From Acute Carditis, Rheumatic Carditis, and Morphologic Cardiac Reactions to Allergic Angina, Allergic Myocardial Infarction, and Kounis Syndrome: A Multidisciplinary and Multisystem Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Antecedents of Kounis Syndrome
3. Allergic Angina and Allergic Myocardial Infarction
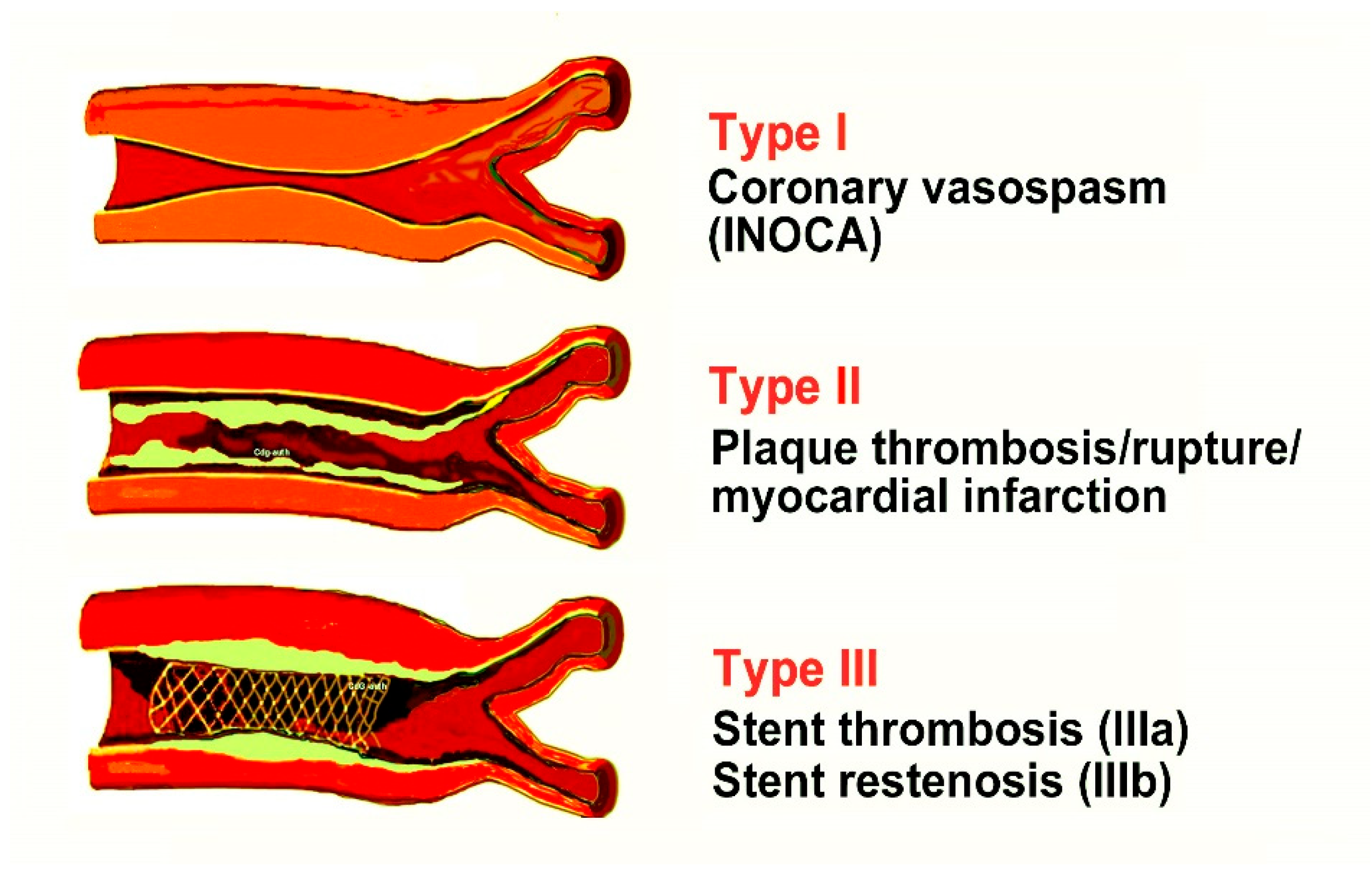
4. Current Views on Kounis Syndrome
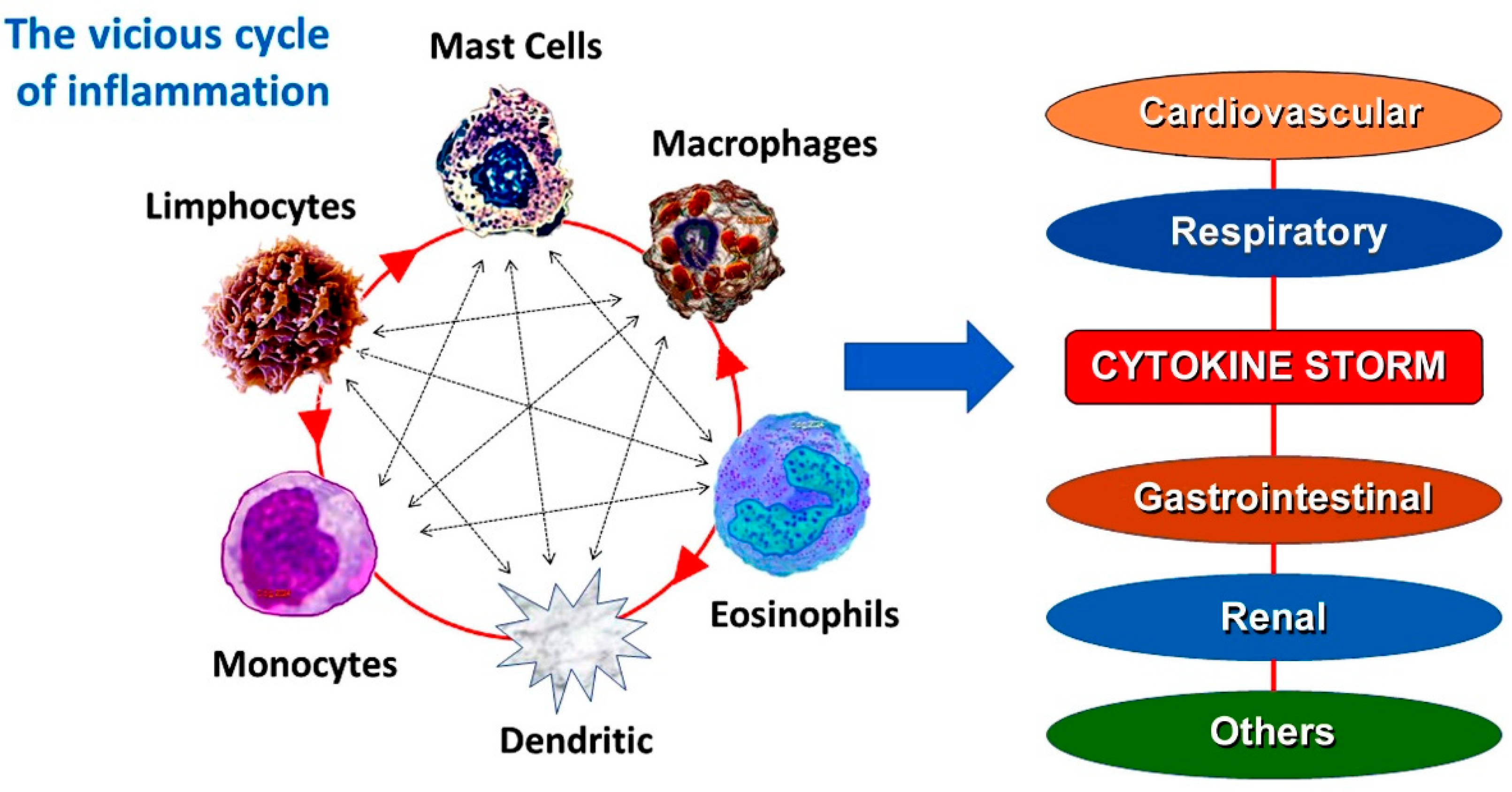
5. Common Pathway Between Allergic and Not Allergic Vascular Events
6. Myocardial Infarction, a Preventable Disease?
7. IgEs and Kounis Syndrome
8. Lower IgEs Are Better for Kounis Syndrome
9. Serum Tryptase, a Unique Mast Cell-Derived Cytokine
10. Kounis Syndrome, COVID-19, and Vaccines
- Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C3b | Complement component 3 |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| FcR | Fragment crystallizable region |
| F FcεRI | Fragment crystallizable epsilon region RI |
| FcεRII | Fragment crystallizable epsilon region RII |
| FcgRI | Fragment crystallizable gamma region RΙ |
| FcgRII | Fragment crystallizable gamma region ΙI |
| IgE | Immunoglobulin E |
| Ι IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IgE | Immunoglobulin G |
| SCF | Stem cell factor |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
References
- Krombach, J.W.; Kampe, S.; Keller, C.A.; Wright, P.M. Pharaoh Menes’ death after an anaphylactic reaction the end of a myth. Allergy 2004, 59, 1234–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, E. Serum carditis: Morphologic cardiac alterations in man with serum disease. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1938, 110, 1098–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth, G.M.; Brown, C.H. Serum reaction complicated by acute carditis. J. Pediatr. 1940, 17, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, A.R.; Gregory, J.E. Experimental evidence that lesions with basic characteristics of rheumatic carditis can result from anaphylactic hypersensitivity. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1943, 73, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czickeli, H. Contribution to the problem of the allergic etiology of angina pectoris and myocardial infarct. Klin. Med. Osterr. Z. Wiss. Prakt. Med. 1950, 5, 364–367. [Google Scholar]
- Schultheiss, E. Clinical aspects of allergic heart diseases. Dtsch. Med. J. 1964, 15, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Auer, J.; Lewis, P.A. The physiology of the immediate reaction of anaphylaxis in the guinea-pig. J. Exp. Med. 1910, 12, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.M.T.; Rupprecht, C.P.; Haque, A.; Pattanaik, D.; Yusin, J.; Krishnaswamy, G. Mechanisms Governing Anaphylaxis: Inflammatory Cells, Mediators, Endothelial Gap Junctions and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; d’Amati, A. Hematopoiesis and Mast Cell Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorro, L.; Geissmann, F. Development and homeostasis of ‘resident’ myeloid cells: The case of the Langerhans cell. Trends Immunol. 