Left Ventricular Apical Cannulation in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Transapical/Left Ventricular Apex Cannulation: Similar Results, Different Procedural Aspects
3. Trans-Apical Cannulation: An Optimal Bail-Out Strategy, but Requiring More Intense Surgical Scenario
3.1. Advantages
3.2. Disadvantages
3.3. Safe Antegrade Inflow: Why the Apical Approach Often Prevails
4. Practical Recommendations
- -
- -
- -
- -
Step-by-Step Operative Procedure
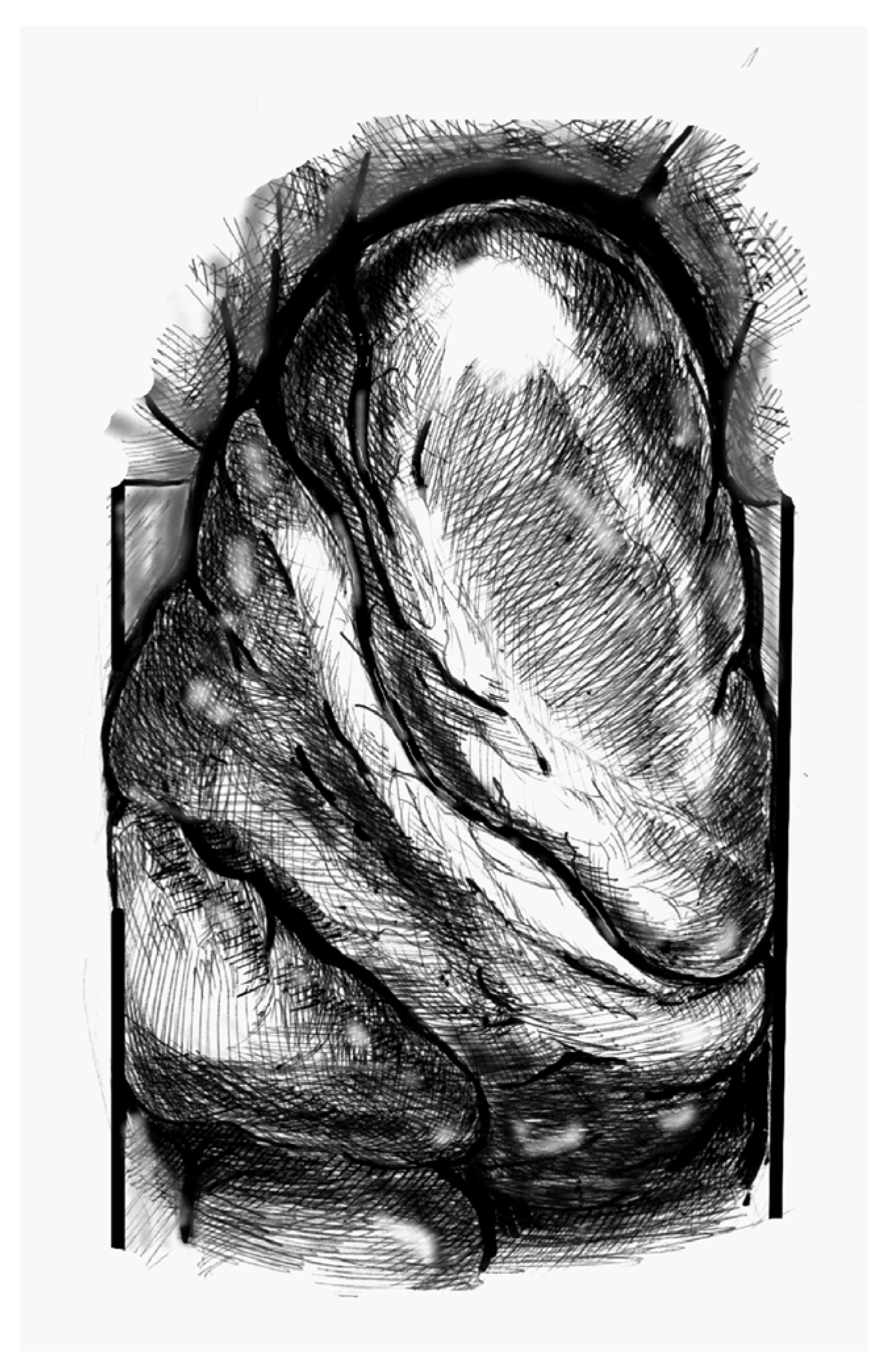
- (1)
- Figure 1. Elevate the heart to expose the apex, then incise the epicardium. Maintain the trajectory towards the outflow tract/aortic valve to avoid deviating into the right ventricle (RV) or causing septal injury. Use transoesophageal echocardiography (TEE) at this stage to confirm the orientation.
