Abstract
Infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) is a major economic problem in commercial chicken farms with acute multiple-system infection, especially in respiratory and urogenital systems. A live-attenuated and killed vaccine is currently immunized to control IBV infection; however, repeated outbreaks occur in both unvaccinated and vaccinated birds due to the choice of inadequate vaccine candidates and continuous emergence of novel infectious bronchitis (IB) variants and failure of vaccination. However, similar clinical signs were shown in different respiratory diseases that are essential to improving the diagnostic assay to detect IBV infections. Various risk factors involved in the failure of IB vaccination, such as various routes of application of vaccination, the interval between vaccinations, and challenge with various possible immunosuppression of birds are reviewed. The review article also highlights and updates factors affecting the diagnosis of IBV disease in the poultry industry with differential diagnosis to find the nature of infections compared with non-IBV diseases. Therefore, it is essential to monitor the common reasons for failed IBV vaccinations with preventive action, and proper diagnostic facilities for identifying the infective stage, leading to earlier control and reduced economic losses from IBV disease.
1. Introduction
Infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) is an acute and highly contagious respiratory pathogen in chickens. In general, coronaviruses are classified into four groups (Alpha, Beta, Gama, and Delta) according to antigenic cross-reactivity and nucleotide sequence analysis [1]. IBV belongs to genus Gammacoronavirus with positive-sense single-stranded RNA (+) ssRNA genome; its gene organization is 5′UTR-1a/1ab-S-3a-3b-E-M-5a-5b-N-3′UTR [2,3]. Moreover, betacoronaviruses are included human coronaviruses such as SARS-CoV (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus) and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) [4,5]. The length of the IBV genome is approximately 27.6 Kb, and the virion is encircling 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) with a poly (A) tail [6], the functional and nonfunctional genes are shown in Figure 1. Nine functional genes were encoded in the IBV genome, four genes were involved as main structural proteins, and another five genes are known as nonstructural proteins (Nsps). Most IBV genotypes and serotypes are closely associated with the vaccine strains or variants that are very distinct based on geographical areas circulating each lineage (GI) on complete nucleotide sequences of S1 (spike) gene [7,8]. Moreover, the distribution and multiplicity of these IBV genotypes vary with different geographical areas [9]. The major IBV serotypes are characterized in Massachusetts in the USA, 4/91 (793B or CR88) in the UK, D274 (D207, D212, or D1466, D3896, and D3128) in Europe, QX-like reported in China, H120 strain in the Netherlands with several variants introducing local and regional region by transmissions [10,11]. Different types of serotype or genotype of IBV failed to cross-protection against multiple genotypes due to continuous evolution of IBV [12,13,14,15]. Immunization with multiple serotype vaccines can be given 90% protection against different types of IBV infection instead of homologous vaccines (i.e., “protectotype concept”) [16,17,18].

Figure 1.
Morphology and genomic structure of infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) with different structural and non-structural genes.
IBV infection has major economic impact on the poultry industry due to mutable tissue tropism and the continuous emergence of various IBV serotypes or genotypes in different geographical regions. Because of its degree of severity and high contagiousness, mortality can reach up to 10%–60% over four to six weeks of broiler age during acute infection with a secondary infection [19,20]. There are no appropriate policies to control or prevent IBV infections without correct vaccination, especially live-attenuated and killed vaccines manufactured from local strains or serotype-specific immunity [21]. Farmers normally follow rotational vaccination programs for controlling IBV; however, the incidence of disease has become a repeated occurrence with local variants [22]. Vaccination is the most significant method for the prevention and control of IBV in the field. Previous reports demonstrated that live vaccines commonly stimulated both local protection and systemic immunity, but inactivated vaccines provide prolonged immunity after inducing with live-attenuated vaccine [23]. The killed IBV vaccine is applied either single or combined of two or more serotypes in bivalent vaccines [24]. Maternally derived antibodies (MDA) of progeny chicks are received from vaccinated breeder hens with inactivated vaccines as a substitute for live vaccine [25,26].
The failure of the vaccine is a consequence of the incapability of birds to produce a satisfactory immune response after vaccination [27]. Various factors are associated with accurate IBV vaccinations, such as the prospect of long-term immunity, the selection of maximal virulent serotypes, and the timing of applications according to flocks requiring revaccination [28]. Farmers blame the vaccine’s lack of effectiveness for failure to immunize their flocks. More than 50% of vaccination failures were recognized in vaccinated flocks due to the improper application of vaccine. Moreover, the increased risk of incorrect administration of vaccines, and cold-chain maintenance and storage of vaccine quality are important issues for vaccine failure leading to outbreaks of IBV in vaccinated farms [29]. Proper attention to those common factors responsible for failure vaccines provides reduced IBV costs and problems in poultry farms. The most significant part of IBV diagnosis identified genotype selection by molecular assay for correct vaccine candidates. Differential diagnosis needs to be established due to similar clinical signs exposed by various respiratory pathogens as required for proper testing to avoid misdiagnosis. This is the reason why diagnosis needs to be set up through the accumulation of combined serology data matched with clinical signs and isolation of the virus for the interpretation of results. Most poultry producers routinely use ELISA testing for the early diagnosis, challenge of infection, and failure of vaccination of IBV. Even though many factors are considered to increase, or abnormal IBV titers as necessary to check the timing of vaccination, seroconversion before and after vaccination, history of field challenge, geometric mean titer (GMT), and coefficient of variation (CV%), are necessary to meet the standards with the purpose of final diagnosis of IBV challenge or good vaccination [30,31].
The aim of this review article is mainly to discuss advanced current challenges related to proper diagnostic assay with evidence of vaccination failure. We describe various factors influenced by IBV vaccination, various routes of vaccination, postvaccine challenge, possible immunosuppression, and differential diagnosis to explore future research to elucidate the immune-pathogenesis response of multiple types of IBV.
2. Factors Influencing IBV Diagnosis
Few assays are established for infectious bronchitis (IB) diagnosis for the identification of viruses from current infections or specific antibody responses from post-viral infection. The selection of the best assay for the successful detection of IBV is difficult and confusing due to various factors, as discussed below.
2.1. Clinical Signs
The clinical signs of IBV are similar to those in other respiratory infections except for a few unique lesions that are part of strain variation and difficult to differentiate from other respiratory viral infections. Although clinical signs are matched according to the manual, a serology study is not ever matched according to autopsy lesions. The serology titer is occasionally given higher trends, but it cannot match with clinical signs; therefore, IBV confirmation is problematic. Thus, conformation diagnosis is based on the accumulation of data from farm records, including egg quality with production graph, mortality, seroconversion or antibody levels, vaccination report, and blood serology, which are clinical signs that concurrently match symptoms of IBV chickens through PM lesions [31,32,33]. Sample collection for IBV isolation is best when immediately achieved, as clinical signs are obvious. PCR on reverse-transcribed RNA is an effective method for detecting IBV in active infections. Some studies suggested that nutritional deficiencies are an important consideration for detecting IBV [34,35].
2.2. Vaccination
Vaccination is the main influence for IBV identification, as it requires the infected IBV-vaccinated strain and other virulent field strains. For unvaccinated flocks, the field challenge can simply be detected by RT-PCR, RT-qPCR, or a positive IBV titer after a few weeks. Therefore, there is great difficulty in identifying a field challenge or active infection in vaccinated flocks due to antibody circulation in the bloodstream. Nowadays, vaccine strains can be distinguished from field strains through the differentiating infected from vaccinated animals (DIVA) technique using inactivated oil emulsion vaccine that can be detected by simple neutralization test, enzyme linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and indirect immunofluorescence test [36,37,38].
2.3. Assay Selection
The selection of diagnostic techniques is important for proper diagnosis related to sample collection and sampling numbers. Advanced ELISA tests can distinguish antibodies owing to vaccination from those from infection. The concentration of antibody titer tends to be abnormally increased after 2–4 weeks post infection; the titer gradually decreased slowly in subsequent weeks [39]. Subsequently, the next blood sample should be collected after 2 weeks, but no later than 4 weeks in the same infected houses [39] because the titer is delayed in the highest level due to the immune-system’s need for time to build up immunity. The highest concentration of virus was found in infected tissue during the first 3–5 days post infection; there is a need for the selection of molecular assays and viral isolation instead of serology monitoring. Common molecular practices are currently applied for IBV diagnosis, particularly in RT-PCR, but the IBV isolate is more challenging, time-consuming, and exclusive from infected chicken due to requiring several passages in embryonated chicken eggs until the virus replicates. Alternatively, primers need to be frequently updated to apply in the molecular assay due to various types of variants that can escape identification because of frequent mutations occurring in the primer binding site.
2.4. Serology
The mean titer provides information on the antibody response of tested birds within a flock after vaccination. Mean titers should reach a predictable range with uniform distribution for normal flocks and unintentionally higher titers for diseased flocks. A study suggested that antibody patterns should not be breached over vaccinal immunity because of field infections [40]. Post infection, the geometric mean titer (GMT) should be abnormally increased when titer level is at least 2 times higher than the expected level after vaccination or at least 2 times the mean titer level before the infection [31,32]. Mean titer is sometimes gradually elevated after vaccination; however, no clinical signs were found with normal production, indicating good protection and better response to vaccine [31].
On the basis of general parameters, a percentage coefficient of variation (CV) that is maintained below 40% after inactivated vaccinations and less than 60% in live vaccines suggests good vaccination uniformity. When CV is less than 20%, the level of titer shows good uniformity, but previous exposure of disease or good vaccination is specified [32]. Therefore, it is necessary to cross-match with mortality, clinical signs, and production records for the final confirmation of IBV. A good assessment of CV percentage is significantly below the expected level after vaccination or significantly below levels in earlier infection cases. Consequently, CV% can reach 40%–70% after a single shot of live IBV vaccine, but below 30% is specified as a suspected challenge. Conversely, after vaccinating with high immunogenic IBV variants, CV percentage is commonly less than 45% [32]. In this situation, a series of multiple live vaccinations are initially used to boost the birds for 100% seroconversion before killed vaccination, which is a major principle for influence on the persistence of titers rather than measure of percent CV [41,42]. In serology detection systems, ELISA tests are commonly used to determine the trend analysis of protective antibody titers by good vaccination or unexpected serology, which is caused by virulent serotype or variant of IBV. However, ELISA results can be difficult to identify seroconversion against specific serotypes or variants except serotype-specific ELISA, e.g., Ark or Mass, Conn or Del 072 [43]. For this reason, the HI (Hemagglutination inhibition) test may contribute more valuable serotype-specific evidence, if birds are exposed to one diverse IB serotype. Apart from that, IBV titers tend to be less stable during production compared with titers of infectious bursal disease (IBD) and Newcastle disease (NDV).
