Seasonality Has Greater Influence on Amphibian Cutaneous Mycobiome than Host Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Specimen Acquisition and Processing Protocol
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatic Processing Pipeline
2.4. Fungal Community Profiling
3. Results
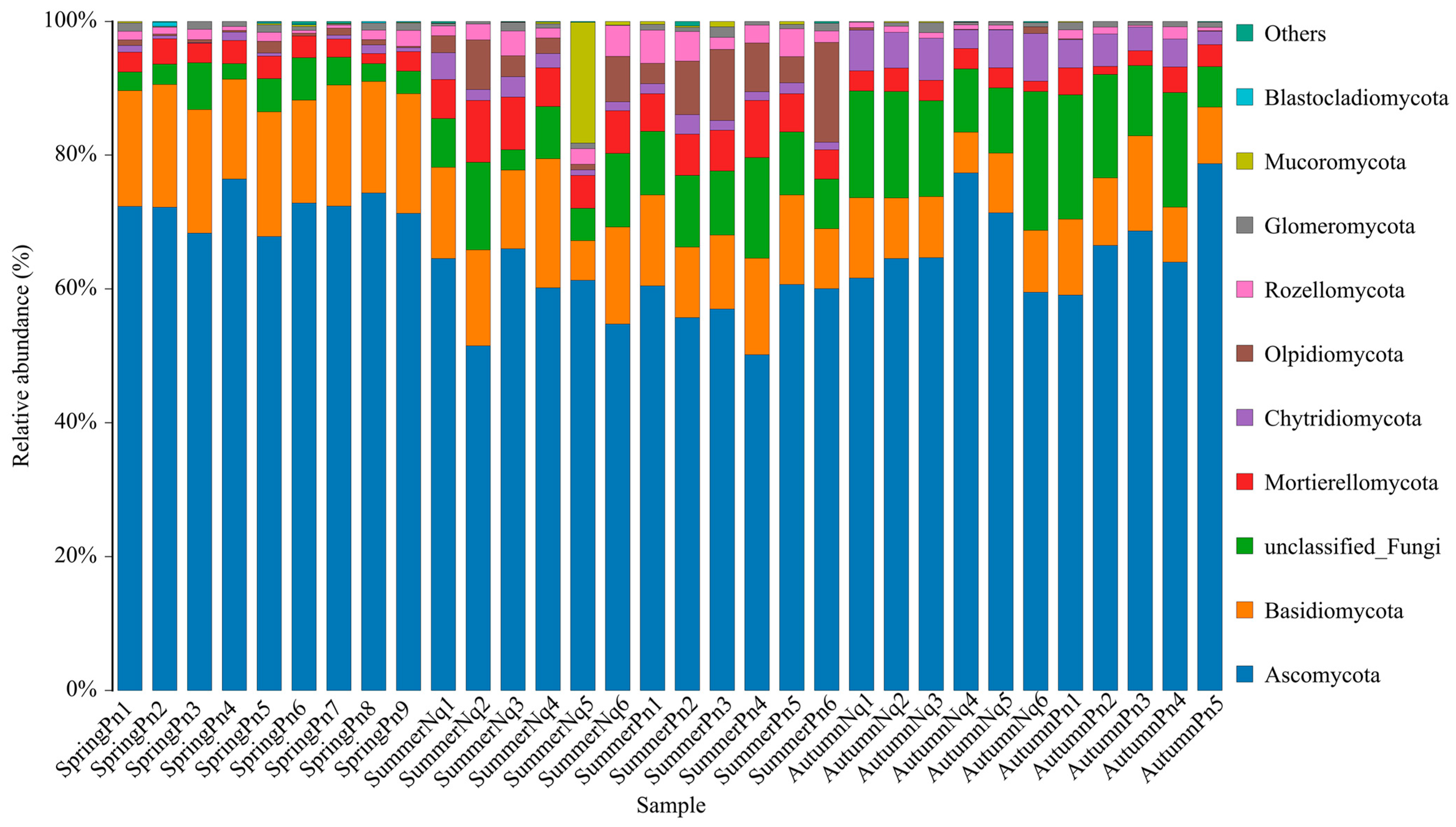
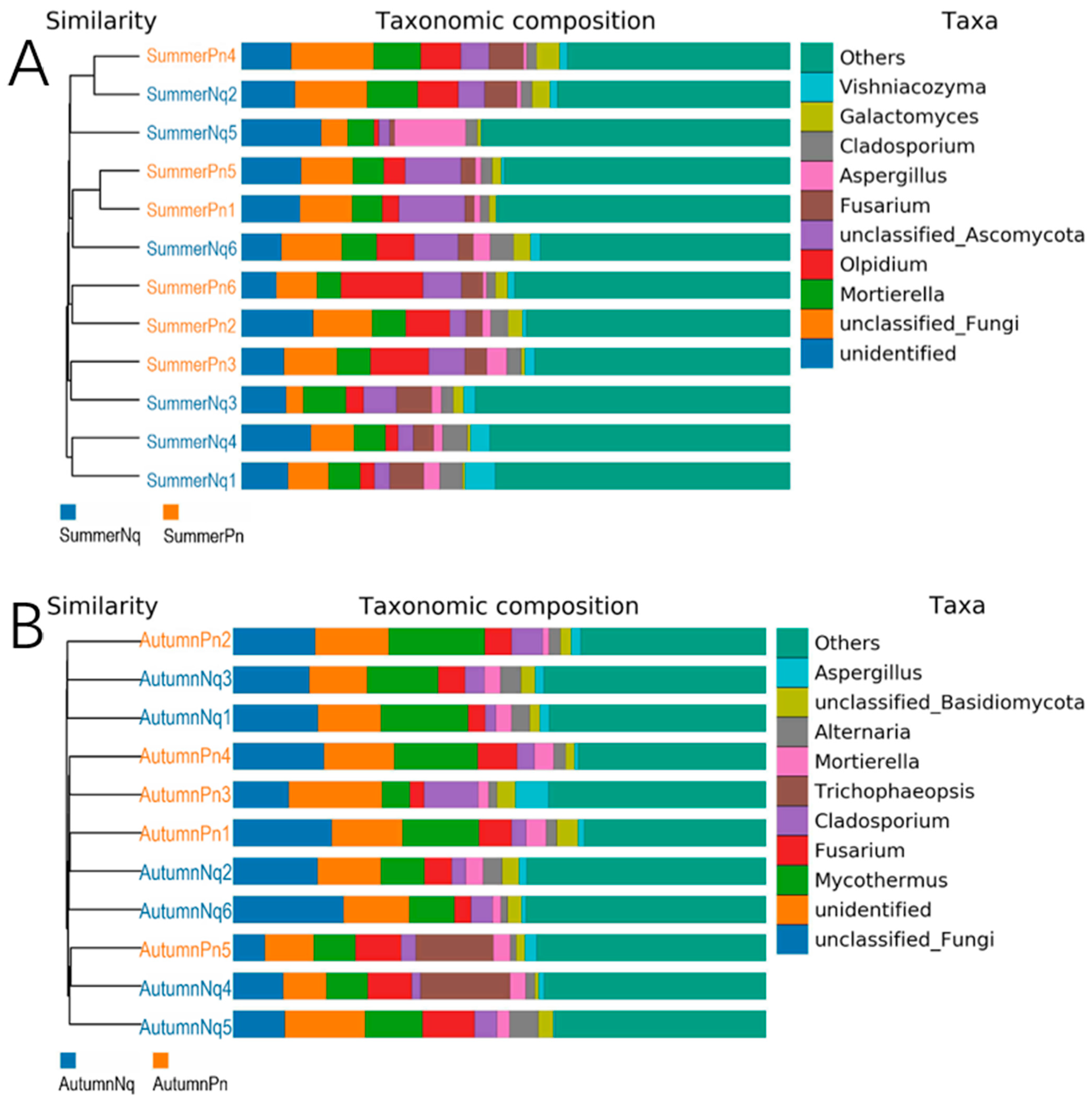
3.1. Overview of Cutaneous Fungal Communities
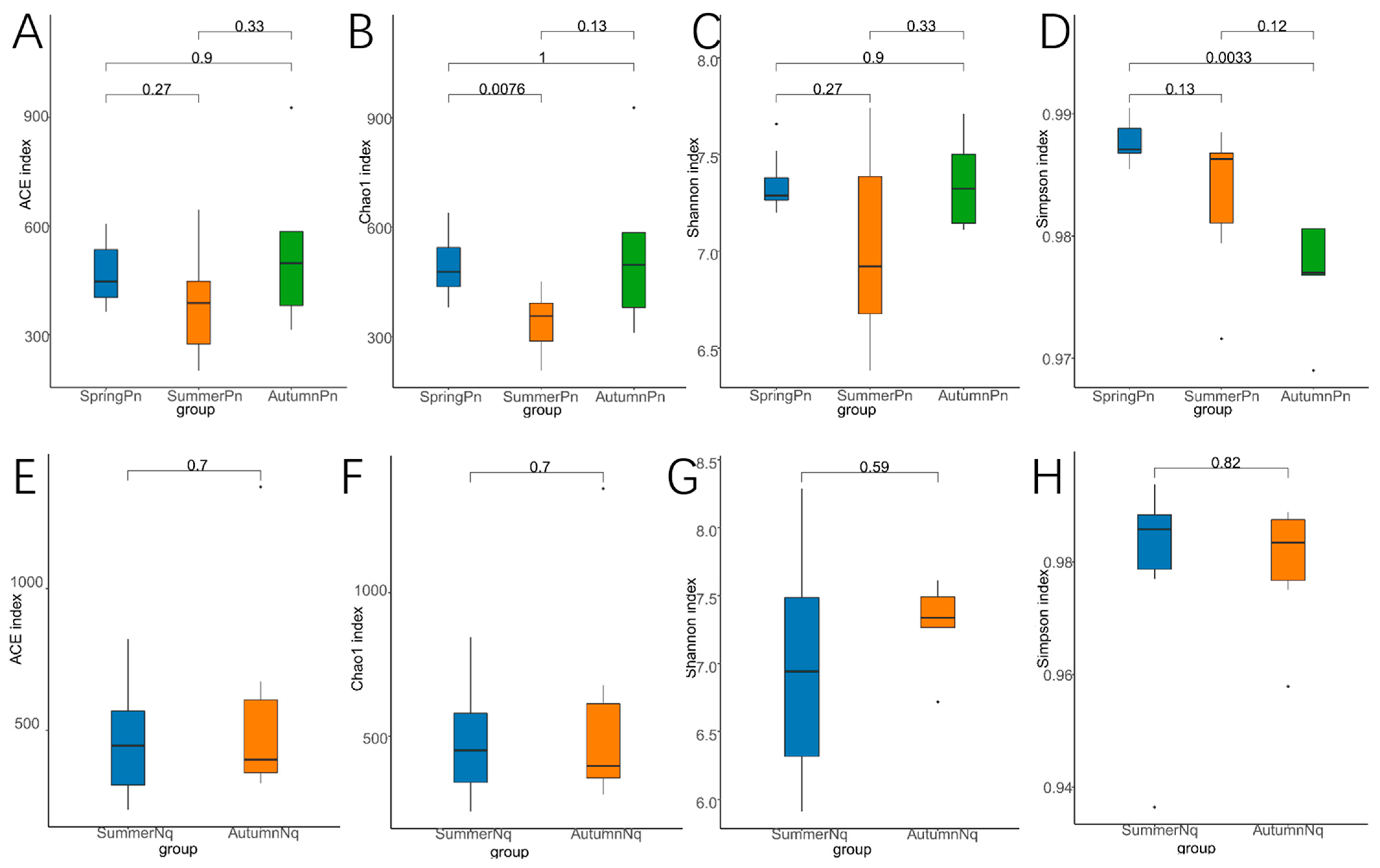
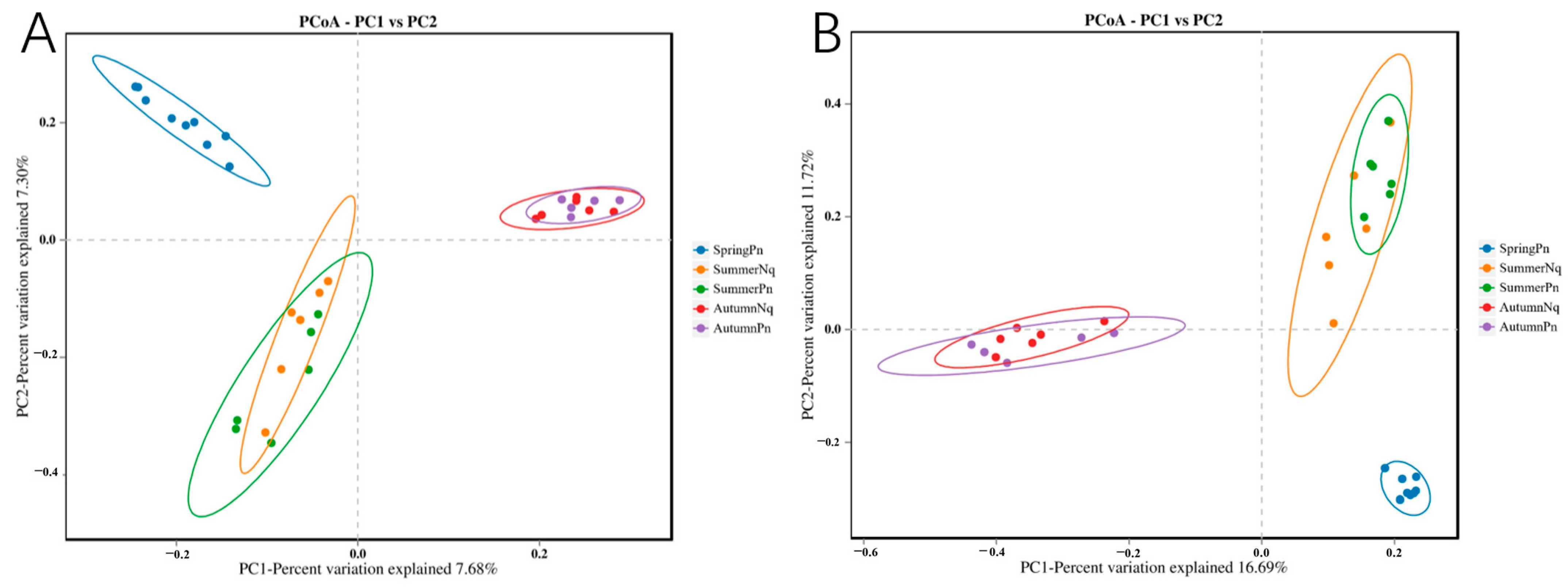
3.2. Seasonal Variation Influenced Fungal Communities
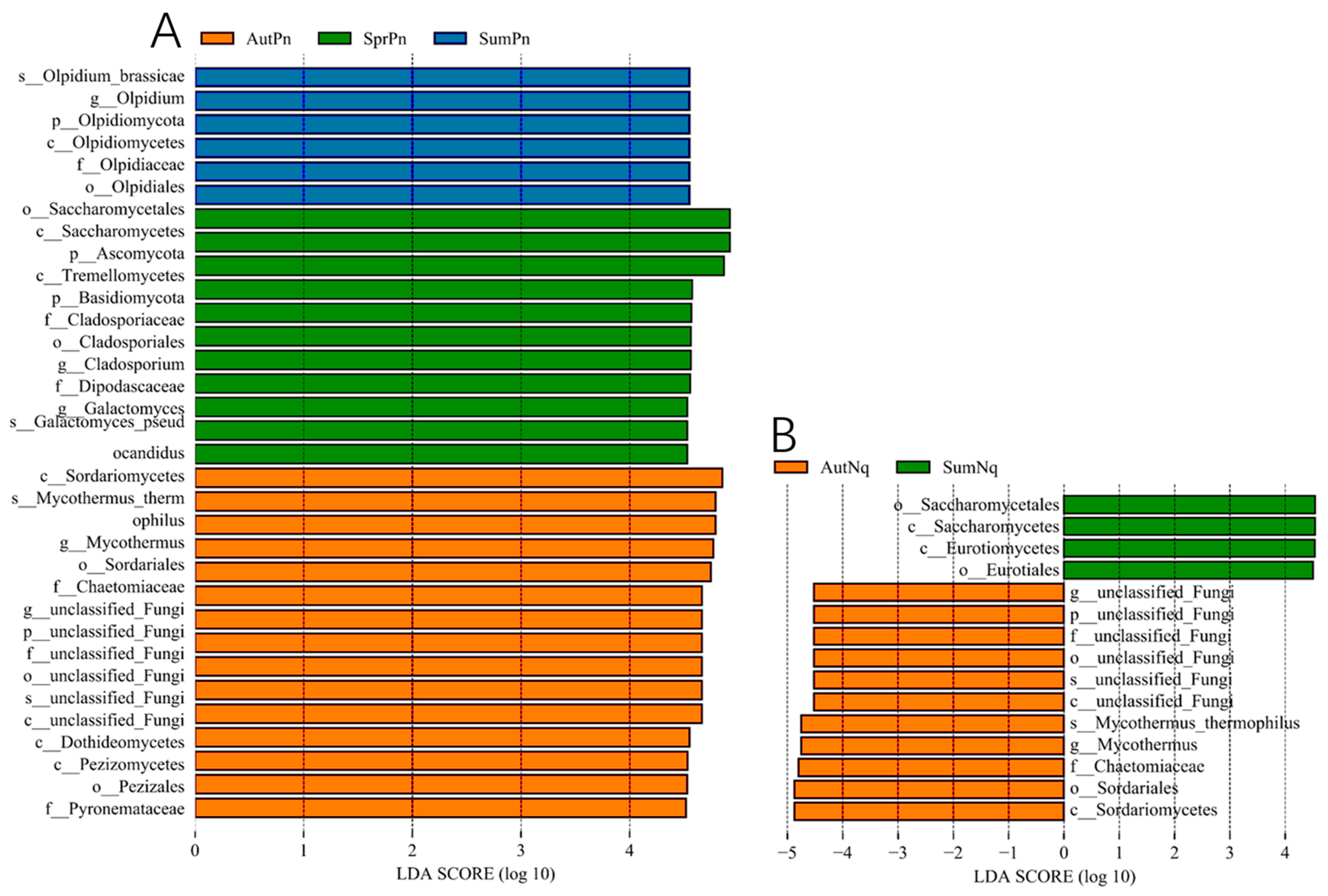
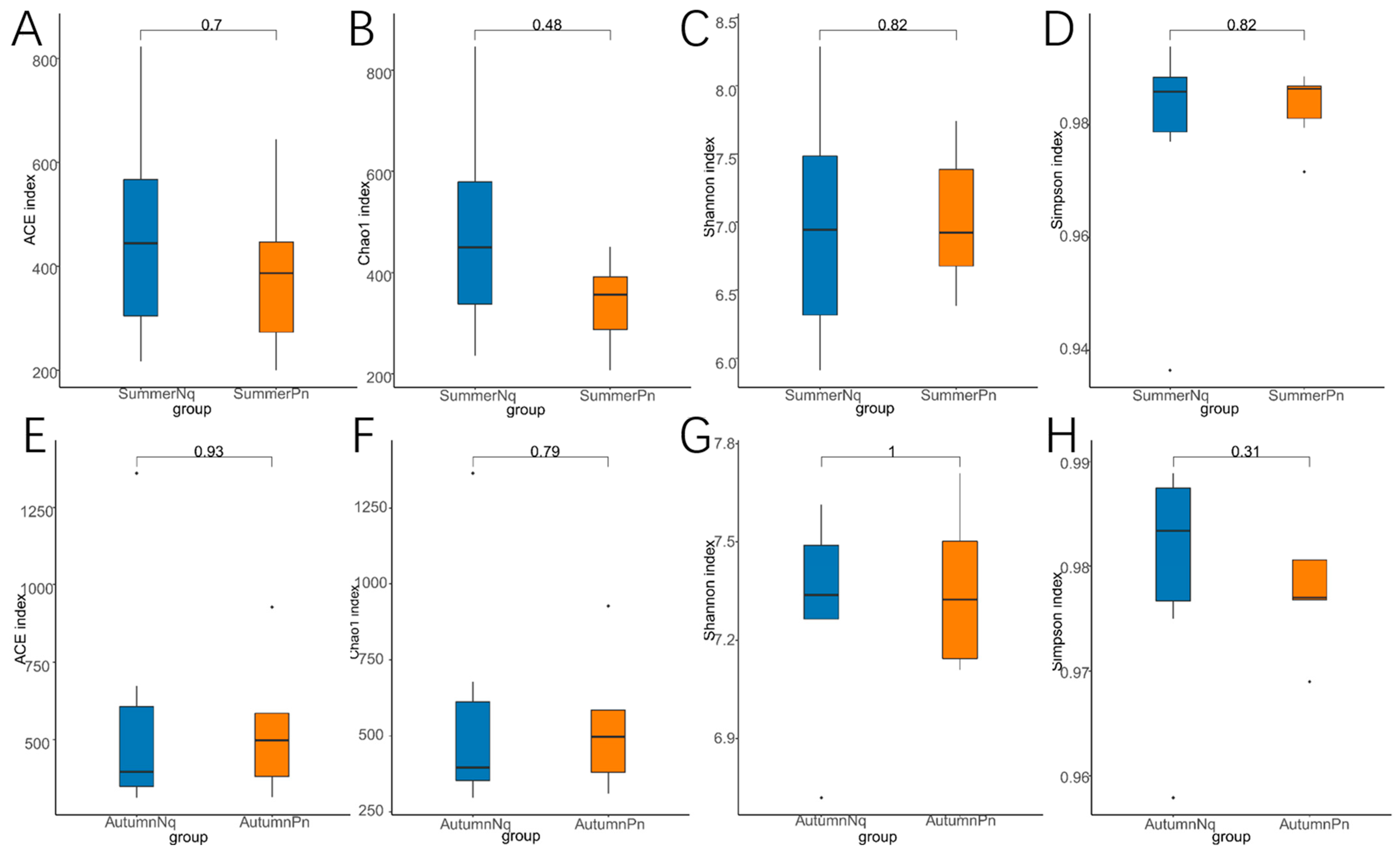
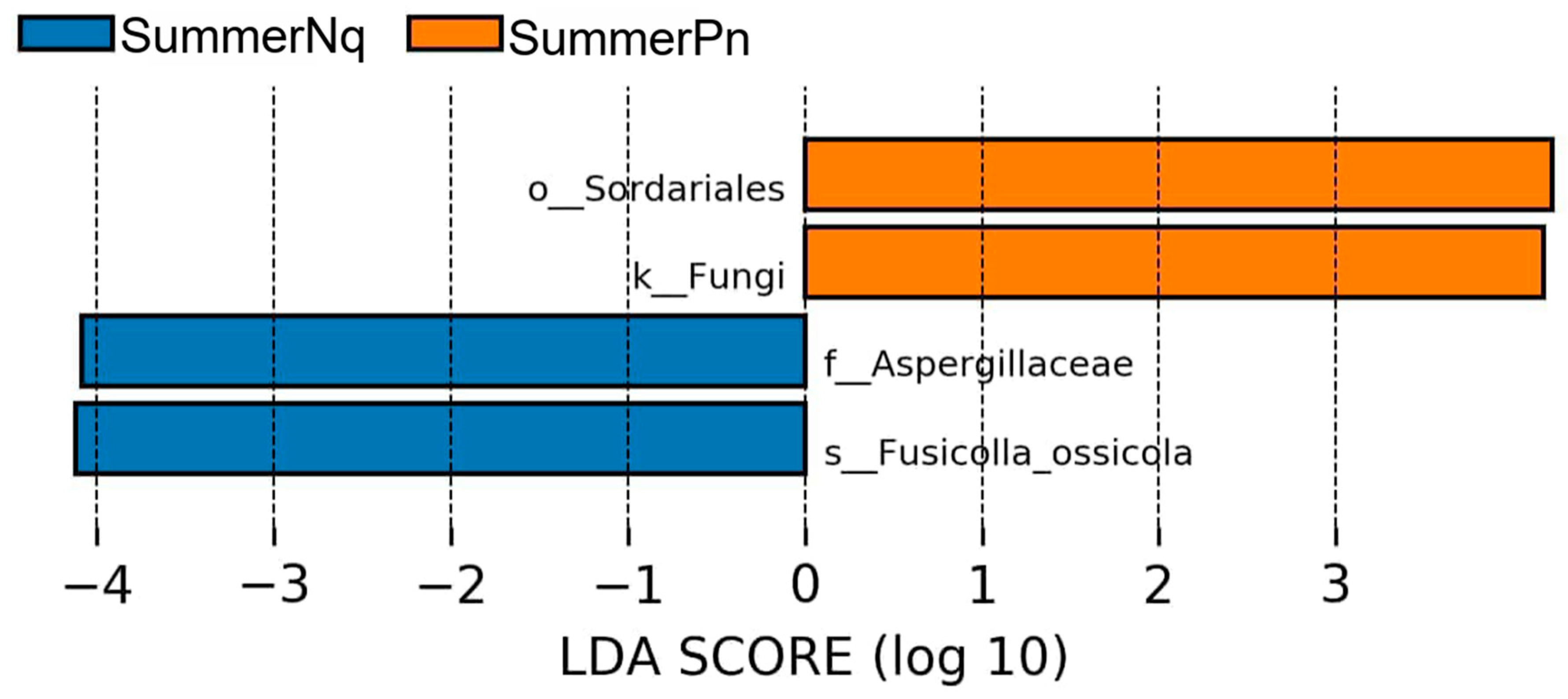
3.3. Effect of Host Species on Cutaneous Fungal Communities
3.4. Presence of Bd-Inhibiting Fungi Across Different Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheele, B.C.; Pasmans, F.; Skerratt, L.F.; Berger, L.; Martel, A.; Beukema, W.; Acevedo, A.A.; Burrowes, P.A.; Carvalho, T.; Catenazzi, A.; et al. Amphibian fungal panzootic causes catastrophic and ongoing loss of biodiversity. Science 2019, 363, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voyles, J.; Young, S.; Berger, L.; Campbell, C.; Voyles, W.F.; Dinudom, A.; Cook, D.I.; Webb, R.; Alford, R.A.; Skerratt, L.F.; et al. Pathogenesis of chytridiomycosis, a cause of catastrophic amphibian declines. Science 2009, 326, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearns, P.J.; Fischer, S.; Fernández-Beaskoetxea, S.; Gabor, C.R.; Bosch, J.; Bowen, J.L.; Tlusty, M.F.; Woodhams, D.C. Fight fungi with fungi: Antifungal properties of the amphibian mycobiome. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, J.; Ellepola, G.; Meegaskumbura, M. Patterns of infection, origins, and transmission of ranaviruses among the ectothermic vertebrates of Asia. