Growth Performance, Survival, Blood Chemistry, and Immune Gene Expression of Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Fed Probiotic-Supplemented Diets
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diet Preparation
2.2. Probiotics and Test Diets
2.3. Water Quality
2.4. Experiment A: Probiotic Assessment
2.5. Experiment B: Growth and Flow-Through with Juvenile Channel Catfish
2.6. Hematocrit Analysis
2.7. Serum Biochemistry Analysis
2.8. qPCR Gene Expression Analyses
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Hematological and Blood Serum Parameters
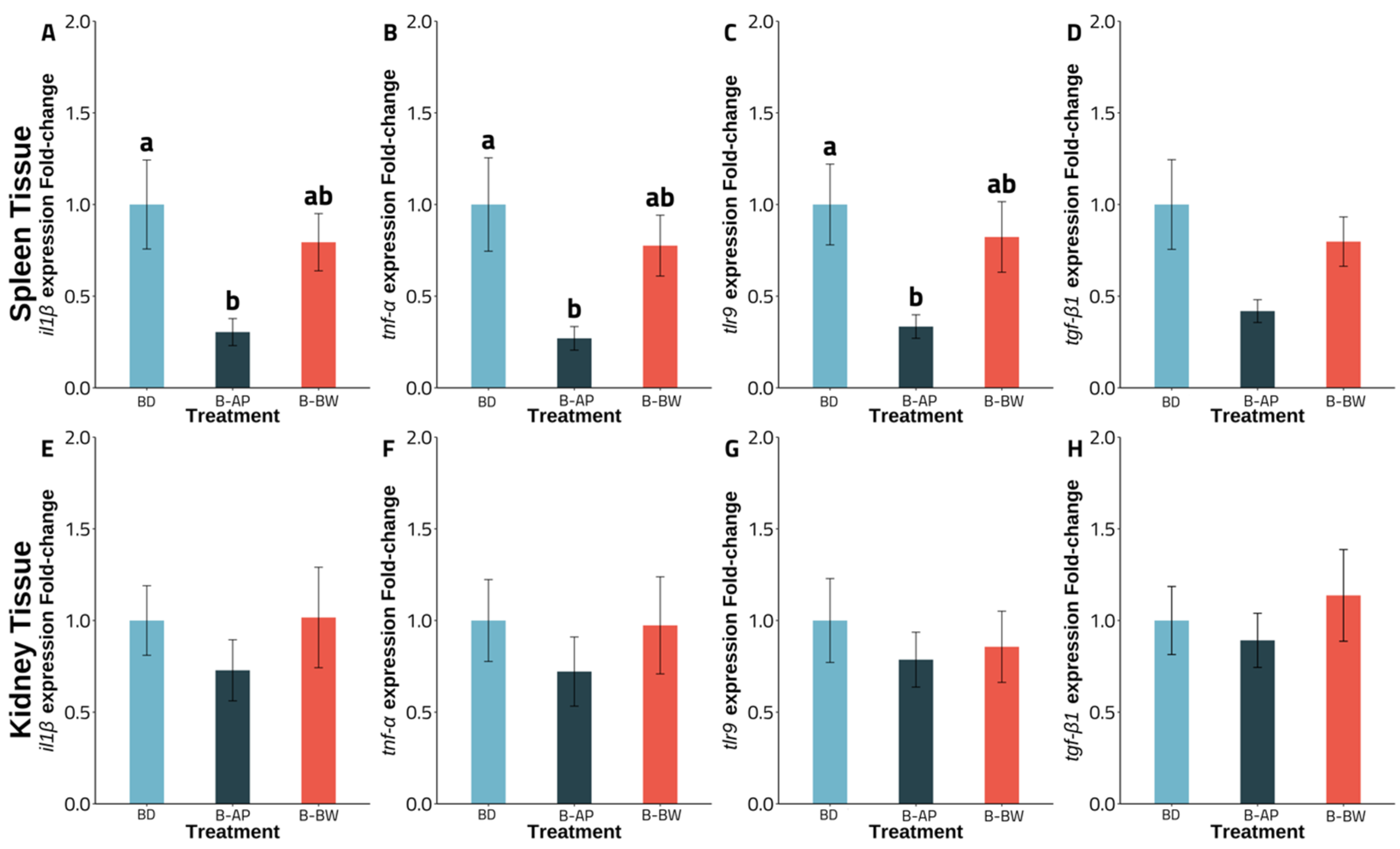
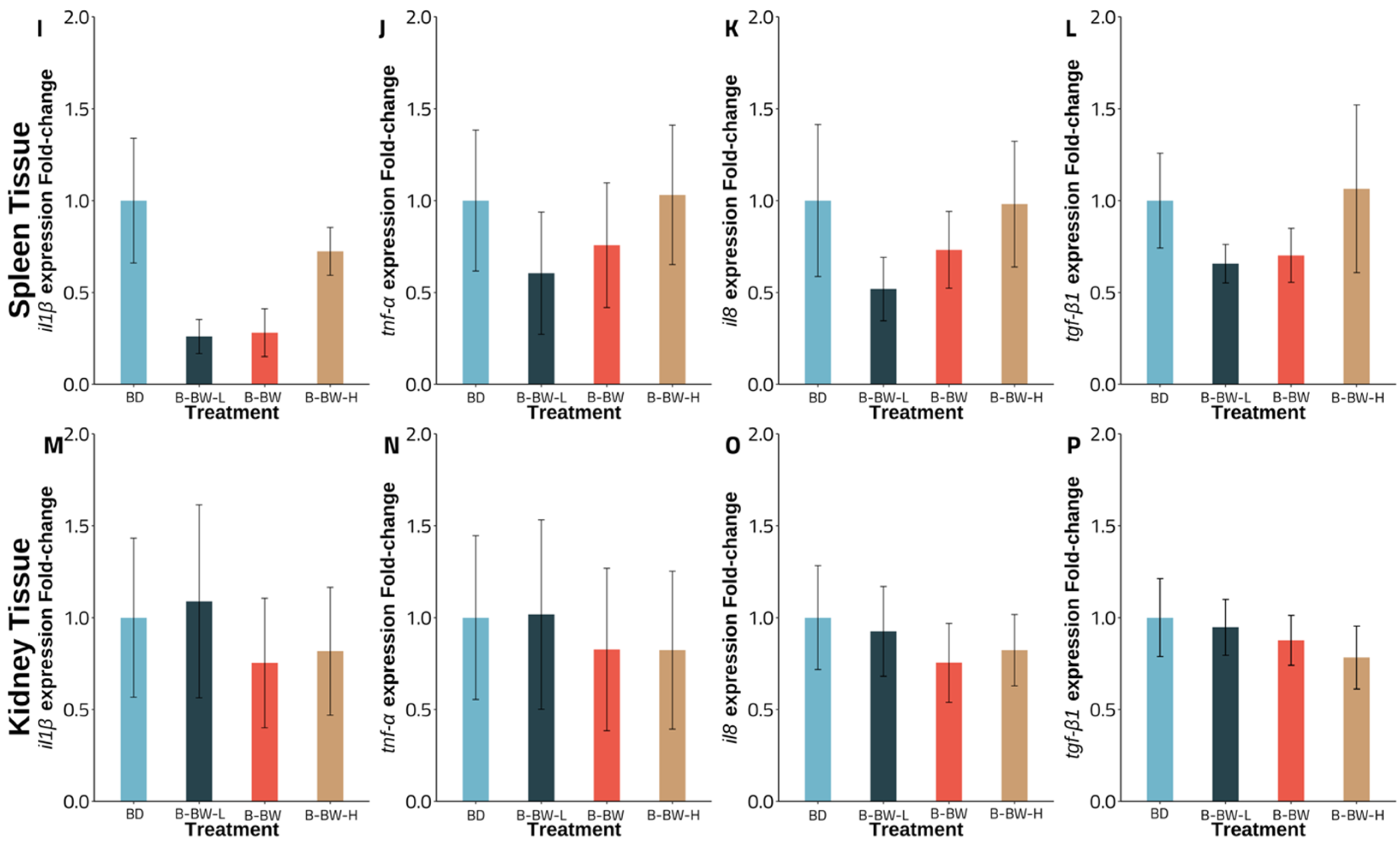
3.3. Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hargreaves, J.A. Channel catfish farming in ponds: Lessons from a maturing industry. Rev. Fish Sci. 2002, 10, 499–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture: Stuttgart, AR, USA. National Agricultural Statistics Service Catfish Production 02/11/2022. 2021; p. 7. Available online: https://usda.library.cornell.edu/concern/publications/bg257f046?locale=en (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Pridgeon, J.; Klesius, P. Molecular identification and virulence of three Aeromonas hydrophila isolates cultured from infected channel catfish during a disease outbreak in west Alabama (USA) in 2009. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 94, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, H.H.; Peatman, E. Winter kill in intensively stocked channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus): Coinfection with Aeromonas veronii, Streptococcus parauberis and Shewanella putrefaciens. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, C.A.; Olivares-Fuster, O.; Arias, C.R.; Klesius, P.H. Flavobacterium columnare genomovar influences mortality in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 127, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilodeau, A.L.; Waldbieser, G.C. Activation of TLR3 and TLR5 in channel catfish exposed to virulent Edwardsiella ictaluri. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, B.A.; Wise, D.J.; Khoo, L.H.; Terhune, J.S. The epidemiology of bacterial diseases in food-size channel catfish. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2002, 14, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.R.; Diao, Z.H.; Sun, K.F.; Hao, Q.W.; Liu, S.S.; Ying, G.G. Tissue distribution, bioaccumulation characteristics and health risk of antibiotics in cultured fish from a typical aquaculture area. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.R.; Liu, S.S.; Zhou, G.J.; Sun, K.F.; Zhao, J.L.; Ying, G.G. Antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding Hailing Island, South China: Occurrence, bioaccumulation and human dietary exposure. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.E.M.; Schreier, H.J.; Lanska, L.; Hale, M.S. The rising tide of antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: Sources, sinks and solutions. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Ramos, F. Antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: Current knowledge and alternatives to tackle the problem. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citarasu, T. Herbal biomedicines: A new opportunity for aquaculture industry. Aquacult. Int. 2009, 18, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Van Doan, H.; Lee, S.H.; Soltani, M.