Cardiac Morphofunctional Characteristics of Individuals with Early Repolarization Pattern: A Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diagnostic Criteria
3. Prevalence
4. Arrhythmic Risk
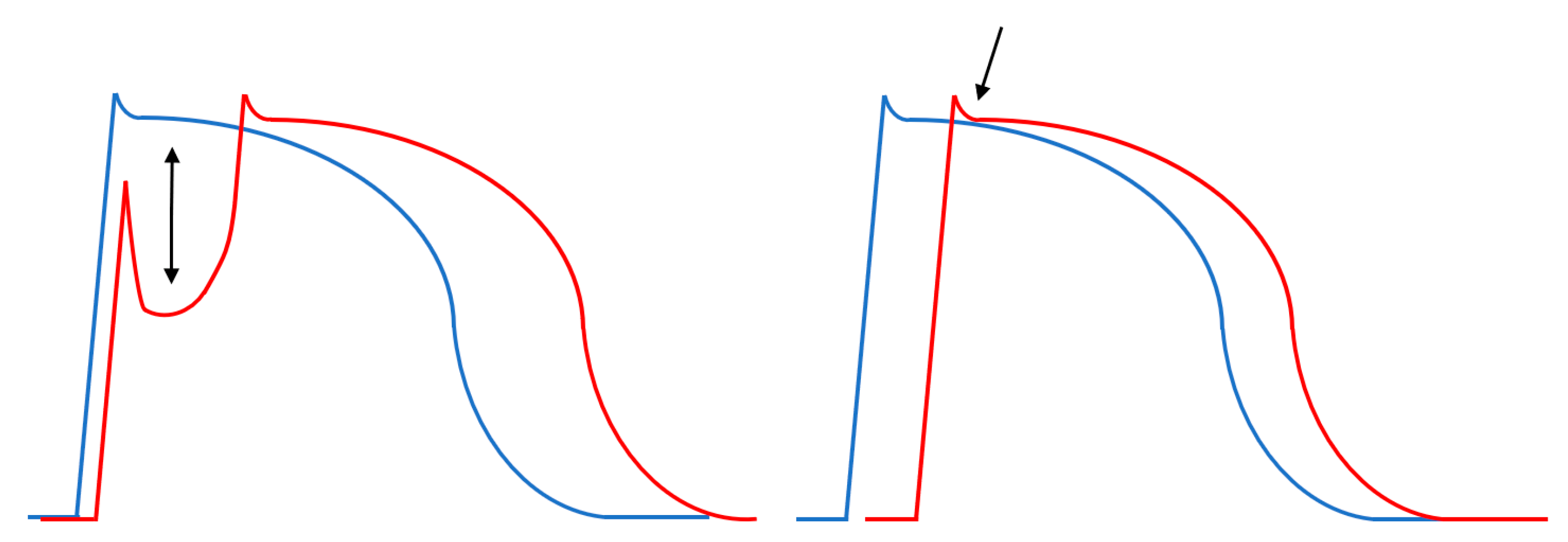
5. Electrophysiological and Genetic Background
6. Cardiac Morphofunctional Characteristics of Individuals with ERP
6.1. Conventional Echocardiography
6.2. Speckle Tracking Echocardiography
6.3. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
6.4. Particularities of Cardiac Morphofunctional Characteristics of Athletes with ERP
6.5. Particularities of Cardiac Morphofunctional Characteristics in the General Population with ERP
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antzelevitch, C.; Dendramis, G. Genetics, Molecular Biology, and Emerging Concepts of Early Repolarization Syndrome. In Cardiac Repolarization: Basic Science and Clinical Management, 1st ed.; El-Sherif, N., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antzelevitch, C.; Yan, G.-X.; Ackerman, M.J.; Borggrefe, M.; Corrado, D.; Guo, J.; Gussak, I.; Hasdemir, C.; Horie, M.; Huikuri, H.; et al. J-Wave Syndromes Expert Consensus Conference Report: Emerging Concepts and Gaps in Knowledge. J. Arrhythm. 2016, 32, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antzelevitch, C.; Yan, G.-X. J-Wave Syndromes: Brugada and Early Repolarization Syndromes. Heart Rhythm 2015, 12, 1852–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, S.D.; Hurst, J.W. Diagnostic Value of Electrocardiographic Abnormalities Observed in Subjects Accidentally Exposed to Cold. Am. J. Cardiol. 1972, 29, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, M.R.; Horan, L.G. Electrocardiographic J Wave of Hypercalcemia. Am. J. Cardiol. 1984, 54, 672–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Tanabe, Y.; Chinushi, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Ito, E.; Izumi, D.; Iijima, K.; Yagihara, N.; Watanabe, H.; et al. Analysis of J Waves during Myocardial Ischaemia. Europace 2011, 14, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antzelevitch, C.; Yan, G.-X. J Wave Syndromes. Heart Rhythm 2010, 7, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haïssaguerre, M.; Derval, N.; Sacher, F.; Jesel, L.; Deisenhofer, I.; de Roy, L.; Pasquié, J.-L.; Nogami, A.; Babuty, D.; Yli-Mayry, S.; et al. Sudden Cardiac Arrest Associated with Early Repolarization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2016–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, R.; Kogan, E.; Belhassen, B.; Rozovski, U.; Scheinman, M.M.; Zeltser, D.; Halkin, A.; Steinvil, A.; Heller, K.; Glikson, M.; et al. J-Point Elevation in Survivors of Primary Ventricular Fibrillation and Matched Control Subjects. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.-B.; Kim, Y.