E-cadherin Expression in Canine Gastric Carcinomas: Association with Clinicopathological Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Selection
2.2. Histological Classification
2.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.4. Immunohisochemistry Evaluation of E-cadherin
2.5. Statistical Analysis
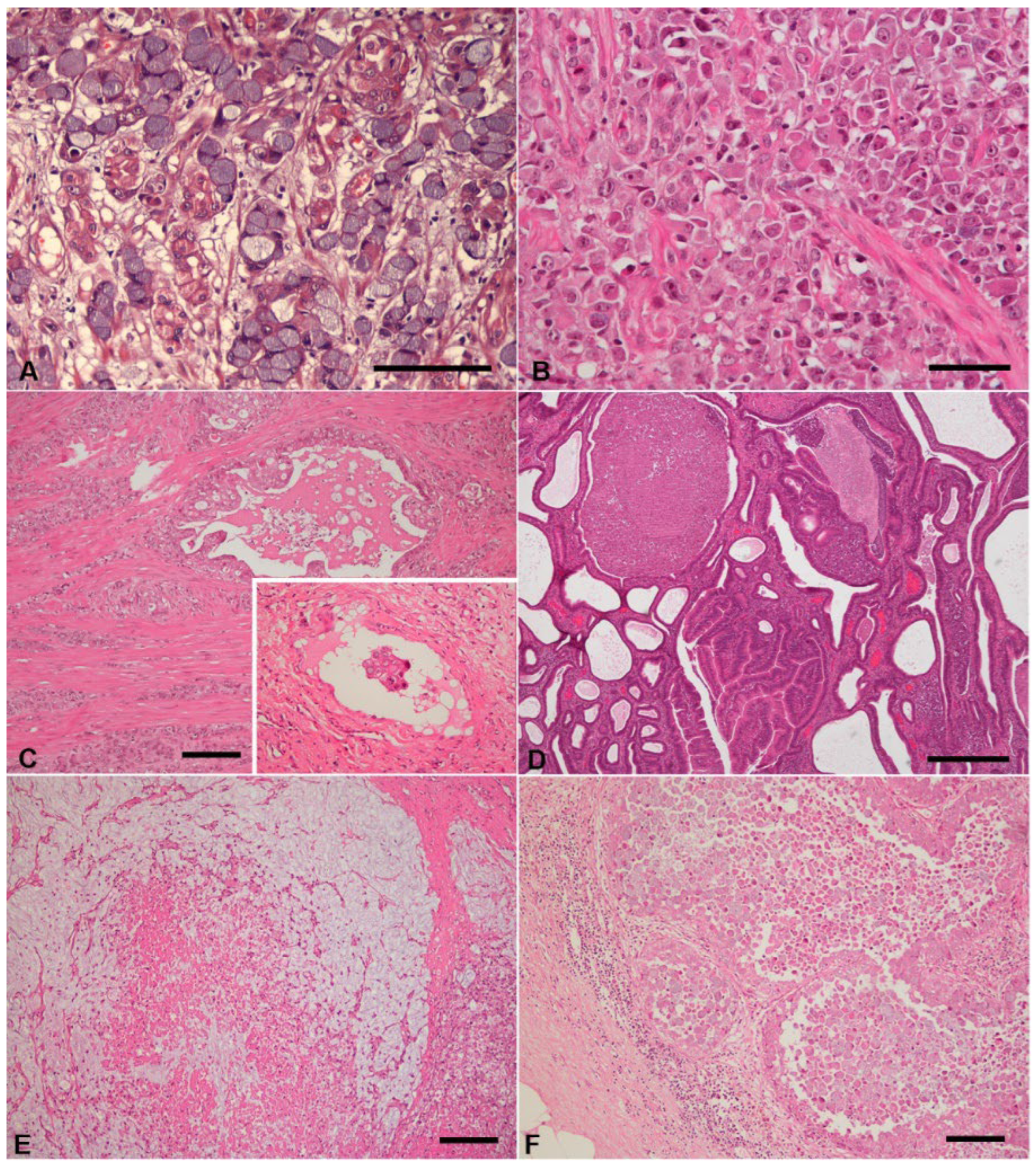
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathological Data
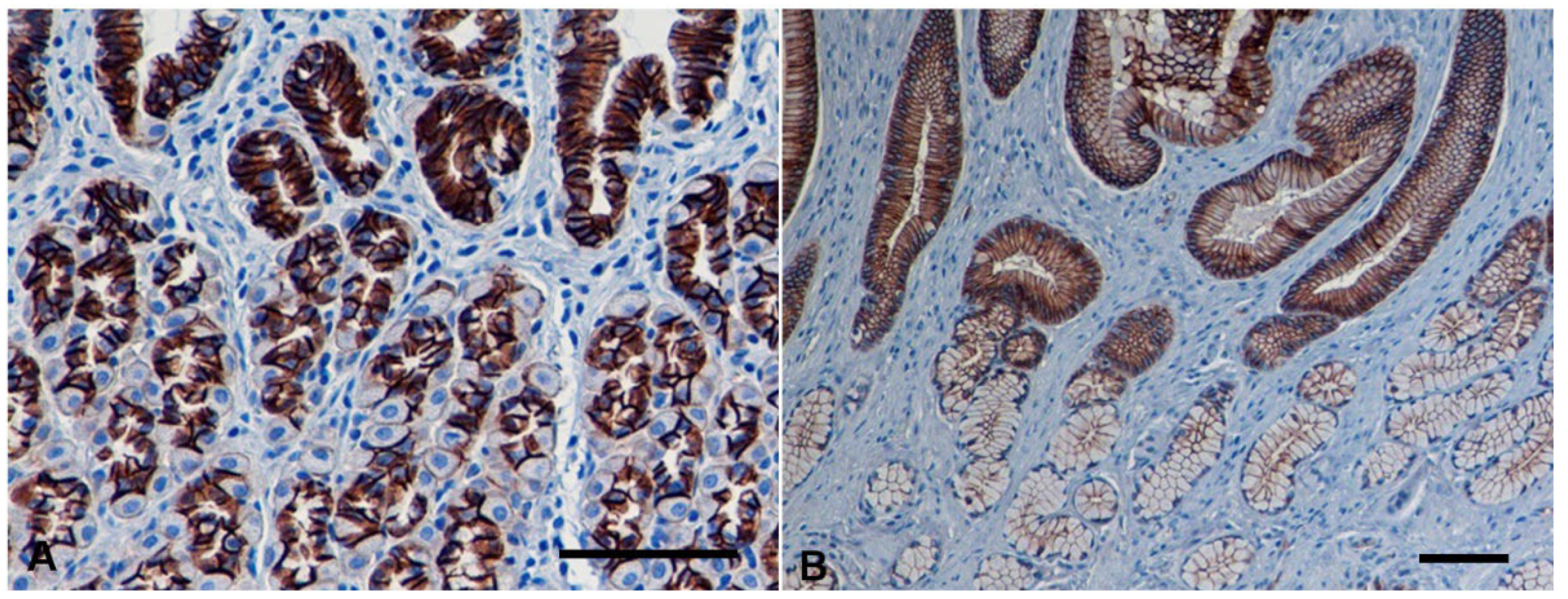
3.2. Immunohistochemistry
3.2.1. Normal Gastric Mucosa
3.2.2. Non-Neoplastic Gastric Mucosa Adjacent to Carcinomas
3.2.3. Gastric Carcinomas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, I.; Taulescu, M.A.; Day, M.J.; Catoi, C.; Reis, C.A.; Carneiro, F.; Gärtner, F. Canine Gastric Pathology: A Review. J. Comp. Pathol. 2016, 154, 9–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugen, S.; Thomas, R.E.; German, A.J.; Burgener, I.A.; Mandigers, P.J.J. Gastric carcinoma in canines and humans, a review. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lecoindre, P.; Bystricka, M.; Chevallier, M.; Peyron, C. Gastric carcinoma associated with Menetrier’s-like disease in a West Highland white terrier. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 53, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Aberdein, D.; Cullen, G.D.; French, A.F. Ménétrier disease and gastric adenocarcinoma in 3 Cairn terrier littermates. Vet. Pathol. 2012, 49, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koterbay, A.M.; Muthupalani, S.; Fox, J.G.; McNiel, E.A. Risk and characteristics of gastric carcinoma in the chow chow dog. Can. Vet. J. 2020, 61, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, A.K.; Hurvitz, A.I.; Johnson, G.F. Canine gastric adenocarcinoma. Vet. Pathol. 1978, 15, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, H.M.; Holt, D.E. Canine gastric adenocarcinoma and leiomyosarcoma: A retrospective study of 21 cases (1986–1999) and literature review. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2002, 38, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonda, D.; Gualtieri, M.; Scanziani, E. Gastric carcinoma in the dog: A clinicopathological study of 11 cases. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1989, 30, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddingham, W.; Graham, D.; Banks, M.; Jansen, M. The evolving role of endoscopy in the diagnosis of premalignant gastric lesions. F1000Res 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, B.; Wavreille, V.A.; Husbands, B.D.; Matz, B.M.; Massari, F.; Liptak, J.M.; Cray, M.T.; de Mello Souza, C.H.; Wustefeld-Janssens, B.G.; Oblak, M.L.; et al. Perioperative complications and outcome after surgery for treatment of gastric carcinoma in dogs: A Veterinary Society of Surgical Oncology retrospective study of 40 cases (2004–2018). Vet. Surg. 2019, 48, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualtieri, M.; Costa Devoit, C.; Riccardi, E.; Olivero, D. Intestinal Metaplasia and Over-Expression of c-erb2 and p53 in Tissue Adjacent to Dog Gastric Carcinoma. Pak. Vet. J. 2017, 37, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Head, K.W.; Cullen, J.M.; Dubielzig, R.R.; Else, R.W.; Misdorp, W.; Patnaik, A.K.; Tateyama, S.; van der Gaag, I. Histological Classification of Tumors of the Alimentary System of Domestic Animals. Armed Forces Inst. Pathol. 2003, 10, 73–110. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, H.; Jass, J.R.; Sobin, L.H.; Ota, K.; Jass, J.R. Histological typing of oesophageal and gastric tumours. In WHO International Histological Classification of Tumours, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1990; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.T.; Zeng, L.; Yang, J.; Zeng, C.; Chen, Y. Analysis of the Incidence and Survival of Gastric Cancer Based on the Lauren Classification: A Large Population-Based Study Using SEER. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez Fonseca, P.; Carmona-Bayonas, A.; Hernández, R.; Custodio, A.; Cano, J.M.; Lacalle, A.; Echavarria, I.; Macias, I.; Mangas, M.; Visa, L.; et al. Lauren subtypes of advanced gastric cancer influence survival and response to chemotherapy: Real-world data from the AGAMENON National Cancer Registry. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flores, A.R.; Lemos, I.; Rema, A.; Taulescu, M.; Seixas, F.; Reis, C.A.; Gärtner, F.; Amorim, I. Tn and Sialyl-Tn antigens in canine gastric tissues. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2020, 18, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, A.R.; Castro, M.; Rêma, A.; Mesquita, J.R.; Taulescu, M.; Gärtner, F.; Seixas, F.; Amorim, I. Immunoexpression of Trefoil Factor 1 in Non-Neoplastic and Neoplastic Canine Gastric Tissues. Animals 2021, 11, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, L.; Carlson, C.S.; St Hill, C.A. The novel carbohydrate tumor antigen C2-O-sLe x is upregulated in canine gastric carcinomas. Vet. Pathol. 2010, 47, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gumbiner, B.M. Cell adhesion: The molecular basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis. Cell 1996, 84, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeichi, M. Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science 1991, 251, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, P.; Fernandes, M.S.; Figueiredo, J.; Caldeira, J.; Carvalho, J.; Pinheiro, H.; Leite, M.; Melo, S.; Oliveira, P.; Simões-Correia, J.; et al. E-cadherin dysfunction in gastric cancer--cellular consequences, clinical applications and open questions. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2981–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedrazzani, C.; Corso, G.; Marrelli, D.; Roviello, F. E-cadherin and hereditary diffuse gastric cancer. Surgery 2007, 142, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, M.; Ringwald, M.; Kemler, R. Uvomorulin-catenin complex formation is regulated by a specific domain in the cytoplasmic region of the cell adhesion molecule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4246–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paredes, J.; Figueiredo, J.; Albergaria, A.; Oliveira, P.; Carvalho, J.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Caldeira, J.; Costa, A.M.; Simões-Correia, J.; Oliveira, M.J.; et al. Epithelial E- and P-cadherins: Role and clinical significance in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1826, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.J.; Lewis-Tuffin, L.J.; Anastasiadis, P.Z. E-cadherin’s dark side: Possible role in tumor progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1826, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machado, J.C.; Carneiro, F.; Beck, S.; Rossi, S.; Lopes, J.; Taveira-Gomes, A.; Cardoso-Oliveira, M. E-Cadherin Expression Is Correlated with the Isolated Cell/Diffuse Histotype and with Features of Biological Aggressiveness of Gastric Carcinoma. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 1998, 6, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazăr, D.; Tăban, S.; Ardeleanu, C.; Dema, A.; Sporea, I.; Cornianu, M.; Lazăr, E.; Vernic, C. The immunohistochemical expression of E-cadherin in gastric cancer; correlations with clinicopathological factors and patients’ survival. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2008, 49, 459–467. [Google Scholar]
