The Glymphatic System and Diaphragmatic Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Chronic Heart Failure: The Importance of Inspiratory Rehabilitation Training
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Cognitive Decline
1.2. Chronic Heart Failure and Cognitive Decline
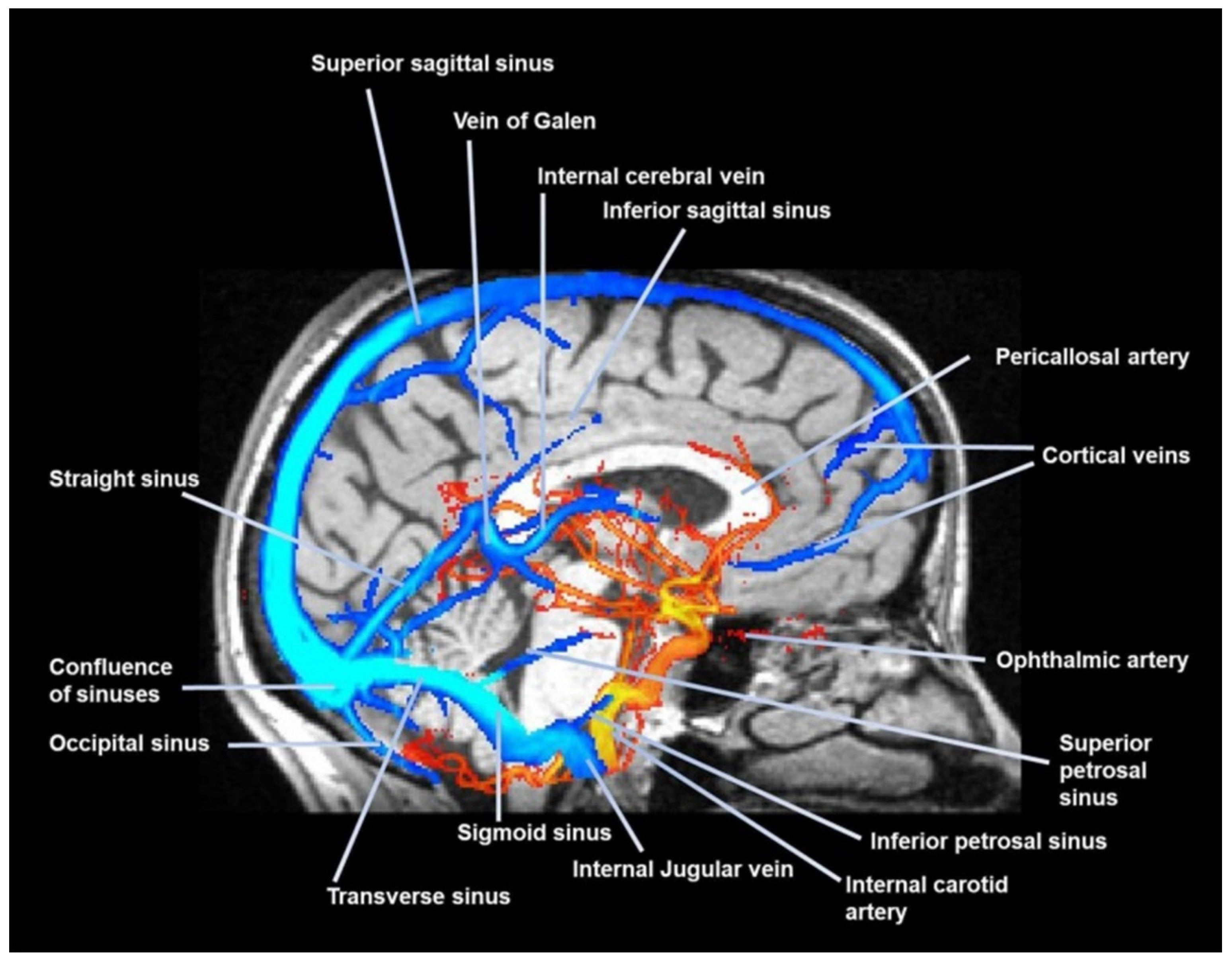
1.3. Glymphatic System
1.4. The Cerebrospinal Fluid and the Glympatic System
1.5. Assessments for Dementia Detection
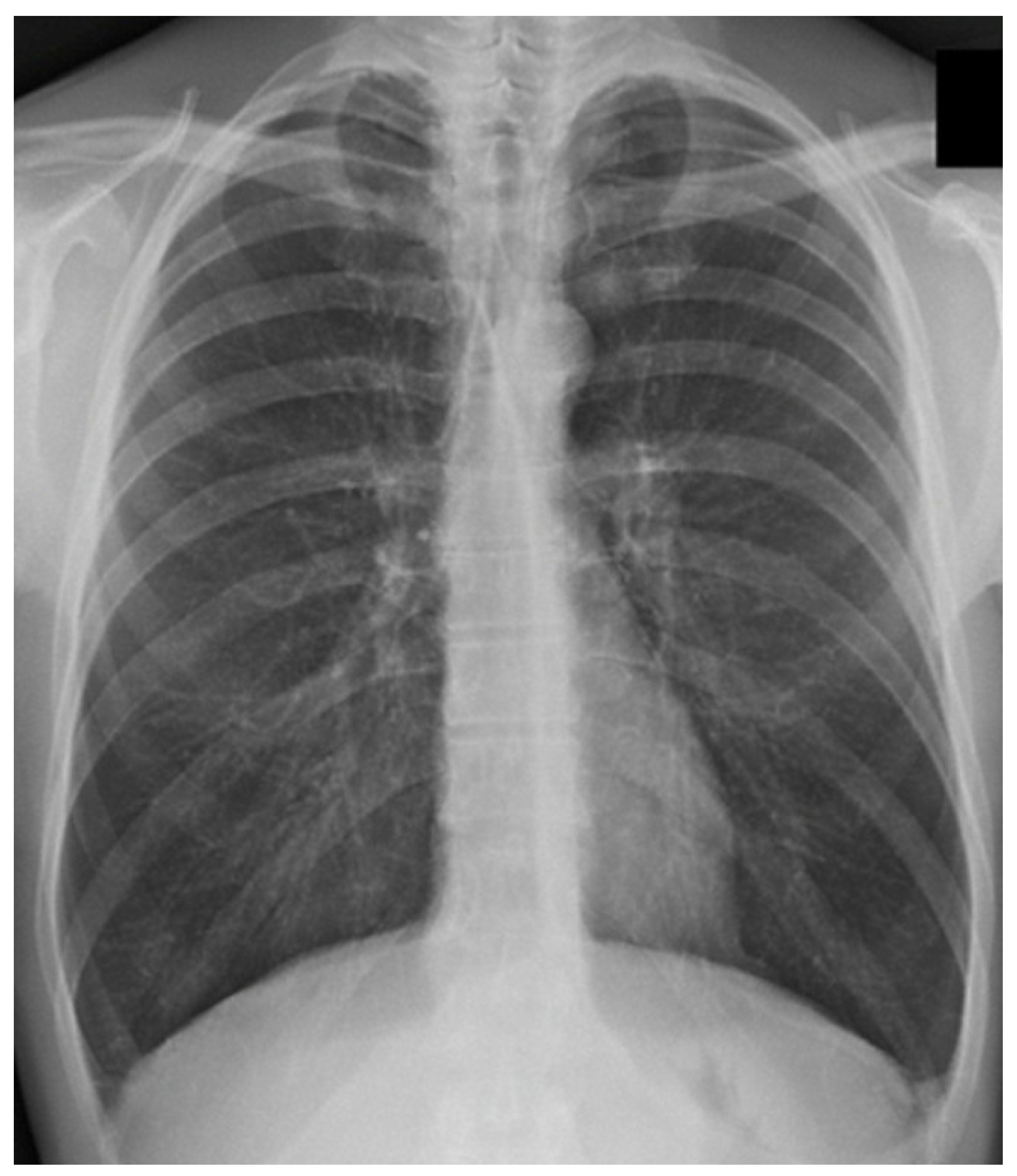
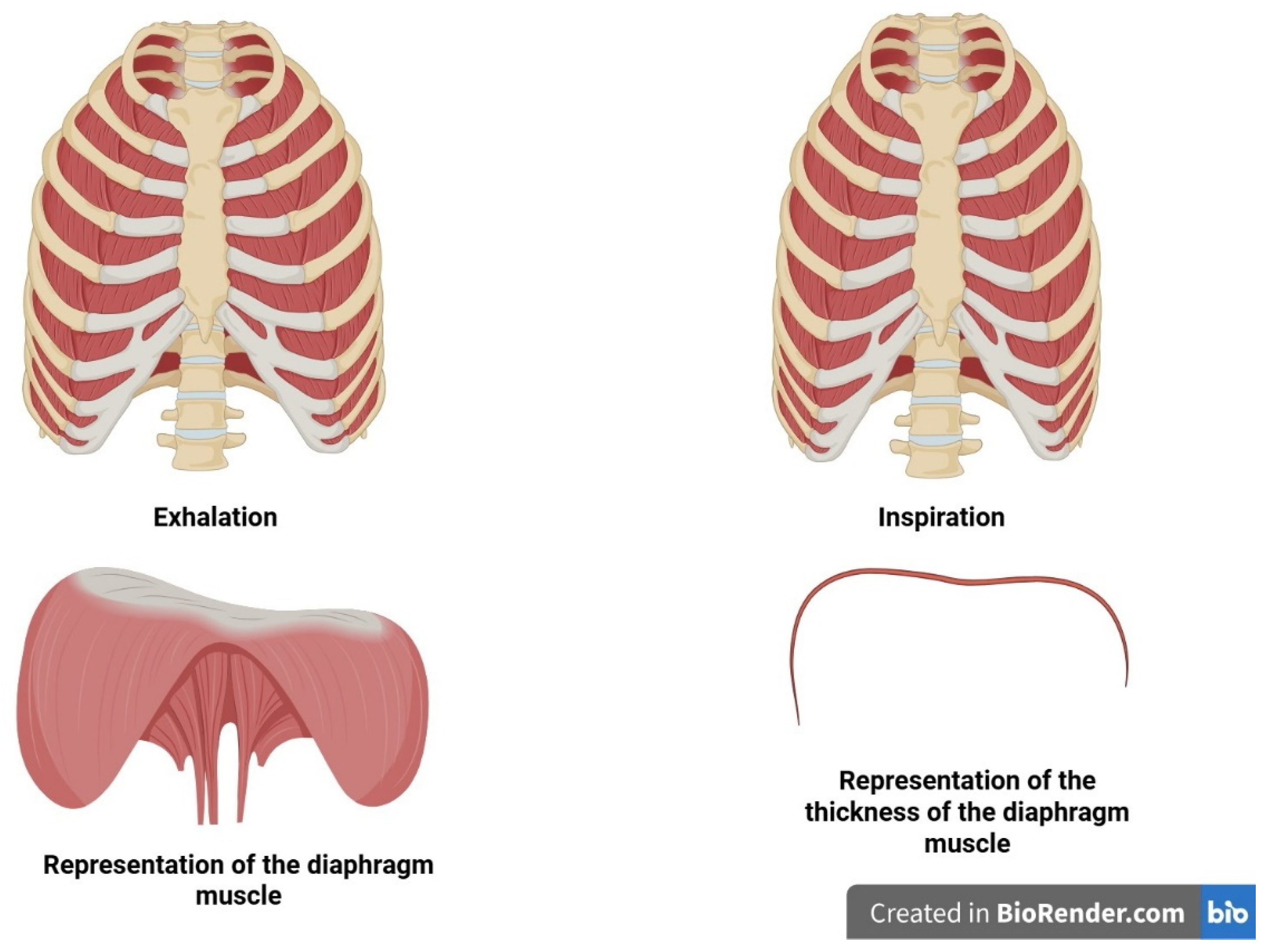
1.6. COPD and the Diaphragm
1.7. CHF and Diaphragm
1.8. Inspiratory Muscle Training (IMT)
1.9. Future Challenges
2. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, J.; Cong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, N.; Fang, L.; Chen, Y. Associations of pre-COPD indicators with lung function decline and their longitudinal transitions. Pulmonology 2025, 31, 2486881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Strategy for Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of Copd: 2025 Report. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD, Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) 2025. Available online: https://goldcopd.org/2025-gold-report/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Xiong, T.; Bai, X.; Wei, X.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Shi, H.; Shi, Y. Exercise Rehabilitation and Chronic Respiratory Diseases: Effects, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Benefits. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2023, 18, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Castro, R.; Caicedo-Trujillo, S.; Gimeno-Santos, E.; Gutiérrez-Arias, R.; Alsina-Restoy, X.; Vasconcello-Castillo, L.; Seron, P.; Spruit, M.A.; Blanco, I.; Vilaró, J. Effectiveness of inspiratory muscle training in patients with a chronic respiratory disease: An overview of systematic reviews. Front. Sports Act. Living 2025, 7, 1549652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, G.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Tramontano, A.; Iannone, F.P.; D’Angelo, A.; Pezzella, R.; Testa, C.; Parlato, A.; Merone, P.; Pacileo, M.; et al. Exercise Training in Patients with Heart Failure: From Pathophysiology to Exercise Prescription. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoicescu, L.; Crişan, D.; Morgovan, C.; Avram, L.; Ghibu, S. Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: The Pathophysiological Mechanisms behind the Clinical Phenotypes and the Therapeutic Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmons-Bell, S.; Johnson, C.; Roth, G. Prevalence, incidence and survival of heart failure: A systematic review. Heart 2022, 108, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragazzi, N.L.; Zhong, W.; Shu, J.; Abu Much, A.; Lotan, D.; Grupper, A.; Younis, A.; Dai, H. Burden of heart failure and underlying causes in 195 countries and territories from 1990 to 2017. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sánchez, I.; Rodríguez-Alzueta, E.; Cabrera-Martos, I.; López-Torres, I.; Moreno-Ramírez, M.P.; Valenza, M.C. Cognitive impairment in COPD: A systematic review. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2015, 41, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, A.; Månsson, T.; Egervall, K.; Elmståhl, S.; Overton, M. Cognitive decline and risk of dementia in older adults after diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2023, 33, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Khubchandani, J.; England-Kennedy, E.; McIntyre, R.; Kopera-Frye, K.; Batra, K. Cognitive Functioning Influences Mortality Risk Among Older Adults with COPD. Healthcare 2024, 12, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militaru, M.; Lighezan, D.F.; Tudoran, C.; Tudoran, M.; Militaru, A.G. Factors Influencing the Development and Severity of Cognitive Decline in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Medicina 2024, 60, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Dewan, P.; Ferreira, J.P.; Cunningham, J.W.; Jhund, P.S.; Anand, I.S.; Chandra, A.; Chiang, L.M.; Claggett, B.; Desai, A.S.; et al. Clinical Correlates and Prognostic Impact of Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction: Insights from PARAGON-HF. Circulation 2024, 150, 1913–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, J.S.; Oyelade, T.; Sreedharan, J.; Aldhahir, A.M.; Alghamdi, S.M.; Alrajeh, A.M.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Alsulayyim, A.; Aldabayan, Y.S.; Alobaidi, N.Y.; et al. Diagnostic and clinical values of non-cardiac ultrasound in COPD: A systematic review. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2020, 7, e000717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangner, N.; Garbade, J.; Heyne, E.; van den Berg, M.; Winzer, E.B.; Hommel, J.; Sandri, M.; Jozwiak-Nozdrzykowska, J.; Meyer, A.L.; Lehmann, S.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Diaphragm Myopathy in Humans with Severe Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Faner, R.; Pavord, I.; Baraldi, F.; McDonald, V.M.; Thomas, M.; Miravitlles, M.; Roche, N.; Agustí, A. From treatable traits to GETomics in airway disease: Moving towards clinical practice. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2024, 33, 230143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, D.; Casas-Recasens, S.; Faner, R.; Palange, P.; Agusti, A. When GETomics meets aging and exercise in COPD. Respir. Med. 2023, 216, 107294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiamutai, F.N.U.; Hatfield, A.; Herbert, A.; Majumdar, D.; Shankar, V.; Lackey, L. Altered polyadenylation site usage in SERPINA1 3’UTR in response to cellular stress affects A1AT protein expression. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.P.; Nakhmani, A.; Fortis, S.; Strand, M.J.; Silverman, E.K.; Sciurba, F.C.; Bodduluri, S. FEV1/FVC Severity Stages for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 208, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, I.L.; Ting-Chia, C.; Huang, T.H.; Chang-Wen, C.; Hsiue, T.R.; Tsung, Y.; Kuo, C.W. Comparison of stability of the GOLD and STAR lung function classification for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2025, 12, e002830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sanz, M.T.; Cánive-Gómez, J.C.; Senín-Rial, L.; Aboal-Viñas, J.; Barreiro-García, A.; López-Val, E.; González-Barcala, F.J. One-year and long-term mortality in patients hospitalized for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fan, Z.; Xie, Z.; Sun, Q. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting the risk of cognitive impairment among chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2528448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siraj, R.A.; Alrajeh, A.M.; Alahmari, M.A.; Alahmadi, F.H.; Aldhahir, A.M.; Alqarni, A.A.; Alqahtani, J.S.; Alghamdi, S.M.; Alanazi, T.M.; Alruwaili, A.; et al. Managing cognitive impairment in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in Saudi Arabia: What are the current practices? Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2413924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wu, H.; Xu, H.; Zhao, J.; Chang, Z.; Zhao, Q. The relationship between social isolation and cognitive function in older patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A latent profile analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2025, 25, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xiao, H.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Meng, X.; Wang, F. The Lung-Brain Axis in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease-Associated Neurocognitive Dysfunction: Mechanistic Insights and Potential Therapeutic Options. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2025, 21, 3461–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, D.J.; Ditor, D.S. The common inflammatory etiology of depression and cognitive impairment: A therapeutic target. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lull, M.E.; Block, M.L. Microglial activation and chronic neurodegeneration. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2010, 7, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.K. Hypoxia. 3. Hypoxia and neurotransmitter synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C743–C751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanclares, C.; Colmena, I.; Muñoz-Montero, A.; Baraibar, A.M.; de Pascual, R.; Wojnicz, A.; Ruiz-Nuño, A.; García, A.G.; Gironda-Martínez, A.; Gandía, L. Beyond the brain: Early autonomic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2025, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.W.; Yang, M.M.; Zhou, M.X.; Wei, Y.Y.; Hu, L.; Hong, M.; Chen, T.T.; Wang, X.M.; Ding, Y.C.; Wei, C.S.; et al. Sestrin2 alleviates cognitive impairment via inhibiting hippocampus ferroptosis in cigarette smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Redox Biol. 2025, 85, 103673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Liu, Y.; Guan, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. Neuroimaging insights into lung disease-related brain changes: From structure to function. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2025, 17, 1550319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yu, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Guan, H.; Tang, R.; Yan, L.; Zhou, P. Gray matter and cognitive alteration related to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients: Combining ALE meta-analysis and MACM analysis. Brain Imaging Behav. 2025, 19, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghini, A.; Sammartino, A.M.; Papp, Z.; von Haehling, S.; Biegus, J.; Ponikowski, P.; Adamo, M.; Falco, L.; Lombardi, C.M.; Pagnesi, M.; et al. 2024 update in heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2025, 12, 8–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Năstasie, O.C.; Radu, D.A.; Onciul, S.; Drăgoescu, M.B.; Popa-Fotea, N.M. Nexilin mutations, a cause of chronic heart failure: A state-of-the-art review starting from a clinical case. World J. Cardiol. 2025, 17, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahim, B.; Kapelios, C.J.; Savarese, G.; Lund, L.H. Global Public Health Burden of Heart Failure: An Updated Review. Card Fail Rev 2023, 9, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2023 Focused Update of the 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2024, 26, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrominski, J.W.; DeFilippis, E.M.; Bansal, K.; Riello, R.J., 3rd; Bozkurt, B.; Heidenreich, P.A.; Vaduganathan, M. Contemporary American and European Guidelines for Heart Failure Management: JACC: Heart Failure Guideline Comparison. JACC Heart Fail. 2024, 12, 810–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, M.C.; Vigna, M.; Saglietto, A.; Iuliano, M.A.; Mandoli, G.E.; Stefanini, A.; Carrucola, C.; Fusini, L.; Cavigli, L.; D’ascenzi, F.; et al. Prognostic value of left atrial strain in acute and chronic heart failure: A meta-analysis. ESC Heart Fail. 2025, 12, 2921–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metra, M.; Tomasoni, D.; Adamo, M.