Natural Prevalence, Molecular Characteristics, and Biological Activity of Metarhizium rileyi (Farlow) Isolated from Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) Larvae in Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
2.2. Fungal Isolates
2.3. Single-Concentration Bioassays
2.4. Genetic Characterization
2.4.1. DNA Extraction
2.4.2. Amplification of the β-Tubulin Gene
2.5. Conidia Concentration–Mortality and Speed of Kill Response
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fungi Field Collection
3.2. Single-Concentration Bioassays
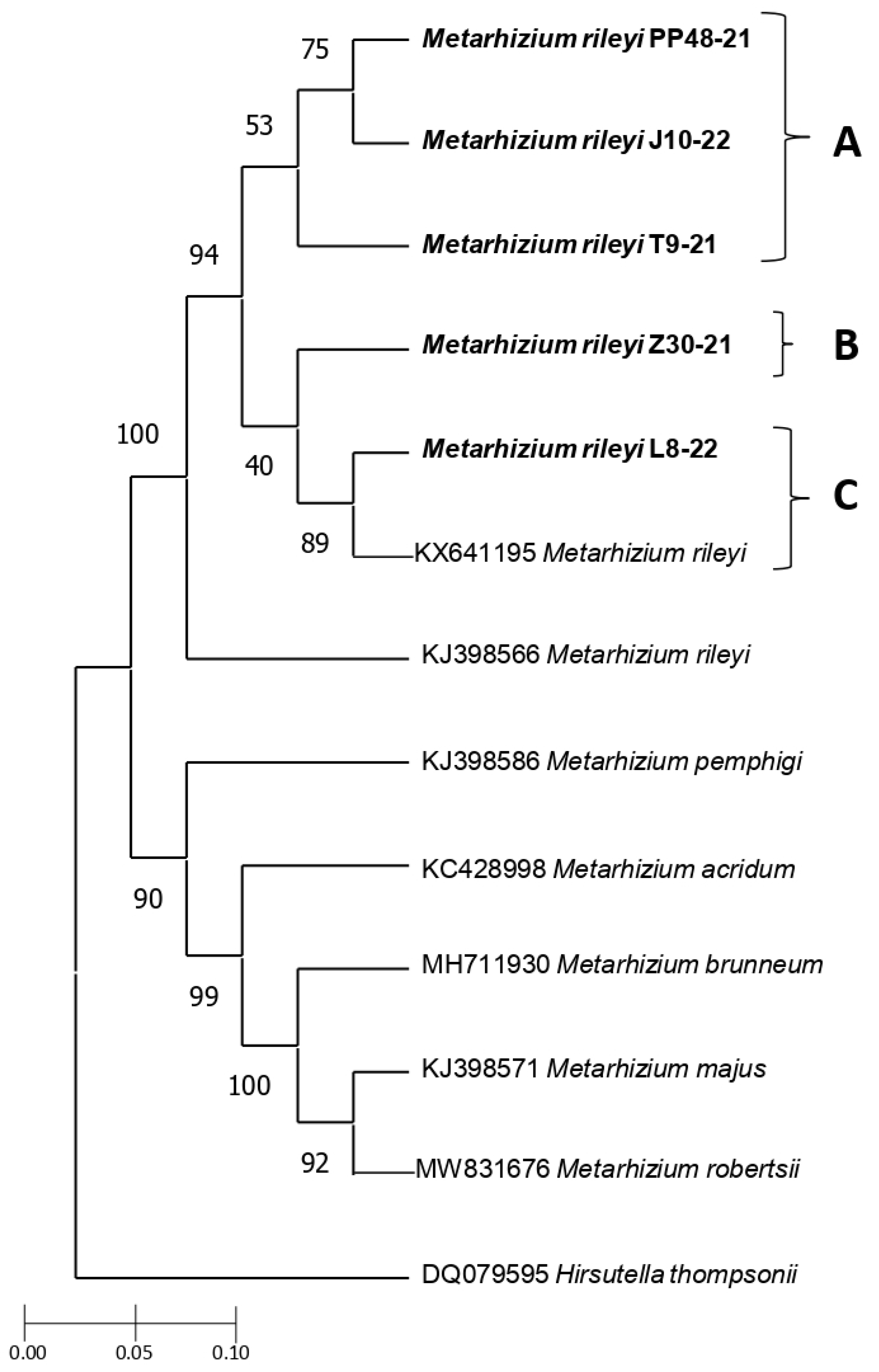
3.3. Genetic Characterization
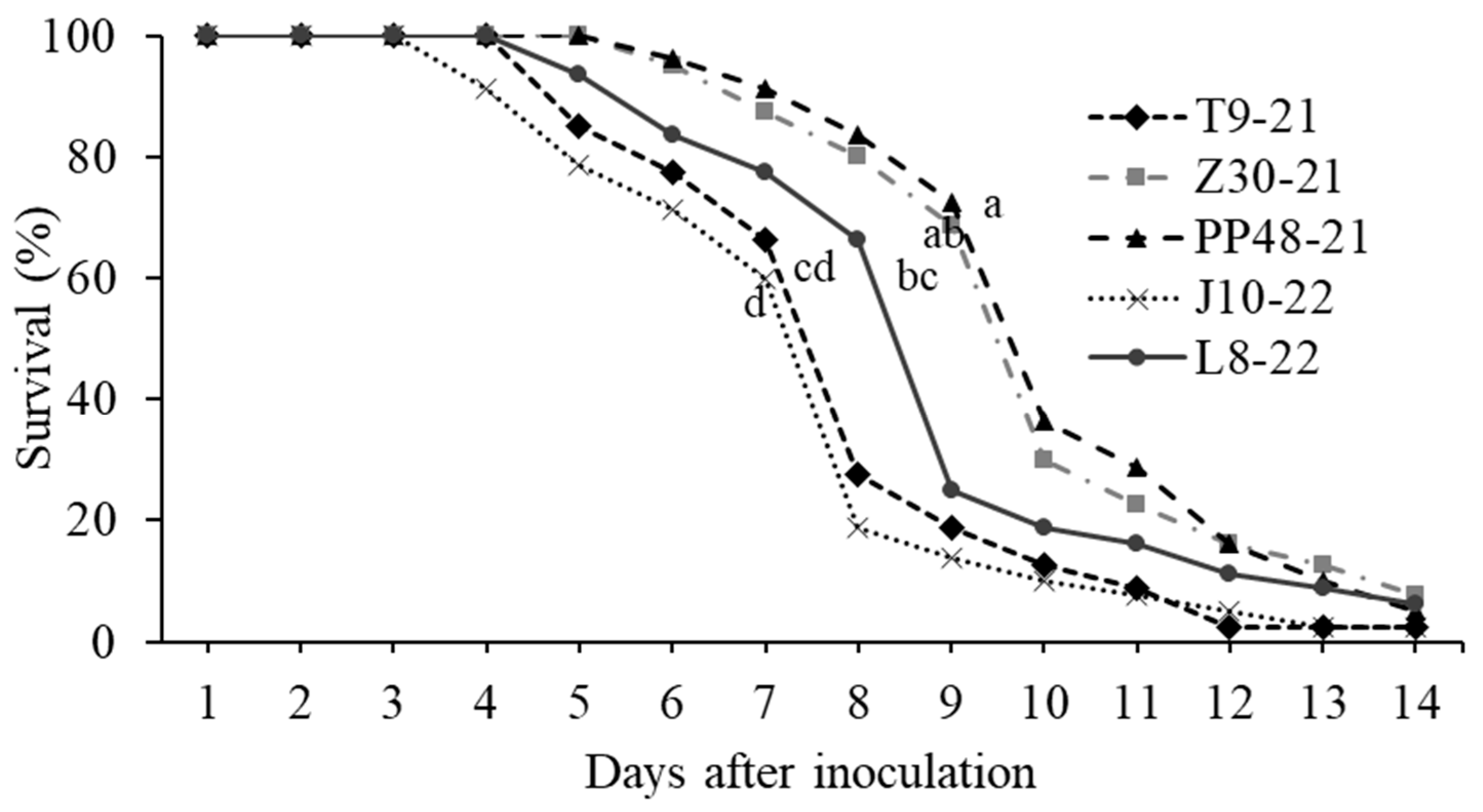
3.4. Bioassays with Five Selected Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neupane, D.; Adhikari, P.; Bhattarai, D.; Rana, B.; Ahmed, Z.; Sharma, U.; Adhikari, D. Does climate change affect the yield of the top three cereals and food security in the world? Earth 2022, 3, 45–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Sairam, M.; Sahoo, U.; Shankar, T.; Maitra, S. Growth, productivity and economics of maize as influenced by maize-legume intercropping system. Farming Manag. 2022, 7, 61–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Yainna, S.; Tay, W.T.; Durand, K.; Fiteni, E.; Hilliou, F.; Legeai, F.; Clamens, A.; Gimenez, S.; Asokan, R.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; et al. The evolutionary process of invasion in the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, W.T.; Meagher, R.L., Jr.; Czepak, C.; Groot, A.T. Spodoptera frugiperda: Ecology, evolution, and management options of an invasive species. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2023, 68, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimweta, M.; Nyakudya, I.W.; Jimu, L.; Mashingaidze, A.B. Fall armyworm [Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith)] damage in maize: Management options for flood-recession cropping smallholder farmers. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2020, 66, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, C.A.; Pellegaud, J.G.; Nava-Camberos, U.; Lugo-Barrera, D.; Vega-Aquino, P.; Coello, J.; Terán-Vargas, A.P.; Vargas-Camplis, J. Maize pests in Mexico and challenges for the adoption of integrated pest management programs. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2014, 5, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cech, R.M.; Jovanovic, S.; Kegley, S.; Koen Hertoge, K.; Leisch, F.; Zaller, J.G. Reducing overall herbicide use may reduce risks to humans but increase toxic loads to honeybees, earthworms, and birds. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenis, M.; Benelli, G.; Biondi, A.; Calatayud, P.A.; Day, R.; Desneux, N.; Harrison, R.; Kriticos, D.; Rwomushana, I.; van den Berg, J.; et al. Invasiveness, biology, ecology, and management of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Entomol. Gen. 2022, 43, 187–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronza, E.; Specht, A.; Heinzen, H.; de Barros, N. Metarhizium (Nomuraea) rileyi as biological control agent. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 1243–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Xie, W.; Ye, J.Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, D.Y.; Zhi, J.R.; Zou, X. New potential strains controlling Spodoptera frugiperda in China: Cordyceps cateniannulata and Metarhizium rileyi. BioControl 2020, 65, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razinger, J.; Praprotnik, E.; Schroers, H.-J. Bioaugmentation of entomopathogenic fungi for sustainable Agriotes larvae (Wireworms) management in maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 535005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, W.; Adnan, M.; Shabbir, A.; Naveed, H.; Abubakar, Y.S.; Qasim, M.; Tayyab, M.; Noman, A.; Nisar, M.S.; Khan, K.A.; et al. Insect-fungal-interactions: A detailed review on entomopathogenic fungi pathogenicity to combat insect pests. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 159, 105122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johny, S.; Kyei-Poky, G.; Gauthier, D.; Van Frankenhuyzen, K.; Krell, P.J. Characterization and virulence of Beauveria spp. recovered from emerald ash borer in southwestern Ontario, Canada. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 11, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, B.; St. Leger, R.J. Genetically engineering better fungal biopesticides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanujam, B.; Poornesha, B.; Shylesha, A.N. Effect of entomopathogenic fungi against invasive pest Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in maize. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2020, 30, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Vimala, P.S.; Prasad, Y.G.; Chowdary, D.A.; Rao, L.M.; Balakrishnan, K. Identification of virulent isolates of the entomapathogenic fungus Nomuraea rileyi (F) Samson for the management of Helicoverpa armigera and Spodoptera litura. Mycopathologia 2003, 156, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepler, R.M.; Humber, R.A.; Bischoff, J.F.; Rehner, S.A. Clarification of generic and species boundaries for Metarhizium and related fungi through multigene phylogenetics. Mycologia 2014, 106, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajek, A.E.; St. Leger, R.J. Interactions between fungal pathogens and insect hosts. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1994, 39, 293–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; O’Neil, R.J. Population dynamics of Spodoptera frugiperda Smith (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and associated arthropod natural enemies in Honduran subsistence maize. Crop Prot. 2006, 25, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucias, D.G.; Liu, S.; Meagher, R.; Baniszewski, J. Fungal dimorphism in the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium rileyi: Detection of an in vivo quorum-sensing system. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 136, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, B.; Verma, S.; Sharma, P.L.; Chandel, R.S.; Gaikwad, M.B.; Banshtu, T.; Sharma, P. Evaluation of Metarhizium rileyi Farlow (Samson) impregnated with azadirachtin and indoxacarb against Helicoverpa armigera. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2021, 31, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biaggioni, R.; Faria, M.; Souza, D.; Sosa-Gómez, D.R. The potential impact of chemical fungicides on the efficacy of Metarhizium rileyi and the occurrence of Pandora gammae on caterpillars in soybean crops. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 647–657. [Google Scholar]
- Bosa, C.F.; Chávez, D.; Torres, L.; Paríz, A.; Villamizar, L.; Cotes, A.M. Evaluación de aislamientos nativos de Nomuraea rileyi para el control de Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Rev. Colomb. Entomol. 2004, 30, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firake, D.M.; Behere, G.T. Natural mortality of invasive fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in maize agroecosystems of northeast India. Biol. Control 2020, 148, 104–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visalakshi, M.; Kishore, P.; Chandra, V.; Bharathalaxmi, M.; Manisha, B.L.; Upendhar, S. Studies on mycosis of Metarhizium (Nomuraea) rileyi on Spodoptera frugiperda infesting maize in Andhra Pradesh, India. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2020, 30, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Yang, K.H.; Li, X.L.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.X.; Liu, X.S. Infection of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium rileyi suppresses cellular immunity and activates humoral antibacterial immunity of the host Spodoptera frugiperda. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 2828–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, Z.; Niu, H.; Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Guo, H. Characterization of entomopathogenic fungi from invasive fall armyworm in China and their risk to native pests. J. Appl. Entomol. 2023, 17, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Inglis, G.D.; Hausner, G. Phylogenetic relationships among strains of the entomopathogenic fungus, Nomuraea rileyi, as revealed by partial beta-tubulin sequences and inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) analysis. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 34, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.R.; Elkinton, J. Pathogenicity and virulence. