AoMbp1 Governs Conidiation and Trap Morphogenesis in Arthrobotrys oligospora Via Direct Transcriptional Activation of the MAPK Sensor AoSho1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmids, Strains, Nematodes and Culture Conditions
2.2. Analysis of the Molecular Characteristics of the AoMbp1 Protein
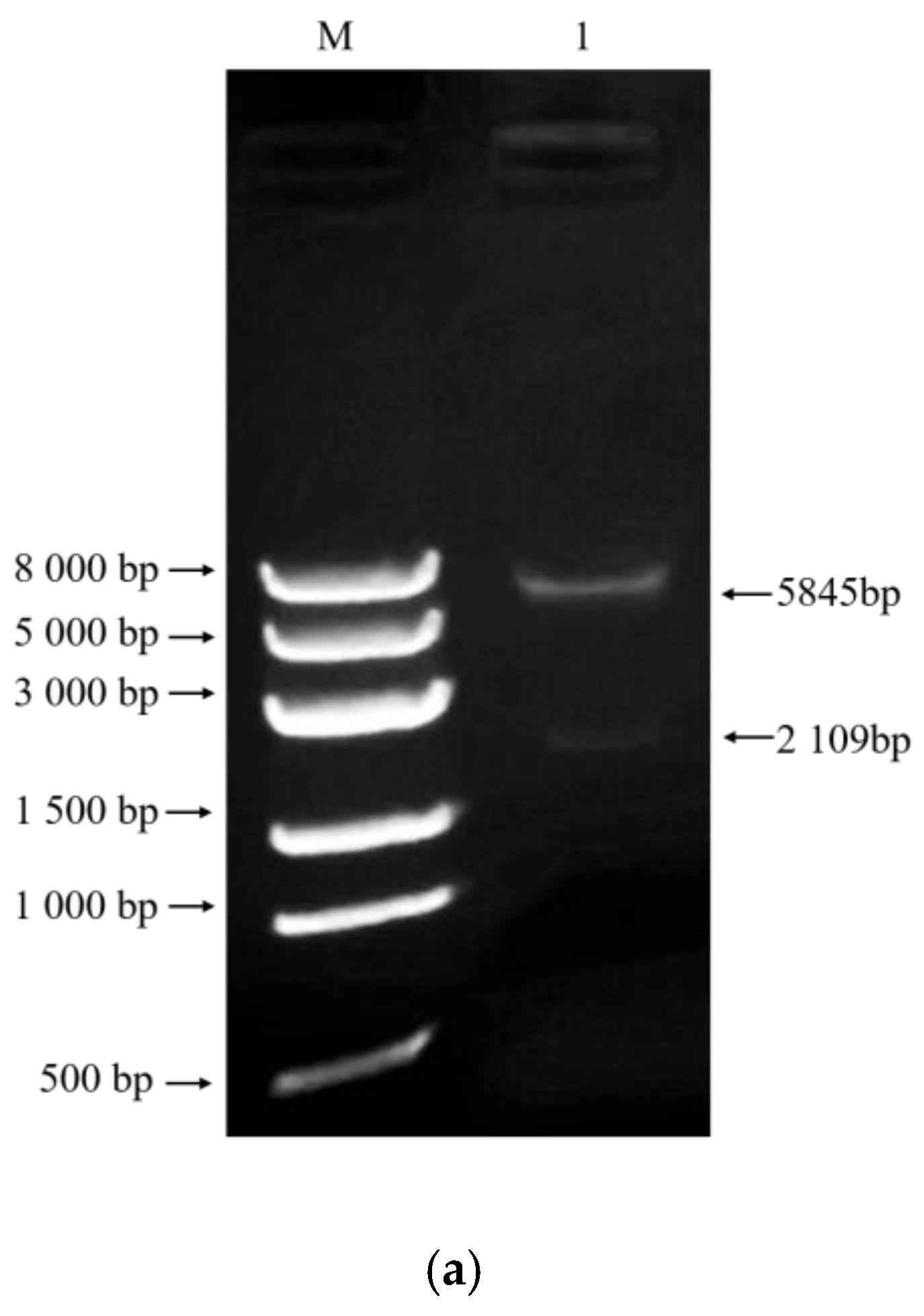
2.3. Construction of AoMbp1 Gene Deletion and Complementation Strains
2.4. Phenotypic Analysis of Different Strains
2.5. Analysis of Stress Tolerance
2.6. Transcriptome Sequencing and Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
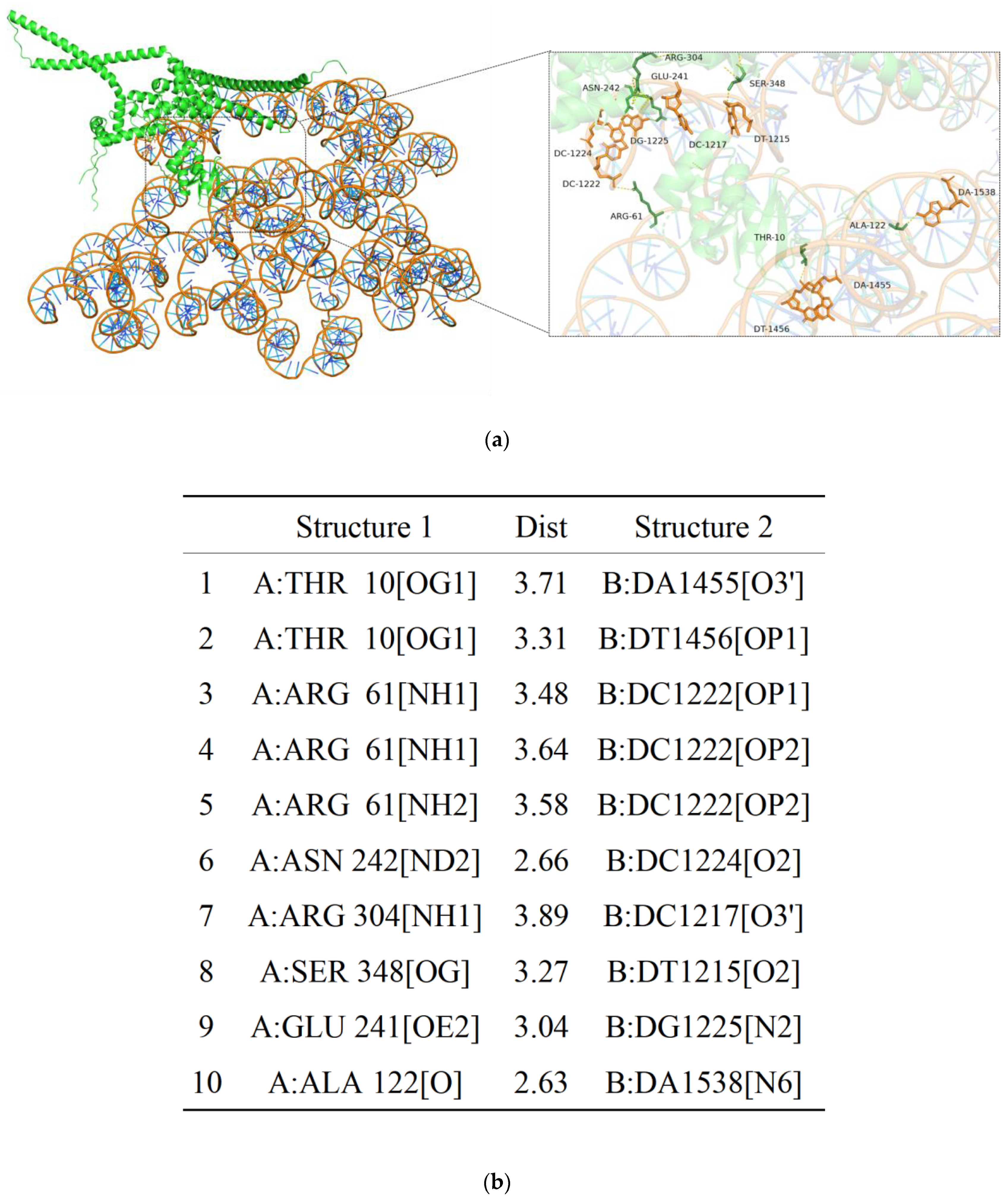
2.7. Molecular Docking Analysis of AoMbp1 with the Promoter of a Downstream Target Gene
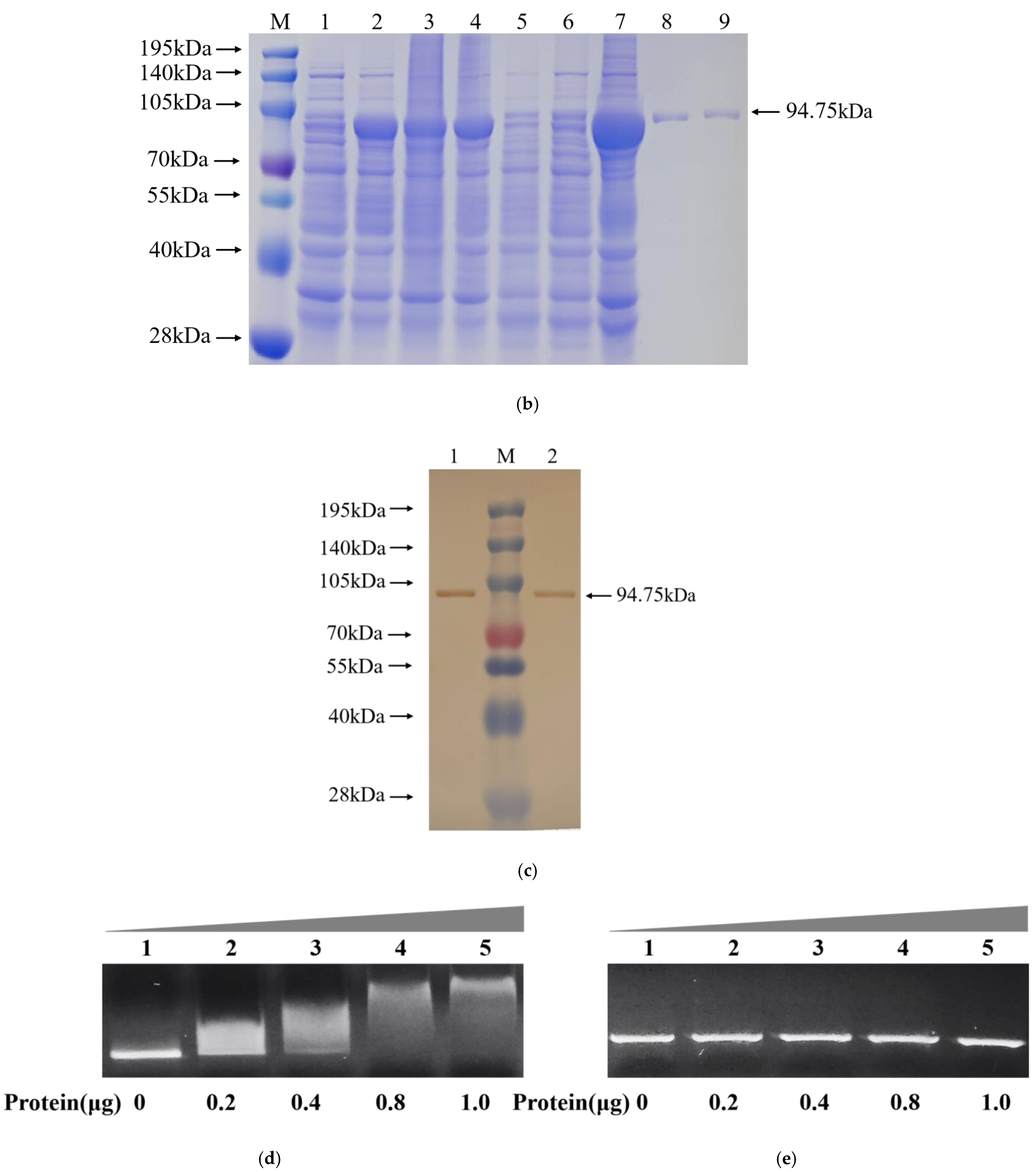
2.8. Yeast One-Hybrid (Y1H) Assay
2.9. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
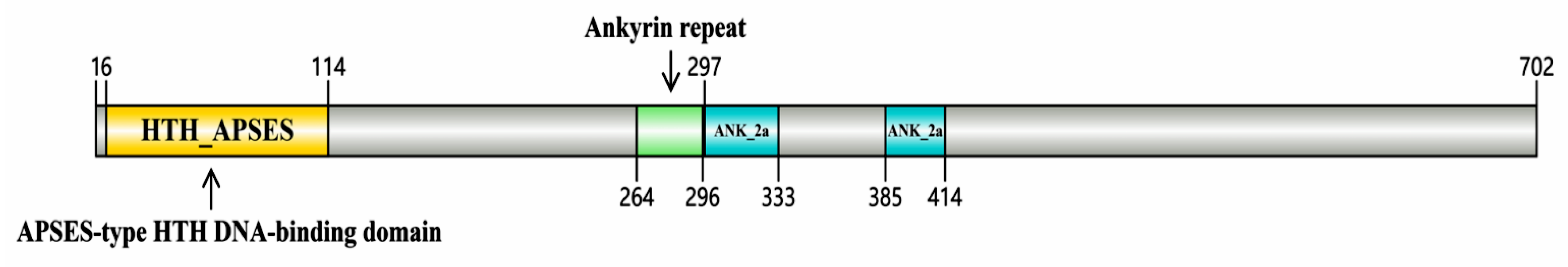
3.1. Molecular Characterization of the Transcription Factor AoMbp1 of A. oligospora
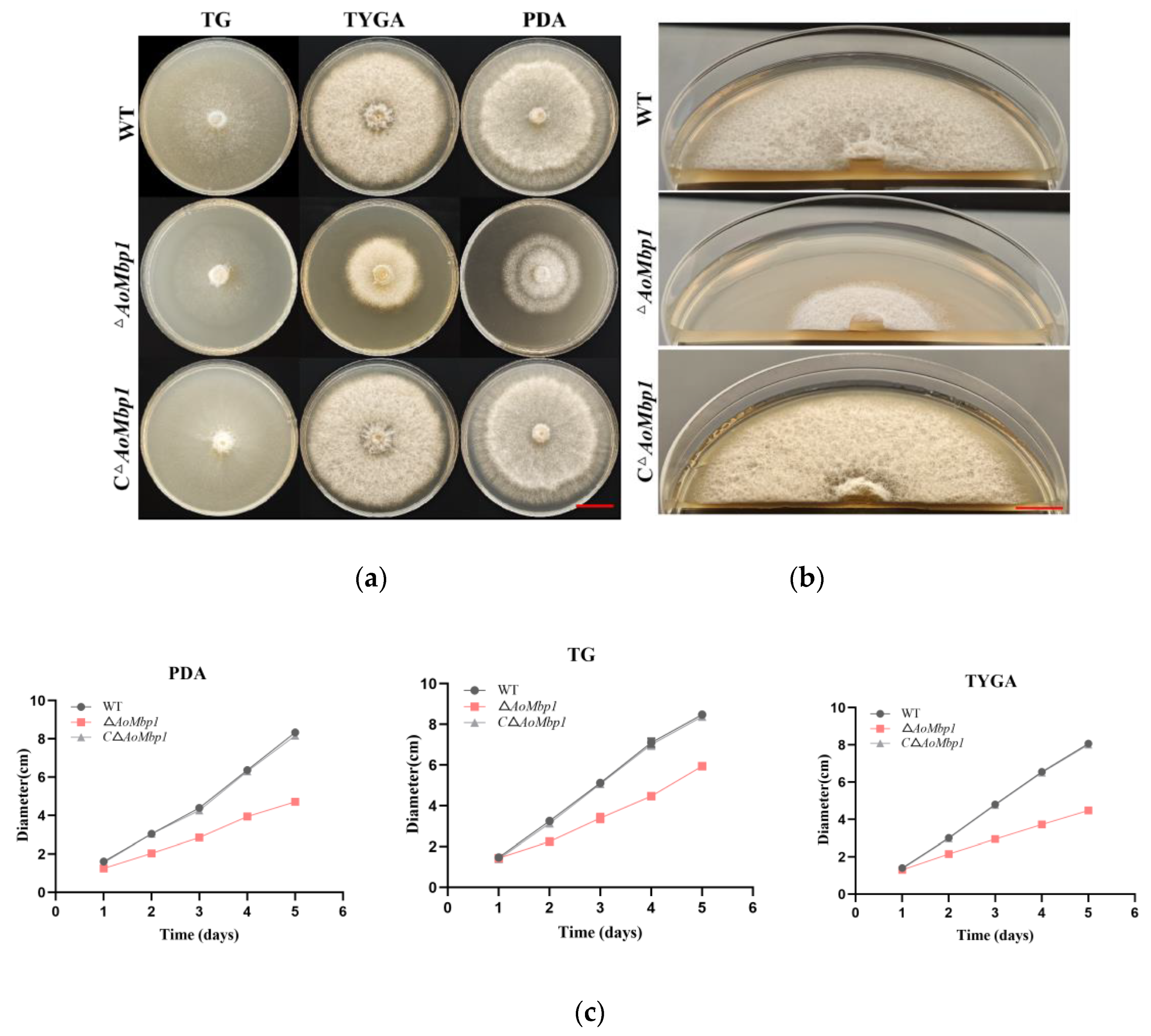
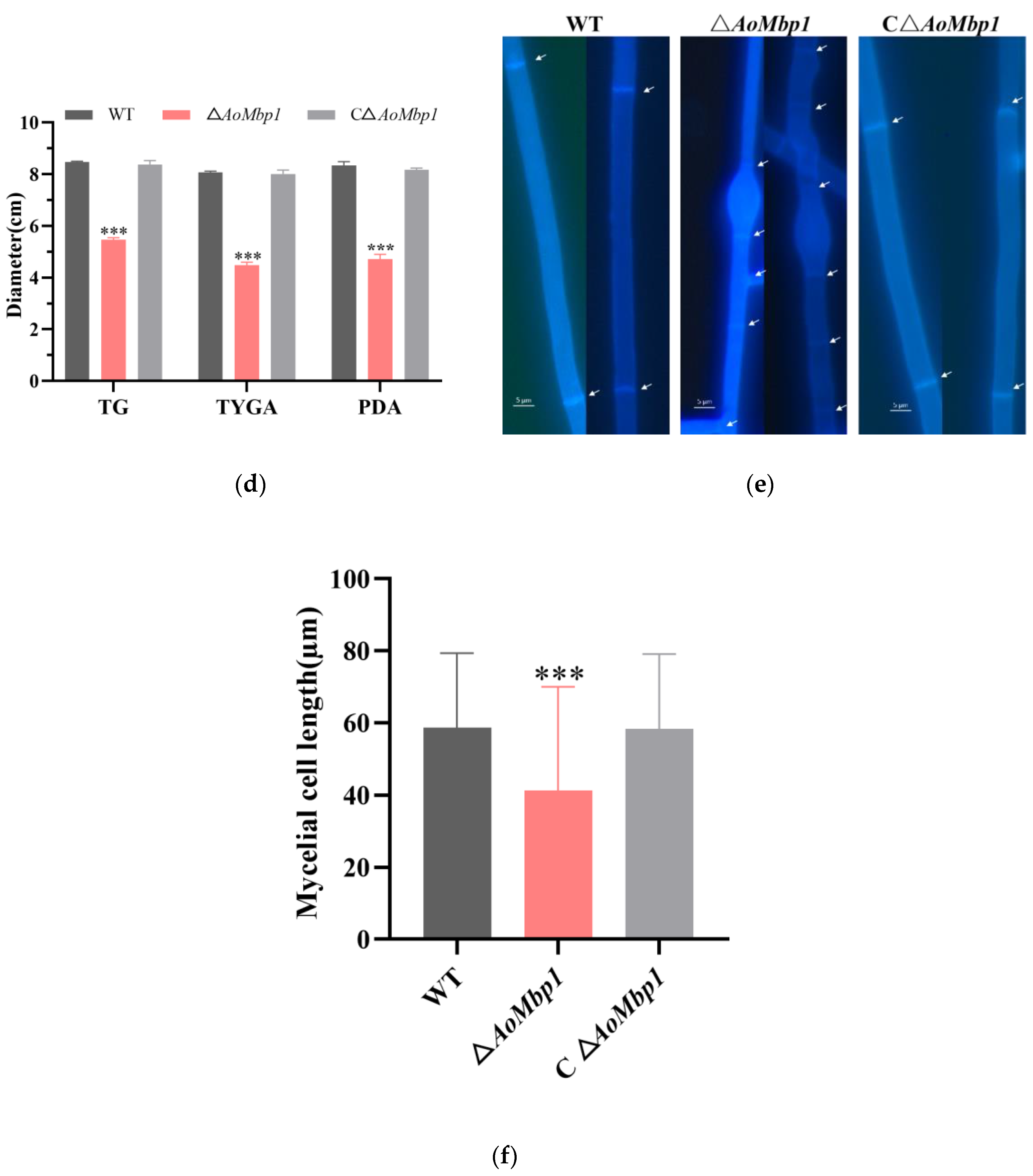
3.2. AoMbp1 Is Involved in the Regulation of Mycelial Growth
3.3. Deletion of AoMbp1 Impairs Conidial Production and Morphology
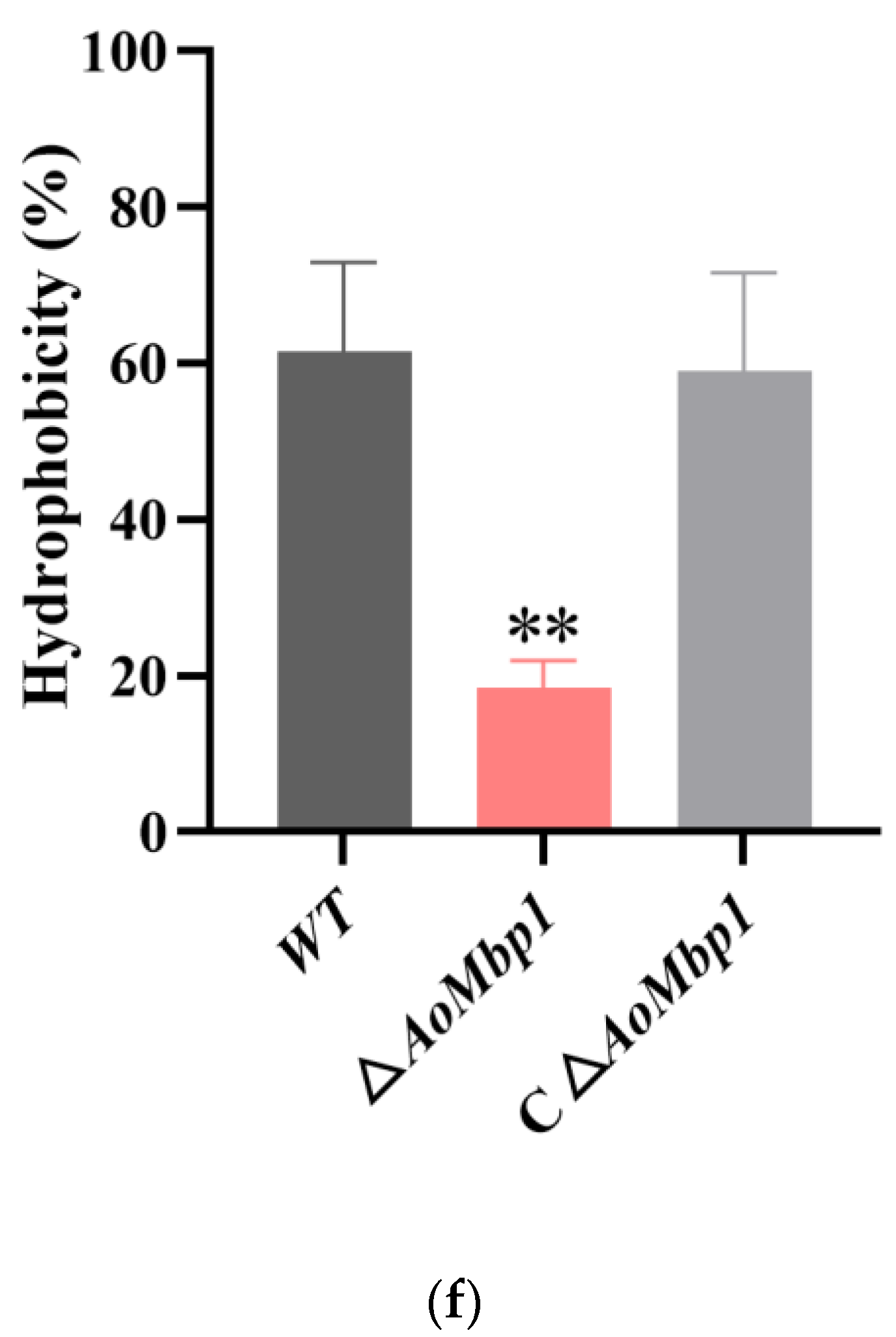
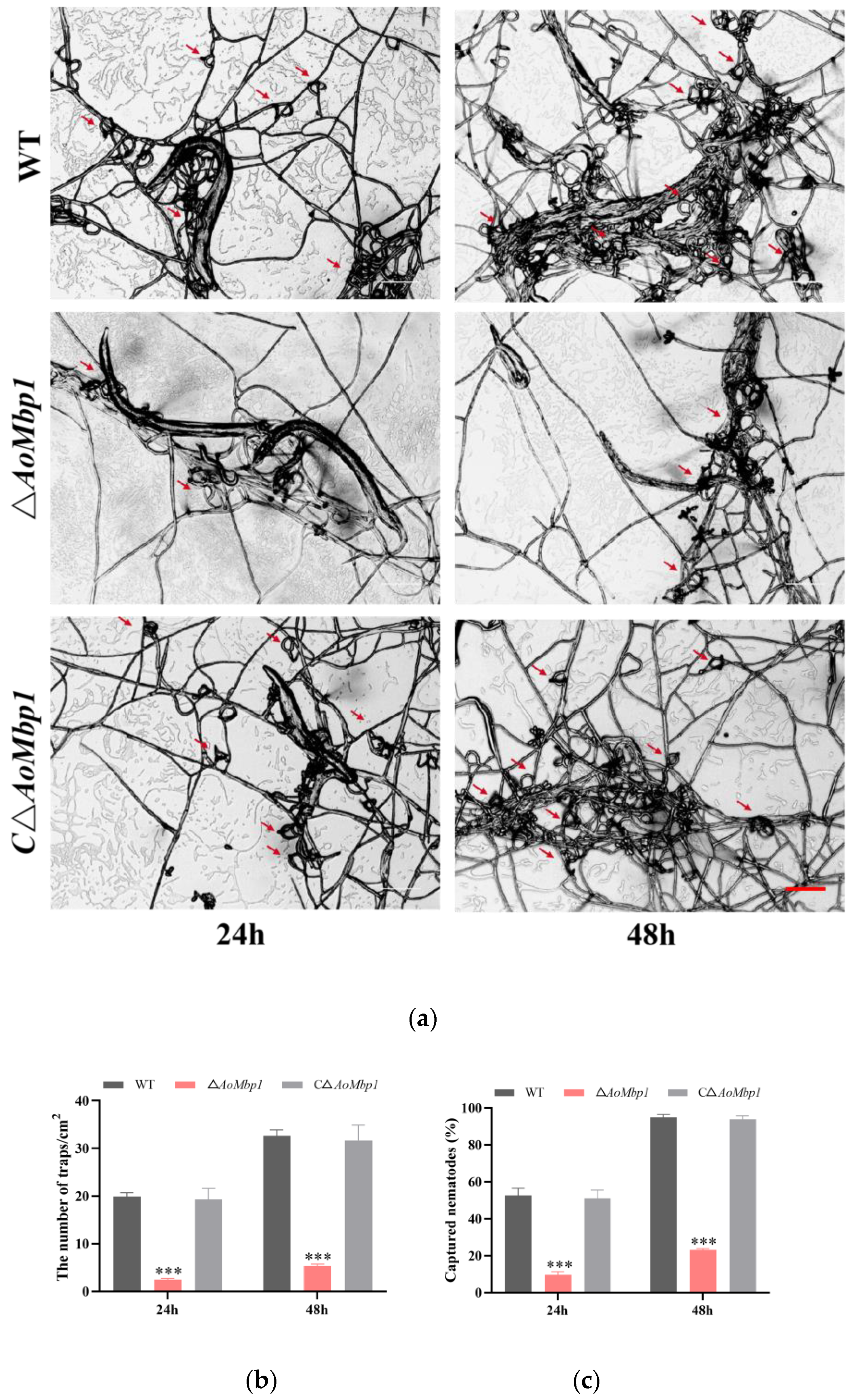
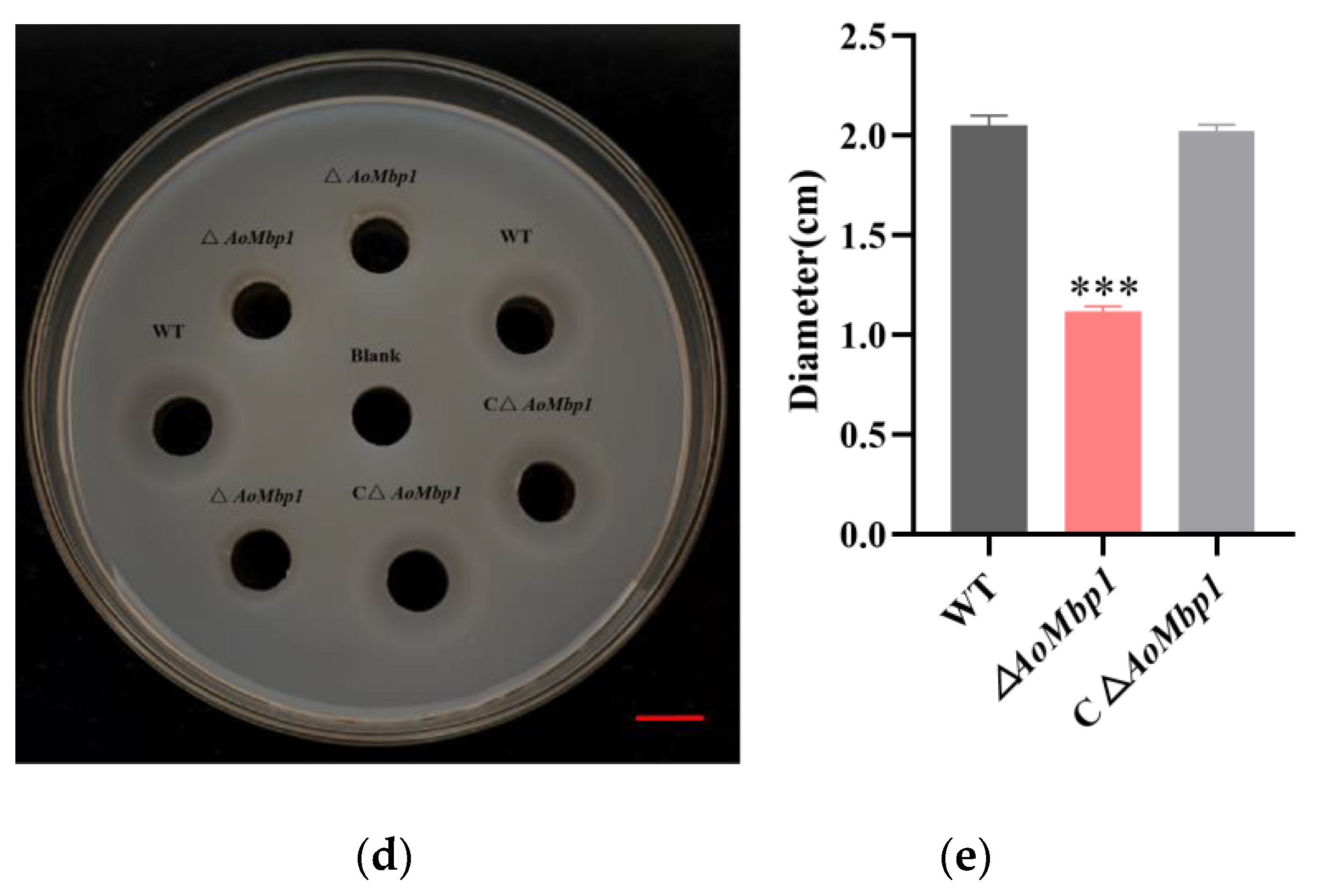
3.4. AoMbp1 Contributes to Trap Formation, Predatory Capability and Extracellular Protein Hydrolase Expression
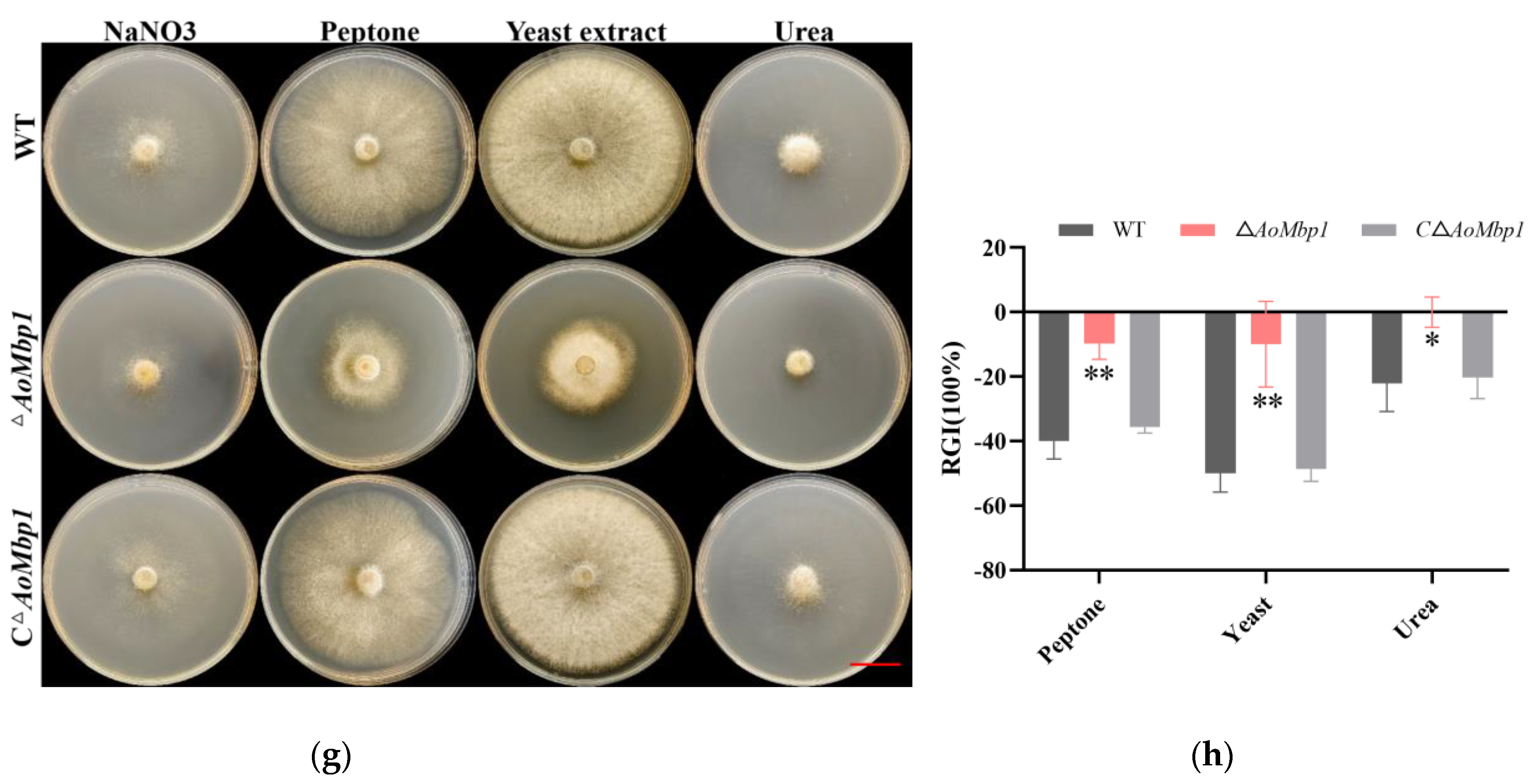
3.5. AoMbp1 Is Required for Stress Resistance and Nutrient Utilization
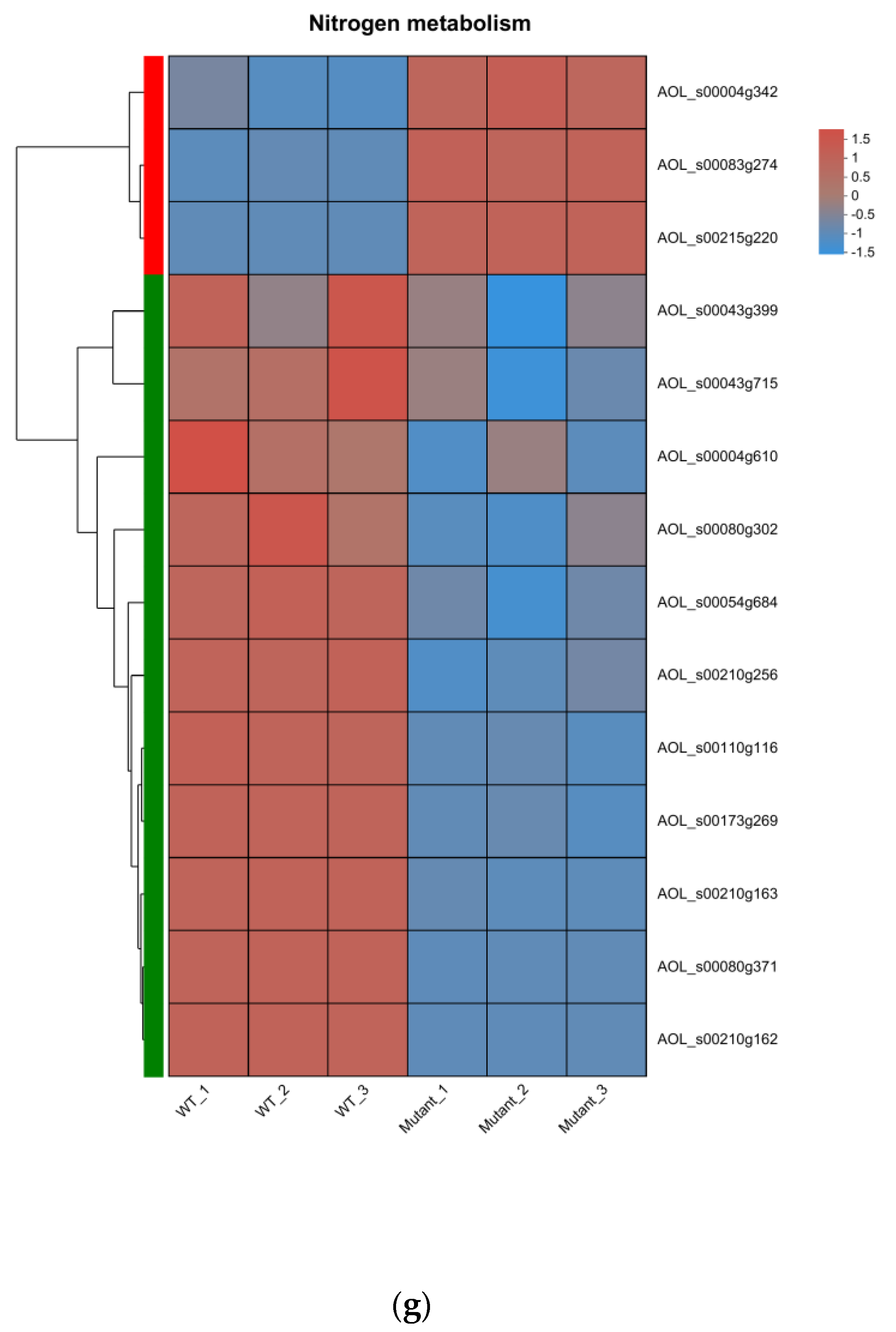
3.6. Transcriptome Analysis of the WT and ΔAoMbp1 Strains
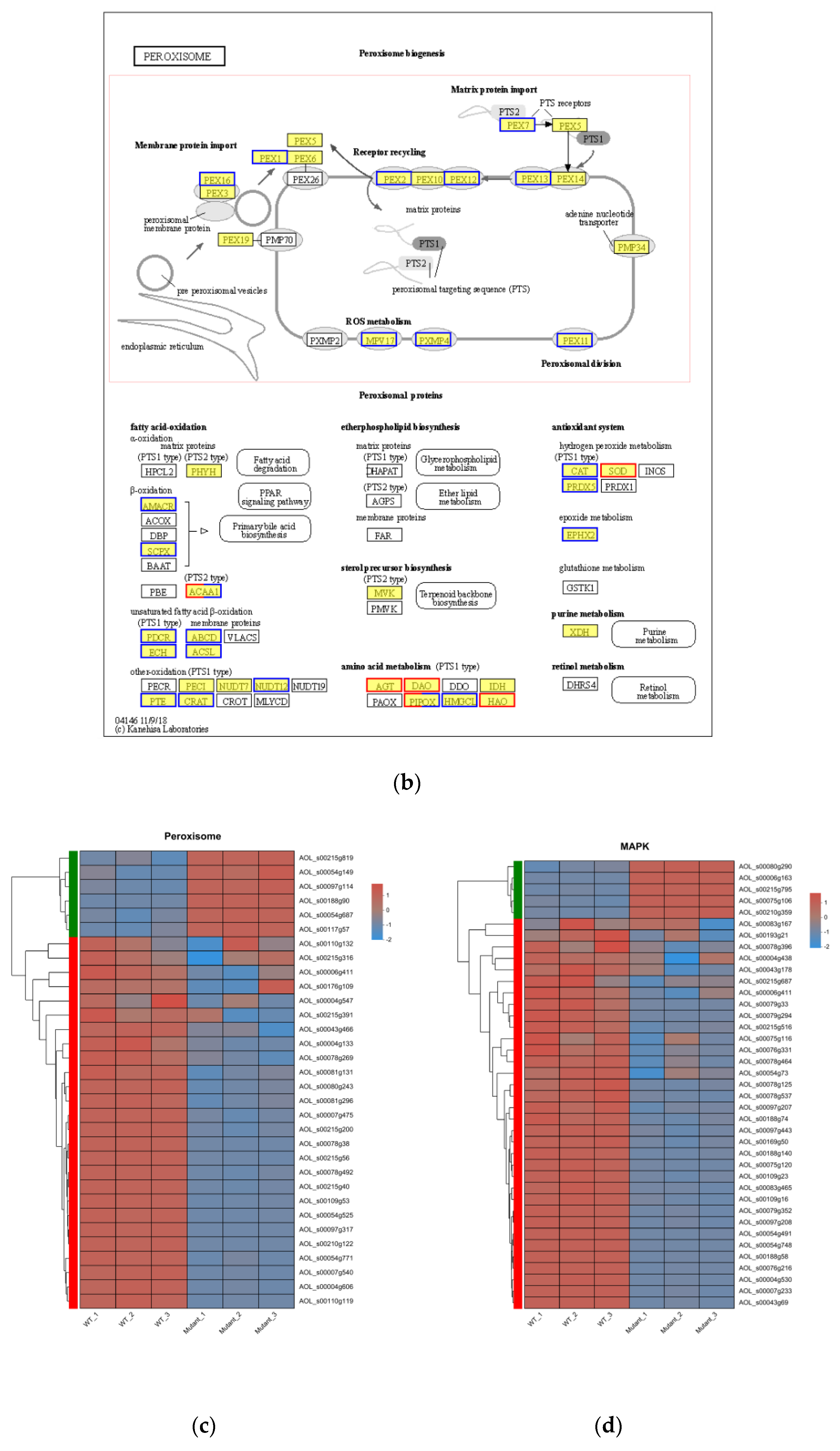
