The Association Between Short-Term Blood Pressure Variability and Inflammation in Healthy Young Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population/Trial Design
2.2. Anthropometry Measurements
2.3. Blood Pressure Variability
2.4. Plasma Inflammatory Marker Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
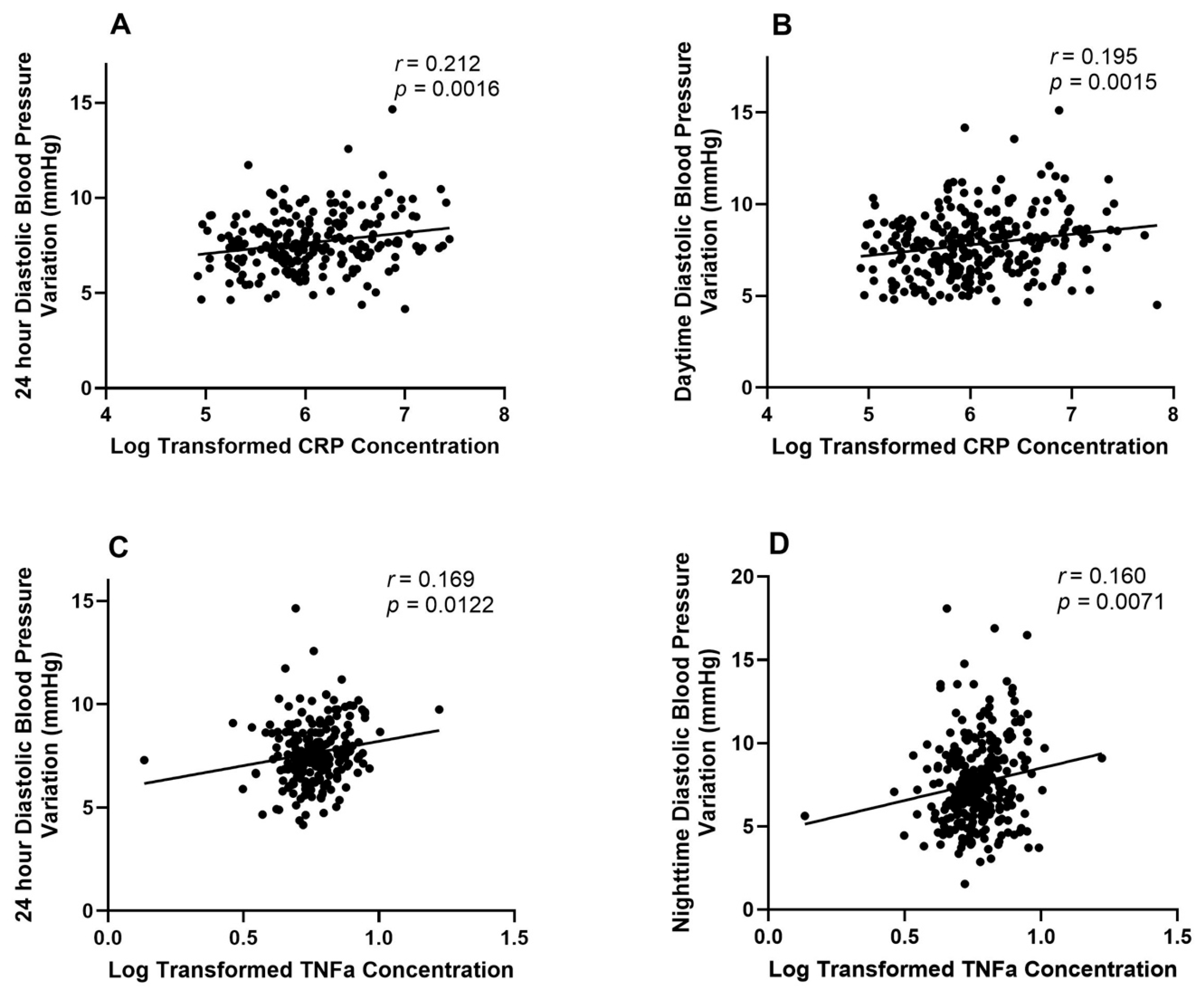
3.2. Associations Between BPV and Inflammation
4. Discussion
4.1. Diastolic BPV
4.2. Systolic BPV
4.3. Inflammatory Cytokines
4.4. Limitations
4.5. Implications
4.6. Future Steps
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPV | Blood pressure variation |
| ABPM | Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring |
| ABP | Ambulatory blood pressure |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| CRP | C-reactive Protein |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| GSH | Georgia Stress and Heart |
| ARV | Average Real Variability |
| GEE | Generalized Estimating Equations |
| QIC | Quasi-likelihood under the Independence model Criterion |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
References
- Fuchs, F.D.; Whelton, P.K. High Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Disease. Hypertension 2020, 75, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayedi, A.; Rahimi, K.; Bautista, L.E.; Nazarzadeh, M.; Zargar, M.S.; Shab-Bidar, S. Inflammation Markers and Risk of Developing Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Heart Br. Card. Soc. 2019, 105, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, F.; Ma, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y. Association of Short-Term Blood Pressure Variability with Cardiovascular Mortality among Incident Hemodialysis Patients. Ren. Fail. 2018, 40, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolarz-Skrzypek, K.; Thijs, L.; Richart, T.; Li, Y.; Hansen, T.W.; Boggia, J.; Kuznetsova, T.; Kikuya, M.; Kawecka-Jaszcz, K.; Staessen, J.A. Blood Pressure Variability in Relation to Outcome in the International Database of Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Relation to Cardiovascular Outcome. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.W.; Thijs, L.; Li, Y.; Boggia, J.; Kikuya, M.; Björklund-Bodegård, K.; Richart, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Jeppesen, J.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; et al. Prognostic Value of Reading-to-Reading Blood Pressure Variability Over 24 Hours in 8938 Subjects from 11 Populations. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, Y.; Karasu, M.; Gelen, M.A.; Şahin, Ş.; Yavçin, Ö.; Yaman, İ.; Hidayet, Ş. Systemic Immune Inflammatory Index as Predictor of Blood Pressure Variability in Newly Diagnosed Hypertensive Adults Aged 18–75. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.-H.; Muddasani, V.; Peterson, C.; Sheibani, N.; Arkin, C.; Cheong, I.; Majersik, J.J.; Biffi, A.; Petersen, N.; Falcone, G.J.; et al. Baseline Serum Biomarkers of Inflammation and Subsequent Visit-to-Visit Blood Pressure Variability: A Post Hoc Analysis of MESA. Am. J. Hypertens. 2023, 36, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatasciore, A.; Zimarino, M.; Renda, G.; Zurro, M.; Soccio, M.; Prontera, C.; Emdin, M.; Flacco, M.; Schillaci, G.; De Caterina, R. Awake Blood Pressure Variability, Inflammatory Markers and Target Organ Damage in Newly Diagnosed Hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2008, 31, 2137–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parati, G.; Bilo, G.; Kollias, A.; Pengo, M.; Ochoa, J.E.; Castiglioni, P.; Stergiou, G.S.; Mancia, G.; Asayama, K.; Asmar, R.; et al. Blood Pressure Variability: Methodological Aspects, Clinical Relevance and Practical Indications for Management—A European Society of Hypertension Position Paper*. J. Hypertens. 