Genomic Insights into Neofusicoccum laricinum: The Pathogen Behind Chinese Larch Shoot Blight
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. N. laricinum Collection and Isolation
2.3. Genomic DNA Quality Control, Library Preparation, and Sequencing
2.4. Short Read Pre-Processing, Variants Calling, and Quality Control
2.5. Population Structure Analysis with Principal Component Analysis and Phylogenetic Tree
2.6. Annotation Analysis and Functional Enrichment Analyses
3. Results
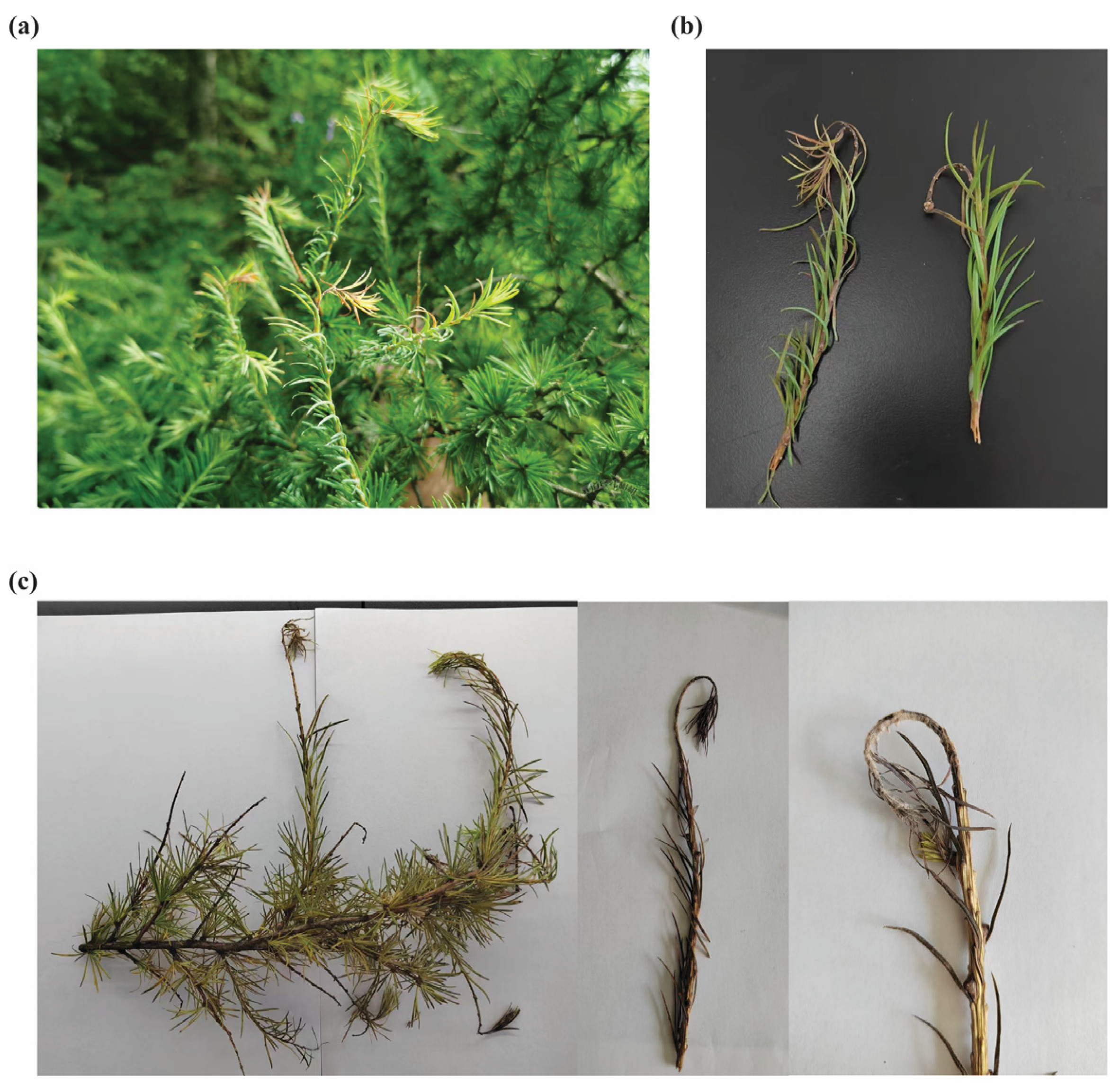
3.1. Phenotypic Observations of Larch Shoot Blight
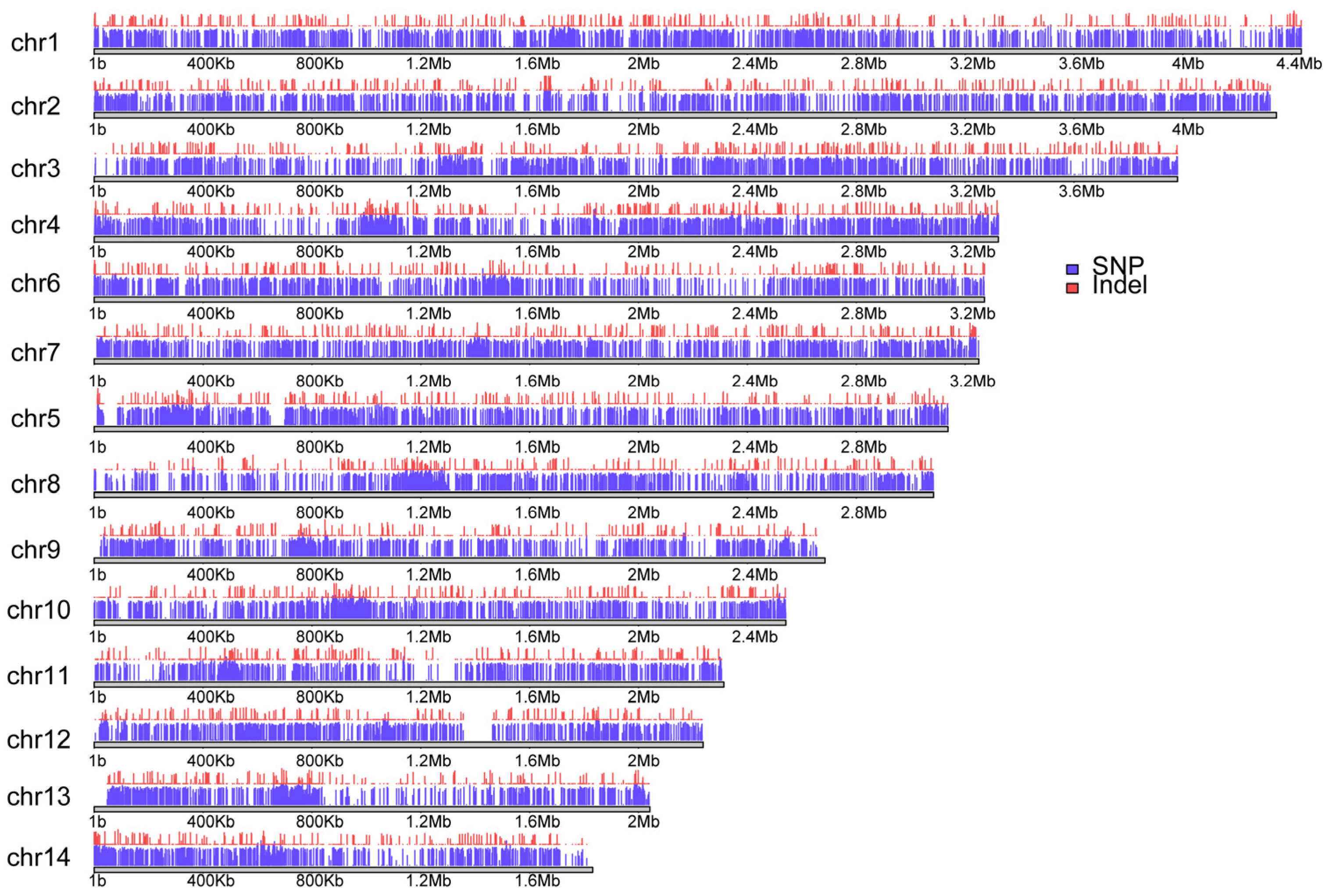
3.2. Distribution of Variants in Chinese Indigenous N. laricinum Isolates
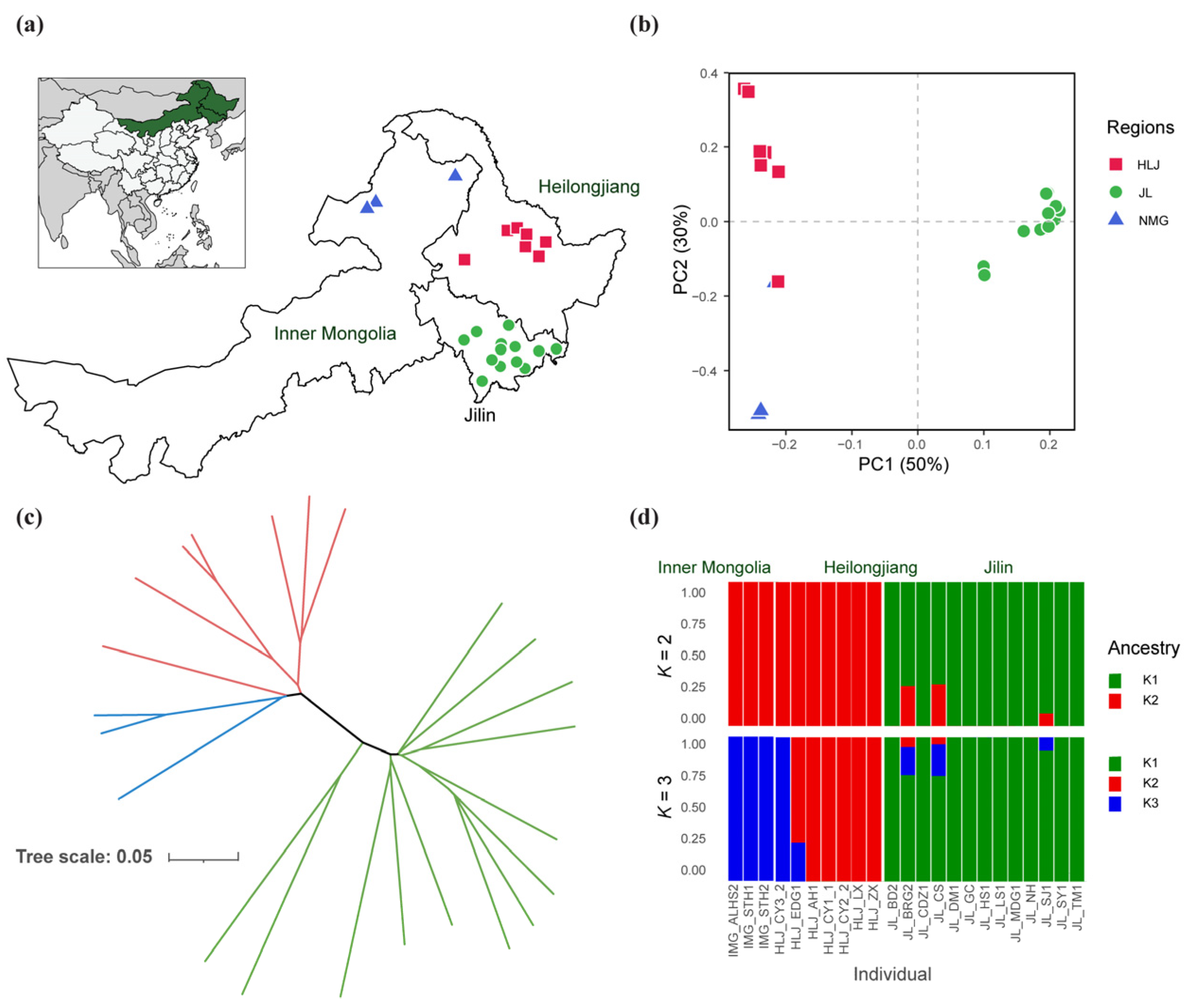
3.3. Genetic Relationship Among Chinese Indigenous N. laricinum
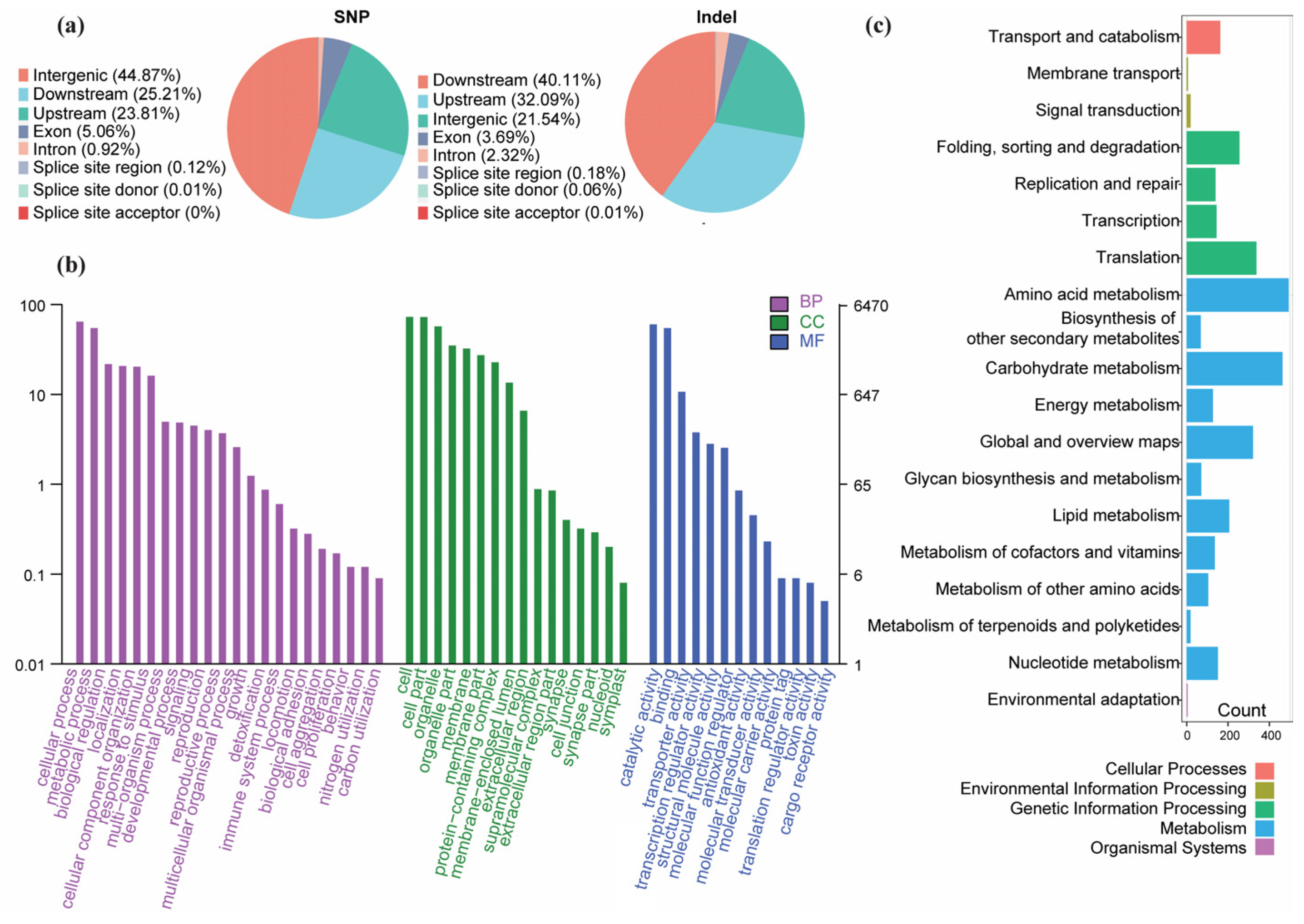
3.4. Variants Annotation and Enrichment Analyses
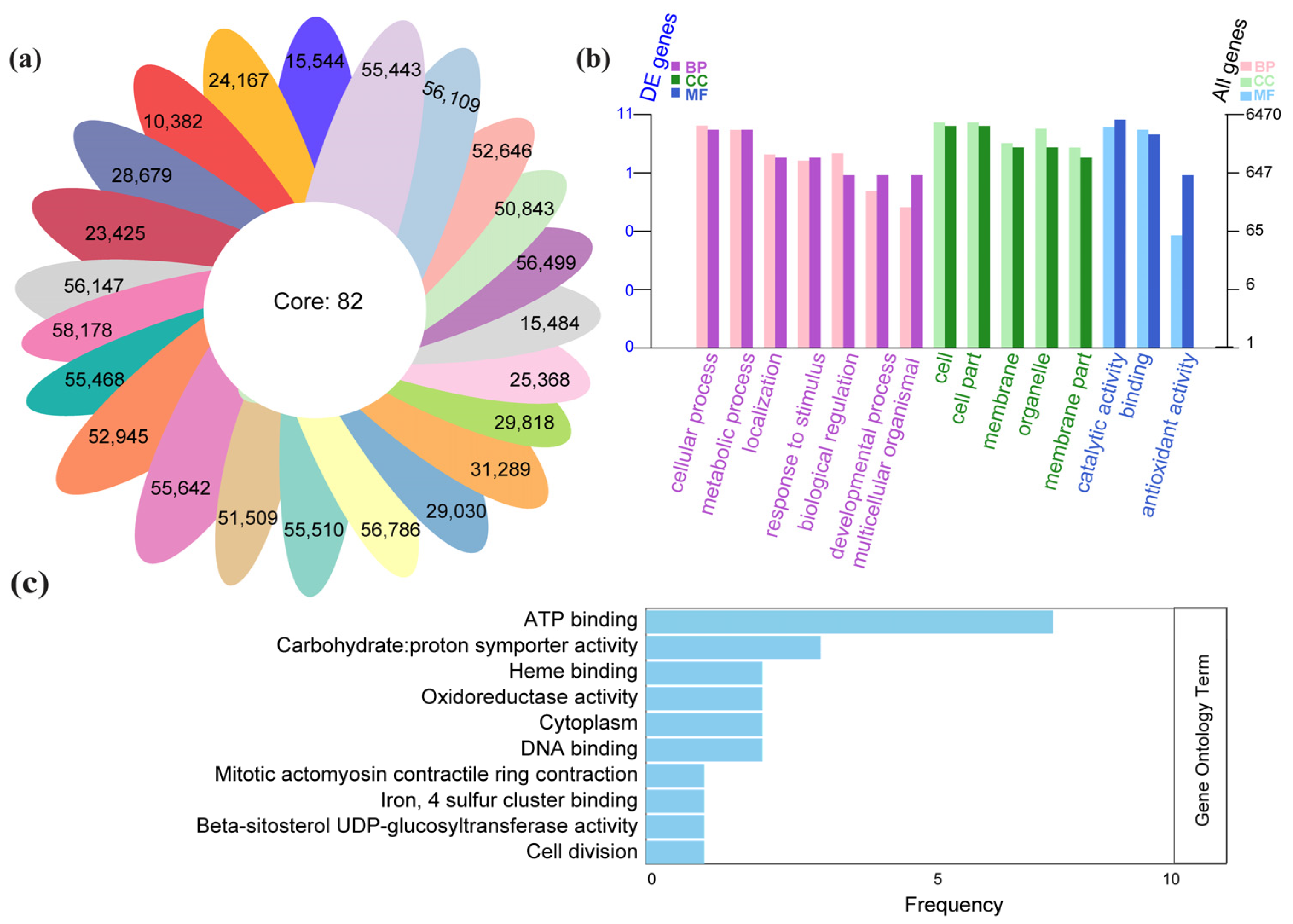
3.5. Comparison of Core and Region-Specific Variants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.-H.; Purusatama, B.D.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, N.-H. A Comparative Study of the Bending Properties of Dahurian Larch and Japanese Larch Grown in Korea. Forests 2022, 13, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruda, E.A.; Xia, R.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H.; Yu, Q.; Hu, M.; Wang, F. Evaluation on the Efficacy of Farrerol in Inhibiting Shoot Blight of Larch (Neofusicoccum laricinum). Plants 2024, 13, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhouma, A.; Hajji-Hedfi, L.; Khaire, P.B. Comprehensive analysis of Botryosphaeriaceae-induced panicle and shoot blight and its management strategies. DYSONA-Appl. Sci. 2025, 6, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Song, L.