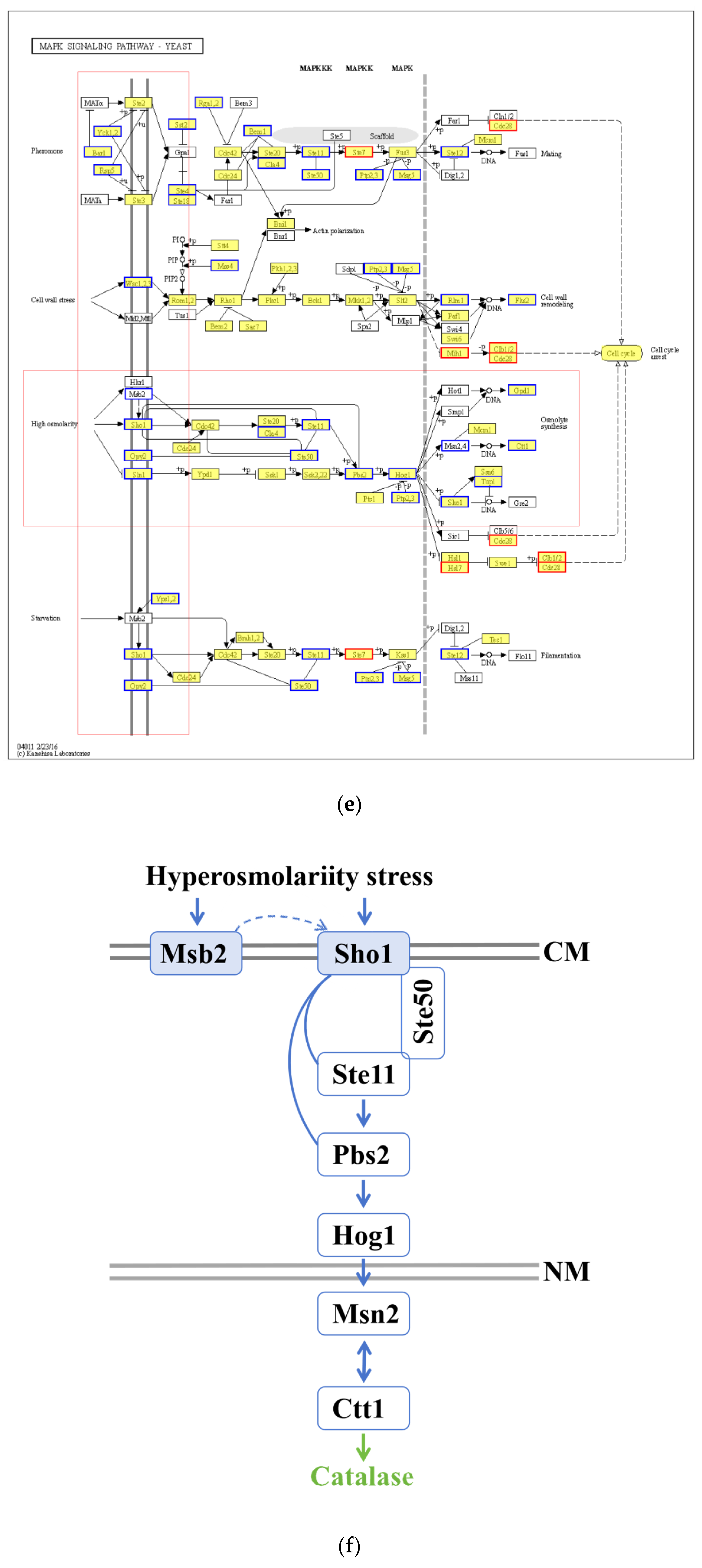
3.7. Functional Analysis of DEGs
3.8. AoMbp1 Directly Binds to the Promoter of the AoSho1 Gene
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freitas, L.A.; Savegnago, R.P.; Menegatto, L.S.; Bem, R.D.D.; Stafuzza, N.B.; Paz, A.; Pires, B.V.; Costa, R.; Paz, C.C.P. Cluster analysis to explore additive-genetic patterns for the identification of sheep resistant, resilient and susceptible to gastrointestinal nematodes. Vet. Parasitol. 2022, 301, 109640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besier, R.B.; Kahn, L.P.; Sargison, N.D.; Van Wyk, J.A. The Pathophysiology, Ecology and Epidemiology of Haemonchus contortus Infection in Small Ruminants. Adv. Parasitol. 2016, 93, 95–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, D.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y. Individual and Combined Application of Nematophagous Fungi as Biological Control Agents against Gastrointestinal Nematodes in Domestic Animals. Pathogens 2022, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.; Yong, R.; Wuen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Buyin, B.; Subu, D.; Zha, H.; Li, H.; Hasi, S. Positivity Rate Investigation and Anthelmintic Resistance Analysis of Gastrointestinal Nematodes in Sheep and Cattle in Ordos, China. Animals 2022, 12, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, R.M. Biology, Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Anthelmintic Resistance in Gastrointestinal Nematodes of Livestock. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Xu, J.; Dong, J.