- Shino, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Yamada, Y.; Tanase, M.; Yamada, T.; Matsuda, M.; Yamashita, J.; Tatsumi, M.; Miwa, T.; Nakano, H. Clinicopathologic evaluation of immunohistochemical E-cadherin expression in human gastric carcinomas. Cancer 1995, 76, 2193–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemura, Y.; Nojima, N.; Kaji, M.; Fujimura, T.; Itoh, H.; Ninomiya, I.; Miyazaki, I.; Endo, Y.; Sasaki, T. E-cadherin and urokinase-type plasminogen activator tissue status in gastric carcinoma. Cancer 1995, 76, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbert, H.E.; Mueller, W.; Schneiders, A.; Meier, S.; Moll, R.; Birchmeier, W.; Hommel, G. Prognostic value of E-cadherin expression in 413 gastric carcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 69, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardas, A.; Suárez-Bonnet, A.; Beck, S.; Becker, W.E.; Ramírez, G.A.; Priestnall, S.L. Canine Gastric Carcinomas: A Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study and Similarities with the Human Counterpart. Animals 2021, 11, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Chambers, J.K.; Nakashima, K.; Nibe, K.; Ohno, K.; Tsujimoto, H.; Uchida, K.; Nakayama, H. Immunohistochemical analysis of beta-catenin, E-cadherin and p53 in canine gastrointestinal epithelial tumors. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 82, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prachasilpchai, W.; Nuanualsuwan, S.; Chatsuwan, T.; Techangamsuwan, S.; Wangnaitham, S.; Sailasuta, A. Diagnosis of Helicobacter spp. infection in canine stomach. J. Vet. Sci. 2007, 8, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosman, F.T.; Carneiro, F.; Hruban, R.H.; Theise, N. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lauren, P. The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: Diffuse and so-called intestinal-type carcinoma. An attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 1965, 64, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, F.M.; Craig, L.; Donovan, T.A.; Meuten, D.J.; Miller, M.; Munday, J.S.; Roccabianca, P. Lymphovascular Invasion Guideline, Version 1.0. Veterinary Cancer Guidelines and Protocols. Available online: http://vetcancerprotocols.org (accessed on 5 March 2002).
- Jawhari, A.; Jordan, S.; Poole, S.; Browne, P.; Pignatelli, M.; Farthing, M.J. Abnormal immunoreactivity of the E-cadherin-catenin complex in gastric carcinoma: Relationship with patient survival. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Chu, R.Y.; Hsu, P.N.; Hsu, P.I.; Lu, J.Y.; Lai, K.H.; Tseng, H.H.; Chou, N.H.; Huang, M.S.; Tseng, C.J.; et al. Loss of E-cadherin expression correlates with poor differentiation and invasion into adjacent organs in gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancer Lett. 2003, 201, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorudi, S.; Sheffield, J.P.; Poulsom, R.; Northover, J.M.; Hart, I.R. E-cadherin expression in colorectal cancer. An immunocytochemical and in situ hybridization study. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 142, 981–986. [Google Scholar]