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Pan, M.; Tan, J. Screening of bacterial endophytes of larch against Neofusicoccum laricinum and validation of their safety. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e04112–e04123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjon, A. A Handbook of the World’s Conifers; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yokota, S.-i. Ecological Studies on Guignardia Laricina (Sawada) w. Yamamoto et k, Ito, the Causal Fungus of the Shoot Blight of Larch Trees, and Climatic Factors Influencing the Outbreak of the Disease; FFPRI: Tsukuba, Japan, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, Y.; Ando, Y.; Nakashima, C. Taxonomical re-examination of the genus Neofusicoccum in Japan. Mycoscience 2021, 62, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massonnet, M.; Morales-Cruz, A.; Figueroa-Balderas, R.; Lawrence, D.P.; Baumgartner, K.; Cantu, D. Condition-dependent co-regulation of genomic clusters of virulence factors in the grapevine trunk pathogen Neofusicoccum parvum. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotel-Aziz, P.; Robert-Siegwald, G.; Fernandez, O.; Leal, C.; Villaume, S.; Guise, J.-F.; Abou-Mansour, E.; Lebrun, M.-H.; Fontaine, F. Diversity of Neofusicoccum parvum for the Production of the Phytotoxic Metabolites (-)-Terremutin and (R)-Mellein. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Liu, Z.; O, S.; Yao, C.; Chen, J.; Dong, A.; Liu, X. First report of Aplosporella javeedii causing branch blight disease of Mulberry (Morus alba) in China. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2019, 126, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hao, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Ma, W.; Gao, F. Identification of Caragana arborescens shoot blight disease caused by Phaeobotryon caraganae sp. nov.