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2004, 85, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitout, S.; Blues, R. Elevage de chenilles de vingt-huit especes de Lepidopteres Noctuidae et de deux especes d’Arctiidae sur milieu artificiel simple. Particularites de l’elevage selon les especes. Ann. Zool. Ecol. Anim. 1974, 6, 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, S.W.; Hanway, J.J.; Benson, G.O. How a Corn Plant Develops; Special Report No. 48; Iowa State University of Science and Technology Cooperative Extension Service: Ames, IA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Akutse, K.S.; Maniania, N.K.; Fiaboe, K.K.; Van Den Berg, M.J.; Ekesi, S. Endophytic colonization of Vicia faba and Phaseolus vulgaris (Fabaceae) by fungal pathogens and their effects on the life history parameters of Liriomyza huidobrensis (Diptera: Agromyzidae). Fungal Ecol. 2013, 6, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettel, M.S.; Inglis, G.D. Fungi: Hyphomycetes. In Manual of Techniques in Insect Pathology, 2nd ed.; Lacey, L.A., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2012; pp. 213–249. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, M.C. Production of Beauveria bassiana (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) sympoduloconidia in-submerged culture. Entomophaga 1989, 34, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevim, A.; Demir, I.; Demirbağ, Z. Molecular characterization and virulence of Beauveria spp. from the pine processionari moth, Thaumetopoea pityocampa (Lepidoptera: Thaumetopoeidae). Mycopathologia 2010, 170, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvo, M.L.; Pereira-Junior, R.A.; Rodrigues, J.; López Lastra, C.C.; García, J.J.; Fernandes, É.K.K.; Luz, C. UV-B radiation reduces in vitro germination of Metarhizium anisopliae s.l. but does not affect virulence in fungus-treated Aedes aegypti adults and development on dead mosquitoes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humber, R.A. Identification of entomopathogenic fungi. In Manual of Techniques in Insect Pathology, 2nd ed.; Lacey, L.A., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2012; pp. 151–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakuwela, T.; Hatting, J.; Bock, C.; Vega, F.E.; Wells, L.; Mbata, G.N.; Shapiro-Ilan, D. Establishment of Beauveria bassiana as a fungal endophyte in pecan (Carya illinoinensis) seedlings and its virulence against pecan insect pests. Biol. Control 2020, 140, 104102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkerli, J.; Widmer, F. Molecular ecology of fungal entomopathogens: Molecular genetic tools and their applications in population and fate studies. BioControl 2010, 55, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez-García, M.; Rios-Velasco, C.; Berlanga-Reyes, D.I.; Acosta-Muñiz, C.H.; Salas-Marina, M.A.; Cambero-Campos, J. Occurrence of natural enemies of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Chihuahua, Mexico. Fla. Entomol. 2015, 98, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Velasco, C.; Cerna-Chávez, E.; Sánchez-Peña, S.; Gallegos-Morales, G. Natural epizootic of the entomopathogenic fungus Nomuraea rileyi (Farlow) Samson infecting Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Coahuila México. J. Res. Lepid. 