Abstract
From 2013 to 2021, 112 binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. (BNR) isolates were obtained from the strawberry, tomato, pepper, bean, apple, cherry, meadow grass, and soil previously cropped with strawberries from 16 locations in Serbia. Morphological and molecular analyses (ITS, LSU rDNA, RPB2, tef-1α, and atp6) confirmed infections caused by four BNR AGs: AG-G on the cherry (globally new host), bean, and tomato; AG-U on meadow grass (globally new host) and apple, AG-A on the strawberry (the most frequently isolated), and AG-F on pepper. ITS sequence analysis revealed 24 haplotypes within the worldwide population of BNR AG-A, with Serbian isolates belonging to nine. The aggressiveness of AG-A (ten isolates), AG-G (three isolates), AG-F (one isolate), and AG-U (two isolates) was tested on seedlings of 14 hosts from Poaceae, Brassicaceae, Solanaceae, Asteraceae, Fabaceae, Cucurbitaceae, Apiaceae, and Chenopodiaceae, and on detached leaf petioles of the strawberry, tomato, sunflower, and bean, as well as on two pea cultivars. Sunflower and sugar beet were the most susceptible, with AG-G being the most aggressive and AG-A the least aggressive. AG-A could not infect cabbage, while at least one isolate of each remaining AG infected all tested hosts. The consistency between seedling and petiole tests highlights the latter as a rapid method for evaluating the pathogenicity and aggressiveness of BNR isolates.
1. Introduction
Rhizoctonia species are soil-borne, mostly pathogenic basidiomycetes that are frequently associated with plant roots. They are very diverse in terms of morphology, host specificity, and pathogenicity and are present in many geographical areas. The host range of Rhizoctonia spp. is broad [1] and includes fruit and forest trees, as well as a range of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous herbaceous plants. The mycelium of Rhizoctonia spp. can survive for a long time on plant debris and can be spread with soil particles and sclerotia [2]. The control of diseases caused by Rhizoctonia spp. is complex and costly due to their soil-borne nature and long persistence, while the lack of resistant plant varieties and an insufficient number of effective fungicides with expensive applications contribute to this problem [3].
Widespread infections with Rhizoctonia spp. are associated with symptoms of stem canker, black scurf, seedling damping-off, foliar blight, leaf spots, and sheath blight in a large number of different plants [1]. Infections can occur at different stages of plant development [3], while roots and stolons can be infected at any time during the growing season. Numerous reports have linked Rhizoctonia diseases to significant yield reductions, including up to 30% losses in potatoes [4,5], 30% in soybeans [6], 20% in rice [7], and 40% in oilseed rape [8].
The most important historical principle and criterion for the classification of Rhizoctonia spp. is the status of the nuclei, which can be divided into three subgroups: uninucleate, binucleate, and multinucleate Rhizoctonia (UNR, BNR, and MNR) [9,10,11]. Each subgroup consists of different anastomosis groups (AGs), which are further subdivided into intraspecific groups (IGs) that differ in colony appearance (e.g., pigmentation, zonation, presence of sclerotia and moniloid cells, and growth rate), physiological characteristics, pathogenicity, and/or fungicide sensitivity [3,9]. BNR (teleomorph Ceratobasidium spp.) consists of 19 AGs, referred to as AG-A to AG-W [12,13].
The study of Rhizoctonia spp. diversity and population structure is of great importance, and the AGs with the most pronounced diversity include MNR AG-1, AG-2, AG-4, and AG-6, and BNR AG-B and AG-D [1,12,14,15]. Most studies focus on identifying which AGs are present in specific crops, including wheat and clover [16], various vegetables [17], potato and tobacco [18], beans [19], and strawberries [20,21] or soil [22,23,24], while data on the population structure of certain AGs are limited. More detailed analyses of a small number of selected AGs have shown the existence of diversity. For example, haplotype diversity was confirmed in the R. solani AG-3 population from the potato, while no genetic diversity was found within tobacco populations [25]. Differences in population structure are reported for R. solani AG-1-IA, with 12 and 39 haplotypes identified [26,27]. Haplotype heterogeneity is also detected in R. cerealis AG-D [28].
Despite the great diversity of BNRs in terms of their virulence and host range [10], only a few AGs are examined in-depth due to their importance. The BNRs AG-A and AG-G are described as the most common and the most virulent, with the widest host range [12]. In Serbia, data on the diversity of BNRs are limited, and only Rhizoctonia spp. AG-A and AG-I have been described as strawberry pathogens [20,29]. Due to the importance of BNR for the production of various crops, the objectives of our study were to (i) isolate Rhizoctonia spp. AGs from different diseased host plants and soils of agricultural land in Serbia, (ii) identify isolates based on morphology and nuclear status, (iii) investigate the diversity of morphology within and between different AGs, (iv) test pathogenicity to fulfill Koch’s postulates, (v) perform molecular and phylogenetic characterization based on the sequencing of the ITS (ITS1, 5.8S rDNA, and ITS2) and LSU of the rDNA, RPB2, tef-1α, and atp6 genomic regions, (vi) investigate the structure of the BNR AG-A population in Serbia and worldwide based on haplotype analyses, and (vii) compare the host range and aggressiveness of isolates within and between different AGs using different approaches.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Surveys, Sample Collection, and Morphological Identification
This survey was conducted during 2013–2021 at 16 locations across Serbia, and symptomatic plant (14 locations) and soil (2 locations) samples were collected in seven different crops: strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), pepper (Capsicum annuum), bean (Phaseolus vulgaris), apple (Malus domestica), cherry (Prunus avium), and meadow grass (Poa annua). At each location, the incidence of the disease was estimated by walking through the crop in a zigzag pattern and randomly rating 100 plants in three replicates. A total of 163 samples of plants with visible symptoms of root and root neck rot, wilting, and decay were collected and analyzed within 48 h. The number of samples at each locality was different and depended on the field size and disease incidence (Table 1). For isolation, small sections (0.5 cm diameter) were taken from the edge of diseased plant tissue, washed in running tap water for 2 h, surface sanitized with 2% sodium hypochlorite for 1 min, plated on potato dextrose agar (PDA, 200 g potato, 20 g dextrose, 17 g agar, and 1 L distilled H2O) [30], and incubated at 24 °C for 3 days.

Table 1.
Sample data collected in Serbia and disease intensity.
Soil samples from the 10–15 cm depth of the soil profiles, from two fields with strawberry as a previous crop, were collected (approximately 500 g) and transferred to pots and kept in the greenhouse (20 °C). Pathogens were isolated from the soil samples using the bait plant method [30] by sowing (one day after sampling) sterile bean seeds (previously shown to be susceptible to the various BNR AGs). The pots were then irrigated to soil capacity. From symptomatic bait plants in the phenophase of cotyledons, re-isolation was performed using the same method as for isolation.
Rhizoctonia-like colonies were selected based on colony appearance and branching pattern. Hyphal tip isolates were obtained after subculturing colonies on water agar (WA, 17 g agar, and 1 L distilled H2O) and transferring the isolated tips of individual hyphae to PDA. Selected isolates from each locality were identified based on the number of nuclei in three-day-old hyphal cells, hyphal branching pattern, growth rate, and colony morphology 15 days post-inoculation (dpi) on PDA at 24 °C in the dark [10]. One isolate representing uniform isolates from each site was selected for detailed characterization.
