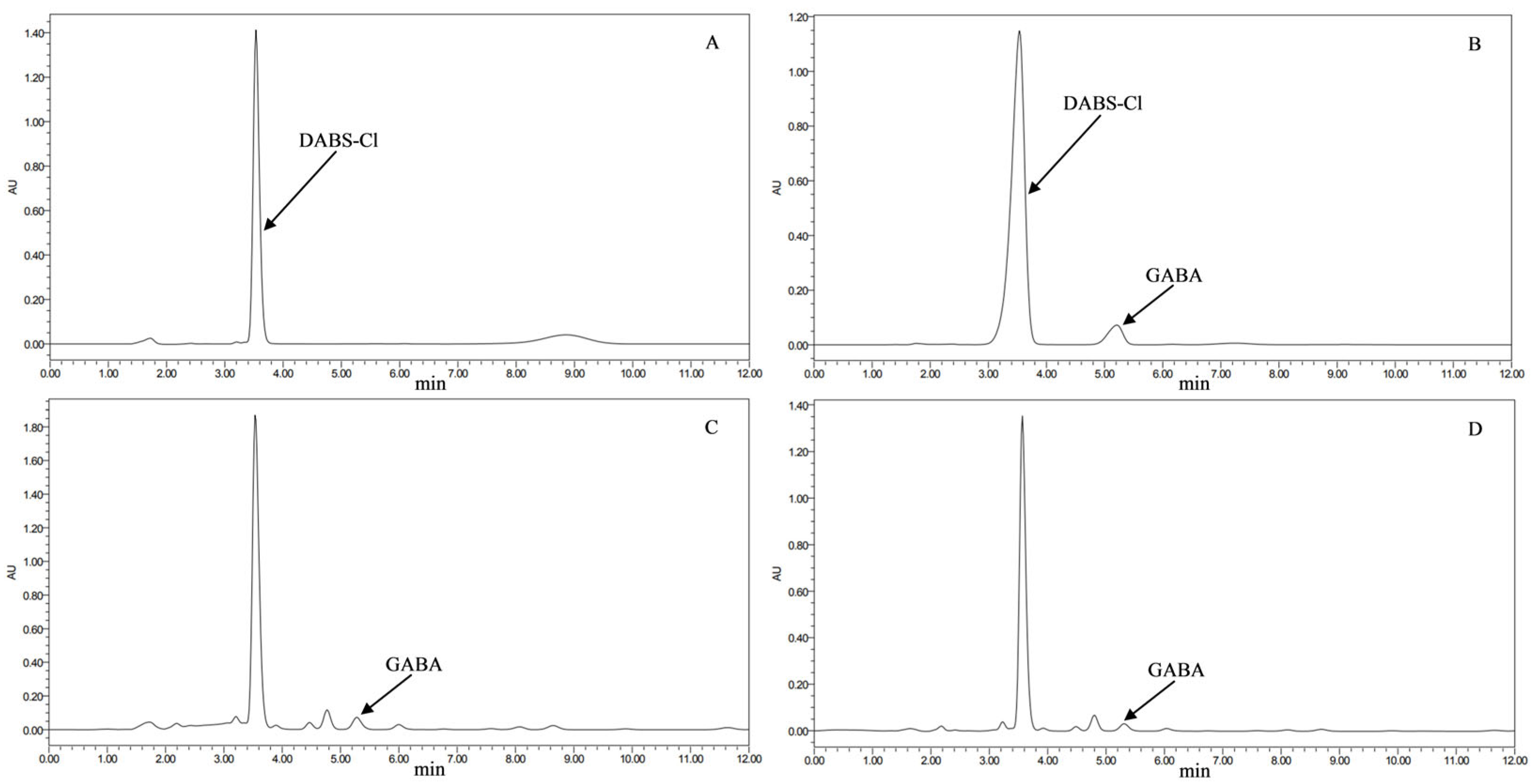
2.7. HPLC Detection of GABA Content in Transformant Strains
2.8. Multi-Omics Analysis of High MK and GABA Yield in Transformant Strains
2.8.1. Transcriptomic Analysis
2.8.2. Metabolomic Analysis
2.8.3. Integrated Omics Analysis
2.9. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Acquisition of GAD Gene Overexpression Strains
3.1.1. Construction of the Eukaryotic Expression Vector for the GAD Gene
3.1.2. Transformation of Monascus pilosus via Agrobacterium-Mediated Method and PCR Verification
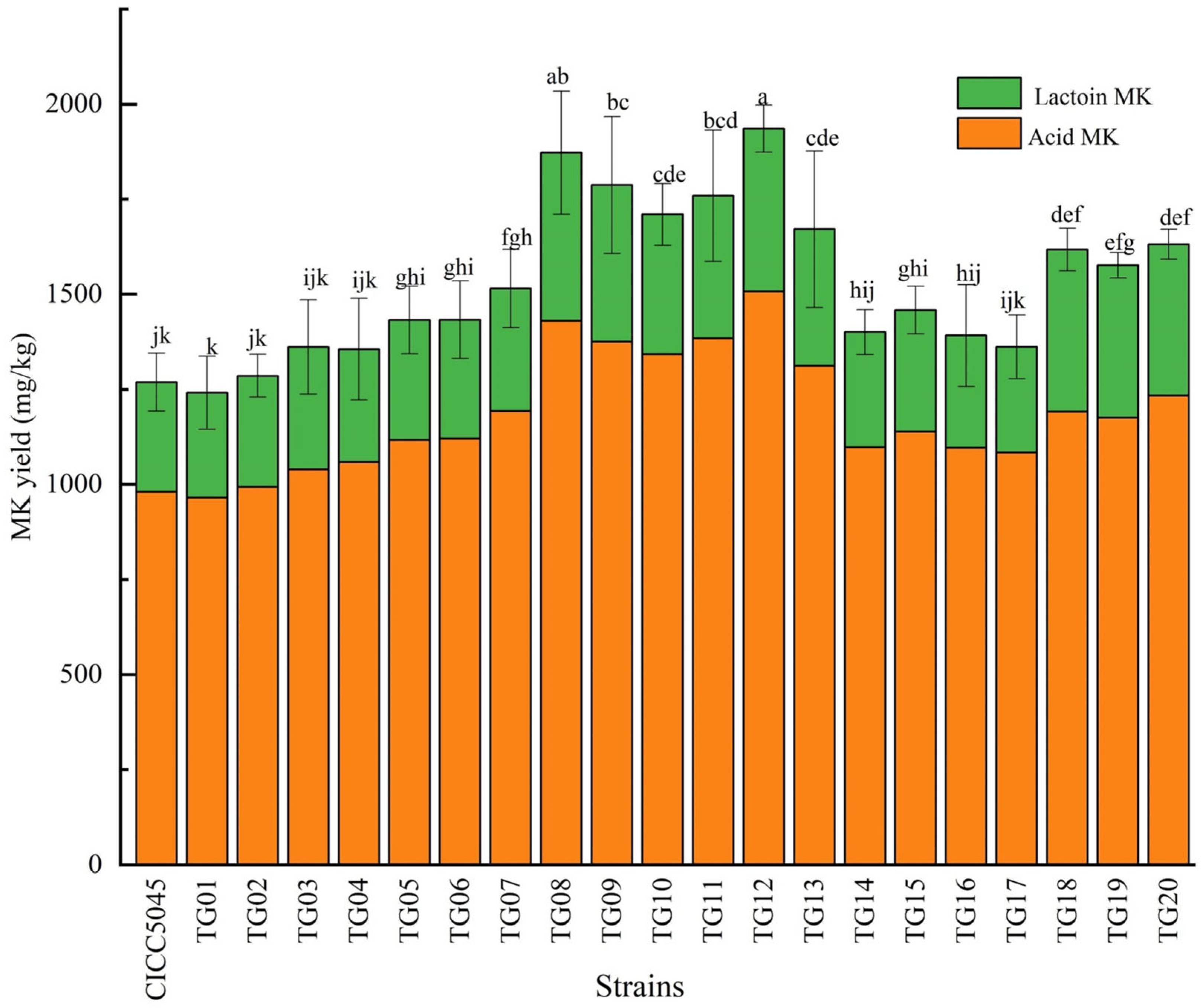
3.2. MK Content in Transformed Strains (HPLC Detection)
3.3. GABA Content in Transformed Strains (HPLC Detection)
3.4. Transcriptomic Analysis of High MK and GABA Producing Transformed Strains
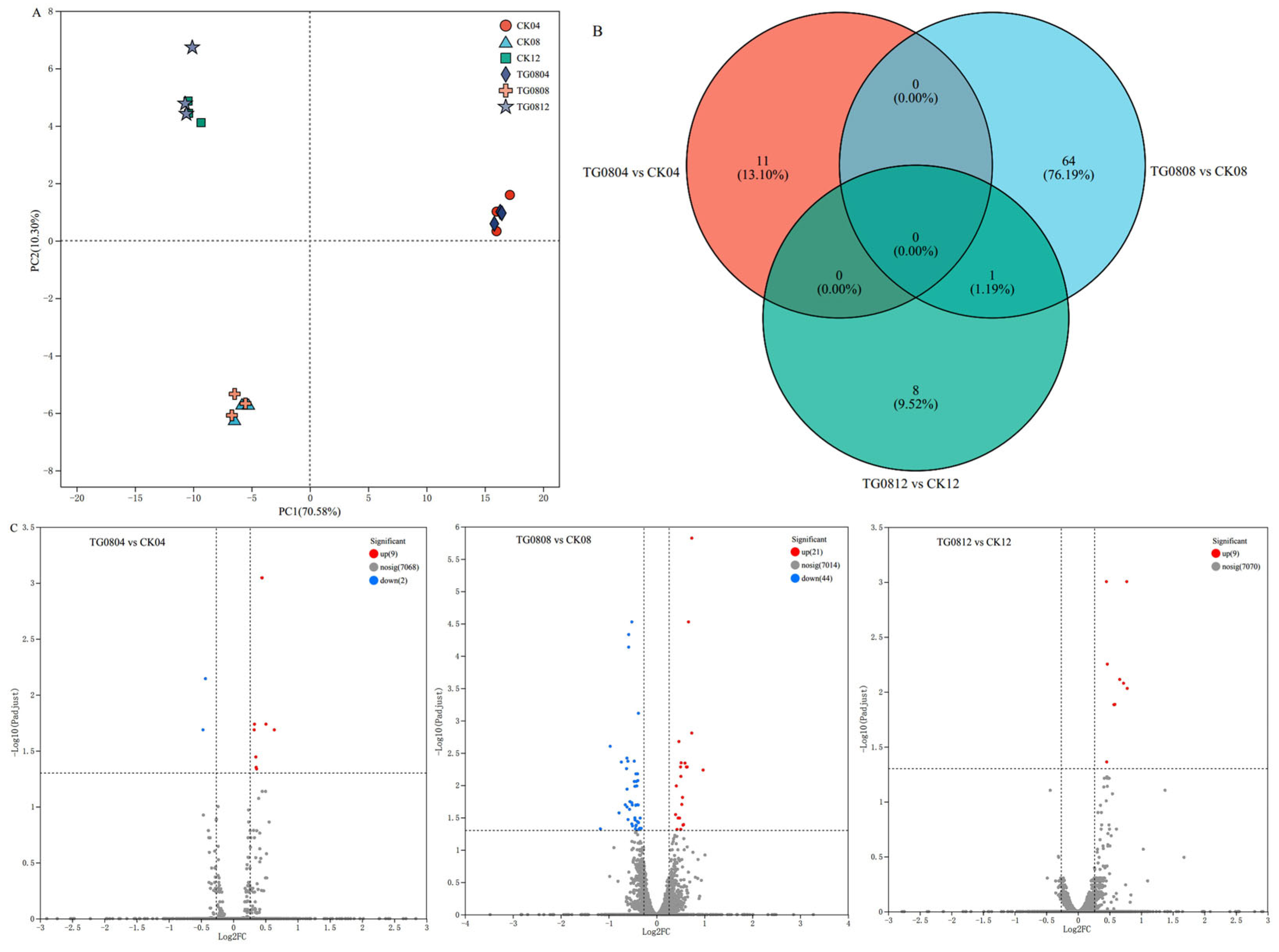
3.4.1. Differential Gene Expression Analysis of Transformed Strains
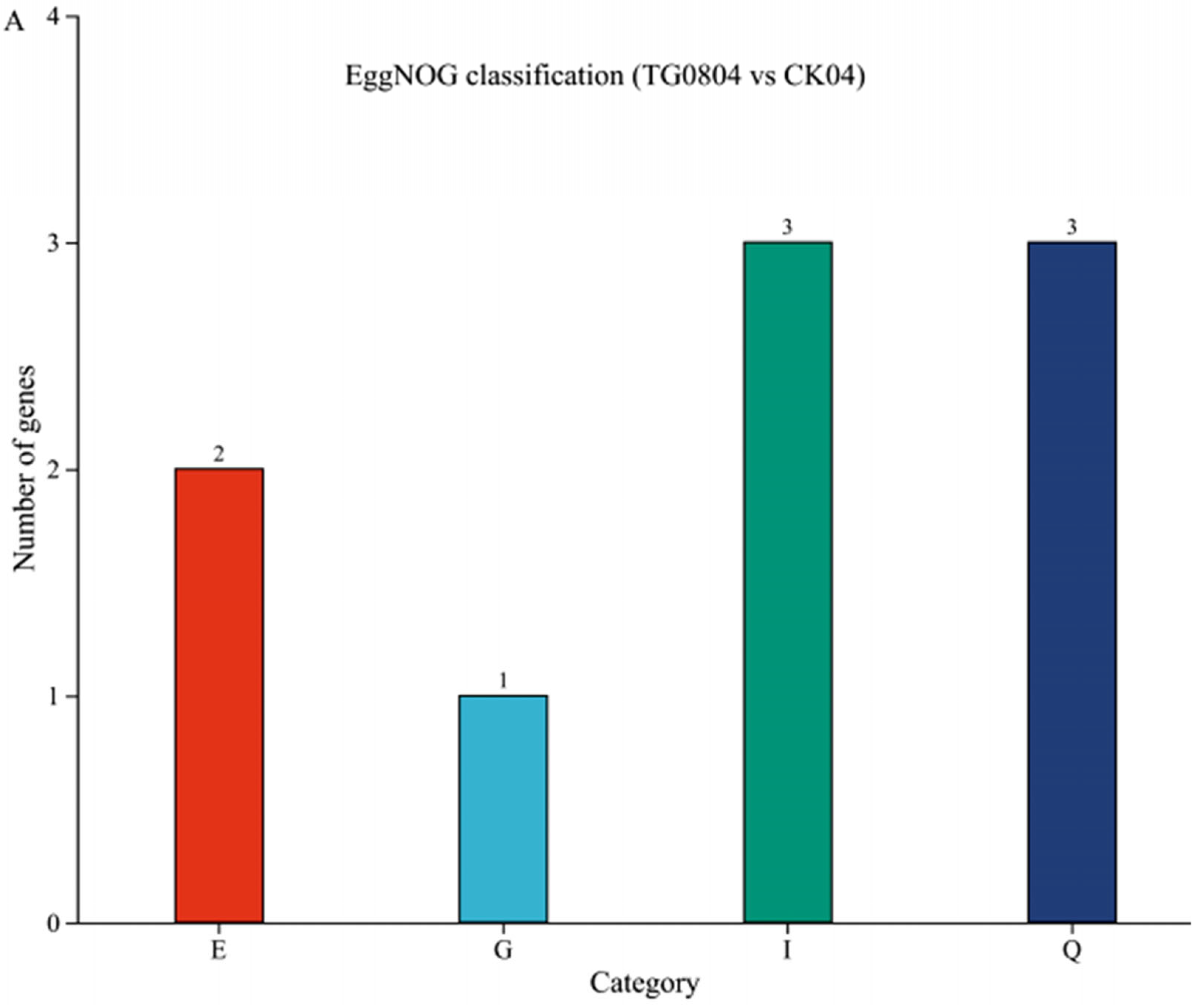
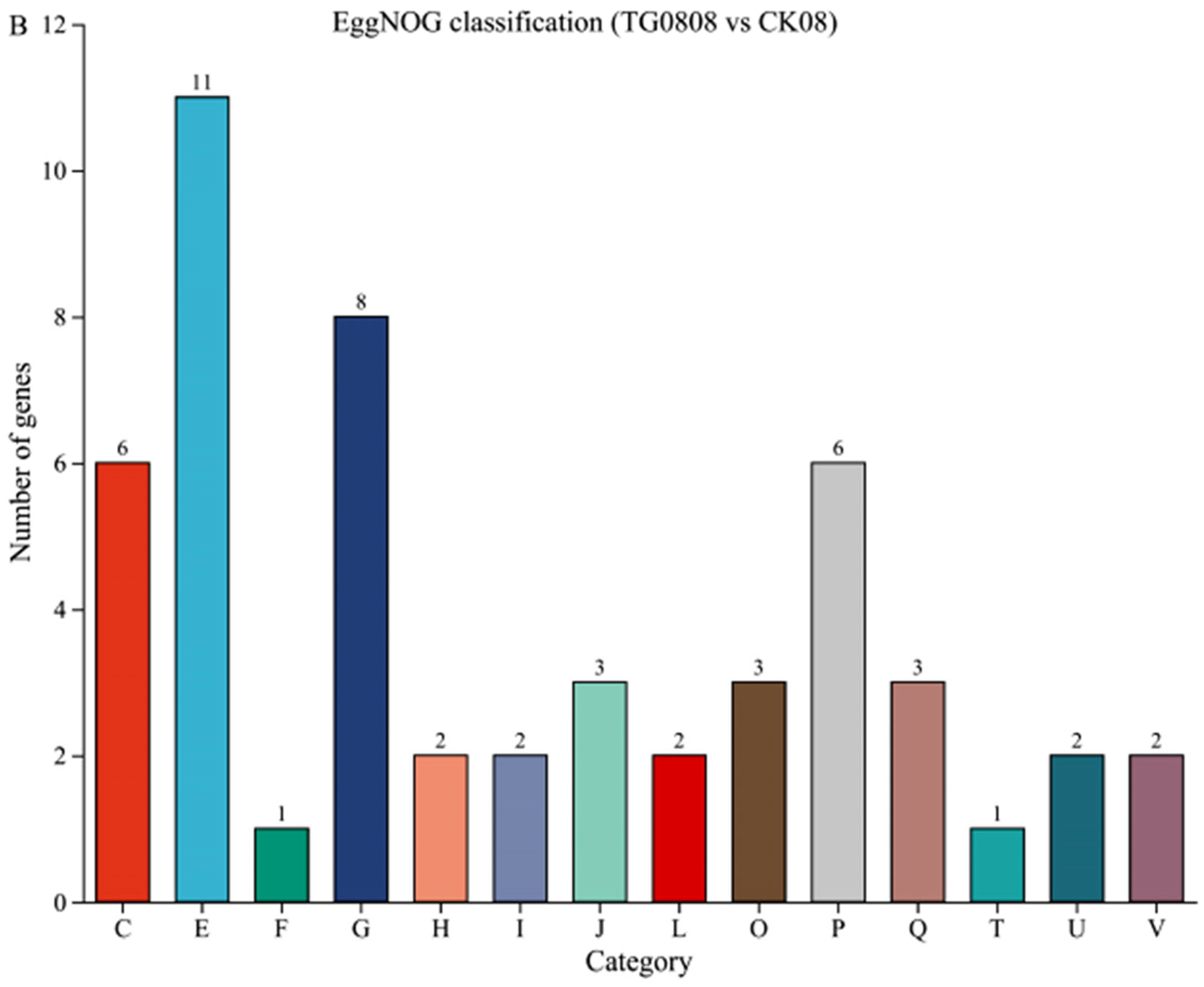
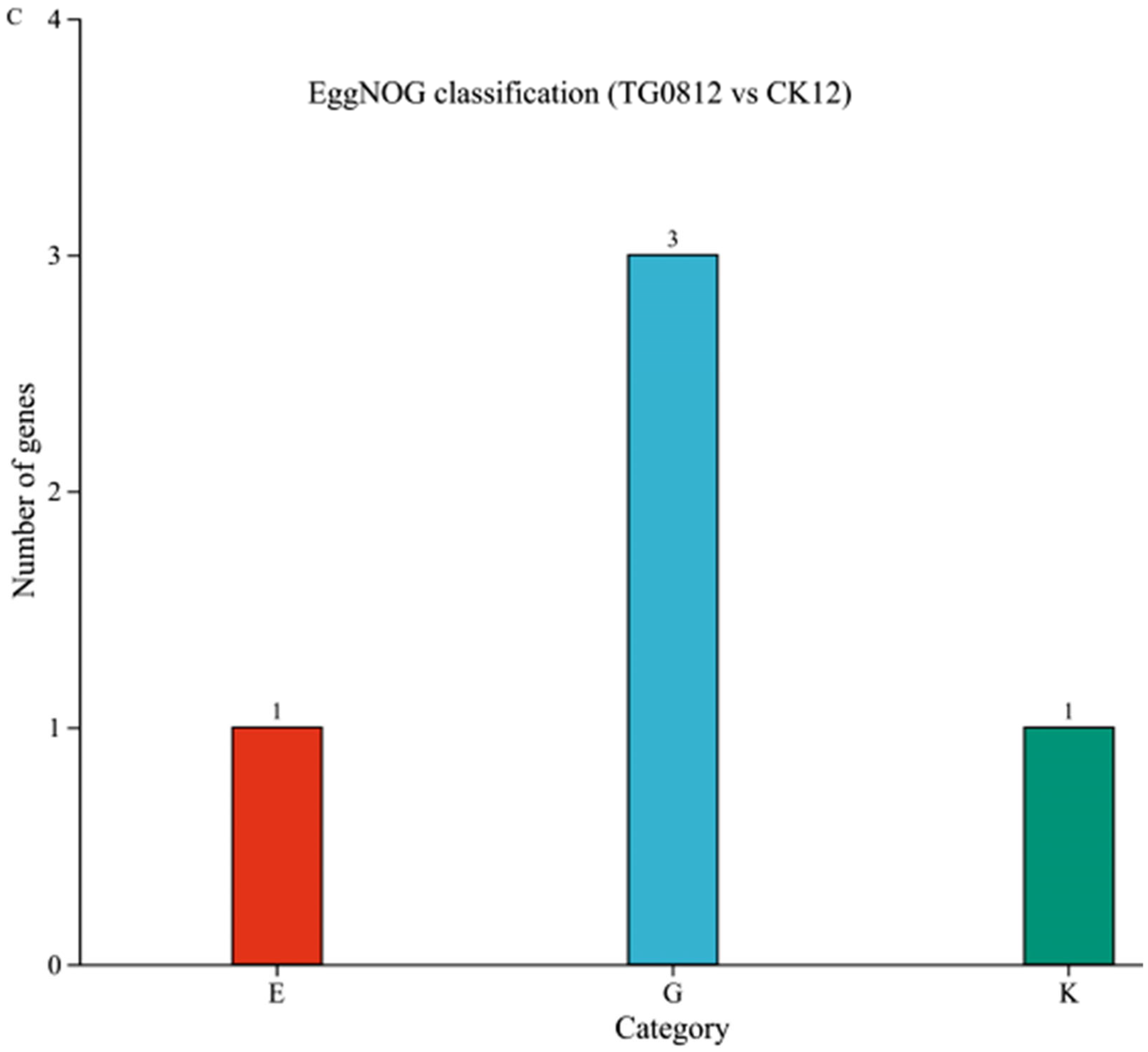
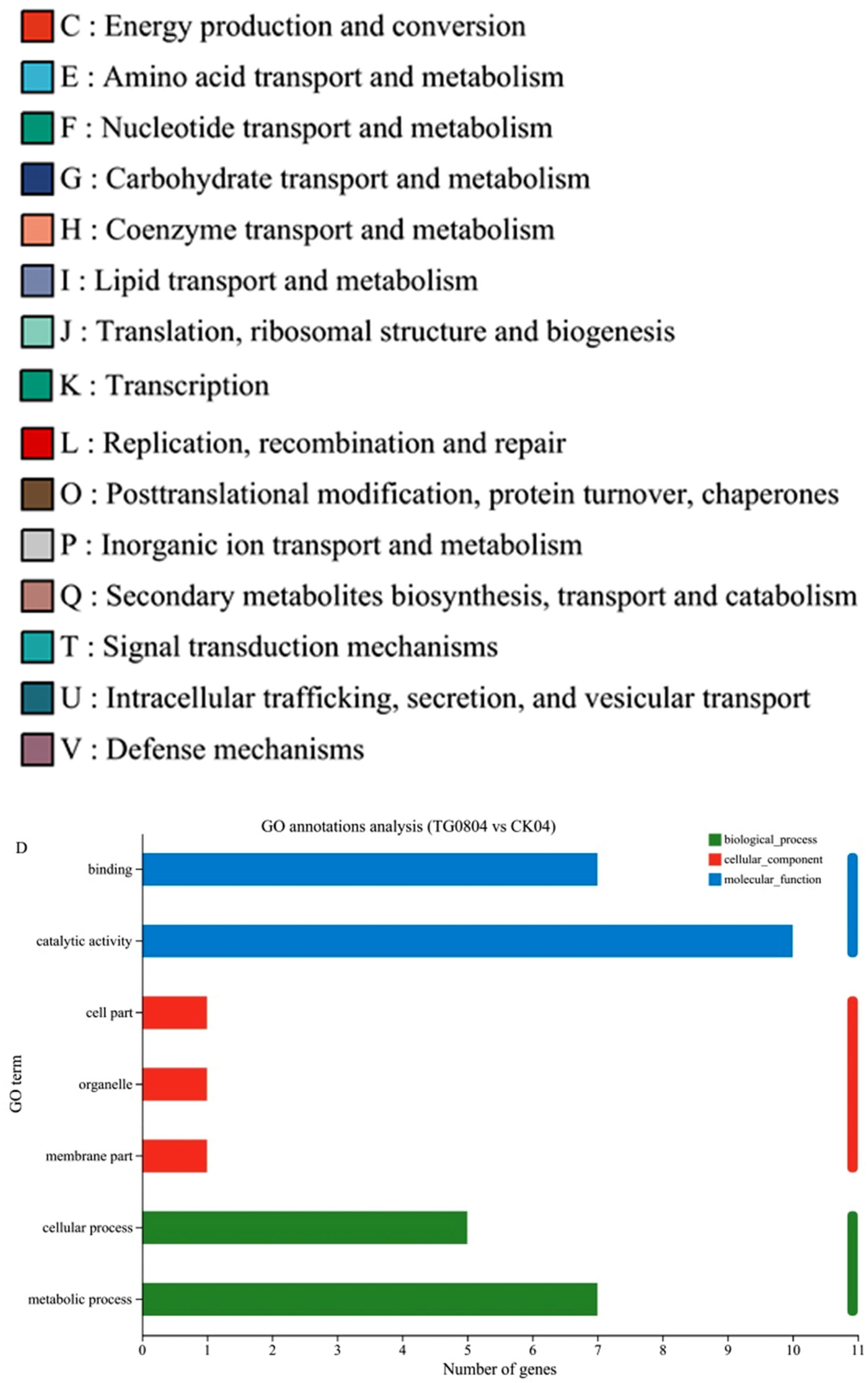
3.4.2. Functional Annotation Analysis of Differential Genes in Transformed Strains
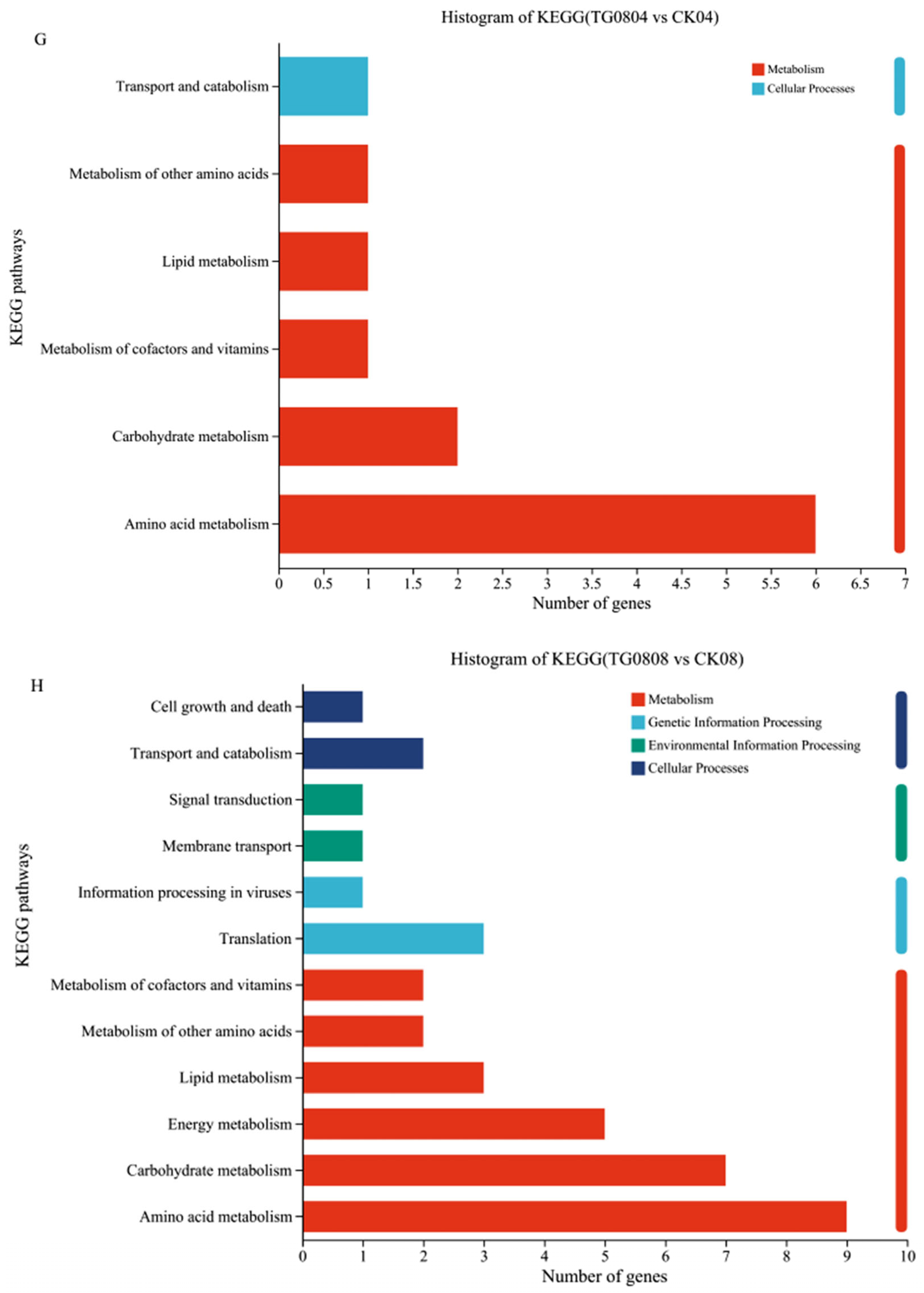
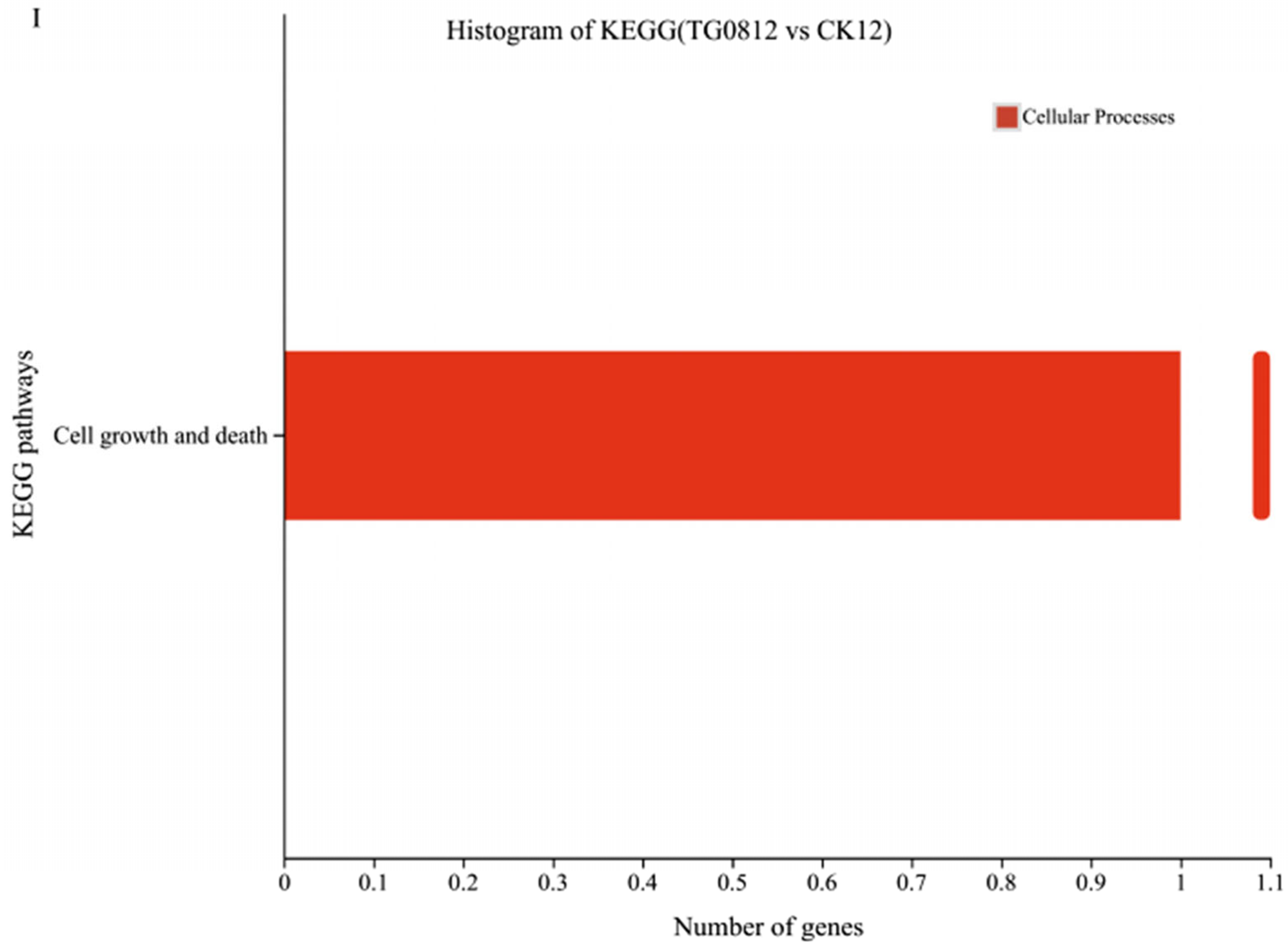
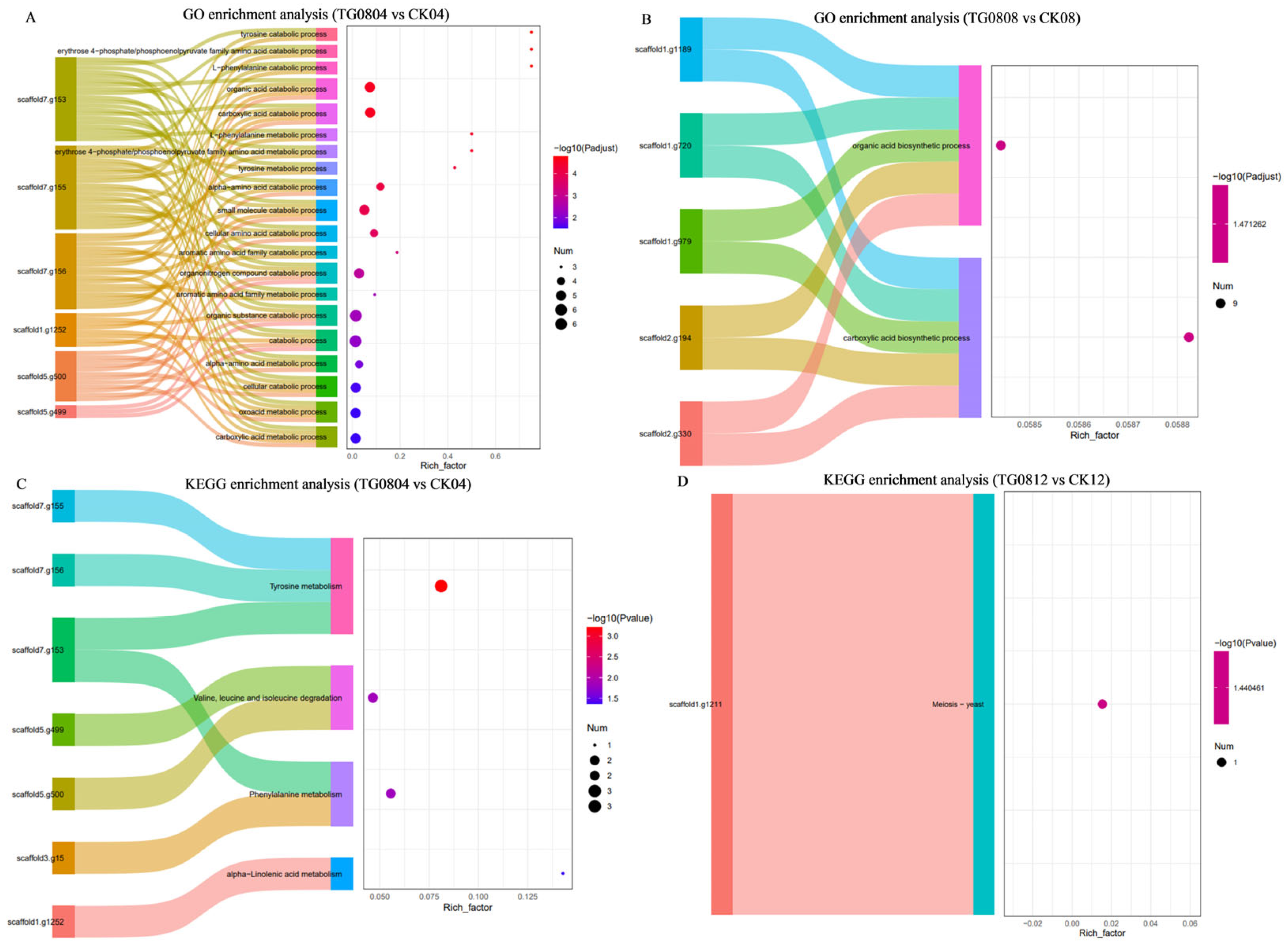
3.4.3. Enrichment Analysis of Differential Genes in Transformed Strains
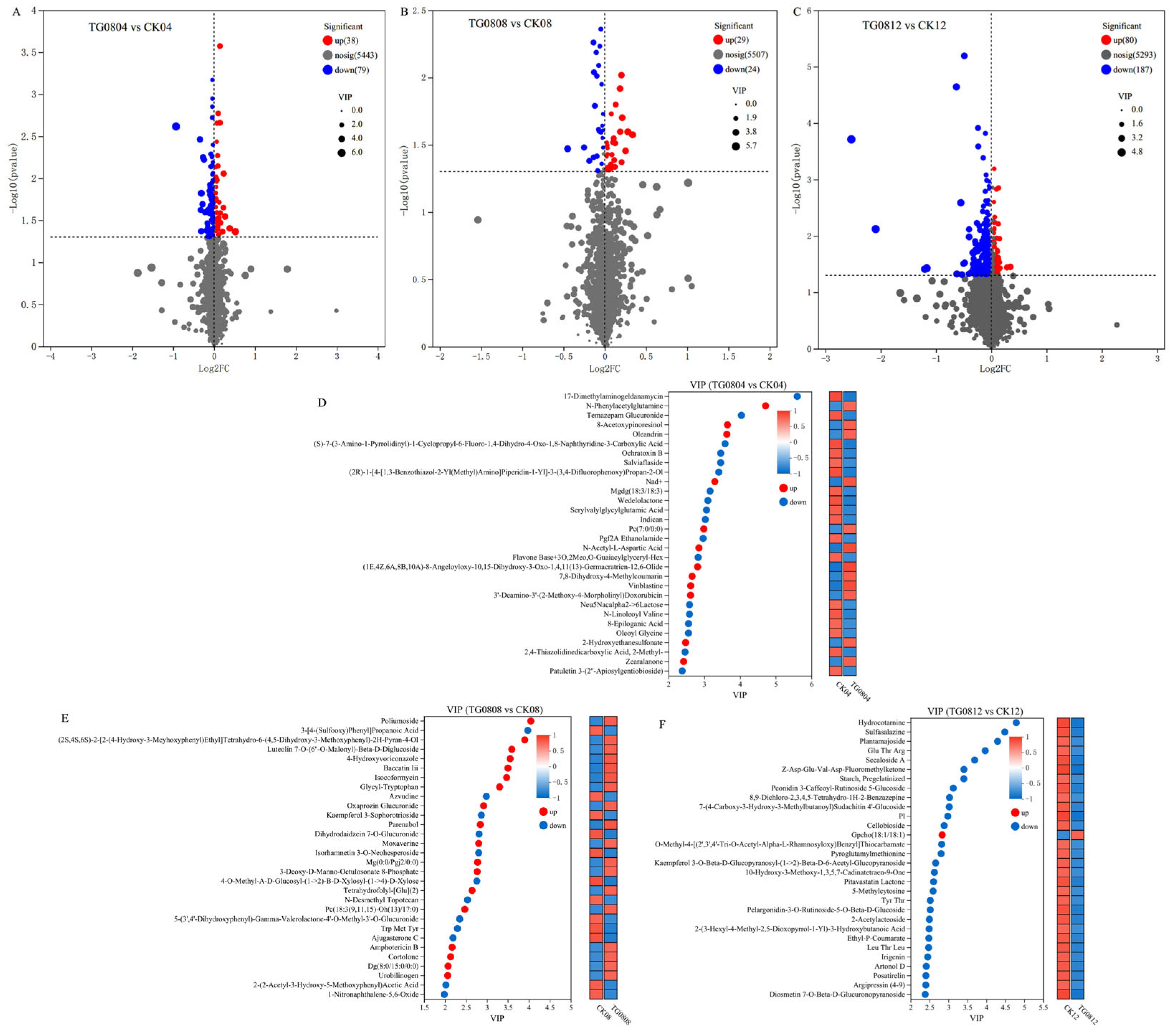
3.5. Metabolomics Analysis of High MK and GABA Production Mechanisms in Transformed Strains
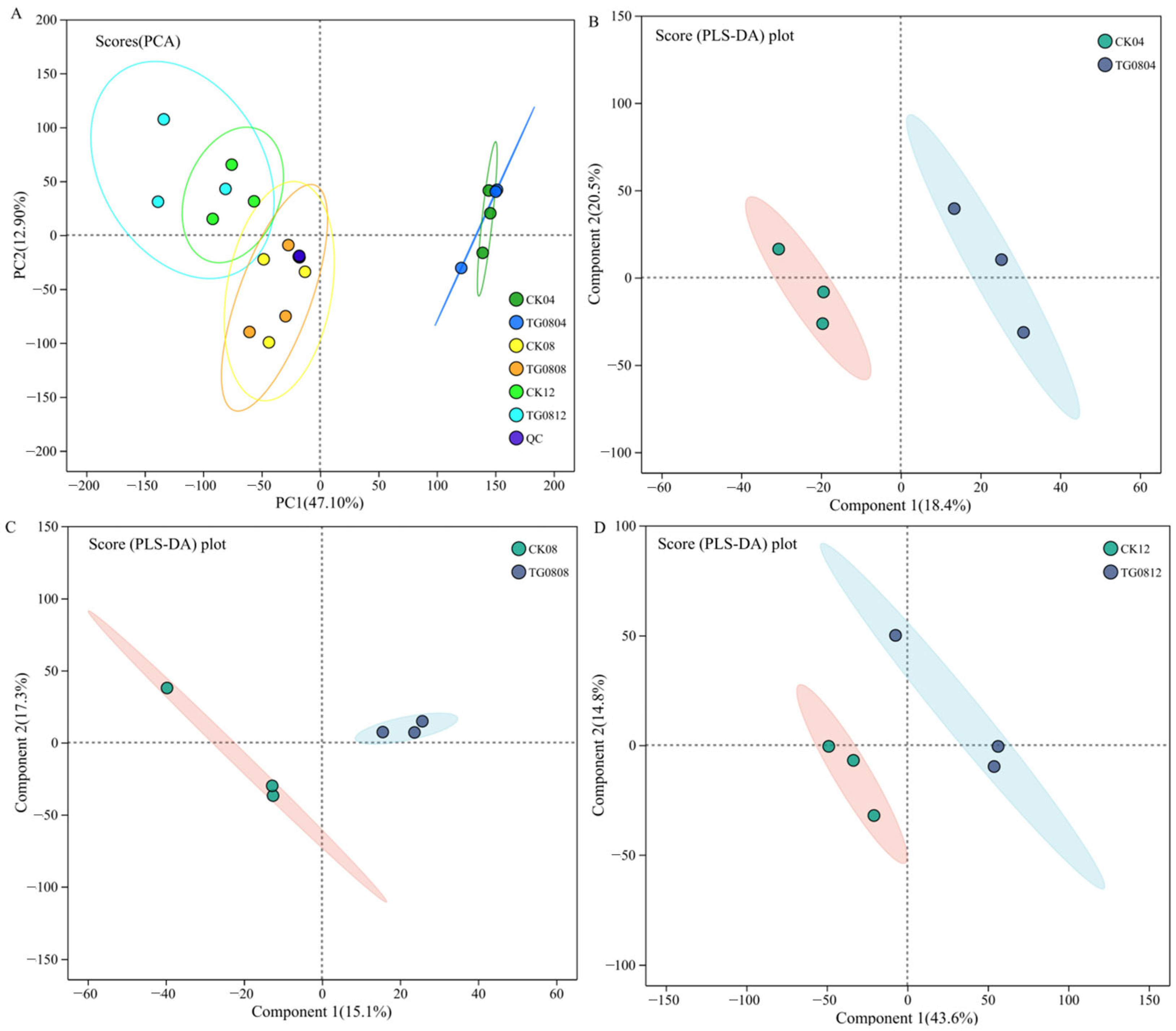
3.5.1. Metabolomic Detection and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of MFB Samples
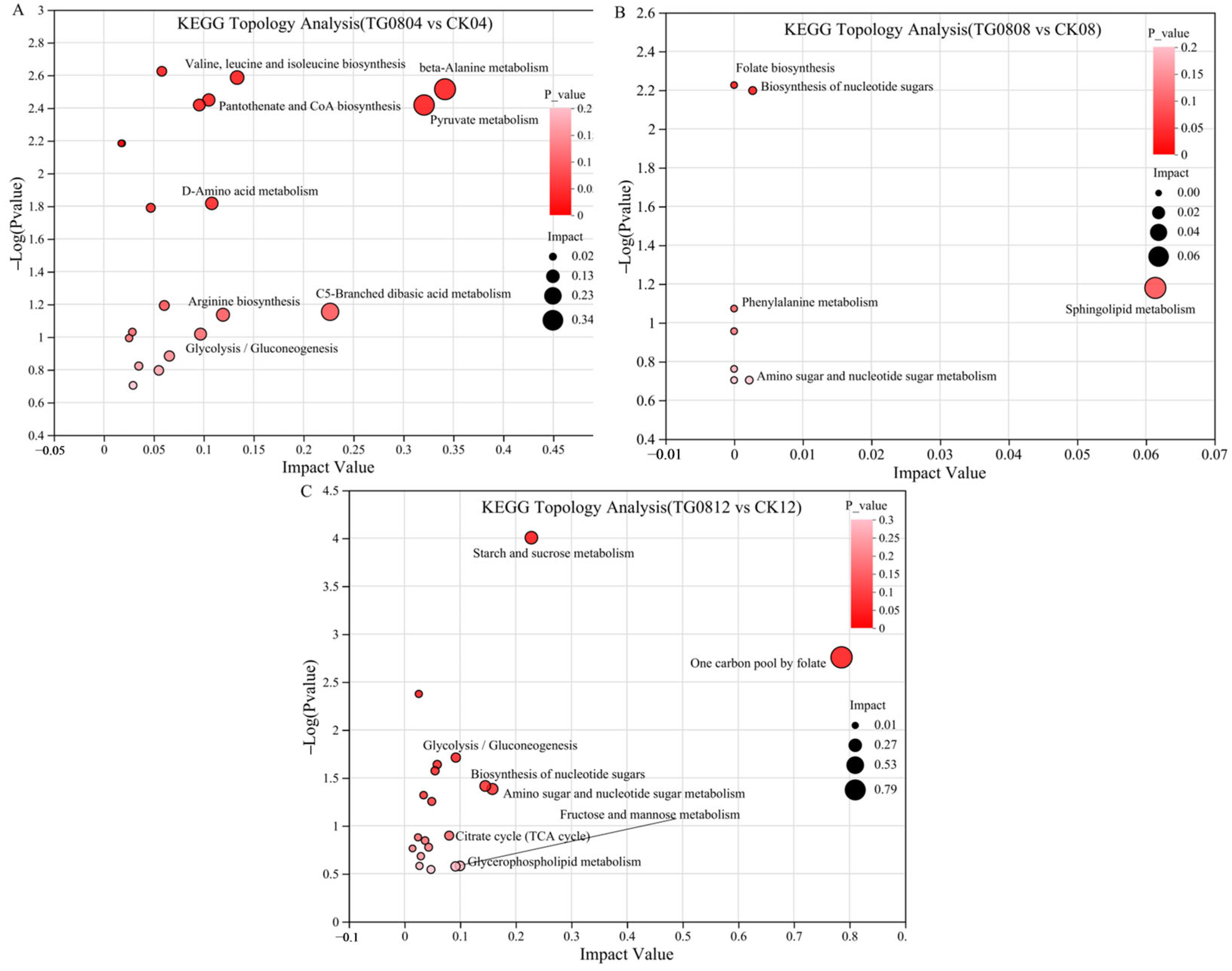
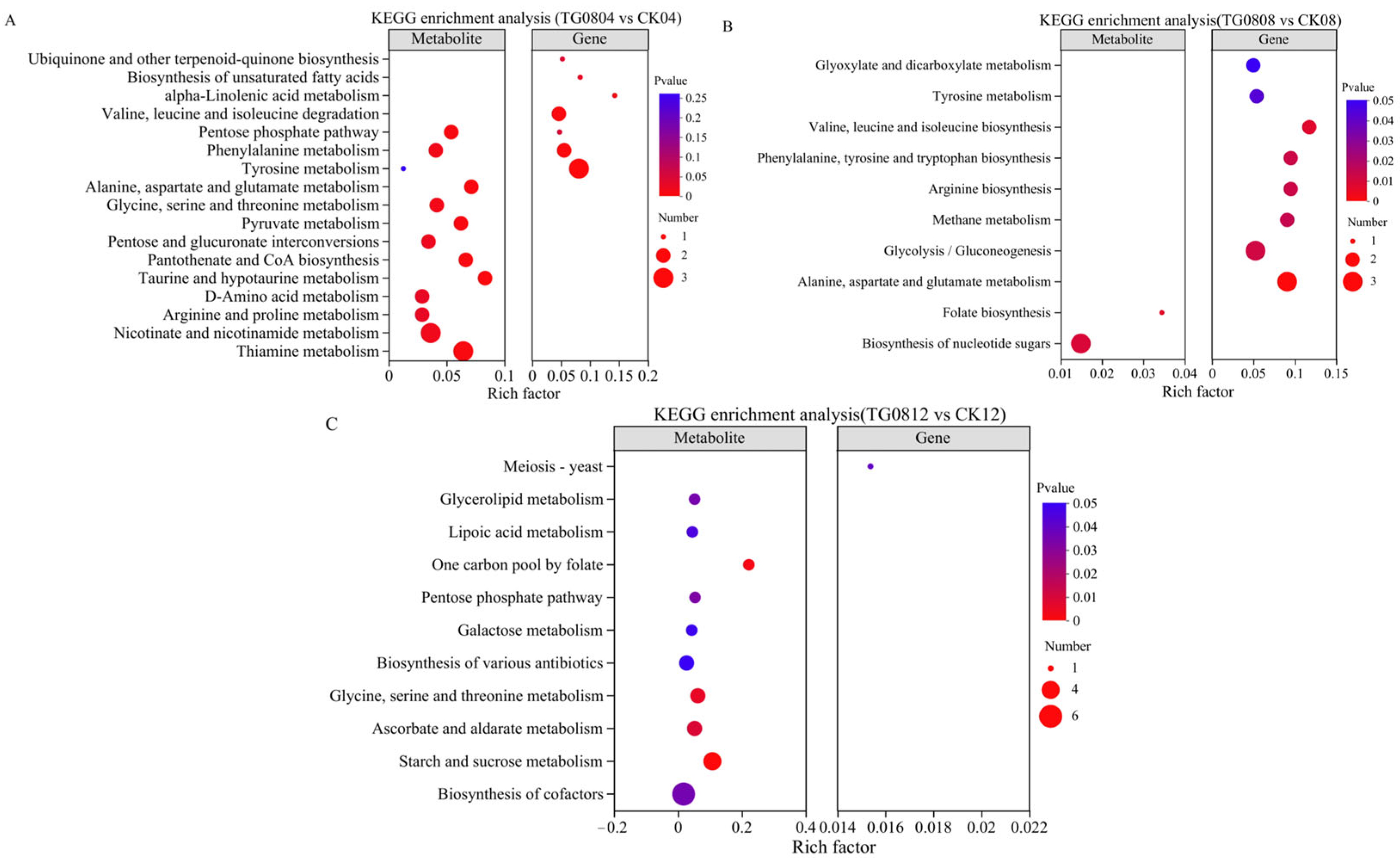