2023, 41, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Havenon, A.; Anadani, M.; Prabhakaran, S.; Wong, K.-H.; Yaghi, S.; Rost, N. Increased Blood Pressure Variability and the Risk of Probable Dementia or Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Post Hoc Analysis of the SPRINT MIND Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e022206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Havenon, A.; Fino, N.F.; Johnson, B.; Wong, K.-H.; Majersik, J.J.; Tirschwell, D.; Rost, N. Blood Pressure Variability and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Prior Stroke: A Secondary Analysis of PRoFESS. Stroke 2019, 50, 3170–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, M.E.; Ryan, J.; Chowdhury, E.K.; Margolis, K.L.; Beilin, L.J.; Reid, C.M.; Nelson, M.R.; Woods, R.L.; Shah, R.C.; Orchard, S.G.; et al. Long-Term Blood Pressure Variability and Risk of Cognitive Decline and Dementia Among Older Adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Shlipak, M.G.; Stawski, R.S.; Peralta, C.A.; Psaty, B.M.; Harris, T.B.; Satterfield, S.; Shiroma, E.J.; Newman, A.B.; Odden, M.C.; et al. Visit-to-Visit Blood Pressure Variability and Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes Among Older Adults: The Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2017, 30, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezue, K.; Goyal, A.; Pressman, G.S.; Matthew, R.; Horrow, J.C.; Rangaswami, J. Blood Pressure Variability Predicts Adverse Events and Cardiovascular Outcomes in SPRINT. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2018, 20, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, M.E.; Chowdhury, E.K.; Beilin, L.J.; Margolis, K.L.; Nelson, M.R.; Wolfe, R.; Tonkin, A.M.; Ryan, J.; Woods, R.L.; McNeil, J.J.; et al. Long-Term Blood Pressure Variability and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Events Among Community-Dwelling Elderly. Hypertension 2020, 76, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrand, W.K.; Visser, C.A.; Hermens, W.T.; Niessen, H.W.M.; Verheugt, F.W.A.; Wolbink, G.-J.; Hack, C.E. C-Reactive Protein as a Cardiovascular Risk Factor. Circulation 1999, 100, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Carter, P.; Bruzelius, M.; Vithayathil, M.; Kar, S.; Mason, A.M.; Lin, A.; Burgess, S.; Larsson, S.C. Effects of Tumour Necrosis Factor on Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlay, S.M.; Weston, S.A.; Redfield, M.M.; Killian, J.M.; Roger, V.L. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNFα) and Mortality in Heart Failure: A Community Study. Circulation 2008, 118, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossmann, M.; Wainstein, M.V.; Mariani, S.; Machado, G.P.; de Araújo, G.N.; Andrades, M.; Gonçalves, S.C.; Bertoluci, M.C. Increased Serum IL-6 Is Predictive of Long-Term Cardiovascular Events in High-Risk Patients Submitted to Coronary Angiography: An Observational Study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ye, D.; Wang, Z.; Pan, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; et al. The Role of Interleukin-6 Family Members in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 818890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerabhadrappa, P.; Diaz, K.M.; Feairheller, D.L.; Sturgeon, K.M.; Williamson, S.; Crabbe, D.L.; Kashem, A.; Ahrensfield, D.; Brown, M.D. Enhanced Blood Pressure Variability in a High Cardiovascular Risk Group of African Americans: FIT4Life Study. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. JASH 2010, 4, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Novo, G.; Bellia, C.; Fiore, M.; Bonomo, V.; Pugliesi, M.; Giovino, M.; Sasso, B.L.; Meraviglia, S.; Assennato, P.; Novo, S.; et al. A Risk Score Derived from the Analysis of a Cluster of 27 Serum Inflammatory Cytokines to Predict Long Term Outcome in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Pilot Study. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 45, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Calvillo, L.; Gironacci, M.M.; Crotti, L.; Meroni, P.L.; Parati, G. Neuroimmune Crosstalk in the Pathophysiology of Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhur, M.S.; Lob, H.E.; McCann, L.A.; Iwakura, Y.; Blinder, Y.; Guzik, T.J.; Harrison, D.G. Interleukin 17 Promotes Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension and Vascular Dysfunction. Hypertension 2010, 55, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.G.; Guzik, T.J.; Lob, H.E.; Madhur, M.S.; Marvar, P.J.; Thabet, S.R.; Vinh, A.; Weyand, C.M. Inflammation, Immunity, and Hypertension. Hypertension 2011, 57, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frattola, A.; Parati, G.; Cuspidi, C.; Albini, F.; Mancia, G. Prognostic Value of 24-Hour Blood Pressure Variability. J. Hypertens. 1993, 11, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, T.G.; Hall, J.E.; Appel, L.J.; Falkner, B.E.; Graves, J.; Hill, M.N.; Jones, D.W.; Kurtz, T.; Sheps, S.G.; Roccella, E.J. Recommendations for Blood Pressure Measurement in Humans and Experimental Animals: Part 1: Blood Pressure Measurement in Humans: A Statement for Professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation 2005, 111, 697–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G.; Ferrari, A.; Gregorini, L.; Parati, G.; Pomidossi, G.; Bertinieri, G.; Grassi, G.; di Rienzo, M.; Pedotti, A.; Zanchetti, A. Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Variabilities in Normotensive and Hypertensive Human Beings. Circ. Res. 1983, 53, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilo, G.; Dolan, E.; O’Brien, E.; Facchetti, R.; Soranna, D.; Zambon, A.; Mancia, G.; Parati, G. The Impact of Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure Variability on Mortality Is Modified by Ageing. Data from the Dublin Outcome Study. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulè, G.; Calcaterra, I.; Costanzo, M.; Geraci, G.; Guarino, L.; Foraci, A.C.; Vario, M.G.; Cerasola, G.; Cottone, S. Relationship Between Short-Term Blood Pressure Variability and Subclinical Renal Damage in Essential Hypertensive Patients. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2015, 17, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoncini, G.; Viazzi, F.; Storace, G.; Deferrari, G.; Pontremoli, R. Blood Pressure Variability and Multiple Organ Damage in Primary Hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2013, 27, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhee, J.H.; Oh, D.; Seo, J.; Lee, C.J.; Chung, M.-Y.; Park, J.T.; Han, S.H.; Kang, S.-W.; Park, S.; Yoo, T.-H. Short-Term Blood Pressure Variability and Incident CKD in Patients with Hypertension: Findings from the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Etiology Research Center-High Risk (CMERC-HI) Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2023, 81, 384–393.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-I.; Lee, J.-H.; Chang, H.-J.; Cho, Y.-S.; Youn, T.-J.; Chung, W.-Y.; Chae, I.-H.; Choi, D.-J.; Park, K.U.; Kim, C.