-H.; Antzelevitch, C. Augmentation of J Waves and Electrical Storms in Patients with Early Repolarization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, J.T.; Huikuri, H.V. Characteristics of “Malignant” vs. “Benign” Electrocardiographic Patterns of Early Repolarization. J. Electrocardiol. 2015, 48, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, R.; Adler, A.; Halkin, A.; Viskin, S. Risk of Sudden Death among Young Individuals with J Waves and Early Repolarization: Putting the Evidence into Perspective. Heart Rhythm 2011, 8, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, P.W.; Antzelevitch, C.; Haissaguerre, M.; Huikuri, H.V.; Potse, M.; Rosso, R.; Sacher, F.; Tikkanen, J.T.; Wellens, H.; Yan, G.-X. The Early Repolarization Pattern. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, J.T.; Junttila, M.J.; Anttonen, O.; Aro, A.L.; Luttinen, S.; Kerola, T.; Sager, S.J.; Rissanen, H.A.; Myerburg, R.J.; Reunanen, A.; et al. Early Repolarization. Circulation 2011, 123, 2666–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, R.; Halkin, A.; Viskin, S. J Waves and Early Repolarization: Do Not Confuse Me with the Facts! Heart Rhythm 2012, 9, 1603–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, K.K.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.; Kowey, P.; Lubitz, S.A.; Perez, M.; Piccini, J.; Turakhia, M.; Wang, P.; Viskin, S. Electrocardiographic Early Repolarization. Circulation 2016, 133, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, J.T.; Anttonen, O.; Junttila, M.J.; Aro, A.L.; Kerola, T.; Rissanen, H.A.; Reunanen, A.; Huikuri, H.V. Long-Term Outcome Associated with Early Repolarization on Electrocardiography. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2529–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinner, M.F.; Reinhard, W.; Müller, M.; Beckmann, B.-M.; Martens, E.; Perz, S.; Pfeufer, A.; Winogradow, J.; Stark, K.; Meisinger, C.; et al. Association of Early Repolarization Pattern on ECG with Risk of Cardiac and All-Cause Mortality: A Population-Based Prospective Cohort Study (MONICA/KORA). PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, D.; Matsuo, K.; Tsuneto, A.; Ichimaru, S.; Hida, A.; Sera, N.; Imaizumi, M.; Nakashima, E.; Maemura, K.; Akahoshi, M. Incidence and Prognostic Value of Early Repolarization Pattern in the 12-Lead Electrocardiogram. Circulation 2011, 123, 2931–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hünük, B. The Impact of Testosterone Levels on J-Wave Patterns Observed in Healthy Turkish Males. Eur. Res. J. 2019, 6, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, M.J.; Tikkanen, J.T.; Porthan, K.; Oikarinen, L.; Jula, A.; Kenttä, T.; Salomaa, V.; Huikuri, H.V. Relationship between Testosterone Level and Early Repolarization on 12-Lead Electrocardiograms in Men. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1633–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahida, S.; Derval, N.; Sacher, F.; Leenhardt, A.; Deisenhofer, I.; Babuty, D.; Schläpfer, J.; de Roy, L.; Frank, R.; Yli-Mayry, S.; et al. Role of Electrophysiological Studies in Predicting Risk of Ventricular Arrhythmia in Early Repolarization Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noseworthy, P.A.; Tikkanen, J.T.; Porthan, K.; Oikarinen, L.; Pietilä, A.; Harald, K.; Peloso, G.M.; Merchant, F.M.; Jula, A.; Väänänen, H.; et al. The Early Repolarization Pattern in the General Population. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 2284–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigy, A.; Gábor-Kelemen, H.; László, S.A.; Szabó, I.A.; Kocsis, L. Electrocardiographic Changes Associated with Early Repolarization Pattern in Healthy Young Males. Medicina 2022, 58, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado Arroyo, R.; Sieira, J.; Kubala, M.; Latcu, D.G.; Maeda, S.; Brugada, P. Electrophysiological Basis for Early Repolarization Syndrome. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Ikami, Y.; Otsuki, S.; Iijima, K.; Yagihara, N.; Sato, A.; Izumi, D.; Minamino, T. Early Repolarization and Risk of Lone Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2019, 30, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G.; Piras, P.; Evangelista, A.; Nuzzi, V.; Nardinocchi, P.; Pannarale, G.; Torromeo, C.; Puddu, P.E. Improving Performance of 3D Speckle Tracking in Arterial Hypertension and Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation by Using Novel Strain Parameters. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppenfeld, K.; Tfelt-Hansen, J.; de Riva, M.; Winkel, B.G.; Behr, E.R.; Blom, N.A.; Charron, P.; Corrado, D.; Dagres, N.; de Chillou, C.; et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3997–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haïssaguerre, M.; Nademanee, K.; Hocini, M.; Cheniti, G.; Duchateau, J.; Frontera, A.; Sacher, F.; Derval, N.; Denis, A.; Pambrun, T.; et al. Depolarization versus Repolarization Abnormality Underlying Inferolateral J-Wave Syndromes: New Concepts in Sudden Cardiac Death with Apparently Normal Hearts. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogendijk, M.G.; Potse, M.; Linnenbank, A.C.; Verkerk, A.O.; den Ruijter, H.M.; van Amersfoorth, S.C.M.; Klaver, E.C.; Beekman, L.; Bezzina, C.R.; Postema, P.G.; et al. Mechanism of Right Precordial ST-Segment Elevation in Structural Heart Disease: Excitation Failure by Current-To-Load Mismatch. Heart Rhythm 2010, 7, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, H.; Noda, T.; Yamada, Y.; Okamura, H.; Satomi, K.; Aiba, T.; Takaki, H.; Aihara, N.; Isobe, M.; Kamakura, S.; et al. Effect of Sodium-Channel Blockade on Early Repolarization in Inferior/Lateral Leads in Patients with Idiopathic Ventricular Fibrillation and Brugada Syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2012, 9, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Nagase, S.; Morita, H.; Ito, H. Left Ventricular Epicardial Electrogram Recordings in Idiopathic Ventricular Fibrillation with Inferior and Lateral Early Repolarization. Heart Rhythm 2014, 11, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hocini, M.; Strom, M.; Cuculich, P.S.; Cooper, D.H.; Sacher, F.; Haïssaguerre, M.; Rudy, Y. The Electrophysiological Substrate of Early Repolarization Syndrome. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Cooper, D.H.; Vijayakumar, R.; Zhang, J.; Pollak, S.; Haïssaguerre, M.; Rudy, Y. Early Repolarization Associated with Sudden Death: Insights from Noninvasive Electrocardiographic Imaging. Heart Rhythm 2010, 7, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haïssaguerre, M.; Hocini, M.; Cheniti, G.; Duchateau, J.; Sacher, F.; Puyo, S.; Cochet, H.; Takigawa, M.; Denis, A.; Martin, R.; et al. Localized Structural Alterations Underlying a Subset of Unexplained Sudden Cardiac Death. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2018, 11, e006120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nademanee, K.; Raju, H.; de Noronha, S.V.; Papadakis, M.; Robinson, L.; Rothery, S.; Makita, N.; Kowase, S.; Boonmee, N.; Vitayakritsirikul, V.; et al. Fibrosis, Connexin-43, and Conduction Abnormalities in the Brugada Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1976–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugada, J.; Pappone, C.; Berruezo, A.; Vicedomini, G.; Manguso, F.; Ciconte, G.; Giannelli, L.; Santinelli, V. Brugada Syndrome Phenotype Elimination by Epicardial Substrate Ablation. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Diego, J.M.; Antzelevitch, C. J Wave Syndromes as a Cause of Malignant Cardiac Arrhythmias. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 684–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frustaci, A.; Priori, S.G.; Pieroni, M.; Chimenti, C.; Napolitano, C.; Rivolta, I.; Sanna, T.; Bellocci, F.; Russo, M.A. Cardiac Histological Substrate in Patients with Clinical Phenotype of Brugada Syndrome. Circulation 2005, 112, 3680–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, P. Brugada Syndrome and Myocardial Histology: Where May the Truth Lie? Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 112, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronel, R.; Casini, S.; Koopmann, T.T.; Wilms-Schopman, F.J.G.; Verkerk, A.O.; de Groot, J.R.; Bhuiyan, Z.; Bezzina, C.R.; Veldkamp, M.W.; Linnenbank, A.C.; et al. Right Ventricular Fibrosis and Conduction Delay in a Patient with Clinical Signs of Brugada Syndrome: A Combined Electrophysiological, Genetic, Histopathologic, and Computational Study. Circulation 2005, 112, 2769–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, H.; Parsons, S.; Thompson, T.N.; Morgan, N.; Zentner, D.; Trainer, A.H.; James, P.A.; Winship, I.M.; Kalman, J.M.; Vohra, J. Insights into Sudden Cardiac Death: Exploring the Potential Relevance of Non-Diagnostic Autopsy Findings. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 40, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, A.; Radmilovic, J.; D’Amato, A.; Tagliamonte, E.; Sperlongano, S.; Riegler, L.; Scarafile, R.; Forni, A.; Muscogiuri, G.; Pontone, G.; et al. Echocardiography in Athletes in Primary Prevention of Sudden Death. J. Cardiovasc. Echogr. 2019, 29, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 233–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukoshi, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Nagata, Y.; Addetia, K.; Lang, R.M.; Akashi, Y.J.; Otsuji, Y. Normal Values of Left Ventricular Mass Index Assessed by Transthoracic Three-Dimensional Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2016, 29, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBounty, T.M.; Bach, D.S.; Bossone, E.; Kolias, T.J. Effect of Race on Echocardiographic Measures of Cardiac Structure and Function. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 124, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrini, F.M.; Pelliccia, A.; Assorgi, R.; DiPaolo, F.M.; Squeo, M.R.; Culasso, F.; Castelli, V.; Link, M.S.; Maron, B.J. Benign Clinical Significance of J-Wave Pattern (Early Repolarization) in Highly Trained Athletes. Heart Rhythm 2014, 11, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, W.; Trenkwalder, T.; Haller, B.; Meindl, C.; Schoenfeld, J.; Kaess, B.M.; Hengstenberg, C.; Schunkert, H.; Pressler, A.; Halle, M.; et al. The Early Repolarization Pattern: Echocardiographic Characteristics in Elite Athletes. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2018, 24, e12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Grima, R.; Doñate, M.; Álvarez-García, J.; Barradas-Pires, A.; Ferrero, A.; Carballeira, L.; Puig, T.; Rodríguez, E.; Cinca, J. Long-Term Follow-up of Early Repolarization Pattern in Elite Athletes. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 192.e1–192.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagaard, P.; Braunschweig, F.; Wecke, L.; Sahlén, A.; Bergfeldt, L. Early Repolarization in Middle-Age Runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miragoli, M.; Goldoni, M.; Demola, P.; Paterlini, A.; Li Calzi, M.; Gioia, M.I.; Visioli, F.; Rossi, S.; Pelà, G. Left Ventricular Geometry Correlates with Early Repolarization Pattern in Adolescent Athletes. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkwalder, T.; Rübsamen, N.; Schmitt, V.H.; Arnold, N.; Kaess, B.M.; Sinning, C.R.; Zeller, T.; Beutel, M.E.; Schmidtmann, I.; Nickels, S.; et al. Left Ventricular Geometry and Function in Early Repolarization: Results from the Population-Based Gutenberg Health Study. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2019, 108, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilkhanoff, L.; Ning, H.; Soliman, E.; Liu, K.; Gidding, S.; Lima, J.; Lloyd-Jones, D. Early Repolarization is Associated with More Favorable Cardiac Structure and Function Over 25 Years of Follow-Up in a Young, Biracial Cohort: The Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Circulation 2017, 136, A15168. [Google Scholar]