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Harikrishnan, R.; Song, S.K. Probiotics, lactic acid bacteria and bacilli: Interesting supplementation for aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, K.; Steinbach, A.; Helms, V. Interfering with bacterial quorum sensing. Perspect. Medicin. Chem. 2016, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, N.V. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, R.; Balasundaram, C.; Heo, M.-S. Impact of plant products on innate and adaptive immune system of cultured finfish and shellfish. Aquaculture 2011, 317, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Byars, T.S.; Greenway, T.E.; Aarattuthodiyil, S.; Khoo, L.H.; Griffin, M.J.; Wise, D.J. Economic assessment of commercial-scale Edwardsiella ictaluri vaccine trials in U.S. catfish industry. Aquac. Econ. Manag. 2019, 23, 254–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridgeon, J.W.; Klesius, P.H. Development of a novobiocin-resistant Edwardsiella ictaluri as a novel vaccine in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Vaccine 2011, 29, 5631–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hai, N. The use of medicinal plants as immunostimulants in aquaculture: A review. Aquaculture 2015, 446, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P. Aquaculture environment interactions: Past, present and likely future trends. Aquaculture 2015, 447, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Boyd, C.E. Influence of a bacterial amendment on water quality in small research ponds for channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, production. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2016, 47, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, R.A.; Lim, C.; Yildirim-Aksoy, M.; Klesius, P.H. Effects of probiotic bacteria as dietary supplements on growth and disease resistance in young channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque). J. Appl. Aquac. 2007, 19, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Bai, X.; Chen, C. Integrated application of two different screening strategies to select potential probiotics from the gut of channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Fish Sci. 2014, 80, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Song, S.K. Application of dietary supplements (synbiotics and probiotics in combination with plant products and β-glucans) in aquaculture. Aquacult. Nutr. 2016, 22, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sinha, A.K.; Makkar, H.P.; De Boeck, G.; Becker, K. Phytate and phytase in fish nutrition. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 96, 335–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatesoupe, F.J. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture 1999, 180, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Carrias, A.; Williams, M.A.; Capps, N.; Dan, B.C.; Newton, J.C.; Kloepper, J.W.; Ooi, E.L.; Browdy, C.L.; Terhune, J.S.; et al. Identification of Bacillus strains for biological control of catfish pathogens. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloepper, J.W.; Ryu, C.-M.; Zhang, S. Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp. Phytopathology 2004, 94, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, F.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Salminen, S.J. Effect of temperature on in vitro adhesion of potential fish probiotics. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2004, 16, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurlow, C.M.; Williams, M.A.; Carrias, A.; Ran, C.; Newman, M.; Tweedie, J.; Allison, E.; Jescovitch, L.N.; Wilson, A.E.; Terhune, J.S.; et al. Bacillus velezensis AP193 exerts probiotic effects in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) and reduces aquaculture pond eutrophication. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisapoome, P.; Areechon, N. Efficacy of viable Bacillus pumilus isolated from farmed fish on immune responses and increased disease resistance in nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Laboratory and on-farm trials. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; Romaire, R.P.; Johnston, E. Water quality in channel catfish production ponds. J. Environ. Qual. 1979, 8, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, G.; Shoemaker, C.; Zhang, D.; Xu, D.H. Expression of immune genes in skin of channel catfish immunized with live theronts of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Parasite Immunol. 2017, 39, e12397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiong, G.; Bai, C.; Liao, T. Anesthetic efficacy of two plant phenolics and the physiological response of juvenile Ictalurus punctatus to simulated transport. Aquaculture 2021, 538, 736566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordon, A.O.; Abdelhamed, H.; Ahmed, H.; Baumgartner, W.; Karsi, A.; Pinchuk, L.M. Assessment of the live attenuated and wild-type Edwardsiella ictaluri-induced immune gene expression and Langerhans-like cell profiles in the immune-related organs of catfish. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Yao, J.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Song, L.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Complement regulatory protein genes in channel catfish and their involvement in disease defense response. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 53, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, M.; Fu, L.; Zhong, L.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Bian, W. Liver transcriptome analysis and cortisol immune-response modulation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 101, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, K.; Yuan, S.; Yu, F.; Chen, X.H.; Bian, W.J.; Feng, Y.H.; Zhao, Z. Acyclovir inhibits channel catfish virus replication and protects channel catfish ovary cells from apoptosis. Virus Res. 2021, 292, 198249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manera, M.; Britti, D. Assessment of blood chemistry normal ranges in rainbow trout. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, T.J.; Ma, J.; Sudheesh, P.S.; Cain, K.D. Quantification and comparison of gene expression associated with iron regulation and metabolism in a virulent and attenuated strain of Flavobacterium psychrophilum. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, G.; Ray, A.K. The advancement of probiotics research and its application in fish farming industries. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 115, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahangiri, L.; Esteban, M.