Fungal-Induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Literature Review in Non-HIV Populations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. Definition
2.4. Outcome Measure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
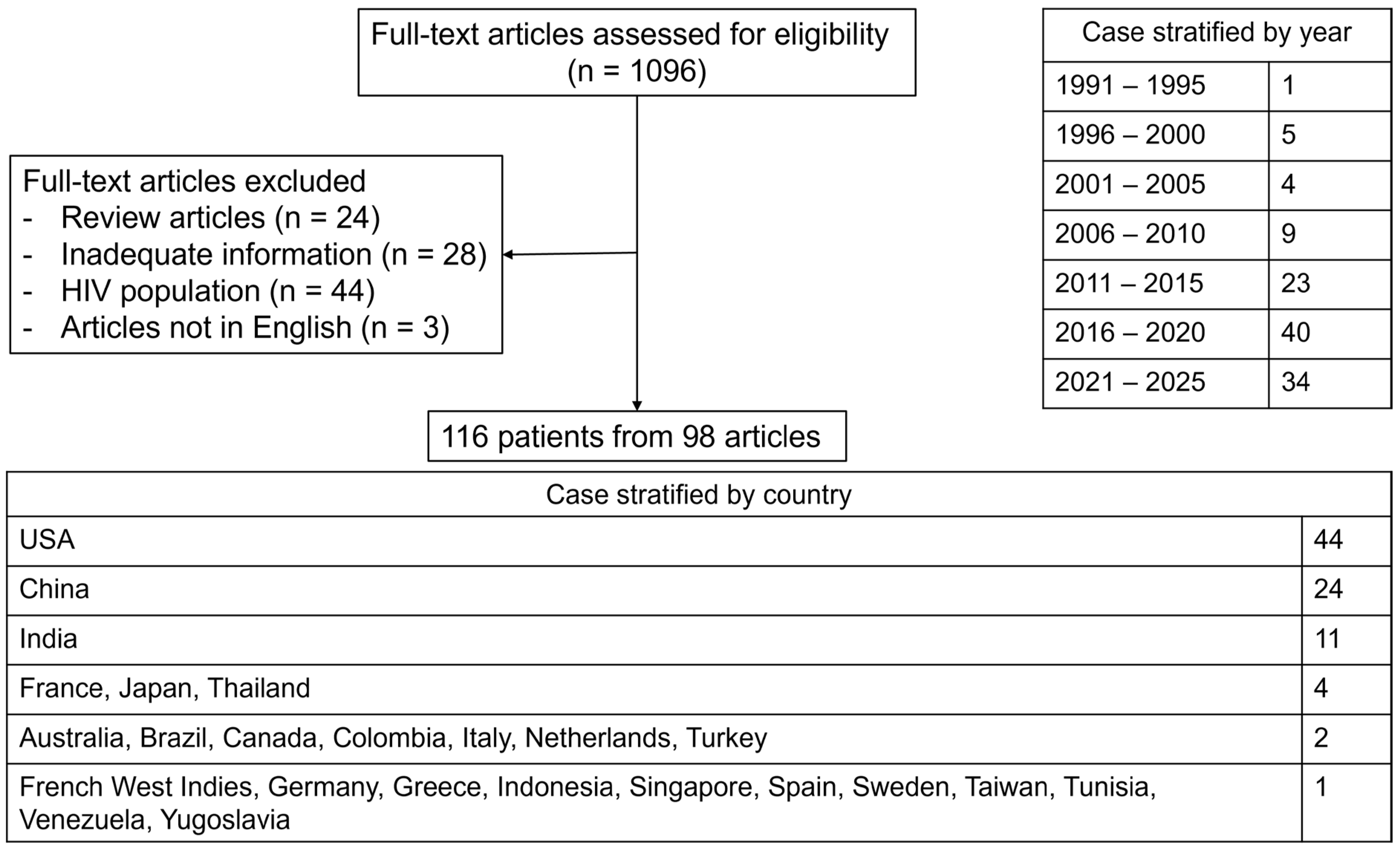
3. Results
3.1. Frequency of IFI-Induced HLH in Study Included >1000 Patients
3.2. Frequency of IFI-Induced HLH in HIV Population
3.3. Frequency of IFI-Induced HLH in Non-HIV Population
3.4. Clinical Presentation and Laboratory Findings in Cases of Fungal-Induced HLH
3.5. Clinical/Laboratory Features of HLH
3.6. Therapeutic Approach and Outcome of Fungal-Induced HLH
3.7. Prognostic Factors Associated with HLH Triggers
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cox, M.F.; Mackenzie, S.; Low, R.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Carr, A.; Carpenter, B.; Bishton, M.; Duncombe, A.; Akpabio, A.; et al. Diagnosis and Investigation of Suspected Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults: 2023 Hyperinflammation and HLH Across Speciality Collaboration (HiHASC) Consensus Guideline. Lancet Rheumatol. 2024, 6, e51–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brito-Zerón, P.; López-Guillermo, A.; Khamashta, M.A.; Bosch, X. Adult Haemophagocytic Syndrome. Lancet 2014, 383, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henter, J.-I.; Horne, A.; Aricó, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Imashuku, S.; Ladisch, S.; McClain, K.; Webb, D.; Winiarski, J.; et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Guidelines for Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 48, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhay, A.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Al Ali, O.; Hashem, A.; Orakzai, A.; Jamshed, S. Epidemiology, Characteristics, and Outcomes of Adult Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in the USA, 2006–2019: A National, Retrospective Cohort Study. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 62, 102143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, J.L.; Shanbhag, S.; Hancock, J.; Bowman, K.; Nijhawan, A.E. Histoplasmosis-Induced Hemophagocytic Syndrome: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, ofv055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaja, H.; Kanj, A.; El Zein, S.; Comba, I.Y.; Chehab, O.; Mahmood, M. A Review of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Patients With HIV. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camous, L.; Surel, A.; Kallel, H.; Nicolas, M.; Martino, F.; Valette, M.; Demoule, A.; Pommier, J.-D. Factors Related to Mortality in Critically Ill Histoplasmosis: A Multicenter Retrospective Study in Guadeloupe and French Guyana. Ann. Intensive Care 2023, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Quezada, A.; Moreno, J.; Solís-Bravo, M.Á.; López Chávez, C.A.; Santos, T.; Fonseca-Mata, J.J.; Araiza, J.; Bonifaz, A. Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in People Living with HIV and Disseminated Histoplasmosis at a Tertiary Hospital in Mexico. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofae385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Dong, X.; Wan, H.; Zhang, B.; Yu, L.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, K.; Wang, M.; Xu, A.; et al. Characteristics and Risk Factors for Death in HIV-Positive Talaromycosis Marneffei Patients with Sepsis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, A.P.; Spivak, J.L. Hematophagic Histiocytosis. A Report of 23 New Patients and a Review of the Literature. Medicine 1988, 67, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningsanond, V. Infection Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome: A Report of 50 Children. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2000, 83, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, A.; Thervet, E.; Legendre, C.; Groupe Coopératif de transplantation d’Ile de France. Hemophagocytic Syndrome in Renal Transplant Recipients: Report of 17 Cases and Review of Literature. Transplantation 2004, 77, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, N.; Sugawara, Y.; Tamura, S.; Matsui, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Imamura, H.; Kokudo, N.; Makuuchi, M. Hemophagocytic Syndrome after Adult-to-Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2006, 38, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.-T.; Sheng, W.-H.; Lin, B.-H.; Lin, C.-W.; Wang, J.-T.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chang, S.-C. Causes, Clinical Symptoms, and Outcomes of Infectious Diseases Associated with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Taiwanese Adults. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2011, 44, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-S.; Kim, D.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, S.-D.; Park, Y.-H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Jeon, M.; Kang, Y.-A.; et al. Clinical Features of Adult Patients with Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis from Causes Other than Lymphoma: An Analysis of Treatment Outcome and Prognostic Factors. Ann. Hematol. 2012, 91, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, V.; Das, S.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, P.; Ray, S.; Bhattacharya, S. A Clinicopathological Analysis of 26 Patients with Infection-Associated Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and the Importance of Bone Marrow Phagocytosis for the Early Initiation of Immunomodulatory Treatment. Postgrad. Med. J. 2013, 89, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delavigne, K.; Bérard, E.; Bertoli, S.; Corre, J.; Duchayne, E.; Demur, C.; Mansat-De Mas, V.; Borel, C.; Picard, M.; Alvarez, M.; et al. Hemophagocytic Syndrome in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Undergoing Intensive Chemotherapy. Haematologica 2014, 99, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, D.; Nath, U.K. Disseminated Histoplasmosis in Immunocompetent Individuals- Not a so Rare Entity, in India. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 7, e2015028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, S.F.; Ammann, S.; Al-Herz, W.; Bataneant, M.; Dvorak, C.C.; Gehring, S.; Gennery, A.; Gilmour, K.C.; Gonzalez-Granado, L.I.; Groß-Wieltsch, U.; et al. The Syndrome of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Primary Immunodeficiencies: Implications for Differential Diagnosis and Pathogenesis. Haematologica 2015, 100, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerolle, N.; Laanani, M.; Rivière, S.; Galicier, L.; Coppo, P.; Meynard, J.-L.; Molina, J.-M.; Azoulay, E.; Aumont, C.; Marzac, C.; et al. Diversity and Combinations of Infectious Agents in 38 Adults with an Infection-Triggered Reactive Haemophagocytic Syndrome: A Multicenter Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 268.e1–268.