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Gu, J.; Zhang, K.Q.; Zhang, Y. Historical Differentiation and Recent Hybridization in Natural Populations of the Nematode-Trapping Fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora in China. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ma, N.; Rao, W.; Zhang, Y. Recent Advances in Life History Transition with Nematode-Trapping Fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora and Its Application in Sustainable Agriculture. Pathogens 2023, 12, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewc, M.; De Waal, T.; Zintl, A. Biological methods for the control of gastrointestinal nematodes. Vet. J. 2021, 268, 105602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo, T.A.; Fonseca, J.D.S.; Braga, F.R.; Paz-Silva, A.; de Soutello, R.V.G.; de Araújo, J.V. Exploring the Use of Helminthophagous Fungi in the Control of Helminthoses in Horses: A Review. Animals 2025, 15, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Wang, Y.; Tang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, D.; Li, Q.; Niu, X.; Zhang, K.Q.; Yang, J. AoStuA, an APSES transcription factor, regulates the conidiation, trap formation, stress resistance and pathogenicity of the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 4648–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Ma, N.; Bai, N.; Yang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, K.Q.; Yang, J. PKC-SWI6 signaling regulates asexual development, cell wall integrity, stress response, and lifestyle transition in the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 2455–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendler, A.; Medina, E.M.; Buchler, N.E.; de Bruin, R.A.M.; Aharoni, A. The evolution of a G1/S transcriptional network in yeasts. Curr. Genet. 