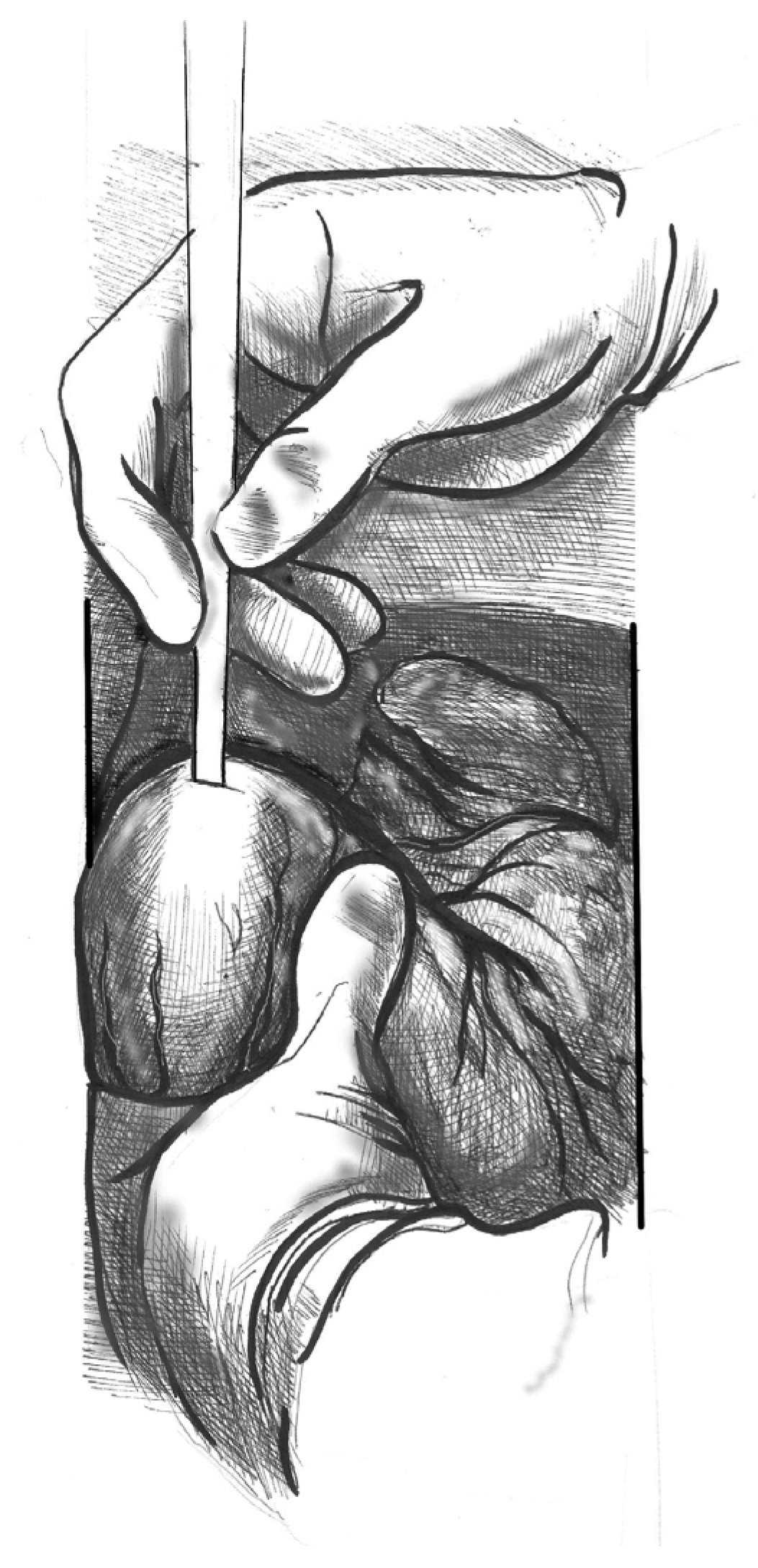
- (2)
- Figure 2. Make a small (approximately 1 cm) apical incision with a No. 11 blade. The incision should be oriented cranially towards the aortic valve. Insert the cannula through the apex.