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Filippatos, G.; Abdelhamid, M.; Adamopoulos, S.; Anker, S.D.; Antohi, L.; Böhm, M.; et al. Worsening of chronic heart failure: Definition, epidemiology, management and prevention. A clinical consensus statement by the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 776–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.A.; Zaccardi, F.; Squire, I.; Okhai, H.; Davies, M.; Huang, W.; Mamas, M.; Lam, C.S.P.; Khunti, K.; Kadam, U.T. Risk Factors for Heart Failure: 20-Year Population-Based Trends by Sex, Socioeconomic Status, and Ethnicity. Circ. Heart Fail. 2020, 13, e006472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, A.M.; Boyd, C.M.; Manemann, S.M.; Dunlay, S.M.; Gerber, Y.; Killian, J.M.; Weston, S.A.; Roger, V.L. Risk Factors for Heart Failure in the Community: Differences by Age and Ejection Fraction. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, e237–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.V.; Segar, M.W.; Lavie, C.J.; Kondamudi, N.; Neeland, I.J.; Almandoz, J.P.; Martin, C.K.; Carbone, S.; Butler, J.; Powell-Wiley, T.M.; et al. Diabetes Status Modifies the Association Between Different Measures of Obesity and Heart Failure Risk Among Older Adults: A Pooled Analysis of Community-Based NHLBI Cohorts. Circulation 2022, 145, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, W.C.; de Boer, R.A. Common risk factors for heart failure and cancer. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, M.W.; Vo, J.B.; Rodgers, J.E.; Ferrari, A.M.; Nohria, A.; Deswal, A.; Cheng, R.K.; Kittleson, M.M.; Upshaw, J.N.; Palaskas, N.; et al. Cardio-Oncology and Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement from the Heart Failure Society of America. J. Card. Fail. 2025, 31, 415–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, C.J.; Luchkanych, A.M.S.; Boyes, N.G.; Champagne, A.A.; Kelly, M.E.; Nelson, M.D.; Marshall, R.A.; Karjala, G.; Zhai, A.; Haddad, H.; et al. Cardiac dysfunction is associated with indices of brain atrophy and cognitive impairment in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. J. Appl. Physiol. 2025, 138, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting Liu, Y.; Ting Yang, Y.; Xiang Tang, C.; Qing Ma, J.; Kong, X.; Hua Li, J.; Ming Li, Y.; Yu Liu, S.; Sheng Zhou, C.; Jiang Zhang, L. Brain structural and functional changes in patients with chronic heart failure. Neuroscience 2025, 565, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Yadav, S.K.; Palomares, J.A.; Park, B.; Joshi, S.H.; Ogren, J.A.; Macey, P.M.; Fonarow, G.C.; Harper, R.M.; Woo, M.A. Reduced regional brain cortical thickness in patients with heart failure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havakuk, O.; King, K.S.; Grazette, L.; Yoon, A.J.; Fong, M.; Bregman, N.; Elkayam, U.; Kloner, R.A. Heart Failure-Induced Brain Injury. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanninen, S.A.; Darling, P.B.; Sole, M.J.; Barr, A.; Keith, M.E. The prevalence of thiamin deficiency in hospitalized patients with congestive heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi-Namini, P.; Ahmed, M.; Yan, A.T.; Desjardins, S.; Al-Hesayen, A.; Mangat, I.; Keith, M. Prevalence of Thiamin Deficiency in Ambulatory Patients with Heart Failure. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 119, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abete, P.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Basile, C.; Langellotto, A.; Galizia, G.; Testa, G.; Canonico, V.; Bonaduce, D.; Cacciatore, F. Cognitive impairment and cardiovascular diseases in the elderly. A heart-brain continuum hypothesis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2014, 18, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doehner, W.; Ural, D.; Haeusler, K.G.; Čelutkienė, J.; Bestetti, R.; Cavusoglu, Y.; Peña-Duque, M.A.; Glavas, D.; Iacoviello, M.; Laufs, U.; et al. Heart and brain interaction in patients with heart failure: Overview and proposal for a taxonomy. A position paper from the study group on heart and brain interaction of the heart failure association. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, F.Q.; Kong, W.K.F.; Wong, R.C.C.; Chong, Y.F.; Chew, N.W.S.; Yeo, T.C.; Sharma, V.K.; Poh, K.K.; Sia, C.H. Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure-A Review. Biology 2022, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyrou, A. The Misfolding of Proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1195, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasana, E.; Fregno, I.; Galli, C.; Soldà, T.; Molinari, M. ER-to-lysosome-associated degradation acts as failsafe mechanism upon ERAD dysfunction. EMBO Rep. 2024, 25, 2773–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, M.; Patterson, C. Proteotoxicity and Cardiac Dysfunction—Alzheimer’s Disease of the Heart? N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Didomenico, R.J.; Pressler, S.J.; Ibeh, C.; White-Williams, C.; Allen, L.A.; Gorodeski, E.Z. HFSA Scientific Statement Committee Members Cognitive Impairment in Heart Failure: A Heart Failure Society of America Scientific Statement, J. Card. Fail. 2024, 30, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, G.; Franssen, C.F.M.; Perna, A.F.; Massy, Z.A.; Menzies, R.I.; Zoccali, C.; Tessitore, A.; Nedergaard, M.; Okusa, M.D.; Ortiz, A.; et al. Drivers and mechanisms of cognitive decline in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2025, 21, 536–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliff, J.J.; Lee, H.; Yu, M.; Feng, T.; Logan, J.; Nedergaard, M.; Benveniste, H. Brain-wide pathway for waste clearance captured by contrast-enhanced MRI. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.R.; Lv, Q.K.