2018, 64, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, R.; Luo, Z.; Lu, Q.; Guan, N.; Chen, D. Deletion of the MBP1 Gene, Involved in the Cell Cycle, Affects Respiration and Pseudohyphal Differentiation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0008821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, L.V.G.; Ray, S.C.; Puccia, R.; Rappleye, C.A. Characterization of the APSES-family transcriptional regulators of Histoplasma capsulatum. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018, 18, foy087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Kawauchi, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Schiphof, K.; Tsuji, K.; Yoshimi, A.; Tanaka, C.; Yano, S.; Nakazawa, T.; Honda, Y. Putative APSES family transcription factor mbp1 plays an essential role in regulating cell wall synthesis in the agaricomycete Pleurotus ostreatus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2024, 175, 103936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, H.; Izumi, T.; Kawauchi, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Tsuji, K.; Yoshimi, A.; Tanaka, C.; Yano, S.; Nakazawa, T.; Honda, Y. Role of putative APSES family transcription factor Swi6 in cell wall synthesis regulation in the agaricomycete Pleurotus ostreatus. Fungal Biol. 2025, 129, 101526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.L.; Hou, J.; Li, X.H.; Feng, M.G.; Ying, S.H. Transcription Activator Swi6 Interacts with Mbp1 in MluI Cell Cycle Box-Binding Complex and Regulates Hyphal Differentiation and Virulence in Beauveria bassiana. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.L.; Lin, H.Y.; Feng, M.G.; Ying, S.H. Mbp1, a component of the MluI cell cycle box-binding complex, contributes to morphological transition and virulence in the filamentous entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Xia, H.; Gao, Z.; Gu, Q.; Liu, W.; Tang, G. FvMbp1-Swi6 complex regulates vegetative growth, stress tolerance, and virulence in Fusarium verticillioides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 473, 134576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, K.Q.; Yang, J. AoPEX1 and AoPEX6 Are Required for Mycelial Growth, Conidiation, Stress Response, Fatty Acid Utilization, and Trap Formation in Arthrobotrys oligospora. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0027522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, L.; Yang, J. The Hog1-Nmd5 signaling pathway regulates asexual development, lipid metabolism, stress response, trap morphogenesis, and secondary metabolism of Arthrobotrys oligospora. Virulence 2025, 16, 2468294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Li, N.A.; Ning, C.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ji, C.; Zhu, X.; Meng, Q.; Xia, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. A Novel LysR Family Factor STM0859 is Associated with the Responses of Salmonella typhimurium to Environmental Stress and Biofilm Formation. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrezuelo, F.; Colomina, N.; Futcher, B.; Aldea, M. The transcriptional network activated by Cln3 cyclin at the G1-to-S transition of the yeast cell cycle. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörter, I.; Momany, M. Fungal Cell Cycle: A Unicellular versus Multicellular Comparison. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Chen, S.A.; Hsueh, Y.P. The High Osmolarity Glycerol (HOG) Pathway Functions in Osmosensing, Trap Morphogenesis and Conidiation of the Nematode-Trapping Fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, M.; Cui, M.; Jia, K.; Lei, D.; Wang, F. Effect of the Sho1 gene on the pathogenicity of Candida albicans and immune function in vivo. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Li, Y.; Bi, Y.; Prusky, D.B. The sensor protein AaSho1 regulates infection structures differentiation, osmotic stress tolerance and virulence via MAPK module AaSte11-AaPbs2-AaHog1 in Alternaria alternata. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 1594–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Han, L.; Ren, Y.; Hu, W.; Xie, X.; Chen, H.; Tang, M. The receptor kinase RiSho1 in Rhizophagus irregularis regulates arbuscule development and drought tolerance during arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. New Phytol. 2024, 242, 2207–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Mu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Wu, J.; Tang, H.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Generic Diagramming Platform (GDP): A comprehensive database of high-quality biomedical graphics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1670–D1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, K.; Duan, S.; Zhao, N.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, K.Q.; Yang, J. Identification of a transcription factor AoMsn2 of the Hog1 signaling pathway contributes to fungal growth, development and pathogenicity in Arthrobotrys oligospora. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 68, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tower, R.J.; Fagarasanu, A.; Aitchison, J.D.; Rachubinski, R.A. The peroxin Pex34p functions with the Pex11 family of peroxisomal divisional proteins to regulate the peroxisome population in yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 1727–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Bai, N.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J. Peroxin Pex14/17 Is Required for Trap Formation, and Plays Pleiotropic Roles in Mycelial Development, Stress Response, and Secondary Metabolism in Arthrobotrys oligospora. mSphere 2023, 8, e0001223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valsecchi, I.; Dupres, V.; Stephen-Victor, E.; Guijarro, J.I.; Gibbons, J.; Beau, R.; Bayry, J.; Coppee, J.Y.; Lafont, F.; Latgé, J.P.; et al. Role of Hydrophobins in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Fungi 2017, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Fang, W. Evolution of the chitin synthase gene family correlates with fungal morphogenesis and adaption to ecological niches. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, T.; Kawauchi, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Han, J.; Koshi, D.; Schiphof, K.; Ramírez, L.; Pisabarro, A.G.; Honda, Y. Pleurotus ostreatus as a model mushroom in genetics, cell biology, and material sciences. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinomiya, M.; Yamada, E.; Yamashita, S.; Ohta, A.; Horiuchi, H. Class I and class II chitin synthases are involved in septum formation in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujimatsu, R.; Takino, J.; Aoki, S.; Nakamura, M.; Haba, H.; Minami, A.; Hiruma, K. A