Progression of Structural Lung Disease in Different Aspergillus fumigatus Disease Phenotypes in Children with CF
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data Collection and Phenotype Classification
2.3. Chest CT Acquisition and Scoring
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Aspergillus Disease Phenotypes
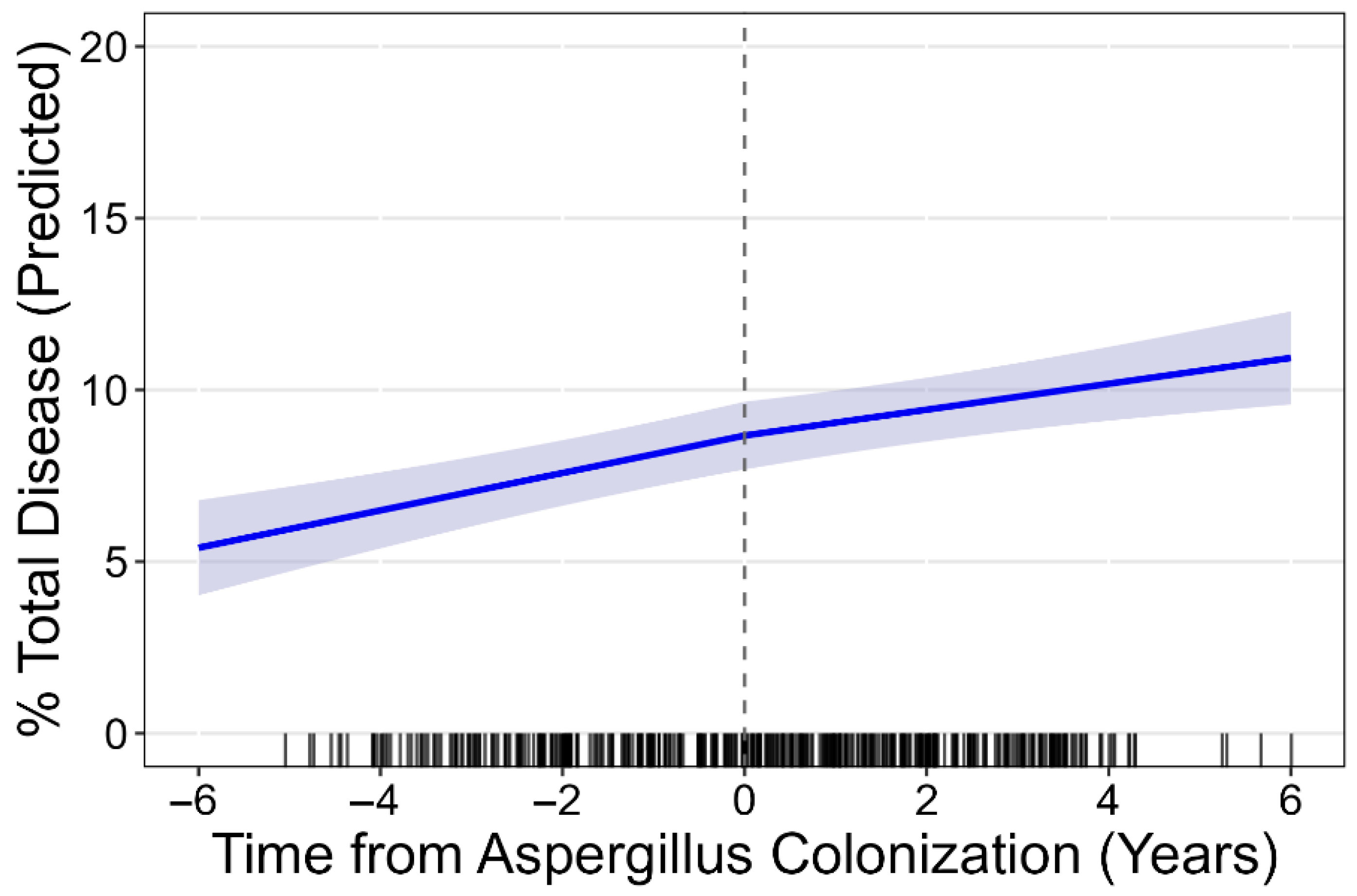
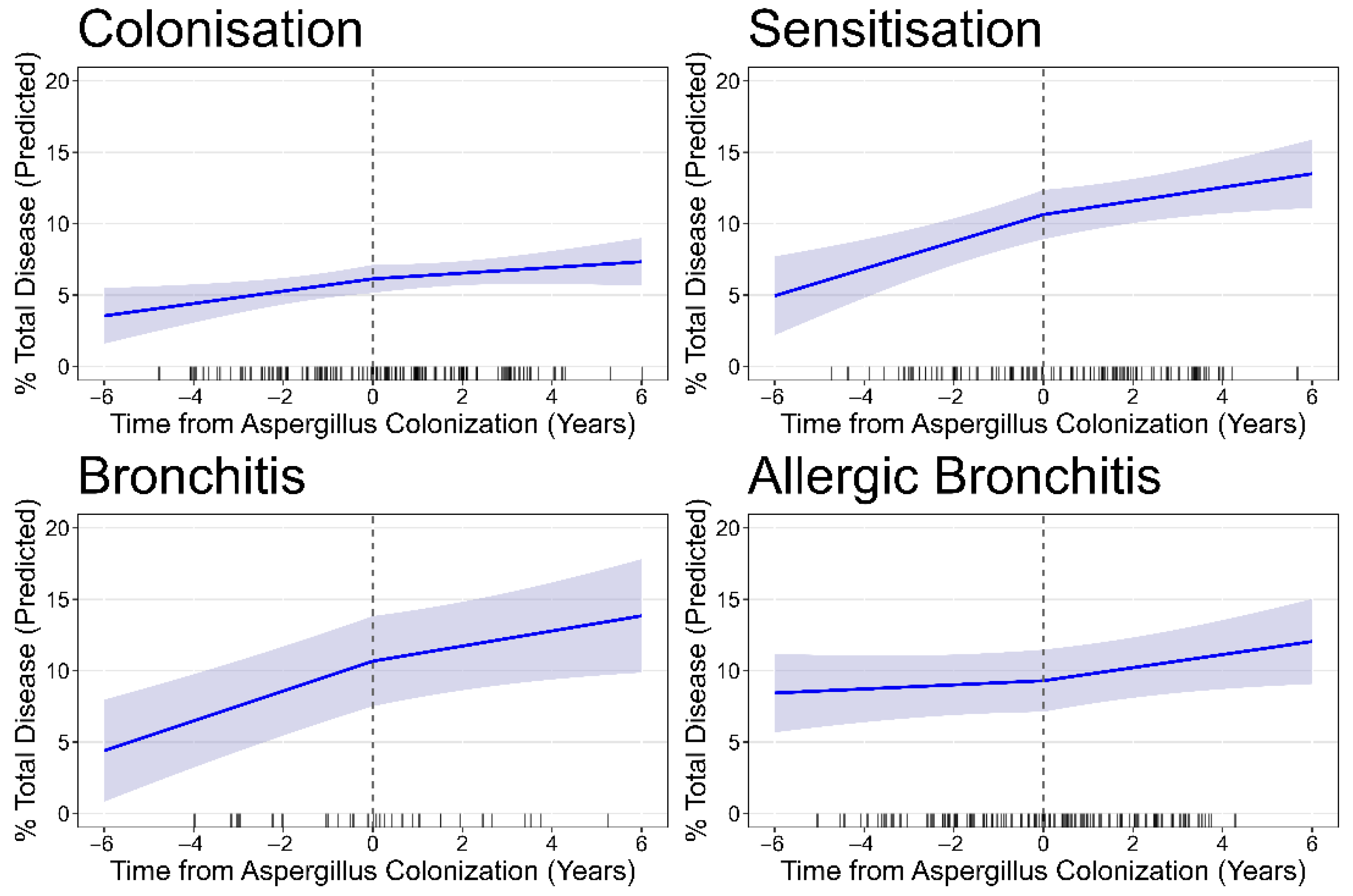
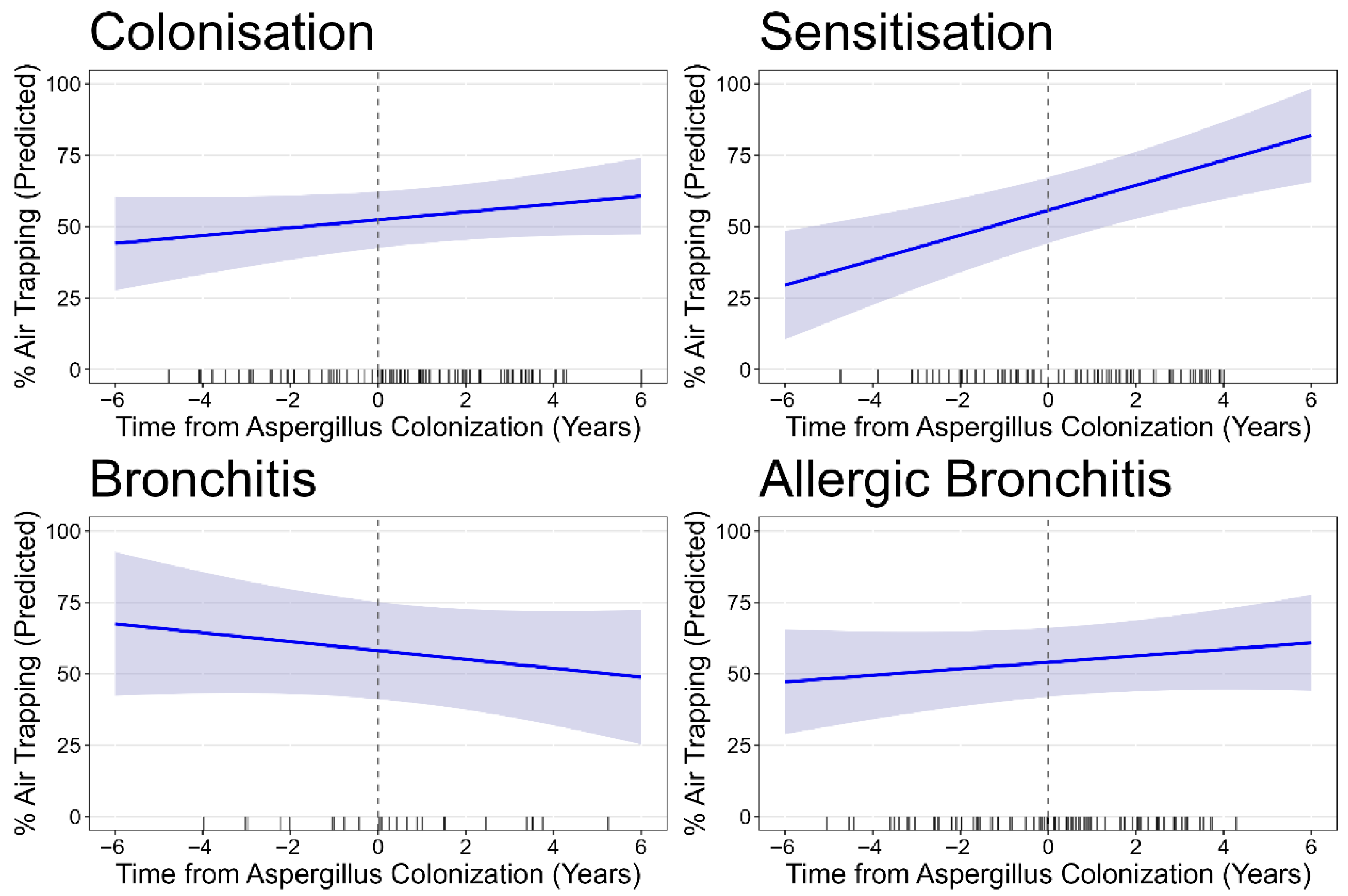
3.2. Progression of Structural Lung Disease
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABPA | Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis |
| Asp | Aspergillus fumigatus |
| Asp+ | Positive Aspergillus fumigatus Culture |
| AT | Air Trapping |
| CF | Cystic Fibrosis |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| CwCF | Children with Cystic Fibrosis |
| IgEAsp | Specific Aspergillus fumigatus IgE |
| IgGAsp | Specific Aspergillus fumigatus IgG |
| PRAGMA | Perth Rotterdam Annotation Grid Morphometric Analysis |
| PsA | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| Pts | Patients |
| SLD | Structural Lung Disease |
Appendix A
References
- Flume, P.A.; Mogayzel, P.J., Jr.; Naureckas, E.T.; Robinson, K.A.; Mueller, G.; Hadjiliadis, D.; Hoag, J.B.; Lubsch, L.; Hazle, L.; Sabadosa, K.; et al. Cystic fibrosis pulmonary guidelines: Chronic medications for maintenance of lung health. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elborn, J.S. Cystic fibrosis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fainardi, V.; Sodini, C.; Deolmi, M.; Ciuni, A.; Skenderaj, K.; Stabile, M.B.; Neglia, C.; Zani, E.M.; Spaggiari, C.; Sverzellati, N.; et al. Clinical Impact of Aspergillus fumigatus in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, C.G.; Dunn, G.; Jones, A.M.; Webb, K.; Gore, R.; Richardson, M.D.; Denning, D.W. Novel immunologic classification of aspergillosis in adult cystic fibrosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 560–566.