Characterization of the Expression of Angiogenic Factors in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Domestic Cats
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection Selection and Preparation
2.2. RNA Purification and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.4. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.5. Quantification of IHC Staining
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
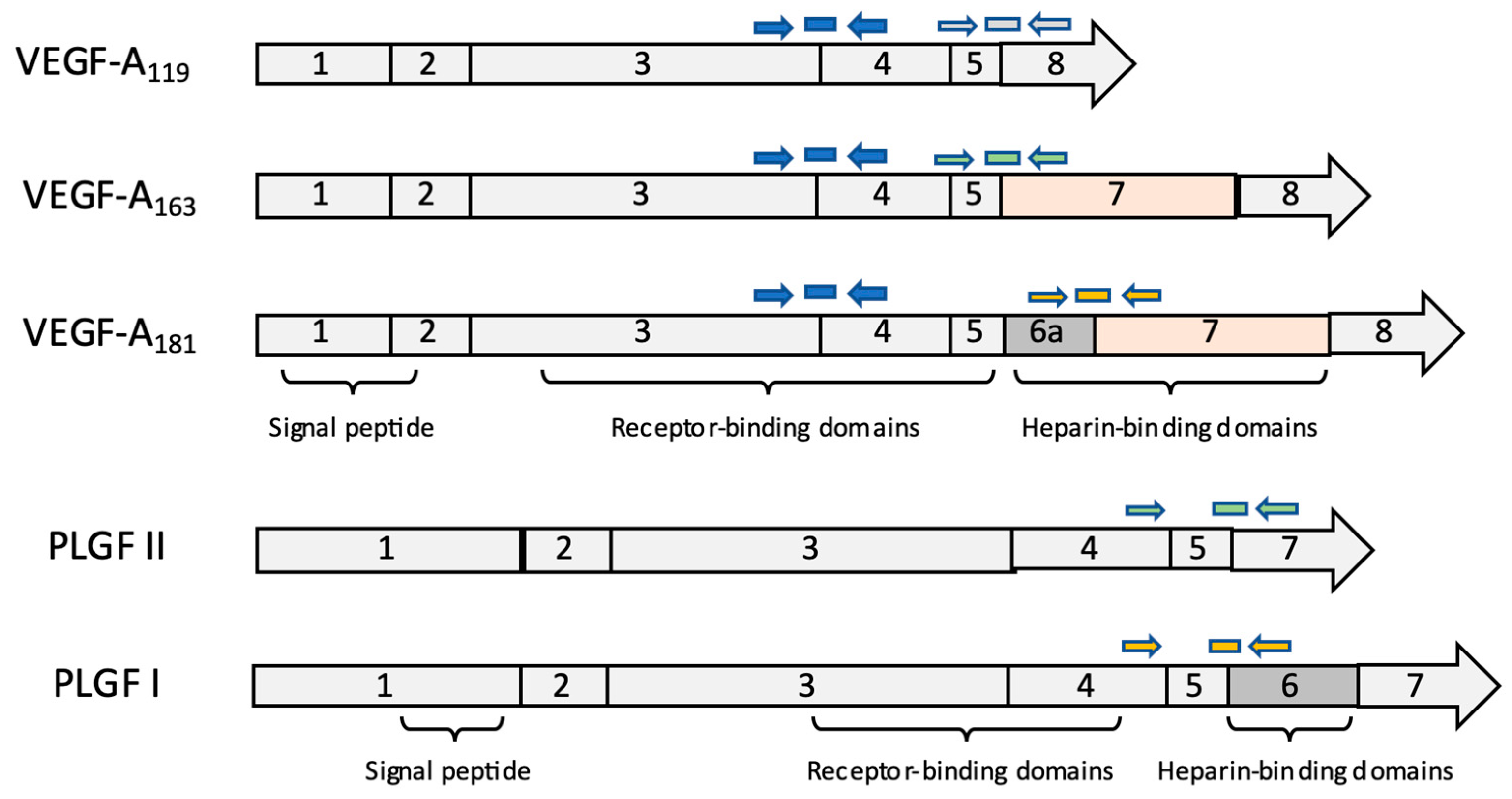
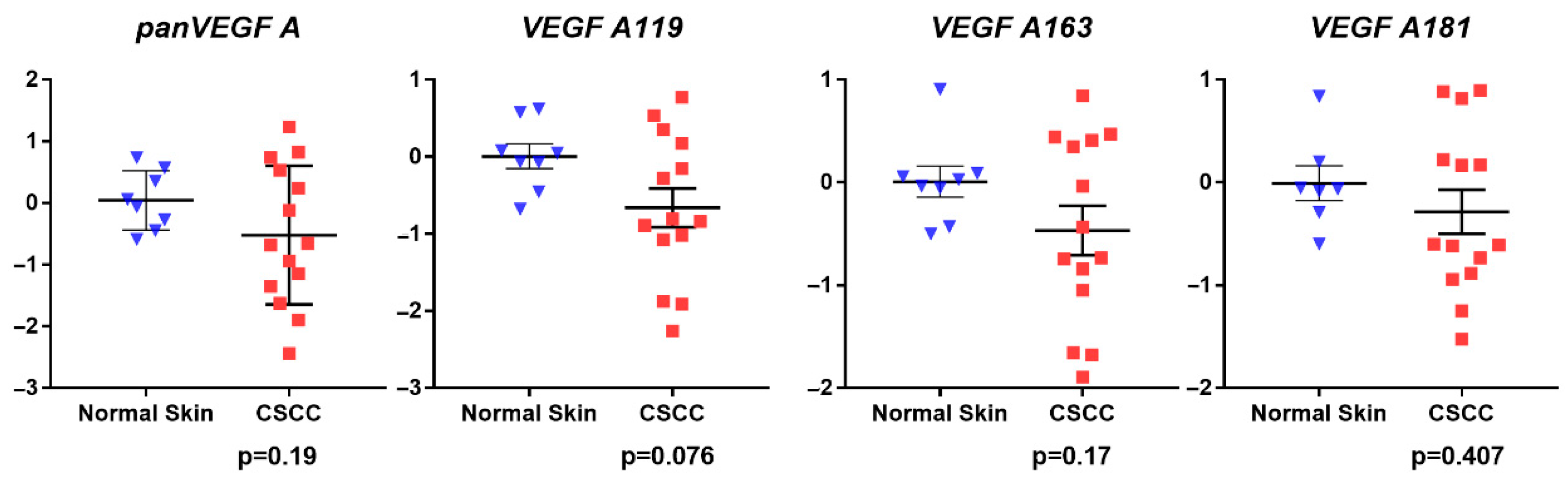
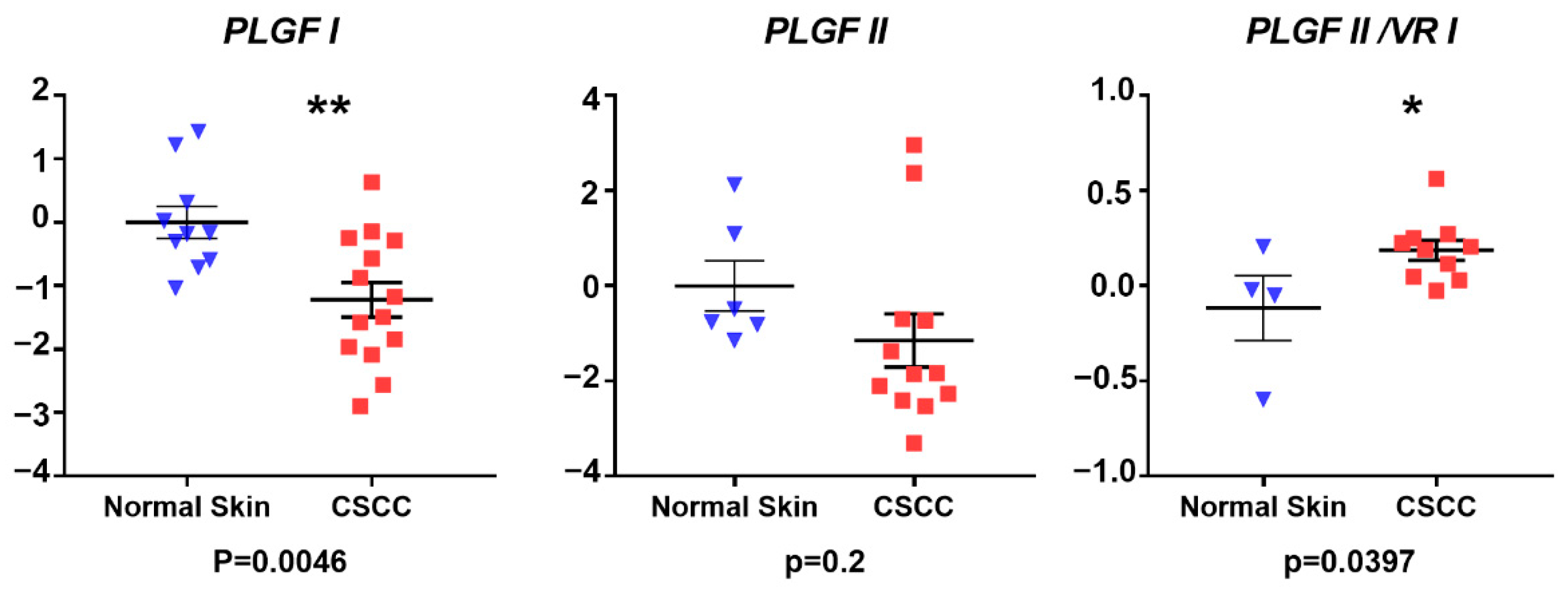
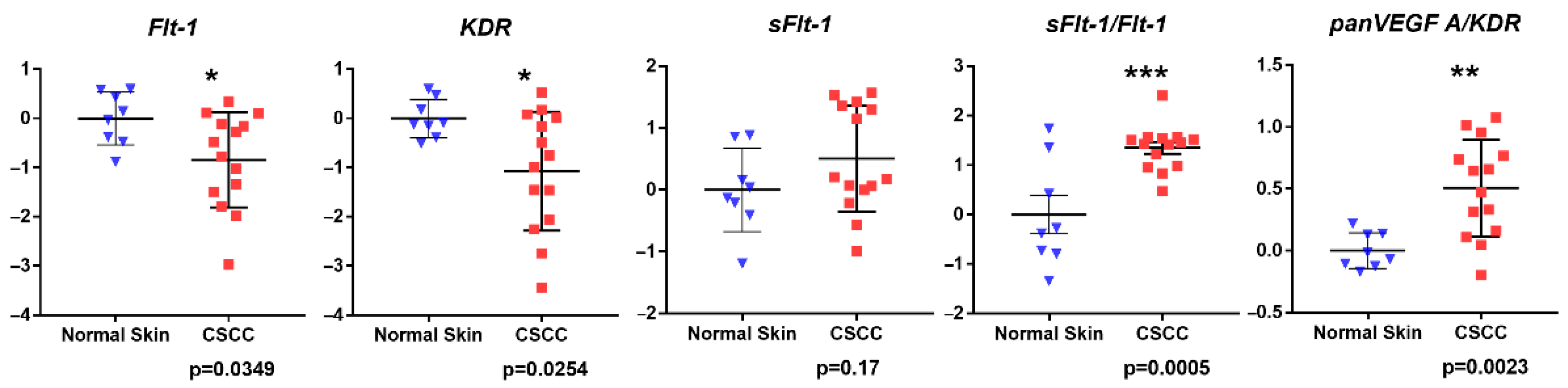
3.1. Gene Expression Analysis
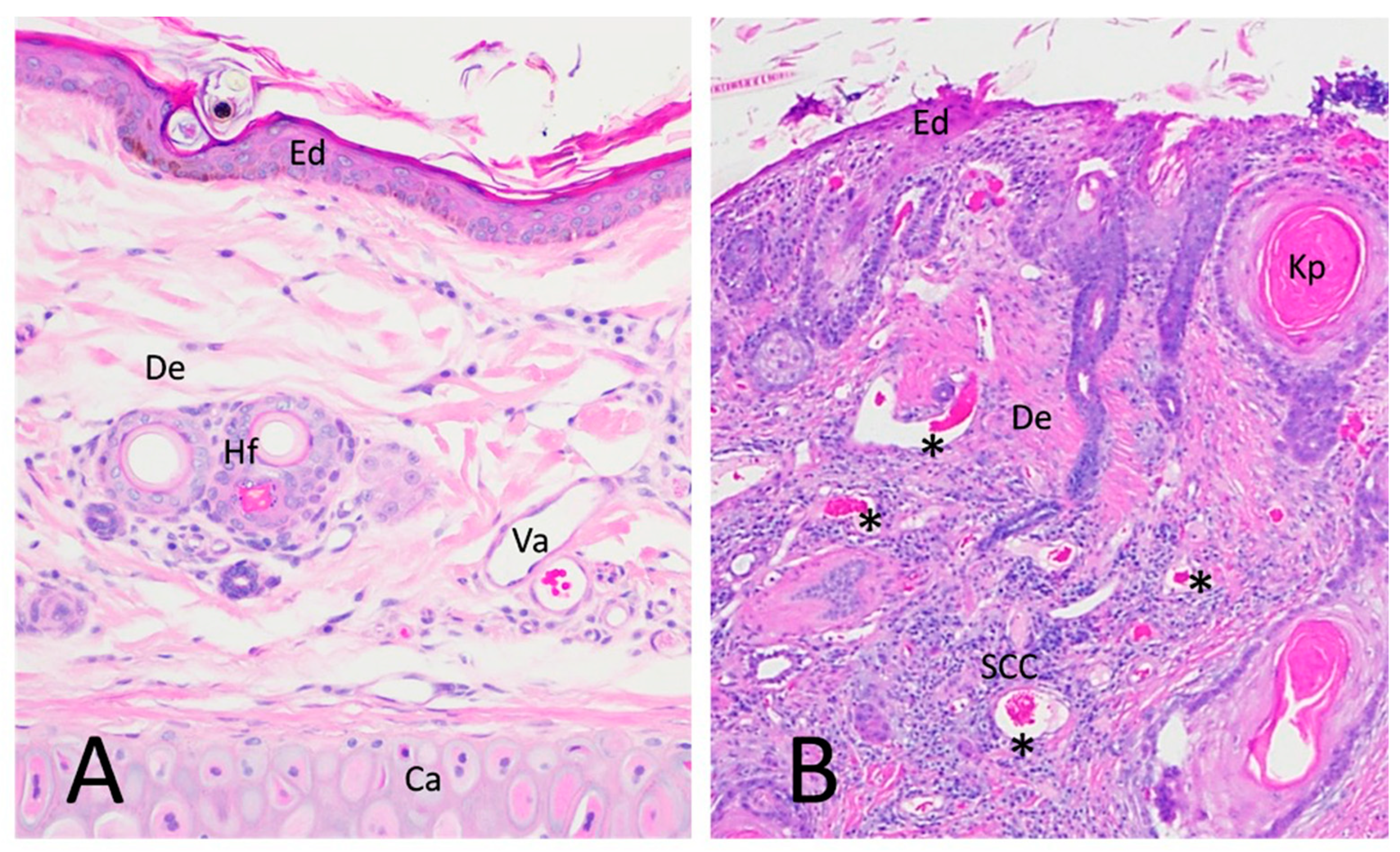
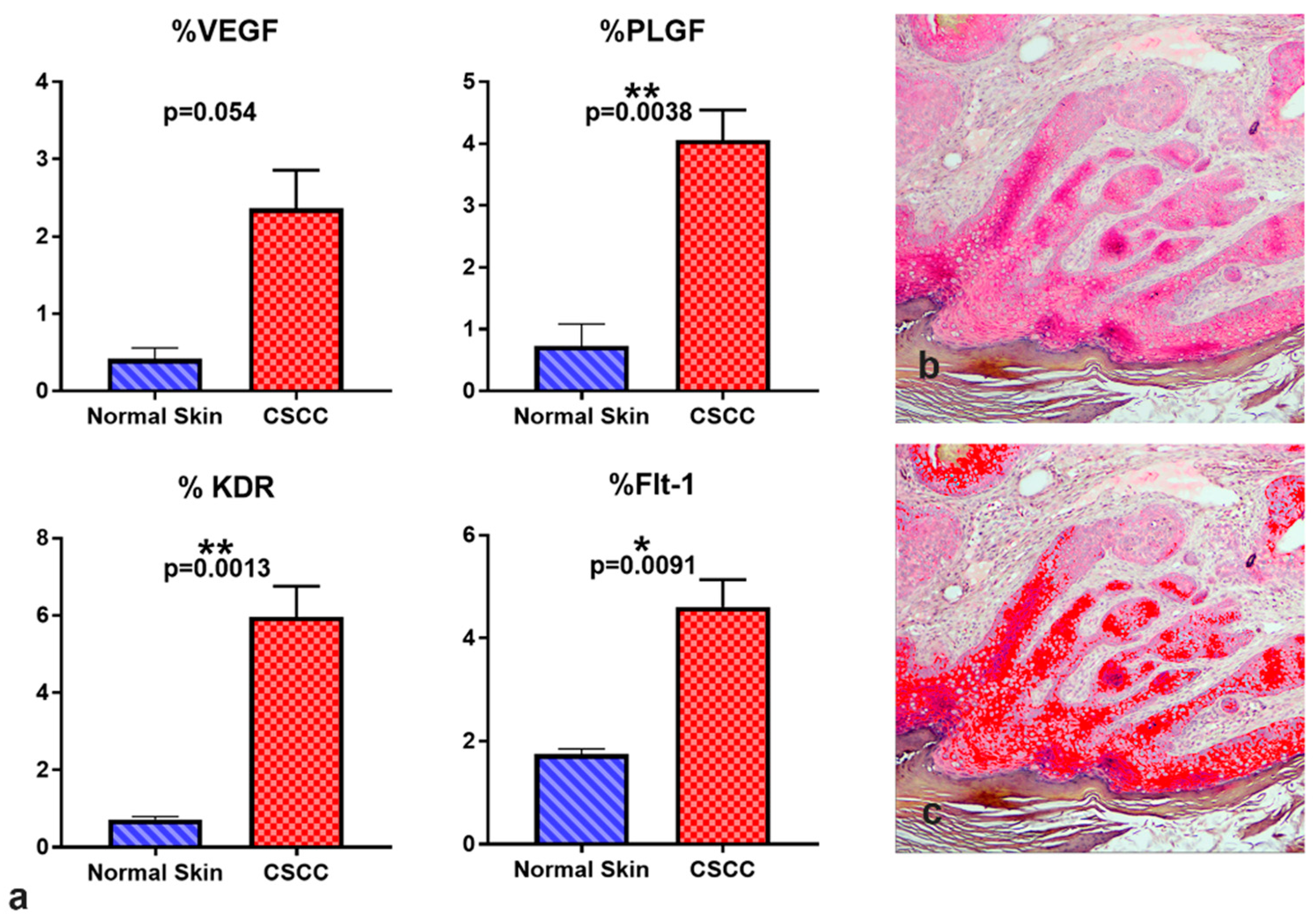
3.2. Immunohistochemistry Results
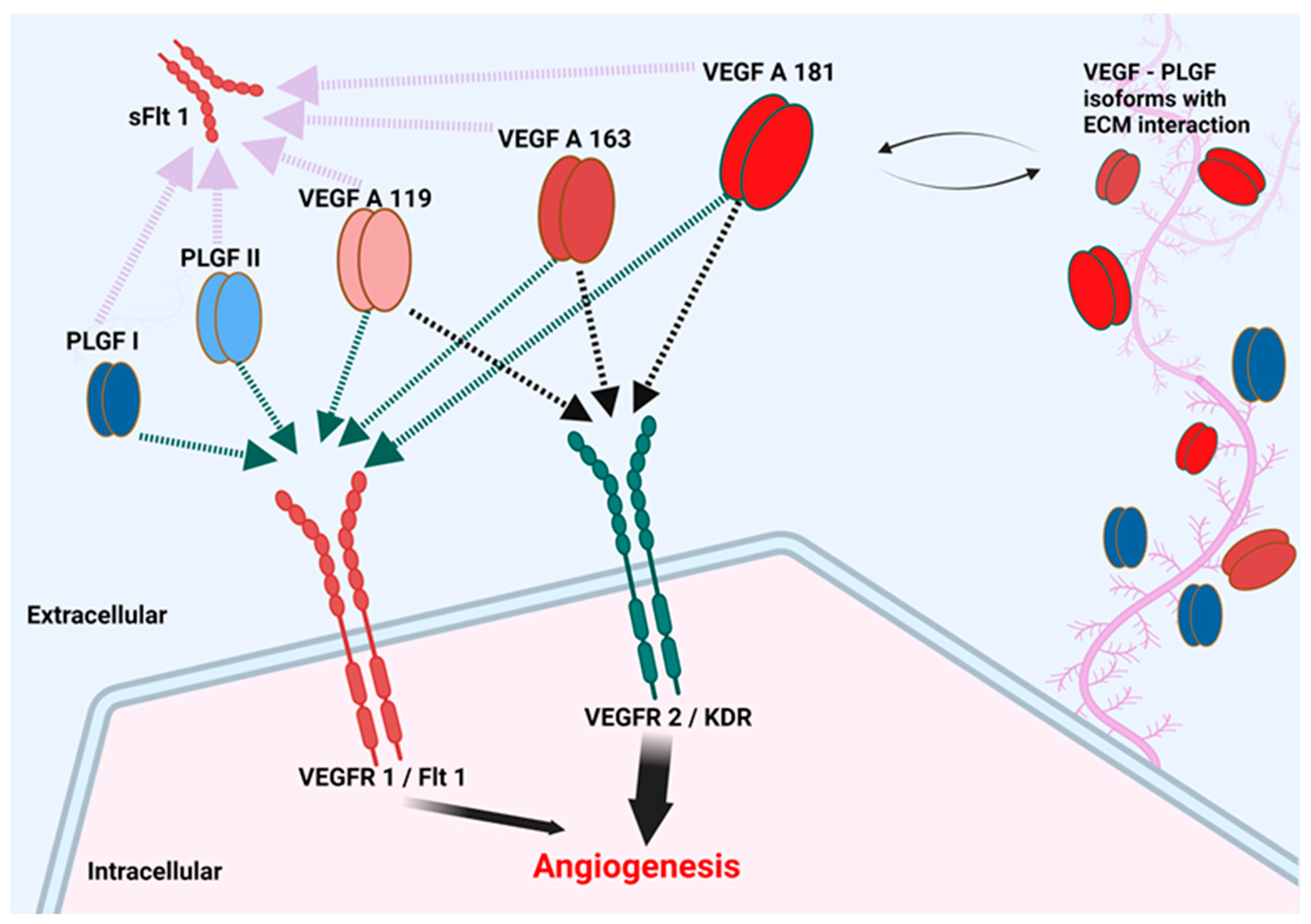
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldschmidt, M.H.; Goldschmidt, K.H. Epithelial and melanocytic tumors of the skin. In Tumors in Domestic Animals, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 88–141. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, A.I.; Câtoi, C. Chapter 4, Epithelial and melanocytic tumors of the skin. In Comparative Oncology; The Publishing House of the Romanian Academy: Bucuresti, Romania, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, T.M.; Rowe, D.E.; Nelson, B.R.; Swanson, N.A. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin (excluding lip and oral mucosa). J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1992, 26, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, R.P.; Hill, G.B.; Bajdik, C.D.; Coldman, A.J.; Fincham, S.; McLean, D.I.; Threlfall, W.J. Sunlight exposure, pigmentation factors, and risk of nonmelanocytic skin cancer: II. Squamous cell carcinoma. Arch. Dermatol. 1995, 131, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, R.P.; Ma, B.; McLean, D.I.; Yang, C.P.; Ho, V.; Carruthers, J.A.; Warshawski, L.M. Trends in basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma of the skin from 1973 through 1987. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1990, 23, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.T.; Suman, V.J.; Su, W.D.; Clay, R.P.; Harmsen, W.S.; Roenigk, R.K. Trends in the population-based incidence of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin first diagnosed between 1984 and 1992. Arch. Dermatol. 1997, 133, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Ratner, D. Cutaneous Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Amonkar, M.M.; Högberg, D.; Kasteng, F. Economic burden of resected squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in an incident cohort of patients in the UK. Head Neck Oncol. 2011, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, J.A.; Santana, I.A.; de Castro, G., Jr.; de Lima Lopes, G., Jr.; Shih, Y.-C.T. Economic analyses in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A review of the literature from a clinical perspective. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 89, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.A.; Kohn, E.C. The microenvironment of the tumour–host interface. Nature 2001, 411, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuspa, S.H.; Dlugosz, A.A.; Cheng, C.K.; Denning, M.F.; Tennenbaum, T.; Glick, A.B.; Weinberg, W.C. Role of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in multistage carcinogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 103, 90S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Smith, C.W.; Kiel, D.; Van Waes, C. Metastastic variants derived following in vivo tumor progression of an in vitro transformed squamous cell carcinoma line acquire a differential growth advantage requiring tumor-host interaction. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1997, 15, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.W.; Chen, Z.; Dong, G.; Loukinova, E.; Pegram, M.Y.; Nicholas-Figueroa, L.; Van Waes, C. The host environment promotes the development of primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinomas that constitutively express proinflammatory cytokines IL-1a, IL-6, GM-CSF, and KC. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1998, 16, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, F.; Götte, K.; Schwalb, J.; Schäfer, C.; Hörmann, K. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression Correlates with p53 Mutation and Angiogenesis in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2000, 120, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.; Jonason, A.S.; Leffellt, D.J.; Simon, J.A.; Sharma, H.W.; Kimmelman, J.; Remington, L.; Jacks, T.; Brash, D.E. Sunburn and p53 in the onset of skin cancer. Nature 1994, 372, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.; Vala, H.; Pinto, C.; Pinho, M.; Peleteiro, M. Immunohistochemical studies of epithelial cell proliferation and p53 mutation in bovine ocular squamous cell carcinoma. Vet. Pathol. 2005, 42, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teifke, J.P.; Löhr, C.V. Immunohistochemical detection of P53 overexpression in paraffin wax-embedded squamous cell carcinomas of cattle, horses, cats and dogs. J. Comp. Pathol. 1996, 114, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypij, J.M. A Naturally Occurring Feline Model of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in the cat: Current understanding and treatment approaches. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2013, 15, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, L.; Kanitakis, J. Histological classification of cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas with different severity. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnerdt, G.; Schmitz, K.J.; Dost, P.; Koch, D.A.; Jahnke, K. Histological criteria and metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the pinna. Laryngorhinootologie 2005, 84, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petter, G.; Haustein, U.F. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin—Histopathological features and their significance for the clinical outcome. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 1998, 11, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caruntu, A.; Moraru, L.; Lupu, M.; Ciubotaru, D.A.; Dumitrescu, M.; Eftimie, L.; Hertzog, R.; Zurac, S.; Caruntu, C.; Voinea, O.C. Assessment of Histological Features in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Involving Head and Neck Skin and Mucosa. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacEwen, E.G. Spontaneous tumors in dogs and cats: Models for the study of cancer biology and treatment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990, 9, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrán Hernández, I.; Kromhout, J.Z.; Teske, E.; Hennink, W.E.; van Nimwegen, S.A.; Oliveira, S. Molecular targets for anticancer therapies in companion animals and humans: What can we learn from each other? Theranostics 2021, 11, 3882–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, J.M.; Breen, M. An overview of molecular cancer pathogenesis, prognosis, and diagnosis. In Tumors in Domestic Animals, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Horak, E.R.; Klenk, N.; Leek, R.; LeJeune, S.; Smith, K.; Stuart, N.; Harris, A.L.; Greenall, M.; Stepniewska, K. Angiogenesis, assessed by platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule antibodies, as indicator of node metastases and survival in breast cancer. Lancet 1992, 340, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Laidler, P.; Davies, R.; Horgan, K.; Hughes, L. The prognostic significance of tumor vascularity in intermediate-thickness (0.76–4.0 mm thick) skin melanoma. A quantitative histologic study. Am. J. Pathol. 1988, 133, 419. [Google Scholar]