(Botryosphaeriales) in China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 155, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U’Ren, J.M.; Moore, L. Large Volume Fungal Genomic DNA Extraction Protocol for PacBio. 2021. Available online: https://www.protocols.io/view/large-volume-fungal-genomic-dna-extraction-protoco-14egn59mg5dy/v1 (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- de Sena Brandine, G.; Smith, A.D. Falco: High-speed FastQC emulation for quality control of sequencing data. F1000Research 2021, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasimuddin, M.; Misra, S.; Li, H.; Aluru, S. Efficient architecture-aware acceleration of BWA-MEM for multicore systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium (IPDPS), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 314–324. [Google Scholar]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Auwera, G.A.; Carneiro, M.O.; Hartl, C.; Poplin, R.; Del Angel, G.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Jordan, T.; Shakir, K.; Roazen, D.; Thibault, J. From FastQ data to high-confidence variant calls: The genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 43, 11.10.11–11.10.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Wickham, M.H. Package ‘ggplot2’. Create elegant data visualisations using the grammar of graphics. Version 2016, 2, 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. APE: Analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Beck, J.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; DiCuccio, M.; Farrell, C.M.; Feldgarden, M. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 52, D33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Galperin, M.Y.; Natale, D.A.; Koonin, E.V. The COG database: A tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Kawashima, S.; Okuno, Y.; Hattori, M. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D277–D280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y. Integrated nr database in protein annotation system and its localization. Comput. Eng. 2006, 32, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J. Pfam: The protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt Consortium, T. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautasso, M. Responding to Diseases Caused by Exotic Tree Pathogens. Infect. For. Dis. 2013, 592–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arno, S.F. Larix lyallii Parl. alpine larch. Silv. N. Am. 1990, 1, 330–347. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Lu, C.; Yu, Z.; Hu, H.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Neofusicoccum laricinum in China. Forests 2025, 16, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayon, C.; Yuan, Z.-W.; Ruiz, C.; Liesebach, M.; Pei, M.H. Genetic diversity in the mycoparasite Sphaerellopsis filum inferred from AFLP analysis and ITS–5.8 S sequences. Mycol. Res. 2006, 110, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbish, T.J.; Koehn, R.K. The adaptive importance of genetic variation. Am. Sci. 1987, 75, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, R.D.; Schluter, D. Adaptation from standing genetic variation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ježić, M.; Schwarz, J.M.; Prospero, S.; Sotirovski, K.; Risteski, M.; Ćurković-Perica, M.; Nuskern, L.; Krstin, L.; Katanić, Z.; Maleničić, E. Temporal and spatial genetic population structure of Cryphonectria parasitica and its associated hypovirus across an invasive range of chestnut blight in Europe. Phytopathology 2021, 111, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ježić, M.; Mlinarec, J.; Vuković, R.; Katanić, Z.; Krstin, L.; Nuskern, L.; Poljak, I.; Idžojtić, M.; Tkalec, M.; Ćurković-Perica, M. Changes