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, O.; Schultz, A.; Garratt, L.W.; Turkovic, L.; Rosenow, T.; Murray, C.P.; Karpievitch, Y.V.; Akesson, L.; Dalton, S.; Sly, P.D.; et al. Aspergillus Infections and Progression of Structural Lung Disease in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, M.; Emerson, J.; Accurso, F.; Armstrong, D.; Castile, R.; Grimwood, K.; Hiatt, P.; McCoy, K.; MN, S.M.; Ramsey, B.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of oropharyngeal cultures in infants and young children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1999, 28, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesshyre, E.; Wooding, E.; Sey, E.; Warris, A. Aspergillus in Children and Young People with Cystic Fibrosis: A Narrative Review. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Alby, K.; Ng, S.C.; Fleck, V.; Kubrak, C.; Rubenstein, R.C.; Dorgan, D.J.; Kawut, S.M.; Hadjiliadis, D. The presence of Aspergillus fumigatus is associated with worse respiratory quality of life in cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, A.L.; Feng, R.; Glaser, L.J.; Kubrak, C.; Rubenstein, R.C.; Dorgan, D.J.; Hadjiliadis, D.; Kawut, S.M.; Hong, G. The Clinical Association between Aspergillus fumigatus and Respiratory Outcomes in Adolescents and Adults with Cystic Fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2023, 20, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuer, O.; Schultz, A.; Turkovic, L.; de Klerk, N.; Keil, A.D.; Brennan, S.; Harrison, J.; Robertson, C.; Robinson, P.J.; Sly, P.D.; et al. Changing Prevalence of Lower Airway Infections in Young Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mésinèle, J.; Ruffin, M.; Kemgang, A.; Guillot, L.; Boëlle, P.-Y.; Corvol, H. Risk factors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa airway infection and lung function decline in children with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, L.L.; Carver, P.L. Adverse Effects Associated with Long-Term Administration of Azole Antifungal Agents. Drugs 2019, 79, 833–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.R.; Nguyen, M.-V.H.; A Donnelley, M.; Iii, G.R.T. Tolerability of long-term fluconazole therapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, N.Z.; Southern, K.W. Antifungal therapies for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in people with cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 9, Cd002204. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, C.G.; Moore, C.B.; Jones, A.M.; Webb, A.K.; Denning, D.W. IgE-mediated immune responses and airway detection of Aspergillus and Candida in adult cystic fibrosis. Chest 2013, 143, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, C.; Eschenhagen, P.; Schmidt, H.; Hohnstein, T.; Iwert, C.; Grehn, C.; Roehmel, J.; Steinke, E.; Stahl, M.; Lozza, L.; et al. Antigen specificity and cross-reactivity drive functionally diverse anti-Aspergillus fumigatus T cell responses in cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e161593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poore, T.S.; Zemanick, E.T. Infection, Allergy, and Inflammation: The Role of Aspergillus fumigatus in Cystic Fibrosis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Garg, M.; Saikia, B.; Chakrabarti, A. Cut-off values of serum IgE (total and A. fumigatus-specific) and eosinophil count in differentiating allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis from asthma. Mycoses 2014, 57, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, P.A.; Tiddens, H.A. Cystic fibrosis specific computed tomography scoring. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2007, 4, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, N.R.; Janssens, H.M.; Andrinopoulou, E.; Tiddens, H.A.W.M. Airway disease on chest computed tomography of preschool children with cystic fibrosis is associated with school-age bronchiectasis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 55, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speirs, J.J.; van der Ent, C.K.; Beekman, J.M. Effects of Aspergillus fumigatus colonization on lung function in cystic fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2012, 18, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Elders, B.B.; Warris, A.; Caudri, D.; Ciet, P.; Tiddens, H.A. Aspergillus-related lung disease in people with cystic fibrosis: Can imaging help us to diagnose disease? Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomquist, A.; Inghammar, M.; Al Shakirchi, M.; Ericson, P.; Krantz, C.; Svedberg, M.; Lindblad, A.; Påhlman, L.I. Persistent Aspergillus fumigatus infection in cystic fibrosis: Impact on lung function and role of treatment of asymptomatic colonization-a registry-based case-control study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, M.; McKay, K.; Koch, C.; Cooper, P.J. Prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis in an area with a high frequency of atopy. Respir. Med. 2005, 99, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Muthu, V.; Sehgal, I.S.; Dhooria, S.; Prasad, K.T.; Soundappan, K.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Chakrabarti, A. Aspergillus Sensitization and Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis in Asthmatic Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Desai, S.; Moss, R.B.; Eschenhagen, P.; Quon, B.S.; Schwarz, C. Clinician variability in the diagnosis and treatment of aspergillus fumigatus-related conditions in cystic fibrosis: An international survey. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düesberg, U.; Wosniok, J.; Naehrlich, L.; Eschenhagen, P.; Schwarz, C. Risk factors for respiratory Aspergillus fumigatus in German Cystic Fibrosis patients and impact on lung function. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.W.; Somers, M.E.; Burgener, E.B. Highly effective cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance (regulator) modulator therapy: Shifting the curve for most while leaving some further behind. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2024, 36, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southern, K.W.; Castellani, C.; Lammertyn, E.; Smyth, A.; VanDevanter, D.; van Koningsbruggen-Rietschel, S.; Barben, J.; Bevan, A.; Brokaar, E.; Collins, S.; et al. Standards of care for CFTR variant-specific therapy (including modulators) for people with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 22, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, C.; Romanowska, E.; Mainz, J.; Grassmann, F.; Steidle, F.; Genierlich, K.; Martin-Souto, L.; Eschenhagen, P. P167 Pulmonary infections due to fungi in the era of CFTR modulator therapy. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2025, 24, S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Descriptive | All Patients | Asp Colonisation | Asp Sensitisation | Asp Bronchitis | Asp Allergic Bronchitis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgEAsp − IgGAsp − | IgEAsp + IgGAsp − | IgEAsp − IgGAsp + | IgEAsp + IgGAsp + | ||