2.5. Organ Selection and Sample Quality
The upper respiratory tract (UTI) is the principal site of IBV replication; subsequently, viremia causes viral multiplication to disseminate to other tissue through blood circulation [44,45,46]. IBV can be persistent in the long term in the cecal tonsils and kidneys due to the continuous cross-infection of infected or immune flocks [44,47]. In acute cases, clinical signs are identified in the respiratory tract, which is the preferred spot for pooling samples. Furthermore, kidney, cecal tonsil, and cloaca samples are selected in chronic infections in vaccinated chickens in the laying stage, whereas small amounts of the virus are predictable in the respiratory tract [48]. The pooling organ should be refrigerated faster to preserve viral viability for further molecular diagnosis. If there is no freezing or refrigerating facility, samples should be kept in 50% glycerin for several days.
2.6. Immunization and Challenge during Infection
Serological monitoring can be directly helpful for the assessment of the immune status of birds, viral challenge, and the duration of viral infection [19]. Different types of commercial ELISA kits were calculated using different cut-offs and mathematical formulations to convert the ELISA result. The most common practice in farming to build up immunity for controlling IBV infection is by live-attenuated vaccines followed by inactivated vaccines given the normal titer level for good protection against IBV [49]. Two phases of serum samples are essential to compare for proper diagnosis, as first samples are taken from the early infection, and the second stage of samples are taken after 3–4 weeks. The delay of the first sampling can prevent the detection of seroconversion [50]. For unvaccinated flocks, an IBV field challenge can simply be to confirm by identifying positive IBV titers in serology. For vaccinated IBV flocks, the presence of a field challenge is more difficult due to vaccinated birds showing a certain limit of titer level, which is required to compare with abnormal titers. However, unexpectedly increasing titers were significantly higher than expected vaccination titers with a lower CV%, indicating the existence of a field challenge [51]. IBV challenge normally shows respiratory signs while examining abnormally high IBV titers after 6–8 weeks post infection. In the case of breeder chicken, the normal instruction to calculate challenged birds is the mean titer of post infection being at least a 2 or 3 times the link to be expected from vaccination titers (baseline), as shown in Figure 2A,B [31,32]. In the case of broilers, an abnormal IBV titer is normally shown in the challenge, while the mean titer post-infection should be over 3–4 K (Idexx std) after a live vaccination link to normal serology, as presented in Figure 2C,D, respectively. In this review article, all serological data are evaluated on the basis of field trials collected from Turan breeder and broiler farms, Sabah, Malaysia, using commercial ELISA Kit (IDEXX, Westbrook, ME, USA). In the ELISA test, diagnosis should be established through expected vaccination titers depending on the vaccination program, the geographical distribution of IBV, outbreak history, specific vaccines, and type of inspected bird. Those respective factors are associated with the combination of periodic flock reports to determine whether serological results are normal or abnormal. Many factors influence levels of antibodies, particularly the strain of the virus, and some factors related to the chicken (e.g., breed, type, age, immune status, and nutrition), vaccine (e.g., levels of attenuation, dosage, live or killed vaccine, and storage conditions), and vaccination schedule (e.g., proper schedule, preparation, and route of administration) [52].

Figure 2.
Compared serology analysis of IBV in two broiler breeder houses at 26 weeks of (A) challenged and (B) normal flock. Probable calculation of mean titer of challenged flock was three times more than that of the normal flock, and coefficient of variation (CV%) was too low compared with previous serology using Symbiotic test kit, USA. High-challenge titer after IBV infection in peak laying located almost in a single bar. In broilers, (C) high-challenge titer after IBV infection observed at the age of 35 days over 3–4 K titer calculated as post-IBV infection compared with (D) normal serology based on standard of Idexx ELISA test kit, USA. (Source: Personal communication; collected from Tuaran Broiler Farm, Sabah, Malaysia).
2.7. Genetics and Immunosuppression
Genetic traits have great influence on resistance and susceptibility to IBV. Some experimental studies showed the different genetic traits, mortality, viral growth, and variable histopathology found in different breeding lines after IBV immunization [53]. However, different detection methods have some dissimilarity because of the difference in susceptibility among chicken lines. Some immunosuppressive infections are associated with exacerbating the IBV disease, such as infectious bursal disease (IBD), Marek’s disease (MD), inclusion body hepatitis (IBH), and chicken infectious anemia (CIA) potentially suppress immune status at an early age, which can disturb the acquired vaccinal immunity of IBV by stimulated lymphocyte depletion from the bursa and thymus, causing higher resistance to challenge [54]. Major damage is affected by subclinical infection, making it difficult to understand immunosuppressive agents [55]. Laboratory diagnostic methods for confirming IBV infection concern other respiratory viruses that require continuous serology monitoring to identify the actual source of current infections. Similarly, cyclosporine is classified as a T-cell immunosuppressive drug that can significantly reduce the immunity of birds and is highly stimulated in IBV infections [56].
3. Vaccination Factor Influence
The level and duration of vaccination responses rely on many factors that need to be fully considered during vaccination. It is not sufficient to simply describe a specific IBV vaccine that can protect against infection in a particular situation, since regulatory requirements are commonly challenged.
3.1. Stress and Vaccination
According to Dantzer [57], stress is “the nonspecific response to environmental stimulation, the result of extreme demands placed on the physiological and behavioral experiences of birds to adaptation”. All kinds of stress can decrease a bird’s immune system, related to various factors such as temperature fluctuation, high relative humidity, poor nutrition, parasitic infestation, and disease condition. Vaccinations should occur in healthy birds with good conditions to avoid stress. The adverse results of stress on the immune defense system are the main effects of the glucocorticosteroid hormone; therefore, inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandin and leukotriene mediators of inflammation, resulting in the suppression of the immune defense system. A study suggested evidence of a negative impression between stress and antibody response to vaccination, which is the most superficial with thymus-related vaccines and was calculated a long time after vaccination [58] A period of chronic stress was found to significantly decrease the total number of T-helper, T-lymphocyte, and B-lymphocyte cells due to continuous raising of corticosterone hormone levels that exceeded the allostatic load [58,59,60]. However, prolonged stress in young chickens leads to the premature regression of lymphatic or immune organs, for example, the thymus, bursa of Fabricius, and spleen [61]. Combinations of effects on the body metabolism and immune system of stressed birds do not tolerate vaccine acceptance; it is ultimately unclear if they properly confer protection.
3.2. Methods for Protection Studies
A protection study is not a simple method for application, but several factors were considered during designing such studies [62]. Different methods were used for performing in vivo protection studies using the overall concept of vaccinating and challenging groups to assess whether a vaccine protects against a particular challenge of a local strain. Arvidson et al. [63] established a different approach of viral clearance test from the lungs with particular vaccination and challenge via the trachea. This study allowed for determining an index of protection score that was more than 50% as a protection level, while 90% of the rings had regular activity [64]. The titer of a vaccine prohibited the replication of a challenge virus in the lungs evaluated by titrating lung homogenates in an in vitro ciliostasis test [62]. Studies used lung samples rather than the trachea to minimize the risk of detecting residual effects due to lung tissue supporting IBV growth to a similar level as that in the trachea. Ciliary protection stimulated by IBV vaccination programs against three groups of virulent IBV strain challenges on day 21 post vaccine are shown in Figure 3 [65]. Experimental studies reported that killed vaccines applied without priming with live-attenuated vaccines stimulated lower systemic immune responses, as no more local protection, especially tracheal ciliostasis, leads to systemic infection affected by virulent IBV serotypes [66].
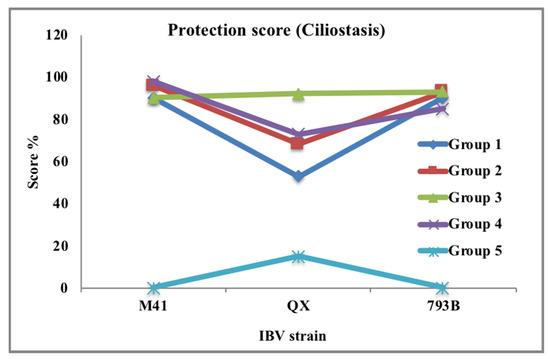
Figure 3.
Ciliary protection stimulated by infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) vaccination programs against three virulent IBV strain challenges on day 21 post vaccine. IBV vaccination programs categorized into Group 1 = Mass1 + D274, Group 2 = Mass1 + 793B1, Group 3 = Mass2 + 793B2, Group 4 = Mass3 + Ark, and Group 5 = sterile water (SW). In this study, the monovalent Mass vaccines (H120 or Ma5) are referred to as Mass1 and Mass2, and the 793B vaccines are referred to as 793B1 and 793B2 (4/91 or CR88) serotypes. IBV challenged by M41, QX, or 793B initiated severe ciliostasis in unvaccinated–challenged birds. Ciliary scores indicated that vaccination programs gave good protection (>85%) against M41 and 793B. However, Group 3 (Mass2 + 793B2) was the only group to show good protection against QX; other groups were under partial protection. Protection score curve indicated that the higher the score was, the better the protection (Source: Awad et al. [66]).
3.3. Vaccine and Vaccination Program
Prior to vaccination, a program needs to be revised according to epidemiological study, the prevalence of a virulent virus, data of sporadic outbreaks, accurate diagnosis, single or combined IBV vaccine, vaccine potency, and monitoring poultry health systems. Immunization is commonly dependent on the challenge of establishing their effectiveness against multiple variants of viruses; a specific time is favorable for the multiplication of viruses, live-attenuated or killed vaccines, and monitoring the titer level or baseline of determination. Essential information details whether bird immunization is protective or a challenge. Therefore, evaluation of the current immunization schedule is not recommended if certain titer limits exist or a virus challenge is circulating in the field [67]. Because of several IBV serotypes, a single serotype of IBV vaccine does not provide more than 50% protection (Ciliary score ≥20), so it is not sufficient protection from a heterologous challenge on the basis of some clinical studies [16,68]. Higher ciliostasis protection (≥80%) was exposed through diverse vaccination of serotypes with Ma5 or H 120 at 1 day old, 793/B or 4/91 at 2 weeks against challenge at 5 weeks of age with two heterologous IBV is presented to be highly effective and good protecting the respiratory tract [16,69]. The results have revealed that applying two or more IBV live vaccines stimulated a higher expression of CD+, CD8, and IgA-bearing B cell in comparison to single serotype of IBV vaccine that promotes to a higher level of cellular and local immunity at the trachea against heterologous serotype [16,70]. Therefore, a vaccine should be selected from one of those serotypes to generate the broad protection of chicken. Alternative types of “multi/monovalent” vaccines, which have at least two serotypes of IBV vaccine or apply new serotypes depending on the high challenge in the farm and neighboring areas, are circulated via the same serotypes. Thus, virulent serotypes of IBV emerging in flocks can be identified by a serotyping assay, and confirmation of a particular vaccination program to protect against new IB isolates [16]. Several studies reported that IB vaccine with multiple serotypes can stimulate the proper antibody response and better protectives abilities against large number of different IBV types and novel emerging serotypes; especially local protection of the cilia in the trachea carried by the protectotype can inhibit secondary bacterial infections [41,71]. This program is generally used due to the more effective and cross-reaction immunity of birds based on actual practice and principle [19]. Virulent live vaccines are more effective and capable of reducing shedding the field challenge compared to recombinant vaccines, inactivated vaccines, and live vaccines, which are not highly homologous with a field challenge virus [72]. Most vaccines are inactive during the infective stage where birds are previously infected at the time of vaccination. As a result of acute infection, the immune organ is not fully working toward the activation of the immune system, as chickens do not generate a satisfactory level of antibody titer. Excessive rolling-type reactions are rarely found in close-contact houses, causing delayed immunity in the farm. The studied serology was conducted in 9 houses of chicken breeder flocks for the field trail (Tuaran breeder farm, Sabah, Malaysia), previously immunized with a few live and killed vaccines day 1 and day 18: Ma5 in spray; day 10: 4/91 in spray; day 42: IB killed; day 91 in Intramuscular injection: IB Mass in drinking; day 119: IB (4 in 1) killed in intramuscular injection; day 140: IB (4 in 1) killed in the pullet stage, and geometric mean titer (GMT) is shown for 0–30 weeks (Figure 4).