- Page, D.L.; Jensen, R.A. Angiogenesis in human breast carcinoma: What is the question? Hum. Pathol. 1995, 26, 1173–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigawa, N.; Amaya, H.; Matsumura, M.; Shimomatsuya, T. Association of tumour vasculature with tumour progression and overall survival of patients with non-early gastric carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 75, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrem, S.; Žarković, K.; Eškinja, N.; Jonjić, N. Endoglin is a better marker than CD31 in evaluation of angiogenesis in glioblastoma. Croat. Med. J. 2005, 46, 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Ghellal, A.; Li, C.; Byrne, G.; Haboubi, N.; Wang, J.M.; Bundred, N. Breast Carcinoma: Vascular Density Determined Using CD105 Antibody Correlates with Tumor Prognosis. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Qiu, Y.; Ding, Y. Endoglin (CD105) Expression in Angiogenesis of Primary Hepatocellular Carcinomas: Analysis using Tissue Microarrays and Comparisons with CD34 and VEGF. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2007, 37, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klagsbrun, M. Regulators of angiogenesis: Stimulators, inhibitors, and extracellular matrix. J. Cell. Biochem. 1991, 47, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P. Mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, R.; Seval, Y.; Huppertz, B. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis in the early human placenta. Acta Histochem. 2007, 109, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, F.; Baal, N.; Zygmunt, M. Studies of placental vasculogenesis: A way to understand pregnancy pathology? Z. Fur Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 2009, 213, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risau, W.; Flamme, I. Vasculogenesis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1995, 11, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and arteriogenesis: Mechanisms of blood vessel formation and remodeling. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 102, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvan, U.; Diez-Torre, A.; Bonilla, Z.; Moreno, P.; Diaz-Nunez, M.; Arechaga, J. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis in nonseminomatous testicular germ cell tumors. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2015, 33, 268.e17–268.e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicklin, D.J.; Ellis, L.M. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 1011–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.I.N.; Sakata, K.; Miyajima, Y.; Chijiwa, K.-I.; Mori, K.; Nakashima, T. The Predictive Value of p53, Ki-67 and Angiogenetic Factors in Primary Hypopharyngeal Carcinoma. Kurume Med. J. 2001, 48, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakopoulou, L.; Stefanaki, K.; Panayotopoulou, E.; Giannopoulou, I.; Athanassiadou, P.; Gakiopoulou-Givalou, H.; Louvrou, A. Expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2/Flk-1 in breast carcinomas: Correlation with proliferation. Hum. Pathol. 