- Szabó, I.A.; Kocsis, L.; László, S.; Fehérvári, L.; Fárr, A.-M.; Frigy, A. Korai Repolarizációs Mintázatot Mutató Fiatal Férfiak Echokardiográfiás Jellemzőinek Összehasonlító Vizsgálata. Orv. Hetil. 2021, 162, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.K.; Klein, G.J.; Sivaram, C.A.; Zardini, M.; Schleinkofer, D.E.; Nakagawa, H.; Yee, R.; Jackman, W.M. Anatomic Substrate for Idiopathic Left Ventricular Tachycardia. Circulation 1996, 93, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Mi, N.; Zhou, Y.; An, P.; Bai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Hong, C.; Ji, Z.; Ye, P.; Wu, C. Transverse False Tendons in the Left Ventricular Cavity Are Associated with Early Repolarization. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mondillo, S.; Galderisi, M.; Mele, D.; Cameli, M.; Lomoriello, V.S.; Zacà, V.; Ballo, P.; D’Andrea, A.; Muraru, D.; Losi, M.; et al. Speckle-tracking echocardiography: A new technique for assessing myocardial function. J. Ultrasound Med. 2011, 30, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharram, M.A.; Lamberts, R.R.; Whalley, G.; Williams, M.J.A.; Coffey, S. Myocardial Tissue Characterisation Using Echocardiographic Deformation Imaging. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2019, 17, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulel, O.; Dağasan, G.; Yüksel, S.; Soylu, K.; Şahin, M. Evaluation of Left Ventricular Myocardial Deformation Parameters in Individuals with Electrocardiographic Early Repolarization Pattern. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2016, 16, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çöllüoğlu, T.; Önalan, O.; Çakan, F. The Diagnostic Value of 2D-Speckle Tracking Echocardiography for Identifying Subclinical Ventricular Dysfunction in Subjects with Early Repolarization Pattern. Echocardiography 2021, 38, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.R.; McCann, G.P. Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance: Applications and Practical Considerations for the General Cardiologist. Heart 2019, 106, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greupner, J.; Zimmermann, E.; Grohmann, A.; Dübel, H.-P.; Althoff, T.; Borges, A.C.; Rutsch, W.; Schlattmann, P.; Hamm, B.; Dewey, M. Head-To-Head Comparison of Left Ventricular Function Assessment with 64-Row Computed Tomography, Biplane Left Cineventriculography, and Both 2- and 3-Dimensional Transthoracic Echocardiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, D.A.; Bennett, A.J.; Ayers, C.; de Lemos, J.A.; Berry, J.D.; Link, M.S. Early Repolarization Pattern Is Associated with Increased Left Ventricular Mass. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 5, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, T.; Hayashi, K.; Konno, T.; Sakata, K.; Fujita, T.; Hodatsu, A.; Nagata, Y.; Teramoto, R.; Nomura, A.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. J Waves for Predicting Cardiac Events in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, P.; Guerreiro, C.; Ladeiras-Lopes, R.; Ferreira, N.; Faria, R.; Barbosa, R.; Primo, J.; Braga, J. Early Repolarization Pattern and Left Ventricular Mass in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiology 2020, 145, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
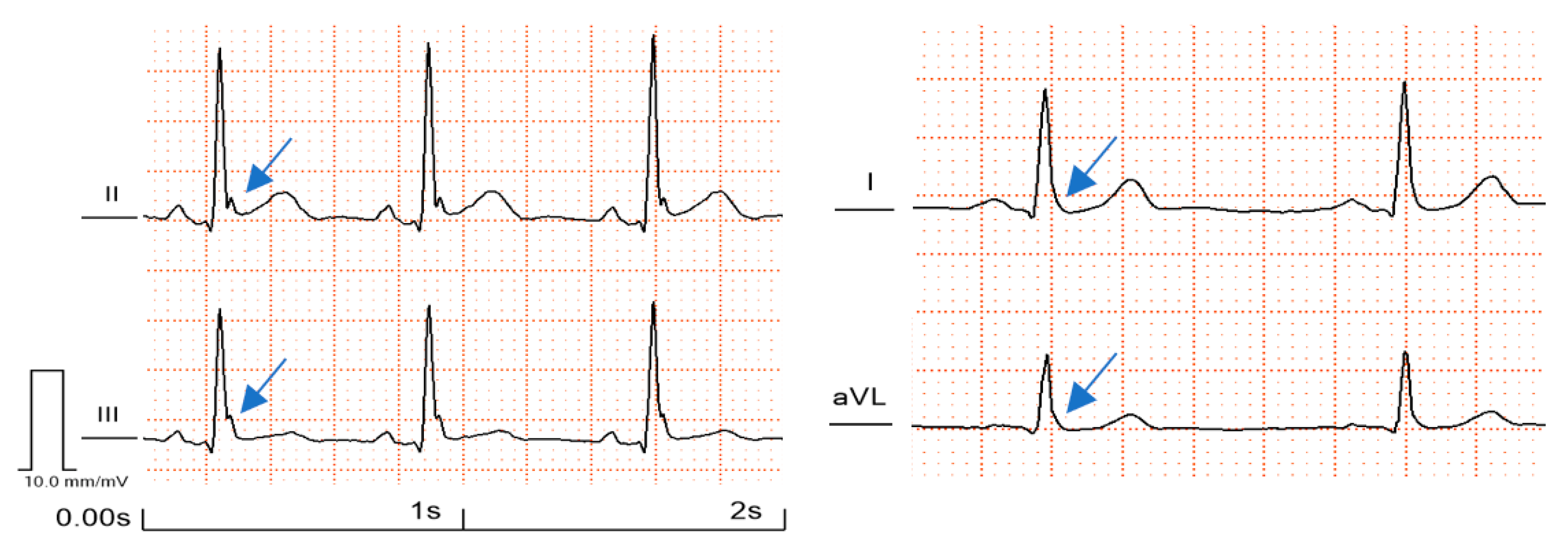
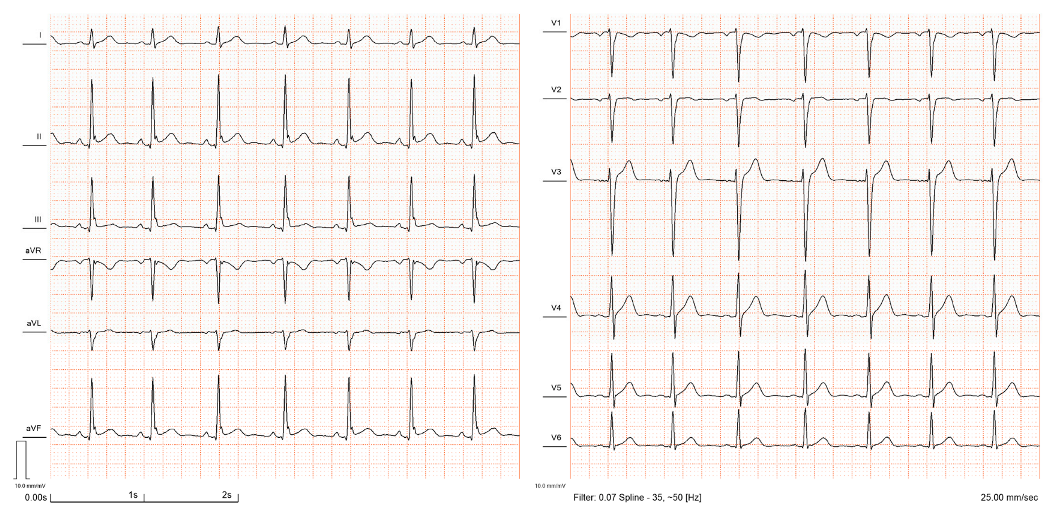
| A QRS terminal notch or slur is present in the descending part of the R wave. If a notch is present, it must be completely above the baseline. In the case of a slur, its starting point must be above the baseline. |
| The amplitude of the J-point elevation is ≥0.1 mV in at least two contiguous leads on the 12-lead ECG. Leads V1 to V3 must be excluded. |
| The QRS length must be <120 ms. |
| Ion Channel | Function | Locus | Gene | Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IK-ATP | ↑ | 12p11.23 | KCNJ8 | Kir6.1 |
| IK-ATP | ↑ | 12p12.1 | ABCC9 | SUR2A |
| ICa | ↓ | 12p13.3 | CACNA1C, | Cav1.2 |
| ICa | ↓ | 10p12.33 | CACNB2b | Cavß2b |
| ICa | ↓ | 7q21.11 | CACNA2D1 | Cavα2δ1 |
| INa | ↓ | 3p21 | SCN5A | Nav1.5 |
| INa | ↓ | 3p22.2 | SCN10A | Nav1.8 |
| Study | Imaging Technique | n | Age, Years | Men, % | ERP, % | Parameter Difference * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Athletes | ||||||
| Quattrini et al. [47] | ECHO | 704 | 25 ± 5 | 62 | 14.0 | 3 |
| Reinhard et al. [48] | ECHO | 623 | 21 ± 5 | 60.7 | 17.3 | 5 |
| Serra-Grim et al. [49] | ECHO | 299 | 20 ± 6.4 | 66 | 31.4 | 1 |
| Aagaard et al. [50] | ECHO | 151 | 50.9 ± 4.9 | 100 | 44.3 | 1 |
| Miragoli et al. [51] | ECHO | 414 | 13.6 ± 1.8 | 72 | 22.0 | 3 |
| Çöllüoğlu et al. [60] | ECHO, STE | 100 | 35.0 ± 11.5 | 49 | 50 | 9 |
| General population | ||||||
| Trenkwalder et al. [52] | ECHO | 13878 | 54.6 ± 11 | 48.9 | 6.6 | 12 |
| Ilkhanoff et al. [53] | ECHO | 1701 | 25.2 ± 3.5 | 41.9 | - | 3 |
| Szabó et al. [54] | ECHO | 62 | 22.5 ± 1.5 | 100 | 48.3 | 2 |
| Liu et al. [56] | ECHO | 77 | 31.6 ± 7.2 | 96.1 | 42.8 | 1 |
| Gülel et al. [59] | ECHO, STE | 60 | 25.5 ± 6.2 | 75 | 58.3 | 5 |
| McNamara et al. [63] | cMRI | 2753 | 43 ± 9.5 | 45.1 | 9.9 | 1 |
| Patients with HCM | ||||||
| Azevedo et al. [65] | cMRI | 85 | 56 ± 15 | 62.3 | 10.5 | 3 |
| Parameter | Imaging Technique | Increased in ERP+ | Decreased in ERP+ | No Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVM | ECHO | [47], [51] | [48]M, [48]F, [50], [60] | |
