Abstract
Salmonella is mostly noted as a food-borne pathogen, but contact with chelonians has also been reported as a source of infection. Moreover, high levels of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) have been reported in Salmonella isolated from wild and captive reptiles. The aim of this study was to assess the occurrence of Salmonella AMR carriage by chelonians admitted to two zoological institutions in Spain, characterizing the isolates to assess the Salmonella AMR epidemiology in wildlife. To this end, 152 chelonians from nine species were sampled upon their arrival at the zoological nuclei. Salmonella identification was based on ISO 6579-1:2017 (Annex D), isolates were serotyped and their AMR analysed according to the EU Decision 2013/652. Moreover, the genetic relationship of the isolates was assessed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Results showed 19% (29/152) of the chelonians positive to Salmonella, all of them tortoises. For all isolates, 69% (20/29) were resistant and 34% (10/29) multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains. PFGE clustered isolates according to the serovar, confirming a low genetic diversity. In conclusion, this study shows a high presence of MDR Salmonella strains in tortoises at their entry into zoological nuclei. This condition highlights the need to establish Salmonella detection protocols for the entry of animals into these centres.
1. Introduction
Salmonella is considered one of the most important zoonotic agents with an estimated annual number of 93.8 million cases of salmonellosis worldwide [1,2]. In the European Union, salmonellosis was responsible for 87,923 human cases in 2019, of which 5.8% corresponded to Spain [3]. The infection usually causes a self-limited gastroenteritis, although some serovars can cause severe syndromes, such as Reiter’s Syndrome or Typhoid Fever, especially in children and elderly people, as they represent a risk population for this infection [4]. Despite the fact that Salmonella is mostly noted as a food-borne pathogen, the potential transmission of Salmonella from direct or indirect contact with reptiles cannot be ignored [5,6,7,8]. Indeed, reptile-associated salmonellosis (RAS), when the human Salmonella infection is acquired through contact with reptiles, is a growing public health concern worldwide [9]. Specifically, contact with turtles and tortoises has been widely associated with high risk of infection [10,11,12]. Indeed, several countries, such as the United States (US), have enacted a ban (40FR5620) to prevent chelonian-associated salmonellosis through the prohibition of turtles or turtle eggs with a carapace length of less than 10.16 cm; however, in Europe prevention is becoming more relevant [13,14,15,16,17]. Results from previous studies have shown a Salmonella incidence as high as 100% in free-living chelonians [18,19] and from 0% to 72.2% in pet chelonians [20,21]. Salmonella can be found in their intestinal tract and even in their environment. However, reptiles infected with Salmonella do not usually show any clinical signs. [12,21]. The close contact between chelonians and humans provides favourable conditions for the transmission of zoonotic infections, with reptile-associated salmonellosis being related to more severe clinical scenarios than those caused by other sources of infection [22,23,24].
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the most important public health concerns and its control has become a goal in most countries [25]. In this sense, Salmonella has been included in the World Health Organisation priority list of twelve antibiotic-resistant bacteria [26]. Moreover, the development of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Salmonella strains could entail therapeutic consequences, with a complication in the treatment of both animals and humans [27,28]. High levels of AMR have been reported in Salmonella isolated from reptiles and there has been an increasing focus on the role of turtles as disseminators [24,29]. Thus, documented data revealed that about 100% and 73% of the Salmonella strains isolated from pet chelonians in Spain were AMR and MDR, respectively [22]. However, the incidence of MDR Salmonella in free-living chelonians in Spain is not well known. In this sense, wildlife rescue centres and zoos are places of entry for chelonians of various origins, where asymptomatic carriers could be vectors for the inter- and intra-specific transmission of resistant Salmonella within the zoological nucleus, and even to the staff [30,31].
In this context, the aim of this study was to assess the occurrence of AMR Salmonella carriage by chelonians admitted to two zoological facilities in Spain, characterising the isolates to gain more in-depth knowledge of Salmonella AMR epidemiology in wildlife.
2. Materials and Methods
All animals were handled according to the principles of animal care published by Spanish Royal Decree 53/2013 [32].
2.1. Sample Collection
For this study, different chelonians were sampled upon their arrival from captivity or from the wild at two different zoological nuclei. The first was the Wildlife and Habitat Rehabilitation Group (GREFA), a wildlife rescue centre located in Central Spain that admits almost 7000 wild animals yearly, including birds (raptors, such as Bonelli’s eagles (Aquila fasciata); waterfowl birds, such as mallards (Anas platyrhynchos); or passerines, such as Eurasian blue tits (Cyanistes caeruleus)), mammals (carnivores, such as red fox (Vulpes vulpes)); or ungulates, such as roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) and reptiles (lizards, such as ocellated lizard (Timon lepidus); chameleons, such as Mediterranean chamaleon (Chamaleo chamaleon); or snakes, such as the Montpellier snake (Malpolon monspessulanus)). All those animals belong to protected species of native Iberian fauna, and GREFA’s aim is to recover and release them back into the wild. The origin of most of the chelonians admitted to this centre is the captive breeding in private facilities or just illegal keeping. The second nucleus was the Oceanogràfic aquarium (OCE) located in the city of Valencia, on the Eastern coast of Spain. The OCE is a public zoological institution that aims to increase social awareness and public education to promote preservation of biodiversity. In addition to public display facilities, the OCE also supports regional government, providing veterinary support to the marine animal stranding network and acting as a rehabilitation centre for local marine fauna (including sea turtles) and with propagation programmes for local endangered species to be reintroduced back into the wild, including two chelonian species: Hermann’s tortoise (Testudo hermanni) and European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis). Finally, the OCE also serves as a holding facility for some confiscated allochthonous species or private owner donations.