in Cryphonectria parasitica populations affect natural biological control of chestnut blight. Phytopathology 2018, 108, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boixel, A.L.; Chelle, M.; Suffert, F. Patterns of thermal adaptation in a globally distributed plant pathogen: Local diversity and plasticity reveal two-tier dynamics. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddya, S.; Meshram, S.; Sarkar, D.; S, R.; Datta, R.; Singh, S.; Avinash, G.; Kumar Kondeti, A.; Savani, A.K.; Thulasinathan, T. Plant stomata: An unrealized possibility in plant defense against invading pathogens and stress tolerance. Plants 2023, 12, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShea, W.J. (Ed.) Oak Forest Ecosystems: Ecology and Management for Wildlife, Revised ed.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2007; pp. 82–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chiapello, H.H.; Mallet, L.M.; Guerin, C.C.; Aguileta, G.G.; Rodolphe, F.F.; Gendrault, A.G.-J.; Kreplak, J.J.; Amselem, J.J.; Ortega-Abboud, E.E.; Lebrun, M.-H.M.-H. Genome evolution of fungal pathogens from the Magnaporthe oryzae/grisea clade. In Proceedings of the 27th Fungal Genetics Conference-Asilomar Conference Grounds, Monterey County, CA, USA, 12–17 March 2013; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- Feurtey, A.; Lorrain, C.; McDonald, M.C.; Milgate, A.; Solomon, P.S.; Warren, R.; Puccetti, G.; Scalliet, G.; Torriani, S.F.; Gout, L. A thousand-genome panel retraces the global spread and adaptation of a major fungal crop pathogen. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanek, L. Proteomic responses to environmentally induced oxidative stress. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1867–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Bai, J.; Zhuo, X.; Zhang, J.; Kuai, B.; Chen, H. Transcriptomic analysis of Stropharia rugosoannulata reveals carbohydrate metabolism and cold resistance mechanisms under low-temperature stress. AMB Express 2022, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütte, D.; Remmo, A.; Baier, M.; Griebel, T. Cold exposure transiently increases resistance of Arabidopsis thaliana against the fungal pathogen Botrytis cinerea. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2025, 136, 102579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Tao, S.; Chen, P.; Lin, W. The basic leucine zipper transcription factor MeaB is critical for biofilm formation, cell wall integrity, and virulence in Aspergillus fumigatus. Msphere 2024, 9, e00619–e00623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badet, T.; Oggenfuss, U.; Abraham, L.; McDonald, B.A.; Croll, D. A 19-isolate reference-quality global pangenome for the fungal wheat pathogen Zymoseptoria tritici. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Z.; Jiao, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Liang, C.; Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Tang, G.; Li, P. Genome sequencing and comparative genomics reveal insights into pathogenicity and evolution of Fusarium zanthoxyli, the causal agent of stem canker in prickly ash. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Gu, Y.; Shi, G.; He, J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of pseudouridine synthase family in Arabidopsis and maize. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Islam, M.S.; Xia, J.; Feng, X.; Noman, M.; Wang, J.; Hao, Z.; Qiu, H.; Chai, R.; Cai, Y. The nucleolin MoNsr1 plays pleiotropic roles in the pathogenicity and stress adaptation in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1482934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Arrigoni, G.; Ebinezer, L.B.; Trentin, A.R.; Franchin, C.; Giaretta, S.; Carletti, P.