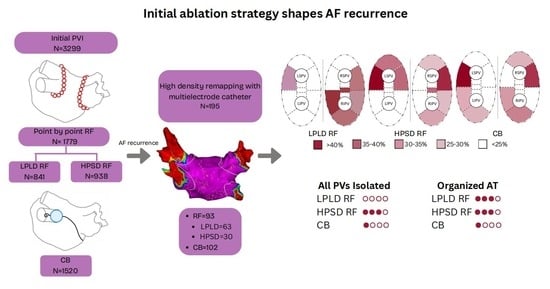
Electrophysiological Substrate and Pulmonary Vein Reconnection Patterns in Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation: Comparing Thermal Strategies in Patients Undergoing Redo Ablation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Mapping and Assessment of Pulmonary Vein Reconnection
2.3. Redo Ablation Procedure
2.4. Index Ablation
- AI-guided low-power, long-duration (LPLD) RF ablation;
- AI-guided high-power, short-duration (HPSD) RF ablation;
- Second- or third-generation cryoballoon (CB) ablation.
2.5. LPLD Radiofrequency Ablation
2.6. HPSD Radiofrequency Ablation
2.7. Cryoballoon Ablation
2.8. Procedural Endpoints
2.9. Data Collection and Outcomes
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Demographics
3.2. Remapping Outcomes
3.3. Clinical Outcomes: Complications and Success Rates
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings
4.2. Impact of Initial Ablation Modality on PVR
4.3. Post-PVI Organized Atrial Tachycardia
4.4. Redo Procedure Success Rates
4.5. Clinical Implications for Patient Selection for Redo
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Ablation Index |
| AF | Atrial Fibrillation |
| AT | Atrial Tachycardia |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CB | Cryoballoon |
| HPSD | High Power, Short Duration |
| LAA | Left Atrial Appendage |
| LA | Left Atrium |
| LIPV | Left Inferior Pulmonary Vein |
| LSPV | Left Superior Pulmonary Vein |
| LVEF | Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction |
| LPLD | Low Power, Long Duration |
| PV | Pulmonary Vein |
| PVI | Pulmonary Vein Isolation |
| PVR | Pulmonary Vein Reconnection |
| PFA | Pulsed Field Ablation |
| RF | Radiofrequency |
| RIPV | Right Inferior Pulmonary Vein |
| RSPV | Right Superior Pulmonary Vein |
References
- Haïssaguerre, M.; Jaïs, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; Garrigue, S.; Le Mouroux, A.; Le Métayer, P.; Clémenty, J. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Katritsis, D.G.; Anker, S.D.; Boriani, G.; Camm, A.J.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): Developed by the task force for the management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Endorsed by the European Stroke Organisation (ESO). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2025, 7, ehaf306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, P.B.; Belliveau, D.; Nair, G.M.; Bernick, J.; Redpath, C.J.; Szczotka, A.; Sadek, M.M.; Green, M.S.; Wells, G.; Birnie, D.H. Relationship between pulmonary vein reconnection and atrial fibrillation recurrence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. EP 2016, 2, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, P.A.; Heeger, C.H.; Barra, S.; Luther, V.; Steinfurt, J.; Fernandez-Armenta, J.; Silberbauer, J. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: Results from a European survey. Heart Rhythm. 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V.; Poudyal, A.; Abid, Q.U.A.; Larsen, T.; Krishnan, K.; Sharma, P.S.; Trohman, R.G.; Huang, H.D. High-power short duration vs. conventional radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EP Europace 2021, 23, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourier, F.; Duchateau, J.; Vlachos, K.; Lam, A.; Martin, C.A.; Takigawa, M.; Kitamura, T.; Frontera, A.; Cheniti, G.; Pambrun, T.; et al. High-power short-duration versus standard radiofrequency ablation: Insights on lesion metrics. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.G. Cryoballoon ablation for pulmonary vein isolation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phlips, T.; Taghji, P.; El Haddad, M.; Wolf, M.; Knecht, S.; Vandekerckhove, Y.; Tavernier, R.; Duytschaever, M. Improving procedural and one-year outcome after contact force-guided pulmonary vein isolation: The role of interlesion distance, ablation index, and contact force variability in the ‘CLOSE’-protocol. Europace 2018, 20, f419–f427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francke, A.; Taha, N.S.; Scharfe, F.; Schoen, S.; Wunderlich, C.; Christoph, M. Procedural efficacy and safety of standardized, ablation index guided fixed 50 W high-power short-duration pulmonary vein isolation and substrate modification using the CLOSE protocol. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2021, 32, 2676–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boveda, S.; Bartoletti, S. Cryoballoon Application Duration: Back to the Future? JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 5, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, S.K.; Johannessen, A.; Worck, R.; Hansen, M.L.; Ruwald, M.H.; Hansen, J. Differential gap location after radiofrequency versus cryoballoon pulmonary vein isolation: Insights from a randomized trial with protocol-mandated repeat procedure. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2023, 34, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Joo, Y.H.; Lee, E.; Lee, S.-R.; Cha, M.-J.; Choi, E.-K.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, W. Left atrial wall thickness and its relationship with reconnection after pulmonary vein isolation in patients with atrial fibrillation evaluated using a three-dimensional wall thickness map. Int. J. Arrhythmia 2021, 22, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galuszka, O.M.; Baldinger, S.H.; Servatius, H.; Seiler, J.; Madaffari, A.; Kozhuharov, N.; Thalmann, G.; Kueffer, G.; Muehl, A.; Maurhofer, J. Durability of CLOSE-guided pulmonary vein isolation in persistent atrial fibrillation: A prospective remapping study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. EP 2024, 10, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beinart, R.; Abbara, S.; Blum, A.; Ferencik, M.; Heist, K.; Ruskin, J.; Mansour, M. Left atrial wall thickness variability measured by CT scans in patients undergoing pulmonary vein isolation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2011, 22, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavin, H.D.; Leshem, E.; Shapira-Daniels, A.; Sroubek, J.; Barkagan, M.; Haffajee, C.I.; Cooper, J.M.; Anter, E. Impact of high-power short-duration radiofrequency ablation on long-term lesion durability for atrial fibrillation ablation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. EP 2020, 6, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Schmidt, B.; Bordignon, S.; Perrotta, L.; Bologna, F.; Chun, K.R.J. Impact of cryoballoon freeze duration on long-term durability of pulmonary vein isolation: ICE Re-Map study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. EP 2019, 5, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansom, S.P.; Alqarawi, W.; Birnie, D.H.; Golian, M.; Nery, P.B.; Redpath, C.J.; Klein, A.; Green, M.S.; Davis, D.R.; Sheppard-Perkins, E.; et al. High-power, short-duration atrial fibrillation ablation compared with a conventional approach: Outcomes and reconnection patterns. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2021, 32, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuck, K.H.; Albenque, J.P.; Chun, K.R.J.; Fürnkranz, A.; Busch, M.; Elvan, A.; Schlüter, M.; Braegelmann, K.M.; Kueffer, F.J.; Hemingway, L.; et al. Repeat ablation for atrial fibrillation recurrence post cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation in the FIRE AND ICE trial. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e007247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassa, K.I.; Nagy, Z.; Simkovits, D.; Kis, Z.; Ferenci, T.; Som, Z.; Foldesi, C.; Kardos, A. Evaluation of isolation area, myocardial injury and left atrial function following high-power short-duration radiofrequency or second-generation cryoballoon ablation for atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Riascos, J.F.; Vemulapalli, H.S.; Muthu, P.; Raman, A.; Prajapati, P.; Iyengar, S.; Iyengar, S.; El Masry, H.; Valverde, A.M.; Srivathsan, K. Post–pulmonary vein isolation voltage remapping–guided incremental lesions: A feasible strategy to improve long-term outcomes. Heart Rhythm. O2 2025, 6, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riesz, T.J.; Bencsik, G.; Sághy, L.; Pap, R. Does