2010, 31, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cline, M.J. Histiocytes and histiocytosis. Blood 1994, 84, 2840–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, H.F. Rheumatic fever. JAMA 1929, 92, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, I.; Loewe, I.; Eliasoph, B. Attempts to reproduce rheumatic fever in animals. J. Exp. Med. 1929, 50, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besterman, E.M.M. Some notes on the history of rheumatic carditis. West. Indian Med. J. 2001, 50, 180–182. [Google Scholar]
- Moukabary, T. Willem Einthoven (1860–1927): Father of electrocardiography. Cardiol. J. 2007, 14, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pfister, C.W.; Plice, S.G. Acute myocardial infarction during a prolonged allergic reaction to penicillin. Am. Heart J. 1950, 40, 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kounis, N.G.; Zavras, G.M. Histamine-induced coronary artery spasm: The concept of allergic angina. Br. J. Clin. Pract. 1991, 45, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, P. Infiltrates of activated mast cells at the site of coronary atheromatous erosion or rupture in myocardial infarction. Circulatory 1995, 92, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brawnvald, E. Unstable angina. An etiologic approach to management. Circulation 1998, 98, 2219–2222. [Google Scholar]
- González-de-Olano, D.; Alvarez-Twose, I.; Matito, A.; Sánchez-Muñoz, L.; Kounis, N.G.; Escribano, L. Mast cell activation disorders presenting with cerebral vasospasm-related symptoms: A “Kounis-like” syndrome? Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 150, 210–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastogiannis, H.; Litsardopoulos, P.; Anastopoulou, G.G.; Petsas, A.; Tsigkas, G.; Kounis, N.G.; Ravani, I.; Argyriou, A.A. Irreversible diffuse hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, secondary to type I Kounis syndrome. Int. J. Neurosci. 2020, 130, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peláez-Pérez, J.M.; Sánchez Casado, M.; Álvarez-Twose, I.; Kounis, N.G. Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid-induced type II Kounis syndrome during general anaesthesia complicated with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Rev. Esp. Anestesiol. Reanim. 2021, 68, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.; Koniari, I.; Tsigkas, G.; Davlouros, P. Rectosigmoid ischemia and cerebral coma following gadolinium induced anaphylaxis: A new manifestation of Kounis syndrome presented as devastating complication. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2020, 91, 442–444. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, M.; Matsuzaki, M.; Fuchinoue, A.; Urabe, N.; Kawagoe, N.; Takemoto, I.; Tanaka, H.; Watanabe, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Takeuchi, M.; et al. Chronic athero-sclerotic mesenteric ischemia that started to develop symptoms just after anaphylaxis. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2012, 6, 300–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, H.; Ihara, M.; Nojima, Y.; Kurimoto, T.; Nanto, S. Kounis syndrome caused by anaphylaxis without skin manifestations after cefazolin administration. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakarla, P.; Rijey, J.; Venugopal Reddy, Y.C.; Manechala, U.B. Central retinal vein occlusion with concurrent paracentral acute middle maculopathy secondary to honeybee sting. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 4, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G.; Koniari, I.; Velissaris, D.; Tzanis, G.; Hahalis, G. Kounis Syndrome—Not a Single-organ Arterial Disorder but a Multisystem and Multidisciplinary Disease. Balk. Med. J. 2019, 36, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, P.; Kachhadia, M.P.; Sardana, P.; Bhagat, R.; Dekowski, S.; Fohle, E. Adrenaline, Takotsubo, Anaphylaxis, and Kounis Syndrome (ATAK) Complex Unveiled: Integrating Takotsubo and Kounis Syndromes in the Context of Chemotherapy-Related Anaphylaxis. Cureus 2024, 16, e53145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kounis, N.G.; Mplani, V.; de Gregorio, C.; Koniari, I. Attack the ATAK. A Challenging Contemporary Complex: Pathophysiologic, Therapeutic, and Preventive Considerations. Balk. Med. J. 2023, 40, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Klei, W.A.; Szabo, M.D.; Hesterberg, P.E. Case 22–2023: A 59-Year-OldWoman with Hypotension and Electrocardiographic Changes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levick, S.P. Histamine receptors in heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2022, 27, 1355–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G. Kounis syndrome (allergic angina and allergic myocardial infarction): A natural paradigm? Int. J. Cardiol. 2006, 110, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Ma, Q. Arachidonic acid metabolism in health and disease. MedComm 2023, 4, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliargyris, E.N.; Raymond, R.J.; Theoharides, T.C.; Boucher, W.S.; Tate, D.A.; Dehmer, G.J. Sites of interleukin-6 release in patients with acute coronary syndromes and in patients with congestive heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2000, 86, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsioufis, P.; Theofilis, P.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. The Impact of Cytokines in Coronary Atherosclerotic Plaque: Current Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaartinen, M.; Penttila, A.; Kovanen, P.T. Accumulation of activated mast cells in the shoulder region of human coronary atheroma, the prediction site of atheromatous rupture. Circulation 1994, 90, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kounis, N.G.; Koniari, I.; Soufras, G.D.; Chourdakis, E.; Despotopoulos, S.; Davlouros, P.; Hahalis, G. The Humble Relation of Kounis Syndrome, MINOCA (Myocardial Infarction With Nonobstructive Coronary Arteries) and MACE (Major Adverse Cardiac Events). Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 1089.