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.F. New perspectives on the glymphatic system and the relationship between glymphatic system and neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2025, 205, 106791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Luo, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, R.; Ba, W.; Lian, X.; et al. Poor glymphatic function is associated with mild cognitive impairment and its progression to Alzheimer’s disease: A DTI-ALPS study. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2025, 12, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, T.; Hjorth, P.G.; Holst, S.C.; Hrabětová, S.; Kiviniemi, V.; Lilius, T.; Lundgaard, I.; Mardal, K.A.; Martens, E.A.; Mori, Y.; et al. The glymphatic system: Current understanding and modeling. iScience 2022, 25, 104987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, B.; Escher, A.; Compalati, E.; Mapelli, L.; Toccafondi, A. The Importance of the Diaphragm in Neuromotor Function in the Patient with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2023, 18, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, M.S.; Kittipibul, V.; Fudim, M. Sympathetic Nervous System in Heart Failure: Targets for Treatments. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2025, 27, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordoni, B.; Morabito, B.; Myftari, V.; D’Amato, A.; Severino, P. Chronic Heart Failure Rehabilitation: Diaphragm Training Needs More Attention. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, S.O.; Heptinstall, A.B.; Marjenberg, Z.; Marshall, J.; Mullerova, H.; Rogliani, P.; Nordon, C.; Hawkins, N.M. Temporal Dynamics of Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease During Stable Disease and Exacerbations: Review of the Mechanisms and Implications. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2024, 19, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Plá, V.; Giannetto, M.; Vinitsky, H.S.; Stæger, F.F.; Metcalfe, T.; Nguyen, R.; Benrais, A.; Nedergaard, M. Circadian control of brain glymphatic and lymphatic fluid flow. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gędek, A.; Koziorowski, D.; Szlufik, S. Assessment of factors influencing glymphatic activity and implications for clinical medicine. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1232304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldea, R.; Weller, R.O.; Wilcock, D.M.; Carare, R.O.; Richardson, G. Cerebrovascular Smooth Muscle Cells as the Drivers of Intramural Periarterial Drainage of the Brain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eide Therkelsen, H.; Enger, R.; Eide, P.K.; Ringstad, G. Evidence for cellular and solute passage between the brain and skull bone marrow across meninges: A systematic review. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2025, 45, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggini, T.; Duckworth, J.; Ji, X.; Liu, R.; Xia, X.; Mächler, P.; Shaked, I.; Munting, L.P.; Iyengar, S.; Kotlikoff, M.; et al. Long-wavelength traveling waves of vasomotion modulate the perfusion of cortex. Neuron 2024, 112, 2349–2367.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Hardebo, J.E.; Bouskela, E. Influence of cerebrovascular parasympathetic nerves on resting cerebral blood flow, spontaneous vasomotion, autoregulation, hypercapnic vasodilation and sympathetic vasoconstriction. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1994, 49, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Hardebo, J.E.; Bouskela, E. Influence of cerebrovascular sympathetic, parasympathetic, and sensory nerves on autoregulation and spontaneous vasomotion. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1995, 154, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiviniemi, V.; Wang, X.; Korhonen, V.; Keinänen, T.; Tuovinen, T.; Autio, J.; LeVan, P.; Keilholz, S.; Zang, Y.F.; Hennig, J.; et al. Ultra-fast magnetic resonance encephalography of physiological brain activity-Glymphatic pulsation mechanisms? J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2016, 36, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhu, J. Glymphatic system: An emerging therapeutic approach for neurological disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1138769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, B.; Koundal, S.; Al Bizri, E.; Chen, X.; Gursky, Z.; Dai, F.; Lim, A.; Heerdt, P.; Kipnis, J.; Tannenbaum, A.; et al. Continuous positive airway pressure increases CSF flow and glymphatic transport. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e170270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, D.; Liu, N.; Luan, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, H. Modulation of lymphatic transport in the central nervous system. Theranostics 2022, 12, 1117–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plog, B.A.; Kim, K.; Verhaege, D.; Kim, M.W.; Papadopoulos, Z.; Dikranian, K.; Dykstra, T.; Cao, J.; Perrin, R.J.; Schwetye, K.E.; et al. A route for cerebrospinal fluid flow through leptomeningeal arterial-venous overlaps enables macromolecule and fluid shunting. Nat. Neurosci. 2025, 28, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Han, Y. Targeting the brain’s glymphatic pathway: A novel therapeutic approach for cerebral small vessel disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2026, 21, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astara, K.; Pournara, C.; de Natale, E.R.; Wilson, H.; Vavougios, G.D.; Lappas, A.S.; Politis, M.; Christodoulou, N.G. A novel conceptual framework for the functionality of the glymphatic system. J. Neurophysiol. 