organized atrial tachycardia after a pulmonary vein isolation-only procedure portend better outcome of repeat ablation compared to recurrent atrial fibrillation? J. Arrhythmia 2025, 41, e70049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Bolao, I.; Ballesteros, G.; Ramos, P.; Menéndez, D.; Erkiaga, A.; Neglia, R.; Martín, M.J.; Vives-Rodríguez, E. Identification of pulmonary vein reconnection gaps with high-density mapping in redo atrial fibrillation ablation procedures. EP Europace 2018, 20, f351–f358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameter | LPLD RF (63) | HPSD RF (30) | CB (102) | p-Value (LPLD vs. HPSD) | p-Value (HPSD vs. CB) | p-Value (LPLD vs. CB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65.6 ± 2.56 | 64.43 ± 4.37 | 61.88 ± 2.14 | 0.627 | 0.269 | 0.031 |
| Sex (male) (%) | 49.2% | 43.3% | 38.3% | 0.601 | 0.619 | 0.168 |
| Type of AF (parox) | 55.6% | 53.3% | 48% | 0.843 | 0.613 | 0.351 |
| Duration of AF (months) | 60.8 ± 22.25 | 38.68 ± 23.32 | 45.00 ± 10.27 | 0.192 | 0.569 | 0.142 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30.3 ± 1.86 | 29.26 ± 1.99 | 29.71 ± 1.28 | 0.454 | 0.717 | 0.565 |
| LVEF (%) | 57.9 ± 3.20 | 57.05 ± 7.20 | 59.44 ± 2.56 | 0.800 | 0.434 | 0.449 |
| LA size (mm) | 58.2 ± 2.46 | 55.38 ± 3.85 | 58.88 ± 2.04 | 0.226 | 0.108 | 0.649 |
| Parameter | LPLD RF (63) | HPSD RF (30) | CB (102) | p-Value (LPLD vs. HPSD) | p-Value (HPSD vs. CB) | p-Value (LPLD vs. CB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proc. time (min) | 130.4 ± 8.21 | 142.07 ± 15.83 | 136.21 ± 7.39 | 0.147 | 0.467 | 0.310 |
| Ablation time (min) | 96.2 ± 7.64 | 103.93 ± 13.92 | 97.01 ± 6.75 | 0.289 | 0.343 | 0.877 |
| X-ray time (min) | 1.5 ± 1.28 | 6.03 ± 7.64 | 7.54 ± 0.78 | 0.555 | 0.456 | 0.966 |
| X-ray dose (Gy) | 554.7 ± 202.79 | 410.17 ± 168.94 | 355.80 ± 89.38 | 0.363 | 0.566 | 0.044 |
| Parameter | LPLD RF (63) | HPSD RF (30) | CB (102) | p-Value (LPLD vs. HPSD) | p-Value (HPSD vs. CB) | p-Value (LPLD vs. CB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All veins isolated | 0 (0%) | 7 (23.3%) | 11 (10.1%) | 0.000 | 0.079 | 0.007 |
| N. of reconnected segments | 8.3 ± 1.08 | 4.47 ± 1.54 | 6.00 ± 0.91 | 0.000 | 0.091 | 0.001 |
| N. of reconnected veins | 2.7 ± 0.27 | 1.77 ± 0.48 | 2.36 ± 0.26 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.068 |
| Most common reconnected segment | right carina | LSPV ridge/ant | LSPV ridge/ant | - | - | - |
| Most common reconnected vein | RIPV | LSPV | LSPV | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kassa, K.I.; Shakya, A.; Som, Z.; Foldesi, C.; Kardos, A. Electrophysiological Substrate and Pulmonary Vein Reconnection Patterns in Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation: Comparing Thermal Strategies in Patients Undergoing Redo Ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12080298
Kassa KI, Shakya A, Som Z, Foldesi C, Kardos A. Electrophysiological Substrate and Pulmonary Vein Reconnection Patterns in Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation: Comparing Thermal Strategies in Patients Undergoing Redo Ablation. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(8):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12080298
Chicago/Turabian StyleKassa, Krisztian Istvan, Adwity Shakya, Zoltan Som, Csaba Foldesi, and Attila Kardos. 2025. "Electrophysiological Substrate and Pulmonary Vein Reconnection Patterns in Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation: Comparing Thermal Strategies in Patients Undergoing Redo Ablation" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 8: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12080298
APA StyleKassa, K. I., Shakya, A., Som, Z., Foldesi, C., & Kardos, A. (2025). Electrophysiological Substrate and Pulmonary Vein Reconnection Patterns in Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation: Comparing Thermal Strategies in Patients Undergoing Redo Ablation. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(8), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12080298