From 2015 to 2019, all chelonians admitted to GREFA and OCE were sampled in order to assess their sanitary status before their accommodation at the zoological facilities. A total of 152 individuals were sampled in this study: tortoises (n = 81), pond turtles (n = 37) and sea turtles (n = 34). Overall, 77 individuals were sampled in GREFA and 75 in OCE. According to the origin of the animals, 84.6% from GREFA and 54.7% from OCE came from captivity; the rest of the animals were free-living individuals that were taken to these centres for their recovery (Table 1). Moreover, captivity Hermann’s tortoises from GREFA were donated by an owner that bred them yearly in his private garden, and all the European pond turtles were from the official GREFA´s captive breeding programme. Thus, all samples submitted by OCE came from tortoises from the same owner; where Aldabra, leopard and some radiated tortoises were kept together in one enclosure, with the rest of the radiated and all the marginated tortoises and other Hermann’s tortoises housed in a third facility. All sea turtle samples came from free living individuals.

Table 1.
Species, origin details of chelonians sampled in this study.
From each individual, a cloacal swab was obtained using sterile cotton swabs during the first clinical examination. The swab cotton was inserted into the cloaca, and the swab was slowly twirling for 15 s to obtain the sample, and then kept in Cary–Blair transport medium (Cary–Blair sterile transport swabs, Deltalab®, Barcelona, Spain).
In tiny turtles, when the cloacal swab collection was not possible, each individual was housed singly in a plastic container with one litre of sterile water to prevent bacterial transmission. No filtration or antimicrobial treatment was added before sampling [19]. As bacteria excretion is not continuous, water samples were taken after two days in captivity. Then, 30 mL of water was taken and analysed. Negative control samples have been included in the analyses in order to detect possible contaminations.
Cloacal swabs and water samples were stored at 4 °C and processed for Salmonella detection within 24 h after collection.
2.2. Salmonella Detection and Serotyping
Samples were processed according to the ISO 6579-1:2017 (Annex D) recommendations for detection of Salmonella spp [33]. First, samples were pre-enriched in Buffered Peptone Water 2.5% (BPW; Scharlau®, Barcelona, Spain), in 1:10 vol/vol proportion, and incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 18 ± 2 h. Then, pre-enriched samples were inoculated on a Modified Rappaport Vassiliadis agar plate (MSRV; Difco®, Valencia, Spain) and incubated at 41.5 ± 1 °C for 48 h. Colonies obtained on positive plates were transferred onto two specific agar plates for Salmonella spp. detection: Xylose-Lysine-Deoxycholate (XLD, Liofilchem®, Valencia, Spain) and a selective chromogenic medium (ASAP; bioMerieux®, Marcy l’Étoile, France). Both plates were incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 24–48 h. A biochemical test (API-20E, bioMerieux, Marcy l’Étoile, France) was also performed to confirm Salmonella. Finally, Salmonella strains isolated were serotyped using the Kauffman–White scheme [34] and stored at −80 °C for further analysis.
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Salmonella strains were inoculated onto Müller–Hinton agar plates to perform the antimicrobial susceptibility test, based on the Kirby–Bauer disc diffusion method [35]. Antibiotics used for the test were those recommended by the 2013/652/EU document, including two quinolones: ciprofloxacin (CIP; 5 µg) and nalidixic acid (NA; 30 µg); one aminoglycoside: gentamicin (CN, 10 μg); one potentiated sulphonamide: trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMT-SXT; 25 µg); one phenicol: chloramphenicol (C; 30 µg); one pyrimidine: trimethoprim (TM; 5 µg); three b-lactams: ampicillin (AMP; 10 µg), cefotaxime (CTX; 30 µg) and ceftazidime (CAZ; 30 µg); one macrolide: azithromycin (AZM; 15 µg); one polymyxin: colistin (COL; 10 µg); and one glycylcycline: tigecycline (TGC; 15 µg) [36]. After 24 h of incubation at 37 °C, the inhibition zone around each disc was measured and interpreted according to the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) (http://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/, accessed on 22 July 2021) for Enterobacteriaceae and where this was not possible, according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) indications (https://clsi.org/media/2663/m100ed29_sample.pdf, accessed on 22 July 2021) [22]. The isolates were classified as susceptible (S) or resistant (R) according to EUCAST Guidelines [37]. MDR was defined as acquired resistance to at least one agent in three or more antimicrobial classes [38].
