Postnatal Dynamics of Circulating Steroid Hormones in Mule and Equine Neonates
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Sample Collection and Storage
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analyses
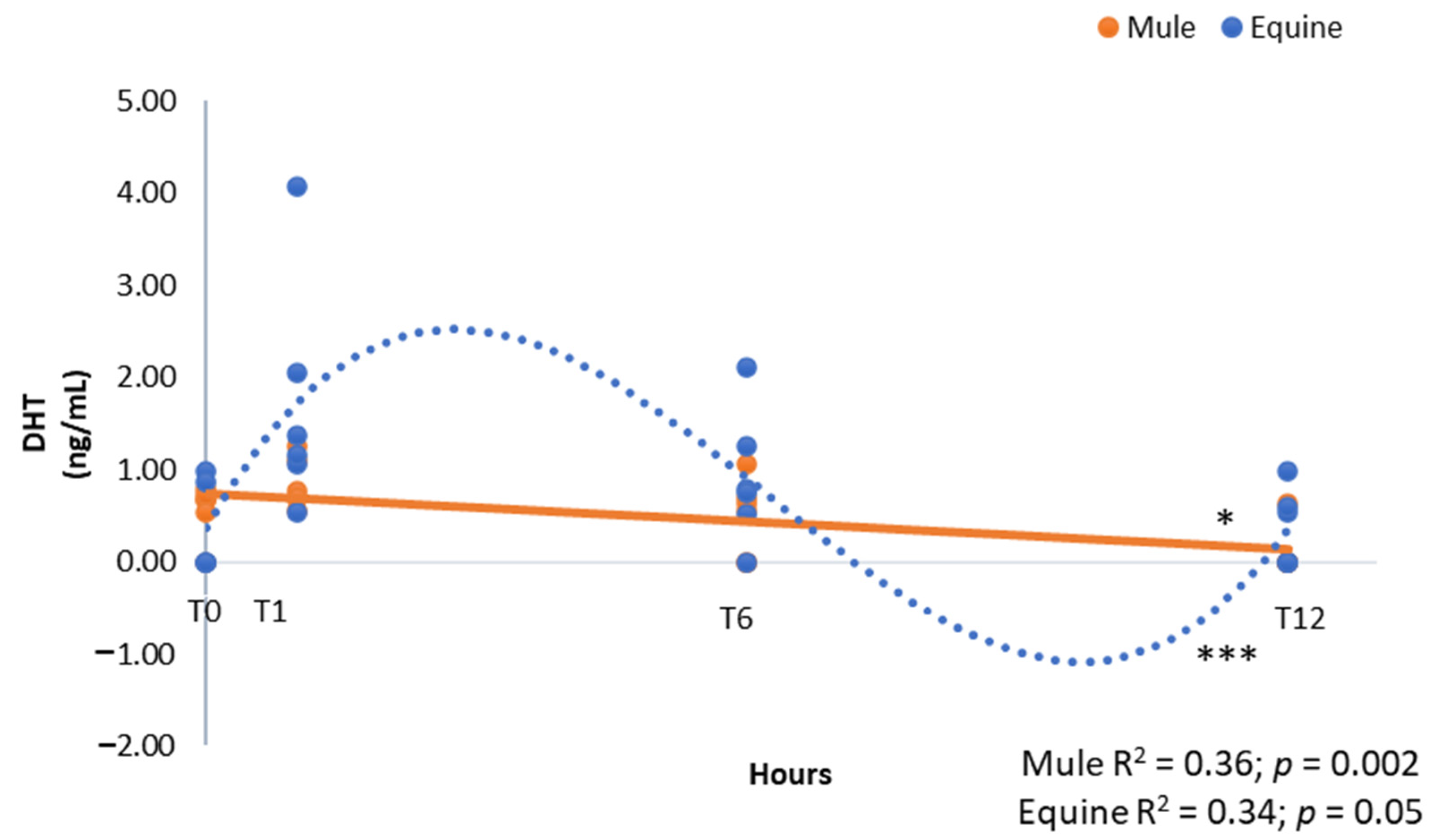
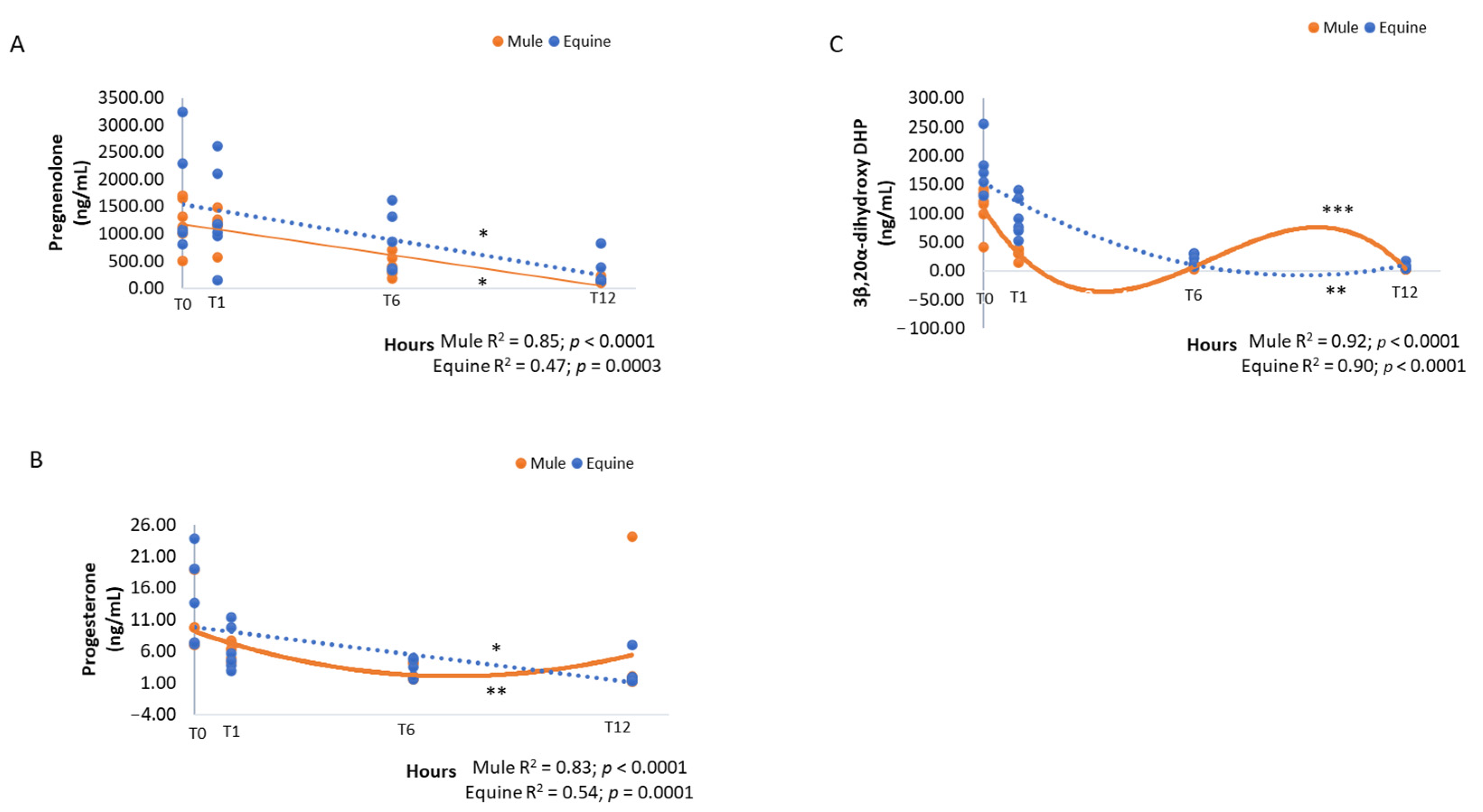
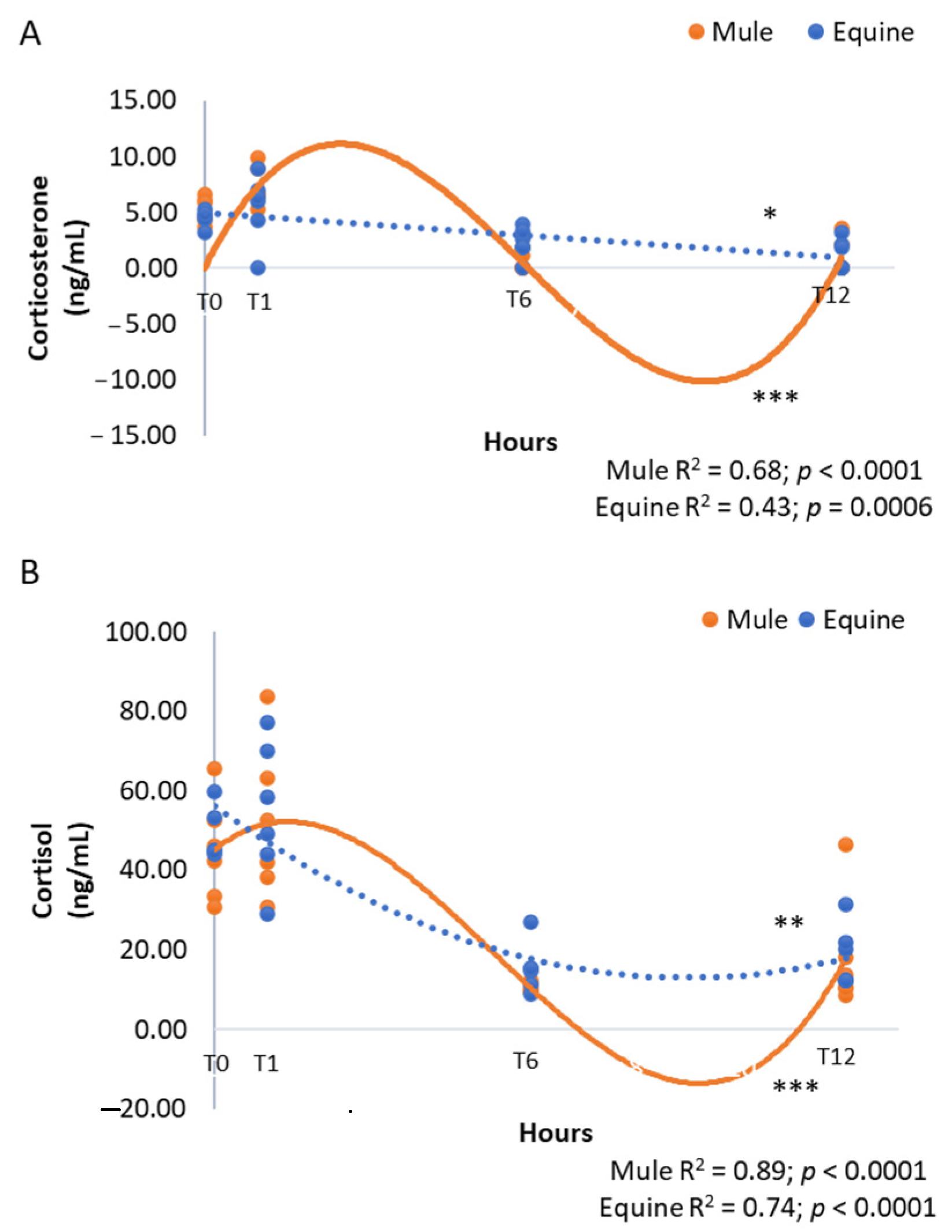
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Camillo, F.; Vannozzi, I.; Rota, A.; Di Luzio, B.; Romagnoli, S.; Aria, G.; Allen, W. Successful non-surgical transfer of horse embryos to mule recipients. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2003, 38, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, M.L.; Moreira, C.G.; Schmidt, B.L.; Brandi, R.A.; Ianni, A.C.; Cancian, P.H.; Lima, M.C. Particularidades dos muares (uma revisão). Rev. Bras. De Med. Equi. 2013, 8, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, L. História Dos Muares No Brasil. Available online: http://jumentoemuar.blogspot.com.br/2011/09/historia-dos-muares-no-brasil.html (accessed on 4 December 2017).