3.5.2. Differential Metabolites and Pathway Enrichment Analysis of MFB Samples
3.6. Multi-Omics Joint Analysis of High MK and GABA Production Mechanisms in Transformed Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Huang, D.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.M.; Bai, J.; Zhang, H.J.; Jiang, X.L.; Yuan, J.; Lu, G.G.; Jiang, L.Y.; et al. Integrative Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Uncover Metabolic Alterations and Pigment Diversity in Monascus in Response to Different Nitrogen Sources. Msystems 2021, 6, e80721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhou, K.X.; Chen, F.; Chen, G.M.; Yu, Y.; Lv, X.C.; Zhang, W.; Rao, P.F.; Ni, L. Comparative study on the antioxidant activity of Monascus yellow pigments from two different types of Hong Qu—Functional Qu and coloring Qu. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 715295. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liang, J.; Yang, L.; Sun, B.G.; Wang, C.T. De novo RNA sequencing and transcriptome analysis of Monascus purpureus and analysis of key genes involved in Monacolin K biosynthesis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e170149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Stoian, A.P.; Toth, P.P. Red yeast rice for the improvement of lipid profiles in mild-to-moderate hypercholesterolemia: A narrative review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.W.; Chen, L.C.; Xiao, L.S.; Ye, Y.F.; Mo, W.L.; Zheng, Z.H.; Li, X.Y. Monascus-fermented quinoa alleviates hyperlipidemia in mice by regulating the amino acid metabolism pathway. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 9210–9223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monu, M.; Sehrawat, K.D.; Singh, A.; Chaudhary, G.; Bamal, D.; Sehrawat, A.R. An overview on the therapeutic potential and anticancer mechanism of monacolin K/lovastatin. Pharmacol. Res. Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 5, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.X.; Cao, X.H.; Wen, Q.Y.; Chen, Z.T.; Cheng, Z.X.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Long, C.N.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.W. An overview of the bioactivity of monacolin K/lovastatin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Li, M.; Huang, Q.M.; Xie, L.M.; Huang, Z.B. Monacolin K induces apoptosis of human glioma U251 cells by triggering ROS-mediated oxidative damage and regulating MAPKs and NF-κB pathways. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chai, S.; Hao, S.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C. Effects of glutamic acid on the production of monacolin K in four high-yield monacolin K strains in Monascus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 5301–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, T.; Lu, D.; Zhou, X. Optimization of medium compositions and X-ray irradiation to enhance monacolin K production by Monascus purpureus in submerged fermentation. Process Biochem. 2024, 141, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.C.; Ablimit, A.; Chen, M.X.; Sun, Q.; Dong, H.J.; Liu, W.B.; Huang, A.; Zhang, B.B.; Hu, W.L.; et al. Development of red grapefruit jam fermented with Monascus purpureus: Effect of naringenin on Monascus purpureus growth and metabolism. Food Biosci. 