2.4. Molecular Typing of Salmonella Isolates
Fresh bacterial cultures of Salmonella strains were prepared on Nutrient Agar (Oxoid Ltd., Madrid, Spain). The isolates were genotyped by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) according to the PulseNet standard operating procedure (www.pulsenetinternational.org, accessed on 22 July 2021). We performed the restriction enzyme digests with Xbal (Roche Applied Science, Indianapolis, IN, USA) and fragments were separated by electrophoresis in a CHEF-DR III System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). PFGE band patterns were analysed using Fingerprinting II software, v3.0 (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Cluster analysis was performed using the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA), using the Dice correlation coefficient with a band position tolerance of 1.5%. The isolates with a minimum level of similarity of 90% were considered genetically similar or identical and were assigned the same pulsotype.
2.5. Statistical analysis
A Generalised Linear Model, which assumed a binomial distribution for Salmonella shedding and AMR, was fitted to the data to determine whether there was an association with the categorical variables (chelonian species, and sample type). A reptile was considered Salmonella-positive if one of the samples collected (cloacal swabs or aquarium water samples) tested positive. A p ≤ 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Data are presented as least squares means ± standard error of the least squares means. Analyses were carried out using a commercially available software application (SPSS 24.0 software package; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA, 2002).
3. Results
From all samples collected, 19.1% (29/152) tested positive for Salmonella. No significant differences were obtained between zoological nuclei (p > 0.05). However, all the positive samples were obtained from tortoises that arrived from captivity (36%; 29/81) (p < 0.001) (Table 2). Significant statistical differences for Salmonella isolation were found among the different tortoise species (p = 0.004), observing the highest percentage of positivity in Hermann’s tortoises (52.0%, 14/27) and marginated tortoise (40.0%, 8/20), followed by Aldabra giant tortoise and leopard tortoise (50.0%, 1/2, each), Greek tortoise (25.0%, 4/16), and finally radiated tortoise (7.0%, 1/14). None of the individuals presented symptomatology related to Salmonella infection.

Table 2.
Details of Salmonella detection among the different chelonian species.
From the 29 strains isolated, 28 Salmonella were identified as Salmonella enterica subsp enterica and one as Salmonella enterica subsp salamae (serovar 9,12:z29:1,5) (Table 3). The most represented serovar of Salmonella enterica subsp enterica was ser. Abony (37.0%, 10/27), followed by ser. Treforest (25.9%, 7/27), ser. Cerro and ser. Postdam (14.8%, 4/27, each), and finally ser. Warengo (11.1%, 3/27).
For all strains isolated, 69.0% (20/29) were resistant to at least one of the 12 antimicrobials tested. Salmonella strains isolated from marginated tortoise (n = 8), Aldabra giant tortoise, radiated tortoise, and leopard tortoise (n = 1, each) were AMR (Table 3). For Hermann’s tortoise and Greek tortoises, 50.0% of the isolated strains (7/14 and 2/4, respectively) were AMR. The highest percentages of AMR were found to CN (62.0%, n = 18), and CAZ (45.0%, n = 13), followed by TGC (34.0%, n = 10) and AZM (28.0%, n = 8), and finally AMP (3.0%, n = 1) (p < 0.05) (Table 3). Of the 12 antibiotics studied, no resistance was found against C, COL, CTX, NA, SXT, CIP, and TM.

Table 3.
Antimicrobial resistance pattern of Salmonella strains.
Table 3.
Antimicrobial resistance pattern of Salmonella strains.
| Specie | Serovar | n | CIP | NA | CN | SXT | C | TM | AMP | CTX | CAZ | AZM | COL | TGC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. enterica subsp enterica | Abony | 10 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Postdam | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Treforest | 7 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 6 | |
| Cerro | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 2 | |
| Warengo | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | |
| S. enterica subsp salamae | 9,12:z29:1,5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
n: number of strains, CIP: ciprofloxacin, NA: nalidixic acid, CN: gentamicin, SXT: trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole, C: chloramphenicol, TM: trimethoprim, AMP: ampicillin, CTX: cefotaxime, CAZ: ceftazidime, AZM: azithromycin, COL: colistin, TGC: tigecycline.
Furthermore, 34.5% (10/29) of Salmonella AMR isolates were considered MDR: ser. Cerro (50.0%, 2/4), ser. Treforest (71.4%, 5/7) and ser. Warengo (66.7%, 2/3). MDR Salmonella strains were isolated from marginated tortoises (100%, 7/7), Aldabra Giant tortoise (50%, 1/2), leopard tortoise (50%, 1/2) and Greek tortoise (6.2%, 1/16). Regarding the relationship among the serovar and MDR carriage, no association was observed (p = 0.777).
Overall, nine different AMR patterns were observed (Figure 1). The combination of CN-AZM-CAZ-TGC (25.0%, 5/20) was the most frequently observed, followed by CN alone (20.0%, 4/20) and CN-CAZ (15.0%, 3/20), CAZ alone and CAN-ACZ-TGC (10.0%, 2/20, each), and finally AMP-CN-AZM-TGC, CN-AZM-CAZ, CN-AZM-TGC, CN-TGC (5.0%, 1/20, each).