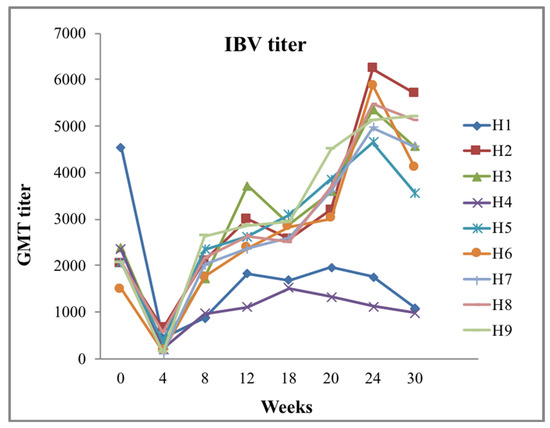
Figure 4.
Geometric mean (IDEXX, USA) titer of nine broiler breeder houses in serology graph of 0–30 weeks. Birds vaccinated with infectious bronchitis (IB) live-attenuated vaccines followed by IBV variants and inactivated IBV-killed vaccination for 20 weeks during pullet stage. Out of 9 houses, House-1 and House-4 represent very low titer after vaccination compared with that of other houses. GMT titer was still below standard, indicating inappropriate vaccination with various involved factors during vaccination (X axis, weeks; Y axis, geometric mean titer (GMT)). (Source: personal communication; collected from Tuaran breeder farm, Sabah, Malaysia).
3.4. Group Size and Sample Number
Sample collection is important for the confirmation of diagnosis and identification during active and post-viral infection. In the acute infection of IBV, the majority of birds have a similar typical clinical sign; then, the number of samples can be reduced. At least five birds are enough to achieve higher confidence of the successful detection of infection by molecular assay [67]. In serology, more collection samples of birds having higher specific results are detected after infection; nevertheless, the costs and risk of false-positive results should be considered. In chronic infections in immunized birds, small quantities of the virus exist with lower prevalence, but require more birds for detecting infection. In the farm, a minimum of 20–25 bird samples should be taken from the group or every farm flock after vaccination, or results do not provide a good statistical data analysis. For the evaluation of vaccine efficiency, IBV antibodies were identified using a commercial ELISA kit according to manufacturer’s orders. Awad et al. [13] reported that serum was collected from days 3, 6, 10, 14, 18, and 25 post vaccination from 8 chicks/group to establish the mean or geometric antibody titer of an in vitro study. Therefore, statistical analysis is associated with bird welfare and financial reasons, and the choice of the number of chickens per group in experiments is relevant. Estimation of the required number of samples depends on studying the difference in levels of protection, the expected variability of the results between and within groups of chickens, and the desired confidence level [67,73]. A few researchers demonstrated sampling of the ciliostasis protection score system (CPSS) that was used to collect 10 tracheal organ cultures (TOCs) from 10 chickens per group using a five-class (scores 0–4) scoring system [74,75,76]. The principles of an official European publication reported that the efficiency of IB vaccines were required to use the binomial interpretation of CT on 10 TOCs from no less than 20 chickens per group, as used in many studies. Birds were protected, as no fewer than 9 of 10 rings presented normal ciliary activity [77].
3.5. Immunity at Time of Vaccination/Infection
The level of acquired immunity depends on many factors, especially at the time of vaccination or exposure of infection. Vaccines collaborate with the immune system to generate the same immune response as that in natural infection in birds. The humoral immune response has a significant role in the stimulation of certain levels of immune response compared with natural infection. Some researchers reported that vaccination is the process of immune development of the body originating from previous vaccination or earlier infection [78,79]. The humoral response normally increases after infection in vaccinated chickens, but could gradually decline or be delayed on the basis of current infection exposure in the farm. Therefore, the sensitivity of antibody tests could be much lower in vaccinated chickens compared to in unvaccinated chickens [48]. A study reported experimental IBV infections applied in vaccinated and unvaccinated birds, with results identifying a homologous virus challenge in much shorter and lower amounts in vaccinated than in unvaccinated chickens [80]. Different levels of humoral response could be identified by serology testing after 4 weeks of infection or 6 weeks after vaccination [81]. Neutralizing antibody (anti-IBV IgA) responses appear to follow the challenge, becoming more enhanced as time went by between vaccinations and challenge [82]. For instance, vaccines require a certain time to develop body immunity, subsequently carefully investigating the optimal period for applying primary and following booster immunization with the purpose of generating an optimal immune response in birds. The immunized are either too early or too late with secondary vaccinations, or it might fail to adequately strengthen the immune stimulation resulting in poor immune protection [83]. To prolong built-up immunity, primary immunization is followed by secondary immunization at an interval of 2 to 4 weeks; then, it may need an additional killed vaccine to develop complete immune protection [84], as shown in Figure 5A. Moreover, annual booster shots are needed to ensure that the immune system is still operative and to increase the boost of immunity. Although the early vaccination of IBV has a negative impact on circulating maternal antibodies until 4 weeks, local antibodies subsidize the local protection of respiratory epithelium against homologous IBV challenge. Therefore, primary vaccinations (live and killed) allow for overcoming the immunity gap, as they require a balance to generate the active immunity in a maternally derived antibody (MDA) period decline rather than in the late vaccination [85] (Figure 5B).
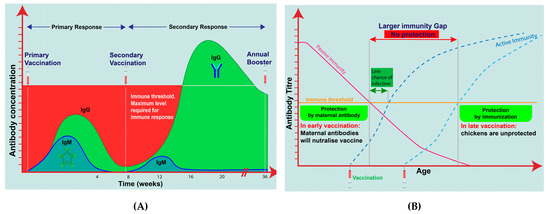
Figure 5.
(A) Activity of primary and secondary immune response correlated to chicken vaccination with maintaining maximal level of immune response in full cycle of laying birds by using repeated annual boosting during decline of active immunity (https://microbiologynotes.com/differences-between-primary-and-secondary-immune-response/); (B) Assessment of immunity gap or no protection period between decline of passive immunity and start of active or acquired immunity causing birds to be unprotected and challenged, as active immunization is given protection in immunity gap (https://www.thepoultrysite.com/articles/protecting-the-immune-system-in-poultry-early-vaccination-with-vaxxitek-hvtibd).
3.6. Age and Maternally Derived Antibodies
Maternal antibodies can provide passive immunity to chicks from hatching and temporarily protect against pathogens to the young immune system [86,87]. Age and maternally derived antibodies (MDA) are two significant reasons for the detection of antibodies during viral challenge or vaccination. However, high levels of MDAs in young chickens affect the multiplication and development of live vaccine virus, reducing the number of titers in serology. Studies suggested that only DNA vaccines (ovo- or intramuscularly) can provide the complete protection of day old chicks (DOC) due to vaccine antibodies, but they do not neutralize MDA [88]. Passive immunity has a comparatively short period, and MDA level was significantly increased after 3–4 days of age until invisible levels at 2–3 weeks of age [87,89]. Birds were more susceptible to infection at 2–3 weeks of age, while MDA protection declined, and the immune system of birds did not ever fully develop to respond against an early challenge [90]. The degree of immune response relies on age or MDA variation since humoral immune response gradually decreases if infection comes at a young age. The capacity of young chicks to develop their own antibodies after a response to antigenic processes is from hatching to older than 5–6 weeks of age. Antibody titers were considerably higher in specific-pathogen-free (SPF) chickens when immunized with S1, S2, and N proteins at 14 days of age than in those vaccinated at 1 or 7 days of age [91]. During that time, immunoglobulin (IgM) was not identified after the vaccination of DOC broilers with MDA, whereas IgM was noticeable after vaccination at 14 days of age. Some researchers worked on SPF chicks to apply live-attenuated IBV vaccines in a DOC hatchery receiving good local protection, which is currently applied in most broiler farms [92,93]. Moreover, some vaccination studies reported testing broilers after 2 weeks of age [94,95] and applying vaccination in 3 weeks [96] or even after 5 weeks of age [97]. Result comparison between variations of age is too difficult; nevertheless, the recurrent immunization of broiler chickens (one or two diverse variants) is now common practice in DOC followed by a boosted immunization at 2 weeks of age. The results of those studies revealed that the assessment value is more productive and protective against variant IBV challenges [18].
3.7. Genetics
Chicken breeding line is an important factor to genetic resistance to vaccination since variations can be genetically exposed and significantly influenced between inbred chicken lines that are infected with IBV and E. coli. Cook et al. [98] reported that there was no significant variation in serum antibody titers using VNT and ELISA after IB infection in experiments in highly resistant and highly susceptible chicken lines. However, another study showed that using inbred chicken lines challenges only IBV, indicating that the inbred line carrying the MHC B2 haplotype was more susceptible to IBV than line 15I (MHC B15 type) birds [99]. Joiner et al. [100] applied the same inbred chicken lines to show that the occurrence of clinical symptoms of an IBV challenge was considerably lower in a B2/B15 line than that in a B2/21 line. The MHC B15 haplotype was shown to be closely linked with resistance to IBV infection. However, no other study has been conducted to examine current commercial or SPF chicken breeds.