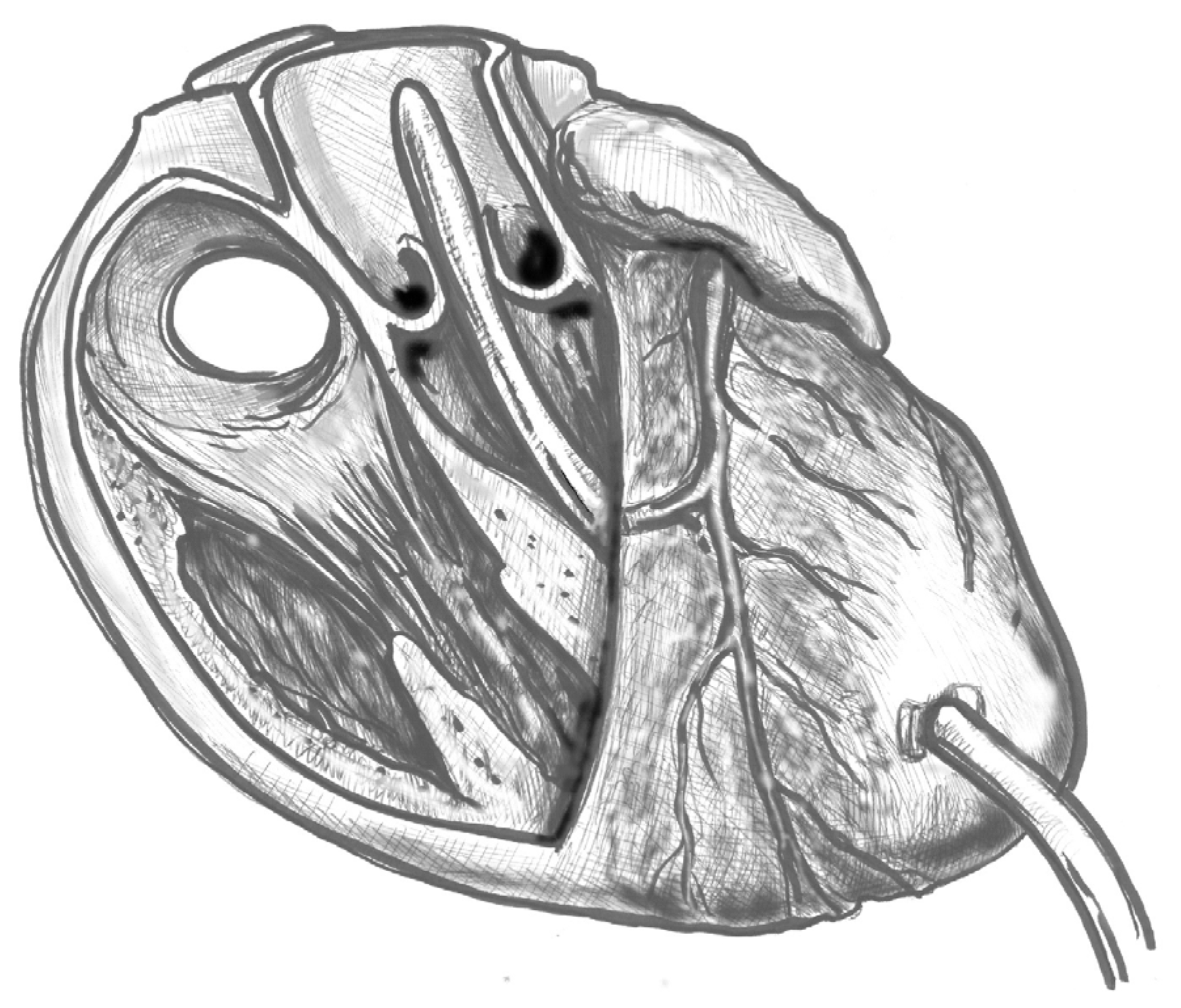
- (3)
- Figure 3. Gently advance the cannula along the LVOT axis towards the ascending aorta under continuous TEE guidance. Fix the cannula in place using two transmural prolene 2-0 sutures with pledgets and tourniquets.