2002, 33, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, C.; Mazzone, M.; Jonckx, B.; Carmeliet, P. FLT1 and its ligands VEGFB and PlGF: Drug targets for anti-angiogenic therapy? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor and the regulation of angiogenesis. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2000, 55, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Falco, S. The discovery of placenta growth factor and its biological activity. Exp. Mol. Med. 2012, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D. The discovery of the placental growth factor and its role in angiogenesis: A historical review. Angiogenesis 2008, 11, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Moons, L.; Luttun, A.; Vincenti, V.; Compernolle, V.; De Mol, M.; Wu, Y.; Bono, F.; Devy, L.; Beck, H.; et al. Synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor contributes to angiogenesis and plasma extravasation in pathological conditions. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, M. Structure and Function of VEGF/VEGF-receptor System Involved in Angiogenesis. Cell Struct. Funct. 2001, 26, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.-R.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Fu, H. Vascular endothelial growth factor and microvascular density in esophageal and gastric carcinomas. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2003, 9, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, G.M.K.; Lui, P.C.W.; Lee, C.S.; Kung, F.Y.L.; Scolyer, R.A.; Law, B.K.B.; Lau, T.-S.; Karim, R.; Putti, T.C. Stromal expression of vascular endothelial growth factor correlates with tumor grade and microvessel density in mammary phyllodes tumors: A multicenter study of 185 cases. Hum. Pathol. 2004, 35, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcellini, M.; De Luca, N.; Riccioni, T.; Ciucci, A.; Orecchia, A.; Lacal, P.M.; Ruffini, F.; Pesce, M.; Cianfarani, F.; Zambruno, G. Increased melanoma growth and metastasis spreading in mice overexpressing placenta growth factor. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacal, P.M.; Failla, C.M.; Pagani, E.; Odorisio, T.; Schietroma, C.; Falcinelli, S.; Zambruno, G.; D’Atri, S. Human melanoma cells secrete and respond to placenta growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, C.; Watkins, G.; Boulton, M.; Cai, J.; Jiang, W.G. Placenta growth factor is over-expressed and has prognostic value in human breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 2819–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Ke, Y.; Mansel, R.E.; Jiang, W.G. Expression of Placenta growth factor (PlGF) in non-Small cell Lung cancer (NSCLC) and the clinical and prognostic significance. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2005, 3, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.C.; Tsao, P.N.; Yu, S.C.; Shun, C.T.; Tsai-Wu, J.J.; Wu, C.H.H.; Su, Y.N.; Hsieh, F.J.; Wong, J.M. Placenta growth factor expression is correlated with survival of patients with colorectal cancer. Gut 2005, 54, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-J.; Lee, J.-J.; Kok, S.-H.; Chou, C.-H.; Chang, H.-H.; Ling Chiang, M.; Chen, H.-M.; Kuo, M.Y.-P.; Chiang, C.-P. Expression of placenta growth factor: An independent factor for prediction of progression and prognosis of oral cancer. Head Neck 2010, 32, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houck, K.A.; Ferrara, N.; Winer, J.; Cachianes, G.; Li, B.; Leung, D.W. The vascular endothelial growth factor family: Identification of a fourth molecular species and characterization of alternative splicing of RNA. Mol. Endocrinol. 