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, N.; Wu, L.; Chen, L.; Song, D.; Wang, Z. Non-EBV Infection-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Distinct Subgroup Where Pathogen-Directed Therapy Is Essential and Favorable Outcomes Are Expected. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 62, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, D.; Xu, W.; You, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, M.; Bi, X.; Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Xian, Y. Clinical Descriptive Analysis of Severe Pneumocystis Jirovecii Pneumonia in Renal Transplantation Recipients. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Jin, Y.; Yin, G.; Yang, D.; Li, W.; Shi, T.; Lu, G.; Huang, L.; Fan, H. Peripheral Immune Profile of Children with Talaromyces Marneffei Infections: A Retrospective Analysis of 21 Cases. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Bao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zheng, Y. Talaromyces Marneffei Infection and Complicate Manifestation of Respiratory System in HIV-Negative Children. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acker, W.B.; Nixon, S.L.; Lee, J.J.; Jacobson, N.A.; Haftel, H.; Farley, F.A. Septic Arthritis of the Hip in the Setting of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Case Report. JBJS Case Connect. 2015, 5, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Moodley, J.; Ajani Goel, G.; Theil, K.S.; Mahmood, S.S.; Lang, R.S. A Rare Trigger for Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Rheumatol. Int. 2011, 31, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, S.; Sundareshan, V.; West, B.; Prakash, V.; Bergman, S.; Koirala, J. Successful Primary Therapy With Posaconazole for Fulminant Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis in a Renal Transplant Recipient. Infect. Dis. Clin. Pract. 2018, 26, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alby-Laurent, F.; Dollfus, C.; Ait-Oufella, H.; Rambaud, J.; Legrand, O.; Tabone, M.-D.; Hennequin, C. Trichosporon: Another Yeast-like Organism Responsible for Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Patients with Hematological Malignancy. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.S.; Sen, M.; Tan, I.J. Pulmonary Aspergillosis Complicated by Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, H.; Pancoast, M.; Finstad, K.; Pele, N.; Fasipe, F.; Elsaid, M. Rare Case of Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a Patient with Disseminated Histoplasmosis. Pediatr. Investig. 2023, 7, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.E.; Naik, U.; Wang, W.; Elzamly, S.; Bhattacharjee, M.B. Fatal Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Resulting in the Death of a Previously Healthy 49-Year-Old Man in Ten Days. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2023, 53, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Apriany, N.; Sukorini, U.; Ratnaningsih, T.; Asdie, R.H.; Subronto, Y.W.; Hutajulu, S.H.; Purwanto, I.; Hardianti, M.S. Two Cases of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Associated with Disseminated Histoplasmosis Presented with Transient Pancytopenia. Case Rep. Med. 2022, 2022, 9521128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, V.; De-Giorgio, F.; Pennacchia, I.; Manna, R.; Vetrugno, G.; Stigliano, E.; Milic, N.; Gasbarrini, G.; Abenavoli, L. Haemophagocytic Syndrome Associated with Mucormycosis Infection. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2012, 25, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanase, N.; Imbert, Y.; Ratrimoharilala, F. An Unusual Cause of Perianal Ulceration in an HIV-Negative Patient. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1701–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, A.; Cortez, R. Successful Management of Aspergillus Induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a Child with Underlying Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018, 18, S187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Iyer, R.; Nallasamy, K.; Vaiphei, K. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis with Pulmonary Mucormycosis: Fatal Association. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e230587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broglie, L.; Phelan, R.; Talano, J.-A. First Report That Prior ECMO Therapy Does Not Preclude Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 35, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarata, E.; Esposto, E.; Andreassi, M.; Fiori, S.; Lorenzini, D.; Gironi, L.C.; Veronese, F.; Savoia, P. Primary Cutaneous Gamma Delta T-Cell Lymphoma: A Unique Polymorphic Cutaneous Presentation with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis, and Bone Marrow Acremonium Kiliense Infection. Ital. J. Dermatol. Venerol. 2022, 157, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebi, N.; Vallejo, J.G.; Eckstein, O.S.; Geer, J.; Punia, J.N.; Elenberg, E. Persistent Fever in a Pediatric Renal Transplant Patient: Answers. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Raina, M.K.; Gaur, D.S.; Agarwal, V.K. Cytological Diagnosis of Primary Cutaneous Histoplasmosis with Hemophagocytosis in Immunocompetent Patient—A Rare Case from Non Endemic Region. Indian. J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2020, 63, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, Q.; Hu, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, M.; Yang, Q.; Qu, T. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Disseminated Histoplasmosis in HIV Seronegative Patients: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 847950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Hu, D.; Zhang, C.; Wu, T.; Cheng, X.; Hagen, F.; Zhu, H.; Deng, S. Histoplasmosis: An Epidemiological and Clinical Update in China, Review and a Case Report. Mycology 2024, 15, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Pan, L.; Li, M.; Al-Hatmi, A.M.S.; Meis, J.F.; Lai, W.; Feng, P. Neonatal Cutaneous Invasive Aspergillosis Accompanied by Hemophagocytic Lymphohistocytosis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chim, C.S.; Fong, C.Y.; Ma, S.K.; Wong, S.S.; Yuen, K.Y. Reactive Hemophagocytic Syndrome Associated with Penicillium Marneffei Infection. Am. J. Med. 1998, 104, 196–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirotski, D.S.; Cunningham, M.T.; Loew, T.; Panicker, J. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Syndrome Secondary to Disseminated Histoplasmosis in a Presumably Immunocompetent Adolescent: A Novel Case. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 39, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Columbus-Morales, I.; Maahs, L.; Husain, S.; Gordon, S.C.; Inamdar, K.V.; Gonzalez, H.C. A Case of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Disseminated Histoplasmosis. Case Rep. Hepatol. 