2010, 43, 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ríos-Velasco, C.; Gallegos-Morales, G.; Cambero-Campos, J.; Cerna-Chávez, E.; Del Rincón-Castro, M.C.; Valenzuela-García, R. Natural enemies of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Coahuila, México. Fla. Entomol. 2011, 94, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Vírgen, O.; Campos, J.C.; Bermudez, A.R.; Velasco, C.R.; Cazola, C.C.; Aquino, N.I.; Cancino, E. Parasitoids and entomopathogens of the Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Nayarit, Mexico. Southwest. Entomol. 2013, 38, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezama-Gutiérrez, R.; Hamm, J.J.; Molina-Ochoa, J.; López-Edwards, M.; Pescador-Rubio, A.; González-Ramírez, M.; Styer, E.L. Occurrence of entomopathogens of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the Mexican states of Michoacán, Colima, Jalisco, and Tamaulipas. Fla. Entomol. 2001, 84, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Nájera, R.E.; Ruíz-Estudillo, R.A.; Sánchez-Yañez, J.M.; Molina-Ochoa, J.; Skoda, S.R.; Coutiño-Ruíz, R.; Pinto-Ruíz, R.; Guevara-Hernández, F.; Foster, J.E. Occurrence of entomopathogenic fungi and parasitic nematodes on Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae collected in central Chiapas, México. Fla. Entomol. 2013, 96, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginting, S.; Nadrawati, N.; Zarkani, A.; Sumarni, T. Natural incidence of entomopathogenic fungus Nomuraea rileyi on Spodoptera frugiperda infesting corn in Bengkulu. J. Hama Penyakit Tumbuh. Trop. 2020, 20, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Gu, Z.; Zhou, J. High virulence of a naturally occurring entomopathogenic fungal isolate, Metarhizium (Nomurea) rileyi, against Spodoptera frugiperda. J. Appl. Entomol. 2022, 146, 659–665. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.; Peng, Y.; Di, T.; Du, G.; Chen, B. Virulence of Metarhizium rileyi is determined by its growth and antioxidant stress and the protective and detoxifying enzymes of Spodoptera frugiperda. Insects 2023, 14, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Ochoa, J.; Lezama-Gutiérrez, R.; González-Ramírez, M.; Lopez-Edwards, M.; Rodríguez-Vega, M.A.; Arceo-Palacios, F. Pathogens and parasitic nematodes associated with populations of fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae in Mexico. Fla. Entomol. 2003, 86, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Ramírez, A.; Enríquez-Vara, J.N.; Guizar-Gonzalez, C.; Lobit, P.; Gómez-Donrantes, N.; Rincón-Enríquez, G.; Quiñones-Aguilar, E.E.; López-Pérez, L. Presencia de hongos entomopagótenos nativos en suelos cultivados con maíz del municipio de Epitacio Huerta, Michoacán. Biotecnol. Sustentabilidad 2018, 3, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell, T.E.; Shapiro-Ilan, I. Susceptibility of endemic and exotic North American ladybirds (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to endemic fungal entomopathogens. Eur. J. Entomol. 