1991, 5, 1806–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglione, D.; Guerriero, V.; Viglietto, G.; Ferraro, M.G.; Aprelikova, O.; Alitalo, K.; Del Vecchio, S.; Lei, K.J.; Chou, J.Y.; Persico, M.G. Two alternative mRNAs coding for the angiogenic factor, placenta growth factor (PlGF), are transcribed from a single gene of chromosome 14. Oncogene 1993, 8, 925–931. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.E.; Keller, G.-A.; Ferrara, N. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) isoforms: Differential deposition into the subepithelial extracellular matrix and bioactivity of extracellular matrix-bound VEGF. Mol. Biol. Cell 1993, 4, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vempati, P.; Popel, A.S.; Mac Gabhann, F. Extracellular regulation of VEGF: Isoforms, proteolysis, and vascular patterning. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Rundqvist, H.; Branco, C.; Johnson, R.S. Autocrine VEGF Isoforms Differentially Regulate Endothelial Cell Behavior. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamer, S.B.; Wittenkeller, A.; Imoukhuede, P.I. VEGF-A splice variants bind VEGFRs with differential affinities. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jilani, S.M.; Nikolova, G.V.; Carpizo, D.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. Processing of VEGF-A by matrix metalloproteinases regulates bioavailability and vascular patterning in tumors. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Im, M.; Yim, N.H.; Ma, J.Y. Reduction of metastatic and angiogenic potency of malignant cancer by Eupatorium fortunei via suppression of MMP-9 activity and VEGF production. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tischer, E.; Mitchell, R.; Hartman, T.; Silva, M.; Gospodarowicz, D.; Fiddes, J.; Abraham, J. The human gene for vascular endothelial growth factor. Multiple protein forms are encoded through alternative exon splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 11947–11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.-G.; Yang, H.S.; Cao, Z.; Danielsson, J.; Duh, E.J. Upregulation of placental growth factor by vascular endothelial growth factor via a post-transcriptional mechanism. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-Y.; Nagane, M.; Huang, H.-J.S.; Cavenee, W.K. Intracerebral tumor-associated hemorrhage caused by overexpression of the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms VEGF121 and VEGF165 but not VEGF189. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12081–12087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunstein, J.; Masbad, J.J.; Hickey, R.; Giordano, F.; Johnson, R.S. Isoforms of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Act in a Coordinate Fashion To Recruit and Expand Tumor Vasculature. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 7282–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhrberg, C.; Gerhardt, H.; Golding, M.; Watson, R.; Ioannidou, S.; Fujisawa, H.; Betsholtz, C.; Shima, D.T. Spatially restricted patterning cues provided by heparin-binding VEGF-A control blood vessel branching morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2684–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozer, G.M.; Akerman, S.; Cross, N.A.; Barber, P.R.; Björndahl, M.A.; Greco, O.; Harris, S.; Hill, S.A.; Honess, D.J.; Ireson, C.R. Blood vessel maturation and response to vascular-disrupting therapy in single vascular endothelial growth factor-A isoform–producing tumors. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2301–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.L.; Rak, J.W.; Klement, G.; Kerbel, R.S. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Isoform Expression as a Determinant of Blood Vessel Patterning in Human Melanoma Xenografts. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar]