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G.; Mplani, V.; Koniari, I. Kounis syndrome: A natural paradigm for preventing mast cell activation-degranulation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2025, 419, 132704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollam, J.; Solomon, M.; Villescaz, C.; Lanier, M.; Evans, S.; Bacon, C.; Freeman, D.; Vasquez, A.; Vest, A.; Napora, J.; et al. Inhibition of mast cell degranulation by novel small molecule MRGPRX2 antagonists. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 154, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takematsu, E.; Massidda, M.; Auster, J.; Chen, P.C.; Im, B.; Srinath, S.; Canga, S.; Singh, A.; Majid, M.; Sherman, M.; et al. Transmembrane stem cell factor protein therapeutics enhance revascularization in ischemia without mast cell activation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemmar, A.; Hoet, P.H.; Vermylen, J.; Nemery, B.; Hoylaerts, M.F. Pharmacological stabilization of mast cells abrogates late thrombotic events induced by diesel exhaust particles in hamsters. Circulation 2004, 110, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G.; Hahalis, G. Serum IgE levels in coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2016, 251, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.G.; Kwak, M.W.; Kang, T.H. Fc Receptor Variants and Disease: A Crucial Factor to Consider in the Antibody Therapeutics in Clinic. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kounis, N.G.; Mazarakis, A.; Almpanis, G.; Gkouias, K.; Kounis, G.N.; Tsigkas, G. The more allergens an atopic patient is exposed to, the easier and quicker anaphylactic shock and Kounis syndrome appear: Clinical and therapeutic paradoxes. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2014, 5, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kounis, N.G.; Koniari, I.; Velissaris, D.; Soufras, G.; Hahalis, G. Aortic aneurysm and dissection in systemic lupus erythematosus-pathophysiologic and therapeutic considerations. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 5, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morena, D.; Anta, Y.; Dbouk, C. Hyper IgE Syndrome With Multiple Respiratory Infections. Review About a Clinical Case. Open Respir. Arch. 2023, 5, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovanen, P.T.; Mänttäri, M.; Palosuo, T.; Manninen, V.; Aho, K. Prediction of myocardial infarction in dyslipidemic men by elevated levels of immunoglobulin classes A, E, and G, but not M. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A.; Chruszcz, M.; Chapman, M.D.; Pomés, A. Human Monoclonal IgE Antibodies-a Major Milestone in Allergy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023, 23, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, M.; Engeroff, P. A Comparison of Natural and Therapeutic Anti-IgE Antibodies. Antibodies 2024, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, M.; Irani, A.A.; Scwartz, L.B. Evaluation of human peripheral blood leucocytes for mast cell tryptase. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 2814–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, A.T.; Kristiansen, H.P.; Winther-Larsen, A. Short-term biological variation of serum tryptase. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2023, 62, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateja, A.; Wang, Q.; Chovanec, J.; Kim, J.; Wilson, K.J.; Schwartz, L.B.; Glover, S.C.; Carter, M.C.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Brittain, E.; et al. Defining baseline variability of serum tryptase levels improves accuracy in identifying anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1010–1017.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, L.B.; Bradford, T.R.; Rouse, C.; Irani, A.M.; Rasp, G.; Van der Zwan, J.K.; Van der Linden, P.W. Development of a new, more sensitive immunoassay for human tryptase: Use in systemic anaphylaxis. J. Clin. Immunol. 1994, 14, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baretto, R.L.; Beck, S.; Heslegrave, J.; Melchior, C.; Mohamed, O.; Ekbote, A.; Huissoon, A.P.; Krishna, M.T. Validation of international consensus equation for acute serum total tryptase in mast cell activation: A perioperative perspective. Allergy 2017, 72, 2031–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G. Serum tryptase levels and Kounis syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2007, 114, 407–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervinen, H.; Kaartinen, M.; Makynen, H.; Palosuo, T.; Manttari, M.; Kovanen, P.T. Serum tryptase levels in acute coronary syndromes. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 104, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S. Mast cell tryptase level should be checked in all patients with suspected Kounis syndrome. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valent, P.; Hoermann, G.; Bonadonna, P.; Hartmann, K.; Sperr, W.R.; Broesby-Olsen, S.; Brockow, K.; Niedoszytko, M.; Hermine, O.; Chantran, Y.; et al. The Normal Range of Baseline Tryptase Should Be 1 to 15 ng/mL and Covers Healthy Individuals With HαT. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023, 11, 3010–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiga, M.; Wang, D.W.; Han, Y.; Lewis, D.B.; Wu, J.C. COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease: From basic mechanisms to clinical perspectives. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, E.; Gao, K. Mast cells: A double-edged sword in inflammation and fibrosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1466491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budnevsky, A.V.; Avdeev, S.N.; Kosanovic, D.; Ovsyannikov, E.S.; Savushkina, I.A.; Alekseeva, N.G.; Feigelman, S.N.; Shishkina, V.V.; Filin, A.A.; Esaulenko, D.I.; et al. Involvement of Mast Cells in the Pathology of COVID-19: Clinical and Laboratory Parallels. Cells 2024, 13, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaba, C.N.; Ekabe, C.J.; Ayuk, H.S.; Gwanyama, B.N.; Bitazar, R.; Bukong, T.N. Interplay of TLR4 and SARS-CoV-2: Unveiling the Complex Mechanisms of Inflammation and Severity in COVID-19 Infections. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 5077–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poto, R.; Marone, G.; Galli, S.J.; Varricchi, G. Mast cells: A novel therapeutic avenue for cardiovascular diseases? Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 120, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, A.; Kalurami, V.K. Kounis syndrome in the era of COVID-19: Pathophysiology, clinical challenges, and therapeutic approaches. Front. Emerg. Med. 2024, 8, e35F. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G.; Koniari, I.; de Gregorio, C. COVID-19 and Kounis Syndrome: Deciphering Their Relationship. Balk. Med. J. 2021, 38, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, L.; Gerosa, C.; Wintermark, M.; Hedin, U.; Fanni, D.; Suri, J.S.; Balestrieri, A.; Faa, G. Can COVID19 trigger the plaque vulnerability-a Kounis syndrome warning for “asymptomatic subjects”. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 10, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lei, R.; Liu, S.; Zhao, M. Kounis syndrome following COVID-19 vaccination: Clinical manifestations, mechanisms and management. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2024, 20, 23654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S.M. Allergic Reactions and Anaphylaxis to LNP-Based COVID-19 Vaccines. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awaya, T.; Hara, H.; Moroi, M. Cytokine Storms and Anaphylaxis Following COVID-19 mRNA-LNP Vaccination: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Diseases 2024, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiolet, T.; Kherabi, Y.; MacDonald, C.J.; Ghosn, J.; Peiffer-Smadja, N. Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: A narrative review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G.; Koniari, I.; Mplani, V.; Kouni, S.N.; Plotas, P.; Tsigkas, G. Acute Myocardial Infarction Within 24 Hours After COVID-19 Vaccination: Is Kounis Syndrome the Culprit? Am. J. Cardiol. 2022, 162, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowicz, A.L.; Carrazana, E.; Maggio, E.T. Improvement of Intranasal Drug Delivery with Intravail® Alkylsaccharide Excipient as a Mucosal Absorption Enhancer Aiding in the Treatment of Conditions of the Central Nervous System. Drugs R D 2021, 21, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutel, M.; Torres, M.J.; Palomares, O.; Akdis, C.A.; Eiwegger, T.; Untersmayr, E.; Barber, D.; Zemelka-Wiacek, M.; Kosowska, A.; Palmer, E.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination in patients receiving allergen immunotherapy (AIT) or biologicals-EAACI recommendations. Allergy 2022, 77, 2313–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Tryptase | Chymase | Cathepsin D |
|---|---|---|