2023, 129, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, J.; Haughton, V. Motion of the cerebellar tonsils in the foramen magnum during the cardiac cycle. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 1587–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwotchouang, B.S.T.; Eppelheimer, M.S.; Pahlavian, S.H.; Barrow, J.W.; Barrow, D.L.; Qiu, D.; Allen, P.A.; Oshinski, J.N.; Amini, R.; Loth, F. Regional Brain Tissue Displacement and Strain is Elevated in Subjects with Chiari Malformation Type I Compared to Healthy Controls: A Study Using DENSE MRI. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 49, 1462–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, S.E.; Hardy, C.J.; Jolesz, F.A. Brain and cerebrospinal fluid motion: Real-time quantification with M-mode MR imaging. Radiology 1994, 193, 477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsushiro, S.; Sunohara, S.; Tokushima, T.; Takizawa, K.; Matsumae, M.; Atsumi, H.; Horie, T.; Kajihara, N.; Kuroda, K. Characterization of Cardiac- and Respiratory-driven Cerebrospinal Fluid Motions Using a Correlation Mapping Technique Based on Asynchronous Two-dimensional Phase Contrast MR Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2021, 20, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, H.; Mori, Y.; Nedergaard, M. The Brain’s Glymphatic System: Current Controversies. Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kritsilis, M.; Vanherle, L.; Rosenholm, M.; In ‘t Zandt, R.; Yao, Y.; Swanberg, K.M.; Weikop, P.; Gottschalk, M.; Shanbhag, N.C.; Luo, J.; et al. Loss of glymphatic homeostasis in heart failure. Brain 2025, 148, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, I.F. From heart to head: Glymphatic disruption as a new pathway in heart failure. Brain 2025, 148, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, S.; Schnieder, M.; Polster, L.; Dechent, P.; Bähr, M. Atrial fibrillation reduces CSF flow dynamics. A multimodal MRI study. Neuroimage 2025, 317, 121337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertan, E.; Hung, C.; Danial, J.S.H.; Lam, J.Y.L.; Preman, P.; Albertini, G.; English, E.A.; Böken, D.; Livesey, F.J.; De Strooper, B.; et al. Clearance of beta-amyloid and tau aggregates is size dependent and altered by an inflammatory challenge. Brain Commun. 2024, 7, fcae454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, D.I.; de-Lima-Oliveira, M.; Nogueira, R.C.; Carvalho-Pinto, R.M.; Bor-Seng-Shu, E.; Panerai, R.B.; Carvalho, C.R.F.; Salinet, A.S. Integrative assessment of cerebral blood regulation in COPD patients. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2024, 319, 104166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glodzik, L.; Randall, C.; Rusinek, H.; de Leon, M.J. Cerebrovascular reactivity to carbon dioxide in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 35, 427–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Yin, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, W. The Relationship Between Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Assessed by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Case-Control Study from a Single Center in Beijing, China. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e925703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menze, I.; Bernal, J.; Kaya, P.; Aki, Ç.; Pfister, M.; Geisendörfer, J.; Yakupov, R.; Coello, R.D.; Valdés-Hernández, M.D.C.; Heneka, M.T.; et al. Perivascular space enlargement accelerates in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease pathology: Evidence from a three-year longitudinal multicentre study. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.K.; Heo, E.Y.; Kim, D.K.; Chung, H.S. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is independently associated with hypertension in men. Medicine 2017, 96, e6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsi, V.; Marketou, M.; Maragkoudakis, S.; Didagelos, M.; Charalambous, G.; Parthenakis, F.; Tsioufis, C.; Tousoulis, D. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction: The undervalued frontier of hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2020, 34, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jukkola, J.; Kaakinen, M.; Singh, A.; Moradi, S.; Ferdinando, H.; Myllylä, T.; Kiviniemi, V.; Eklund, L. Blood pressure lowering enhances cerebrospinal fluid efflux to the systemic circulation primarily via the lymphatic vasculature. Fluids Barriers CNS 2024, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelbich, P.; Hrach, K.; Spicka, J.; Vachata, P.; Radovnicky, T.; Hanuljakova, E.; Krejsek, J. Basic Analysis of the Cerebrospinal Fluid: An Important Framework for Laboratory Diagnostics of the Impairment of the Central Nervous System. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 3666–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelgrim, C.E.; Wang, L.; Peralta Marzal, L.N.; Korver, S.; van Ark, I.; Leusink-Muis, T.; Braber, S.; Folkerts, G.; Garssen, J.; van Helvoort, A.; et al. Increased exploration and hyperlocomotion in a cigarette smoke and LPS-induced murine model of COPD: Linking pulmonary and systemic inflammation with the brain. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell Mol. Physiol. 2022, 323, L251–L265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badoer, E. New Insights Into the Role of Inflammation in the Brain in Heart Failure. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 837723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogland, I.C.; Houbolt, C.; van Westerloo, D.J.; van Gool, W.A.; van de Beek, D. Systemic inflammation and microglial activation: Systematic review of animal experiments. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, L.J.; Wroblewski, K.E.; Pinto, J.M.; Wang, E.; McClintock, M.K.; Dale, W.; White, S.R.; Press, V.G.; Huisingh-Scheetz, M. Beyond the Lung: Geriatric Conditions Afflict Community-Dwelling Older Adults with Self-Reported Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 814606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadziakiewicz, P.; Szczurek-Wasilewicz, W.; Szyguła-Jurkiewicz, B. Heart Failure in Elderly Patients: Medical Management, Therapies and Biomarkers. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhi, H.; Peng, H.; Xie, M.; Li, R.; Li, K.; Ma, Y.; Sun, P. Advances in the study of the glymphatic system and aging. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordoni, B.; Morabito, B.; Simonelli, M. Ageing of the Diaphragm Muscle. Cureus 2020, 12, e6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleg, J.L.; Strait, J. Age-associated changes in cardiovascular structure and function: A fertile milieu for future disease. Heart Fail. Rev. 2012, 17, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, T.M.; Cherrington, A.L.; Bhatia, S.; Turan, B.; Patel, S.B.; Kim, Y.I.; Turan, J.M.; Dransfield, M.T. The Association of Low Income and High Stress with Acute Care Use in COPD Patients. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2020, 7, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzeciono, A.; Czech, O.; Buchta, K.; Zabłotni, S.; Gos, E.; Tłuczykont, Ł.; Górecka, D.; Pastuła, A.; Adamczyk, M.; Jach, E.; et al. Assessment of Stress, Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms in Patients with COPD during In-Hospital Pulmonary Rehabilitation: An Observational Cohort Study. Medicina 2021, 57, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.M.; Jacoby, D.L.; Lampert, R.; Soucier, R.J.; Burg, M.M. Psychological Stress in Heart Failure: A Potentially Actionable Disease Modifier. Heart Fail. Rev. 2021, 26, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, G.; Moradikor, N. Cardiovascular influence on cognitive decline: The heart’s role in neurodegenerative disorders. Prog. Brain Res. 2025, 294, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Song, J.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J.; Xue, R.; Shan, L.D.; Gong, S.; Zhang, G.X.; Qin, Z.H.; Xu, G.Y.; et al. Chronic stress impairs the aquaporin-4-mediated glymphatic transport through glucocorticoid signaling. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1367–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulous, F.E.; Cruz-Hernández, J.C.; Yang, C.; Kaya, Ζ.; Paccalet, A.; Wojtkiewicz, G.; Capen, D.; Brown, D.; Wu, J.W.; Schloss, M.J.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid can exit into the skull bone marrow and instruct cranial hematopoiesis in mice with bacterial meningitis. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzitelli, J.A.; Smyth, L.C.D.; Cross, K.A.; Dykstra, T.; Sun, J.; Du, S.; Mamuladze, T.; Smirnov, I.; Rustenhoven, J.; Kipnis, J. Cerebrospinal fluid regulates skull bone marrow niches via direct access through dural channels. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Deng, Q.; Chen, X. Skull bone marrow and skull meninges channels: Redefining the landscape of central nervous system immune surveillance. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soladoye, A.A.; Aderinto, N.; Osho, D.; Olawade, D.B. Explainable machine learning models for early Alzheimer’s disease detection using multimodal clinical data. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2025, 204, 106093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Dong, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, A.; Cheng, B.; Cai, S.; Bao, Q.; et al. Cognitive function assessed by Mini-mental state examination and risk of all-cause mortality: A community-based prospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, E.N.; Gramegna, C.; Esposito, A.; Gazzaniga, V.; Zago, S.; Difonzo, T.; Maddaluno, O.; Appollonio, I.; Bolognini, N. Normative data for the Montreal Cognitive Assessment in an Italian population sample. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36, 585–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoka, T.; Ito, R.; Nakamichi, R.; Nakane, T.; Kawai, H.; Naganawa, S. Diffusion Tensor Image Analysis ALong the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS): Revisiting the Meaning and Significance of the Method. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2024, 23, 268–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, W. Diaphragm Dysfunction and Rehabilitation Strategy in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 872277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, F.; Hazenberg, A.; Duiverman, M.; Wijkstra, P. Diaphragm dysfunction: How to diagnose and how to treat? Breathe 2025, 21, 240218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaps, S.; Langer, D.; Gosselink, R.; Dacha, S.; Louvaris, Z.; Jacobs, N.; Janssens, W.; Janssens, L. The value of extra-diaphragmatic inspiratory muscle surface electromyography during postural control tasks in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Med. 2025, 243, 108127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ye, C.; Okamoto, T.; Iwao, Y.; Kawata, N.; Shimada, A.; Haneishi, H. Multi-modal evaluation of respiratory diaphragm motion in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease using MRI series and CT images. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2024, 42, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Hsu, C.H.; Tsai, S.H.; Lin, C.