Impact of Water Sources and Shared Fence Lines on Bovine Respiratory Disease Incidence in the First 45 Days on Feed
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, T.A. Control Methods for Bovine Respiratory Disease for Feedlot Cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2010, 26, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duff, G.C.; Galyean, M.L. BOARD-INVITED REVIEW: Recent Advances in Management of Highly Stressed, Newly Received Feedlot Cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 823–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakebrough-Hall, C.; McMeniman, J.P.; González, L.A. An Evaluation of the Economic Effects of Bovine Respiratory Disease on Animal Performance, Carcass Traits, and Economic Outcomes in Feedlot Cattle Defined Using Four BRD Diagnosis Methods. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.D.; Fulton, R.W.; Lehenbauer, T.W.; Step, D.L.; Confer, A.W. The Epidemiology of Bovine Respiratory Disease: What Is the Evidence for Predisposing Factors? Can. Vet. J. 2010, 51, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Arthington, J.D.; Eicher, S.D.; Kunkle, W.E.; Martin, F.G. Effect of Transportation and Commingling on the Acute-Phase Protein Response, Growth, and Feed Intake of Newly Weaned Beef Calves1. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 81, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthington, J.D.; Qiu, X.; Cooke, R.F.; Vendramini, J.M.B.; Araujo, D.B.; Chase, C.C.; Coleman, S.W. Effects of Preshipping Management on Measures of Stress and Performance of Beef Steers during Feedlot Receiving1. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, 2016–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.W.; Meek, A.H. A Path Model of Factors Influencing Morbidity and Mortality in Ontario Feedlot Calves. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1986, 50, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, D.; Chengappa, M.M.; Kuszak, J.; McVey, D.S. Bacterial Pathogens of the Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2010, 26, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klima, C.L.; Zaheer, R.; Cook, S.R.; Booker, C.W.; Hendrick, S.; Alexander, T.W.; McAllister, T.A. Pathogens of Bovine Respiratory Disease in North American Feedlots Conferring Multidrug Resistance via Integrative Conjugative Elements. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsit, E.; Christensen, H.; Bareille, N.; Seegers, H.; Bisgaard, M.; Assié, S. Transmission Dynamics of Mannheimia Haemolytica in Newly-Received Beef Bulls at Fattening Operations. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 161, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsit, E.; Arcangioli, M.-A.; Bareille, N.; Seegers, H.; Assié, S. Transmission Dynamics of Mycoplasma Bovis in Newly Received Beef Bulls at Fattening Operations. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickell, J.S.; Hutcheson, J.P.; Renter, D.G.; Amrine, D.A. Comparison of a Traditional Bovine Respiratory Disease Control Regimen with a Targeted Program Based upon Individualized Risk Predictions Generated by the Whisper On Arrival Technology. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2021, 5, txab081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Word, A.B.; Wickersham, T.A.; Trubenbach, L.A.; Mays, G.B.; Sawyer, J.E. Effects of Metaphylaxis on Production Responses and Total Antimicrobial Use in High-Risk Beef Calves. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2020, 36, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, S.E.; Richeson, J.T. Use of Antimicrobial Metaphylaxis for the Control of Bovine Respiratory Disease in High-Risk Cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2015, 31, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeson, J.T.; Falkner, T.R. Bovine Respiratory Disease Vaccination: What Is the Effect of Timing? Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, V.I.; Samuelson, K.L.; Tomczak, D.J.; Seiver, H.A.; Smock, T.M.; Richeson, J.T. Comparative Efficacy of Metaphylaxis with Tulathromycin and Pentavalent Modified-Live Virus Vaccination in High-Risk, Newly Received Feedlot Cattle. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2020, 36, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, A.M.; Hu, D.; Totton, S.C.; Scott, N.; Winder, C.B.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Glanville, J.; Wood, H.; White, B.; et al. A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Bacterial and Viral Vaccines, Administered at or near Arrival at the Feedlot, for Control of Bovine Respiratory Disease in Beef Cattle. Anim. Health. Res. Rev. 2019, 20, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picault, S.; Ezanno, P.; Smith, K.; Amrine, D.; White, B.; Assié, S. Modelling the Effects of Antimicrobial Metaphylaxis and Pen Size on Bovine Respiratory Disease in High and Low Risk Fattening Cattle. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, K.E.; Morton, J.M.; Clements, A.C.A.; Mahony, T.J.; Barnes, T.S. Population-Level Effects of Risk Factors for Bovine Respiratory Disease in Australian Feedlot Cattle. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 140, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, H.A.; White, B.J.; Amrine, D.E.; Larson, R.L.; Capik, S.F. Associations between Pen Management Characteristics and Bovine Respiratory Disease Incidence in the First 45 Days Post-Arrival in Feedlot Cattle. Bov. Pract. 2022, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schibrowski, M.L.; Gibson, J.S.; Hay, K.E.; Mahony, T.J.; Barnes, T.S. Mycoplasma Bovis and Bovine Respiratory Disease: A Risk Factor Study in Australian Feeder Cattle. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 157, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babcock, A.H.; Cernicchiaro, N.; White, B.J.; Dubnicka, S.R.; Thomson, D.U.; Ives, S.E.; Scott, H.M.; Milliken, G.A.; Renter, D.G. A Multivariable Assessment Quantifying Effects of Cohort-Level Factors Associated with Combined Mortality and Culling Risk in Cohorts of U.S. Commercial Feedlot Cattle. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 108, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, M.W.; Dargatz, D.A.; Wagner, B.A. Risk Factors for Initial Respiratory Disease in United States’ Feedlots Based on Producer-Collected Daily Morbidity Counts. Can. Vet. J. 2008, 49, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Kilgore, W.R.; Spensley, M.S.; Sun, F.; Nutsch, R.G.; Rooney, K.A.; Skogerboe, T.L. Clinical Effectiveness of Tulathromycin, a Novel Triamilide Antimicrobial, for the Control of Respiratory Disease in Cattle at High Risk for Developing Bovine Respiratory Disease. Vet. Ther. 2005, 6, 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, A.M.; Sorden, S.D.; Apley, M.D. Association between the Existence of Calves Persistently Infected with Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus and Commingling on Pen Morbidity in Feedlot Cattle. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2005, 66, 2130–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzkopf-Genswein, K.S.; Booth-McLean, M.E.; Shah, M.A.; Entz, T.; Bach, S.J.; Mears, G.J.; Schaefer, A.L.; Cook, N.; Church, J.; McAllister, T.A. Effects of Pre-Haul Management and Transport Duration on Beef Calf Performance and Welfare. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 108, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Step, D.L.; Krehbiel, C.R.; DePra, H.A.; Cranston, J.J.; Fulton, R.W.; Kirkpatrick, J.G.; Gill, D.R.; Payton, M.E.; Montelongo, M.A.; Confer, A.W. Effects of Commingling Beef Calves from Different Sources and Weaning Protocols during a 42-Day Receiving Period on Performance and Bovine Respiratory Disease. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 37, 3146–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, C.D.; Busby, W.D.; Corah, L.R. Relationship of Various Incoming Cattle Traits with Feedlot Performance and Carcass Traits1. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, 3030–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowell, B.F.; Branine, M.E.; Bowman, J.G.; Hubbert, M.E.; Sherwood, H.E.; Quimby, W. Feeding and Watering Behavior of Healthy and Morbid Steers in a Commercial Feedlot. J. Anim. Sci. 1999, 77, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfger, B.; Schwartzkopf-Genswein, K.S.; Barkema, H.W.; Pajor, E.A.; Levy, M.; Orsel, K. Feeding Behavior as an Early Predictor of Bovine Respiratory Disease in North American Feedlot Systems1. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christman, M.C.; Leone, E.H. Statistical Aspects of the Analysis of Group Size Effects in Confined Animals. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 103, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W. Making Valid Causal Inferences from Observational Data. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 113, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable & Category | Number (%) of Cohorts |
|---|---|
| Cohort size at arrival | |
| 25–99 | 854 (55.74) |
| 100–175 | 447 (29.18) |
| >175 | 231 (15.10) |
| Average Arrival Weight, kg. | |
| 227–272 | 116 (7.57) |
| 273–318 | 317 (20.69) |
| 319–363 | 558 (36.23) |
| 364–408 | 407 (26.57) |
| 409–453 | 134 (8.74) |
| Sex | |
| Heifers | 819 (53.46) |
| Steers | 599 (39.09) |
| Mixed | 114 (7.44) |
| Arrival Date Quarter | |
| Jan–March (1) | 398 (25.97) |
| April–June (2) | 433 (28.26) |
| July–September (3) | 419 (27.34) |
| October–December (4) | 282 (18.40) |
| Total Water Sources | |
| One source (0) | 1342 (87.60) |
| Multiple sources (1) | 190 (12.40) |
| Shared Pen Waters | |
| No (0) | 531 (31.10) |
| Yes (1) | 1001 (68.9) |
| Shared Fence Lines | |
| One (0) | 428 (27.94) |
| Two (1) | 1104 (72.06) |
| Variable | Mean | SD 2 | Median | Range | IQR 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort Size at arrival | 108.69 | 55.88 | 87 | 25–324 | 64–144 |
| Average arrival weight, kg | 345.2 | 102.9 | 346 | 228–453 | 314–378 |
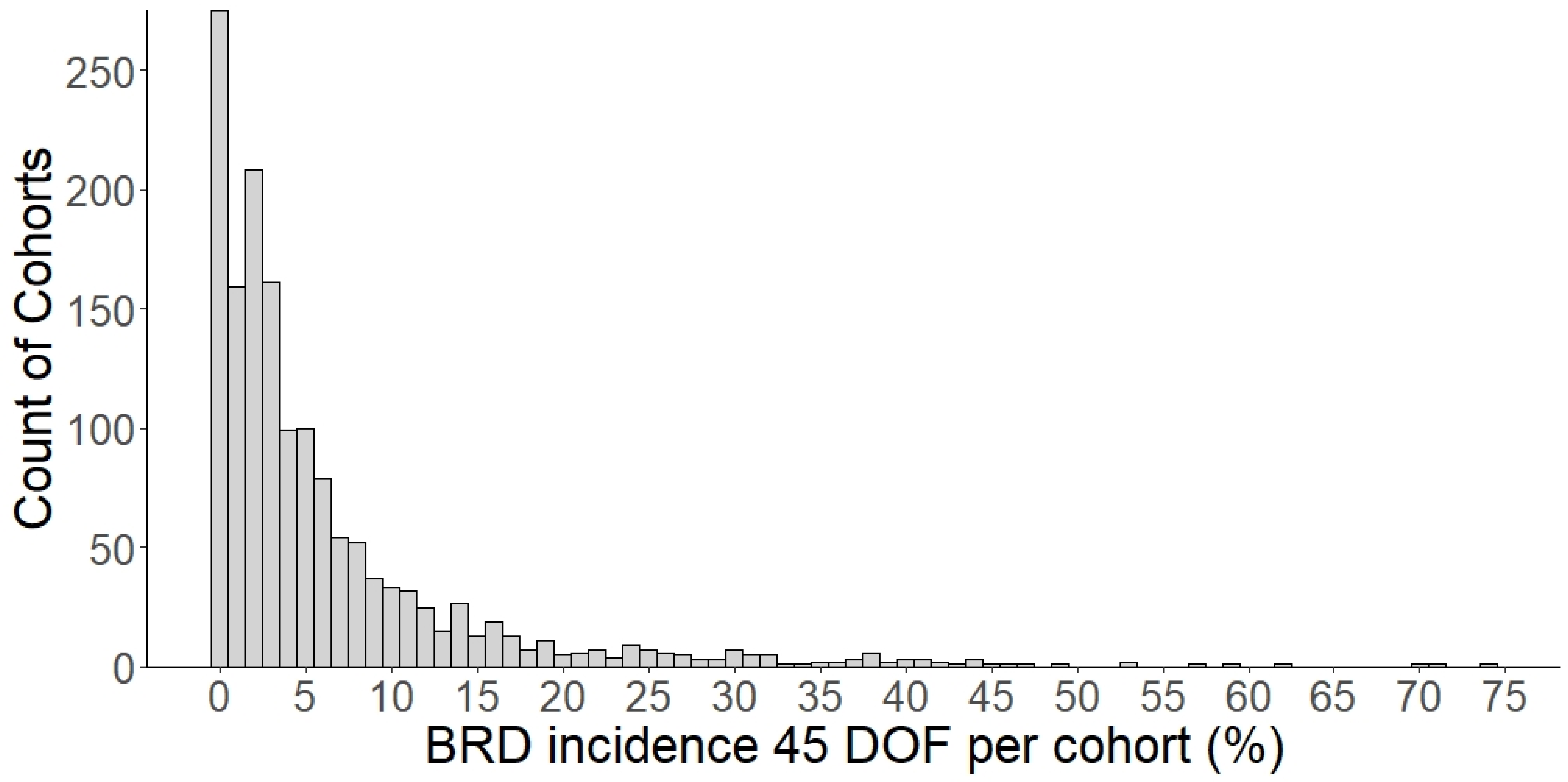
| BRD incidence 1, % | 6.44 | 9.00 | 3.26 | 0–74.07 | 1.28–7.84 |
| Variable | NWmod p-Values | SWmod p-Values | SFmod p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Cohort size at arrival | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Average arrival weight | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Arrival date quarter | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| NW 1 | <0.01 | --- 4 | --- |
| SW 2 | --- | 0.27 | --- |
| SF 3 | --- | --- | <0.01 |