fungal transcription factor converts a beneficial root endophyte into an anthracnose leaf pathogen. Curr. Biol. 2025, 35, 1989-2005.e1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Wei, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Nie, Y.; Meng, Q.; Chen, S.; Wu, M.; Cai, X.; Li, J.; et al. AoMbp1 Governs Conidiation and Trap Morphogenesis in Arthrobotrys oligospora Via Direct Transcriptional Activation of the MAPK Sensor AoSho1. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100736
Li R, Wei L, Sun Y, Zhang C, Nie Y, Meng Q, Chen S, Wu M, Cai X, Li J, et al. AoMbp1 Governs Conidiation and Trap Morphogenesis in Arthrobotrys oligospora Via Direct Transcriptional Activation of the MAPK Sensor AoSho1. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(10):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100736
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ruobing, Lixiang Wei, Yanseng Sun, Chengzhi Zhang, Yuhang Nie, Qinglong Meng, Shuang Chen, Ming Wu, Xuepeng Cai, Jie Li, and et al. 2025. "AoMbp1 Governs Conidiation and Trap Morphogenesis in Arthrobotrys oligospora Via Direct Transcriptional Activation of the MAPK Sensor AoSho1" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 10: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100736
APA StyleLi, R., Wei, L., Sun, Y., Zhang, C., Nie, Y., Meng, Q., Chen, S., Wu, M., Cai, X., Li, J., Meng, Q., & Qiao, J. (2025). AoMbp1 Governs Conidiation and Trap Morphogenesis in Arthrobotrys oligospora Via Direct Transcriptional Activation of the MAPK Sensor AoSho1. Journal of Fungi, 11(10), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100736