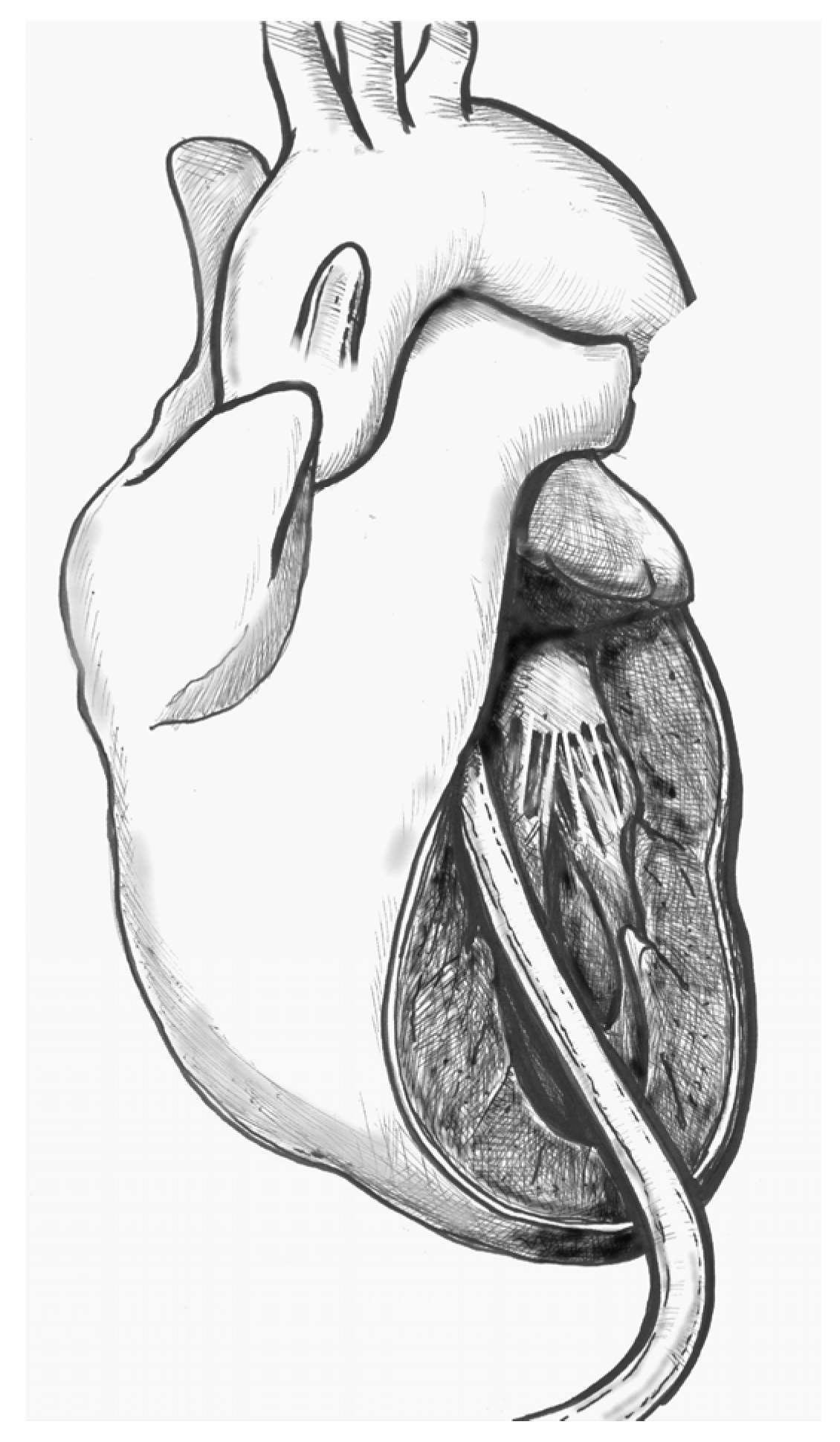
- (4)
- Figure 4. Ideally, the tip should pass the aortic valve and be positioned in the ascending aorta at the level of the sinus-tubular junction. Confirm this with TEE before starting CPB and reconfirm immediately after the start of perfusion. Avoid “short” positioning in the ventricular cavity, as this is ineffective and potentially dangerous.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Djukanovic, B.; Micovic, S.; Peric, M.; Milojevic, P.; Cirkovic, M.; Boricic, M.; Vukovic, P. The role of transapical cannulation in the operative management of acute aortic dissection. Perfusion 2015, 30, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Lingala, B.; Baiocchi, M.; Tao, J.J.; Toro Arana, V.; Khoo, J.W.; Williams, K.M.; Traboulsi, A.A.-R.; Hammond, H.C.; Lee, A.M.; et al. Type A Aortic Dissection—Experience Over 5 Decades. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Honda, J.; Hiramoto, A.; Wada, H.; Hosoda, Y. Transapical aortic cannulation for cardiopulmonary bypass in type A aortic dissection operations. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2006, 132, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suenaga, E.; Sato, M.; Fumoto, H.; Kawasaki, H.; Koga, S. Impact of Transapical Aortic Cannulation for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 21, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, A.; Manabe, S.; Tabata, M.; Fukui, T.; Shimokawa, T.; Takanashi, S. Efficacy and Pitfalls of Transapical Cannulation for the Repair of Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 93, 1905–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, H.; Matsumura, H.; Minematsu, N.; Amako, M.; Nishimi, M.; Tashiro, T. Direct and Transapical Central Cannulation for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.; Cao, Y.; Xie, B.; Qiu, D.; Deng, L.; Wang, M.; Han, H. Cannulation strategies in type A aortic dissection: A novel insight narrative review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 2551–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, S.K.; Reddy, P.R. Cannulation strategies in aortic surgery: Techniques and decision making. Indian J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 38 (Suppl. S1), 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, I.; Saifullah, H.; Mandal, A.K.; Almadhoun, M.K.I.K.; Elsheikh Elabadi, H.M.; Eugene, M.; Suleman, M.; Bushra Himedan, H.O.; Fariha, F.; Ahmed, H.; et al. Cannulation Strategies in Type A Aortic Dissection: Overlooked Details and Novel Approaches. Cureus [Internet]. 10 October 2023. Available online: https://www.cureus.com/articles/187992-cannulation-strategies-in-type-a-aortic-dissection-overlooked-details-and-novel-approaches (accessed on 14 September 2025).