- Moll, R.; Mitze, M.; Frixen, U.H.; Birchmeier, W. Differential loss of E-cadherin expression in infiltrating ductal and lobular breast carcinomas. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, P.E.; Fonseca-Alves, C.E.; Rivera-Calderón, L.G.; Carvalho, M.; Kuasne, H.; Rogatto, S.R.; Laufer-Amorim, R. Deregulation of E-cadherin, β-catenin, APC and Caveolin-1 expression occurs in canine prostate cancer and metastatic processes. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 118, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Restucci, B.; Papparella, S.; De Vico, G.; Maiolino, P. E cadherin expression in normal and neoplastic canine mammary gland. J. Comp. Pathol. 1997, 116, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aresu, L.; Pregel, P.; Zanetti, R.; Caliari, D.; Biolatti, B.; Castagnaro, M. E-cadherin and β-catenin expression in canine colorectal adenocarcinoma. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 89, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Nibe, K.; Chambers, J.K.; Uneyama, M.; Nakashima, K.; Ohno, K.; Tsujimoto, H.; Uchida, K.; Nakayama, H. A histopathological study on spontaneous gastrointestinal epithelial tumors in dogs. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2020, 33, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terragni, R.; Casadei Gardini, A.; Sabattini, S.; Bettini, G.; Amadori, D.; Talamonti, C.; Vignoli, M.; Capelli, L.; Saunders, J.H.; Ricci, M.; et al. EGFR, HER-2 and KRAS in canine gastric epithelial tumors: A potential human model? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawla, P.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of gastric cancer: Global trends, risk factors and prevention. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seim-Wikse, T.; Jörundsson, E.; Nødtvedt, A.; Grotmol, T.; Bjornvad, C.R.; Kristensen, A.T.; Skancke, E. Breed predisposition to canine gastric carcinoma--a study based on the Norwegian canine cancer register. Acta Vet. Scand. 2013, 55, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patnaik, A.K.; Hurvitz, A.I.; Johnson, G.F. Canine gastrointestinal neoplasms. Vet. Pathol. 1977, 14, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Washabau, R.J.; Day, M.J. Canine and Feline Gastroenterology; Elsivier Health Sciences: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, V.; Canfrán, S.; Rodríguez-Franco, F.; Benito, A.; Sáinz, A.; Rodríguez-Bertos, A. Canine gastric carcinoma: Immunohistochemical expression of cell cycle proteins (p53, p21, and p16) and heat shock proteins (Hsp27 and Hsp70). Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanziani, E.; Giusti, A.M.; Gualtieri, M.; Fonda, D. Gastric carcinoma in the Belgian shepherd dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1991, 32, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoyama, Y.; Hirohashi, S. Expression of E- and P-cadherin in gastric carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, B.; Johnson, J.P.; Leitl, F.; Jauch, K.W.; Heiss, M.M.; Schildberg, F.W.; Birchmeier, W.; Funke, I. E-cadherin expression in primary and metastatic gastric cancer: Down-regulation correlates with cellular dedifferentiation and glandular disintegration. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 1690–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Graziano, F.; Arduini, F.; Ruzzo, A.; Mandolesi, A.; Bearzi, I.; Silva, R.; Muretto, P.; Testa, E.; Mari, D.; Magnani, M.; et al. Combined analysis of E-cadherin gene (CDH1) promoter hypermethylation and E-cadherin protein expression in patients with gastric cancer: Implications for treatment with demethylating drugs. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berx, G.; Cleton-Jansen, A.M.; Nollet, F.; de Leeuw, W.J.; van de Vijver, M.; Cornelisse, C.; van Roy, F. E-cadherin is a tumour/invasion suppressor gene mutated in human lobular breast cancers. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 6107–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks-Wilson, A.R.; Kaurah, P.; Suriano, G.; Leach, S.; Senz, J.; Grehan, N.; Butterfield, Y.S.; Jeyes, J.; Schinas, J.; Bacani, J.; et al. Germline E-cadherin mutations in hereditary diffuse gastric cancer: Assessment of 42 new families and review of genetic screening criteria. J. Med. Genet. 2004, 41, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.F.; Rosivatz, E.; Blechschmidt, K.; Kremmer, E.; Sarbia, M.; Höfler, H. Analysis of the E-cadherin repressor Snail in primary human cancers. Cells Tissues Organs 2007, 185, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.C.; Carneiro, F.; Hoefler, H.; Becker, K.F. Role of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulator Slug in primary human cancers. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 3035–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, J.; van Grieken, N.C.; Pereira, P.M.; Sousa, S.; Tijssen, M.; Buffart, T.E.; Diosdado, B.; Grabsch, H.; Santos, M.A.; Meijer, G.; et al. Lack of microRNA-101 causes E-cadherin functional deregulation through EZH2 up-regulation in intestinal gastric cancer. J. Pathol. 2012, 228, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashige, J.; Kamohara, H.; Watanabe, M.; Hiyoshi, Y.; Iwatsuki, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kinoshita, K.; Saito, S.; Baba, Y.; Baba, H. MicroRNA-200b regulates cell proliferation, invasion, and migration by directly targeting ZEB2 in gastric carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19 (Suppl. S3), S656–S664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinck, L.; Näthke, I.S.; Papkoff, J.; Nelson, W.J. Dynamics of cadherin/catenin complex formation: Novel protein interactions and pathways of complex assembly. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 125, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoyama, Y.; Nagafuchi, A.; Fujita, S.; Gotoh, M.; Takeichi, M.; Tsukita, S.; Hirohashi, S. Cadherin dysfunction in a human cancer cell line: Possible involvement of loss of alpha-catenin expression in reduced cell-cell adhesiveness. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 5770–5774. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, P.R.; Ferreira, V.A.; Santos, C.C.; Rocha-Filho, F.D.; Feitosa, R.R.; Falcão, E.A.; Cavada, B.K.; Ribeiro, R.A. E-cadherin immunoexpression patterns in the characterisation of gastric carcinoma histotypes. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 63, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, H.; Tahara, H.; Oka, H.; Miyata, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Tamura, S.; Iihara, K.; Doki, Y.; Hirano, S.; Takeichi, M.; et al. Expression of immunoreactive E-cadherin adhesion molecules in human cancers. Am. J. Pathol. 1991, 139, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri, S.; Porcellato, I.; Mechelli, L.; Menchetti, L.; Iussich, S.; De Maria, R.; Sforna, M.; Bongiovanni, L.; Brachelente, C. E-Cadherin Expression in Canine Melanocytic Tumors: Histological, Immunohistochemical, and Survival Analysis. Vet. Pathol. 2020, 57, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartenbeck, J.; Schmelz, M.; Franke, W.W.; Geiger, B. Endocytosis of junctional cadherins in bovine kidney epithelial (MDBK) cells cultured in low Ca2+ ion medium. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 113, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, K.F.; Atkinson, M.J.; Reich, U.; Huang, H.H.; Nekarda, H.; Siewert, J.R.; Höfler, H. Exon skipping in the E-cadherin gene transcript in metastatic human gastric carcinomas. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1993, 2, 803–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelka, M.; Ludwig, H. Ultrastructural studies of myeloma cells: Observations concerning the Golgi apparatus and intermediate-size filaments. Am. J. Hematol. 1983, 15, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restucci, B.; Martano, M.; De Vico, G.; Muzio, L.L.; Maiolino, P. Expression of E-cadherin, beta-catenin and APC protein in canine colorectal tumours. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 2919–2925. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Nagafuchi, A.; Tsukita, S.; Suzuki, H. Co-expression of E-cadherin and alpha-catenin molecules in colorectal cancer. Surg. Today 1999, 29, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabizadeh, Z.; Nosrati, A.; Sajadi Saravi, S.N.; Yazdani Charati, J.; Janbabai, G. Evaluation of E-cadherin Expression in Gastric Cancer and Its Correlation with Clinicopathologic Parameters. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem. Cell Res. 2017, 11, 158–164. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y.Q.; Ye, Z.Y.; Tao, H.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhao, Z.S. Relationship between cell adhesion molecules expression and the biological behavior of gastric carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Ikeguchi, M.; Tsujitani, S.; Maeta, M.; Liu, J.; Kaibara, N. Significant correlation between micrometastasis in the lymph nodes and reduced expression of E-cadherin in early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2001, 4, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frixen, U.H.; Behrens, J.; Sachs, M.; Eberle, G.; Voss, B.; Warda, A.; Löchner, D.; Birchmeier, W. E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of human carcinoma cells. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 113, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behrens, J.; Mareel, M.M.; Van Roy, F.M.; Birchmeier, W. Dissecting tumor cell invasion: Epithelial cells acquire invasive properties after the loss of uvomorulin-mediated cell-cell adhesion. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 108, 2435–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleminckx, K.; Vakaet, L., Jr.; Mareel, M.; Fiers, W.; van Roy, F. Genetic manipulation of E-cadherin expression by epithelial tumor cells reveals an invasion suppressor role. Cell 1991, 66, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Tang, Y.B.; Yuan, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, M. The prognostic value of E-cadherin in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 2589–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Case No. | Breed | Sex/ Age (Years) | Weight, kg | Tumor Location | Histological Classification | Metastases | E-cad Immunoexpression (Score) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHO Classification | Lauren | Primary Tumors | Emboli | Metastases | |||||||
| 1 | Crossbreed | F/13 | ≤10 | Body | Tubular | Intestinal | - | N (3) | - | - | |
| 2 | Labrador Retriever | F/14 | 26–45 | Body | Tubular | Intestinal | NA | Ab (2) | - | - | |
| 3 | Collie | M/11 | 26–45 | Body and antrum | Tubular | Intestinal | Lymph node, Pancreas, Intestine * | Ab (2) | N (3) | Ab (2) | |
| 4 | Miniature Poodle | F/14 | ≤10 | Antrum | Tubular | Intestinal | - | N (3) | - | - | |
