A Recurrent Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor-like Lesion of the Splenic Capsule in a Kitten: Clinical, Microscopic and Ultrastructural Description
Abstract
:1. Introduction
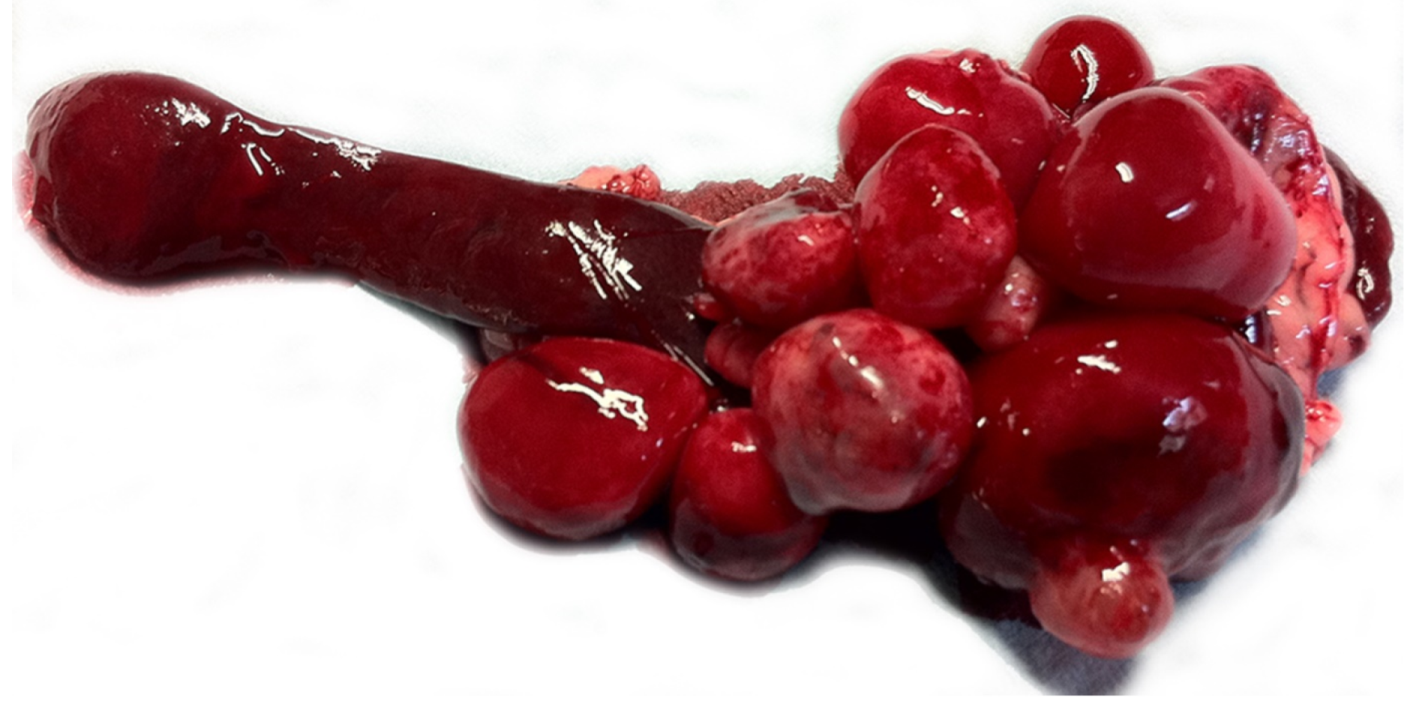
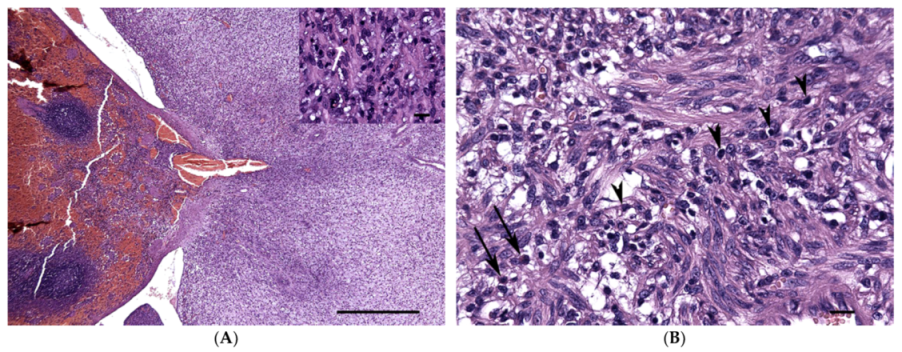
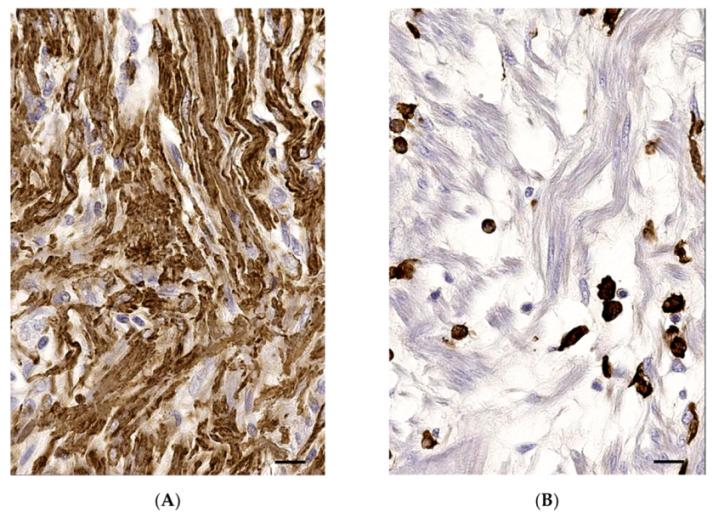
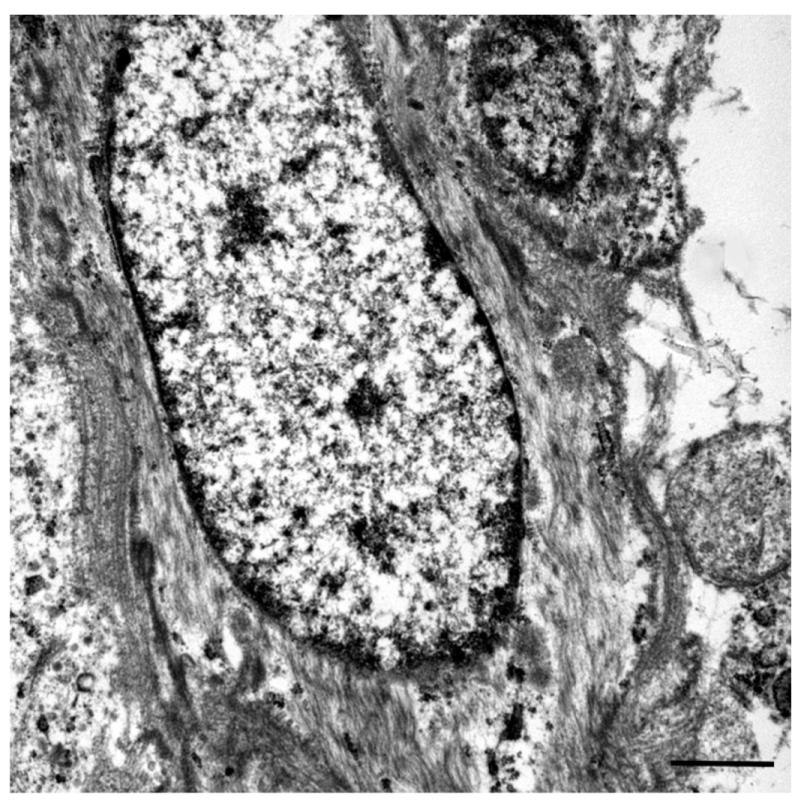
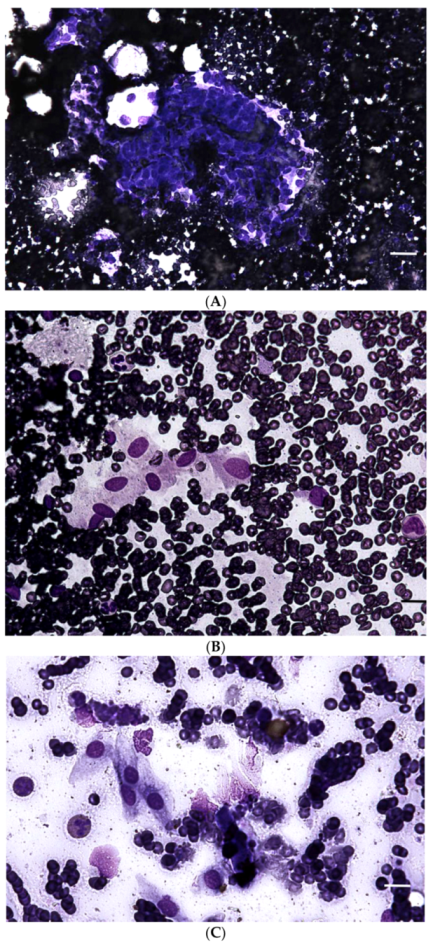
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldblum, J.; Weiss, S.; Folpe, A. Borderline and Malignant Fibroblastic/Myofibroblastic Tumors. In Enzinger and Weiss’s Soft Tissue Tumors, 7th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 322–323. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, M.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Gupta, S.D.; Chatterjee, U.; Banerjee, S. Intra-abdominal infantile inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors: A report of three cases. J. Indian Assoc. Pediatr. Surg. 2014, 19, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chavez, C.; Hoffman, M.A. Complete remission of ALK-negative plasma cell granuloma (inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor) of the lung induced by celecoxib: A case report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 2013, 5, 1672–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Treissman, S.P.; Gillis, D.A.; Lee, C.L.; Giacomantonio, M.L. Omental-mesenteric inflammatory pseudotumor. Cytogenetic demonstration of genetic changes and monoclonality in one tumor. Cancer 1994, 73, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, C.M.; Watterson, J.; Priest, J.R.; Dehner, L.P. Extrapulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor). A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 84 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1995, 19, 859–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, C.R.; Mohta, A.; Khurana, N.; Paik, S. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the omentum: An uncommon pediatric tumor. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2009, 52, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Min, B.W.; Song, T.J.; Son, G.S.