| Number of patients | 125 | 44 | 32 | 10 | 39 |
| Number of scans | 382 | 131 | 102 | 30 | 119 |
| Male gender (n, %) | 59 (47.2%) | 20 (45.4%) | 14 (31.8%) | 5 (50%) | 20 (52.3%) |
| Age first Asp+ culture (yrs) (median [IQR]) | 9 [6] | 6.5 [8.25] | 10 [5] | 8.5 [4.5] | 11 [4] |
| Age first included CT (yrs) (years: median [IQR]) | 7 [5] | 6 [7] | 7.5 [5] | 4.5 [6] | 8 [3] |
| Age last included CT (yrs) (median [IQR]) | 12 [7] | 9 [7.25] | 13.5 [5.25] | 11 [2.5] | 13 [3.8] |
| Any positive PsA culture (n, %) | 96 (76.8%) | 28 (63.6%) | 26 (81.3%) | 9 (90.0%) | 33 (84.6%) |
| Developed ABPA (n, %) * | 17 (13.6%) | 1 (2.3%) | 3 (9.4%) | 1 (10.0%) | 12 (30.7%) |
| Time between first Asp+ and diagnosis ABPA (months) (median [IQR]) | 10 [21] | 60 | 5 [22.5] | 19 | 7.5 [16] |
| Total % Disease | Bronchiectasis% | Atelectasis% | Airway Wall Thickening% | Mucus Plugging% | Air Trapping% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full study population | 125 pts with 382 CTs | 105 pts; 266 CTs | |||||
| At first Asp+ | 8.51 (7.59, 9.43) | 6.16 (5.45, 6.86) | 0.88 (0.70, 1.07) | 1.04 (0.97, 1.12) | 1.27 (0.98, 1.56) | 57.49 (53.14, 61.84) | |
| Progression/year | 0.46 (0.35, 0.57) | 0.42 (0.32, 0.51) | −0.05 (−0.11, 0.01) | 0.01(−0.01, 0.03) | 0.04 (−0.02, 0.10) | 1.53 (0.40, 2.67) | |
| Asp colonisation | 44 pts; 131 CTs | 37 pts; 90 CTs | |||||
| Baseline | 5.92 (5.09, 6.75) | 4.35 (3.66, 5.04) | 0.81 (0.50, 1.11) | 0.99 (0.87, 1.11) | 0.58 (0.36, 0.81) | 53.60 (44.59, 62.61) | |
| Progression/year | 0.31 (0.13, 0.49) | 0.24 (0.08, 0.39) | −0.08 (−0.2, 0.05) | 0.04 (0.001, 0.08) | 0.02 (−0.04, 0.08) | 1.53 (−0.42, 3.48) | |
| Asp sensitisation | 32 pts; 102 CTs | 25 pts; 67 CTs | |||||
| Baseline | 10.16 (8.61, 11.70) | 7.73 (6.48, 8.98) | 0.65 (0.44, 0.85) | 1.00 (0.85, 1.15) | 1.34 (0.82, 1.86) | 57.65 (51.10, 64.20) | |