2008, 105, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.H.; Borgemeister, C.; Poehling, H.M.; Zimmermann, G. Laboratory investigations on the potential of entomopathogenic fungi for biocontrol of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae and pupae. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldarriaga-Ausique, J.J.; D’Alessandro, C.P.; Conceschi, M.R.; Mascarin, G.M.; Delalibera Júnior, I. Efficacy of entomopathogenic fungi against adult Diaphorina citri from laboratory to field applications. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidochka, M.J.; Kamp, A.M.; Lavender, T.M.; Dekoning, J.; De Croos, J.N.A. Habitat association in two genetic groups of the insect-pathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae: Uncovering cryptic species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couceiro, J.C.; De Fine Licht, H.H.; Delalibera, I., Jr.; Meyling, N.V. Comparative gene expression and genomics reflect geographical divergence in the plant symbiotic and entomopathogenic fungal genus Metarhizium. Fungal Ecol. 2022, 60, 101190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Y. Complete mitogenome of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium rileyi. Mitochondrial DNA Part B Resour. 2021, 5, 1492–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Yin, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. The high osmotic response and cell wall integrity pathways cooperate to regulate morphology, microsclerotia development, and virulence in Metarhizium rileyi. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Zhang, J.; Nian, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Ren, G. Analogous and diverse functions of APSES-type transcription factors in the morphogenesis of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium rileyi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02928-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yin, Y.; Li, R.; Lin, Y.; Deng, C.; Yang, K.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z. Pathogenicity of Metarhizium rileyi against Spodoptera litura larvae: Appressorium differentiation, proliferation in hemolymph, immune interaction, and reemergence of mycelium. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2021, 150, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begerow, D.; Beate, J.; Oberwinkler, F. Evolutionary relationships among β-tubulin gene sequences of basidiomycetous fungi. Mycol. Res. 2004, 108, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Luan, F.; He, L.; Pu, S.; Li, Z. Genetic diversity and population structure of the Chinese fungus Metarhizium rileyi causing green muscardine in silkworm. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 140, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucias, D.; Tigano, M.S.; Sosa-Gomez, D.R.; Glare, T.R.; Inglis, P.W. Genotypic properties of the entomopathogenic fungus Nomuraea rileyi. Biol. Control 2000, 19, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, J.F.; Rehner, S.A.; Humber, R.A. A multilocus phylogeny of the Metarhizium anisopliae linage. Mycologia 2009, 101, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, L.R.B.; Rossato, M.; Ribeiro, R.T.D.S.; Barros, N.M.D. Characterization of Nomuraea rileyi strains using polymorphic DNA, virulence and enzyme activity. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2003, 46, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, U.K.; Reineke, A.; Rao, U.C.M.; Reddy, N.R.; Khan, A.P. AFLP and single-strand conformation polymorphism studies of recombination in the entomopathogenic fungus Nomuraea rileyi. Mycol. Res. 2007, 111, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, G.D.; Goettel, M.S.; Butt, T.M.; Strasser, H. Use of Hyphomycetous fungi for managing insect pests. In Fungi as Biocontrol Agent Progress, Problems and Potential; Butt, T.M., Jackson, C., Magan, N., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2001; p. 2370. [Google Scholar]
- De La Rosa, W.; Lopez, F.L.; Liedo, P. Beauveria bassiana as a pathogen of the Mexican fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) under laboratory conditions. J. Econ. Entomol. 2002, 95, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xia, Y.Y.; Kim, B.; Keyhani, N.O. Two hydrophobins are involved in fungal spore coat rodlet layer assembly and each play distinct roles in surface interactions, development and pathogenesis in the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Avalos, A.M.; Bivián-Hernández, M.A.; Ibarra, J.E.; Del Rincón-Castro, M.C. High virulence of Mexican entomopathogenic fungi against Fall Armyworm, (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 112, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
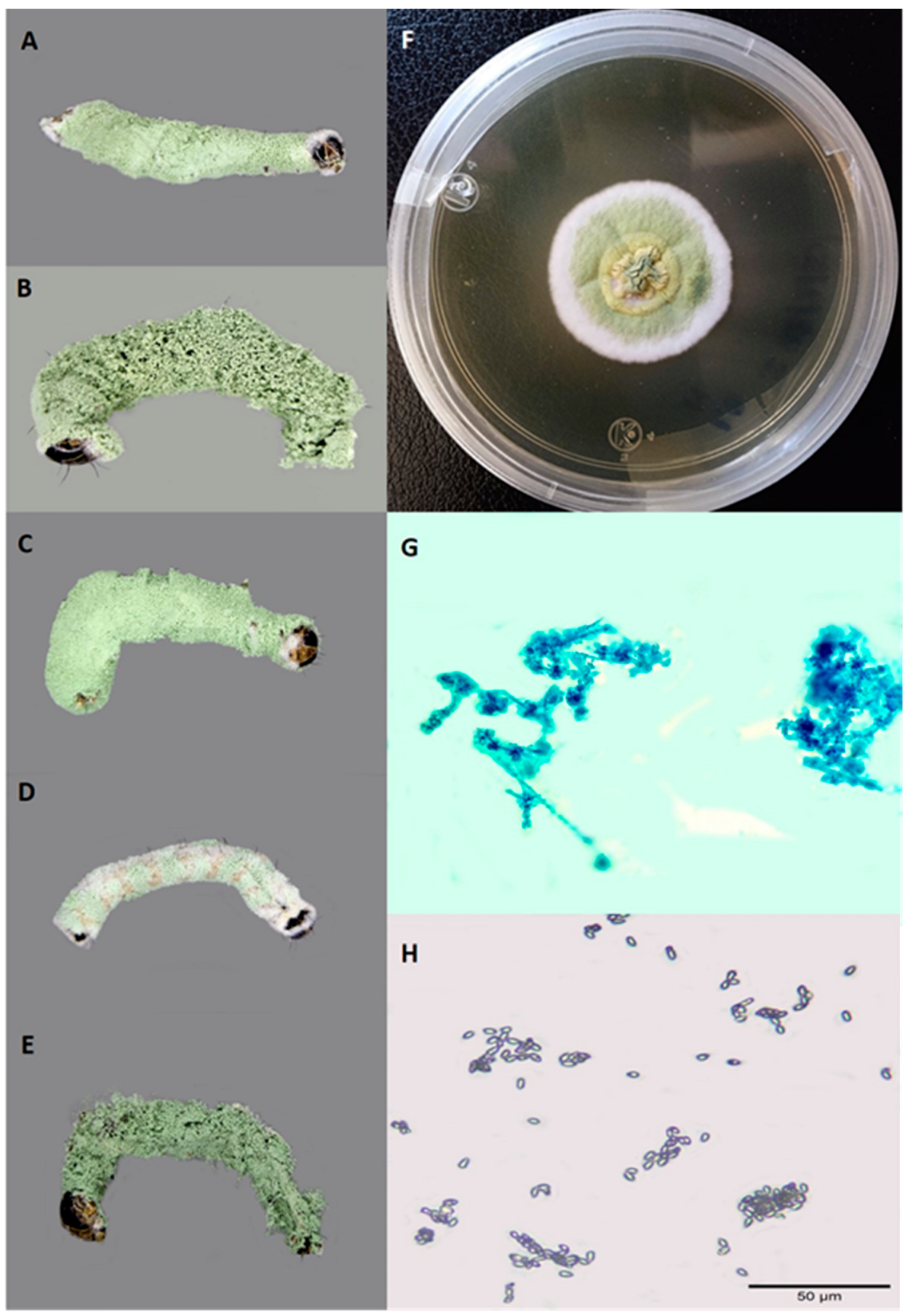
| Collection Site/Municipality | Collection Date | Number of Larvae Collected | Coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|
| El Trébol, Tarímbaro | 2 September 2021 | 137 | 19°46′12.5076″ N—101°09′17.6724″ W |
| Peña del Panal, Tarímbaro | 7 September 2021 | 78 | 19°46′27.8976″ N—101°11′04.452″ W |
| Zinapécuaro, Zinapécuaro | 15 September 2021 | 44 | 19°50′46.2703″ N—101°01′40.2930″ W |
| Lagunillas, Pátzcuaro | 7 September 2022 | 25 | 19°36′40.554″ N—101°25′23.7″ W |
| El Jacal, Chucándiro | 21 September 2022 | 11 | 19°53′16.3644″ N—101°20′12.1632″ W |
| Isolates | Mortality (%) ± SEM | Sporulation (%) ± SEM |
|---|---|---|
| T1-21 | 70.0 ± 4.1 a | 60.5 ± 1.7 a |
| T69-21 | 90.0 ± 2.0 b | 82.0 ± 1.0 bcd |
| T70-21 | 90.0 ± 3.0 b | 84.9 ± 5.3 bcdef |
| T72-21 | 95.0 ± 2.0 b | 88.0 ± 3.6 bcdef |
| T5-21 | 93.7 ± 2.4 b | 87.6 ± 4.7 bcdef |
| T9-21 | 97.5 ± 3.2 b | 94.6 ± 2.3 bcdef |
| T8-21 | 95.0 ± 3.5 b | 81.3 ± 2.2 bc |
| T2-21 | 97.5 ± 1.4 b | 91.1 ± 1.3 bcdef |
| PP1-21 | 93.7 ± 3.7 b | 80.2 ± 3.4 ab |
| PP12-21 | 95.0 ± 2.0 b | 81.5 ± 1.8 bc |
| PP18-21 | 88.7 ± 4.3 b | 88.4 ± 4.5 bcdef |
| PP48-21 | 97.5 ± 1.4 b | 94.9 ± 3.0 bcdef |
| Z2-21 | 93.7 ± 1.2 b | 84.0 ± 2.1 bcdef |
| Z30-21 | 97.5 ± 1.4 b | 96.1 ± 2.5 cdef |
| Z32-21 | 95.0 ± 2.0 b | 88.0 ± 2.7 bcdef |