- Yamamoto, S.; Hosoda, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Ishikawa, N.; Fuchimoto, K.; Fukuda, T. Transapical aortic cannulation for acute aortic dissection to prevent malperfusion and cerebral complications. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2001, 28, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kusadokoro, S.; Kimura, N.; Hori, D.; Hattori, M.; Matsunaga, W.; Itagaki, R.; Yuri, K.; Mieno, M.; Nakamura, M.; Yamaguchi, A. Utility of double arterial cannulation for surgical repair of acute type A dissection. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 57, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, I.; Aikawa, S.; Imazuru, T.; Osaka, M. Transapical aortic cannulation for acute aortic dissection with diffuse atherosclerosis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2002, 123, 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamura, J.; Yamamoto, S.; Oshima, S.; Ozaki, K.; Fujikawa, T.; Sakurai, S.; Hirai, Y.; Hirokami, T.; Moriya, N.; Hase, S.; et al. Surgical outcomes of aortic repair via transapical cannulation and the adventitial inversion technique for acute Type A aortic dissection. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 54, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flege, J.B.; Åberg, T. Transventricular aortic cannulation for repair of aortic dissection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2001, 72, 955–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosnowski, A.W.; Jutley, R.S.; Masala, N.; Alexiou, C.; Swanevelder, J. How I do it: Transapical cannulation for acute type—A aortic dissection. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2008, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Hosoda, Y. Reply to the Editor. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2007, 133, 1393–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, S.; Sarralde, J.A.; San Román, J.A.; Stepanenko, A. Challenges in cannulation of left ventricular apex for temporary circulatory support: A case report. AME Case Rep. 2021, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altobaishat, O.; Bataineh, O.A.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Al-zoubi, A.K.; Khan, U.; Abdelgalil, M.S.; Abouzid, M.; Rezq, H.; Abuelazm, M. Single Arterial Cannulation vs. Dual Arterial Cannulation during Acute Type A Aortic Dissection Repair: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2025, 39, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| In-Hospital Mortality | Postoperative Stroke | Myocardial Infarction | Acute Kidney Failure | Revision for Bleeding | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Djukanovic, 2015 [1] | 17% | 6% | 6% | 9% | 20% |
| Kusadokoro, 2020 [11] | 18% | 12% | - | 5% | 6% |
| Matsushita, 2012 [5] | 8% | 15% | - | 17% | 6% |
| Shimamura, 2018 [13] | 8% | 6% | 3% | 4% | 5% |
| Suenaga, 2015 [4] | - | 11% | - | 2% | 15% |
| Wada, 2006 [6] | 19% | 4% | 5% | - | - |
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Transapical | Very fast cardiopulmonary bypass start; antegrade true-lumen flow; no extra incisions; reliable when femoral/axillary are poor; easy to add second inflow. | Needs strict echocardiographic guidance and experience; not ideal with hard-to-cross valves; requires dedicated left ventricular vent; potential apical bleeding. |
| Femoral | Widely available, quick; useful as a bridge in arrest. | Retroperfusion leading to embolism and/or false-lumen malperfusion; limb ischemia; worsens with atheroma. |
| Axillary | More proximal inflow than femoral cannulation; facilitates selective antegrade cerebral perfusion; avoids groin complications. | Flow to the arch remains largely retrograde and true-lumen perfusion is not guaranteed in extensive dissections; slower; small/dissected vessels; local injury |
| Carotid/Innominate | Direct antegrade cerebral perfusion; rapid when anatomy is favorable. | Extra exposure; plaque/dissection risk; need contralateral protection. |
| Central aortic (direct) | Excellent when true lumen is secure; rapid central inflow. | Risk of false-lumen cannulation without rigorous ultrasound; manipulation of fragile wall. |
| Double arterial cannulation | Rescue when malperfusion appears/persists; allows pressure balancing. | Added complexity and lines; more potential complications; not inherently superior. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferraresi, B.; Nenna, A.; Jawabra, M.; Corrado, D.; Barberi, F.; Dominici, C.; Casali, G.; Chello, M.; Lusini, M. Left Ventricular Apical Cannulation in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12110451
Ferraresi B, Nenna A, Jawabra M, Corrado D, Barberi F, Dominici C, Casali G, Chello M, Lusini M. Left Ventricular Apical Cannulation in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(11):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12110451
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerraresi, Benedetto, Antonio Nenna, Mohamad Jawabra, Diletta Corrado, Filippo Barberi, Carmelo Dominici, Giovanni Casali, Massimo Chello, and Mario Lusini. 2025. "Left Ventricular Apical Cannulation in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 11: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12110451
APA StyleFerraresi, B., Nenna, A., Jawabra, M., Corrado, D., Barberi, F., Dominici, C., Casali, G., Chello, M., & Lusini, M. (2025). Left Ventricular Apical Cannulation in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(11), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12110451