- Alonso, M.A.; Boakari, Y.L.; Riccio, A.V.; Belli, C.B.; Fernandes, C.B. Behavior and perinatal parameters of mule and equine foals: Similarities and differences. J. Vet. Behav. 2022. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Farias, K. Muares Estão Em Alt No Mercado Rural. Available online: http://www.opopular.com.br/editorias/economia/muares-est%C3%A3o-em-alta-no-mercado-rural-1.688407 (accessed on 20 April 2017).
- Ribeiro, K. Muares Para Lida E O Lazer. Available online: http://www.opopular.com.br/editoriais/economia/muares-para-lida-e-o-lazer-1.1212583 (accessed on 20 April 2017).
- Fowden, A.; Forhead, A.; Ousey, J. The endocrinology of equine parturition. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2008, 116, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavatte, P.; Holtan, D.; Ousey, J.C.; Rossdale, P. Biosynthesis and possible biological roles of progestagens during equine pregnancy and in the newborn foal. Equine Vet. J. 1997, 29, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legacki, E.L.; Ball, B.A.; Corbin, C.J.; Loux, S.C.; Scoggin, K.E.; Stanley, S.D.; Conley, A.J. Equine fetal adrenal, gonadal and placental steroidogenesis. Reproduction 2017, 154, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, R.; Weng, Q.; Tanaka, Y.; Tsunoda, N.; Taniyama, H.; Haramaki, S.; Nambo, Y.; Watanabe, G.; Taya, K. Changes in circulating follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, immunoreactive inhibin, progesterone, testosterone and estradiol-17B in fillies from birth to 6 months of age. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2007, 18, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dhakal, P.; Tsunoda, N.; Nakai, R.; Nagaoka, K.; Nambo, Y.; Sato, F.; Taniyama, H.; Watanabe, G.; Taya, K. Post-natal dynamic changes in circulating follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, immunoreactive inhibin, progesterone, testosterone and estradiol-17β in Thoroughbred colts until 6 months of age. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2011, 22, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, E.; Holtan, D.; Grainger, L.; Voller, B.; Rossdale, P.; Ousey, J. Plasma progestagen concentrations in the normal and dysmature newborn foal. J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 1991, 44, 609–617. [Google Scholar]
- Holtan, D.; Houghton, E.; Silver, M.; Fowden, A.; Ousey, J.; Rossdale, P. Plasma progestagens in the mare, fetus and newborn foal. J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 1991, 44, 517–528. [Google Scholar]
- Aleman, M.R.; Pickles, K.; Conley, A.J.; Standley, S.; Haggett, E.; Toth, B.; Madigan, J.E. Abnormal plasma neuroactive progestagen derivatives in ill, neonatal foals presented to the neonatal intensive care unit. Equine. Vet. J. 2013, 45, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swink, J.M.; Rings, L.M.; Snyder, H.A.; McAuley, R.C.; Burns, T.A.; Dembek, K.A.; Gilsenan, W.F.; Browne, N.; Toribio, R.E. Dynamics of androgens in healthy and hospitalized newborn foals. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanci, A.; Mariella, J.; Ellero, N.; Faoro, A.; Peric, T.; Prandi, A.; Freccero, F.; Castagnetti, C. Hair Cortisol and DHEA-S in Foals and Mares as a Retrospective Picture of Feto-Maternal Relationship under Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Animals 2022, 12, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, K.; Slovis, N.; Barton, M. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction in hospitalized neonatal foals. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2009, 23, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montillo, M.; Sergiacomo, M.; Contri, A.; Gloria, A.; Peric, T.; Veronesi, M. IGF-I, NEFA and Cortisol Plasma Concentrations in Newborn Donkey Foals. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the European Society for Domestic Animal Reproduction (ESDAR), Bologna, Italy, 12–14 September 2013; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Legacki, E.L.; Corbin, C.; Ball, B.; Wynn, M.; Loux, S.; Stanley, S.D.; Conley, A.J. Progestin withdrawal at parturition in the mare. Reproduction 2016, 152, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ousey, J.; McArthur, A.; Rossdale, P. Metabolic changes in thoroughbred and pony foals during the first 24 h post partum. J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 1991, 44, 561–570. [Google Scholar]