3.8. Vaccine Dosage
Vaccine doses are commonly monitored with regard to recommended manufacturer labels and instructions to deliver the correct volume to each chicken [18]. In a good immunization program, vaccine doses are a key factor in order for every bird to properly receive protection against IBV challenges [73]. Limited methods were established to determine the vaccine titer used in protection studies in embryonated eggs, calculated as the 50% egg infective dose (EID50). However, tracheal organ cultures (TOCs) were used to observe sensitivity in embryonated eggs for isolating IBV and to provide reproducible test results [101]. Moreover, titers are significantly varied depending on the expression in EID50 or median ciliostatic doses [62]. Alternatively, great variation was observed in different studies on the actual vaccine dose applied in many experiments. Another study suggested that vaccine dose is commonly applied at approximately log10 3.0 EID50/bird, but it is difficult to calculate the actual dose received by each chick [102,103]. Special attention is specified in the earlier preparation of vaccine suspension; the uses of a calibrated dropper and application directions have great impact on the actual vaccine dose received by each chick. It was determined that the dose of spray (hatchery or farm) and eye drop vaccine with IB Mass strain are followed with the manufacturer-recommended dose (1×) as ensued in 99%–100% of the birds positive for the vaccine virus at days 7–10 post vaccination, except the doses of ArkDPI vaccine strain tested in a hatchery spray cabinet with 100 times higher dose, which is not economically acceptable [104]. Moreover, spray vaccine is more preferred for IB virus, particularly while vaccinating for the early stage for local protection by adhering to the mucosa cells of the bird’s eyes and upper respiratory tract.
3.9. Vaccination Schedule
The timing of the IBV vaccination is given much attention due to the incidence of viruses circulating in certain farms being vaccinated. Broiler chickens are immunized 1 or 2 times against IBV due to their short lifespan [105]. Currently, DOC broiler chicks from hatcheries are mass-vaccinated with 1–3 serotypes of live-attenuated IBV vaccine for local protection before being shipped to the farm [106]. In several broiler farms, only a single vaccination is preferred for IBV due to shorter-lifetime broilers (≤35–45 days) [107]. In the case of longer-living broilers (≥49 days), a booster needs to be frequently applied between days 14 and 18 of age boost immunity duration. For IBV variants, vaccines can be administered (3.6 log10 EID50/dose) at day 1 for chicks and day 7 of older chickens by spray, intranasally or ocularly, or via drinking water. For breeding and laying birds, much longer cycles require both live-attenuated and killed vaccines starting from DOC followed by 18–20 weeks of pullet age for immunity longevity [108]. On the basis of the vaccine program, a live-attenuated IBV vaccine received by birds on the first day in a hatchery continues to 2–3 weeks of age on the farm, followed by 4 and 6 weeks of age. This vaccination schedule is properly standardized in the flock base for closely monitoring the serology status of vaccinated farms. Once birds start producing eggs, most killed IBV vaccines are given for longer immunity duration until the beginning of laying. Some farmers occasionally give a live-attenuated booster vaccine every 6 weeks in the laying stage if there is any challenge circulating in the farm area. It is common that killed IBV vaccine are combined with other killed vaccines, such as Newcastle disease virus (NDV), Reo virus, and IBD vaccines, to enhance layer variability and reduce stress during intramuscular injection.
3.10. Cross-Reactions between Serotypes
Diverse types of serotypes or IBV genotypes are globally documented, but different serotypes of the virus are not fully cross-protected. Despite this, novel, more infectious variants have emerged, but the amino acid sequence of the spike protein (S1) and genome are unchanged. Cross-reaction is particularly protected in chickens because of the interaction of multiple vaccinations covered by more than one included serotype [42,81]. Birds are challenged by new serotypes that differ from the serotypes of selection vaccines, so they are not fully protected against the prevalent serotype. On the basis of serological analysis, those heterologous cross-reactions in serotype-specific tests can be distinguished from homologous responses. Periodically, serological cross-reactivity is exposed to be higher in older birds depending on whether the birds had been previously contracted with infection or immunized many times with different serotypes. Few heterologous vaccines can decrease productivity and reduce the shedding of field viruses during the challenge of infection, initiating huge amounts of virus multiplication in the surroundings and leading to poor immune responses to vaccines. For this reason, serological data can be difficult to analyze in such conditions, which hinders the quality of diagnosis. A specific IB serotype can be recognized if the serotype is included in the group of tested IBV; otherwise, maximal cross-reaction should be undervalued.
3.11. Vaccine Handling and Storage
The supervision of vaccine handling, transportation, and storage greatly influences the efficacy and quality of vaccines. A live vaccine is sensitive to over 2–8 °C in storage temperature, so it should be continuously monitored to avoid over freezing until hardening [109,110,111]. Vaccines can spoil or lose superiority when in contact with extreme heating and intense light, leading to faster loss of strength, which greatly affects immunity development in birds (https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/69387). A diluent is mixed before application, and temperature should be maintained by a cooler dropper during ocular and drinking live vaccinations. For IBV vaccinations, the process of live vaccination requires no more than 1–2 h of inoculation or drinking time after exposure to the vaccine [112]. In drinking-water vaccination, the water tank should be clean and containing ice cubes or chiller water until the temperature is maintained at below 20 °C. The actual amount of drinking water needs to be calculated the on previous day to avoid longer vaccination. For killed vaccines, a vaccine is thawed from storage around 24 h before vaccination, but should not exceed 37 °C for more than 5 h. Sunlight can directly destroy the vaccine, so it is prohibited to come into contact with direct sunlight, and the vigorous handling of bottles should be avoided [109]. To ensure vaccine quality, the broken emulsion layer in each batch of received killed vaccines needs to be observed before vaccination (Figure 6). Temperature-monitoring devices (TMDs) are used in recording intervals of at least 30 min that set up vaccine storage and transportation for monitoring the frequency of temperature readings, suitably maintained as required.
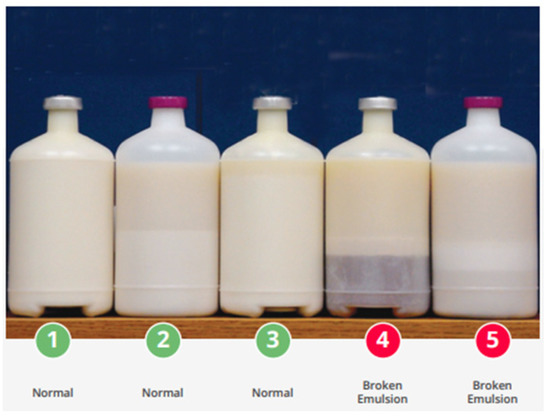

Figure 6.
Broken emulsion shown in inactivated killed vaccine is caused by mishandling and storage issue (Source: www.cobb-vantress.com accessed on 28 December 2020).
3.12. Postvaccine Challenge and Reaction
Signs of postvaccine reactions or challenges are characterized on the basis of local reaction, fever, and delayed reaction, and anaphylaxis is a common lesion or systemic reaction indicating that the chicken is reacting to a satisfactorily vaccination or good immunized response against IBV. These types of adverse postvaccine reactions are commonly found in infectious laryngotracheitis (ILT) rather than in IBV. A reaction is more severe in a few cases, with secondary infections such as conjunctivitis and swelling in the facial region, as shown in Figure 7. In most cases, birds react approximately 3–7 days after inoculation, showing slight respiratory symptoms of IBV [113]. Eventually, there are no clear symptoms in a successful vaccination, and blood samples should be collected for monitoring the actual titer in the serum for conformation.
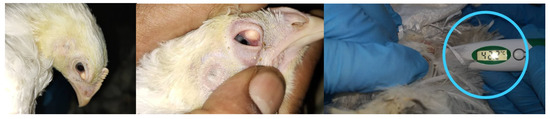
Figure 7.
Sign of vaccine reactions or IBV postvaccine challenge in mildly infected eyes with slightly high temperature after 3 days post vaccination of IB Mass (day 21 and day 93) in field application.
3.13. Management Factors
The purpose of vaccines is for disease control and prevention against respective pathogens that are correlated with the limits of good biosecurity measures. However, if there is a sudden breakdown of the biosecurity program with a higher load of field challenge, a vaccination program does not help at a satisfactory level. Many management issues, such as congested spaces, uncontrolled temperature and humidity in the shed, poor nutrition, worm infestations, poor uniformity, and other secondary infections that reduce the bird’s immune system, can directly affect vaccination efficacy. Several studies suggested that continuous exposure to 30 ppm [114], 52 ppm [115] NH3 levels which are critical environmental stressors to laying and broiler chicken leading to reduced immunity as proven by decreased total plasma (IgA, IgG, and IgM) and complement concentrations. Furthermore, ammonia level in sheds being more than 70–100 ppm has adverse effects on chickens’ ability to yield local immunity, and birds become exposed to viral infections [116,117,118,119,120].
Ventilation Quality
The operation of ventilation systems is a vital part to regulate sufficient air exchange to meet the air quality in poultry houses to reduce disease susceptibility and stress. Poultry houses’ ventilation systems impact its ammonia levels, harmful concentrations of CO2, and hydrogen sulfide (H2S), which are continuously produced by chickens through defecation and urination [121,122,123]. The ventilation system with an exhaust fan is needed to provide a suitable environment in poultry houses by removing excess heat, moisture, dust, and odors [124]. A good vaccine response has been observed during the proper ventilation system, which is essential to maintain in the whole flock during vaccination except spray vaccine, fans should be off because of the uniform vaccine distribution. Poor quality ventilation can damage the lining of the respiratory tract through initiating the immune system and can cause chronic inflammation that leads to less (15% lower IgM response) efficiency or no response to vaccination. [109,125].
3.14. Possible Immunosuppression
Some immunosuppressive diseases and cyclosporine are the most common agents that directly influence IBV vaccination. Immunosuppressive agents are stimulated in early bird age to reduce the response of IBV vaccination. Thompson et al. [126] compared the humoral immune response after the IBV immunization of 5-week-old SPF chickens that were divided into two groups, vaccinated and unvaccinated, with IBD as day 1 chicks. The percentage of antibody responses after IBV inoculation was significantly higher in the vaccinated group than in the group given both viruses. Several viral diseases developed immunosuppression, such as infectious bursal disease (IBD) or Marek’s’ disease, inclusion body hepatitis (IBH), chicken infectious anemia (CAV), and mycotoxins, causing an increased chance of susceptibility to IBV infection [54,127]. Immunosuppression can reduce the activation or efficacy of the immune system, where the humoral and cell-mediated immune system does not work effectively.
3.15. Routes of IBV Vaccination
3.15.1. Spray Vaccination
Spray vaccination is currently practiced in modern hatcheries at an early age of birds in farms, where a huge number of chicks require to be simultaneously vaccinated. The live vaccine of IBV is usually used for mass vaccinations in hatcheries or farms by fine/coarse spray via forcing through small spray nozzles, forming aerosolized droplets that chicks can easily inhale to uptake the vaccine [127,128,129], as shown in Figure 8A–C. Many factors are involved in correct spray vaccination (Table 1), such as droplet size with pressure, spray duration and constancy, maintained sanitation and hygiene, handling the equipment with a correct vaccine dosage, and the skills of workers, confirming the quality of vaccine delivery. A coarse rather than fine spray is more favorable to apply in DOC because fine droplets can be deeply inhaled in the respiratory tract, causing adverse reactions. The specific spray nozzle depends on the variety of sizes that form the measured droplet size. It was suggested that the minimal droplet size makes it harder for chicks to effortlessly inhale [130]. Several laboratory studies were conducted to measure the effectiveness of spray vaccination through electron microscopy, but no evidence was found for structural damage of the spike protein or the cracking of the virion membrane of the virus. Sometimes, the titer is superficially missed from the mechanical force applied to the vaccine during the handling process of vaccination [131]. Alternative studies observed a significant drop in vaccine response while comparing droplets from the spray nozzle to the absorbed level by the chicks, and proposed that the virus was being lost to the environment during the spray process [132,133]. Smaller volumes are used through a smaller nozzle flow rate, which helps the creation of smaller droplets upon aeroionization in spray vaccines. Generally, maximum hatchery coarse spray vaccination is accomplished with 100–150 µL droplets; however, this range is not persistent as it is just a normal of the total droplet sizes used [134,135].