2020, 2020, 6901514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, L.N.; He, R. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Iatrogenic Disseminated Histoplasmosis. Blood 2016, 127, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousa, K.M.; De la Hoz, A.; Church, E.; Onger, T.; Perez, F.; Saade, E. Progressive and Disseminated Histoplasma Infection and Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in an Immunocompetent Adult. Clin. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson-Paul, K.; Mangum, S.; Porter, A.; Leventaki, V.; Campbell, P.; Wolf, J. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1119–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandotra, A.; Mehtani, R.; Premkumar, M.; Duseja, A.; De, A.; Mallik, N.; Durgadevi, S.; Das, A.; Kalra, N. Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis and Tuberculosis Complicated by Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis—Sequelae of COVID-19 in a Liver Transplant Recipient. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Posada, J.M.; Hernández, D.; Martin, A.; Raya, J.M.; Pitti, S.; Bonilla, A.; Astigarraga, I.; Alarcó, A. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a Pancreas-Kidney Transplant Recipient: Response to Dexamethasone and Cyclosporine. Clin. Nephrol. 2008, 70, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, H.; Yadav Kl, P.; Totaganti, M.; Kant, R.; Monica Devi, Y. A Rare Case of Disseminated Histoplasmosis with Hemophagocytic Syndrome in a Patient With Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Report. Cureus 2023, 15, e36333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Vinod, K.S.; Mittal, A.; Ajay Kumar, A.P.; Kumar, A.; Wig, N. Histoplasmosis, Heart Failure, Hemolysis and Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, S.; Alduaij, W.; Biggs, C.M.; Belga, S.; Luecke, K.; Merkeley, H.; Chen, L.Y.C. Ruxolitinib as Adjunctive Therapy for Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Case Series. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 106, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegerova, L.T.; Lin, Y. Disseminated Histoplasmosis: A Cause of Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huapaya, J.A.; Yogiaveetil, E.; Qamer, S.; Sidawy, M.; Anderson, E. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Secondary to Histoplasmosis-Induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Arch. Bronconeumol. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 55, 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabr, R.; El Atrouni, W.; Male, H.J.; Hammoud, K.A. Histoplasmosis-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Review of the Literature. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 7107326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapinar, D.Y.; Karadaş, N.; Yazici, P.; Polat, S.H.; Karapinar, B. Trichosporon Asahii, Sepsis, and Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Children with Hematologic Malignancy. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 31, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommanan, B.K.; Naseem, S.; Varma, N. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Histoplasmosis. Blood Res. 2017, 52, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kashif, M.; Tariq, H.; Ijaz, M.; Gomez-Marquez, J. Disseminated Histoplasmosis and Secondary Hemophagocytic Syndrome in a Non-HIV Patient. Case Rep. Crit. Care 2015, 2015, 295735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, F.G.; Kurtzberg, J. Disseminated Histoplasmosis: A Cause of Infection-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Am. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 1994, 16, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Asakura, T.; Kawada, I.; Hasegawa, H.; Chubachi, S.; Ohara, K.; Kuramoto, J.; Sugiura, H.; Fujishima, S.; Iwata, S.; et al. Disseminated Histoplasmosis from a Calcified Lung Nodule after Long-Term Corticosteroid Therapy in an Elderly Japanese Patient: A Case Report. Medicine 2019, 98, e15264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusne, Y.; Christiansen, M.; Conley, C.; Gea-Banacloche, J.; Sen, A. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Disseminated Histoplasmosis in Rheumatologic Disease. Case Rep. Crit. Care 2021, 2021, 6612710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larbcharoensub, N.; Aroonroch, R.; Kanoksil, W.; Leopairut, J.; Nitiyanant, P.; Khositseth, A.; Tangnararatchakit, K.; Chuansumrit, A.; Yoksan, S. Infection-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome among Patients with Dengue Shock Syndrome and Invasive Aspergillosis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. S. A. J. Trop. Med. Public. Health 2011, 42, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lo, M.M.; Mo, J.Q.; Dixon, B.P.; Czech, K.A. Disseminated Histoplasmosis Associated with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machaczka, M.; Vaktnas, J. Haemophagocytic Syndrome Associated with Hodgkin Lymphoma and Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonitis. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 138, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, V.C.R.; Colombo, S.A.; Freitas, G.J.C.; Moura, A.S.; Vieira, F.C.L.; Lyon, A.C.; Azevedo, M.I.; de Peres, N.T.A.; Santos, D.A. Late Diagnosis of Disseminated Sporothrix Brasiliensis Infection with Bone Marrow Involvement in an HIV-Negative Patient. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, K.; Mahon, N.; Rosario, A.; Mirza, I.; Keys, T.F.; Ratliff, N.B.; Starling, R.C. Reactive Hemophagocytic Syndrome Associated with Disseminated Histoplasmosis in a Heart Transplant Recipient. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2003, 22, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, B.M.; Hashkes, P.J.; Avery, R.; Deal, C.L. A 21-Year-Old Man with Still’s Disease with Fever, Rash, and Pancytopenia. Arthritis Care Res. 2010, 62, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgj, S.; Hoeven Jg, V.D. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a Patient with Influenza and Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis – A Case Report. Clin. Case Rep. Rev. 2017, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, M.; Vanguru, V.; Shin, J.-S.; Ronnachit, A. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Disseminated Histoplasmosis in an Immunocompetent Patient. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2024, 43, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mufarrih, S.; Lusby, H.; Watson, P. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Disseminated Histoplasmosis in a Patient with Leprosy. BMJ Case Rep. 2024, 17, e262041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, T.; Basu, A. Disseminated Histoplasmosis Presenting as a Case of Erythema Nodosum and Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2015, 71, S598–S600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.; Sukumaran, L.; Siegel, D.A.; Jernigan, S.M.; Greenbaum, L.A. Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO) in a Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipient: Questions and Answers. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2015, 30, 2109–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Gu, W.; Mei, Y.; Miao, K.; Zhang, S.; Shao, Y. A Rare Life-Threatening Kodamaea Ohmeri Endocarditis Associated With Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2018, 71, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Ríos, J.F.; Aristizabal-Alzate, A.; Ocampo, C.; Serrano-Gayubo, A.K.; Serna-Higuita, L.M.; Zuluaga-Valencia, G. Disseminated Histoplasmosis and Haemophagocytic Syndrome in Two Kidney Transplant Patients. Nefrologia 2012, 32, 683–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, K.; Tsutsumi, H.; Wakai, S.; Tachi, N.; Chiba, S. A Child Case of Haemophagocytic Syndrome Associated with Cryptococcal Meningoencephalitis. J. Infect. 1998, 36, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omo-Ogboi, A.C.; Shirai, S.; Ur Rehman, A.; Ederhion, J.O.; Buja, M. A Rare Case of Disseminated Histoplasmosis With Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Mimicking a Flare of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Middle-Aged Man: A Case Report. Cureus 2023, 15, e46068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oya, S.; Muta, T. Breakthrough Infection of Geotrichum Capitatum during Empirical Caspofungin Therapy after Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation. Int. J. Hematol. 2018, 108, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Qiu, Y.; Zeng, W.; Tang, S.; Feng, X.; Deng, J.; Wei, X.; He, Z.; Zhang, J. Talaromycosis-Associated Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Nine Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Negative Patients: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3807–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, I.; Baraboutis, I.G.; Karnesis, L. Late Onset Combined Immunodeficiency Presenting with Recurrent Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonia. Case Rep. Med. 2014, 2014, 801805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasic, S.; Jankovic, I.; Rosic, R.; Ognjanovic, M. Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonitis in Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Acta Paediatr. 2001, 90, 1480–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.; Staszewski, H.; Garrison, M. Successful Treatment of Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a Patient with Disseminated Histoplasmosis. Hematology 2008, 13, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picavia, R.; Luu, L.A.; Crane, I.; Flowers, R.H. Overlapping Features of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and DRESS in an Immunocompromised Patient with Disseminated Histoplasmosis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2024, 63, 381–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powel, M.S.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Budvytiene, I.; Schaenman, J.M.; Banaei, N. First Isolation of Cryptococcus Uzbekistanensis from an Immunocompromised Patient with Lymphoma. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1125–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puing, A.G.; Raghavan, S.S.; Aleshin, M.A.; Ho, D.Y. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis Presenting as Cellulitis. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2021, 33, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.; Bence-Bruckler, I.; Huebsch, L.; Jessamine, P.; Toye, B.; Padmore, R. Disseminated Histoplasmosis Associated with Acquired Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Clin. Case Rep. 2015, 3, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsi, M.; Alvira, C.; Purohit, P.; Cornfield, D. Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Associated with Coccidiomycosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014, bcr2014205681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.D.; Morice, W.G.; Phyliky, R.L. Hemophagocytosis in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Histoplasmosis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2002, 77, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudier, M.; Lamaury, I.; Strobel, M. Human T Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) and Pneuocystis Carinii Associated with T Cell Proliferation and Haemophagocytic Syndrome. Leukemia 1997, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ruan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Dong, Z. Heterozygous Gain-of-Function Mutations in Human STAT1: A Case of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Due to Chronic Mucocutaneous Candidiasis in a 17-Month-Old Male. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, A.B.; Heptner, B.; Kessler, T.; Baumgarten, B.; Stoica, V.; Mohr, M.; Wiewrodt, R.; Warneke, V.S.; Hartmann, W.; Wüllenweber, J.; et al. Progressive Histoplasmosis with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and Epithelioid Cell Granulomatosis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Eur. J. Haematol. 2017, 99, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Kodati, R.; Rohilla, M.; Sharma, P. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Rare Association with Pulmonary Cryptococcosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e230255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonavane, A.D.; Sonawane, P.B.; Chandak, S.V.; Rathi, P.M. Disseminated Histoplasmosis with Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in an Immunocompetent Host. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, OD03–OD05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, T.; Pan, Y.; Wei, A.; Shi, Y.; Bai, J.; Liu, L.; Tian, H.; An, N. SARS-CoV-2 Reactivates Fungal-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 142, 113141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto Filho, J.T.D.; Lima, P.D.A.; Paulo, A.B.; Souza, A.L.S. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Disseminated Histoplasmosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Hematol. 2017, 106, 727–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, N.; Vinicius, J.M.; Serrins, J. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in a Patient with Disseminated Histoplasmosis. Case Rep. Hematol. 2020, 2020, 5638262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umekawa, S.; Evans, T. Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Associated with Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untanu, R.V.; Akbar, S.; Graziano, S.; Vajpayee, N. Histoplasmosis-Induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in an Adult Patient: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2016, 2016, 1358742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeveringe, M.P.; Brouwer, R.E. Histoplasma Capsulatum Reactivation with Haemophagocytic Syndrome in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia. Neth. J. Med. 2010, 68, 418–421. [Google Scholar]