2025, 65, 106061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Chen, Z.T.; Wen, Q.Y.; Xiong, Z.X.; Cao, X.H.; Zheng, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Huang, Z.W. An overview on the biosynthesis and metabolic regulation of monacolin K/lovastatin. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5738–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.F.; Cai, Q.H.; Liu, Q.R.; Gong, Y.X.; Zhao, D.Q.; Wan, J.; Wang, D.J.; Shao, Y.C. Effective enhancement of the ability of Monascus pilosus to produce lipid-lowering compound monacolin K via perturbation of metabolic flux and histone acetylation modification. Food Res. Int. 2024, 195, 114961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liang, J.; Zhang, A.A.; Hao, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Sun, B.G.; Wang, C.T. Overexpression of Monacolin K biosynthesis genes in the Monascus purpureus azaphilone polyketide pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2563–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Yuan, G.F.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Wang, W.Y.; Liaw, L.L.; Tseng, C.P. Identification of the mok H gene encoding transcription factor for the upregulation of Monacolin K biosynthesis in Monascus pilosus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.W.; Xiao, L.S.; Mo, W.L.; Zhang, Y.R.; Cai, Y.Y.; Huang, S.M.; Chen, Z.T.; Long, C.N. Molecular mechanism of mok I gene overexpression in enhancing monacolin K production in Monascus pilosus. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Hao, S.; Chai, S.