2.2. Pathogenicity Testing
Pathogenicity was tested depending on the origin of the isolate. After all tests, the challenging isolates were recovered from symptomatic plants using the same method as for isolation and used for further characterization.
The pathogenicity of 10 selected isolates from the strawberry was tested by inoculating six plants each (replicates) of stolon-propagated disease-free strawberry daughter plants of the cultivar ‘Senga-Sengana’ according to the published method [31]. Negative control plants were inoculated with sterile PDA. Each healthy, non-wounded strawberry plant was transplanted into a pot (12.5 cm diameter and 9 cm height) containing a sterilized commercial substrate, and a 7-day-old Rhizoctonia colony (9 cm diameter) was placed in the root zone. Plants were maintained in the greenhouse (23 °C, 12 h photoperiods), and the appearance of symptoms was assessed up to 30 days post-inoculation. Similarly, the pathogenicity of an isolate from meadow grass was tested on five healthy, commercially obtained grass blocks of meadow grass planted in a sterile substrate in pots (15 cm diameter) and grown under greenhouse conditions with regular watering. After two weeks, the grass blocks were transplanted and inoculated with a seven-day-old isolate colony grown on PDA inserted near the roots. The control grass blocks were inoculated with sterile PDA. The appearance of symptoms was monitored at weekly intervals. Re-isolation was performed from all plants with symptoms. The experiment was repeated twice.
The pathogenicity of five isolates from the tomato, pepper, bean, apple, and cherry was tested by inoculating seedlings of the respective host plant. Tomato, pepper, and bean seeds were purchased commercially. Apple and cherry seeds were collected from commercially available ripe fruits and stored in the refrigerator at 5 °C for three months for vernalization and then sawed. Seedlings were inoculated when the first true leaves developed by placing mycelial plugs near the roots during transplanting. Five plugs (2r = 5 mm) from 7-day-old cultures were used per isolate and per seedling, and five seedlings were inoculated with each isolate. Seedlings inoculated with sterile PDA served as the control. Plants were maintained under greenhouse conditions and monitored for symptom development. The experiment was repeated twice.
2.3. DNA Amplification and Sequencing
Total genomic DNA was extracted from 100 mg of dry mycelium grown in potato dextrose broth (PDB) for 5 days using the Dneasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR amplification of the ITS (ITS1, 5.8S rDNA, and ITS2) and LSU of rDNA, RPB2, tef-1α, and atp6 used the primers ITS1F (CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA)/ITS4 (TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC) [32,33], LROR (GTACCCGCTGAACTTAAGC)/LR5 (ATCCTGAGGGAAACTTC) [34], BRPB26F (TGGGGYATGGNTTGYCCYGC)/BRPB271R (CCCATRGCYTGYTTMCCCAT) [35,36], EF986F (GCYCCYGGHCAYCGTGAYTTYAT)/EF1567R (ACHGTRCCRATACCACCRATCTT) [37], and ATP61 (ATTAATTSWCCWTTAGAWCAATT)/ATP62 (TAATTCTANWGCATCTTTAATRTA) [38], respectively. The conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, corresponding to annealing temperatures, elongation at 72 °C for 1 min, and final elongation for 10 min at 72 °C. Amplification reactions were performed in a total reaction volume of 25 μL, consisting of 12.5 μL of 2X PCR Master mix (Fermentas, Vilnius, Lithuania), 6.5 μL of RNase-free water, 2.5 μL of both forward and reverse primers (100 pmol/μL, Metabion International, Planegg, Germany), and 1 μL of template DNA. The PCR products were stained with ethidium bromide in a 1% agarose gel for electrophoresis and visualized with a UV transilluminator. The obtained PCR products were sequenced in both directions in an automated sequencer (Automatic Sequencer Macrogen Inc., Maastricht, The Netherlands) using the same primers as for amplification. The consensus sequences were computed using ClustalW [39], integrated into the MEGA X software [40], and deposited in GenBank (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) (assessed on 1 May 2022). All generated sequences were compared with each other by calculating nucleotide (nt) identities and with previously deposited isolates of Rhizoctonia spp. in GenBank using the similarity search tool BLAST.
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
The generated ITS sequences of 16 Serbian BNR isolates were analyzed with 21 previously listed type-derived sequences of nine BNRs [12] and one outgroup taxon Athelia rolfsii retrieved from GenBank (Table 2). A phylogenetic tree was inferred using the maximum likelihood method implemented in MEGA X software [40]. Distances in the ITS rDNA region were determined using Kimura’s two-parameter model [41], and all sites with gaps were omitted. The reliability of the obtained trees was evaluated using 1000 bootstrap replicates.

Table 2.
Binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. and related internal transcribed spacer sequences derived from GenBank and included in the phylogenetic analysis.
2.5. Haplotype Analysis of Binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-A Sequences
The analysis of BNR AG-A haplotypes was performed on the basis of all 159 available sequences of the ITS region in GenBank (accessed 30 March 2025), together with 10 Serbian BNR AG-A sequences. Sequences that were too short, those that belonged to the unverified category, or those that had high nucleotide differences and degenerate codons were eliminated, and a total of 76 sequences were included in the analysis. The number of haplotypes (h), haplotype diversity (Hd), number of variable sites (S), and nt diversity (p) of the ITS region were determined using the program DnaSP version 6.0 [46], after which the data on the composition of haplotypes and their frequency were further examined using the PopART software version 1.7. The visualization of haplotypes generated mutual genealogical relationships, using the median-joining network algorithm [47] implemented in the PopART (population analysis with reticulate trees) program [48]. All sequences were compared by calculating nt identities using the MEGA X software [40].
2.6. Host Range and Aggressiveness Testing
The host range and aggressiveness of 16 selected Serbian BNR AGs isolates were tested using two methods: inoculation of seedlings (9 isolates) and inoculation of detached leaf petioles (16 isolates).
The inoculation of seedlings of 14 plant species belonging to eight families (wheat (Triticum aestivum) and maize (Zea mays) from the Poaceae; cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) and oilseed rape (B. napus var. oleifera) from the Brassicaceae, tomato, pepper, and tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) from the Solanaceae, lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and sunflower (Helianthus annuus) from the Asteraceae, peas (Pisum sativum) and beans from the Fabaceae, cucumber (Cucumis sativus) from the Cucurbitaceae, carrot (Daucus carota) from the Apiaceae, and sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) from the Chenopodiaceae) was used to study the host range and aggressiveness of 4 isolates of AG-A, 3 isolates of AG-G, 1 AG-F isolate, and 1 AG-U isolate. Sanitized seeds were incubated on moist filter paper at room temperature for germination until true leaves were formed and inoculated with colony fragments during transplantation, as described for the pathogenicity experiments. The aggressiveness of the isolates was evaluated 7 dpi based on the symptoms observed and according to the scale established for this experiment: 0—no symptoms, 1—up to 30% of roots are necrotic, 2—up to 40% of roots are affected, 3—up to 60% of roots are necrotic, and 4—complete necrosis of roots and decaying of the entire plantlet. Each isolate was inoculated on five seedlings per host plant and the experiment was repeated three times. Seedlings of each host plant inoculated with sterile PDA served as a negative control.