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 15498–15519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisachova, L.S.; Lisachov, A.P.; Ermakov, O.A.; Svinin, A.O.; Chernigova, P.I.; Lyapkov, S.M.; Zamaletdinov, R.I.; Pavlov, A.V.; Zaks, S.S.; Fayzulin, A.I.; et al. Continent-wide distribution of CMTV-like ranavirus, from the Urals to the Atlantic Ocean. Ecohealth, 2025; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Price, S.J.; Garner, T.W.J.; Nichols, R.A.; Balloux, F.; Ayres, C.; Mora-Cabello de Alba, A.; Bosch, J. Collapse of amphibian communities due to an introduced ranavirus. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 2586–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echaubard, P.; Leduc, J.; Pauli, B.; Chinchar, V.G.; Robert, J.; Lesbarrères, D. Environmental dependency of amphibian-ranavirus genotypic interactions: Evolutionary perspectives on infectious diseases. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhams, D.C.; Brandt, H.; Baumgartner, S.; Kielgast, J.; Küpfer, E.; Tobler, U.; Davis, L.R.; Schmidt, B.R.; Bel, C.; Hodel, S.; et al. Interacting symbionts and immunity in the amphibian skin mucosome predict disease risk and probiotic effectiveness. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, A.E.; Bunk, B.; Lyra, M.L.; Fuzo, C.A.; Marani, M.M.; Spröer, C.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Lopes, N.P.; Overmann, J. Molecular basis of a bacterial-amphibian symbiosis revealed by comparative genomics, modeling, and functional testing. ISME J. 2021, 16, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, A.J.; Bushell, J.; Arisdakessian, C.G.; Belcaid, M.; Boiano, D.M.; Brown, C.; Knapp, R.A. The amphibian microbiome exhibits poor resilience following pathogen-induced disturbance. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1628–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, A.V.; Savage, A.E.; Hewson, L.; Zamudio, K.R. Seasonal and ontogenetic variation of skin microbial communities and relationships to natural disease dynamics in declining amphibians. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 140377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.H.; Brucker, R.M.; Schwantes, C.R.; Harris, R.N.; Minbiole, K.P.C. The bacterially produced metabolite violacein is associated with survival of amphibians infected with a lethal fungus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6635–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucker, R.M.; Harris, R.N.; Schwantes, C.R.; Gallaher, T.N.; Flaherty, D.C.; Lam, B.A.; Minbiole, K.P.C. Amphibian chemical defense: Antifungal metabolites of the microsymbiont Janthinobacterium lividum on the salamander Plethodon cinereus. J. Chem. Ecol. 2008, 34, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodhams, D.C.; LaBumbard, B.C.; Barnhart, K.L.; Becker, M.H.; Bletz, M.C.; Escobar, L.A.; Flechas, S.V.; Forman, M.E.; Lannetta, A.A.; Joyce, M.D.; et al. Prodigiosin, violacein, and volatile organic compounds produced by widespread cutaneous bacteria of amphibians can inhibit two Batrachochytrium fungal pathogens. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 1049–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walke, J.B.; Becker, M.H.; Loftus, S.C.; House, L.L.; Teotonio, T.L.; Minbiole, K.P.C.; Belden, L.K. Community structure and function of amphibian skin microbes: An experiment with bullfrogs exposed to a chytrid fungus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.N.; Brucker, R.M.; Walke, J.B.; Becker, M.H.; Schwantes, C.R.; Flaherty, D.C.; Lam, B.A.; Woodhams, D.C.; Briggs, C.J.; Vredenburg, V.T.; et al. Skin microbes on frogs prevent morbidity and mortality caused by a lethal skin fungus. ISME J. 2009, 3, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueneman, J.G.; Woodhams, D.C.; Harris, R.; Archer, H.M.; Knight, R.; McKenzie, V.J. Probiotic treatment restores protection against lethal fungal infection lost during amphibian captivity. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20161553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffnagle, G.B.; Noverr, M.C. The emerging world of the fungal microbiome. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Herath, J.; Zhou, S.; Ellepola, G.; Meegaskumbura, M. Associations of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis with skin bacteria and fungi on Asian amphibian hosts. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peay, K.G.; Kennedy, P.G.; Talbot, J.M. Dimensions of biodiversity in the earth mycobiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underhill, D.M.; Iliev, I.D. The mycobiota: Interactions between commensal fungi and the host immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, D.; Hughey, M.C.; Walke, J.B.; Becker, M.H.; Pontarelli, K.; Sun, S.; Badgley, B.; Belden, L.K. Amphibian skin fungal communities vary across host species and do not correlate with infection by a pathogenic fungus. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 2905–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupar, M.; Savković, Ž.; Breka, K.; Stamenković, S.; Krizmanić, I.; Vukojević, J.; Grbić, M.L. A variety of fungal species on the green frogs’ skin (Pelophylax esculentus complex) in South Banat. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, H.; Deng, J.; Zhao, H.; Fang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W.; Kong, F. Seasonality influences skin bacterial community structure and anti-Bd function in two anuran species. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1463563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA). In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; Balakrishnan, N., Colton, T., Everitt, B., Piegorsch, W., Ruggeri, F., Teugels, J.