| Progression/year | 0.70 (0.47, 0.92) | 0.62 (0.43, 0.80) | 0.02 (−0.01, 0.05) | −0.01 (−0.05, 0.02) | 0.12 (−0.01, 0.24) | 4.30 (1.75, 6.85) | |
| Asp bronchitis | 10 pts; 30 CTs | 8 pts; 25 CTs | |||||
| Baseline | 10.15 (0.80, 13.49) | 7.07 (4.62, 9.51) | 0.87 (−0.06, 1.80) | 1.29 (1.03, 1.55) | 1.72 (0.52, 2.92) | 62.01 (53.01, 71.02) | |
| Progression/year | 0.85 (0.57, 1.13) | 0.60 (0.34, 0.86) | 0.11 (−0.04, 0.25) | −0.03 (−0.11, 0.05) | 0.23 (0.01, 0.46) | −2.38 (−5.59, 0.082) | |
| Asp allergic bronchitis | 39 pts; 119 CTs | 35 pts; 84 CTs | |||||
| Baseline | 9.59 (7.48, 11.70) | 6.65 (5.09, 8.22) | 1.14 (0.74, 1.55) | 1.08 (0.09, 1.23) | 1.81 (1.12, 2.50) | 57.85 (50.37, 65.33) | |
| Progression/year | 0.28 (0.07, 0.50) | 0.36 (0.18, 0.54) | −0.06 (−0.18, 0.07) | 0.01 (−0.03, 0.04) | −0.06 (−0.20, 0.90) | 1.29 (−0.33, 2.92) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mollica, F.; Andrinopoulou, E.-R.; Ikiz, B.Y.; Makani, P.; Tiddens, H.A.W.M.; Caudri, D. Progression of Structural Lung Disease in Different Aspergillus fumigatus Disease Phenotypes in Children with CF. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100689
Mollica F, Andrinopoulou E-R, Ikiz BY, Makani P, Tiddens HAWM, Caudri D. Progression of Structural Lung Disease in Different Aspergillus fumigatus Disease Phenotypes in Children with CF. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(10):689. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100689
Chicago/Turabian StyleMollica, Federico, Eleni-Rosalina Andrinopoulou, Beyza Y. Ikiz, Punitkumar Makani, Harm A. W. M. Tiddens, and Daan Caudri. 2025. "Progression of Structural Lung Disease in Different Aspergillus fumigatus Disease Phenotypes in Children with CF" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 10: 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100689
APA StyleMollica, F., Andrinopoulou, E.-R., Ikiz, B. Y., Makani, P., Tiddens, H. A. W. M., & Caudri, D. (2025). Progression of Structural Lung Disease in Different Aspergillus fumigatus Disease Phenotypes in Children with CF. Journal of Fungi, 11(10), 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100689







