The Red and Orange Complex Subgingival Microbiome of Cognitive Impairment and Cognitively Normal Elderly with Periodontitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Sampling and DNA Extraction
2.3. 16S Metagenomic Workflow Using iSeq™ 100 Sequencing System
2.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
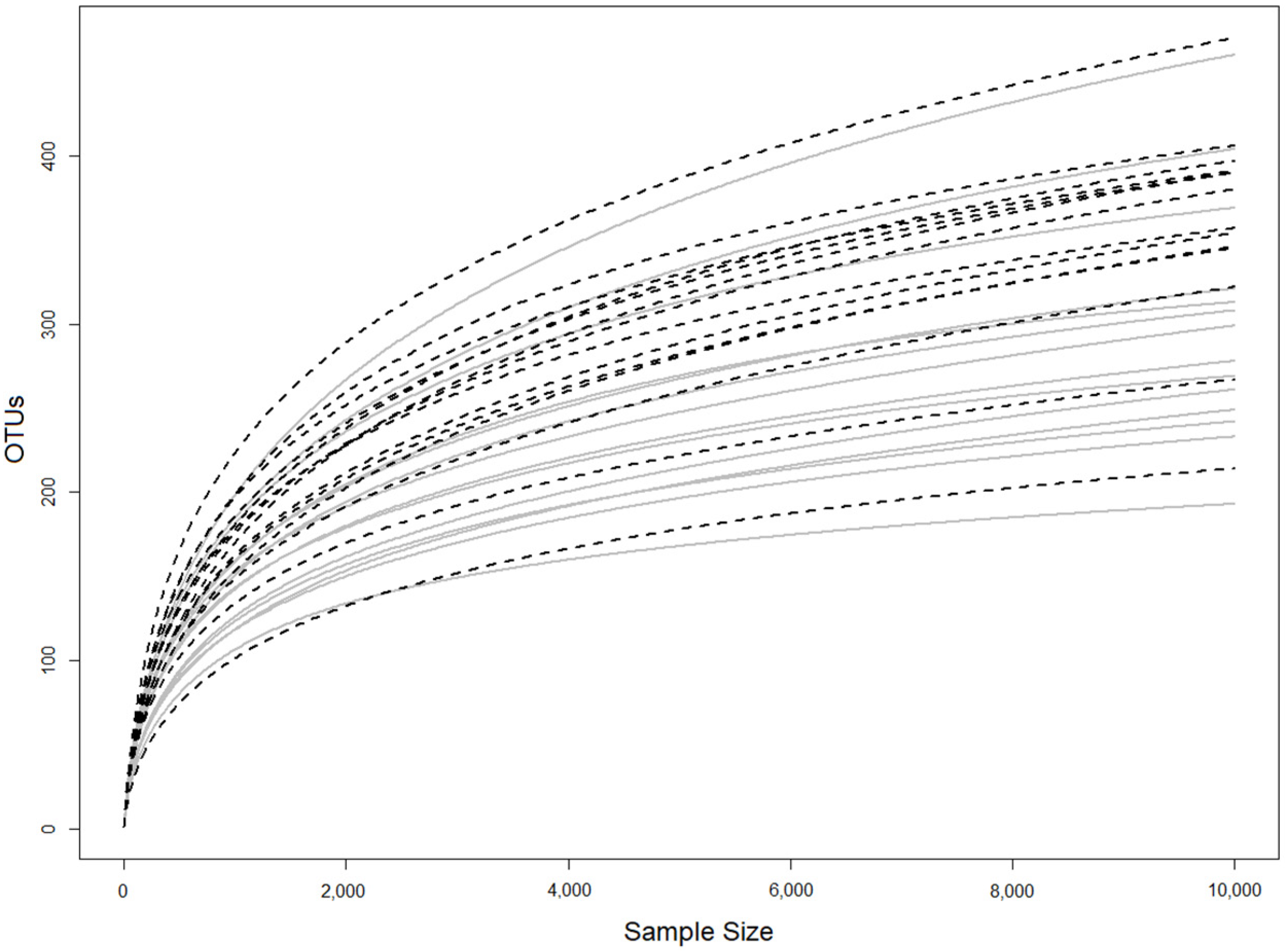
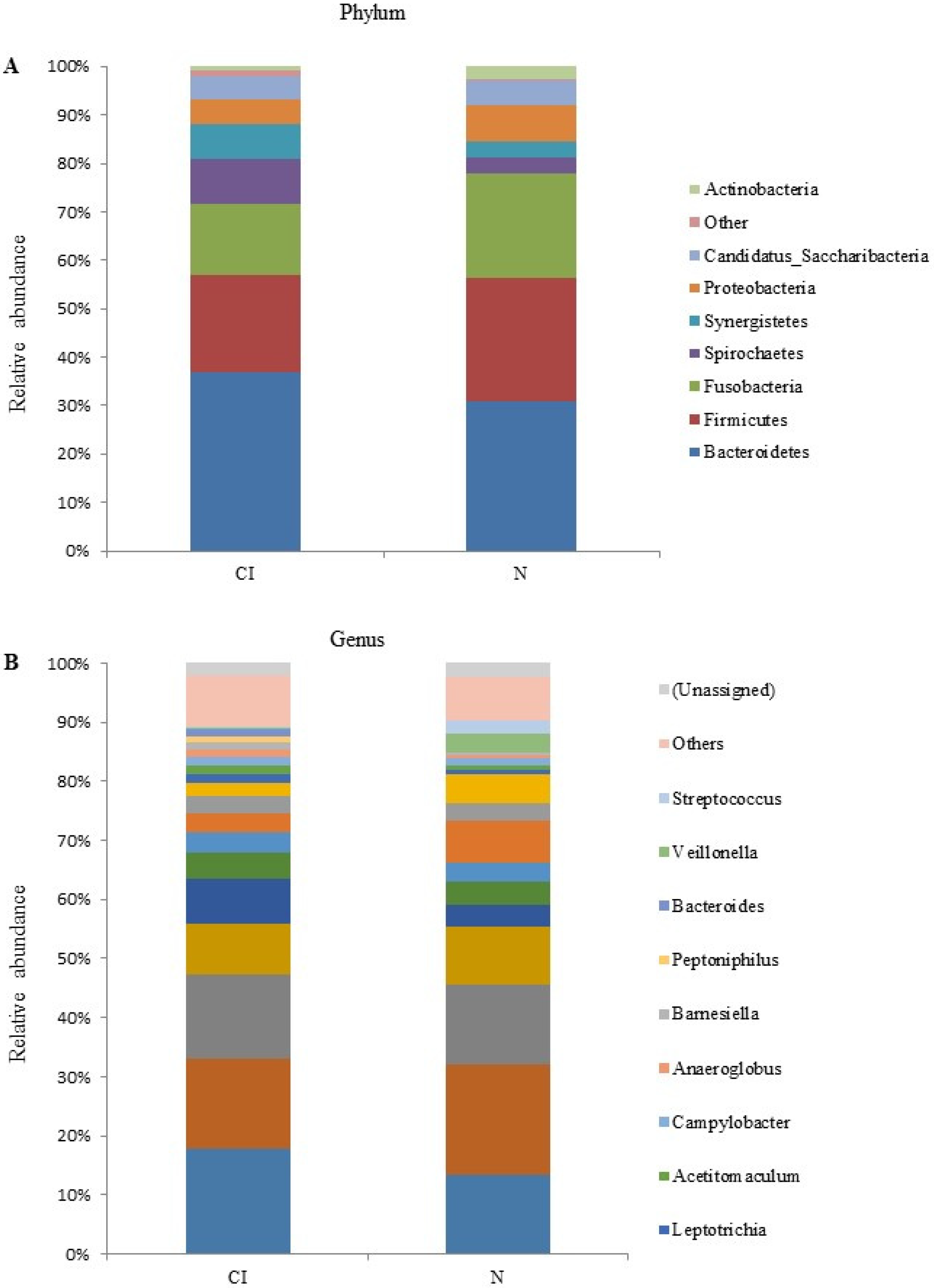
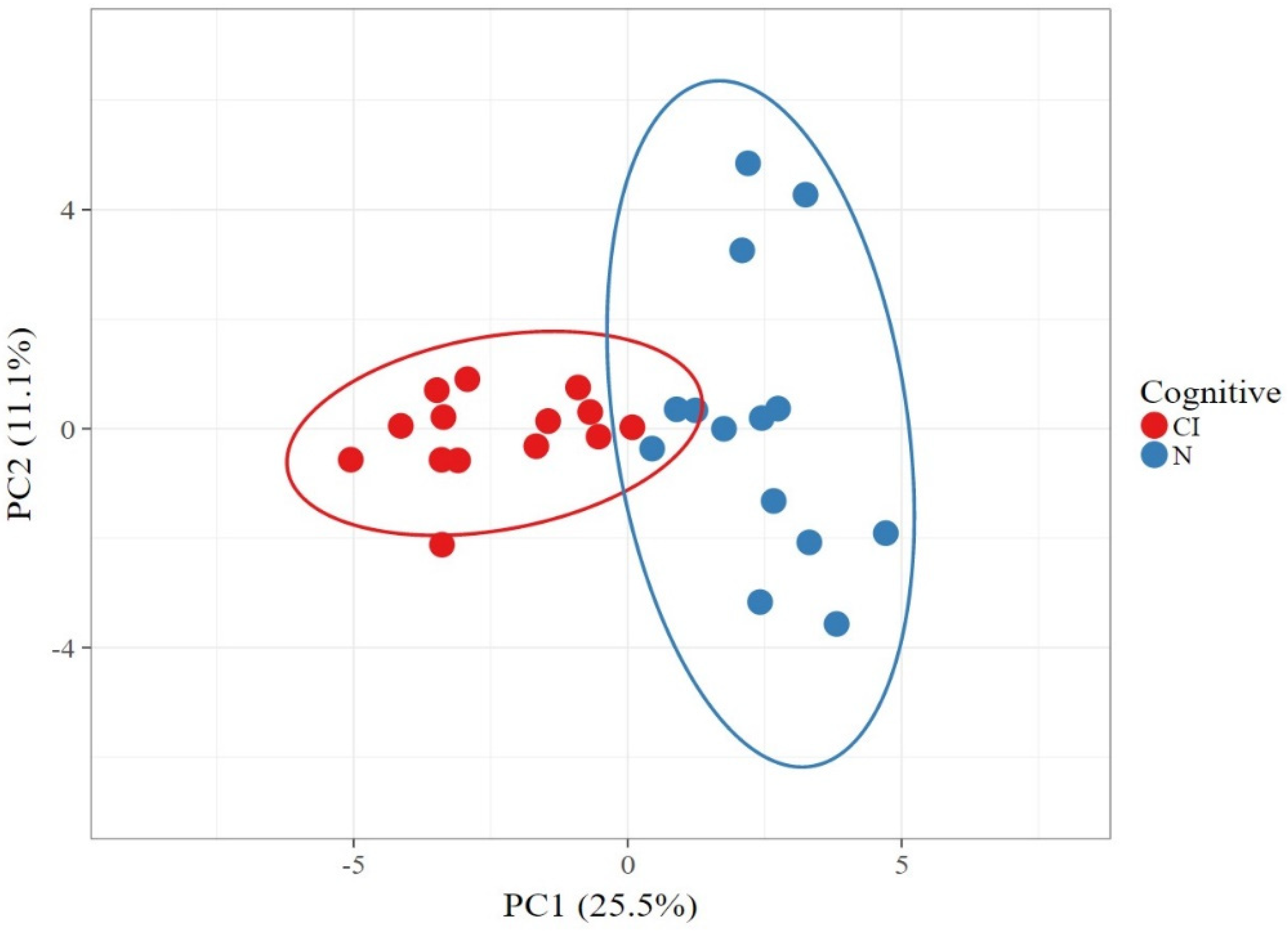
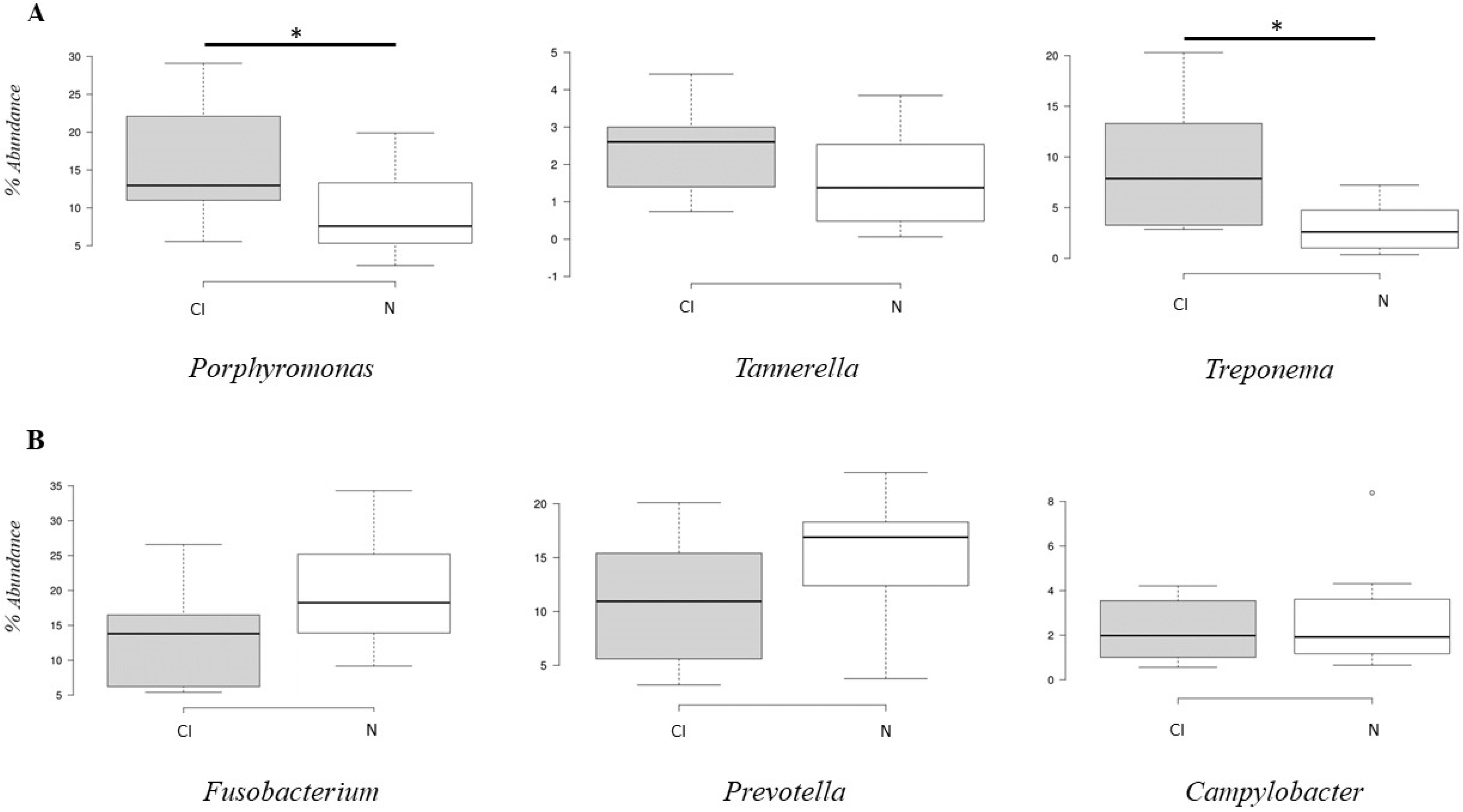
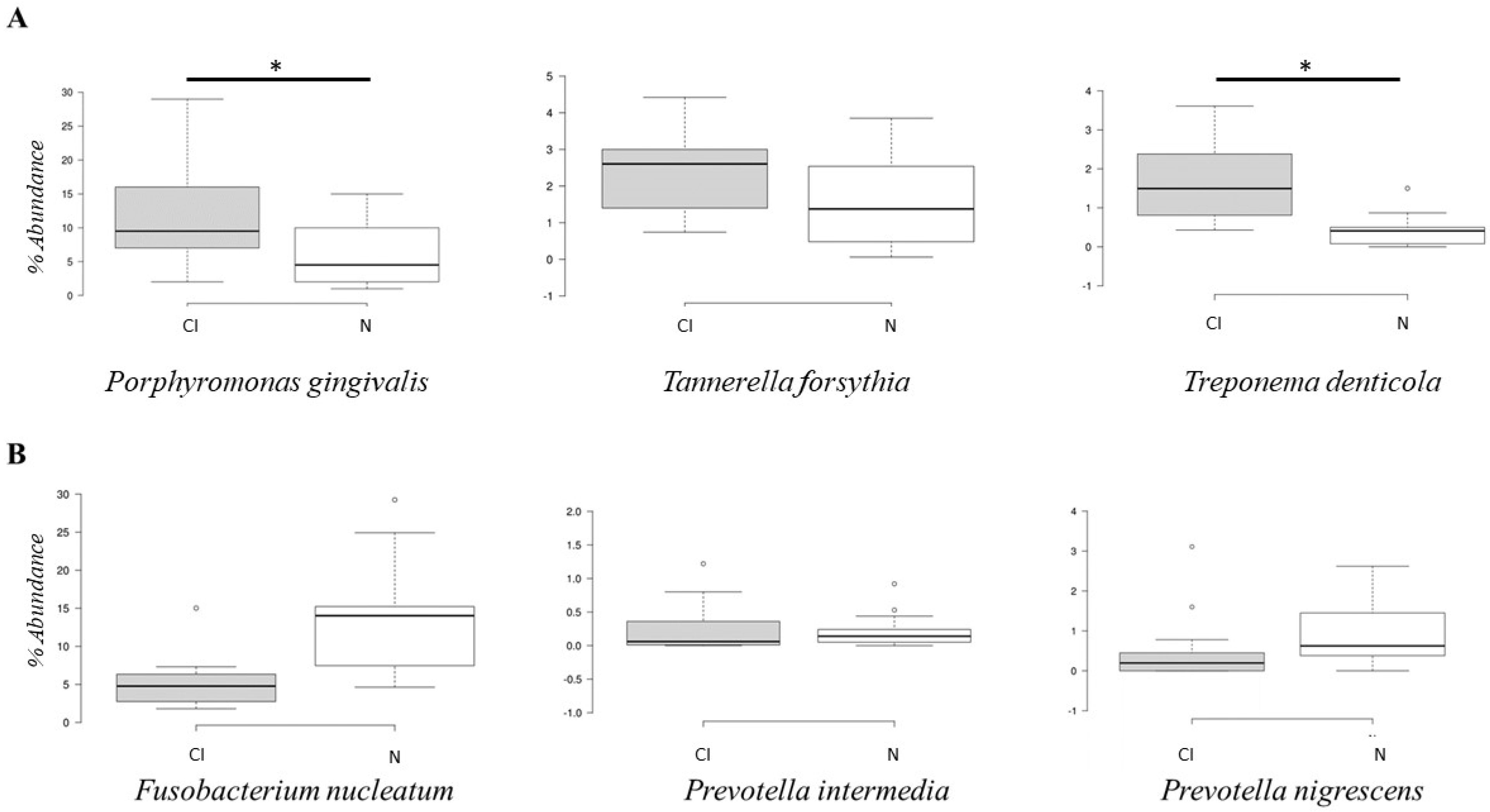
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. In World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision-Key Findings and Advance Tables; Working Paper No. ESA/P/WP/248; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Adioetomo, S.M.; Mujahid, G. Indonesia on the Threshold of Population Ageing; Monograph Series: No.1; UNFPA: Indonesia, Jakarta, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, C. World Alzheimer Report 2018-The State of the Art of Dementia Research: New Frontiers; Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI): London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Montoya, J.A.; Sanchez-Lara, I.; Carnero-Pardo, C.; Fornieles, F.; Montes, J.; Vilchez, R.; Burgos, J.S.; Gonzales-Moles, M.A.; Barrios, R.; Bravo, M. Is periodontitis a risk factor for cognitive impairment and dementia? A case-control study. J. Periodontol. 