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.W.; Chung, H.H.; Lee, J.H.; Um, J.W. Exophytic inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the stomach in an adult woman: A rare cause of hemoperitoneum. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, C.M.; Hornick, J.L.; Fletcher, C.D. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: Comparison of clinicopathologic, histologic, and immunohistochemical features including ALK expression in atypical and aggressive cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaskar, S.; Koshti, S.; Maralingannavar, M.; Bartake, A. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2011, 2, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, C.; Fan, E.; Riis, R.; McDonough, S. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumors in Two Dogs. Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.; Špičić, S.; Butorović-Dujmović, M.; Račić, I.; Huber, D.; Gudan Kurilj, A.; Beck, R.; Cvetnić, Ž. Mucocutaneous Inflammatory Pseudotumours in Simultaneous Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium and Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis Infection in a Cat. J. Comp. Pathol. 2015, 153, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spangler, W.L.; Culbertson, M.R. Prevalence and type of splenic diseases in cats: 455 cases (1985–1991). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1992, 201, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanson, J.A.; Papageorges, M.; Girard, E.; Menard, M.; Hebert, P. Ultrasonographic appearance of splenic disease in 101 cats. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound. 2001, 42, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, L.E.; Hardam, E.E.; Hertzke, D.M.; Flatland, B.; Rohrbach, B.W.; Moore, R.R. Feline Gastrointestinal Eosinophilic Sclerosing Fibroplasia. Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Antibody, Brand | Dilution | Antigen Retrieval | Incubation | Amplifier | Antibody, Brand | Positive Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VWF, Dako | 1:1000 | 30’ at 100 °C | 8’ | No | VWF, Dako | Internal control (endothelium) |
| Desmin, Dako | 1:50 | 30’ at 100 °C | 16’ | No | Desmin, Dako | Muscle |