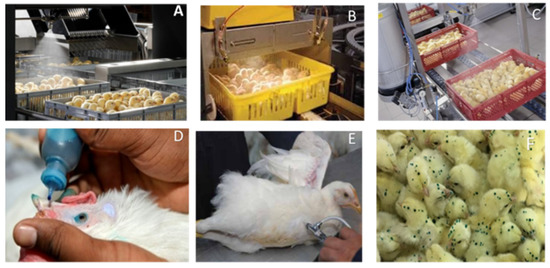
Figure 8.
Different vaccination methods for respiratory infectious bronchitis virus. (A–C) Spray vaccine in hatchery; (D) oculonasal; (E) Intramuscular injection; (F) Gel-Pac vaccination of Cocci combined with IBV live vaccine (Sources: www.immucox.com, accessed on 29 December 2020).

Table 1.
Different types of spray vaccines with droplet size applied in poultry (source: www.wattagnet.com/articles/16484 [136]).
3.15.2. Oculonasal
The perfect route of IBV vaccination is normally evaluated through the oculonasal route against respiratory pathogens causing respiratory diseases [73], as shown in Figure 8D. However, this method is not suitable for application in commercial mass vaccination, and vaccines are much better stimulated in respiratory or conjunctival rather than parenteral routes [137]. It is assumed that immunization in the nasal or conjunctival route can avoid the neutralization effect of serum antibodies causing losses of epithelium lining. Chicks normally produce three classes of immunoglobulins, namely, IgA, IgG, and IgM or IgY, where IgM and IgA predominate in the serum and tears after local vaccination, and the IgA class prevails in most secretory channels. Huge amounts of plasma cells secreting antibodies against viral antigens are observed in the Harderian gland. Similarly, an increased number of antibodies in the serum and lacrimal fluid are associated with a reduction in viral concentration that can play a vital role in the stimulation of both systemic and local immunity [138]. Toro et al. [139] experimented on all routes of vaccination with cloacal route, resulting in higher identified IgG levels in the ocular route than those in drinking immunization. Experimental studies reported that several dilutions of the IBV vaccine (H120) immunized specific-pathogen-free (SPF) broilers by different vaccine routes, resulting in higher and rapid IBV-specific IgM response, at least 10 times the recommended dose (1000 times higher) given via drinking water [73].
3.15.3. Drinking water
Most live IBV vaccines are applied in drinking water in broiler chickens 1 week following the booster dose if needed, depending on the farm situation. Broiler breeder and layer birds are commonly chosen for live vaccines in drinking at the pullet stage, and subsequently prime-boosted every 6 weeks in the laying stage, while the birds have lower titers or lower protection. In an attempt to mimic field conditions, drinking-water application is a good technique to avoid stress [140,141]; nevertheless, it is too difficult to quantify the actual dose received by each chick, and the consistency of vaccination within the group is impossible to determine. Monitoring should be performed to ensure that vaccination via drinking water is free from other medications, disinfectants, or chlorine at least 48 h before vaccination [142].
3.15.4. Intramuscular Injection
Inactivated killed IBV vaccines are applied in the breast or leg muscle using intramuscular (IM) injections, as shown in Figure 8E. Killed vaccines should be maintained at ambient temperature (approximately 28 °C), properly shaken, and thawed before being applied in the field. If stored in a cool box in a dark site, an inactivated vaccine can restore its potency in 1–2 weeks outside a freezer. Killed vaccines are relatively more active when the birds receive earlier immunization with live vaccines, and revaccination is commonly advised every 6 weeks for prolonged immunity action [66,143]. The accidental injection or contamination injectors into the vaccinator of killed vaccines lead to serious local reactions, or muscle or skin inflammation [12]. A trained vaccine team should be knowledgeable during every shot of the vaccine in the breast muscle, maintaining a 45° angle, and the team should sanitize all vaccine instrument after vaccination.
3.15.5. Gel Vaccination
A gel diluent is another of the latest practices for the application of the IBV vaccine. This technique was first used in the cocci vaccine in poultry as a delivery route of the vaccination process [144,145,146]. Due to gel thickness, it is created as a large droplet on which chicks obtain persistence steady until chicks are groomed by shank. The advantage of this technique is the increased ingestion of cocci oocysts that are currently used in cocci vaccine with live IBV, as shown in Figure 8F. This application system is currently trialed for IBV application for immunization against IBV [147,148]. However, laboratory study and commercial field trials revealed it to be more effective than spray vaccination [144,149,150]. It still needs additional trials or field research to review gel vaccination as a practical replacement of the spray route for IBV vaccines.
3.16. Vaccine Index (VI)
The success of vaccination performance is measured by mean titer response (mean antibody level) and percentages of coefficient of variation (CV) (value of measure’s uniformity) in vaccinated flocks. The overall standard for CV% uniformity after vaccination is measured as follows: less than 40%, excellent; 40%–60%, good vaccination; and more than 60%, vaccine methods need to be improved [151]. The ratio between mean titer and CV percentage is critical in assessing vaccine quality, defined as the vaccine index (VI), which is calculated as follows:
The VI score is estimated to provide a higher score (high mean titer, low CV percentage) in a good vaccination, and a low score with poor vaccination (low mean titer, high CV percentage). Depending on the standard parameters of different commercial kits.
4. Differential Diagnosis of Infectious Bronchitis Virus
The actual diagnosis of IBV infection is confusing with regard to clinical signs and postmortem lesions due to similar clinical signs produced by several respiratory pathogens, such as Newcastle disease (ND), avian influenza (AI), infectious laryngotracheitis (ILT) and infectious coryza (IC), and mycoplasma (Mg) [7]. Earlier reports stated that all respiratory pathogens can cause upper and lower respiratory infection, and significantly reduce egg production, requiring evidence from both field and laboratory results [152]. Likewise, typical signs of various poultry diseases are compared with other related diseases, for example, ND virus is involved with nervous symptoms, the bloody vomiting of ILT, facial swelling with lacrimation of IC, higher mortality in AI, and edema-swollen eyelids in MG. Egg-drop syndrome (EDS) is differentiated from IBV by shell quality and dropped production without infection. The whitish shell color is an important mark in ND and IBV infections, but watery albumin is found only in IBV infections [153]. The mortality of birds can be increased through the combined infection of IBV with ILT or coinfection of IBV with IC followed by high respiratory challenge and dyspnea [154,155]. However, APV can aggravate respiratory signs associated with IBV, but both viruses prefer coinfection together [156]. APV signs mainly fluctuate in egg production with drop hatchability, but egg-drop severity is found in IB infections. Few respiratory pathogens are associated with synergistic or mixed infection with IBV, MG, and E. coli, leading to the increased severity of infection [157,158]. There is no more evidence of dual infections with IBV and fowl cholera, and it is uncertain if there is more coinfection of IBV and CAV [159]. The synergistic role of IBV with interaction of mycoplasmosis is characterized by the combination of cold stress causing severe airsacculitis problems in the initial stages of laying [160,161]. Moreover, IBD can increased susceptibility to IBV and reduce IBV antibody levels [162].