Of the 29 Salmonella isolates obtained in this study, 27 could be recovered for PFGE analysis. Two isolates could not be revived. A low genetic diversity was found with a total of eight different PFGE pulsotypes and isolates clustering according to their serovar; only two serovars ser. Abony and ser. Postdam showed two pulsotypes each, and the remaining serovars were represented by a single pulsotype (5, 6, 7 and 8, respectively) (Figure 1). The three most prevalent pulsotypes (3, 5 and 7) accounted for 66.7% of isolates (18/27) and 50% of serovars (3/6). The most frequent pulsotype (3) was found only in Hermann’s tortoise, while the second most frequent pulsotype (7) was isolated from Hermann’s tortoise and marginated tortoise. Hermann’s tortoise was the species with the highest diversity of Salmonella serovars and pulsotypes. The same AMR pattern was found among different pulsotypes and within each pulsotype.
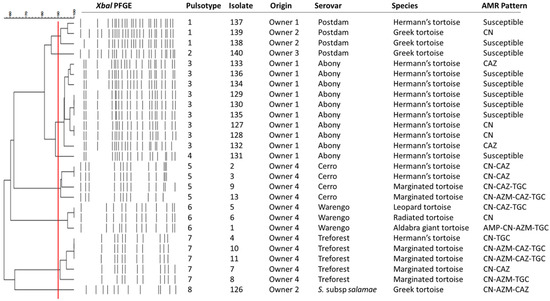
Figure 1.
Dendrogram of the XbaI PGFE profiles from a subset of Salmonella strains isolated from chelonials. AMR: Antimicrobial resistance.
4. Discussion
Historically, reptiles have been considered carriers of Salmonella spp. worldwide, which may pose a hazard as a source of environmental dissemination of the bacteria, while also being an important cause of animal and human infection [39,40,41]. Numerous studies have been conducted in pet reptiles, including chelonians, looking for different serovars of Salmonella that reptiles can host [21,42,43], but no studies have assessed the presence of Salmonella in chelonians admitted to wildlife rescue centres and zoos and the potential risk that can represent in releasable animals. The present study demonstrates that 36% of the tortoises examined upon arrival at the zoological facilities from private collections carry Salmonella. Nevertheless, Salmonella was not detected in pond turtles, sea turtles or other chelonians coming from the wild. Moreover, 69% of the strains isolated showed resistance to at least one antimicrobial, and 34% of them were MDR strains.
Salmonella has been isolated previously in 19% of the tortoises in households and pet shops from the Valencian Region, Spain [22]. This prevalence is lower than what was found in the present study (36%), highlighting the risks of the spread of the bacterium among tortoises housed in collectives, the risk of infection of animals from different species present in the facilities, and staff involved in rehabilitation practices and conservation projects [31]. It should be noted that the excretion of Salmonella by reptiles is extremely variable [44] and can be increased with stress, among other factors [9]. In this sense, prevalence obtained in the present study could be underestimated due to the intermittent shedding of Salmonella. In previous studies involving wild tortoises, the prevalence of Salmonella infection ranged from 34% to 100% [18,45,46]. Indeed, similarly to our study, a recent report of the incidence of Salmonella in captive tortoises in Italy revealed Hermann’s tortoise as the species in which the bacterium was most commonly isolated [31]. Moreover, none of the Salmonella-positive animals in our study had salmonellosis-related symptoms. Although clinical salmonellosis in reptiles is rare, it could occur, usually limited to intestinal signs or other symptoms such as dermatitis, salpingitis, septicaemia, osteomyelitis and granulomatous diseases, increasing the risk of transmission to humans [47,48].
No Salmonella-positive samples were found in free-living chelonians. Likewise, all the pond turtles and sea turtles were negative for Salmonella. Similarly, Strohl et al. [45] also reported no positive samples, while Hidalgo-Vila et al. [18] showed a low prevalence (12% and 15%) in the Mediterranean pond turtle (Mauremys leprosa) and the European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis), respectively. This difference with tortoises could be explained by the shorter time that Salmonella spends on the skin and in the cloaca in the aquatic animals. In terrestrial habitats, Salmonella persists for longer periods and is directly transmitted among individuals, favoured by the geophagy and coprophagy by tortoises, including faeces of feral animals such as birds or rodents [18,31,49]. Nevertheless, another hypothesis considered free-living reptiles as non-shedding carriers of Salmonella, excreting the bacteria only after long periods of stress [50]. Tortoises donated by private owners to both zoological nuclei had been kept in captivity for a long time, generally in high densities and in limited hygienic conditions. In contrast, free-living chelonians from nature have not, including sea turtles. On the other hand, European pond turtles were bred in captivity with all the proper biosecurity measures to ensure that those animals would not represent a potential risk to free-living populations when released.
In the present study, two subspecies of S. enterica belonging to seven different serovars were isolated (S. enterica enterica [I] and S. enterica salamae [II]). The most commonly reported serovars responsible for human salmonellosis, such as S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium, or monophasic S. Typhimurium, were not isolated in our study, similarly to other studies carried out in captive tortoises [18,31]. Nevertheless, the serovars isolated have been previously reported in human salmonellosis [18,41,46,51,52]. This includes ser. Abony, the most common in captive tortoises and wild tortoises in Spain [18,31,45], which has been associated with various cases of salmonellosis in infants and children [53], and in immunocompromised individuals [41,52], causing sepsis, meningitis, lung abscess and purulent pleuropneumonia [41,53]. Salmonella serovars Cerro, Postdam and Treforest have previously been isolated in chelonians in Spain, Italy and Taiwan [18,46,51], although is rarely associated with human disease [54,55]. To the author’s best knowledge, this is the first report of serovar Warengo in tortoises, and even in reptiles. S. enterica subsp salamae has been previously identified in turtles [18,56] and tortoises [18,46,49], but it is not associated with human infections [31].