| Sex x Average arrival weight | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Average arrival weight × Arrival date quarter | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Sex × NW | <0.01 | --- | --- |
| Average arrival weight × NW | <0.01 | --- | --- |
| Cohort size at arrival NW | <0.01 | --- | --- |
| Arrival date quarter × NW | <0.01 | --- | --- |
| Sex × SW | --- | 0.77 | --- |
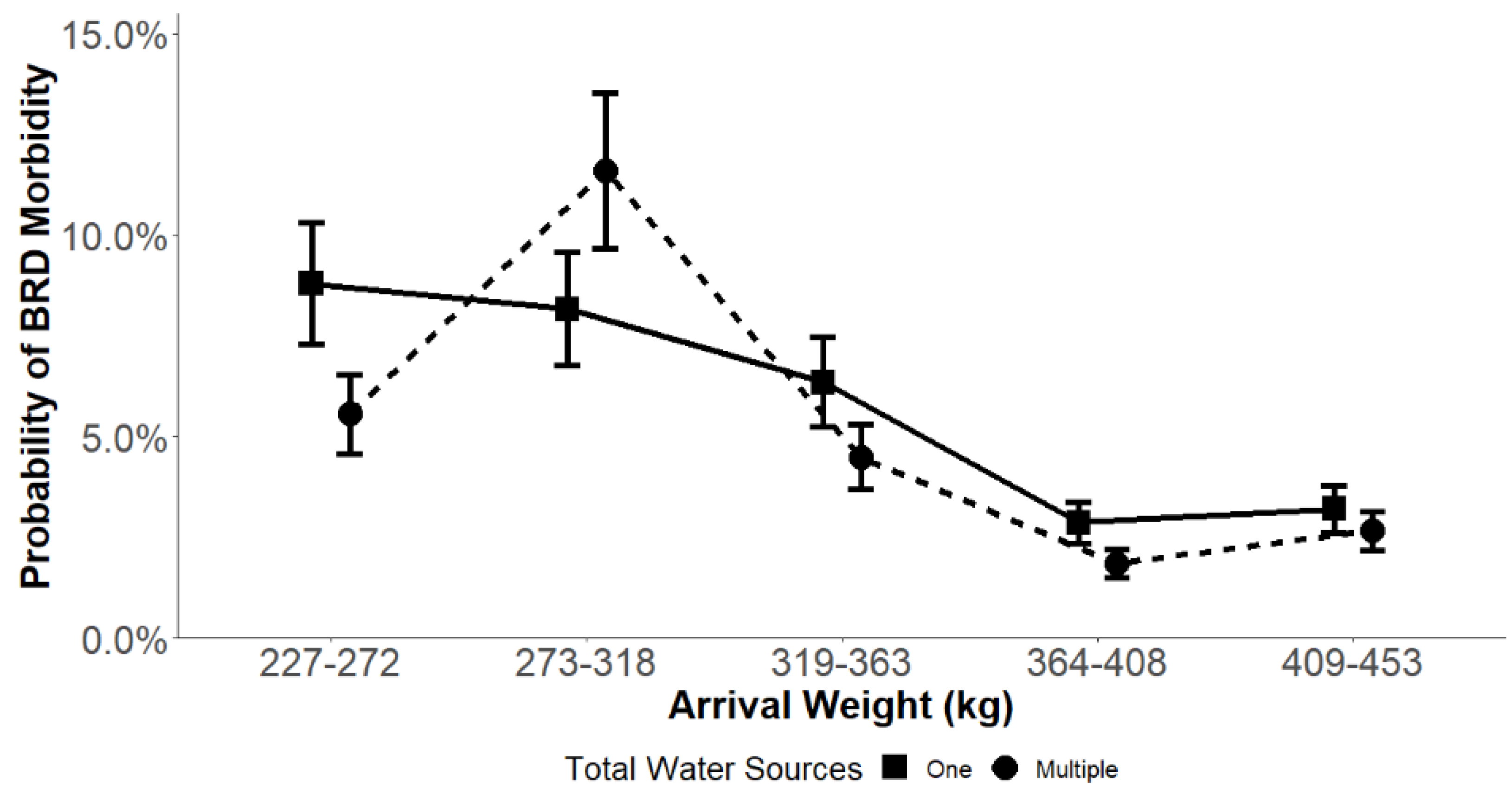
| Average arrival weight × SW | --- | 0.07 | --- |
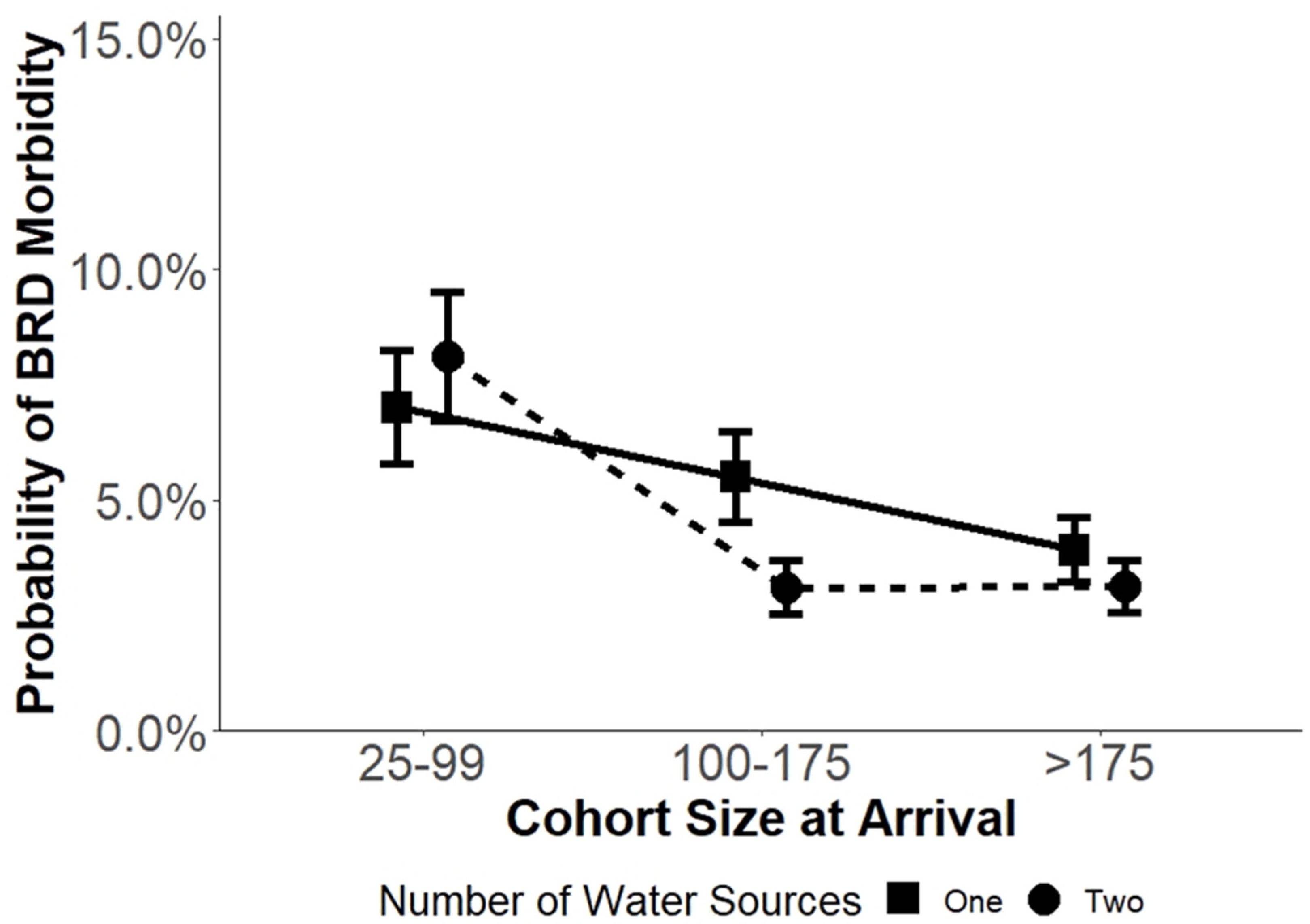
| Cohort size at arrival SW | --- | <0.01 | --- |
| Arrival Date Quarter × SW | --- | 0.63 | --- |
| Sex × SF | --- | --- | <0.01 |
| Average arrival weight × SF | --- | --- | <0.01 |
| Cohort size at arrival × SF | --- | --- | <0.01 |
| Arrival Date Quarter × SF | --- | --- | <0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rojas, H.A.; White, B.J.; Amrine, D.E.; Larson, R.L.; Capik, S.F.; Depenbusch, B.E. Impact of Water Sources and Shared Fence Lines on Bovine Respiratory Disease Incidence in the First 45 Days on Feed. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110646
Rojas HA, White BJ, Amrine DE, Larson RL, Capik SF, Depenbusch BE. Impact of Water Sources and Shared Fence Lines on Bovine Respiratory Disease Incidence in the First 45 Days on Feed. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(11):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110646
Chicago/Turabian StyleRojas, Hector A., Brad J. White, David E. Amrine, Robert L. Larson, Sarah F. Capik, and Brandon E. Depenbusch. 2022. "Impact of Water Sources and Shared Fence Lines on Bovine Respiratory Disease Incidence in the First 45 Days on Feed" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 11: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110646
APA StyleRojas, H. A., White, B. J., Amrine, D. E., Larson, R. L., Capik, S. F., & Depenbusch, B. E. (2022). Impact of Water Sources and Shared Fence Lines on Bovine Respiratory Disease Incidence in the First 45 Days on Feed. Veterinary Sciences, 9(11), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110646