5. Conclusions
Currently, a live-attenuated and inactivated vaccine is commonly used in IBV vaccination. However, IBV outbreaks in poultry farms usually persist due to a lack of actual serotypes or variants in vaccination programs, and vaccine failure, which is a significant problem in commercial farming. Laboratory diagnosis is a useful tool for the identification of actual serotypes or variants for vaccination programs to select accurate vaccines for the prevention and control of IBV. Moreover, we reviewed the best ways to protect from IBV through the successful vaccinations in every bird to maintain all necessary factors affecting the failure of vaccines. This review outlines this present situation of various vaccine applications, with correct approaches and factors that influence IBV diagnosis with differential diagnosis to assist in the accurate identification of IBV for necessary prophylactic measures to reduce economic losses from IBV outbreaks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S.A.B., S.S. (Shafiquzzaman Siddiquee) and Z.A.; investigation, S.S. (Suryani Saallah) and N.H.M.Y.; resources, A.M.S.A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.A.B.; writing—review and editing, S.S. (Shafiquzzaman Siddiquee), Z.A., N.H.M.Y. and S.M.S.; supervision, S.S. (Shafiquzzaman Siddiquee), Z.A. and S.M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to thanks to the Research Grant (UMSGreat) Scheme (GUG108-1/2017) in University Malaysia Sabah (UMS) Malaysia, for funding supports.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The study did not report any data.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate all researchers who were directly or indirectly involved in the global IBV study. This work was supported by the University Malaysia Sabah Scheme, UMSGreat (GUG0108-1/2017).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Papineau, A.; Berhane, Y.; Wylie, T.N.; Wylie, K.M.; Sharpe, S.; Lung, O. Genome organization of Canada Goose Coronavirus, a novel species identified in a mass die-off of Canada Geese. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, e5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legnardi, M.; Tucciarone, C.M.; Franzo, G.; Cecchinato, M. Infectious Bronchitis Virus Evolution, Diagnosis and Control. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keep, S.; Oade, M.S.; Lidzbarski-Silvestre, F.; Bentley, K.; Stevenson-Leggett, P.; Freimanis, G.L.; Tennakoon, C.; Sanderson, N.; Hammond, J.A.; Jones, R.C.; et al. Multiple novel non-canonically transcribed sub-genomic mRNAs produced by avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaro, N.; Lorusso, A. Novel human coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): A lesson from animal coronaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 104, 252–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ali, A.; Siddique, R.; Nabi, G. Novel coronavirus is putting the whole world on alert. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 104, 252–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, M.; Huang, B.; Wei, P.; Wei, T.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Fan, W. Complete genome sequences of two Chinese virulent avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus variants. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10903–10904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bande, F.; Arshad, S.S.; Omar, A.R.; Bejo, M.H.; Abubakar, M.S.; Abba, Y. Pathogenesis and diagnostic approaches of avian infectious bronchitis. Adv. Virol. 2016, 2016, 4621659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Youn, H.N.; Kwon, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, S.; Song, C.S. Characterization of a novel live attenuated infectious bronchitis virus vaccine candidate derived from a Korean nephropathogenic strain. Vaccine 2010, 28, 2887–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valastro, V.; Holmes, E.C.; Britton, P.; Fusaro, A.; Jackwood, M.W.; Cattoli, G.; Monne, I. S1 gene-based phylogeny of infectious bronchitis virus: An attempt to harmonize virus classification. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 39, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J.; Cook, J.K.A.; der Heijden, H.M. Infectious bronchitis virus variants: A review of the history, current situation and control measures. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackwood, M.W. Review of infectious bronchitis virus around the world. Avian Dis. 2012, 56, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.K.A.; Jackwood, M.; Jones, R.C. The long view: 40 years of infectious bronchitis research. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, F.; Chhabra, R.; Forrester, A.; Chantrey, J.; Baylis, M.; Lemiere, S.; Hussein, H.A.; Ganapathy, K. Experimental infection of IS/885/00-like infectious bronchitis virus in specific pathogen free and commercial broiler chicks. Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 105, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohaim, M.A.; El Naggar, R.F.; Abdelsabour, M.A.; Mohamed, M.H.; El-Sabagh, I.M.; Munir, M. Evolutionary analysis of infectious bronchitis virus reveals marked genetic diversity and recombination events. Genes 2020, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennaji, Y.; Khataby, K.; Ennaji, M.M. Infectious Bronchitis Virus in Poultry: Molecular Epidemiology and Factors Leading to the Emergence and Reemergence of Novel Strains of Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Emerg. Reemerging Viral Pathog. 2020, 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, J.K.; Orbell, S.J.; Woods, M.A.; Huggins, M.B. Breadth of protection of the respiratory tract provided by different live-attenuated infectious bronchitis vaccines against challenge with infectious bronchitis viruses of heterologous serotypes. Avian Pathol. 1999, 28, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cheng, J.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.X.; Zhang, G.Z. Safety and efficacy of an attenuated Chinese QX-like infectious bronchitis virus strain as a candidate vaccine. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 180, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terregino, C.; Toffan, A.; Beato, M.S.; De Nardi, R.; Vascellari, M.; Meini, A.; Ortali, G.; Mancin, M.; Capua, I. Pathogenicity of a QX strain of infectious bronchitis virus in specific pathogen free and commercial broiler chickens, and evaluation of protection induced by a vaccination programme based on the Ma5 and 4/91 serotypes. Avian Pathol. 2008, 37, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Li, M.; Wei, P.; Mo, M.L.; Wei, T.C.; Li, K.R. Complete genome sequence of an infectious bronchitis virus chimera between co-circulating heterotypic strains. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13887–13888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignjatovic, J.; Gould, G.; Sapats, S. Isolation of a variant infectious bronchitis virus in Australia that further illustrates diversity among emerging strains. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 1567–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D. Coronavirus avian infectious bronchitis virus. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinley, E.T.; Jackwood, M.W.; Hilt, D.A.; Kissinger, J.C.; Robertson, J.S.; Lemke, C.; Paterson, A.H. Attenuated live vaccine usage affects accurate measures of virus diversity and mutation rates in avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Virus Res. 2011, 158, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, A.; Albina, E.; Barret, T.; Chapman, D.A.; Czub, M.; Dixon, L.K.; Keil, G.M.; Klonjkowski, B.; Le Potier, M.F.; Libeau, G.; et al. Antigen delivery systems for veterinary vaccine development. Viral-Vector based delivery systems. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6508–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Li, H.; Qian, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Yi, Q. Optimizing dendritic cell vaccine for immunotherapy in multiple myeloma: Tumour lysates are more potent tumour antigens than idiotype protein to promote anti-tumour immunity. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 170, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewiesk, S. Maternal antibodies: Clinical significance, mechanism of interference with immune responses, and possible vaccination strategies. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boelm, G.J. Influence of maternally derived antibodies on vaccination using a IBV H120 vaccine virus. J. Vet. Med. Res. 2018, 5, 1124. [Google Scholar]
- Bosha, J.A.; Nongo, N.N. Common breaches in poultry vaccine handling and administration in Makurdi metropolis: A recurrent phenomenon in the tropics. J. Vet. Med. Res. 2012, 9, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly, S.; Paul, I.; Mukhopadhayay, S.K. Different types of vaccines and vaccination—The most accepted trend to control and eradicate infections. Indian Pet. J. 2010, 5, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullahi, U.S.; Adamu, S.B.; Ahmed, A.F. 2009 Investigations on some causes of poultry vaccination failures in Bauchi metropolis and environs. Niger. J. Exp. Appl Biol. 2009, 10, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- De Herdt, P.; Ducatelle, A.R.; Uyttebroek, A.E.; Sneep, A.; Torbeyns, R. Infectious bronchitis serology in broilers and broiler breeders: Correlations between antibody titers and performance in vaccinated flocks. Avian Dis. 2001, 45, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leerdam, B.; Kuhne, P. Diagnosis of IBV Field Challenge—PoultryWorld. 2010. Available online: https://www.poultryworld.net/Home/General/2010/7/Diagnosis-of-IBV-field-challenge-WP007714W/ (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Van Leerdam, B.; Kuhne, P. Understanding Elisa Results. 2017. Available online: https://www.biochek.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/IBV-Understanding-ELISA.pdf?x14571 (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Messaï, C.R.; Salhi, O.; Khelef, D.; Lounas, A.; Mohamed-Cherif, A.; Kaidi, R.; Aït-Oudhia, K. Serological, clinical, and risk factors of the Newcastle disease on broilers flocks in Algeria. Vet World. 2019, 12, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagha, D.; Gelb, J., Jr. Infectious Bronchitis. In Diseases of Poultry, 12th ed.; Saif, Y.M., Fadly, A.M., Glisson, J.R., McDougald, L.R., Nolan, L.K., Swayne, D.E., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Professional: Ames, IA, USA, 2008; pp. 117–135. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, B.M.; Raj, G.D.; Kumanan, K.; Nachimuthu, K.; Nainar, A.M. Interaction between genomes of infectious bronchitis and Newcastle disease viruses studied by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Acta Virol. 2004, 48(2), 123–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capua, I.; Terregino, C.; Cattoli, G.; Mutinelli, F.; Rodriguez, J.F. Development of a DIVA-Differentiating infected from vaccinated animals strategy using a vaccine containing a heterologous neuraminidase for the control of avian influenza. Avian Pathol. 2003, 32, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, D.; Lublin, A.; Rosenbluth, E.; Heller, E.D.; Pitcovski, J. Differentiating infected from vaccinated animals, and among virulent prototypes of reovirus. J. Virol Methods. 2011, 177, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capua, I.; Cattoli, G.; Marangon, S. DIVA–a vaccination strategy enabling the detection of field exposure to avian influenza. Dev. Biol. 2004, 119, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin, C.; Kitching, R.P.; Donaldson, A.I.; Crowther, J.R.; Barnett, I.T.R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of antibodies against foot-and-mouth disease virus: III. Evaluation of antibodies after infection and vaccination. Epidemiol. Infect. 1987, 99, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, A.S. Fundamentals of vaccine immunology. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2011, 3, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, B. Vaccination against infectious bronchitis virus: A continuous challenge. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, S.; Kappala, D. Avian infectious bronchitis virus. In Recent Advances in Animal Virology; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 301–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zavala, G. Fundamental Basics of Use and Interpretation of Serology. 2019. Available online: https://avicultura.info/en/fundamental-basics-of-the-use-and-interpretation-of-serology (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Darbyshire, J.H.; Cook, J.K.; Peters, R.W. Growth comparisons of avian infectious bronchitis virus strains in organ cultures of chicken tissues. Arch. Virol. 1978, 56, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.T.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.P.; Ma, L.N.; Ding, Y.Z.; Liu, X.T.; Cai, X.P.; Ma, L.Q.; Zhang, Y.G.; Liu, Y.S. Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for the rapid detection of infectious bronchitis virus in infected chicken tissues. Mol. Cell Probes 2010, 24, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najimudeen, S.M.; Hassan, M.S.H.; Cork, S.C.; Abdul-Careem, M.F. Infectious Bronchitis Coronavirus Infection in Chickens: Multiple System Disease with Immune Suppression. Pathogens 2020, 9, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Han, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, S.; Ma, D. Multiple recombination events between field and vaccine strains resulted in the emergence of a novel infectious bronchitis virus with decreased pathogenicity and altered replication capacity. Poult Sci. 2020, 99, 1928–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, L.Y.B. Diagnosis of infectious bronchitis: An overview of concepts and tools. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 2010, 12, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.M.; Fernando, F.S.; Montassier, M.F.S.; Silva, K.R.; Lopes, P.D.; Pavani, C.; Borzi, M.M.; Okino, C.H.; Montassier, H.J. Memory immune responses and protection of chickens against a nephropathogenic infectious bronchitis virus strain by combining live heterologous and inactivated homologous vaccines. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackwood, M.W.; de Wit, J.J. Infectious Bronchitis. In Diseases of Poultry, 3rd ed.; Swayne, D.E., Glisson, J.R., McDougald, L.R., Nolan, L.K., Suarez, D.L., Nair, V., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Professional: Ames, IA, USA, 2013; pp. 117–135. [Google Scholar]