- Vasseur, M.; Valade, S.; Suner, L.; Lafarge, A. Severe Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Kidney Transplant Recipient: The Etiology Is on the Tip of the Tongue! Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 1237–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignesh, P.; Loganathan, S.K.; Sudhakar, M.; Chaudhary, H.; Rawat, A.; Sharma, M.; Shekar, A.; Vaiphei, K.; Kumar, N.; Singh Sachdeva, M.-U.; et al. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Children with Chronic Granulomatous Disease-Single-Center Experience from North India. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 771–782.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.; Feng, A.; Lenert, P.; Kumar, B. Tongue Necrosis as a Manifestation of Immune Dysfunction: A Complex Case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Histoplasmosis, and Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 11, e7735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Duarte, A.G.; Schnadig, V.J. Fatal Reactive Hemophagocytosis Related to Disseminated Histoplasmosis with Endocarditis: An Unusual Case Diagnosed at Autopsy. South. Med. J. 2007, 100, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Islam, S.T.; Makarie-Rofail, L.; Barnsley, L.; Limaye, S. Successful Use of Subcutaneous Anakinra in Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Precipitated by Candidiasis in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Case Report and Description of a Novel Therapeutic Regimen. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 26, 2284–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Mo, Y.; Liu, S.; Luo, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, K. Case Report: Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a Child with Primary Immunodeficiency Infected with Talaromyces Marneffei. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1038354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, M.; Xu, N.; Yang, L.; Wen, S.; Wang, S.; Qu, C.; Xu, K.; Sun, E.; Cui, W.; et al. Disseminated Talaromyces Marneffei Infection Associated with Haemophagocytic Syndrome in an HIV-Negative Patient in Northern China: A Case Report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, K.; Zou, F.; Wang, X.; Yin, J.; Wu, Y.; Chai, X.; Zheng, L. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Candida Albicans and Reactivated EBV Infections: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Indian. J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2021, 64, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, E.-S.; Chee, Y.-L. Disseminated Histoplasma Capsulatum Diagnosed on Peripheral Blood Film. Eur. J. Haematol. 2013, 90, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Lin, Y.-M.; Lin, Y.-C. Tuberculosis and Aspergillosis-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Case Report. 內科學誌 2023, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Ordaya, E.E.; Fernandez, S.D.; Lescalleet, K.; Larson, D.; Pritt, B.; Berbari, E. Disseminated Histoplasmosis and Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a Patient Receiving TNF-Alpha Inhibitor Therapy. IDCases 2022, 29, e01603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Park, S.-S.; Jeon, Y.-W.; Lee, S.-E.; Cho, B.-S.; Eom, K.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, S.; Min, C.-K.; et al. Treatment Outcomes and Prognostic Factors in Adult Patients with Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Not Associated with Malignancy. Haematologica 2019, 104, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Wang, G.; Guan, E.; Song, L.; Song, A.; Liu, X.; Yi, Z.; Sun, L.-R. Treatment Outcomes and Prognostic Factors for Non- Malignancy Associated Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Children. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yao, R.; Cao, L.; Wang, Z.; Liang, R.; Jia, Y.; Su, Y. Prognostic Factors in Patients with Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistioc Ytosis in a Chinese Cohort. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. The Outcome of Induction Therapy for EBV-Related Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Model for Risk Stratification. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 876415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, E.; Ohga, S.; Imashuku, S.; Yasukawa, M.; Tsuda, H.; Miura, I.; Yamamoto, K.; Horiuchi, H.; Takada, K.; Ohshima, K.; et al. Nationwide Survey of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Japan. Int. J. Hematol. 2007, 86, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.A.; Kapoor, P.; Letendre, L.; Kumar, S.; Wolanskyj, A.P. Prognostic Factors and Outcomes of Adults with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otrock, Z.K.; Eby, C.S. Clinical Characteristics, Prognostic Factors, and Outcomes of Adult Patients with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apodaca, E.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, S.; Tuna-Aguilar, E.J.; Demichelis-Gómez, R. Prognostic Factors and Outcomes in Adults with Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Single-Center Experience. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018, 18, e373–e380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, D.; Ma, S.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, M.; et al. Risk Factors of Early Death in Adult Patients with Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Single-Institution Study of 171 Chinese Patients. Hematology 2019, 24, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaak, C.; Schuster, F.S.; Nyvlt, P.; Spies, C.; Feinkohl, I.; Beutel, G.; Schenk, T.; La Rosée, P.; Janka, G.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; et al. Treatment and Mortality of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adult Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review with Pooled Analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, e1137–e1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Ling, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gu, W. Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Factors of 75 Cases with Acquired Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Hematology 2023, 28, 2247887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, D.; Li, L.; Xie, W.; Tan, Y.; Ye, X. Risk Factors and Prognosis of Early Death in Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 2301–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongdee, P.; Julamanee, J.; Rattarittamrong, E.; Mukura, S.; Wanitpongpun, C.; Deoisares, R.; Surawong, A.; Chajuwan, T.; Chanswangphuwana, C. Prognostic Factors of Adult Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and Clinical Utility of HLH-2004 Diagnostic Criteria and HScore: A Real-World Multicenter Study from Thailand. Acta Haematol. 