From a One Health approach, where the environment, animals and humans are connected in a continuum, another epidemiological problem is the growing frequency of MDR strain threats [39]. A high percentage of Salmonella strains (69.0%) showed some AMR phenotype. Many studies have confirmed contamination of the environment with AMR bacteria [57] in soil [58], plants [59], and water [60]. In this context, Salmonella-positive tortoises could acquire AMR strains from contaminated soil or food and, of course, from previous antibiotic treatment.
The most frequent resistance pattern observed was CN-AZM-CAZ-TGC. CN-resistant Salmonella has been previously reported in tortoises, ranging from 1% to 23% [46,61]. In the present study, CN resistance was the most frequent. In this sense, the high prevalence of resistance has been observed previously in pet chelonians, with frequencies up to 100% [22]. CAZ is one of the first-line antimicrobial used in reptile medicine [62,63], commonly used for the treatment of salmonellosis in human and animals [64]. Salmonella isolates from the present survey showed a high percentage of resistance to CAZ, according to previous results [65], while most of the AMR studies carried out on chelonians show a high susceptibility to this antimicrobial [61,66]. To our best knowledge, this is the first report of AZM-resistant Salmonella detection in chelonians. AZM is one of the antimicrobials recommended by authorities to control salmonellosis in adults and children. Moreover, it represented the only option to treat extensively drug-resistant Salmonella Typhi in some regions of Asia before the emergence of AZM-resistant Salmonella [67]. TGC is another antimicrobial used against MDR bacteria. Detection of TGC-resistant Salmonella is rare [68], but Bertelloni et al. [66] observed 93.1% of isolates resistant to this antimicrobial in captive reptiles. Therefore, the control of MDR strains upon entry of new animals into wildlife nuclei must be very stringent to prevent their spread among individuals and the environment and to avoid future therapeutic failures [69].
Treforest has been reported as one of the most important serovars in human cases from the South-East Asian region [51]. While Hsu et al. [70] obtained only pansusceptible strains of this serovar from reptiles, Chen et al. [51] detected a high resistance prevalence to streptomycin among Treforest isolates. In our study, streptomycin was not analysed but instead, another aminoglycoside was included in the AMR test: CN. All the Treforest strains obtained in the present study showed a high frequency of AMR with 100% resistance to CN, 85.7% to TGC and 71.4% to both CAZ and AMZ.
The ability to link certain isolates to specific animals presented a unique opportunity to study Salmonella genetic diversity among chelonians. The PFGE typing showed the isolates were clustered according to the serovar, and a low genetic diversity within serovars was observed. It is important to remember the origin of animals: all the tortoises from OCE came from the same private owner, whereas captive animals from GREFA came from different sources (Figure 1). PFGE results could demonstrate the ability of the same strains to spread within the same population when there is close contact between individuals [22]. Finally, the higher Salmonella genetic diversity found in Hermann’s tortoise is also related to the origin of the animals, as this is the only species that was admitted at both zoological facilities.
5. Conclusions
The characterising of the isolates obtained from chelonians showed that only tortoises were positive for Salmonella spp., being Abony the main serovar isolated. Moreover, a high presence of MDR Salmonella strains was found at the individual’s arrival into zoological nuclei, with, a strong genetic relationship between the 66.7% of the strains isolated. These facts highlight the importance of establishing strict Salmonella detection protocols upon the arrival of new animals at a zoological nucleus to prevent the spread of resistant bacteria to other resident animals or to the workers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.M. and S.V.; methodology, C.M, S.V. and B.M.-M.; software, C.M., B.M.-M., M.C.-C. and L.L.-R.; validation, C.M. and S.V.; formal analysis, C.M., B.M.-M., M.C.-C. and L.L.-R.; investigation, B.M.-M., S.S.-N., L.M.-D., A.M., T.A., A.M.-G., J.J., F.G., C.R.-S., C.B. and D.G.-P.; resources, C.M. and S.V.; data curation, C.M., B.M.-M., M.C.-C. and L.L.-R.; writing—original draft preparation, C.M., B.M.-M. and L.L.-R.; writing—review and editing, C.M., B.M.-M., M.C.-C., L.L.-R., L.M.-D., A.M., T.A., A.M.-G., J.J., F.G., C.R.-S., C.B., D.G.-P. and S.V.; visualization, C.M., B.M.-M. and L.L.-R.; supervision, C.M. and S.V.; project administration, C.M. and S.V.; funding acquisition, C.M., S.V., L.L.-R. and A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the CEU-Cardenal Herrera University, as a part of the “Programa de Consolidación de Indicadores de Investigación” (INDI 20/29 and 21/35). L.L-R. was supported by a research grant from the Generalitat Valenciana-Fondo Social Europeo (ACIF/2020/376). A.M. was supported by a research grant (PRE2019-087435) from the Ministry of Science and Innovation of the Spanish Government.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animals were handled according to the principles of animal care published by Spanish Royal Decree 53/2013.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the GEMAS Research Group (Grupo de Estudio de Medicina y Conservación de Animales Salvajes) and Oceanogràfic staff for their support. Finally, we want to thank the Laboratorio Central de Veterinaria (Ministry of Rural Affairs, Algete, Madrid) and CECAV for the serotyping of Salmonella strains, likewise to the “Improvement of Production System-related Food Safety and End Products” research group (Veterinary Faculty, University Cardenal Herrera-CEU) for the technical support, and the volunteers from GREFA for their help with the sampling. The CERCA programme from the Generalitat de Catalunya is also acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M. The Global Burden of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO Salmonella (Non-Typhoidal). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salmonella-(non-typhoidal) (accessed on 22 July 2021).