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Hsu, H.Y.; Chen, C.Z.; Kuo, L.C. Association Between Muscle Activity of Upper Limbs and Respiratory Parameters During Functional Performance in People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Occup. Ther. Int. 2025, 2025, 3023322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, E.; Salazar-Degracia, A.; Sancho-Muñoz, A.; Aguiló, R.; Rodríguez-Fuster, A.; Gea, J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response in diaphragm muscle dysfunction of patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 1572–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottenheijm, C.A.; Heunks, L.M.; Hafmans, T.; van der Ven, P.F.; Benoist, C.; Zhou, H.; Labeit, S.; Granzier, H.L.; Dekhuijzen, P.N. Titin and diaphragm dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 527–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordoni, B.; Marelli, F.; Morabito, B.; Sacconi, B. Depression, anxiety and chronic pain in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: The influence of breath. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2017, 87, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bordoni, B.; Kotha, R.; Escher, A.R. Symptoms Arising from the Diaphragm Muscle: Function and Dysfunction. Cureus 2024, 16, e53143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordoni, B.; Marelli, F.; Morabito, B.; Sacconi, B. Depression and anxiety in patients with chronic heart failure. Future Cardiol 2018, 14, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, H.M.; Goldberg, L.R.; Molinger, J.; Felker, G.M.; Applefeld, W.; Rassaf, T.; Tedford, R.J.; Mirro, M.; Cleland, J.G.; Fudim, M. Diaphragmatic Function in Cardiovascular Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 1647–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, R.C. Ferreira LF. Diaphragm abnormalities in heart failure and aging: Mechanisms and integration of cardiovascular and respiratory pathophysiology. Heart Fail. Rev. 2017, 22, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, B.; Escher, A.R. Functional evaluation of the diaphragm with a noninvasive test. J. Osteopath. Med. 2021, 121, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiso, D.; Villanueva, J.A.; Belarte-Tornero, L.C.; Fort, A.; Blázquez-Bermejo, Z.; Ruiz, S.; Farré, R.; Rigau, J.; Martí-Almor, J.; Farré, N. Surface respiratory electromyography and dyspnea in acute heart failure patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlata, S.; Di Matteo, E.; Finamore, P.; Perri, G.; Mancini, D.; Sogaro, L.; Grandi, T.; Brando, E.; Travaglino, F.; Sambuco, F.; et al. Diaphragmatic ultrasound evaluation in acute heart failure: Clinical and functional associations. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagiyama, N.; Kamiya, K.; Toki, M.; Saito, H.; Iwata, K.; Matsue, Y.; Yoshioka, K.; Saito, K.; Kitai, T.; Maekawa, E. Prognostic Impact of Diaphragm Thickness in Geriatric Patients with Heart Failure: The SONIC-HF Multicenter Registry. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2025, 18, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, A.L.; Yaffe, K. Depression and risk of developing dementia. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 323–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aunsmo, R.H.; Strand, B.H.; Anstey, K.J.; Bergh, S.; Kivimäki, M.; Köhler, S.; Krokstad, S.; Livingston, G.; Matthews, F.E.; Selbæk, G. Associations between depression and anxiety in midlife and dementia more than 30 years later: The HUNT Study. Alzheimers Dement 2024, 16, e70036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosetti, M.; Abreu, A.; Corrà, U.; Davos, C.H.; Hansen, D.; Frederix, I.; Iliou, M.C.; Pedretti, R.F.E.; Schmid, J.P.; Vigorito, C.; et al. Secondary prevention through comprehensive cardiovascular rehabilitation: From knowledge to implementation. 2020 update. A position paper from the Secondary Prevention and Rehabilitation Section of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 460–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 1757–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, M.; Higashimoto, Y.; Sugiya, R.; Mizusawa, H.; Takeda, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Nishiyama, O.; Yamazaki, R.; Kudo, S.; Kimura, T.; et al. Enhanced diaphragm excursion and exercise tolerance in COPD patients through inspiratory muscle training after standardised pulmonary rehabilitation: Randomised controlled trial. ERJ Open Res. 2024, 10, 00035–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.E.; Kim, J.H.; Moon, H.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Cheon, S.; Shin, H.S.; Han, D.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.H.; Choi, S.H. Long-term physical exercise facilitates putative glymphatic and meningeal lymphatic vessel flow in humans. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, L.; Huang, S.; Chen, L. Aerobic exercise improves clearance of amyloid-β via the glymphatic system in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2025, 222, 111263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azambuja, A.C.M.; de Oliveira, L.Z.; Sbruzzi, G. Inspiratory Muscle Training in Patients with Heart Failure: What Is New? Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Phys. Ther. 2020, 100, 2099–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xue, F.; Li, M.; Chen, Y. Long-term benefits of pulmonary rehabilitation with respiratory muscle training in people with COPD: A retrospective cohort study. Respir. Med. 2025, 245, 108214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begrambekova, Y.L. Remodeling of the External Respiratory System in Chronic Heart Failure—a Factor of Pathogenesis and a Therapeutic Target. Kardiologiia 2025, 65, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevizan, P.F.; Antunes-Correa, L.M.; Lobo, D.M.L.; Oliveira, P.A.; de Almeida, D.R.; Abduch, M.C.D.; Mathias Junior, W.; Hajjar, L.A.; Kalil Filho, R.; Negrão, C.E. Effects of inspiratory muscle training combined with aerobic exercise training on neurovascular control in chronic heart failure patients. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 3845–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witt, J.D.; Guenette, J.A.; Rupert, J.L.; McKenzie, D.C.; Sheel, A.W. Inspiratory muscle training attenuates the human respiratory muscle metaboreflex. J. Physiol. 2007, 584 Pt 3, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdz, T.; Bilo, G.; Debicka-Dabrowska, D.; Klocek, M.; Malfatto, G.; Kielbasa, G.; Styczkiewicz, K.; Bednarek, A.; Czarnecka, D.; Parati, G.; et al. Blood pressure changes in patients with chronic heart failure undergoing slow breathing training. Blood Press. 2016, 25, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tembhurne, H.; Dumbre, D. Effectiveness of video assisted teaching program of pranayama on selected physiological parameters among patients with COPD. J. Educ. Health Promot. 2024, 13, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, S.; Schmid, J.P.; Dendale, P.; Poerschke, D.; Hansen, D.; Dritsas, A.; Kouloubinis, A.; Alders, T.; Gkouziouta, A.; Reyckers, I.; et al. Combined aerobic/inspiratory muscle training vs. aerobic training in patients with chronic heart failure: The Vent-HeFT trial: A European prospective multicentre randomized trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Rubio, H.; Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Rodríguez-Sanz, D.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; Vicente-Campos, D.; Chicharro, J.L. Inspiratory Muscle Training in Patients with Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelarungrayub, J.; Puntumetakul, R.; Sriboonreung, T.; Pothasak, Y.; Klaphajone, J. Preliminary study: Comparative effects of lung volume therapy between slow and fast deep-breathing techniques on pulmonary function, respiratory muscle strength, oxidative stress, cytokines, 6-minute walking distance, and quality of life in persons with COPD. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2018, 13, 3909–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F.; Kanbay, M.; Tuttle, K.R.; Kotanko, P.; De Caterina, R.; Grassi, G.; Mancia, G. The autonomic nervous system and inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2025, 40, 1470–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Chen, Z.; Ruan, B.; Chen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, L. Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Training in People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2024, 14, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupper, N.; Bonhof, C.; Westerhuis, B.; Widdershoven, J.; Denollet, J. Determinants of Dyspnea in Chronic Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2016, 22, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosnak-Guclu, M.; Arikan, H.; Savci, S.; Inal-Ince, D.; Tulumen, E.; Aytemir, K.; Tokgözoglu, L. Effects of inspiratory muscle training in patients with heart failure. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, S.; Gurses, H.N.; Bayram, M. Does inspiratory muscle training (IMT) reduce depression in patients with COPD? Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2021, 44, 101418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohani, Z.N.; Samaan, Z. Does Depression Impact Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Heart Failure? Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 524325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salik, Y.; Ozalevli, S.; Cimrin, A.H. Cognitive status among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2007, 45, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Lin, S.; Zhang, H.; Liang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, B.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Glymphatic dysfunction associated with cortisol dysregulation in major depressive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2025, 15, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bordoni, B.; Morabito, B.; Myftari, V.; D’Amato, A.; Severino, P. The Glymphatic System and Diaphragmatic Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Chronic Heart Failure: The Importance of Inspiratory Rehabilitation Training. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100390
Bordoni B, Morabito B, Myftari V, D’Amato A, Severino P. The Glymphatic System and Diaphragmatic Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Chronic Heart Failure: The Importance of Inspiratory Rehabilitation Training. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(10):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100390
Chicago/Turabian StyleBordoni, Bruno, Bruno Morabito, Vincenzo Myftari, Andrea D’Amato, and Paolo Severino. 2025. "The Glymphatic System and Diaphragmatic Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Chronic Heart Failure: The Importance of Inspiratory Rehabilitation Training" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 10: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100390
APA StyleBordoni, B., Morabito, B., Myftari, V., D’Amato, A., & Severino, P. (2025). The Glymphatic System and Diaphragmatic Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Chronic Heart Failure: The Importance of Inspiratory Rehabilitation Training. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(10), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100390