- Gharaibeh, S.; Mahmoud, K.; Al-Natour, M. Field evaluation of maternal antibody transfer to a group of pathogens in meat-type chickens. Poult Sci. 2008, 87, 1550–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coakley, C.M.; Staszewski, V.; Herborn, K.A.; Cunningham, E.J. Factors affecting the levels of protection transferred from mother to offspring following immune challenge. Front. Zool. 2014, 11(1), 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Cook, J.K.A.; Frazier, J.A.; Narita, M. Escherichia coli multiplication and lesions in the respiratory tract of chickens inoculated with infectious bronchitis virus and/or Escherichia coli. Avian Dis. 1992, 36, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerr, F.J. Clinical aspects of immunosuppression in poultry. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schat, K.A.; Skinner, M.A. Avian Immunosuppressive Diseases and Immunoevasion. Avian Immunol. 2014, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, G.D.; Jones, R.C. Immunopathogenesis of infection in SPF chicks and commercial broilers of a variant infectious bronchitis virus of economic importance. Avian Pathol. 1996, 25, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R. Stress, stereotypies and welfare. Behav. Process. 1991, 25, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, V.E.; Carroll, D.; Drayson, M.; Whitham, M.; Ring, C. Life events, perceived stress and antibody response to influenza vaccination in young, healthy adults. J. Psychosom Res. 2003, 55, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Flanigan, M.E.; McEwen, B.S.; Russo, S.J. Aggression, Social Stress, and the Immune System in Humans and Animal Models. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, T.; Schmucker, S.S.; Bessei, W.; Grashorn, M.; Stefanski, V. Impact of Housing Environment on the Immune System in Chickens: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, A.H.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Leung, F.C. Cloning of chicken glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and characterization of its expression in pituitary and extrapituitary tissues. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J.; Cook, J.K. Factors influencing the outcome of infectious bronchitis vaccination and challenge experiments. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvidson, Y.; Tannock, G.A.; Senthilselvan, A.; Zerbes, M. A model for determining immunogenic relationships between avian infectious bronchitis virus. Arch. Virol. 1990, 111, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackwood, M.W.; Jordan, B.J.; Roh, H.J.; Hilt, D.A.; Williams, S.M. Evaluating protection against infectious bronchitis virus by clinical signs, ciliostasis, challenge virus detection, and histopathology. Avian Dis. 2015, 59, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, F.; Hutton, S.; Forrester, A.; Baylis, M.; Ganapathy, K. Heterologous live infectious bronchitis virus vaccination in day-old commercial broiler chicks: Clinical signs, ciliary health, immune and protection against variant infectious bronchitis viruses. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bande, F.; Arshad, S.S.; Bejo, M.H.; Moeini, H.; Omar, A.R. Progress and challenges toward the development of vaccines against avian infectious bronchitis. J. Immunol Res. 2015, 2015, 424860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J. Detection of infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Pathol. 2000, 29, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, V.; Mohammadi, P.; Ghalyanchilangeroudi, A.; Ghafouri, S.A.; Hashemzadeh, M.; Farahani, R.K.; Maghsouldoo, H.; Isakakroudi, N. Including 793/B type avian infectious bronchitis vaccine in 1-day-old chicken increased the protection against QX genotype. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J.; Nieuwenhuisen-van Wilgen, J.; Hoogkamer, A.; van de Sande, H.; Zuidam, G.J.; Fabri, T.H. Induction of cystic oviducts and protection against early challenge with infectious bronchitis virus serotype D388 (genotype QX) by maternally derived antibodies and by early vaccination. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, F.; Forrester, A.; Baylis, M.; Lemiere, S.; Ganapathy, K. Protection conferred by live infectious bronchitis vaccine viruses against variant Middle East IS/885/00-like and IS/1494/06-like isolates in commercial broiler chicks. Vet. Rec. Open 2015, 2, e000111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bru, T.; Vila, R.; Cabana, M.; Geerligs, H.J. Protection of chickens vaccinated with combinations of commercial live infectious bronchitis vaccines containing Massachusetts, Dutch and QX-like serotypes against challenge with virulent infectious bronchitis viruses 793B and IS/1494/06 Israel variant 2. Avian Pathol. 2017, 46, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagnozzi, A.; García, M.; Riblet, S.M.; Zavala, G. Protection induced by infectious laryngotracheitis virus vaccines alone and combined with Newcastle disease virus and/or infectious bronchitis virus vaccines. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J. Underestimation of the difficulties of vaccination against viral respiratory diseases by mass application methods. In Proceedings of the XVIIIth International Congress of the World Veterinary Poultry Association, Nantes, France, 19–23 August 2013; pp. 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Di Fabio, J.; Rossini, L.I.; Orbell, S.J.; Paul, G.; Huggins, M.B.; Malo, A.; Silva, B.G.; Cook, J.K.A. Characterization of infectious bronchitis viruses isolated from outbreaks of disease in commercial flocks in Brazil. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J.; Van Gerwe, T.W.J.M. Statistical approach of the required number of birds per group and number of TOCs per bird for ciliostasis testing in efficacy trials of IBV vaccines. In Proceedings of the IV International Symposium on Corona-And Pneumovirus Infections, Rauischholzhausen, Germany, 20–23 June 2004; pp. 213–219, VVB Laufersweiler Verlag. [Google Scholar]
- Benyeda, Z.; Mato, T.; Suveges, T.; Szabo, E.; Kardi, V.; Abonyi-Toth, Z.; Rusvai, M.; Palya, V. Comparison of the pathogenicity of QX-like, M41 and 793/B infectious bronchitis strains from different pathological conditions. Avian Pathol. 2009, 38, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerligs, H.J.; Boelm, G.J.; Meinders, C.A.; Stuurman, B.G.; Symons, J.; Tarres-Call, J.; Bru, T.; Vila, R.; Mombarg, M.; Karaca, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of an attenuated live QX-like infectious bronchitis virus strain as a vaccine for chickens. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, B. The contribution of vaccination to global health: Past, present and future. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 2014, 369, 20130433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbyshire, J.H.; Peters, R.W. Sequential development of humoral immunity and assessment of protection in chickens following vaccination and challenge with avian infectious bronchitis virus. Res Vet Sci. 1984, 37, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensaert, M.; Lambrechts, C. Vaccination of chickens against a Belgian nephropathogenic strain of infectious bronchitis virus B1648 using attenuated homologous and heterologous strains. Avian Pathol. 1994, 23, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wit, J.J.; Mekkes, D.R.; Kouwenhoven, B.; Verheijden, J.H. Sensitivity and specificity of serological tests for infectious bronchitis virus antibodies in broilers. Avian Pathol. 1997, 26, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, R.; Chantrey, J.; Ganapathy, K. Immune Responses to Virulent and Vaccine Strains of Infectious Bronchitis Viruses in Chickens. Viral Immunol. 2015, 28, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palgen, J.L.; Tchitchek, N.; Rodriguez-Pozo, A.; Jouhault, Q.; Abdelhouahab, H.; Dereuddre-Bosquet, N.; Contreras, V.; Martinon, F.; Cosma, A.; Lévy, Y.; et al. Innate and secondary humoral responses are improved by increasing the time between MVA vaccine immunizations. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulendran, B.; Ahmed, R. Immunological mechanisms of vaccination. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breytenbach, J.H. Guidelines for effective vaccination of broilers. Int. Poult. Prod. 1999, 13, 7–9. Available online: http://www.positiveaction.info/pdfs/articles/pp13.7p7.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Bar-shira, E.; Sklan, D.; Friedman, A. Establishment of immune competence in the avian GALT during the immediate post-hatch period. Develop. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamal, K.R.; Burgess, S.C.; Pevzner, I.Y.; Erf, G.F. Maternal antibody transfer from dams to their egg yolks, egg whites, and chicks in meat lines of chickens. Poult. Sci. 2006, 85, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapczynski, D.R.; Hilt, D.A.; Shapiro, D.; Sellers, H.S.; Jackwood, M.W. Protection of chickens from infectious bronchitis by in ovo and intramuscular vaccination with a DNA vaccine expressing the S1 glycoprotein. Avian Dis. 2003, 47, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, K.; Sahin, N.; Onderci, M.; Yaralioglu, S.; Kucuk, O. Protective role of supplemental vitamin E on lipid peroxidation, vitamins E, A, and some mineral concentrations of broilers reared under heat stress. Vet. Med. 2001, 46, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Munyaka, P.; Yitbarek, A.; Echeverry, H.; Rodriguez-Lecompte, J.C. Maternal antibody decay and antibody-mediated immune responses in chicken pullets fed prebiotics and synbiotics. Poult Sci. 2017, 96, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignjatovic, J.; Galli, L. Immune responses to structural proteins of avian infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Pathol. 1995, 24, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.Y.; Wang, H.C.; Wang, C.H. Protective effect of vaccination in chicks with local infectious bronchitis viruses against field virus challenge. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2005, 38, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, M.P.; Wakenell, P.S.; Woolcock, P.; O’Connor, B. Evaluation of the effectiveness of two infectious bronchitis virus vaccine programs for preventing disease caused by a California IBV field isolate. Avian Dis. 2007, 51, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, R.; Krispel, S.; Simanov, L.; Pitcovski, J. Immune Responses to Mucosal Vaccination by the Recombinant S1 and N Proteins of Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Viral Immunol. 2012, 25, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelb, J.; Ladman, B.S.; Pope, C.R.; Ruano, J.M.; Brannick, E.M.; Bautista, D.A.; Coughlin, C.M.; Preskenis, L.A. Characterization of nephropathogenic infectious bronchitis virus DMV/1639/11 recovered from Delmarva broiler chickens in 2011. Avian Dis. 2013, 57, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.H.; Kim, M.S.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Park, J.K.; Young, H.N.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, I.S.; Song, C.S. Live attenuated nephropathogenic infectious bronchitis virus vaccine provides broad cross protection against new variant strains. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, J.K.; Alphin, R.L.; Krauss, W.S. Cross-protection studies with a Holland strain of IBV. Avian Dis. 1976, 20, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.K.A.; Otsuki, K.; Martin, N.R.D.S.; Ellis, M.M.; Huggins, M.B. The secretory antibody response of inbred lines of chickens to avian infectious bronchitis virus infection. Avian Pathol. 1992, 21, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, L.D.; Hunter, D.B.; Zhang, H.M.; Brand, K.; Etches, R. Retrospective evidence that the MHC (B haplotype) of chickens influences genetic resistance to attenuated infectious bronchitis vaccine strains in chickens. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, K.S.; Hoerr, F.J.; Ewald, S.J.; van Santen, V.L.; Wright, J.C.; van Ginkel, F.W.; Toro, H. Pathogenesis of infectious bronchitis virus in vaccinated chickens of two different major histocompatibility B complex genotypes. Avian Dis. 2007, 51, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.F.; Villegas, P.; Fletcher, O.J.; Laudencia, R. Evaluation of ciliary movement in tracheal rings to assess immunity against infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Dis. 1982, 26, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthijs, M.G.; van Eck, J.H.; de Wit, J.J.; Bouma, A.; Stegeman, J.A. Effect of IBV-H120 vaccination in broilers on colibacillosis susceptibility after infection with a virulent Massachusetts-type IBV strain. Avian Dis. 2005, 49, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.I.; Cheng, H.H.; Chase-Topping, M.; Mays, J.K.; Anacleto, O.; Dunn, J.R.; Doeschl-Wilson, A. Pathogen transmission from vaccinated hosts can cause dose-dependent reduction in virulence. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyson, C.M.; Hilt, D.A.; Jordan, B.J.; Jackwood, M.W. Minimum Infectious Dose Determination of the Arkansas Delmarva Poultry Industry Infectious Bronchitis Virus Vaccine Delivered by Hatchery Spray Cabinet. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landman, W.J. The downside of broiler vaccination. Vet. Q. 2012, 32, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ismail, M.I.; Tan, S.W.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Omar, A.R. Evaluation of the antigen relatedness and efficacy of a single vaccination with different infectious bronchitis virus strains against a challenge with Malaysian variant and QX-like IBV strains. J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 21, e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, T. Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus: Infection, Evolution, and Immunity. 2020. Available online: https://www.thepoultrysite.com/articles/avian-infectious-bronchitis-virus-infection-evolution-and-immunity (accessed on 16 January 2021).
- Aston, E.J.; Jordan, B.J.; Williams, S.M.; García, M.; Jackwood, M.W. Effect of Pullet Vaccination on Development and Longevity of Immunity. Viruses 2019, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.; Ahmad, T. Preventing Vaccine Failure in Poultry Flocks. Retrieved from Google scholar data base on the World Wide Web. 2018. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.79330 (accessed on 16 January 2021).