Á. Administration of probiotics in the water in finfish aquaculture systems: A Review. Fishes 2018, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, S.; Carrias, A.A.; Williams, M.A.; Liles, M.R.; Terhune, J.S.; Davis, D.A. Effects of Bacillus subtilis strains on growth, immune parameters, and Streptococcus iniae susceptibility in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2017, 48, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, S.; Carrias, A.A.; Williams, M.A.; Liles, M.R.; Terhune, J.S.; Davis, D.A. Effects of Bacillus subtilis strains and the prebiotic Previda® on growth, immune parameters and susceptibility to Aeromonas hydrophilainfection in nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquacult. Res. 2017, 48, 4798–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.; Wood, M.; Booth, N.; Morgan, N.; Tellez, G.; Hargis, B. Feeding Lactobacillus spp. and Bacillus spp. Does not improve growth or survival of channel catfish experimentally challenged with Edwardsiella ictaluri. In Proceedings of the American Society of Animal Science Annual Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 11–15 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Dimitroglou, A.; Bradley, G.; Baker, R.T.M.; Davies, S.J. Probiotic applications for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) I. Effects on growth performance, feed utilization, intestinal microbiota and related health criteria. Aquacult. Nutr. 2010, 16, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, N.V.; Buller, N.; Fotedar, R. Effects of probiotics (Pseudomonas synxantha and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) on the growth, survival and immune parameters of juvenile western king prawns (Penaeus latisulcatus Kishinouye, 1896). Aquacult. Res. 2009, 40, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.A. Stress in Fishes: A diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids1. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggio, C.; Piccione, G.; Marafioti, S.; Arfuso, F.; Trischitta, F.; Fortino, G.; Fazio, F. Monthly variations of haematological parameters of Sparus aurata and Dicentrarchus labrax reared in Mediterranean land off-shore tanks. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2014, 55, 437–443. [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi, A.; Kiron, V.; Satoh, S.; Watanabe, T. Probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus rhamnosus influences the blood profile in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 36, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, T.L.; Lim, C.; Yildirim-Aksoy, M.; Shelby, R.; Klesius, P.H. Immune response and resistance to stress and Edwardsiella ictaluri challenge in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, fed diets containing commercial whole-cell yeast or yeast subcomponents. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2007, 38, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorian, T.J.; Jamali, H.; Farsani, H.G.; Darvishi, P.; Hasanpour, S.; Bagheri, T.; Roozbehfar, R. Effects of probiotic bacteria Bacillus on growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, and hematological parameters of asian sea bass, Lates calcarifer (Bloch). Probiot. Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, S.M.; Abdel-Galil Ahmed, Y.; Abdel-Aziz Ghareeb, A.; Mohamed, M.F. Studies on Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, as potential probiotics, on the immune response and resistance of tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus) to challenge infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reda, R.M.; Selim, K.M. Evaluation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens on the growth performance, intestinal morphology, hematology and body composition of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquacul. Int. 2015, 23, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ceballos-Francisco, D.; Guardiola, F.A.; Esteban, M.