The inoculation of detached leaf petioles of strawberries, tomatoes, sunflowers, beans, and two cultivars of peas, ‘Regina’ and ‘Medicon’, was used to test the aggressiveness of Rhizoctonia AG-A (10 isolates), AG-G (3 isolates), AG-F (1 isolate), and AG-U (2 isolates) [49]. Petioles were taken fresh from healthy, greenhouse-grown plants shortened to 20 mm, surface sterilized for 30 s in 50% commercial bleach (2% sodium hypochlorite), and inclined upright in seven-day-old cultures of Rhizoctonia isolates grown on PDA at 23 °C in the dark. Eight petioles per isolate were inoculated, while the petioles inclined in the sterile PDA served as negative controls. The inoculated petioles were incubated in a moist chamber and aggressiveness was determined 7 dpi by measuring necrosis length. The experiment was repeated twice.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The colony diameters of the isolates were verified for normality using Colmogorov–Smirnov and Liliefors tests in Graph Pad Software 5.0, Boston, MA, USA, and then analyzed using factorial ANOVA using Statistica 7 (StatSoft, Tulsa, OK, USA). Mean values were compared using Tukey’s test at the significance level of p < 0.05.
Ordinal data, as well as necrosis length data in the experiment that failed the normality test, were subjected to the Kruskal–Wallis non-parametric statistical test separately for each host plant. Medians of necrosis length were compared using Dunn’s multiple comparison test at the p < 0.05 level of significance. Data were expressed as means ± standard error.
3. Results
3.1. Symptoms, Morphology, and Pathogenicity
A total of 112 Rhizoctonia spp. were obtained from seven host plants (strawberry, tomato, pepper, bean, meadow grass, apple, and cherry) and two soil samples at 16 locations in Serbia (Table 1, Figure 1). Diseased strawberry plants showed leaf necrosis, partial necrosis on the stolons, and root rot, followed by the wilting and decay of the plants, which were often distributed along the rows. Tomatoes, beans, peppers, and meadow grass showed symptoms of leaf chlorosis and necrosis, as well as wilting of the whole plant, with pronounced root rot and necrosis. Three-year-old apple and cherry plants showed aboveground symptoms, such as stunting, leaf chlorosis, and necrotic zones on the leaves, as a consequence of visible necrosis at the stem base, roots, and root hairs (Figure 2A–D). The estimated disease incidence varied among crops, ranging from 5 to 35% (Table 1), with the highest value in strawberry fields (20–35%).
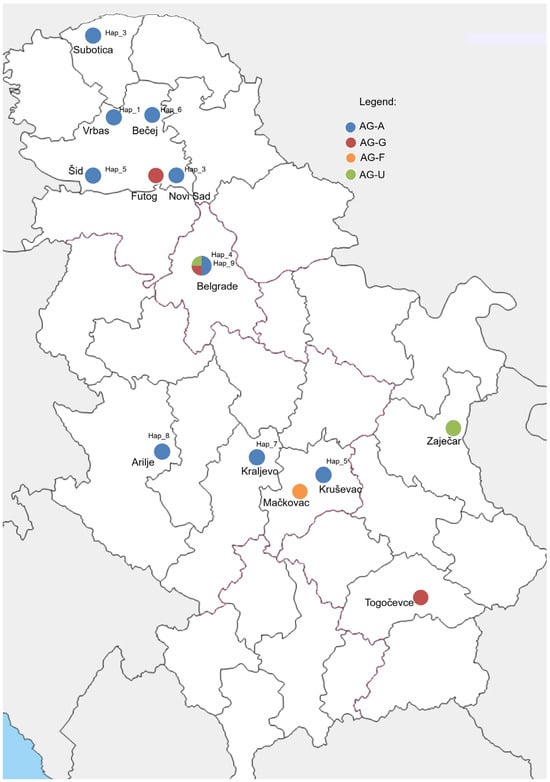
Figure 1.
Geographic distribution of localities in Serbia included in the survey and detected binucleate Rhizoctonia AGs and AG-A haplotypes.
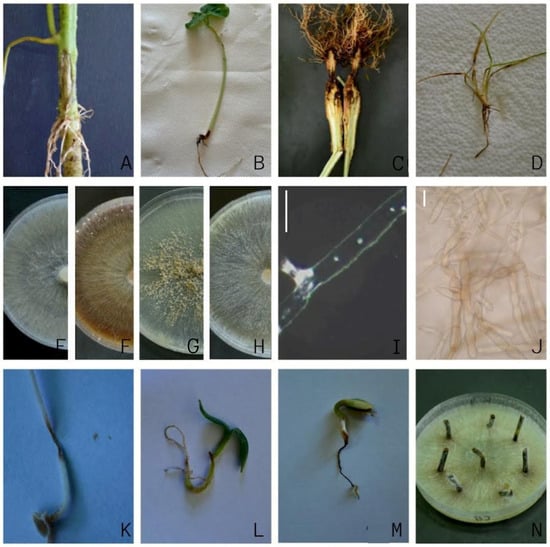

Figure 2.
Binucleate Rhizoctonia AGs: (A–D) root and root neck necrosis of the tomato, bean, pepper, and Poa annua, respectively; (E–H) seven-day-old colonies on PDA of Rhizoctonia spp. AG-A, AG-G, AG-F, and AG-U, respectively; (I) nuclei in hypha (bar = 20 µm); (J) moniloid cells in 5-day-old colonies of Rhizoctonia spp. AG-G (bar = 20 µm); (K,L) root necrosis in tomato plants inoculated with Rhizoctonia spp. AG-G and AG-F, respectively; (M) root necrosis of a sunflower inoculated with Rhizoctonia spp. AG-G; (N) pathogenicity testing on the detached leaf petioles of strawberry Rhizotonia AG-A.
Several Rhizoctonia-like isolates forming fast-growing colonies and of uniform appearance and morphology were obtained from each location and host plant, all of which had hyphae with two nuclei (Figure 2I). One representative isolate from each locality and host plant was selected for further study. The isolates were preliminarily identified as one of the four AGs: AG-A, AG-G, AG-F, and AG-U. The isolates of AG-A initially formed white (later beige-colored) colonies (Figure 2E), with no sclerotia. The members of AG-G also initially formed white colonies, which later turned brown (Figure 2F), with moniloid cells (Figure 2J) and sclerotia that became visible after 4 and 7 days, respectively. The members of AG-F initially formed white colonies, which later turned beige (Figure 2G), similar to the members of AG-A, but with moniloid cells and brown sclerotia visible after 4 and 7 days, respectively. The members of AG-U formed initially white colonies, which later turned salmon beige to brown (Figure 2H), with moniloid cells and beige sclerotia visible after 7 and 10 days, respectively. Differences in growth rate between AGs were significant (p < 0.01) (Figure 3), with isolates within an AG showing uniform growth rates or minor differences (AG-G). In general, isolates from AG-A grew more slowly than the other three AGs, with isolate 107-13 (AG-A) having the lowest growth rate of 12 mm/day, while isolate 190-18 (AG-F) had the highest growth rate of 22 mm/day.