2015, 86, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, M.; Kimura, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Yamaga, T.; Ansai, T.; Wada, T.; Sakamoto, R.; Ishimoto, Y.; Fujisawa, M.; Okumiya, K.; et al. Periodontitis, periodontal inflammation, and mild cognitive impairment: A 5-year cohort study. J. Periodontal Res. 2019, 54, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadjoedin, F.M.; Kusdhany, L.S.; Turana, Y.; Bachtiar, B.M.; Masulili, S.L.C. Periodontal parameters in Indonesian elderly and its association with cognitive impairment. J. Int. Dent. Med. Res. 2020, 13, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Han, G.S. The relationship between periodontal disease and cognitive impairment in older adults of Korea. Spec. Care Dent. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, M.; Yoshihara, A.; Kimura, Y.; Sato, M.; Wada, T.; Sakamoto, R.; Ishimoto, Y.; Fukutomi, E.; Chen, W.; Imai, H.; et al. Longitudinal relationship of severe periodontitis with cognitive decline in older Japanese. J. Periodont. Res. 2016, 51, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.E.; Huang, R.Y.; Cheng, W.C.; Kao, T.W.; Chen, W.L. Association between periodontitis and cognitive impairment: Analysis of national health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES) III. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Chang, S.; Pi, X.; Hua, F.; Jiang, H.; Liu, C.; Minquan, D. The effect of periodontitis on dementia and cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021, 18, 6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Buduneli, N.; Dietrich, T.; Feres, M.; Fine, D.H.; Flemmig, T.F.; Garcia, R.; Giannobile, W.V.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45 (Suppl. S20), S162–S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G. Immunomicrobial pathogenesis of periodontitis: Keystones, pathobionts, and host response. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feres, M.; Teles, F.; Teles, R.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Faveri, M. The subgingival periodontal microbiota of the aging mouth. Periodontology 2000 2016, 72, 30–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socransky, S.S.; Haffajee, A.D.; Cugini, M.A.; Smith, C.; Kent, R.L. Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1998, 25, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, F.Q.; Almeida-da-silva, C.L.C.; Huynh, B.; Trinh, A.; Liu, J.; Woodward, J.; Asadi, H.; Ojcius, D.M. Association between periodontal pathogens and systemic disease. Biomed. J. 