2024, 147, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, K.; Molinari, N.A.M.; Jackson, B.R. Public Awareness of Invasive Fungal Diseases—United States, 2019. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1343–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.; Stilwell, P.; Liu, H.; Ban, L.; Bythell, M.; Card, T.R.; Lanyon, P.; Nanduri, V.; Rankin, J.; Bishton, M.J.; et al. Temporal Trends in the Incidence of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Nationwide Cohort Study from England 2003–2018. Hemasphere 2022, 6, e797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Bosch, X.; Pérez-de-Lis, M.; Pérez-Álvarez, R.; Fraile, G.; Gheitasi, H.; Retamozo, S.; Bové, A.; Monclús, E.; Escoda, O.; et al. Infection Is the Major Trigger of Hemophagocytic Syndrome in Adult Patients Treated with Biological Therapies. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 45, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipitò, L.; Medaglia, A.A.; Trizzino, M.; Mancuso, A.; Catania, B.; Mancuso, S.; Calà, C.; Florena, A.M.; Cascio, A. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to Histoplasmosis: A Case Report in a Patient with AIDS and Recent SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Minireview. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, J.; Callebaut, I.; Raposo, G.; Certain, S.; Bacq, D.; Dumont, C.; Lambert, N.; Ouachée-Chardin, M.; Chedeville, G.; Tamary, H.; et al. Munc13-4 Is Essential for Cytolytic Granules Fusion and Is Mutated in a Form of Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (FHL3). Cell 2003, 115, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.Y.; Jaffray, J.; Woda, B.; Newburger, P.E.; Usmani, G.N. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis with MUNC13-4 Gene Mutation or Reduced Natural Killer Cell Function Prior to Onset of Childhood Leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 56, 856–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Jordan, M.B.; Marsh, R.A.; Johnson, J.A.; Kissell, D.; Meller, J.; Villanueva, J.; Risma, K.A.; Wei, Q.; Klein, P.S.; et al. Hypomorphic Mutations in PRF1, MUNC13-4, and STXBP2 Are Associated with Adult-Onset Familial HLH. Blood 2011, 118, 5794–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faitelson, Y.; Bates, A.; Shroff, M.; Grunebaum, E.; Roifman, C.M.; Naqvi, A. A Mutation in the STAT1 DNA-Binding Domain Associated with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistocytosis. LymphoSign J. 2014, 1, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, N.; Zhao, F.-Y.; Xu, X.-J. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Caused by STAT1 Gain-of-Function Mutation Is Not Driven by Interferon-γ: A Case Report. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 6130–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paccoud, O.; Warris, A.; Puel, A.; Lanternier, F. Inborn Errors of Immunity and Invasive Fungal Infections: Presentation and Management. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 37, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionakis, M.S.; Drummond, R.A.; Hohl, T.M. Immune Responses to Human Fungal Pathogens and Therapeutic Prospects. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadevall, A. Immunity to Invasive Fungal Diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 40, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosée, P.; Horne, A.; Hines, M.; von Bahr Greenwood, T.; Machowicz, R.; Berliner, N.; Birndt, S.; Gil-Herrera, J.; Girschikofsky, M.; Jordan, M.B.; et al. Recommendations for the Management of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults. Blood 2019, 133, 2465–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senjo, H.; Higuchi, T.; Okada, S.; Takahashi, O. Hyperferritinemia: Causes and Significance in a General Hospital. Hematology 2018, 23, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeng, B.E.; Elem, D.E.; Kokelu, A.N.; Onukak, A.; Egbara, W.O.; Benjamin, O.O.; Ogar, A.N.; Chukwuma, S.T.; Okafor, L.E.; Essien, K.A.; et al. Pathophysiology and Clinical Outcomes of Pancytopenia in Disseminated Histoplasmosis: A Scoping Review. Infection 2025, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, J.L.; Badawy, S.M.; Bush, J.W.; Schafernak, K.T. Deconstructing the Diagnosis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Using Illustrative Cases. J. Hematop. 2015, 8, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Polski, J.M.; Imran, H. Sensitivity and Specificity of Bone Marrow Hemophagocytosis in Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2012, 42, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Fardet, L.; Galicier, L.; Lambotte, O.; Marzac, C.; Aumont, C.; Chahwan, D.; Coppo, P.; Hejblum, G. Development and Validation of the HScore, a Score for the Diagnosis of Reactive Hemophagocytic Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Logan, A.C. Diagnosis and Management of Adult Malignancy-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Cancers 2023, 15, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naymagon, L. Can We Truly Diagnose Adult Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)? A Critical Review of Current Paradigms. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 218, 153321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, A.; Lin, M.; Park, S.; Pudek, M.; Schneider, M.; Jordan, M.B.; Mattman, A.; Chen, L.Y.C. Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Is a Sensitive Diagnostic Test in Adult HLH. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 2529–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, V.; Kwatra, K.S.; Kakkar, N.; John, M.J. Spectrum of Hemophagocytosis in Bone Marrow Aspirates: Experience from a Tertiary Care Hospital in North India. Int. J. Appl. Basic. Med. Res. 2023, 13, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gars, E.; Purington, N.; Scott, G.; Chisholm, K.; Gratzinger, D.; Martin, B.A.; Ohgami, R.S. Bone Marrow Histomorphological Criteria Can Accurately Diagnose Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei, M.A.; Berliner, N. Not So Benign Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Rare Yet Clinically Significant Syndrome. Hematologist 2024, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsten, E.; Horne, A.; Aricó, M.; Astigarraga, I.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Ishii, E.; Janka, G.; Ladisch, S.; Lehmberg, K.; et al. Confirmed Efficacy of Etoposide and Dexamethasone in HLH Treatment: Long-Term Results of the Cooperative HLH-2004 Study. Blood 2017, 130, 2728–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionakis, M.S.