Á. Dietary administration of the probiotic Shewanella putrefaciens to experimentally wounded gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) facilitates the skin wound healing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Cerpa, S.; Maisey, K.; Reyes-López, F.; Toro-Ascuy, D.; Sandino, A.M.; Imarai, M. Fish cytokines and immune response. In New Advances and Contributions to Fish Biology; Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Picchietti, S.; Fausto, A.M.; Randelli, E.; Carnevali, O.; Taddei, A.R.; Buonocore, F.; Scapigliati, G.; Abelli, L. Early treatment with Lactobacillus delbrueckii strain induces an increase in intestinal T-cells and granulocytes and modulates immune-related genes of larval Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grayfer, L.; Belosevic, M. Cytokine regulation of teleost inflammatory responses. In New Advances and Contributions to Fish Biology; Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2012; pp. 11281–11286. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadian, T.; Ghanei-Motlagh, R.; Molayemraftar, T.; Mesbah, M.; Zarea, M.; Mohtashamipour, H.; Jangaran Nejad, A. Modulation of growth performance, gut microflora, non-specific immunity and gene expression of proinflammatory cytokines in shabout (Tor grypus) upon dietary prebiotic supplementation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 112, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. The function of fish cytokines. Biology 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, D.; Liu, L.; Tang, Y.; Du, R. Characterization and comparison of the adherence and immune modulation of two gut Lactobacillus strains isolated from Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 2019, 499, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, T.; Jang, W.J.; Tak, J.Y.; Lee, B.-J.; Kim, K.W.; Hur, S.W.; Han, H.-S.; Kim, B.-S.; Min, D.-H.; Kim, S.-K.; et al. Effects of Lactococcuslactis subsp. lactis I2 with β-glucooligosaccharides on growth, innate immunity and Streptococcosis resistance in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhidai, L.; Csaba, G. Chemotaxis and chemotactic selection induced with cytokines (IL-8, Rantes and TNF-A) in the unicellular Tetrahymena pyriformis. Cytokine 1998, 10, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, I.; Chamorro, R.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A. β-Glucan administration enhances disease resistance and some innate immune responses in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.-Y.; Jiang, W.-D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Kuang, S.-Y.; Tang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.-Q.; Feng, L. Mannan oligosaccharides supplementation enhanced head-kidney and spleen immune function in on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Li, E.; Ren, Z.; Wu, Y.; Guo, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y. Beneficial effects of a host gut-derived probiotic, Bacillus pumilus, on the growth, non-specific immune response and disease resistance of juvenile golden pompano, Trachinotus ovatus. Aquaculture 2020, 514, 734446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, J.; Yan, Z.; Xiang, X.; Mu, R.; Zhu, P.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, F.; Chen, K.; Chi, S.; et al. Dietary Glycyrrhiza uralensis extracts supplementation elevated growth performance, immune responses and disease resistance against Flavobacterium columnare in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 97, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients 1 | BD | Amino Acids 1 | BD |