-H. Association between Blood Pressure Variability and Inflammatory Marker in Hypertensive Patients. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, E.R.; Morales-Muñoz, I.; Perry, B.I.; Marwaha, S.; Warwick, E.; Rogers, J.C.; Upthegrove, R. Trajectories of Inflammation in Youth and Risk of Mental and Cardiometabolic Disorders in Adulthood. JAMA Psychiatry 2024, 81, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, G.M.; Pearson, R.M.; Zammit, S.; Lewis, G.; Jones, P.B. Association of Serum Interleukin 6 and C-Reactive Protein in Childhood with Depression and Psychosis in Young Adult Life: A Population-Based Longitudinal Study. JAMA Psychiatry 2014, 71, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solmi, F.; Bulik, C.M.; De Stavola, B.L.; Dalman, C.; Khandaker, G.M.; Lewis, G. Longitudinal Associations between Circulating Interleukin-6 and C-Reactive Protein in Childhood, and Eating Disorders and Disordered Eating in Adolescence. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todendi, P.F.; Possuelo, L.G.; Klinger, E.I.; Reuter, C.P.; Burgos, M.S.; Moura, D.J.; Fiegenbaum, M.; Valim, A.R. de M. Low-Grade Inflammation Markers in Children and Adolescents: Influence of Anthropometric Characteristics and CRP and IL6 Polymorphisms. Cytokine 2016, 88, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balagopal, P.B.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Cook, S.; Daniels, S.R.; Gidding, S.S.; Hayman, L.L.; McCrindle, B.W.; Mietus-Snyder, M.L.; Steinberger, J.; American Heart Association Committee on Atherosclerosis Hypertension and Obesity in Youth of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; et al. Nontraditional Risk Factors and Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanistic, Research, and Clinical Considerations for Youth: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011, 123, 2749–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosovski, I.B.; Bacârea, V.; Ghiga, D.; Ciurea, C.N.; Cucoranu, D.C.; Hutanu, A.; Bacârea, A. Exploring the Link between Inflammatory Biomarkers and Adipometrics in Healthy Young Adults Aged 20–35 Years. Nutrients 2024, 16, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.; Asmar, R.; Beilin, L.; Imai, Y.; Mallion, J.-M.; Mancia, G.; Mengden, T.; Myers, M.; Padfield, P.; Palatini, P.; et al. European Society of Hypertension Recommendations for Conventional, Ambulatory and Home Blood Pressure Measurement. J. Hypertens. 2003, 21, 821–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parati, G.; Stergiou, G.S.; Asmar, R.; Bilo, G.; de Leeuw, P.; Imai, Y.; Kario, K.; Lurbe, E.; Manolis, A.; Mengden, T.; et al. European Society of Hypertension Practice Guidelines for Home Blood Pressure Monitoring. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2010, 24, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Snieder, H.; Su, S.; Harshfield, G.A.; Treiber, F.A.; Wang, X. A Longitudinal Study of Blood Pressure Variability in African-American and European American Youth. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, L.J.; Felix, V.G.; Melgarejo, J.D.; Maestre, G.E. 24-Hour Blood Pressure Variability Assessed by Average Real Variability: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, C.E.; Jeemon, P.; Coleman, H.; McCallum, L.; Patel, R.; Dawson, J.; Sloan, W.; Meredith, P.; Jones, G.C.; Muir, S.; et al. Long-Term and Ultra Long–Term Blood Pressure Variability During Follow-Up and Mortality in 14 522 Patients with Hypertension. Hypertension 2013, 62, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldo, P.; Marusov, G.; Svancara, D.; David, J.; Mor, G. Simple Plex(™): A Novel Multi-Analyte, Automated Microfluidic Immunoassay Platform for the Detection of Human and Mouse Cytokines and Chemokines. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 75, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.H.; Lim, S.Y.; Han, K.-D.; Oh, T.R.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; Ma, S.K.; Kim, S.W. Association Between Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure Variability and the Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease. Hypertension 2019, 74, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, R.; Xu, Y.; Eramudugolla, R.; Sachdev, P.S.; Cherbuin, N.; Tully, P.J.; Mortby, M.E.; Anstey, K.J. Diastolic Blood Pressure Variability in Later Life May Be a Key Risk Marker for Cognitive Decline. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkan, G.; Ulusoy, Ş.; Arıcı, M.; Derici, Ü.; Akpolat, T.; Şengül, Ş.; Yılmaz, R.; Ertürk, Ş.; Arınsoy, T.; Değer, S.M.; et al. Does Blood Pressure Variability Affect Hypertension Development in Prehypertensive Patients? Am. J. Hypertens. 2022, 35, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, Y. Visit-to-Visit Blood Pressure Variability-What Is the Current Challenge? Am. J. Hypertens. 2017, 30, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, T.J.; Touyz, R.M. Vascular Pathophysiology of Hypertension. In The ESC Textbook of Vascular Biology; Krams, R., Bäck, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-0-19-875577-7. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.H.; Kim, R.E.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, N.H.; Yoo, H.J.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; et al. Night Blood Pressure Variability, Brain Atrophy, and Cognitive Decline. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 963648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatini, P.; Reboldi, G.; Beilin, L.J.; Casiglia, E.; Eguchi, K.; Imai, Y.; Kario, K.; Ohkubo, T.; Pierdomenico, S.D.; Schwartz, J.E.; et al. Added Predictive Value of Night-Time Blood Pressure Variability for Cardiovascular Events and Mortality: The Ambulatory Blood Pressure-International Study. Hypertension 2014, 64, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arici Duz, O.; Helvaci Yilmaz, N. Nocturnal Blood Pressure Changes in Parkinson’s Disease: Correlation with Autonomic Dysfunction and Vitamin D Levels. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2020, 120, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X.; Meng, X.; Zhou, X. Role of Inflammation, Immunity, and Oxidative Stress in Hypertension: New Insights and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1098725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Visit 13–15 All Patients (n = 447) | 1 Visit (n = 144) | 2 Visits (n = 210) | 3 Visits (n = 93) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 22.90 ± 3.11 | 23.63 ± 3.21 | 23.69 ± 3.19 | 21.34 ± 2.21 | <0.01 * |
| Sex, n (%) | |||||
| -Male | 212 (47.43%) | 67 (46.53%) | 104 (49.52%) | 41 (44.09%) | - |
| -Female | 235 (52.57%) | 77 (53.47%) | 106 (50.48%) | 52 (55.91%) | - |
| Race, n (%) | |||||
| Non-Hispanic White | 210 (46.98%) | 64 (44.44%) | 92 (43.81%) | 54 (58.06%) | - |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 237 (53.02%) | 80 (55.56%) | 118 (56.19%) | 39 (41.94%) | - |
| Mean Systolic BP, mmHg | 118.44 ± 9.62 | 119.93 ± 11.19 | 118.95 ± 9.43 | 116.91 ± 8.83 | <0.01 * |
| Mean Diastolic BP, mmHg | 70.74 ± 7.50 | 72.19 ± 8.84 | 71.13 ± 7.67 | 69.40 ± 6.20 | <0.01 * |
| 20 h BPV Systolic BP | 7.75 ± 1.41 | 7.87 ± 1.71 | 7.72 ± 1.28 | 7.74 ± 1.46 | 0.74 |