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union One Health 2019 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Azad, S.M.; Mukherjee, A.; Dhar, S. Reiter’s Disease in a 8-Year-Old Boy. Indian J. Paediatr. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzer, K.; Switt, A.I.M.; Wiedmann, M. Animal Contact as a Source of Human Non-Typhoidal Salmonellosis. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikillus, K.H.; Gartrell, B.D.; Motion, E. Prevalence of Salmonella spp., and Serovars Isolated from Captive Exotic Reptiles in New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2011, 59, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.M.; Keel, K.; Sanchez, S.; Trees, E.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Adams, J.K.; Cheng, Y.; Ray, A.; Martin, G.; Presotto, A.; et al. Epidemiology of a Salmonella Enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar Typhimurium Strain Associated with a Songbird Outbreak. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7290–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pees, M.; Rabsch, W.; Plenz, B.; Fruth, A.; Prager, R.; Simon, S.; Schmidt, V.; Münch, S.; Braun, P.G. Evidence for the Transmission of Salmonella from Reptiles to Children in Germany, July 2010 to October 2011. Euro Surveill. 2013, 18, 20634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bjelland, A.M.; Sandvik, L.M.; Skarstein, M.M.; Svendal, L.; Debenham, J.J. Prevalence of Salmonella Serovars Isolated from Reptiles in Norwegian Zoos. Acta Vet. Scand. 2020, 62, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, S.; Rimhanen-Finne, R.; Weill, F.-X.; Rabsch, W.; Thornton, L.; Perevoščikovs, J.; van Pelt, W.; Heck, M. Salmonella Infections Associated with Reptiles: The Current Situation in Europe. Euro Surveill. 2008, 13, 18902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, S.; Tauxe, R.V.; Behravesh, C.B. Turtle-Associated Salmonellosis, United States, 2006–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zając, M.; Skarżyńska, M.; Lalak, A.; Kwit, R.; Śmiałowska-Węglińska, A.; Pasim, P.; Szulowski, K.; Wasyl, D. Salmonella in Captive Reptiles and Their Environment—Can We Tame the Dragon? Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.L.; Potter, M.; Pollard, R.; Feldman, R.A. Turtle-Associated Salmonellosis in the United States: Effect of Public Health Action, 1970 to 1976. JAMA 1980, 243, 1247–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, B.; Andersson, Y.; Ekdahl, K. Effect of Regulation and Education on Reptile-Associated Salmonellosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC Commission Regulation (EU) 2020/205 of 14 February 2020 Amending Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 as Regards Salmonella in Reptile. 2020. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32020R0205&from=EN (accessed on 22 July 2021).
- Meletiadis, A.; Biolatti, C.; Mugetti, D.; Zaccaria, T.; Cipriani, R.; Pitti, M.; Decastelli, L.; Cimino, F.; Dondo, A.; Maurella, C.; et al. Surveys on Exposure to Reptile-Associated Salmonellosis (RAS) in the Piedmont Region—Italy. Animals 2022, 12, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrente, M.; Sangiorgio, G.; Grandolfo, E.; Bodnar, L.; Catella, C.; Trotta, A.; Martella, V.; Buonavoglia, D. Risk for Zoonotic Salmonella Transmission from Pet Reptiles: A Survey on Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices of Reptile-Owners Related to Reptile Husbandry. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 146, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Vila, J.; Díaz-Paniagua, C.; de Frutos-Escobar, C.; Jiménez-Martínez, C.; Pérez-Santigosa, N. Salmonella in Free Living Terrestrial and Aquatic Turtles. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 119, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marin, C.; Ingresa-Capaccioni, S.; González-Bodi, S.; Marco-Jiménez, F.; Vega, S. Free-Living Turtles Are a Reservoir for Salmonella but Not for Campylobacter. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakadai, A.; Kuroki, T.; Kato, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Yamai, S.; Yaginuma, C.; Shiotani, R.; Yamanouchi, A.; Hayashidani, H. Prevalence of Salmonella Spp. in Pet Reptiles in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2005, 67, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marin, C.; Vega, S.; Marco-Jiménez, F. Tiny Turtles Purchased at Pet Stores Are a Potential High Risk for Salmonella Human Infection in the Valencian Region, Eastern Spain. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, C.; Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L.; Laso, O.; Villora-Gonzalez, J.; Vega, S. Pet Reptiles: A Potential Source of Transmission of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 613718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cota, J.B.; Carvalho, A.C.; Dias, I.; Reisinho, A.; Bernardo, F.; Oliveira, M. Salmonella Spp. in Pet Reptiles in Portugal: Prevalence and Chlorhexidine Gluconate Antimicrobial Efficacy. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Tela, I.; Peruzy, M.F.; D’Alessio, N.; di Nocera, F.; Casalinuovo, F.; Carullo, M.R.; Cardinale, D.; Cristiano, D.; Capuano, F. Serotyping and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella Strains Detected in Wildlife and Natural Environments in Southern Italy. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. The European Union Summary Report on Trends and Sources of Zoonoses, Zoonotic Agents and Food-Borne Outbreaks in 2017. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, Research, and Development of New Antibiotics: The WHO Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Threlfall, E.J.; Fisher, I.S.T.; Berghold, C.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Tschäpe, H.; Cormican, M.; Luzzi, L.; Schneider, F.; Wannet, W.; Machado, J.; et al. Antimicrobial Drug Resistance in Isolates of Salmonella Enterica from Cases of Salmonellosis in Humans in Europe in 2000: Results of International Multi-Centre Surveillance. Eurosurveillance 2003, 8, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferstl, P.G.; Reinheimer, C.; Jozsa, K.; Zeuzem, S.; Kempf, V.A.J.; Waidmann, O.; Grammatikos, G. Severe Infection with Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Choleraesuis in a Young Patient with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 2086–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebani, V.; Cerri, D.; Fratini, F.; Meille, N.; Valentini, P.; Andreani, E. Salmonella Enterica Isolates from Faeces of Domestic Reptiles and a Study of Their Antimicrobial in Vitro Sensitivity. Res. Vet. Sci. 2005, 78, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, C.; Stanford, K.; Narvaez-Bravo, C.; Callaway, T.; McAllister, T. Farm Fairs and Petting Zoos: A Review of Animal Contact as a Source of Zoonotic Enteric Disease. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, G.; Bellati, A.; Pugliese, N.; Camarda, A.; Faleo, S.; Lombardi, R.; Occhiochiuso, G.; D’Onghia, F.; Circella, E. Salmonella Infection in Turtles: A Risk for Staff Involved in Wildlife Management? Animals 2021, 11, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Por El Que Se Establecen Las Normas Básicas Aplicables Para La Protección de Los Animales Utilizados En Experimentación y Otros Fines Científicos, Incluyendo La Docencia; Spain Spain 2013. Royal Degree 53/1 February 2013; Boletín Oficial del Estado: Madrid, Spain, 2013; pp. 11370–11421.
- Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Detection of Salmonella spp. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/29315.html (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars, 9th ed.; WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Matuschek, E.; Brown, D.F.J.; Kahlmeter, G. Development of the EUCAST Disk Diffusion Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Method and Its Implementation in Routine Microbiology Laboratories. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O255–O266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boletín Oficial del Estado Decisión 2013/652/UE, 12 de Noviembre Sobre El Seguimiento y La Notificación de La Resistencia de Las Bacterias Zoonóticas y Comensales a Los Antibióticos. 2013, pp. 26–39. Available online: https://www.boe.es/doue/2013/303/L00026-00039.pdf (accessed on 22 July 2021).
- EUCAST New Definitions of S, I and R from 2019. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/newsiandr/ (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2017. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitten, T.; Bender, J.B.; Smith, K.; Leano, F.; Scheftel, J. Reptile-Associated Salmonellosis in Minnesota, 1996–2011. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagarajah, S.; Waldram, A.; Dolan, G.; Jenkins, C.; Ashton, P.M.; Martin, A.I.C.; Davies, R.; Frost, A.; Dallman, T.J.; de Pinna, E.M.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing Reveals an Outbreak of Salmonella Enteritidis Associated with Reptile Feeder Mice in the United Kingdom, 2012–2015. Food Microbiol. 2018, 71, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambino-Shirley, K.; Stevenson, L.; Concepción-Acevedo, J.; Trees, E.; Wagner, D.; Whitlock, L.; Roberts, J.; Garrett, N.; van Duyne, S.; McAllister, G.; et al. Flea Market Finds and Global Exports: Four Multistate Outbreaks of Human Salmonella Infections Linked to Small Turtles, United States—2015. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, N.; le Hello, S.; Weill, F.-X.; de Thoisy, B.; Berger, F. Salmonella Serotypes in Reptiles and Humans, French Guiana. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 170, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, T.P.; Varriale, L.; Borrelli, L.; Pace, A.; Latronico, M.; Menna, L.F.; Fioretti, A.; Dipineto, L. Salmonella Serotypes Isolated in Geckos Kept in Seven Collections in Southern Italy. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 59, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodini, R.J.; Sundberg, J.P. Salmonellosis in Reptiles: A Review. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1981, 113, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohl, P.; Tilly, B.; Frémy, S.; Brisabois, A.; Guérin-Faublée, V. Prevalence of Salmonella Shedding in Faeces by Captive Chelonians. Vet. Rec. 2004, 154, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percipalle, M.; Giardina, G.; Lipari, L.; Piraino, C.; Macrì, D.; Ferrantelli, V. Salmonella Infection in Illegally Imported Spur-Thighed Tortoises (Testudo graeca). Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.G.; Atance, P.M.; Seva, J.; Pallarés, F.J.; Vizcaíno, L.L. Granulomatous Hepatitis Caused by Salmonella Typhimurium in a Spur-Thighed Tortoise (Testudo graeca). Vet. Rec. 2005, 157, 236–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasmans, F.; Blahak, S.; Martel, A.; Pantchev, N. Introducing Reptiles into a Captive Collection: The Role of the Veterinarian. Vet. J. 2008, 175, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomastikova, Z.; Romero, S.B.; Knotek, Z.; Karpiskova, R. Prevalence and Characteristics of Salmonella Species Isolated from Captive Reptiles in the Czech Republic. Orig. Pap. Vet. Med. 2017, 62, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, J.M.; Brown, J.D.; Kelly, T.R.; Fountain, A.L.; Sleeman, J.M. Absence of Detectable Salmonella Cloacal Shedding in Free-Living Reptiles on Admission to the Wildlife Center of Virginia. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2004, 35, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-C.; Chin, S.-C.; Lai, Y.-H.; Tung, K.-C.; Chiou, C.-S.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Chang, C.-C. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Salmonellae Isolates from Reptiles in Taiwan. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitiriga, V.; Dendrinos, J.; Nikitiadis, E.; Vrioni, G.; Tsakris, A. First Case of Lung Abscess Due to Salmonella Enterica Serovar Abony in an Immunocompetent Adult Patient. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2016, 2016, 3159031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Meervenne, E.; Botteldoorn, N.; Lokietek, S.; Vatlet, M.; Cupa, A.; Naranjo, M.; Dierick, K.; Bertrand, S. Turtle-Associated Salmonella Septicaemia and Meningitis in a 2-Month-Old Baby. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1379–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gicquelais, R.E.; Morris, J.F.; Matthews, H.S.; Gladden, L.; Safi, H.; Grayson, C.; Slayton, R.B.; Newton, A.E.; Bordonaro, R.; Wheeler, J.G.; et al. Multiple-Serotype Salmonella Outbreaks in Two State Prisons—Arkansas, August 2012. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2014, 63, 169. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Lian, K.; Luo, D.; Lin, D.; Feng, W.; Xian, H.; Li, T. Salmonella Potsdam Causing Lumbar Vertebral Osteomyelitis: A Case Report. Medicine 2018, 97, e0682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones, V.; Téllez, S.; Goyache, J.; Ballesteros, C.; Lanzarot, M.D.P.; Domínguez, L.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.F. Salmonella Diversity Associated with Wild Reptiles and Amphibians in Spain. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.H.; Moore, L.S.P.; Sundsfjord, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Regmi, S.; Karkey, A.; Guerin, P.J.; Piddock, L.J.V. Understanding the Mechanisms and Drivers of Antimicrobial Resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, K.J.; Reyes, A.; Wang, B.; Selleck, E.M.; Sommer, M.O.A.; Dantas, G. The Shared Antibiotic Resistome of Soil Bacteria and Human Pathogens. Science 2012, 337, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carter, L.J.; Harris, E.; Williams, M.; Ryan, J.J.; Kookana, R.S.; Boxall, A.B.A. Fate and Uptake of Pharmaceuticals in Soil—Plant Systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.L.; Cantón, R. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance in Water Environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacopello, C.; Foti, M.; Fisichella, V.; Latella, G.; Aleo, A.; Mammina, C. Antibiotic Resistance in Salmonella Isolated from Tegus (Tupinambis spp.). J. Exot. Pet Med. 2012, 21, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, P.M.; Steffes, Z.J. Emerging Infectious Diseases of Chelonians. Vet. Clin. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2013, 16, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerreta, A.J.; Masterson, C.A.; Lewbart, G.A.; Dise, D.R.; Papich, M.G. Pharmacokinetics of Ketorolac in Wild Eastern Box Turtles (Terrapene carolina carolina) after Single Intramuscular Administration. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 42, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collignon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases, Food, and Cephalosporin Use in Food Animals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1391–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, M.M.; Davis, M.; Valitutto, M.T.; Nelson, K.; Sykes, J.M. Salmonella Infection and Carriage in Reptiles in a Zoological Collection. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2016, 248, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelloni, F.; Chemaly, M.; Cerri, D.; Le Gall, F.; Ebani, V.V. Salmonella Infection in Healthy Pet Reptiles: Bacteriological Isolation and Study of Some Pathogenic Characters. Acta Microbiol. Et Immunol. Hung. 2016, 63, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sajib, M.; Tanmoy, A.M.; Hooda, Y.; Rahman, H.; Andrews, J.R.; Garrett, D.O.; Endtz, H.P.; Saha, S.K.; Saha, S. Tracking the Emergence of Azithromycin Resistance in Multiple Genotypes of Typhoidal Salmonella. mBio 2021, 12, e03481-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Schneiders, T. Tigecycline Challenge Triggers SRNA Production in Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tardón, A.; Bataller, E.; Llobat, L.; Jiménez-Trigos, E. Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance Detection in Fractures of Wild Birds from Wildlife Rehabilitation Centres in Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 74, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, B.B.; Gibson, T.E.; Yeliseyev, V.; Liu, Q.; Lyon, L.; Bry, L.; Silver, P.A.; Gerber, G.K. Dynamic Modulation of the Gut Microbiota and Metabolome by Bacteriophages in a Mouse Model. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 803–814.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).