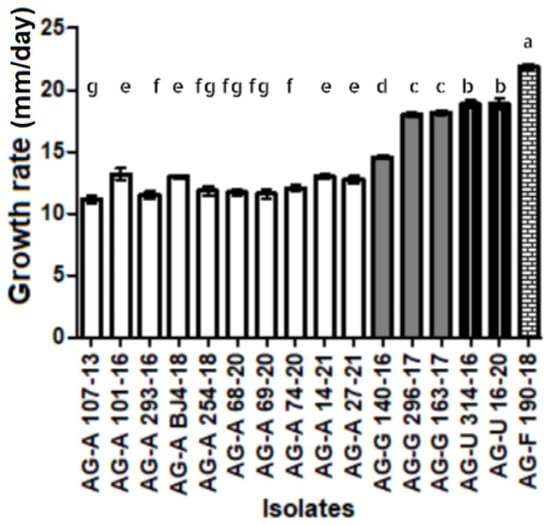
Figure 3.
Growth rate of isolates of binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. AG-A, AG-G, AG-F, and AG-F on PDA at 24 °C in the dark. Bars represent standard deviation. Values marked with the same letter do not differ significantly.
The pathogenicity of five selected isolates from the tomato, pepper, apple, and cherry was confirmed as they caused visible symptoms of root necrosis on the respective seedlings 7 dpi. Ten isolates from the strawberry caused leaf and root necrosis on strawberry daughter plants at 30 dpi, and one isolate from meadow grass caused leaf and root necrosis on meadow grass at 21 dpi (Figure 2K,L). All developed symptoms resembled natural infection, while the control plants remained symptomless. All isolates were re-isolated from the symptomatic tissue of inoculated plants, thus fulfilling Koch’s postulates.
3.2. Molecular and Phylogenetic Characterization
The sequence analyses confirmed the preliminary identification of four Serbian BNR AGs: AG-A, AG-G, AG-F, and AG-U. The BLAST analyses of the ITS sequences of the isolates of AG-A, AG-G, AG-F, and AG-U provided reliable identification as they had the highest nt identities with the respective AG type members and previously identified isolates. Despite numerous attempts and modifications of the protocols, amplification of LSU, RPB2, tef-1α, and atp6 was not possible for isolates from all four AGs. The LSU, tef-1α, and RPB2 sequences of Serbian AG-A (Acc. No. MN977412, MT063197, and MT126788) and AG-F (MN977419, MT006340, and MT150071), as well as the LSU and tef-1α sequences of AG-G (MN977413 and MT063202) and AG-U (MN977420 and MT063204), showed the highest nt similarities with multiple AGs or with isolates of the unidentified category due to the limited number of available characterized isolates. Amplification of the atp6 gene was only successful for the AG-U isolate (MT161366), and BLAST analyses showed the highest nt similarity with the only available isolate belonging to AG-U (DQ301578).
The phylogenetic analyses using the maximum likelihood of reference AGs and Serbian BNR isolates resulted in a well-supported phylogenetic tree with a topology consistent with the previous identification of publicly available isolates (Figure 4). All branches of the different AGs confirmed the expected relationships, while the isolates from Serbia were clustered in the AG-A, AG-G, AG-F, and AG-U branches, which were supported with high bootstrap values, thus confirming the previous identification.
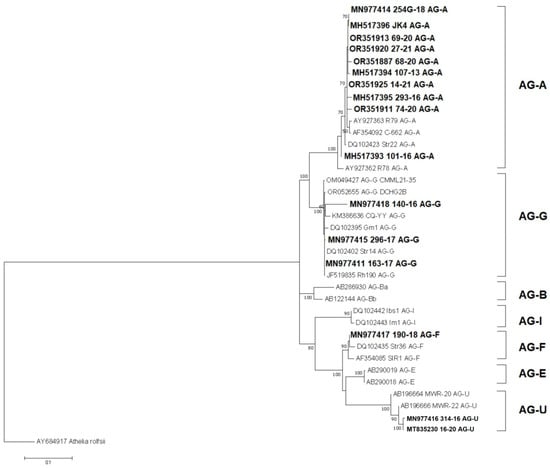
Figure 4.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of the internal transcribed spacer rDNA sequences of 16 Serbian and 21 reference isolates of binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. from nine AGs, and the outgroup taxa Athelia rolfsii. The tree was generated in MEGA X using Kimura’s two-parameter model. Bootstrap analyses were performed with 1000 replicates, and bootstrap values (>50%) are shown next to the corresponding branches. Serbian isolates are in bold.
3.3. Haplotype Structure and Genetic Diversity of BNR AG-A Sequences
A total dataset of 76 ITS sequences of BNR AG-A from Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, and North and South America, including ten Serbian isolates, showed high genetic diversity and was grouped into 24 haplotypes, with 89 variable positions detected. A nucleotide diversity of 0.01643 (0 to 30 nt difference) and a haplotype diversity of 0.84 indicate a high degree of genetic variation. The most numerous haplotypes consisted of 22 and 20 isolates (Hap_6 and Hap_10) containing isolates from different geographic origins and hosts (Table 3). The Serbian BNR AG-A population of 10 isolates belongs to nine different haplotypes (Hap_1–Hap_9), with a 0 to 5 nt difference and 98.6–99.5% similarity, which are distributed in different growing regions (Figure 1). The haplotype network with 24 haplotypes has a complex network-like structure with several branch points and intermediate nodes (Figure 5). Two major haplotypes, Hap_6 and Hap_16, serve as central nodes, indicating their higher frequency and potential ancestral status within the population. Hap_6 was the most widespread, with 22 sequences from five continents and five hosts, including one Serbian isolate. Hap_6 is connected to multiple other haplotypes, suggesting that it may represent a dominant or ancestral lineage. Hap_10 was the second largest haplotype with 20 isolates, but the isolates originated from a single country and host. The remaining haplotypes comprised a smaller number, mainly single sequences.

Table 3.
Binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. AG-A sequences used in haplotype analyses.
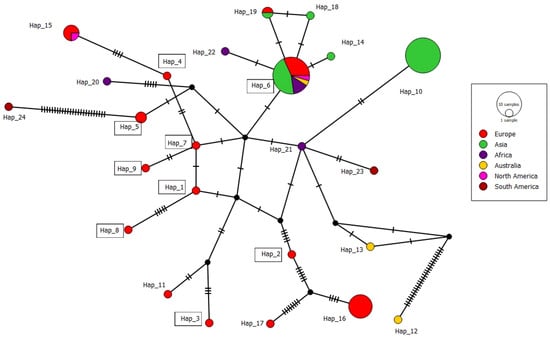
Figure 5.
Median-joining network showing the phylogenetic relationships between the haplotypes of isolates of Rhizoctonia spp. AG-A isolates available in GenBank. The black nodes represent median vectors (missing or not sampled haplotypes) required to connect existing haplotypes within the network with maximum parsimony. Details of the sequences and haplotypes are shown in Table 3. Only the numbers of significant haplotype groups are listed. Haplotypes to which Serbian isolates belong are labeled with rectangles. Different colors indicate the proportions within the haplotypes from different continents.