- Küsters, B.; de Waal, R.M.W.; Wesseling, P.; Verrijp, K.; Maass, C.; Heerschap, A.; Barentsz, J.O.; Sweep, F.; Ruiter, D.J.; Leenders, W.P.J. Differential Effects of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A Isoforms in a Mouse Brain Metastasis Model of Human Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5408–5413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P.; Ng, Y.-S.; Nuyens, D.; Theilmeier, G.; Brusselmans, K.; Cornelissen, I.; Ehler, E.; Kakkar, V.V.; Stalmans, I.; Mattot, V. Impaired myocardial angiogenesis and ischemic cardiomyopathy in mice lacking the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms VEGF 164 and VEGF 188. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers, R.A.; Fisher, M.; Brown, N.J.; Tozer, G.M.; Matcher, S.J. Vascular patterning of subcutaneous mouse fibrosarcomas expressing individual VEGF isoforms can be differentiated using angiographic optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 4551–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalmans, I.; Ng, Y.-S.; Rohan, R.; Fruttiger, M.; Bouché, A.; Ÿuce, A.; Fujisawa, H.; Hermans, B.; Shani, M.; Jansen, S. Arteriolar and venular patterning in retinas of mice selectively expressing VEGF isoforms. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimming, R.; Marmé, D. Endoglin (CD105) expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Head Neck 2002, 24, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzoutzos, K.; Batistatou, A.; Kitsos, G.; Liasko, R.; Stefanou, D. Study of microvascular density and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in cancerous and precancerous lesions of the eyelids. Anticancer. Res. 2014, 34, 4977–4983. [Google Scholar]
- Carlile, J.; Harada, K.; Baillie, R.; Macluskey, M.; Chisholm, D.; Ogden, G.; Schor, S.; Schor, A. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in oral tissues: Possible relevance to angiogenesis, tumour progression and field cancerisation. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2001, 30, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salven, P.; Heikkilä, P.; Anttonen, A.; Kajanti, M.; Joensuu, H. Vascular endothelial growth factor in squamous cell head and neck carcinoma: Expression and prognostic significance. Mod. Pathol. 1997, 10, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Itashiki, Y.; Harada, K.; Takenawa, T.; Ferdous, T.; Ueyama, Y.; Mishima, K. Antitumor effects of bevacizumab in combination with fluoropyrimidine drugs on human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.J.; Cheng, S.L.; Lee, J.J.; Chen, H.M.; Chang, H.H.; Kok, S.H.; Chiang, M.L.; Kuo, M.Y. Increased placenta growth factor mRNA level is significantly associated with progression, recurrence and poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2013, 112, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cheng, S.J.; Lee, J.J.; Cheng, S.L.; Chen, H.M.; Chang, H.H.; Wang, Y.P.; Kok, S.H.; Kuo, M.Y.; Chiang, C.P. Increased serum placenta growth factor level is significantly associated with progression, recurrence and poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiolino, P.; De Vico, G.; Restucci, B. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Basal Cell Tumours and in Squamous Cell Carcinomas of Canine Skin. J. Comp. Pathol. 