| Daytime BPV Systolic BP | 7.79 ± 1.65 | 7.91 ± 1.90 | 7.72 ± 1.59 | 7.85 ± 1.63 | 0.53 |
| Nighttime BPV Systolic BP | 7.80 ± 2.52 | 7.66 ± 2.43 | 8.02 ± 1.28 | 7.54 ± 2.48 | 0.08 |
| 20 h BPV Diastolic BP | 7.62 ± 1.50 | 7.73 ± 1.60 | 7.65 ± 1.46 | 7.53 ± 1.51 | 0.59 |
| Daytime BPV Diastolic BP | 7.79 ± 1.77 | 7.84 ± 1.86 | 7.83 ± 1.75 | 7.71 ± 1.77 | 0.73 |
| Nighttime BPV Diastolic BP | 7.49 ± 2.54 | 7.55 ± 2.41 | 7.65 ± 2.17 | 7.23 ± 2.46 | 0.17 |
| CRP Serum Concentration mg/L | 3.39 × 10−3 ± 7.25 × 10−3 | 4.06 × 10−3 ± 1.06 × 10−2 | 3.51 × 10−3 ± 7.45 × 10−3 | 2.84 × 10−3 ± 4.15 × 10−3 | 0.54 |
| IL6 Serum Concentration pg/mL | 3.83 ± 7.38 | 5.75 ± 10.50 | 3.65 ± 7.90 | 2.97 ± 1.88 | 0.20 |
| TNF-α Serum Concentration pg/mL | 6.30 ± 5.39 | 6.10 ± 1.31 | 6.58 ± 7.27 | 5.94 ± 1.35 | 0.56 |
| IFN-γ Serum Concentration pg/mL | 0.87 ± 1.17 | 0.90 ± 1.28 | 0.94 ± 1.38 | 0.75 ± 0.55 | 0.46 |
| Variable | Estimate (β) | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP | ||||
| 0.048 | 0.03 | −0.010, 0.107 | 0.104 |
| 0.017 | 0.019 | −0.020, 0.054 | 0.364 |
| 0.019 | 0.013 | −0.006, 0.045 | 0.136 |
| 0.076 | 0.023 | 0.031, 0.120 | 0.001 * |
| 0.054 | 0.017 | 0.020, 0.088 | 0.002 * |
| 0.028 | 0.012 | 0.005, 0.052 | 0.020 * |
| IFN-γ | ||||
| 0.002 | 0.016 | −0.029, 0.034 | 0.886 |
| −0.005 | 0.013 | −0.030, 0.020 | 0.677 |
| −0.003 | 0.007 | −0.016, 0.010 | 0.655 |
| −0.003 | 0.011 | −0.025, 0.018 | 0.765 |
| −0.006 | 0.011 | −0.027, 0.016 | 0.605 |
| −0.001 | 0.007 | −0.013, 0.013 | 0.986 |
| TNF-α | ||||
| 0.004 | 0.005 | −0.006, 0.014 | 0.357 |
| 0.000 | 0.004 | −0.007, 0.006 | 0.747 |
| −0.001 | 0.002 | −0.005, 0.003 | 0.443 |
| 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.002, 0.021 | 0.015 * |
| 0.003 | 0.003 | −0.003, 0.009 | 0.915 |
| 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.002, 0.010 | 0.007 * |
| IL6 | ||||
| 0.008 | 0.013 | −0.018, 0.035 | 0.546 |
| 0.008 | 0.009 | −0.009, 0.026 | 0.350 |
| −0.004 | 0.007 | −0.017, 0.010 | 0.574 |
| 0.018 | 0.011 | −0.004, 0.040 | 0.110 |
| 0.010 | 0.009 | −0.009, 0.028 | 0.309 |
| 0.011 | 0.008 | −0.004, 0.026 | 0.150 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weeks, C.J.; Bekele, B.B.; Altvater, M.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, H.; Huang, Y.; Jehu, D.A.; Simon, A.B.; Li, W.; Dong, Y. The Association Between Short-Term Blood Pressure Variability and Inflammation in Healthy Young Adults. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100399
Weeks CJ, Bekele BB, Altvater M, Cheng J, Zhu H, Huang Y, Jehu DA, Simon AB, Li W, Dong Y. The Association Between Short-Term Blood Pressure Variability and Inflammation in Healthy Young Adults. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(10):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100399
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeeks, Charles J., Bayu B. Bekele, Michelle Altvater, Jie Cheng, Haidong Zhu, Ying Huang, Deborah A. Jehu, Abigayle B. Simon, Wenjun Li, and Yanbin Dong. 2025. "The Association Between Short-Term Blood Pressure Variability and Inflammation in Healthy Young Adults" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 10: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100399
APA StyleWeeks, C. J., Bekele, B. B., Altvater, M., Cheng, J., Zhu, H., Huang, Y., Jehu, D. A., Simon, A. B., Li, W., & Dong, Y. (2025). The Association Between Short-Term Blood Pressure Variability and Inflammation in Healthy Young Adults. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(10), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100399