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.; Lopes, I.; Proença, D.N.; Ribeiro, R.; Morais, P.V. Diversity of cutaneous microbiome of Pelophylax perezi populations inhabiting different environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, S.; Rovito, S.; Parra-Olea, G.; Vásquez-Almazán, C.; Flechas, S.V.; Bi, K.; Vredenburg, V.T. The influence of habitat and phylogeny on the skin microbiome of amphibians in Guatemala and Mexico. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muletz-Wolz, C.R.; Almario, J.G.; Barnett, S.E.; DiRenzo, G.V.; Martel, A.; Pasmans, F.; Zamudio, K.R.; Toledo, L.F.; Lips, K.R. Inhibition of fungal pathogens across genotypes and temperatures by amphibian skin bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveau, A.; Bonito, G.; Uehling, J.; Paoletti, M.; Becker, M.; Bindschedler, S.; Hacquard, S.; Hervé, V.; Labbé, J.; Lastovetsky, O.A.; et al. Bacterial-fungal interactions: Ecology, mechanisms and challenges. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Sampling Time | Sample Size | Location | Elevation (m) | Site Description | IUCN Red List Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pelophylax nigromaculatus | 25 April | 9 (F, 4; M, 5) | 33.70964668° N 107.39150169° E | 989 | paddy fields | LC |
| 17 July | 6 (F, 3; M, 3) | |||||
| 19 September | 5 (F, 2; M, 3) | |||||
| Nanorana quadranus | 25 April | \ | 33.70561351° N 107.38986328° E | 988 | stream | NT |
| 17 July | 6 (F, 3; M, 3) | |||||
| 19 September | 6 (F, 3; M, 3) |
| Group | Sample | ASV Number | Abundance Index | Diversity Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1 | ACE | Shannon | Simpson | |||
| SpringPn | SpringPn1 | 376 | 439.0 | 402.528 | 7.2642 | 0.9869 |
| SpringPn2 | 572 | 639.0286 | 606.4556 | 7.5198 | 0.9903 | |
| SpringPn3 | 326 | 380.0769 | 362.7632 | 7.379 | 0.9905 | |
| SpringPn4 | 403 | 513.55 | 534.5982 | 7.3516 | 0.9858 | |