2000, 123, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dissi, A.N.; Haines, D.M.; Singh, B.; Kidney, B.A. Immunohistochemical expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor associated with tumor cell proliferation in canine cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas and trichoepitheliomas. Vet. Pathol. 2007, 44, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, H.; Ehrhart, E.J.; Charles, J.B.; Thamm, D.H.; Larue, S.M. Immunohistochemical characterization of feline oral squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabak, Y.B.; Sozmen, M.; Devrim, A.K.; Sudagidan, M.; Yildirim, F.; Guvenc, T.; Yarim, M.; Gulbahar, Y.M.; Ahmed, I.; Karaca, E.; et al. Expression levels of angiogenic growth factors in feline squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Vet. Hung. 2020, 68, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millanta, F.; Andreani, G.; Rocchigiani, G.; Lorenzi, D.; Poli, A. Correlation Between Cyclo-oxygenase-2 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Canine and Feline Squamous Cell Carcinomas. J. Comp. Pathol. 2016, 154, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huckle, W.R.; Roche, R.I. Post-transcriptional control of expression of sFlt-1, an endogenous inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 93, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.C. Quantitative analysis of histological staining and fluorescence using ImageJ. Anat. Rec. 2013, 296, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, F.; Bukhari, A.B.; Malhotra, R.; De, A. IHC Profiler: An open source plugin for the quantitative evaluation and automated scoring of immunohistochemistry images of human tissue samples. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Ma, X.; Bian, Z.; Ma, J. Digital separation of diaminobenzidine-stained tissues via an automatic color-filtering for immunohistochemical quantification. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cataldo, S.; Ficarra, E.; Acquaviva, A.; Macii, E. Automated segmentation of tissue images for computerized IHC analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 100, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritescu, C.; Pirici, D.; Simionescu, C.; Mogoanta, L.; Raica, M.; Stinga, A.; Ciurea, R.; Stepan, A.; Stinga, A.; Ribatti, D. VEGF and VEGFRs expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2009, 50, 527–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanauer, S.B.; Feagan, B.G.; Lichtenstein, G.R.; Mayer, L.F.; Schreiber, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Rachmilewitz, D.; Wolf, D.C.; Olson, A.; Bao, W.; et al. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn’s disease: The ACCENT I randomised trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleige, S.; Pfaffl, M.W. RNA integrity and the effect on the real-time qRT-PCR performance. Mol. Asp. Med. 2006, 27, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, T.; Güell, M.; Serrano, L. Correlation of mRNA and protein in complex biological samples. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3966–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Beyer, A.; Aebersold, R. On the Dependency of Cellular Protein Levels on mRNA Abundance. Cell 2016, 165, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tae, K.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Yoo, E.; Feng, L.; Lee, J.J.; Hong, W.K.; Hittelman, W.N.; Shin, D.M. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and microvessel density in head and neck tumorigenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2821–2828. [Google Scholar]