3.4. Host Range and Aggressiveness of Four Rhizoctonia spp. AGs
The Serbian BNR isolates caused necrosis in the majority of tested host plants 7 dpi, being very aggressive overall and often causing complete necrosis of the roots (Figure 2K–M). Differences in aggressiveness and host range between AGs and even between some of the isolates within AG-A and AG-G as individual AGs have been documented (Figure 6). BNR AG-A showed the narrowest host range and the lowest aggressiveness, while AG-F, AG-G, and AG-U were able to infect all host plants tested. The isolates of AG-G exhibited the highest aggressiveness. The control seedlings showed no symptoms.
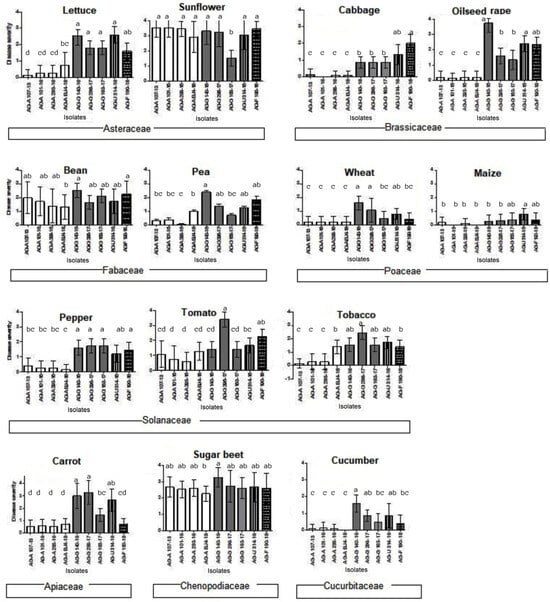
Figure 6.
Root rot disease severity on different host plant seedlings caused by four binucleate Rhizoctonia AGs (AG-A, AG-G, AG-F, and AG-U) isolates rated following the scale: 0—no reaction; 1—up to 30% of roots affected; 2—up to 40% of roots affected; 3—total of 40–60% of roots affected; and 4—roots and entire plantlet necrotic and decayed. Bars represent standard deviation. Values marked with the same letter do not differ significantly.
Of the four isolates of AG-A, none were able to infect cabbage seedlings, and at least one isolate was unable to infect tobacco, lettuce, pea, cucumber, and maize; however, they were most aggressive on sunflower and sugar beet, and partially on bean seedlings. The three AG-G isolates tested were the most aggressive on the majority of the test plants, with no significant differences among them. The highest disease severity was found in oilseed rape, sunflower, and sugar beet, with an average rate of 3.73, 3.33, and 3.26, respectively. AG-F and AG-U also showed medium to high aggressiveness on all 14 host plants. Statistical analysis of the ordinal data revealed that symptom development was significantly influenced by the host plants (p < 0.0001), regardless of the isolate used for inoculations. Sunflower and sugar beet developed the highest disease severity (mean values of 3.12 and 2.6, respectively) (Figure 6), while maize was the least affected (mean value of 0.28). Lettuce and sunflower, as well as peas and beans, showed significant differences in response, although they belong to the same plant family.
With the exception of strawberries, the assessment of aggressiveness, using a test with leaf petioles (Figure 2N), showed similar results. The length of necrosis varied depending on the challenging AG, while no necrosis was visible in control petioles. Isolates of AG-G were found to be the most aggressive on all five host plants (average necrosis length of 13.46 mm), with the exception of AG-A and AG-U on strawberries, where all three AGs showed high and similar aggressiveness (Figure 7). AG-F proved to be the most aggressive on sunflowers (average necrosis length of 13.75 mm) and the least aggressive on strawberries (average necrosis length of 3.01 mm). Statistical analysis of the ordinal data revealed that symptom development was significantly influenced by the host plants (p < 0.0001) (Figure 6). The strawberry developed the highest necrosis length (average of 14.73 mm), while beans and peas, as members of the same plant family, showed a similar response (average of 4.10 mm and 4.07 mm, respectively). BNR isolates exhibited a difference in aggressiveness towards the two pea cultivars. The isolates of AG-A and AG-F were more aggressive to ’Regina’, while the isolates of AG-G and AG-U were more aggressive to ’Medicom’.
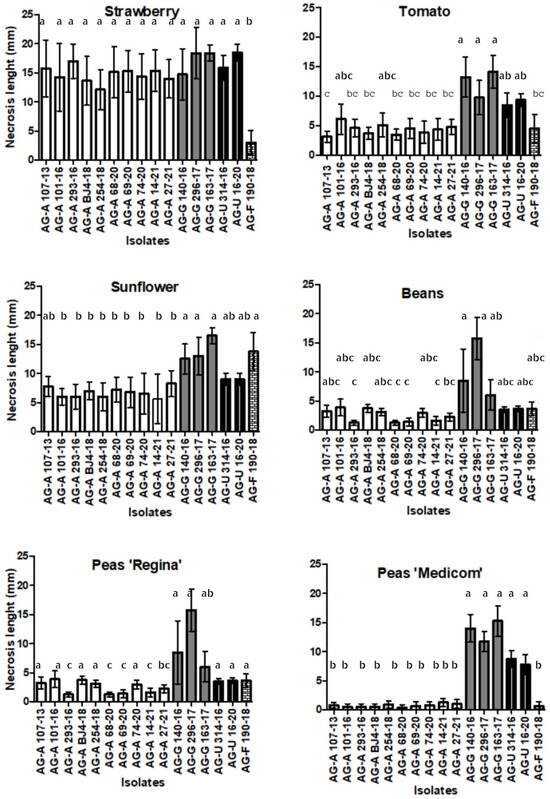
Figure 7.
Aggressiveness of four binucleate Rhizoctonia AGs (AG-A, AG-G, AG-F, and AG-U) on detached leaf petioles of strawberries, sunflowers, tomatoes, beans, and peas (necrosis length mm/day). Bars represent standard deviation. Values marked with the same letter do not differ significantly.
4. Discussion
The study of the diversity of BNRs in Serbia revealed the presence of four AGs, namely AG-A on strawberries, AG-G on tomatoes, beans, and cherries, AG-F on pepper, and AG-U on apples and meadow grass. Before this study, only the presence of AG-A and AG-I, causing black rot, on strawberries was confirmed [20,29], so three additional AGs infecting six host plants are new findings for Serbia. The infection of AG-G, causing root rot in cherries, and AG-U, causing root rot in meadow grass, was detected for the first time in the world. The morphological characteristics of all isolates or all four detected AGs are consistent with those previously reported [50,51,52,53]. The pathogenicity of all isolates was confirmed as they caused necrosis on the non-wounded plants of species from which they were isolated. The identification was also confirmed by BLAST analyses of five molecular markers (ITS, LSU, RPB2, tef-1α, and atp6), as is the case in the study by Gonzalez et al. [15]. Because of the low number of available sequences in GenBank, only ITS sequences were used for phylogenetic studies. A reconstructed phylogenetic tree confirmed the molecular identification, as the sequences of four Serbian AGs were clustered with their respective representatives and the resulting topology was consistent with previously published [13,44]. Phylogenetic analyses of BNR diversity have been extensively studied [31,44]. Sharon et al. [12] conducted the most comprehensive study of 21 AGs, which served as an important reference for global and our BNR research.