2019, 42, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ren, J.; Yu, H.; Yu, W.; Zhou, Y. Porphyromonas gingivalis, a periodontitis causing bacterium, induces memory impairment and age-dependent neuroinflammation in mice. Immun. Ageing. 2018, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hogervorst, E.; Mursjid, F.; Ismail, R.I.; Prasetyo, S.; Nasrun, M.; Mochtar; Ninuk, T.; Bandelow, S.; Subarkah; Kusdhany, L.; et al. Validation of two short dementia screening tests in Indonesia. In Vascular Dementia: Risk Factors, Diagnosis and Treatment; Jacobsen, S.R., Ed.; Nova Science: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 235–256. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, J. The hopkins verbal learning test: Development of a new memory test with six equivalent forms. Clin. Neuropsychol. 1991, 5, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state.” A practical method for grading cognitive state of patients for clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, J.; Aho, V.; Eriksdotter, M.; Paulin, L.; Pietiäinen, M.; Auvinen, P.; Schultzberg, M.; Pussinen, P.J.; Buhlin, K. Subgingival microbiota in a population with and without cognitive dysfunction. J. Oral Microbiol. 2021, 13, 1854552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.; Arthur, R.A.; Zhao, L.; Clark, J.; Hu, Y.; Corwin, E.J.; Lah, J. The oral microbiome and inflammation in mild cognitive impairment. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 147, 111273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Lamont, R.J. Breaking bad: Manipulation of the host response by Porphyromonas gingivalis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Byrne, S.J.; Dashper, S.G.; Darby, I.B.; Adams, G.G.; Hoffmann, B.; Reynolds, E.C. Progression of chronic periodontitis can be predicted by the levels of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola in subgingival plaque. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 24, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Dong, J.; Lu, W.; Song, Z.; Zhou, W. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide induces cognitive dysfunction, mediated by neuronal inflammation via activation of the TLR4 signaling pathway in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, N.; Ishihara, Y.; Ishida, K.; Tada, H.; Funaki-Kato, Y.; Hagiwara, M.; Ferdous, T.; Abdullah, M.; Mitani, A.; Michikawa, M.; et al. Periodontitis induced by bacterial infection exacerbates features of Alzheimer’s disease in transgenic mice. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2017, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leblhuber, F.; Huemer, J.; Steiner, K.; Gostner, J.M.; Fuchs, D. Knock-on effect of periodontitis to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease? Wien Klin. Wochenschr. 2020, 132, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, X.; Tang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, W.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H. Oral Treponema denticola Infection Induces Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 Accumulation in the Hippocampus of C57BL/6 Mice. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Lamont, R.J. Beyond the Red Complex and Into More Complexity: The Polymicrobial Synergy and Dysbiosis (PSD) Model of Periodontal Disease Etiology. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2012, 27, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Genco, R.J.; Borgnakke, W.S. Risk Factors for Periodontal Disease. Periodontol. 2000 2013, 62, 59–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cognitive Impairment (n = 14) | Cognitively Normal (n = 14) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 71.36 ± 6.95 | 67.43 ± 6.30 |
| Gender (M/F) | 4/10 | 5/9 |
| Group | OTUs | Shannon Index |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Impairment | 589 ± 83 | 1.88 ± 0.18 |
| Cognitively Normal | 495 ± 102 | 1.76 ± 0.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tadjoedin, F.M.; Masulili, S.L.C.; Rizal, M.I.; Kusdhany, L.S.; Turana, Y.; Ismail, R.I.; Bachtiar, B.M. The Red and Orange Complex Subgingival Microbiome of Cognitive Impairment and Cognitively Normal Elderly with Periodontitis. Geriatrics 2022, 7, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7010012
Tadjoedin FM, Masulili SLC, Rizal MI, Kusdhany LS, Turana Y, Ismail RI, Bachtiar BM. The Red and Orange Complex Subgingival Microbiome of Cognitive Impairment and Cognitively Normal Elderly with Periodontitis. Geriatrics. 2022; 7(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleTadjoedin, Fatimah Maria, Sri Lelyati C. Masulili, Muhammad Ihsan Rizal, Lindawati S. Kusdhany, Yuda Turana, Raden Irawati Ismail, and Boy M. Bachtiar. 2022. "The Red and Orange Complex Subgingival Microbiome of Cognitive Impairment and Cognitively Normal Elderly with Periodontitis" Geriatrics 7, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7010012
APA StyleTadjoedin, F. M., Masulili, S. L. C., Rizal, M. I., Kusdhany, L. S., Turana, Y., Ismail, R. I., & Bachtiar, B. M. (2022). The Red and Orange Complex Subgingival Microbiome of Cognitive Impairment and Cognitively Normal Elderly with Periodontitis. Geriatrics, 7(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7010012