- Margaritescu, C.; Pirici, D.; Stinga, A.; Simionescu, C.; Raica, M.; Mogoanta, L.; Stepan, A.; Ribatti, D. VEGF expression and angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma: An immunohistochemical and morphometric study. Clin. Exp. Med. 2010, 10, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Goel, M.M.; Chandra, S.; Bhatia, V.; Mehrotra, D.; Kumar, S.; Makker, A.; Rath, S.K.; Agarwal, S.P. VEGF-A immunohistochemical and mRNA expression in tissues and its serum levels in potentially malignant oral lesions and oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.H.; Lee, J.J.; Chen, H.M.; Kok, S.H.; Yen-Ping Kuo, M.; Cheng, S.J.; Chiang, C.P. Upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA level is significantly related to progression and prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinomas. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2015, 114, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-K.; Park, S.-G.; Kim, K.-W. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 41, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, X.Y.; Yang, X.H.; Cai, S.Q.; Bu, Z.Y.; Wu, X.J.; Lu, Z.F.; Zheng, M. Expression and localization of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 in human epidermal appendages: A comparison study by immunofluorescence. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2009, 34, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, X.Y.; Yang, X.H.; Cai, S.Q.; Bu, Z.Y.; Zheng, M. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors on keratinocytes in psoriasis: Regulated by calcium independent of VEGF. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, A. Companion Animal Model in Translational Oncology; Feline Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Canine Oral Melanoma. Biology 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Protein Target | Antibody Name | Antibody Details | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| panVEGF-A | C-1 (sc-7269) Santa Cruz | Mouse monoclonal IgG | 1/100 |
| PLGF | H-90 (sc-20714) Santa Cruz | Rabbit polyclonal IgG | 1/100 |
| KDR | F-10 (sc-393179) Santa Cruz | Mouse monoclonal | 1/200 |
| Flt-1 | H-225 (sc-9029) Santa Cruz | Rabbit polyclonal IgG | 1/200 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gudenschwager-Basso, E.K.; Stevenson, V.; Sponenberg, D.P.; Cecere, T.E.; Huckle, W.R. Characterization of the Expression of Angiogenic Factors in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Domestic Cats. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070375
Gudenschwager-Basso EK, Stevenson V, Sponenberg DP, Cecere TE, Huckle WR. Characterization of the Expression of Angiogenic Factors in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Domestic Cats. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(7):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070375
Chicago/Turabian StyleGudenschwager-Basso, Erwin Kristobal, Valentina Stevenson, Dan Phillip Sponenberg, Thomas E. Cecere, and William R. Huckle. 2022. "Characterization of the Expression of Angiogenic Factors in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Domestic Cats" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 7: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070375
APA StyleGudenschwager-Basso, E. K., Stevenson, V., Sponenberg, D. P., Cecere, T. E., & Huckle, W. R. (2022). Characterization of the Expression of Angiogenic Factors in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Domestic Cats. Veterinary Sciences, 9(7), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070375