| SpringPn5 | 366 | 415.4 | 399.5598 | 7.276 | 0.9871 | |
| SpringPn6 | 387 | 477.2308 | 477.0094 | 7.2877 | 0.9868 | |
| SpringPn7 | 512 | 543.9545 | 544.9311 | 7.6572 | 0.9888 | |
| SpringPn8 | 366 | 555.1 | 441.9499 | 7.2505 | 0.988 | |
| SpringPn9 | 376 | 437.1071 | 446.5383 | 7.2007 | 0.9855 | |
| SummerPn | SummerPn1 | 366 | 400.0 | 414.5363 | 7.5274 | 0.9865 |
| SummerPn2 | 266 | 346.5714 | 359.1739 | 6.8807 | 0.9861 | |
| SummerPn3 | 173 | 207.0 | 200.1321 | 6.609 | 0.9794 | |
| SummerPn4 | 226 | 366.25 | 644.7811 | 6.9626 | 0.9869 | |
| SummerPn5 | 431 | 451.0 | 457.6898 | 7.7415 | 0.9885 | |
| SummerPn6 | 183 | 268.0 | 244.8576 | 6.383 | 0.9716 | |
| AutumnPn | AutumnPn1 | 584 | 585.0 | 584.7134 | 7.7097 | 0.9806 |
| AutumnPn2 | 310 | 310.5 | 312.8443 | 7.144 | 0.9768 | |
| AutumnPn3 | 380 | 380.0 | 380.3383 | 7.1098 | 0.9806 | |
| AutumnPn4 | 496 | 497.0 | 497.0556 | 7.5015 | 0.977 | |
| AutumnPn5 | 927 | 927.0 | 927.0 | 7.3232 | 0.969 | |
| SummerNq | SummerNq1 | 486 | 561.6 | 541.561 | 7.5384 | 0.9877 |
| SummerNq2 | 287 | 337.6 | 347.6141 | 7.3232 | 0.9886 | |
| SummerNq3 | 177 | 235.6667 | 217.6583 | 6.235 | 0.9769 | |
| SummerNq4 | 815 | 846.5 | 823.1168 | 8.2885 | 0.9938 | |
| SummerNq5 | 546 | 585.1364 | 575.9615 | 5.9111 | 0.9364 | |
| SummerNq6 | 244 | 338.0909 | 290.6159 | 6.5623 | 0.9839 | |
| AutumnNq | AutumnNq1 | 372 | 375.0 | 382.08 | 7.2666 | 0.975 |
| AutumnNq2 | 401 | 416.0 | 408.88 | 7.6133 | 0.9883 | |
| AutumnNq3 | 282 | 296.0 | 311.5464 | 7.263 | 0.9851 | |
| AutumnNq4 | 668 | 678.0 | 672.7716 | 6.7187 | 0.9579 | |
| AutumnNq5 | 1358 | 1365.0909 | 1360.4544 | 7.5163 | 0.9817 | |
| AutumnNq6 | 319 | 345.25 | 337.4353 | 7.4075 | 0.9889 | |
| Treat | Variables | Degrees of Freedom | Sums of Squares | Mean Squares | F. Model | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P. nigromaculatus in different seasons | 2 | 1.670135 | 0.835068 | 2.068017 | 0.195686 | 0.001 ** |