- Legacki, E.L.; Scholtz, E.L.; Ball, B.A.; Stanley, S.D.; Berger, T.; Conley, A.J. The dynamic steroid landscape of equine pregnancy mapped by mass spectrometry. Reproduction 2016, 151, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousey, J.; Forhead, A.; Rossdale, P.; Grainger, L.; Houghton, E.; Fowden, A. Ontogeny of uteroplacental progestagen production in pregnant mares during the second half of gestation. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 69, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legacki, E.L.; Corbin, C.J.; Ball, B.A.; Scoggin, K.E.; Stanley, S.D.; Conley, A.J. Steroidogenic enzyme activities in the pre-and post-parturient equine placenta. Reproduction 2018, 155, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossdale, P.; Ousey, J.; McGladdery, A.; Prandi, S.; Holdstock, N.; Grainger, L.; Houghton, E. A retrospective study of increased plasma progestagen concentrations in compromised neonatal foals. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 1995, 7, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, P.; Hirama, A.; Nambo, Y.; Harada, T.; Sato, F.; Nagaoka, K.; Watanabe, G.; Taya, K. Circulating pituitary and gonadal hormones in spring-born Thoroughbred fillies and colts from birth to puberty. J. Reprod. Dev. 2012, 58, 2011–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, K.; Heusner, G.; Norton, N.; Barton, M. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis assessment in healthy term neonatal foals utilizing a paired low dose/high dose ACTH stimulation test. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2009, 23, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, A.K.; Wang, W.; Navas-Gonzalez, F.J.; Rodrigues, J.B. Reference intervals for hematological and blood biochemistry reference values in healthy mules and hinnies. Comp. Clin. Path. 2016, 25, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnahan, M.M. Genetics, Evolution, and Physiology of Donkeys and Mules. Vet. Clin. Equine. Pract. 2019, 35, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, J.; Tadich, T.A. Hematological and biochemical reference intervals for mules in Chile. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, A.; Varnum, A.; Ali, A.; Heleski, C.; Navas González, F.J. Comparing and contrasting knowledge on mules and hinnies as a tool to comprehend their behavior and improve their welfare. Animals 2019, 9, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.B.; Matoock, M.Y.; Fouad, M.A.; Heleski, C.R. Are mules or donkeys better adapted for Egyptian brick kiln work? (Until we can change the kilns). J. Vet. Behav. 2015, 10, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, M.C.; Panzani, S.; Govoni, N.; Kindahl, H.; Galeati, G.; Robbe, D.; Carluccio, A. Peripartal plasma concentrations of 15-ketodihydro-PGF2α, cortisol, progesterone and 17-β-estradiol in Martina Franca jennies. Theriogenology 2011, 75, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, C.; Aurich, J.; Aurich, C. Salivary cortisol, heart rate and heart rate variability in healthy and diseased neonatal foals. Pferdeheilkunde 2018, 34, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J. Serum estrogen concentrations during postnatal development in male pigs. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1983, 174, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtaniemi, I. Endocrine function and regulation of the fetal and neonatal testis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2003, 33, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Corbier, P.; Edwards, D.; Roffi, J. The neonatal testosterone surge: A comparative study. Arch. Int. Physiol. Biochim. Biophys. 1992, 100, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.; Hesse, V. Minipuberty: Why does it happen? Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2020, 93, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlet, D.; Wulf, M.; Kuhl, J.; Köhne, M.; Ille, N.; Conley, A.J.; Aurich, C. Anti-Müllerian hormone profiling in prepubertal horses and its relationship with gonadal function. Theriogenology 2018, 117, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, A.; Hodge, L.; Allen, W. The biosynthesis of 3β-hydroxy-5,7-androstadien-17-one by the horse fetal gonad. FEBS Lett. 1985, 182, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, A.; Santikarn, S.; Allen, W. Identification of 3β-hydroxy-5,7-pregnadien-20-one and 3β-hydroxy-5,7-androstadien-17-one as endogenous steroids in the fetal horse gonad. J. Endocrinol. 1983, 99, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, W. Immunological aspects of the endometrial cup reaction and the effect of xenogeneic pregnancy in horses and donkeys. J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 1982, 31, 57–94. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, W.; Kydd, J.H.; Boyle, M.; Antczak, D. Extraspecific donkey-in-horse pregnancy as a model of early fetal death. J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 1987, 35, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
| Hormones (ng/mL) | Group | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mule | Equine | Group | Time | Group × Time | |
| Androstenedione | 0.16 ± 0.07 | 0.63 ± 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.45 | 0.98 |
| 3β,20α-dihydroxy DHP | 37.58 ± 9.56 | 69.86 ± 15.13 | 0.003 | <0.0001 | 0.11 |
| Corticosterone | 3.48 ± 0.65 | 3.28 ± 0.51 | 0.77 | <0.0001 | 0.05 |
| Cortisol | 31.38 ± 4.47 | 33.88 ± 4.33 | 0.28 | <0.0001 | 0.73 |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone | 14.98 ± 3.11 | 27.45 ± 3.15 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.35 |
| Dihydrotestosterone | 0.50 ± 0.08 | 0.86 ± 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.0005 | 0.17 |
| Progesterone | 6.02 ± 1.14 | 6.23 ± 1.23 | 0.82 | <0.0001 | 0.66 |
| Pregnenolone | 726.19 ± 111.35 | 1002.55 ± 180.63 | 0.36 | <0.0001 | 0.17 |
| Hormones (ng/mL) | TIME | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T6 | T12 | ||
| 3β,20α-dihydroxy DHP | 140.59 ± 16.12 A | 61.40 ± 11.54 B | 12.91 ± 2.64 C | 5.88 ± 1.19 D | <0.0001 |
| Corticosterone | 4.87 ± 0.31 A | 6.35 ± 0.74 A | 1.37 ± 0.41 B | 1.06 ± 0.40 B | <0.0001 |
| Cortisol | 47.11 ± 3.12 A | 53.24 ± 5.12 A | 13.07 ± 1.43 B | 18.22 ± 3.18 B | <0.0001 |
| Dihydrotestosterone | 0.48 ± 0.12 B | 1.28 ± 0.28 A | 0.70 ± 0.17 A,B | 0.23 ± 0.10 B | 0.002 |
| Progesterone | 11.90 ± 1.82 A | 6.28 ± 0.72 A | 2.88 ± 0.38 B | 3.93 ± 1.89 B | <0.0001 |
| Pregnenolone | 1433.18 ± 233.87 A | 1238.09 ± 184.18 A | 605.20 ± 129.73 B | 216.90 ± 59.26 C | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boakari, Y.L.; Legacki, E.; Alonso, M.A.; dos Santos, A.C.F.; Nichi, M.; Conley, A.J.; Fernandes, C.B. Postnatal Dynamics of Circulating Steroid Hormones in Mule and Equine Neonates. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110598
Boakari YL, Legacki E, Alonso MA, dos Santos ACF, Nichi M, Conley AJ, Fernandes CB. Postnatal Dynamics of Circulating Steroid Hormones in Mule and Equine Neonates. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(11):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110598
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoakari, Yatta Linhares, Erin Legacki, Maria Augusta Alonso, Ana Carolina Francisco dos Santos, Marcilio Nichi, Alan J. Conley, and Claudia Barbosa Fernandes. 2022. "Postnatal Dynamics of Circulating Steroid Hormones in Mule and Equine Neonates" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 11: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110598
APA StyleBoakari, Y. L., Legacki, E., Alonso, M. A., dos Santos, A. C. F., Nichi, M., Conley, A. J., & Fernandes, C. B. (2022). Postnatal Dynamics of Circulating Steroid Hormones in Mule and Equine Neonates. Veterinary Sciences, 9(11), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110598