| 5 | Basset Hound | F/12 | 26–45 | Antrum | Tubular | Intestinal | Lymph node * | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | |
| 6 | Siberian Husky | F/12 | 26–45 | Antrum | Tubular | Intestinal | NA | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | - | |
| 7 | Siberian Husky | M/13 | 26–45 | Antrum | Tubular | Intestinal | - | Ab (2) | - | - | |
| 8 | Crossbreed (X poodle) | F/9 | 11–25 | Antrum | Papillary | Intestinal | - | N (3) | - | - | |
| 9 | Crossbreed | M/10 | NR | Body | Mucinous | Diffuse | NA | Ab (2) | N (3) | - | |
| 10 | Chow-Chow | M/6 | 26–45 | Body | Mucinous | Diffuse | - | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | ||
| 11 | English Bulldog | M/6 | 11–25 | Body | Signet ring cell | Diffuse | - | Ab (2) | - | - | |
| 12 | Sharpei | M/5 | 11-25 | Body | Signet ring cell | Diffuse | - | Ab (2) | NA | - | |
| 13 | Golden Retriever | M/14 | 26–45 | Body | Signet ring cell | Diffuse | Lung *, Esophagus, Liver, Adrenal gland * | Ab (2) | Ab (0) | Ab (2) | |
| 14 | Pointer | M/11 | 26–45 | Body | Signet ring cell | Diffuse | Lymph node * | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | |
| 15 | Crossbreed | F/7 | ≤10 | Body and antrum | Signet ring cell | Diffuse | - | Ab (2) | - | - | |
| 16 | Cocker Spaniel | M/13 | 11–25 | Antrum | Signet ring cell | Diffuse | - | Ab (2) | - | - | |
| 17 | Chow-Chow | M/10 | 26–45 | Antrum | Signet ring cell | Diffuse | - | Ab (0) | - | - | |
| 18 | Golden Retriever | M/10 | 26–45 | Antrum | Signet ring cell | Diffuse | - | Ab (2) | - | - | |
| 19 | Boxer | M/7 | 26–45 | Antrum | Signet ring cell | Diffuse | - | N (3) | - | - | |
| 20 | West Highland White Terrier | F/13 | ≤10 | Antrum | Signet ring cell | Diffuse | - | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | - | |
| 21 | Alaska Malamute | M/6 | 26–45 | NA | Signet ring cell | Diffuse | - | Ab (2) | - | - | |
| 22 | Crossbreed | F/8 | 11–25 | Body | Poorly cohesive | Diffuse | Intestine *, Peritoneum, Liver | Ab (2) | N (3) | N (3) | |
| 23 | Crossbreed (X German Shepherd) | F/13 | 26–45 | Body | Poorly cohesive | Diffuse | Liver | Ab (0) | - | - | |
| 24 | Akita | M/9 | 26–45 | Body | Poorly cohesive | Diffuse | NA | Ab (0) | Ab (2) | - | |
| 25 | German Shepherd | M/12 | 26–45 | Body and antrum | Poorly cohesive | Diffuse | Esophagus *, Lymph node | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | |
| 26 | Shih Tzu | F/10 | ≤10 | Antrum | Poorly cohesive | Diffuse | - | Ab (2) | NA | - | |
| 27 | Chow-Chow | M/9 | 26–45 | Antrum | Poorly cohesive | Diffuse | - | Ab (2) | - | - | |
| 28 | Crossbreed | F/7 | NR | Antrum | Poorly cohesive | Diffuse | Intestine * | Ab (2) | - | N (3) | |
| Intestinal component | Diffuse component | ||||||||||
| 29 | Belgian Shepherd | F/11 | 11–25 | Body | Mixed | Indeterminate | Lymph node * | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | Ab (2) |
| 30 | Collie | M/11 | 26–45 | Body | Mixed | Indeterminate | - | Ab (2) | N (3) | N (3) | - |
| 31 | Chow-Chow | F/11 | 26–45 | Antrum | Mixed | Indeterminate | - | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | N (3) | - |
| 32 | Labrador Retriever | M/8 | 26–45 | Antrum | Mixed | Indeterminate | NA | Ab (2) | N (3) | Ab (2) | - |
| 33 | Standard Poodle | M/8 | 11–25 | Antrum | Mixed | Indeterminate | - | Ab (2) | Ab (2) | N (3) | - |
| No. of Cases | Histological Diagnosis | p-Value | Tumor Differentiation | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intestinal | Diffuse | Indeterminate | Well- Differentiated | Poorly/ Undifferentiated | ||||
| Sex | ||||||||