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Ghisi, R.; Masi, A. A proteomic and biochemical investigation on the effects of sulfadiazine in Arabidopsis thaliana. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 178, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, M.; Hu, S.; Cui, Y.; Fang, J.; Yu, X. Revealing the metabolic potential and environmental adaptation of nematophagous fungus, Purpureocillium lilacinum, derived from hadal sediment. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1474180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silao, F.G.S.; Jiang, T.; Bereczky-Veress, B.; Kühbacher, A.; Ryman, K.; Uwamohoro, N.; Jenull, S.; Nogueira, F.; Ward, M.; Lion, T. Proline catabolism is a key factor facilitating Candida albicans pathogenicity. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, A.; Giglio, V.; Asa, J.; Xu, J. Phenotypic divergence along geographic gradients reveals potential for rapid adaptation of the white-nose syndrome pathogen, Pseudogymnoascus destructans, in North America. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00863-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| IDs | Species | Host Tree | Country, Provinece | Geographic City, District | No. of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMG_ALHS2 | Neofusicoccum laricinum | Larix gmeli-nii | China, Inner Mongolia | Hulun Buir, Alihe | 3 |
| NMG_STH1 | Hulun Buir, Oroqen Zizhiqi | ||||
| NMG_STH2 | Hulun Buir, Oroqen Zizhiqi | ||||
| JL_GC | Neofusicoccum laricinum | Larix gmeli-nii | China, Jilin | Liao Yuan, Dongfeng | 13 |
| JL_HS1 | Hunchun, Heshang | ||||
| JL_TM1 | Tumen, Shixian | ||||
| JL_SY1 | Tumen, Shixian | ||||