| Activates the zymogen forms of metalloproteinases such as interstitial collagenase, gelatinase, and stromelysin and can promote plaque disruption or rupture | Converts angiotensin Ι to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II receptors are found in the medial muscle cells of human coronary arteries. Thus, angiotensin II generated by chymase could act synergistically with histamine and aggravate the local spasm of the infracted coronary artery. Chymase can also remove cholesterol from HDL | Angiotensin II-forming protease |
| Degrades the pericellular matrix components fibronectin and vitronectin and neuropeptides such as vasoactive intestinal peptide and calcitonin gene-related peptide | Activates matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2, 9 and plays a major role in the physiologic degradation of fibronectin and thrombin | Degrades both fibronectin and vascular endothelial cadherin, which are necessary for the adhesion of endothelial cells to their basement membrane and to each other |
| Tryptase can degrade high-density lipoprotein, (“good” cholesterol) | ||
| Activates neighboring cells by cleaving and activating protease-activated receptor (PAR)-2 and thrombin receptors |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kounis, N.G.; Stefanidis, A.; Hung, M.-Y.; Özkan, U.; de Gregorio, C.; Ceasovschih, A.; Mplani, V.; Gogos, C.; Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Chatzigrigoriadis, C.; et al. From Acute Carditis, Rheumatic Carditis, and Morphologic Cardiac Reactions to Allergic Angina, Allergic Myocardial Infarction, and Kounis Syndrome: A Multidisciplinary and Multisystem Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12090325
Kounis NG, Stefanidis A, Hung M-Y, Özkan U, de Gregorio C, Ceasovschih A, Mplani V, Gogos C, Assimakopoulos SF, Chatzigrigoriadis C, et al. From Acute Carditis, Rheumatic Carditis, and Morphologic Cardiac Reactions to Allergic Angina, Allergic Myocardial Infarction, and Kounis Syndrome: A Multidisciplinary and Multisystem Disease. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(9):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12090325
Chicago/Turabian StyleKounis, Nicholas G., Alexandros Stefanidis, Ming-Yow Hung, Uğur Özkan, Cesare de Gregorio, Alexandr Ceasovschih, Virginia Mplani, Christos Gogos, Stelios F. Assimakopoulos, Christodoulos Chatzigrigoriadis, and et al. 2025. "From Acute Carditis, Rheumatic Carditis, and Morphologic Cardiac Reactions to Allergic Angina, Allergic Myocardial Infarction, and Kounis Syndrome: A Multidisciplinary and Multisystem Disease" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 9: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12090325
APA StyleKounis, N. G., Stefanidis, A., Hung, M.-Y., Özkan, U., de Gregorio, C., Ceasovschih, A., Mplani, V., Gogos, C., Assimakopoulos, S. F., Chatzigrigoriadis, C., Plotas, P., Dousdampanis, P., Kouni, S. N., Tsigkas, G., Patsouras, N., Calogiuri, G., Pourmasumi, S., & Koniari, I. (2025). From Acute Carditis, Rheumatic Carditis, and Morphologic Cardiac Reactions to Allergic Angina, Allergic Myocardial Infarction, and Kounis Syndrome: A Multidisciplinary and Multisystem Disease. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(9), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12090325