| 2 | N. quadranus in different seasons | 1 | 0.698502 | 0.698502 | 1.604157 | 0.138240 | 0.001 ** |
| 3 | P. nigromaculatus and N. quadranus in summer | 1 | 0.448963 | 0.448963 | 1.064348 | 0.096196 | 0.342 |
| 4 | P. nigromaculatus and N. quadranus in autumn | 1 | 0.435276 | 0.435276 | 1.000984 | 0.100089 | 0.399 |
| Treat | Variables | Degrees of Freedom | Sums of Squares | Mean Squares | F. Model | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P. nigromaculatus in different seasons | 2 | 2.474165 | 1.237082 | 4.260942 | 0.333905 | 0.001 ** |
| 2 | N. quadranus in different seasons | 1 | 1.023472 | 1.023472 | 2.893324 | 0.224405 | 0.001 ** |
| 3 | P. nigromaculatus and N. quadranus in summer | 1 | 0.41986 | 0.41986 | 1.144997 | 0.102736 | 0.232 |
| 4 | P. nigromaculatus and N. quadranus in autumn | 1 | 0.262063 | 0.262063 | 0.868163 | 0.087976 | 0.625 |
| Phylum | SpringPn | SummerPn | AutumnPn | SummerNq | AutumnNq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascomycota | 72.02 ± 0.89% | 57.37 ± 1.66% | 67.42 ± 3.25% | 59.72 ± 2.30% | 65.53 ± 2.71% |
| Basidiomycota | 17.29 ± 0.45% | 11.97 ± 0.87% | 10.45 ± 1.10% | 13.24 ± 1.78% | 9.06 ± 0.76% |
| unclassified_Fungi | 4.08 ± 0.56% | 10.28 ± 1.05% | 13.54 ± 2.32% | 7.85 ± 1.52% | 14.38 ± 1.74% |
| Mortierellomycota | 2.99 ± 0.22% | 6.09 ± 0.55% | 2.92 ± 0.53% | 6.67 ± 0.65% | 2.86 ± 0.27% |
| Chytridiomycota | \ | \ | 3.75 ± 0.47% | \ | 5.54 ± 0.61% |
| Olpidiomycota | \ | 7.97 ± 1.80% | \ | 3.84 ± 1.08% | \ |
| Rozellomycota | 1.16 ± 0.21% | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| Genus | SpringPn | SummerPn | AutumnPn | SummerNq | AutumnNq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cladosporium | 9.02 ± 0.66% | \ | 4.93 ± 1.41% | \ | \ |
| unidentified | 7.54 ± 0.66% | 9.66 ± 0.99% | 13.33 ± 1.32% | 10.18 ± 1.16% | 11.64 ± 0.92% |