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Glucocorticoids and Invasive Fungal Infections. Lancet 2003, 362, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Denning, D.W. The Impact of Corticosteroids on the Outcome of Fungal Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Fungal Infect. Rep. 2023, 17, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, P.P.; Pal, P.; Ghosh, A.; Sinha, R. Infection-Associated Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Case Series Using Steroids Only Protocol for Management. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 1363–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berliner, N.; Kurra, C.; Chou, D. CASE RECORDS of the MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL. Case 1-2016. An 18-Year-Old Man with Fever, Abdominal Pain, and Thrombocytopenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, C.J.; Nguyen, M.H. Diagnosing Invasive Candidiasis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 10–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meersseman, W.; Lagrou, K.; Maertens, J.; Van Wijngaerden, E. Invasive Aspergillosis in the Intensive Care Unit. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Author, Country Year, Reference | Study Type | Study Period | Study Population | Frequency | Organisms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| 1. | Ramos-Casals, Spain, 2014, [2] | Review article of cases | 1974–2011 | Age >17 | 2% (37/2197) | Histoplasma capsulatum (18) Other unspecified fungi (19) |
| 2. | Abdelhay, USA, 2023, [4] | The US National Inpatient Sample database | 2006–2019 | Age ≥18 | 2% (349/16,136) | Histoplasma capsulatum (294) Other unspecified fungi (55) |
| ||||||
| 1. | Tabaja, USA, 2022, [6] | Review article of cases | 2005–2021 | HIV population (Age ≥ 19) | 25% (20/81) | Histoplasma capsulatum (14) Talaromyces marneffei (1) Cryptococcus (1) Other unspecified fungi (4) |
| 2. | Camous, Guadeloupe, 2023, [7] | Multicenter, Retrospective | 2014–2022 | HIV population | 68% (15/22) a | Histoplasma capsulatum (15) |
| 3. | Cruz-Quezada, Mexico, 2024, [8] | Single center, Retrospective | 2018–2023 | HIV population (Age ≥ 18) | 36% (26/72) a | Histoplasma capsulatum (26) |
| 4. | Wang, China, 2024, [9] | Single center, Retrospective | 2013–2023 | HIV population (Age ≥ 18) | 35% (11/31) b | Talaromyces marneffei (11) |
| ||||||
| 1. | Reiner, USA, 1998, [10] | Single center, Retrospective | 1982–1987 | Age ≥ 16 | 9% (2/23) | Histoplasma capsulatum (2) |
| 2. | Ningsanond, Thailand, 2000, [11] | Single center, Retrospective | 1988–1997 | Pediatric population | 6% (3/50) | Histoplasma capsulatum (2) Talaromyces marneffei (1) |
| 3. | Karras, France, 2004, [12] | Multicenter, Retrospective | 1992–2001 | Kidney transplant recipients | 6% (1/17) | Pneumocystis jiroveci (1) |
| 4. | Akamatsu, Japan, 2006, [13] | Single center, Retrospective | 1996–2005 | Liver transplant recipients | 33% (1/3) | Aspergillus (1) |
| 5. | Tseng, Taiwan, 2011 [14] | Single center, Retrospective | 2000–2007 | Age ≥ 16 | 5% (5/96) | Other unspecified fungi (4) Cryptococcus (1) |
| 6. | Park, South Korea, 2012, [15] | Single center, Retrospective | 1999–2010 | Age > 15 | 0% (0/23) | |
| 7. | Nair, India, 2013, [16] | Single center, Retrospective | 2007–2009 | Infection-induced HLH | 4% (1/26) | Aspergillus (1) |
| 8. | Delavigne, France, 2014, [17] | Single center, Retrospective | 2006–2010 | Newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia patients who received intensive chemotherapy | 34% (11/32) | Aspergillus (10) Mucorales (1) |
| 9. | De, India, 2015, [18] | Single center, Retrospective | 2009–2014 | Age > 18 | 29% (2/7) a | Histoplasma capsulatum (2) |
| 10. | Bode, USA/Europe, 2015, [19] | International survey | 2014 | Primary immunodeficiency | 6% (4/63) c | Candida lusitaniae (2) Pneumocystis jiroveci (1) Aspergillus (1) |
| 11. | Lerolle, France, 2016, [20] | Multicenter, Retrospective | 2006–2011 | French registry | 2% (4/162) | Pneumocystis jiroveci (3) Candida (1) |
| 12. | You, China, 2021, [21] | Single center, Retrospective | 2015–2019 | Non-EBV, infection-induced HLH | 5% (2/36) | Histoplasma capsulatum (1) Aspergillus (1) |
| 13. | Xie, China, 2021, [22] | Single center, Retrospective | 2019 | Kidney transplant recipients | 14% (1/7) d | Pneumocystis jiroveci (1) |
| 14. | Zeng, China, 2021, [23] | Single center, Retrospective | 2010–2020 | Pediatric population | 52% (11/21) b | Talaromyces marneffei (11) |
| 15. | Yang, China, 2023, [24] | Single center, Retrospective | 2017–2022 | Pediatric population | 17% (1/6) b | Talaromyces marneffei (1) |
| 16. | Camous, Guadeloupe, 2023, [7] | Multicenter, Retrospective | 2014–2022 | Non-HIV population | 40% (4/10) a | Histoplasma capsulatum (4) |
| Patient Characteristic | |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 72/116 (62%) |
| Age a | |
| Age < 18 | 30/116 (26%) |
| Age ≥ 18 | 86/116 (74%) |
| Immunocompromised condition | 61/116 (53%) |
| Autoimmune disorder b | 21/116 (18%) |
| Solid organ transplant c | 13/116 (11%) |
| Hematologic disorder d | 12/116 (10%) |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 6/116 (5%) |
| Primary immunodeficiency e | 3/116 (3%) |
| Others f | 7/116 (6%) |
| Associated condition | |
| Oral thrush | 9/116 (8%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 7/116 (6%) |
| IFI, location | |
| Disseminated | 88/116 (76%) |
| Pulmonary | 20/116 (17%) |
| Central nervous system | 1/116 (1%) |
| Other g | 7/116 (6%) |
| Fungal infection, pathogen h | |
| Histoplasma capsulatum | 59/116 (51%) |
| Aspergillus spp. | 15/116 (13%) |
| Talaromyces marneffei | 13/116 (11%) |
| Candida spp. | 12/116 (10%) |
| Pneumocystis jiroveci | 7/116 (6%) |
| Cryptococcus spp. | 3/116 (3%) |
| Trichosporon asahii | 3/116 (3%) |
| Mucorales | 3/116 (3%) |
| Other i | 5/116 (4%) |
| >1 fungal pathogen | 4/116 (3%) |
| Co-infection with bacterial pathogen j | 13/116 (11%) |
| Co-infection with viral pathogen k | 5/116 (4%) |
| Co-infection with Mycobacterium l | 2/116 (2%) |
| No. Positive/No. Report | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|
| Relationship between IFI and HLH | ||
| Simultaneous | 75/96 | 78 |
| Sequential (IFI → HLH) a | 21/96 | 22 |
| HLH clinical and laboratory feature | ||
| Fever | 106/108 | 98 |
| Splenomegaly | 64/82 | 78 |
| Met bicytopenia criteria | 90/98 | 92 |
| Triglycerides ≥ 265 mg/dL b | 45/60 | 75 |
| Fibrinogen ≤ 1.5 g/L c | 44/65 | 68 |
| Low/absent NK cell activity | 15/17 | 88 |
| Ferritin ≥ 500 μg/L d | 85/88 | 97 |
| Soluble CD25 ≥ 2400 U/mL e | 29/32 | 91 |
| HLH Positive biopsy | ||
| Bone marrow | 90/98 | 92 |
| Spleen | 6/8 | 75 |
| Lymph node | 7/13 | 54 |