Despite the fact that AG-A was the most frequently detected BNR in Serbia (10 out of 16 locations), only strawberry infection was documented. Compared to previous studies [20], AG-A was detected at six new locations with a significant disease incidence (up to 35%), which correlates with its increasing importance for strawberries, a fact also observed in California, South Africa, Italy, and Israel, with a detection frequency of up to 70% [31,54,55]. The host range of AG-A isolates is mainly associated with the strawberry, but in other parts of the world, it has also been described as a pathogen in sugar beet, beans, peas, sunflowers, and other crops [2,22].
A BNR AG-A haplotype analysis was performed due to its high prevalence and wide distribution in Serbia. Our study revealed a high diversity in the population of BNR AG-A and the well-established 24 separate haplotypes worldwide. The Serbian population of BNR AG-A is also diverse, as our isolates were clustered into nine haplotypes. Published data on the morphological and phylogenetic diversity of BNR AG-A show the variability of the population. Li et al. [50] reported the morphological diversity of BNR AG-A and described three morphotypes based on colony morphology. Phylogenetic analyses by Manici and Bonora [31] confirmed the intra-AG variability of Italian AG-A isolates and showed that they are divided into four sub-clusters. Vojvodić et al. [20] confirmed that isolates from Serbia also show genetic variability and are divided into three defined sub-clusters. To date, there are no data on the haplotype composition of BNR AG-A worldwide, and our analyses represent the first attempt to characterize its status. Regarding the diversity of BNR AGs, Li et al. [28] published haplotype analyses of BNR AG-D and indicated the existence of three evolutionary origins. Ceresini et al. [25] reported two sister populations of R. solani AG-3 from potato and tobacco, representing two genetically distinct and historically divergent lineages that evolved depending on their Solanaceaeous hosts. Wang et al. [27] and Wei et al. [26] reported 43 and 12 haplotypes, respectively, in the Chinese population of MNR AG-1 IC from rice.
BNR AG-G has a broad host range that includes several vegetable species [2], such as the tomato and bean [19,56], which is comparable to the situation in Serbia as it was detected at three locations and on three different host plants: the tomato, bean, and cherry. AG-G on cherries caused chlorosis and necrotic zones on the leaves, as well as necrosis on the stem base, roots, and root hairs. Among the host plants from the Rosaceae family, AG-G has been shown to be pathogenic in strawberries [22] and apples [22,45]. To date, there is little evidence of Rhizoctonia spp. being pathogenic to Prunus spp. There is only one report of an Rhizoctonia spp. of unknown AG as an endophyte on cherries [57], and MNR AG-1-IC causing water-soaked lesions on the roots of Prunus amygdalus × Prunus persica [58] in Tunisia, followed by the subsequent collapse of the entire plant. Our results on AG-G as a cherry pathogen could be particularly valuable with regard to a possible endophytic lifestyle and a possible latent infection that spreads through the planting material and later transforms into a pathogen, especially in stressed or damaged plants.
Similar to Serbia, BNR AG-F has already been detected on peppers in Turkey, causing drying and rotting of the plants [56], but has also been detected on beans [19] and tobacco [59], indicating a preference for vegetable crops. These findings suggest that AG-F could pose a considerable risk to vegetable crops, especially in greenhouses.
Very little information is available on BNR AG-U, which has only been associated with a few hosts worldwide. So far, BNR AG-U has been detected on ornamental plants in Japan and in the southern part of the USA [53,60,61], on onions and carrots in Japan [61,62], on potatoes in China [63], and as a cause of apple root rot in Italy [45]. Our report on meadow grass is the first report on any monocotyledonous host. This study also provides the first detailed insight into the pathogenic properties and experimental host range of BNR AG-U.
Based on our host range tests, significant differences in the specificity and aggressiveness of Rhizoctonia spp. isolates within and between different AGs were observed. The differences have been previously documented either based on seedling inoculation [64,65,66] or derived from natural infections and predicted host ranges [1,3,10,67]. Although most BNRs were originally described as pathogens of monocotyledonous hosts [16,68], the host range of the four BNR AGs characterized in our study showed that the isolates exhibited lower aggressiveness on wheat and maize compared to the dicotyledonous hosts tested. Of the four isolates of AG-A, none were able to infect cabbage seedlings, and at least one isolate was unable to infect tobacco, lettuce, peas, and maize, but were most aggressive on sunflowers and sugar beet, and partially on bean seedlings. The three tested AG-G isolates were the most aggressive on the majority of the test plants, with slight differences between them, while AG-F and AG-U showed medium to high aggressiveness on all 14 host plants. The tested plants from the Solanaceae, Brassicaceae, and Poaceae families showed similar response rates under the same AGs, while the plants from the Asteraceae and Fabaceae families responded differently. Bean seedlings exhibited high susceptibility to all AGs tested. Similarly, bean seedlings were highly susceptible to AG-A, AG-F, and AG-G in the artificial inoculations conducted in Brazil [24], and were found to be very susceptible hosts for different Rhizoctonia AGs: AG-1 IB, AG-2-1, AG-2-2, AG-5, AG-A, AG-G, AG-E, AG-I, and AG-K [10,56]. The results obtained with artificial inoculations correspond to the results on plant susceptibility to natural infections. In natural BNR infections, the most susceptible hosts are beans, peas, tomatoes, peppers, wheat, and maize [19,68,69,70,71,72]. In the study by Blanco et al. [24], the maize seedlings showed similar susceptibility to BNR AG-A, AG-F, and AG-G as our isolates.
The BNR AGs tested showed varying degrees of aggressiveness on leaf petioles, allowing comparisons between isolates within AGs. In general, all four BNR AGs were found to be the most aggressive against strawberry petioles, but also against tomatoes and sunflowers. The least aggressive isolates belonged to BNR AG-A. The degree of aggressiveness in this experiment was similar to the experiment on young seedlings. When comparing the two methods of assessing pathogenicity and aggressiveness, the results were consistent, except for beans, where isolates were more aggressive towards seedlings than petioles. Aggressiveness testing on different petioles proved to be a fast and convenient method compared to the seedling method, providing accurate results in a short time, which is particularly suitable for rapid pathogenicity testing on a large number of isolates.
Soil-borne pathogens are often more difficult to manage than airborne ones as they are usually discovered when severe damage has already occurred [73]. Their frequent polyphagous nature and long survival time in plant residues or in the soil, as well as the non-specific symptoms that they cause, make management even more demanding. For many soil-borne pathogens, growing resistant varieties, when available, is an effective management option. So far, there are only a few or no varieties resistant to Rhizoctonia spp. [74]. To prevent soil-borne disease outbreaks, crop rotation is recommended as a valuable practice. However, for appropriate crop sequence selection, identifying which AGs are present in the soil and which crops/varieties they are pathogenic to is of crucial importance. Chemical control could also be an effective method of controlling some soil-borne diseases, provided that fungicide selection is based on the precise identification of the causal AG, as it was shown that different AGs respond differently to the available fungicides [3].