| JL_BD2 | Yanji, Ba Daolin | ||||
| JL_DM1 | Yanbian, Dongming | ||||
| JL_NH | Yanbiang, Wangqing | ||||
| JL_BRG2 | Yanbiang, Wangqing | ||||
| JL_LS1 | Yanbian, Helong | ||||
| JL_SJ1 | Yanbian, Songjiang | ||||
| JL_MDG1 | Dunhuan, Mu Dangang | ||||
| JL_CDZ1 | Dunhuan, Qing Dingzi | ||||
| JL_CS | Jilin, Changsi | ||||
| HLJ_EDG1 | Neofusicoccum laricinum | Larix gmeli-nii | China, Heilongjiang | Yichun, Yunhao | 7 |
| HLJ_CY1_1 | Yichun, Yunhao | ||||
| HLJ_CY2_2 | Yichun, Yunhao | ||||
| HLJ_CY3_2 | Yichun, Yunhao | ||||
| HLJ_LX | Yichun, Yunhao | ||||
| HLJ_ZX | Yichun, Yunhao | ||||
| HLJ_AH1 | Qiqihar, Kedong |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, J.; Yu, Z.; Dai, W.; Lv, C.; Chen, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, J.; Gao, J. Genomic Insights into Neofusicoccum laricinum: The Pathogen Behind Chinese Larch Shoot Blight. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11050399
Pan J, Yu Z, Dai W, Lv C, Chen Y, Sun H, Chen J, Gao J. Genomic Insights into Neofusicoccum laricinum: The Pathogen Behind Chinese Larch Shoot Blight. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(5):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11050399
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Jialiang, Zhijun Yu, Wenhao Dai, Chunhe Lv, Yifan Chen, Hong Sun, Jie Chen, and Junxin Gao. 2025. "Genomic Insights into Neofusicoccum laricinum: The Pathogen Behind Chinese Larch Shoot Blight" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 5: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11050399
APA StylePan, J., Yu, Z., Dai, W., Lv, C., Chen, Y., Sun, H., Chen, J., & Gao, J. (2025). Genomic Insights into Neofusicoccum laricinum: The Pathogen Behind Chinese Larch Shoot Blight. Journal of Fungi, 11(5), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11050399