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Jiao, Z.; Shi, J.C.; Sun, B.G.; Wang, C.T. Overexpression of global regulator LaeA increases secondary metabolite production in Monascus purpureus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 3049–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.Y.; Luo, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.T.; Meng, G.N.; Chen, W.; Wang, C.T. Effect of γ-butyrolactone, a quorum sensing molecule, on morphology and secondary metabolism in Monascus. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 172, 114225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogeswara, I.B.A.; Maneerat, S.; Haltrich, D. Glutamate decarboxylase from lactic acid bacteria—A key enzyme in GABA synthesis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Ren, C.; Xu, Y. GlnR negatively regulates glutamate-dependent acid resistance in Lactobacillus brevis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e2615–e2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feehily, C.; Karatzas, K.A. Role of glutamate metabolism in bacterial responses towards acid and other stresses. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, E.; Ryan, P.M.; Wiley, N.; Carafa, I.; Sherwin, E.; Moloney, G.; Franciosi, E.; Mandal, R.; Wishart, D.S.; Tuohy, K.; et al. Gamma-aminobutyric acid-producing lactobacilli positively affect metabolism and depressive-like behaviour in a mouse model of metabolic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, D.; Manuel, J.V.; Nigam, P.S. An overview of bioprocesses employing specifically selected microbial catalysts for γ-aminobutyric acid production. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 4th ed.; He, F.C., Ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Long, C.N.