| Poultry meal a | 6.00 | Alanine | 1.60 |
| Soybean meal b | 55.50 | Arginine | 2.34 |
| Menhaden fish oil c | 3.59 | Aspartic Acid | 3.53 |
| Corn Starch d | 3.46 | Cysteine | 0.49 |
| Corn e | 28.00 | Glutamic Acid | 5.77 |
| Mineral premix f | 0.50 | Glycine | 1.64 |
| Vitamin premix g | 0.80 | Histidine | 0.86 |
| Choline chloride h | 0.20 | Hydroxylysine | 0.08 |
| Rovimix Stay-C i | 0.10 | Hydroxyproline | 0.25 |
| CaP-dibasic j | 1.85 | Isoleucine | 1.62 |
| Lanthionine | 0.04 | ||
| Leucine | 2.63 | ||
| Lysine | 2.08 | ||
| Methionine | 0.52 | ||
| Ornithine | 0.04 | ||
| Phenylalanine | 1.68 | ||
| Proline | 1.76 | ||
| Serine | 1.13 | ||
| Taurine | 0.17 | ||
| Threonine | 1.17 | ||
| Tryptophan | 0.42 | ||
| Tyrosine | 1.16 | ||
| Valine | 1.76 | ||
| Proximate composition 1 (g/100g as is) | |||
| Crude protein | 33.7 | ||
| Moisture | 6.57 | ||
| Crude Fat | 4.85 | ||
| Crude Fiber | 4.24 | ||
| Ash | 6.63 | ||
| Diet Abbreviations | Probiotic | Dietary Inclusion Level (g kg−1) | Product Stock Concentration (CFU g−1) | Product Concentration on Feed (CFU g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment A | ||||
| BD | ||||
| B-AP | B. velezensis | 0.025 | 4.0 × 1010 | 1.0 × 106 |
| B-BW | B. subtilis | 0.5 | 3.6 × 107 | 3.6 × 104 |
| Experiment B | ||||
| BD | ||||
| B-BW-L | B. subtilis | 0.25 | 1.8 × 107 | 1.8 × 104 |
| B-BW | B. subtilis | 0.5 | 3.6 × 107 | 3.6 × 104 |
| B-BW-H | B. subtilis | 1.0 | 7.2 × 107 | 7.2 × 104 |
| Gene | Accession Number | Amplification Size (pb) | Forward Primer (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ to 3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell receptor | |||||
| tlr9 | HQ677720 | 110 | GGAGGAACGGGACTGGATAC | AAGCACAGCCACCCTGATTA | [34] |
| Cytokines | |||||
| il1β | NM001200220.1 | 180 | GTGTAAGCAGCAATCCAGTCA | CAAGCACAGAACAGTCAGGTAT | [35] |
| tnf-α | NM_001200172.1 | 277 | GGCCTCTACTTCGTCTAC | GCAGCAGCTTCTCGTCCAT | [35] |
| tgf-β1 | JT417317 ENA | 167 | GAAACATCCCAGCACCTCCA | GCCAAGCAAACAACGGCTAA | [34] |
| il8 | AY145142 | 264 | CAATACTTTGTGAATTTCTGC | TGTCCTTGGTTTCCTTCTGG | [36] |
| Reference gene | |||||
| 18S | AF021880 | GAGAAACGGCTACCACATCC | GATACGCTCATTCCGATTACAG | [37] | |
| ef1α | 118 | GTTGAAATGGTTCCTGGCAA | TCAACACTCTTGATGACACCAAC | [38] | |
| actb | 139 | CCGTGACCTGACTGAATACC | GCCCATCTCCTGCTCAAAG | [39] |
| Parameters | BD | B-AP | B-BW | PSE a | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Final average weight (g) | 52.46 | 50.19 | 50.45 | 2.179 | 0.727 |
| Percent weight gain (%) | 47.60 | 42.76 | 42.84 | 6.669 | 0.843 |
| Survival rate (%) | 95.00 | 100.00 | 98.33 | 1.610 | 0.116 |
| Thermal-unit growth coefficient | 3.07 | 2.71 | 2.76 | 0.414 | 0.808 |
| Parameters | BD a | B-BW-L b | B-BW b | B-BW-H a | PSE c | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Final average weight (g) | 21.78 | 21.19 | 18.92 | 21.17 | 0.806 | 0.122 |
| Percent weight gain (%) | 5832.31 | 6241.15 | 5075.88 | 5680.73 | 280.9 | 0.090 |