| IVS | ECHO | [51] | [48]M, [48]F, [49], [50], [60] | |
| LVPWT | ECHO | [47], [48]F, [51] | [48]M, [48]F, [49] | |
| RWT | ECHO | [51], [60] | ||
| LVEDD | ECHO | [47], [49], [60] | [48]M, [48]F, [50], [51] | |
| LVESD | ECHO | [48]M, [48]F, [51] | ||
| LVEDV | ECHO | [51], [60] | ||
| LVESV | ECHO | [60] | [51] | |
| EF | ECHO | [47], [49], [50], [60] | ||
| E | ECHO | [60] | [47] | |
| A | ECHO | [47], [60] | ||
| E/A | ECHO | [50] | [48]M, [48]F, [60] | |
| DT | ECHO | [48]M, [48]F | ||
| S’ | [47], [50] | |||
| E’ | ECHO | [47], [50] | ||
| A’ | ECHO | [47], [50] | ||
| E/E’ | ECHO | [48]M, [48]F, [60] | ||
| LAD | ECHO | [48], [60] | [47], [48]M, [48]F, [49], [60] | |
| AoR | ECHO | [60] | [48]M, [48]F | |
| RVD | ECHO | [60] | ||
| GLS | STE | [60] | ||
| GCS | STE | [60] |
| Parameter | Imaging Technique | Increased in ERP+ | Decreased in ERP+ | No Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVM | ECHO, cMRI | [63]M, [63]F | [52]M, [53] | [52]F, [54], [59] |
| IVS | ECHO | [52]F | [52]M, [53], [54], [59] | |
| LVPWT | ECHO | [52]F | [52]M, [53], [54], [56], [59] | |
| RWT | ECHO | [52]F | [52]M, [56] | |
| LVEDD | ECHO | [52]F, [53] | [52]M, [52]F | [54], [56], [59] |
| LVESD | ECHO | [52]M, [52]F | [54], [59] | |
| LVEDV | ECHO | [52]M, [52]F | [53], [54] | |
| LVESV | ECHO | [52]M, [53], [54] | [52]F | |
| EF | ECHO | [52]M, [52]F, [53], [54], [59] | ||
| E | ECHO | [54] | ||
| A | ECHO | [54] | ||
| E/A | ECHO | [52]M | [52]F, [54], [59] | |
| DT | ECHO | [52]M, [52]F | ||
| E’ | ECHO | [52]M | [52]F, [54] | |
| E/E’ | ECHO | [52]M, [59] | [52]F, [54] | |
| LAD | ECHO, cMRI | [54], [56], [59], [63] | ||
| AoR | ECHO | [54], [59] | ||
| RVD | ECHO | [54] | ||
| GLS | STE | [59] | ||
| GCS | STE | [59] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kocsis, L.; Pap, Z.; Frigy, A. Cardiac Morphofunctional Characteristics of Individuals with Early Repolarization Pattern: A Literature Review. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10010004
Kocsis L, Pap Z, Frigy A. Cardiac Morphofunctional Characteristics of Individuals with Early Repolarization Pattern: A Literature Review. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2023; 10(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleKocsis, Loránd, Zsuzsanna Pap, and Attila Frigy. 2023. "Cardiac Morphofunctional Characteristics of Individuals with Early Repolarization Pattern: A Literature Review" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 10, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10010004
APA StyleKocsis, L., Pap, Z., & Frigy, A. (2023). Cardiac Morphofunctional Characteristics of Individuals with Early Repolarization Pattern: A Literature Review. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 10(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10010004