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, D.S.; Xie, S.B. A Recombinant Plasmid and Its Method for Constructing High-Yielding Strains of Monascus Pigments. China Patent CN107574173B, 13 July 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z.X.; Luo, X.L.; Cao, X.H.; Wen, Q.Y.; Cheng, Z.X.; Huang, X.Y.; Liu, J.H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.W. Factors affecting the fermentation optimization of Monascus strains with high γ-aminobutyric acid yield. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2019, 22, 454–462. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.X.; Ye, F.Y.; Zhou, B.; Liang, Y.; Lin, Q.L.; Lu, D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J. Comparative analysis of different rice substrates for solid-state fermentation by a citrinin-free Monascus purpureus mutant strain with high pigment production. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Shi, C.P.; Liu, L.M.; Han, J.C.; Yang, Q.Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.D.; Fu, W.Y.; Gao, H.; Huang, H.S.; et al. Majorbio cloud 2024: Update single-cell and multiomics workflows. iMeta 2024, 3, e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Barrau, E.; Olivera, E.R.; Luengo, J.M.; Fernández, C.; Galán, B.; García, J.L.; Díaz, E.; Miñambres, B. The homogentisate pathway: A central catabolic pathway involved in the degradation of L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine, and 3-hydroxyphenylacetate in Pseudomonas putida. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 5062–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zeng, H.W.; Ye, W.J.; Qiu, R.; Zeng, X.; Xin, B.Y.; Xie, T.Y. Integrative addition of sucrose esters and immobilisation technology for enhancing yellow pigment yield of Monascus purpureus HBSD08 under submerged fermentation conditions and its molecular mechanism. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 186, 115233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, H.H.; Shu, L.; Xu, H.M.; Cheng, Y.; Mao, Z.T.; Liu, B.; Liao, X.P.; Huang, D. Metabolomics analysis coupled with weighted gene co-expression network analysis unravels the associations of tricarboxylic acid cycle-intermediates with edible pigments produced by Monascus purpureus (Hong Qu). Foods 2022, 11, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Shim, I. Production of γ-aminobutyric acid and its supplementary role in the TCA cycle in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.J.; Lu, J.Q.; Huang, Z.R.; Huang, Q.Z.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Farag, M.A.; Liu, B.; Zhao, C. Comparative transcriptomics discloses the regulatory impact of carbon/nitrogen fermentation on the biosynthesis of Monascus kaoliang pigments. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liang, J.; Yang, L.; Chai, S.Y.; Zhang, C.X.; Sun, B.G.; Wang, C.T. Glutamic acid promotes monacolin K production and monacolin K biosynthetic gene cluster expression in Monascus. AMB Express 2017, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Samano, M.; Beltran, L.; Sanchez-Thomas, R.; Davalos, A.; Villasenor, T.; Garcia-Garcia, J.D.; Garcia-de, L.S.A. A novel way to synthesize pantothenate in bacteria involves beta-alanine synthase present in uracil degradation pathway. MicrobiologyOpen 2020, 9, e1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Li, Y.Q.; Gu, S.Z.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, T.T.; Hou, J.Y.; Gao, B.N.