Besides the first detection of three AGs in Serbia, AG-F on pepper, AG-G on beans and tomatoes, and AG-U on apples, this study reports the newly discovered hosts of two AGs. For the first time in the world, cherries and meadow grass were found as hosts of AG-G and AG-U, respectively. In addition, differences in the specificity and aggressiveness of Rhizoctonia spp. isolates within and between different AGs were documented. New hosts and observed aggressiveness towards a much larger number of plant species than previously recognized suggest that the impact of BNR on different hosts in the world and in Serbia may be underestimated. To improve our options and protocols for effective disease management, more knowledge concerning AG diversity, host range, and aggressiveness is needed.
Author Contributions
This project was conceptualized and designed by A.B. and M.V.; experimental work was carried out by A.B., M.V., and A.B., and I.V. supervised different aspects of the project. Data analysis was carried out by B.P., and the figures were prepared by M.V. The manuscript was written by M.V. and A.B., with editing contributions provided by all authors. Funding was from the labs of A.B., A.M.J. and P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia grants 451-03-137/2025-03/200116, 451-03-136/2025-03/200214, and 451-03-136/2025-03/200032.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AG | Anastomosis group |
| BNR | Binucleate Rhizoctonia |
| MNR | Multinucleate Rhizoctonia |
| UNR | Uninucleate Rhizoctonia |
| ITS | Internal Transcribed Spacer |
| LSU | Large subunit |
| RPB2 | RNA polymerase II second largest subunit |
| tef-1α | Translation elongation factor 1α |
| atp6 | ATP synthase membrane subunit 6 |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| PDA | Potato Dextrose Agar |
| WA | Water Agar |
| dpi | Days post inoculation |
| nt | Nucleotide |
| Hap | Haplotype |
References
- Sneh, B.; Burpee, L.; Ogoshi, A. Identification of Rhizoctonia Species; APS Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Sneh, B.; Jabaji-Hare, S.; Neate, S.; Dijst, G. Rhizoctonia Species: Taxonomy, Molecular Biology, Ecology, Pathology, and Disease Control; Kluwer Academic Publication: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Tsror, L. Biology, Epidemiology and Management of Rhizoctonia solani on Potato. J. Phytopathol. 2010, 158, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banville, G.J. Yield losses and damage to potato plants caused by Rhizoctonia solani Kühn. Am. J. Potato Res. 1989, 66, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass, S.; Shah, F.A.; Butlera, R.C.; Falloonab, R.E.; Stewartb, A.; Raikarb, S.; Pitman, A.R. Genetic variability and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani associated with black scurf of potato in New Zealand. Plant Pathol. 2013, 63, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetina, K.C.; Stetina, S.R.; Russin, J.S. Comparison of severity assessment methods for predicting yield loss to Rhizoctonia foliar blight in soybean. Plant Dis. 2006, 90, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Zhang, W.; Ou, Z.; Li, C.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Z.; Yin, L. Analyses of the Temporal Development and Yield Losses due to Sheath Blight of Rice (Rhizoctonia solani AG1). Agri. Sci. China 2007, 6, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaweera, D.P.; Ray, R.V. Yield loss and integrated disease control of Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-1 using seed treatment and sowing rate of oilseed rape. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoshi, A. Grouping of Rhizoctonia solani Kühn and their perfect stages. Rev. Plant Protect. Res. 1975, 8, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ogoshi, A. Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and intraspecific groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1987, 25, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoshi, A. Introduction—The genus Rhizoctonia. In Rhizoctonia Species: Taxonomy, Molecular Biology, Ecology, Pathology, and Disease Control; Sneh, B., Jabaji-Hare, S., Neate, S., Dijst, G., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publication: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sharon, M.; Kuninaga, S.; Hyakumachi, M.; Naito, S.; Sneh, B. Classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using rDNA-ITS sequence analysis supports the genetic basis of the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience 2008, 49, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.G.; Zhao, C.; Guo, Z.J.; Wu, X.H. Characterization of new anastomosis group (AG-W) of binucleate Rhizoctonia, causal agent for potato stem cancer. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.K.H.; Bertier, L.; Soltaninejad, S.; Hofte, M. Cropping Systems and Cultural Practices Determine the Rhizoctonia Anastomosis Groups Associated with Brassica spp. in Vietnam. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, D.; Rodriguez-Carres, M.; Boekhout, T.; Stalpers, J.; Kuramae, E.E.; Nakatani, A.K.; Vilgalys, R.; Cubeta, M.A. Phylogenetic relationships of Rhizoctonia fungi within the Cantharellales. Fungal Biol. 2016, 120, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewoldemedhin, Y.T.; Lamprecht, S.C.; McLeod, A.; Mazzola, M. Characterization of Rhizoctonia spp. recovered from crop plants used in rotational cropping systems in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. Plant Dis. 2006, 90, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkura, M.; Abawi, G.S.; Smart, C.D.; Hodge, K.T. Diversity and aggressiveness of Rhizoctonia solani and Rhizoctonia-like fungi on vegetables in New York. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceresini, P.C.; Shew, H.D.; Vilgalys, R.J.; Cubeta, M.A. Genetic diversity of Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 from potato and tobacco in North Carolina. Mycology 2002, 94, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eken, C.; Demirci, E. Anastomosis groups and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani and binucleate Rhizoctonia isolates from bean in Erzurum. Plant Pathol. J. 2004, 86, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojvodić, M.; Tanović, B.; Mihajlović, M.; Mitrović, P.; Vico, I.; Bulajić, A. Molecular identification and characterization of binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. associated with black root rot of strawberry in Serbia. Pestic. Phytomed. 2018, 33, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cara, M.; Merkuri, J.; Salliu, A.; Vojvodić, M.; Knežević, I.; Grkinić, M.; Bulajić, A. Binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-A causing black root rot of strawberry in Albania. J. Phytopathol. 2024, 172, e13265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, M. Identification and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. isolated from apple roots and orchard soils. Phytopathology 1997, 87, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spedaletti, Y.; Mercado, G.; Gisel, T.; Aban, C.; Aparicio, M.; Rodriguero, M.; Vizgarra, O.; Sühring, S.; Galindez, G.; Galván, M. Molecular identification and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. recovered from seed and soil samples of the main bean growing area of Argentina. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2017, 11, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.J.V.; Costa, M.O.; Silva, R.D.N.; Suzart de Albuquerque, F.; Melo, A.T.D.O.; Lopes, F.A.C.; Junior, M.L. Diversity and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia species from the Brazilian Cerrado. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceresini, P.C.; Shew, H.D.; James, T.Y.; Vilgalys, R.J.; Cubeta, M. Phylogeography of the Solanaceae-infecting Basidiomycota fungus Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 based on sequence analysis of two nuclear DNA loci. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Bao, J.; Cao, H.; Zhai, J.; Jantasuriyarat, C.; Zuo, S.; Pan, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, B. Haplotype variation and phylogeography of Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA strains based on rDNA5.8S-ITS and -actin gene sequence analyses. Mycol. Prog. 2013, 13, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L.M.; Hou, X.Y.; Li, L.; Huang, S.W. Pathotypic and genetic diversity in the population of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1-IA causing rice sheath blight in China. Plant Pathol. 2015, 64, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sun, H.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, A.; Chen, H. The heterogeneity of the rDNA-ITS sequence and its phylogeny in Rhizoctonia cerealis, the cause of sharp eyespot in wheat. Curr. Genet. 2014, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vico, I. Investigation of anastomosis groups of binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. isolated from strawberries. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 1994, 33, 165–167. [Google Scholar]