| Galactomyces | 6.79 ± 0.51% | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| Fusarium | 4.67 ± 0.23% | \ | 5.97 ± 1.00% | 4.28 ± 0.91% | 5.74 ± 1.12% |
| unclassified_Saccharomycetales | 4.16 ± 0.26% | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| unclassified_Fungi | \ | 10.28 ± 1.05% | 13.54 ± 2.32% | 7.85 ± 1.52% | 14.38 ± 1.74% |
| Olpidium | \ | 7.97 ± 1.79% | \ | \ | \ |
| unclassified_Ascomycota | \ | 7.32 ± 1.36% | \ | 4.39 ± 0.95% | \ |
| Mortierella | \ | 6.05 ± 0.56% | \ | 6.66 ± 0.66% | \ |
| Mycothermus | \ | \ | 12.25 ± 2.43% | \ | 10.83 ± 1.41% |
| Alternaria | \ | \ | \ | \ | 3.19 ± 0.61% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Ma, H.; Deng, J.; Fang, C.; Zhao, H.; An, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, W.; et al. Seasonality Has Greater Influence on Amphibian Cutaneous Mycobiome than Host Species. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070473
Zhang H, Zhang K, Ma H, Deng J, Fang C, Zhao H, An X, Zhang J, Wang Q, Jiang W, et al. Seasonality Has Greater Influence on Amphibian Cutaneous Mycobiome than Host Species. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(7):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070473
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Han, Kunyang Zhang, Hongying Ma, Jie Deng, Cheng Fang, Hu Zhao, Xiaoran An, Jianlu Zhang, Qijun Wang, Wei Jiang, and et al. 2025. "Seasonality Has Greater Influence on Amphibian Cutaneous Mycobiome than Host Species" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 7: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070473
APA StyleZhang, H., Zhang, K., Ma, H., Deng, J., Fang, C., Zhao, H., An, X., Zhang, J., Wang, Q., Jiang, W., & Kong, F. (2025). Seasonality Has Greater Influence on Amphibian Cutaneous Mycobiome than Host Species. Journal of Fungi, 11(7), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070473