| Survival rate (%) | 99.00 | 100.00 | 98.75 | 97.00 | 1.863 | 0.715 |
| Feed conversion ratio | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.99 | 0.92 | 0.027 | 0.228 |
| Thermal-unit growth coefficient | 1.57 | 1.53 | 1.36 | 1.53 | 0.059 | 0.123 |
| Parameters | BD | B-AP | B-BW | PSE a | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 3.58 | 3.57 | 3.60 | 0.059 | 0.948 |
| Alanine transaminase (U/L) | 3.71 | 3.65 | 3.63 | 0.108 | 0.861 |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase (U/L) | 3.50 | 3.17 | 3.67 | 0.292 | 0.484 |
| Bile acids (µmol/L) | 7.00 | 14.67 | 14.33 | 4.804 | 0.462 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.38 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.053 | 0.521 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 1.40 | 4.23 | 1.62 | 1.479 | 0.347 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 3.50 | 4.17 | 3.83 | 0.240 | 0.179 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 224.00 | 238.50 | 256.50 | 12.601 | 0.222 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 26.94 | 22.33 | 25.72 | 3.598 | 0.652 |
| Parameters | BD a | B-BW-L b | B-BW a | B-BW-H b | PSE c | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 4.15 | 4.13 | 4.18 | 4.35 | 0.088 | 0.383 |
| Alanine transaminase (U/L) | 2.88 | 2.77 | 2.94 | 2.78 | 0.135 | 0.773 |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (U/L) | 2.25 | 2.00 | 2.50 | 3.00 | 0.224 | 0.071 |
| Bile acids (µmol/L) | 23.50 | 24.33 | 12.75 | 19.33 | 4.313 | 0.247 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.026 | 0.104 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 1.93 | 1.77 | 2.00 | 2.10 | 0.109 | 0.285 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 2.75 | 2.67 | 2.75 | 3.00 | 0.249 | 0.830 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 275.75 | 269.00 | 299.00 | 284.00 | 16.51 | 0.608 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 23.08 | 22.33 | 26.92 | 26.56 | 2.780 | 0.570 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, K.Q.; Bruce, T.J.; Afe, O.E.; Liles, M.R.; Beck, B.H.; Davis, D.A. Growth Performance, Survival, Blood Chemistry, and Immune Gene Expression of Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Fed Probiotic-Supplemented Diets. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9120701
Nguyen KQ, Bruce TJ, Afe OE, Liles MR, Beck BH, Davis DA. Growth Performance, Survival, Blood Chemistry, and Immune Gene Expression of Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Fed Probiotic-Supplemented Diets. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(12):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9120701
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Khanh Q., Timothy J. Bruce, Oluwafunmilola E. Afe, Mark R. Liles, Benjamin H. Beck, and Donald Allen Davis. 2022. "Growth Performance, Survival, Blood Chemistry, and Immune Gene Expression of Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Fed Probiotic-Supplemented Diets" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 12: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9120701
APA StyleNguyen, K. Q., Bruce, T. J., Afe, O. E., Liles, M. R., Beck, B. H., & Davis, D. A. (2022). Growth Performance, Survival, Blood Chemistry, and Immune Gene Expression of Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Fed Probiotic-Supplemented Diets. Veterinary Sciences, 9(12), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9120701