| Male | 19 | 2 | 14 | 3 | 0.0929 | 2 | 17 | 0.0322 |
| Female | 14 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 8 | ||
| Age, years | ||||||||
| <10 | 13 | 1 | 10 | 2 | 0.1858 | 1 | 12 | 0.0737 |
| ≥10 | 20 | 7 | 10 | 3 | 7 | 13 | ||
| Weight, kg | ||||||||
| ≤10 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0.6924 | 2 | 3 | 0.6023 |
| 11–25 | 7 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 6 | ||
| 26–45 | 19 | 5 | 11 | 3 | 5 | 14 | ||
| Clinicopathological Parameters | No. of Cases | E-cad Immunoexpression | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal (n = 4) | Abnormal (n = 29) | |||
| n (%) | n (%) | |||
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 19 | 1 (5.3%) | 18 (94.7%) | 0.1597 |
| Female | 14 | 3 (21.4%) | 11 (78.6%) | |
| Age, years | ||||
| <10 | 13 | 2 (15,4%) | 11 (84.6%) | 0.6433 |
| ≥10 | 20 | 2 (10.0%) | 18 (90.0%) | |
| Weight, kg a | ||||
| ≤10 | 5 | 2 (40%) | 3 (60%) | 0.1185 |
| 11–25 | 7 | 1 (14.3%) | 6 (85.7%) | |
| 26–45 | 19 | 1 (5.3%) | 18 (94.7%) | |
| Tumor location b | ||||
| Antrum | 16 | 3 (18.8%) | 13 (81.3%) | 0.5287 |
| Body | 13 | 1 (7.7%) | 12 (92.3%) | |
| Body and antrum | 3 | 0 (0%) | 3 (100%) | |
| Histological diagnosis | ||||
| WHO classification | ||||
| Tubular | 7 | 2 (28.6%) | 5 (71.4%) | 0.0503 |
| Papillary | 1 | 1 (100%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Mucinous | 2 | 0 (0%) | 2 (100%) | |
| Signet ring cell | 11 | 1 (9.1%) | 10 (90.9%) | |
| Poorly cohesive | 7 | 0 (0%) | 7 (100%) | |
| Mixed | 5 | 0 (0%) | 5 (100%) | |
| Lauren | ||||
| Intestinal | 8 | 3 (37.5%) | 5 (62.5%) | 0.0392 |
| Diffuse | 20 | 1 (5.0%) | 19 (95.0%) | |
| Indeterminate | 5 | 0 (0%) | 5 (100%) | |
| Tumor differentiation | ||||
| Well-differentiated | 8 | 3 (37.5%) | 5 (62.5%) | 0.0115 |
| Poorly/undifferentiated | 25 | 1 (4.0%) | 24 (96.0%) | |
| Depth of tumor invasion c | ||||
| Mucosa | 1 | 1 (100%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Muscular | 10 | 2 (20.0%) | 8 (80.0%) | 0.0117 |
| Serosa | 12 | 0 (0%) | 12 (100%) | |
| Neoplastic emboli | ||||
| Present | 18 | 0 (0%) | 18 (100%) | 0.0194 |
| Absent | 15 | 4 (26.7%) | 11 (73.3%) | |
| Metastatic lesions d | ||||
| Present | 9 | 0 (0%) | 9 (100%) | 0.1371 |
| Absent | 19 | 4 (21.1%) | 15 (78.9%) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores, A.R.; Rêma, A.; Mesquita, J.R.; Taulescu, M.; Seixas, F.; Gärtner, F.; Amorim, I. E-cadherin Expression in Canine Gastric Carcinomas: Association with Clinicopathological Parameters. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9040172
Flores AR, Rêma A, Mesquita JR, Taulescu M, Seixas F, Gärtner F, Amorim I. E-cadherin Expression in Canine Gastric Carcinomas: Association with Clinicopathological Parameters. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(4):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9040172
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores, Ana R., Alexandra Rêma, João R. Mesquita, Marian Taulescu, Fernanda Seixas, Fátima Gärtner, and Irina Amorim. 2022. "E-cadherin Expression in Canine Gastric Carcinomas: Association with Clinicopathological Parameters" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 4: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9040172
APA StyleFlores, A. R., Rêma, A., Mesquita, J. R., Taulescu, M., Seixas, F., Gärtner, F., & Amorim, I. (2022). E-cadherin Expression in Canine Gastric Carcinomas: Association with Clinicopathological Parameters. Veterinary Sciences, 9(4), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9040172