| GFAP, Histo-Line Lab | 1:50 | 30’ at 100 °C | 24’ | No | GFAP, Histo-Line Lab | Brain |
| Calponin, Dako | 1:200 | 30’ at 100 °C | 12’ | No | Calponin, Dako | Mammary gland (myoepithelial cells) |
| Vimentin, Dako | 1:150 | 30’ at 100 °C | 28’ | No | Vimentin, Dako | Internal control (mesenchymal cells) |
| PanCK, Dako | 1:100 | 30’ at 100 °C | 28’ | No | PanCK, Dako | Mammary gland (epithelial cells) |
| SMA, Dako | 1:100 | no | 12’ | No | SMA, Dako | Internal control (vessels walls) |
| HLA-dr, Dako | 1:50 | 30’ at 100 °C | 32’ | No | HLA-dr, Dako | Internal control (splenic macrophages) |
| Iba1, Wako | 1:800 | 8’ at 95 °C | 32’ | Yes | Iba1, Wako | Internal control (splenic macrophages) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferro, S.; Chiavegato, D.; Fiorentin, P.; Zappulli, V.; Di Palma, S. A Recurrent Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor-like Lesion of the Splenic Capsule in a Kitten: Clinical, Microscopic and Ultrastructural Description. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8110275
Ferro S, Chiavegato D, Fiorentin P, Zappulli V, Di Palma S. A Recurrent Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor-like Lesion of the Splenic Capsule in a Kitten: Clinical, Microscopic and Ultrastructural Description. Veterinary Sciences. 2021; 8(11):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8110275
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerro, Silvia, David Chiavegato, Piergiorgio Fiorentin, Valentina Zappulli, and Stefano Di Palma. 2021. "A Recurrent Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor-like Lesion of the Splenic Capsule in a Kitten: Clinical, Microscopic and Ultrastructural Description" Veterinary Sciences 8, no. 11: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8110275
APA StyleFerro, S., Chiavegato, D., Fiorentin, P., Zappulli, V., & Di Palma, S. (2021). A Recurrent Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor-like Lesion of the Splenic Capsule in a Kitten: Clinical, Microscopic and Ultrastructural Description. Veterinary Sciences, 8(11), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8110275