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, M. Metabolome combined with intestinal flora reveals a novel mechanistic insight into the collaboration of Monascus vinegar polysaccharide and organic acid in regulating lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemia. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mo, W.; Cai, Y.; Huang, S.; Xiao, L.; Ye, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z. Enhancing Monacolin K and GABA Biosynthesis in Monascus pilosus via GAD Overexpression: Multi-Omics Elucidation of Regulatory Mechanisms. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070506
Mo W, Cai Y, Huang S, Xiao L, Ye Y, Yang B, Zhang C, Huang Z. Enhancing Monacolin K and GABA Biosynthesis in Monascus pilosus via GAD Overexpression: Multi-Omics Elucidation of Regulatory Mechanisms. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(7):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070506
Chicago/Turabian StyleMo, Wenlan, Yiyang Cai, Simei Huang, Lishi Xiao, Yanfang Ye, Bin Yang, Chan Zhang, and Zhiwei Huang. 2025. "Enhancing Monacolin K and GABA Biosynthesis in Monascus pilosus via GAD Overexpression: Multi-Omics Elucidation of Regulatory Mechanisms" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 7: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070506
APA StyleMo, W., Cai, Y., Huang, S., Xiao, L., Ye, Y., Yang, B., Zhang, C., & Huang, Z. (2025). Enhancing Monacolin K and GABA Biosynthesis in Monascus pilosus via GAD Overexpression: Multi-Omics Elucidation of Regulatory Mechanisms. Journal of Fungi, 11(7), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070506