| Z33-21 | 90.0 ± 2.0 b | 93.3 ± 3.4 bcdef |
| J5-22 | 96.2 ± 2.4 b | 94.7 ± 2.1 bcdef |
| J6-22 | 93.7 ± 1.2 b | 92.0 ± 1.5 bcdef |
| J9-22 | 92.5 ± 3.2 b | 90.5 ± 2.7 bcdef |
| J10-22 | 97.5 ± 1.4 b | 97.4 ± 1.5 ef |
| L8-22 | 98.7 ± 1.2 b | 98.7 ± 1.2 bcdef |
| L9-22 | 96.2 ± 1.2 b | 90.8 ± 2.5 bcdef |
| L11-22 | 97.5 ± 1.4 b | 96.2 ± 1.3 def |
| L12-22 | 92.5 ± 1.4 b | 89.1 ± 2.3 bcdef |
| Isolates | Days Post- Inoculation | Slope ± SEM | LC50 (Conidia/mL) | Lower-Upper Limits | χ2 a | LT50 (Days Post-Inoculation) | Lower-Upper Limits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T9-21 | 13 | 0.61 ± 0.07 | 1.05 × 106 | 1.9 × 105–3.49 × 106 | 4.05 | 7.40 | 7.01–7.76 |
| Z30-21 | 13 | 0.41 ± 0.05 | 2.15 × 105 | 5.9 × 104–7.3 × 105 | 3.94 | 9.46 | 9.04–9.90 |
| PP48-21 | 13 | 0.48 ± 0.06 | 4.18 × 105 | 1.3 × 105–2.7 × 106 | 4.87 | 9.65 | 9.30–10.0 |
| J10-22 | 12 | 0.56 ± 0.06 | 2.04 × 105 | 7.7 × 104–4.2 × 105 | 2.20 | 7.04 | 6.59–7.47 |
| L8-22 | 10 | 0.39 ± 0.05 | 7.85 × 105 | 2.5 × 105–1.8 × 106 | 2.36 | 7.49 | 7.04–7.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramos, Y.; Pineda-Guillermo, S.; Tamez-Guerra, P.; Orozco-Flores, A.A.; Figueroa de la Rosa, J.I.; Ramos-Ortiz, S.; Chavarrieta-Yáñez, J.M.; Martínez-Castillo, A.M. Natural Prevalence, Molecular Characteristics, and Biological Activity of Metarhizium rileyi (Farlow) Isolated from Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) Larvae in Mexico. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10060416
Ramos Y, Pineda-Guillermo S, Tamez-Guerra P, Orozco-Flores AA, Figueroa de la Rosa JI, Ramos-Ortiz S, Chavarrieta-Yáñez JM, Martínez-Castillo AM. Natural Prevalence, Molecular Characteristics, and Biological Activity of Metarhizium rileyi (Farlow) Isolated from Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) Larvae in Mexico. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(6):416. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10060416
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamos, Yordanys, Samuel Pineda-Guillermo, Patricia Tamez-Guerra, Alonso Alberto Orozco-Flores, José Isaac Figueroa de la Rosa, Selene Ramos-Ortiz, Juan Manuel Chavarrieta-Yáñez, and Ana Mabel Martínez-Castillo. 2024. "Natural Prevalence, Molecular Characteristics, and Biological Activity of Metarhizium rileyi (Farlow) Isolated from Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) Larvae in Mexico" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 6: 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10060416
APA StyleRamos, Y., Pineda-Guillermo, S., Tamez-Guerra, P., Orozco-Flores, A. A., Figueroa de la Rosa, J. I., Ramos-Ortiz, S., Chavarrieta-Yáñez, J. M., & Martínez-Castillo, A. M. (2024). Natural Prevalence, Molecular Characteristics, and Biological Activity of Metarhizium rileyi (Farlow) Isolated from Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) Larvae in Mexico. Journal of Fungi, 10(6), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10060416