- Dhingra, O.; Sinclair, J. Basic Plant Pathology Methods, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Manici, L.M.; Bonora, P. Molecular genetic variability of Italian binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. isolates from strawberry. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 118, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes—Application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.D.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; White, T.J., Sninsky, J.J., Gelfand, D.H., Innin, M.A., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheny, P.B. Improving phylogenetic inference of mushrooms with RPB1 and RPB2 nucleotide sequences (Inocybe, Agaricales). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 35, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeb, V.; Lutzoni, F.; Roux, C. Contribution of RPB2 to multilocus phylogenetic studies of the euascomycetes (Pezizomycotina, Fungi) with special emphasis on the lichen forming Acarosporaceae and evolution of polyspory. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 32, 1036–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehner, S.A.; Buckley, E. A Beauveria phylogeny inferred from nuclear ITS and EF1-a sequences: Evidence for cryptic diversification and links to Cordyceps teleomorphs. Mycologia 2005, 97, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretzer, A.; Bruns, T.D. Use of atp6 in fungal phylogenetics: An example from the Boletales. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1999, 13, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, C.; Hamid, M.; Ashworth, V.; Garcia, J.F.; Cantu, D.; Rolshausen, P. First Report of Binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-G Causing Grapevine (Vitis vinifera) Trunk Diseases in California Nurseries. Plant Dis. 2023, 108, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.G.; Paul, N.C.; Park, S.; Kim, H.J.; Sang, H. First Report of Binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-G Causing Root Rot of Japanese Bay Tree (Machilus thunbergii) in Korea. Plant Dis. 2022, 107, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Guo, Z.; Wu, X. Potato stem canker caused by Binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-G in China. J. Plant Pathol. 2015, 81, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelderer, M.; Manici, L.M.; Caputo, F.; Thalheimer, M. Planting in the “inter-row” to overcome replant disease in apple orchards: A study on the effectiveness of the practice based on microbial indicators. Plant. Soil 2012, 357, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandelt, H.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. PopART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ercole, N.; Nipoti, P.; Manzali, D. Research on the root rot complex of strawberry plants. Acta Hortic. 1989, 265, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Lei, L.P.; Dong, W.H.; Wang, S.M.; Naito, S.; Yang, G.H. Molecular diversity of binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-A in China. Phytoparasitica 2011, 39, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.; Lawrence, K.; Shannon, D.; Gonzalez, T.; Newman, M. First Report of Binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-G on Common Turmeric (Curcuma longa) in the United States. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaei, H.; Molaei, S.; Mahmoodi, S.G.; Saberi-Riseh, R. New Anastomosis Group F (AG-F) of binucleate Rhizoctonia causing root and stem rot of Pistacia vera. J. Crop Prot. 2017, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyakumachi, M.; Priyatmojo, A.; Kubota, M.; Fukui, H. New Anastomosis Groups, AG-T and AG-U, of Binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. Causing Root and Stem Rot of Cut-Flower and Miniature Roses. Phytopathology 2005, 95, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botha, A.; Denman, S.; Lamprecht, S.C.; Mazzola, M.; Crous, P.W. Characterisation and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia isolates associated with black root rot of strawberries in the Western Cape Province, South Africa. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2003, 32, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, M.; Freeman, S.; Kuninaga, S.; Sneh, B. Genetic diversity, anastomosis groups and virulence of Rhizoctonia spp. from strawberry. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 117, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, E.; Döken, M.T. Anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kühn and binucleate Rhizoctonia isolates from various crops in Türkiye. J. Turk. Phytopathol. 1995, 24, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Haddadderafshi, N.; Halász, K.; Pósa, T.; Péter, G.; Hrotkó, K.; Gáspár, L.; Lukács, N. Diversity of endophytic fungi isolated from cherry (Prunus avium). J. Hortic. For. Biotech. 2011, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jemai, N.; Gargouri, S.; Ksouri, M.F.; Mahmoud, K.B.; Jemmali, A. First report of Rhizoctonia solani affecting Prunus rootstock ‘Garnem’. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 101, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurkanli, C.T.; Ozkoc, I. First Report of B.N. Rhizoctonia from Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) in Samsun. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Rinehart, T.A.; Copes, W.E.; Toda, T.; Cubeta, M.A. Genetic characterization of binucleate Rhizoctonia species causing web blight on azalea in Mississippi and Alabama. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, T.; Toda, T. First report of black scurf on carrot caused by binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-U. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2013, 79, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, T.; Kurose, D.; Kuninaga, S. First report of leaf sheath rot of Welsh onion caused by nine taxa of Rhizoctonia spp. and characteristics of the pathogens. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2017, 83, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Guo, Z.; Wu, X. Anastomosis groups and pathogenicity of binucleate Rhizoctonia isolates associated with stem canker of potato in China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 139, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijer, J.; Korsman, M.G.; Dullemans, A.M.; Houterman, P.M.; de Bree, J.; van Silfhout, C.H. In vitro analysis of host plant specificity in Rhizoctonia solani. Plant Pathol. 1997, 46, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, M.S.; Yu, H.; Labun, T.; Dickson, A.; Boland, G.J. Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. from field crops in Canada. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 38, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharska, K.; Katulski, B.; Goriewa-Duba, K.; Duba, A.; Wachowska, U. Pathogenicity and Fungicide Sensitivity of Rhizoctonia solani and R. cerealis Isolates. Gesunde Pflanz. 2018, 70, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, D.E.; Kuninaga, S.; Brainard, K.A. Hyphal anastomosis reactions, rDNA-internal transcribed spacer sequences, and virulence levels among subsets of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group-2 (AG-2) and AG-BI. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unal, F.; Dolar, F.S.; Yildirim, F.; Demirci, E. Isolation and identification of binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. from wheat field soils in the Central Anatolia Region, Turkey. Turk. J. Agric. Nat. Sci. 2014, SI2, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Fenille, R.C.; Ciampi, M.B.; Souza, N.L.; Nakatani, A.K.; Kuramae, E.E. Binucleate Rhizoctonia sp. AG-G causing rot rot in yacon (Smallanyhus sonchifolius) in Brazil. Plant Pathol. 2005, 54, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, S.; Eken, C. Anastomosis grouping of Rhizoctonia solani and binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. isolated from pepper in Erzincan, Turkey. Plant Protect. Sci. 2013, 49, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma-Poudyal, D.; Paulitz, T.C.; Porter, L.D.; du Toit, L.J. Characterization and Pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia and Rhizoctonia-Like spp. from Pea Crops in the Columbia Basin of Oregon and Washington. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eken, C.; Tuncer, S. Rhizoctonia Species and Anastomosis Groups Isolated from Tomato and Cucumber in Erzincan, Turkey. Int. J. Res. Agric. For. 2019, 6, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, S.G. Soil organisms and global climate change. Plant Pathol. 2011, 60, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisiecki, K.; Lemańczyk, G.; Piesik, D.; Mayhew, C.A. Screening Winter Wheat Genotypes for Resistance Traits against Rhizoctonia cerealis and Rhizoctonia solani Infection. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).