| Received HLH-direct therapy | ||
| No | 30/92 | 33 |
| Yes | 62/92 | 67 |
| Glucocorticoids | 54/92 | 59 |
| Chemotherapy | 26/92 | 28 |
| IVIG | 21/92 | 23 |
| Cyclosporine | 8/92 | 9 |
| Anakinra | 7/92 | 8 |
| Antifungal therapy | 94/94 | 100 |
| Outcome at 30-day | ||
| Survive | 44/69 | 64 |
| Death | 25/69 | 36 |
| No. | Author, Country Year, Reference | Study Type | Study Period | Study Population | Prognostic Factors Related to Secondary Trigger | Other Poor Prognostic Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ishii, Japan, 2007, [116] | Multicenter, Retrospective | 2001–2005 | n = 799 | 5-year overall survival: autoimmune-induced (90%), other infection-induced (89%), EBV-induced (83%), B-cell lymphoma-induced (48%), T/NK cell lymphoma-induced (12%). | NR |
| 2. | Tseng, Taiwan, 2011, [14] | Single center, Retrospective | 2000–2007 | Age ≥ 16, n = 96 | 30-day mortality: non-infection-induced (70%), infection-induced (47%) (p = 0.03). | 30-day mortality: Age ≥ 50; Fever more than 3 days after HLH diagnosis; Disseminated intravascular coagulation. |
| 3. | Ramos-Casals, Spain, 2014, [2] | Review article of cases | 1974–2011 | Age > 17, n = 1109 | Mortality: T/NK cell lymphoma-induced (88%), B cell lymphoma-induced (58%), tuberculosis-induced (51%), autoimmune-induced (20%), EBV-induced (17%), other infection-induced (10%). | This review summarizes the prognostic factors identified in studies of adult HLH in their appendixes. |
| 4. | Parikh, USA, 2014, [117] | Single center, Retrospective | 1996–2011 | Age ≥ 18, n = 62 | Median survival: non-malignancy-induced (23 months), malignancy-induced (1 month) (p = 0.01). | Overall survival: Low albumin. |
| 5. | Otrock, USA, 2015, [118] | Single center, Retrospective | 2003–2014 | Age ≥ 18, n = 73 | Median survival: non-malignancy-induced (47 months), malignancy-induced (1 month) (p < 0.0001). | Overall survival: Ferritin > 50,000 mg/L. |
| 6. | Lerolle, France, 2016, [20] | Multicenter, Retrospective | 2006–2011 | Adult, n = 162 | Median survival: infection-induced (9 months), malignancy-induced (4 months) (p = 0.03). Infection-induced HLH were less likely to receive corticosteroids and/or etoposide than malignancy-induced HLH (47.4% vs. 72.8%; p = 0.007). | NR |
| 7. | Apodaca, Mexico, 2018, [119] | Single center, Retrospective | 1998–2016 | Age ≥ 18, n = 64 | 3-year survival: non-malignancy-induced (41%), malignancy-induced (23%) (p = 0.046). | Overall survival: Nosocomial infection; Neurologic symptoms. |
| 8. | Zhao, China, 2019, [120] | Single center, Retrospective | 2012–2018 | Age ≥ 18, n = 171 | Malignant-induced HLH has a higher 30-day mortality than non-malignancy-induced HLH (HR 3.21; p = 0.001). | 30-day mortality: Age ≥ 54; Platelet ≤ 39.5 × 109/L; Activated partial thromboplastin time ≥ 54 s; Triglyceride ≥ 3.23 mmol/L; Lactate dehydrogenase ≥ 1300 U/L. |
| 9. | Yoon, South Korea, 2019, [112] | Single center, Retrospective | 2001–2017 | Age ≥ 15, excluded malignancy-induced HLH, n = 126 | 5-year survival: autoimmune-induced (82%), other infection-induced (79%), EBV-induced (25%) (p < 0.001). | Overall survival: Platelets < 35 × 109/L; Ferritin > 20,000 ng/mL |
| 10. | Knaak, Germany, 2020, [121] | Review article of cases | Inception–2019 | Age ≥ 18, n = 661 | The mortality rate is different between different infection-induced HLH: EBV (79%), influenza (79%), fungal (74%), bacteria (43%), and Dengue (20%). | In all patients with infection-induced HLH, no significant differences were seen in mortality between patients with and without HLH-direct therapy (58% vs. 51%; p = 0.248). |
| 11. | Pan, China, 2020, [113] | Single center, Retrospective | 2005–2018 | Children, n = 88 | 5-year survival: other infection-induced (76%), autoimmune-induced (65%), EBV-induced (33%), primary immunodeficiency-induced (11%) (p = 0.002). | Overall survival: Not response to treatment at 8 weeks; Hemoglobin < 60 g/L; Albumin < 25 g/L |
| 12. | You, China, 2021, [21] | Single center, Retrospective | 2015–2019 | n = 36, Non-EBV-induced HLH | 69% (25/36) survive. | NR |
| 13. | Yang, China, 2023, [122] | Single center, Retrospective | 2012–2022 | Age ≥15, n = 75 | NR a | 30-day mortality: Platelets < 42.5 × 109/L; Albumin < 27.7 g/L; Fibrinogen < 1.085 g/L; those not following the HLH-2004 protocol, EBV viremia. |
| 14. | Zhang, China, 2023, [123] | Multicenter, Retrospective | 2014–2021 | Adult, n = 324 | 30-day mortality: lymphoma-induced (52%), infection-induced (31%). | 30-day mortality: Age > 60; Platelet ≤ 20.0 × 109/L, Activated partial prothrombin time > 36 s; Lactate dehydrogenase > 1000 U/L. |
| 15. | Abdelhay, USA, 2023, [4] | The US National Inpatient Sample database | 2006–2019 | Age ≥ 18, n = 16,136 | In-hospital mortality: primary immunodeficiency-induced (31%), malignancy-induced (28%), infections-induced (21%), autoimmune-induced (13%), post-organ transplant-induced (14%). The mortality rate is higher in non-Histoplasma-induced HLH (defined as Coccidioides, Paracoccidioides, Blastomyces) than in Histoplasma-induced HLH (46% vs. 10%) | In-hospital mortality: female |
| 16. | Jongdee, Thailand, 2024, [124] | Multicenter, Retrospective | 2006–2020 | Adult, n = 147 | Malignancy-induced HLH has the lowest overall survival compared to infection-induced HLH and autoimmune-induced HLH (HR 6.3 vs. 4.6 vs. 1). | Overall survival: Ferritin > 6000 μg/L. |
| 17. | Pei, China, 2024, [114] | Single center, bidirectional | 2016–2023 | Age ≥ 18, n = 220 | NR ab | 30-day mortality: Age ≥ 38 years, Cytopenia ≥ 2 lines; Platelets ≤ 50 × 109/L; Aspartate aminotransferase ≥ 135 U/L; Prothrombin time ≥ 14.9 s; Activated partial thromboplastin time ≥ 38.5 s, EBV infection, fungal infection. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, C.-Y.; Hicklen, R.S.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Fungal-Induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Literature Review in Non-HIV Populations. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11020158
Chiu C-Y, Hicklen RS, Kontoyiannis DP. Fungal-Induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Literature Review in Non-HIV Populations. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(2):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11020158
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Chia-Yu, Rachel S. Hicklen, and Dimitrios P. Kontoyiannis. 2025. "Fungal-Induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Literature Review in Non-HIV Populations" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 2: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11020158
APA StyleChiu, C.-Y., Hicklen, R. S., & Kontoyiannis, D. P. (2025). Fungal-Induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Literature Review in Non-HIV Populations. Journal of Fungi, 11(2), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11020158