- Lala, M.K.; Lala, K.R. Thermo stability of vaccines. Indian Pediatr. 2003, 40, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Vangroenweghe, F. Good vaccination practice: It all starts with a good vaccine storage temperature. Porc Health Manag. 2017, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butcher, G.D.; Yegani, M. Investigating Vaccine Failure in Poultry Flocks; UF IFAS Extension, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dhama, K.; Singh, S.D.; Barathidasan, R.; Desingu, P.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Tiwari, R.; Kumar, M.A. Emergence of avian infectious bronchitis virus and its variants need better diagnosis, prevention and control strategies: A global perspective. Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 17, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.F.F.; Yan, J.Y.; Hu, Y.W.; Tucker, C.M.; Green, A.R.; Cheng, H.W. Immune Response of Laying Hens Exposed to 30 ppm Ammonia for 25 Weeks. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2017, 16, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudev, D.; Popova-Ralcheva, S. Yanchev, I.; Moneva, Petkov, E.; Ignatova, M. Effect of betaine on egg performance and some blood constituents in laying hens reared indoor under natural summer temperatures and varying levels of air ammonia. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 17, 859–866. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.X.; Xu, B.; Hu, X.F.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, L.Y. The Effect of Ammonia and Humidity in Poultry Houses on Intestinal Morphology and Function of Broilers. J. Anim Vet. Adv. 2012, 11, 3641–3646. [Google Scholar]
- Oyetunde, O.O.; Thomson, R.G.; Carlson, H.C. Aerosol exposure of ammonia, dust and Escherichia coli in broiler chickens. Can. Vet. J. 1978, 19, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.M.; Meng, Q.P.; Guo, Y.M.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Z.L.; Shan, T.Z. Effect of atmospheric ammonia on growth performance and immunological response of broiler chickens. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2010, 9(22), 2802–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.P.; Beard, C.W.; Hanson, R.P. The Adverse Effects of Ammonia on Chickens Including Resistance to Infection with Newcastle Disease Virus. Avian Dis. 1964, 8, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmermark, S.; Lund, V.; Gustafsson, G.; Eduard, W. Ammonia, dust and bacteria in welfare-oriented systems for laying hens. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2009, 16, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Purswell, J.L.; Davis, J.D.; Luck, B.D.; Kim, E.J.; Olanrewaju, H.A.; Kiess, A.S.; Branton, S.L. Effects of elevated carbon dioxide concentrations on broiler chicken performance from 28 to 49 days. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2011, 10, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Broucek, J.; Cermák, B. Emission of harmful gases from poultry farms and possibilities of their reduction. Ekologia 2015, 34, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, B.; Mejdell, C.; Michel, V.; Lund, V.; Moe, R.O. Air Quality in Alternative Housing Systems may have an Impact on Laying Hen Welfare. Part II-Ammonia. Animals 2015, 5, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.D.; Weaver, W.D. Commercial Chicken Production Manual, 5th ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; p. 1416. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, J.J.; Swart, W.A.J.M.; Fabri, T.H.F. Efficacy of infectious bronchitis virus vaccinations in the field: Association between the -IBV IgM response, protection and vaccine application parameters. Avian Pathol 2010, 39, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, G.; Naqi, S. Cytotoxic activity of cells recovered from the respiratory tracts of chickens inoculated with infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Dis. 1997, 41, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, Y.M. Immunosuppression induced by infectious bursal disease virus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1991, 30, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijs, M.G.; Ariaans, M.P.; Dwars, R.M.; van Eck, J.H.; Bouma, A.; Stegeman, A.; Vervelde, L. Course of infection and immune responses in the respiratory tract of IBV infected broilers after superinfection with E. coli. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 127, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinet, W.; Verheye, S.; De Meyer, G.R. Selective depletion of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques via macrophage-specific initiation of cell death. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 17, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purswell, J.L.; Fritz, B.K.; Branton, S.L.; Leigh, S.A. Effects of system pressure and nozzle type on spray application of avian vaccines. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2008, 24, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.J.; Jordan, B.J.; Hilt, D.A.; Ard, M.B.; Jackwood, M.W. Hatchery spray cabinet administration does not damage avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus vaccine based on analysis by electron microscopy and virus titration. Avian Dis. 2015, 59, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, B.J. Spray Application of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Vaccines in the Hatchery: How Efficient are We? In Proceedings of the XXIV Congreso de Avicultura Centroamericano y del Caribe, Antigua, Guatemala, 9–11 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Purswell, J.L.; Branton, S.L.; Evans, J.D. Performance of an Automated Whole-House Spray Vaccination System. J. Appl Poult Res. 2019, 28, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spray Vaccination of Day–Old Chicks at the Hatchery. Available online: https://www.thepoultrysite.com/articles/spray-vaccination-of-dayold-chicks-at-the-hatchery (accessed on 16 January 2021).
- Paniago, M. Spray Vaccination in the Hatcheries, Key Points to Achieve Proper Immunization of the Day-Old Chicks. 2006. Available online: https://5mpublishing.sirv.com/poultry/legacy/focus/contents/ceva/OnlineBulletins/ob_2006/Article-No4-Jan06.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2021).
- Following Best Practice in Administering Hatchery Spray Vaccination. Available online: https://www.wattagnet.com/articles/16484-following-best-practice-in-administering-hatchery-spray-vaccination (accessed on 16 January 2021).
- Perozo, F.; Villegas, P.; Estévez, C.; Alvarado, I.R.; Purvis, L.B.; Williams, S. Protection against infectious bursal disease virulent challenge conferred by a recombinant avian adenoassociated virus vaccine. Avian Dis. 2008, 52, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, P.H.; Ezeifeka, G.O. The Hitchner B1 strain of Newcastle disease virus induces high levels of IgA, IgG and IgM in newly hatched chicks. Vaccine 1995, 13, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, H.; Espinoza, C.; Ponce, V.; Rojas, V.; Morales, M.A.; Kaleta, E.F. Infectious bronchitis: Effect of viral doses and routes on specific lacrimal and serum antibody responses in chickens. Avian Dis. 1997, 41, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, J.W.; Randall, C.J.; McMartin, D.A.; Dagless, M.D. Immunity following inoculation of H120 and H52 vaccine strains of infectious bronchitis virus into the crop of the domestic fowl. Avian Pathol. 1983, 12, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanasethakul, C.; Cumming, R.B. Immune response of chickens to various routes of administration of Australian infectious bronchitis vaccine. Aust. Vet. J. 1983, 60, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide to Successful Spray and Water Vaccination for Poultry Farmers. Available online: https://www.fwi.co.uk/livestock/poultry/guide-successful-spray-water-vaccination-poultry-farmers (accessed on 16 January 2021).
- Box, P.G.; Ellis, K.R. Infectious bronchitis in laying hens: Interference with response to emulsion vaccine by attenuated live vaccine. Avian Pathol. 1985, 14, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danforth, H.D.; Lee, E.H.; Martin, A.; Dekich, M. Evaluation of a gel-immunization technique used with two different Immucox vaccine formulations in battery and floor-pen trials with broiler chickens. Parasitol. Res. 1997, 83, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, T.; Lee, E.H. A gel delivery system for coccidiosis vaccine: Uniformity of distribution of oocysts. Can. Vet. J. 2000, 41, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chapman, H.; Cherry, T.; Danforth, H.; Richards, G.; Shirley, M.; Williams, R. Sustainable coccidiosis control in poultry production: The role of live vaccines. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, A.; Jordan, B.; El-Attrache, J. Replication dynamics of a live Infectious bronchitis virus vaccine in broiler chicks vaccinated by different routes. In Proceedings of the 20th World Veterinary Poultry Association Congress, Edinburgh, Scotland, 4–8 September 2017; p. 362. [Google Scholar]
- Tucciarone, C.M.; Franzo, G.; Bianco, A.; Berto, G.; Ramon, G.; Paulet, P.; Koutoulis, K.C.; Cecchinato, M. Infectious bronchitis virus gel vaccination: Evaluation of Mass-like (B-48) and 793/B-like (1/96) vaccine kinetics after combined administration at 1 day of age. Poult Sci. 2018, 97, 3501–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, G.A.; Tensa, L.R.; Aston, E.J.; Hilt, D.A.; Jordan, B.J. Evaluation of a coccidia vaccine using spray and gel applications. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tensa, L.R.; Jordan, B.J. Comparison of the application parameters of coccidia vaccines by gel and spray. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leerdam, B.V.; Bosman, H. Vaccination Index: A new approach to evaluate Elisa. World Poul. Doetinchem. Elsevier 2010, 26, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J.R.; Souillard, R.; Bertin, J. Avian diseases which affect egg production and quality. In Improving the Safety and Quality of Eggs and Egg Products; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 376–393. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.S.H.; Abdul-Careem, M.F. Avian Viruses that Impact Table Egg Production. Animals. 2020, 10, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispo, M.; Blackall, P.; Khan, A.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Clothier, K.; Sentíes-Cué, C.G.; Cooper, G.; Blakey, J.; Pitesky, M.; Mountainspring, G.; et al. Characterization of an outbreak of infectious coryza (Avibacterium paragallinarum) in commercial chickens in central California. Avian Dis. 2019, 63, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cong, F.; Guan, J.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lian, Y.; Huang, R.; Chen, M.; Guo, P. Development of a sensitive and specific xMAP assay for detection of antibodies against infectious laryngotracheitis and bronchitis viruses. Virol J. 2018, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, M.; Gough, R.E.; Dawson, P.S. The effect of live infectious bronchitis vaccine on the course of infectious laryngotracheitis. Vet. Rec. 1971, 75, 643–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Cook, J.K.A.; Otsuki, K.; Huggins, M.B.; Frazier, J.A. Comparative study of respiratory lesions in two chicken lines of different susceptibility infected with infectious bronchitis virus: Histology, ultrastructure and immunohistochemistry. Avian Pathol. 1991, 20, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawakol, M.M.; Nabil, N.M.; Samy, A. Evaluation of bacteriophage efficacy in reducing the impact of single and mixed infections with Escherichia coli and infectious bronchitis in chickens. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2019, 9, 1686822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, M.A.; Brown, J.; Smeltzer, M.A.; Girshick, T.; Miller, S.L.; Dickson, T.G. Relationship of common avian pathogen antibody-titres in so-called chicken anaemia agent (CAA)-antibodypositive chicks to titers in CAA-antibody-negative chicks. Avian Dis. 1992, 36, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, S.; Murata, S.; Takehara, M.; Katakura, K.; Hmoon, M.M.; Win, S.Y.; Ohashi, K. Molecular detection and genetic characterization of Mycoplasma gallisepticum, Mycoplama synoviae, and infectious bronchitis virus in poultry in Myanmar. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, S.R.; Yoder, H.W. Influence of infectious bronchitis strains and vaccines on the incidence of Mycoplasma synoviae airsacculitis. Avian Dis. 1982, 26, 741–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uenaka, T.; Kishimoto, I.; Sato, S.; Animas, S.B.; Ito, T.; Otsuki, K.; Cook, J.K.A. Intracloacal infection with avian infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Pathol. 1998, 27, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).